
A Machine Learning Model for Estimating Daily Rainfall in
Mediterranean Climate
Ali Karah Bash
1a
, Amin Gharehbaghi
2b
and Shahaboddin Daneshvar
3c
1
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Hasan Kalyoncu University,
27110 Şahinbey, Gaziantep, Turkey
2
Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Hasan Kalyoncu University,
27110, Şahinbey, Gaziantep, Turkey
3
Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Hasan Kalyoncu University,
27110 Şahinbey, Gaziantep, Turkey
Keywords: Rainfall, Prediction, CGSVM Model, RBFNN Model, Türkiye.
Abstract: Rainfall estimation remains a critical yet complex task, especially in Mediterranean regions where climatic
variability poses significant modeling challenges. This study utilizes two regression approaches—Coarse
Gaussian Support Vector Machine (CGSVM) and Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN)—to
predict daily rainfall over Bozcaada station, Türkiye. The models were trained and evaluated using standard
regression performance metrics to investigate their predictive ability under Mediterranean climate conditions.
Both models showed promising results in capturing the overall structure of rainfall variation. The RBFNN
displays slightly greater stability across low-to-moderate precipitation ranges. However, neither model fully
captured the intensity of extreme rainfall events, reflecting a common limitation in data-driven rainfall
modeling. Quantitative assessments using RMSE, MAE, NSE, SI, and R² further highlighted the close
performance of both methods, with RBFNN offering marginally improved accuracy. The findings suggest
that CGSVM and RBFNN can provide useful estimations in operational contexts, though additional
enhancements are needed. This work contributes to the growing literature on machine learning applications
in hydrometeorological forecasting and highlights the need for adaptable models suited to the specific
complexities of Mediterranean climates.
1 INTRODUCTION
Freshwater resources are becoming increasingly
constrained and vulnerable as a result of
anthropogenic pollution, population growth, and
natural climate variability (Gharehbaghi and Kaya
2022; Rajput et al. ,2023, Gharehbaghi et al. 2024).
Undoubtedly, rainfall, as a primary component of
precipitation, is one of the main sources of freshwater
and constitutes a climatic event that significantly
impacts human life. Accurate rainfall forecasting can
lead to optimal planning and management in different
fields, such as agriculture, hydroelectric power
generation, water supply, and disaster prevention
(Ananth (2020); Abdel Azeem and Dev (2024);
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6513-9180
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2898-3681
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0917-7254
Karah Bash et al. (2025)). Despite the significance of
accurate precipitation forecasting, it is still
challenging due to the fast-changing, uncertainty and
complexity of the atmospheric processes that affect
precipitation.
In recent decades, machine learning (ML)
techniques have provided a significant advantage in
the prediction process. “ML …can be applied to
rainfall prediction by using historical data of
meteorological variables and learning patterns or
relationships that can be used to forecast future
rainfall. Abdel Azeem and Dev (2024).
A short literature review focusing on recent
advance in this field is provided below:
Karah Bash, A., Gharehbaghi, A. and Daneshvar, S.
A Machine Learning Model for Estimating Daily Rainfall in Mediterranean Climate.
DOI: 10.5220/0014375200004848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences (ICEEECS 2025), pages 295-299
ISBN: 978-989-758-783-2
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
295
Liyew and Melese (2021) used three ML
techniques (viz., multivariate linear regression, RF,
and Extreme Gradient Boost) to identify the relevant
atmospheric features that cause rainfall and predict
the intensity of daily rainfall. They used climate data
measured in Ethiopia and finally observed that the
Extreme Gradient Boost ML model outperformed
other models. Ojo and Ogunjo (2022) employed two
multivariate polynomial regressions (MPR) and
twelve ML models (e.g., support vector machine
(SVM) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems
(ANFIS)) for Nigeria. To this end, they used 31-year
data. The results illustrated that the adaptive ANFIS
model’s algorithms outscored the MPR, ANN, and
SVM models in the ten months of the year. Baig et
al., 2024, investigated the potential of various ML and
ensemble models, including XGBoost, Long Short-
Term Memory (LSTM), Random Forest (RF),
Gradient Boost (GB), Support Vector Machine
(SVM), Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Linear
Regression (LR), and ensemble methods for monthly
rainfall prediction in hyperarid environments. They
reported that although initially using limited input
parameters, the models used could not provide
reliable outputs, but after adding meteorological
parameters such as wind speed, temperature,
humidity, and evapotranspiration, all models,
especially XGB and LSTM, showed significant
improvements in results. Farooq et al., 2024, utilized
2 ML models (i.e., RF and LSTM) to examine how
multiple climate indices simultaneously influence
wet-period rainfall patterns at two Northern Territory
(NT) stations in Australia. They announced that
large-scale climate factors such as the Madden Julian
Oscillation and lagged Indian Ocean Dipole
significantly influence wet-period rainfall predictions
of the NT. Moreover, the LSTM model provided
more accurate outcomes than the RF model. Mesta et
al. (2024) assessed the efficiency of ensemble
analysis for south and southwestern Türkiye. They
applied three ensemble methodologies: simple
average of the models, multiple linear regression for
super ensemble, and artificial neural networks
(ANN). The outcomes revealed that ensembled time
series performed better than individual regional
climate models.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Description of the Study Area
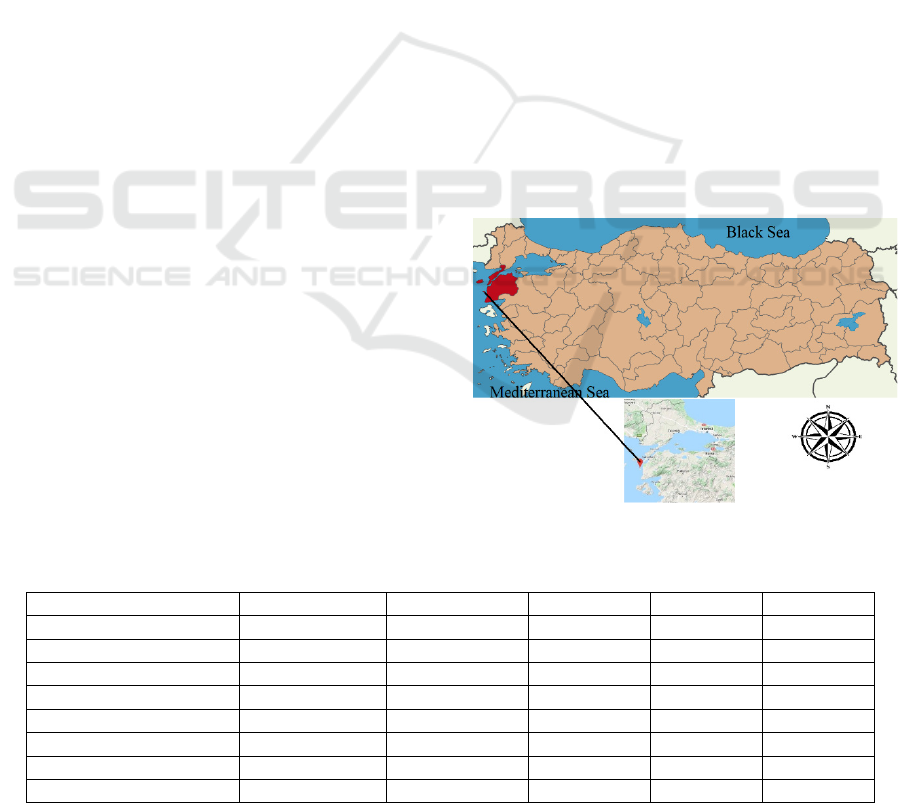
Bozcaada is an island in the Çanakkale province of
Türkiye with a surface area of 40 km2. In the region
where this station is located, summers are warm, dry,
and clear; winters are long, cold, rainy, and partly
cloudy, and the weather is windy all year round
(Köppen classification: Csa). The temperature varies
typically between 5°C and 30°C throughout the year.
In this study, average temperature (Tmean), relative
humidity (RH), maximum wind speed (Umax), and
wind direction (Udir) were utilized as input
parameters, while rainfall was selected as the target
variable. The location of the Bozcaada station on the
map of Türkiye is depicted in Figure 1. Furthermore,
the statistical data for the Bozcaada station covering
the period from 2008 to 2019, along with its
geographical coordinates, are presented in Tables 1
and 2.
Figure 1: Location of the Bozcaada station in Türkiye.
Table 1: Statistical values of the Bozcaada station from 2008 to 2019.
Tmean RH Umax Udi
r
Rainfall
Mean 16.48675565 74.11213 11.73742 196.5554 1.497582
Standar
d
Erro
r
0.095480415 0.136026 0.077683 2.068534 0.102267
Median 16.9 74 11.3 180 0
Mode 22.8 73.8 13.4 360 0
Standar
d
Deviation 6.321207299 9.005518 5.142971 136.9457 6.770497
Sam
p
le Variance 39.95766172 81.09935 26.45015 18754.13 45.83962
Kurtosis -0.681687415 0.009872 3.424785 -1.62117 410.6713
Skewness -0.354301381 0.042623 1.145221 -0.049 14.90925
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
296

Table 2: Geographical coordinates of the meteorological
station.
Station Latitude (N) Longitude(E) Elavation(M)
Bozcaada 39.8326 26.0728 30
2.2 Regression Methods
Coarse Gaussian Support Vector Machine
(CGSVM). Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a
supervised learning algorithm originally designed for
classification and regression tasks through a method
known as Support Vector Regression (SVR). In a
regression task, SVM seeks to find a function that
approximates the target variable within a specified
margin of tolerance ( 𝜀), while minimizing model
complexity. The Coarse Gaussian version refers to
using a Gaussian Kernel (GK) with a large kernel
scale, leading to smoother decision boundaries that
generalize well in cases with relatively low noise. The
Gaussian kernel function is given by:
𝐾
(
𝑥,𝑥
)
=exp −
(1)
where 𝑥 and 𝑥
are feature vectors, and 𝜎
is the
kernel scale (larger in coarse SVMs), which controls
the spread of the Gaussian function.
Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN).
The Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN)
is a form of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) that
uses radial basis functions as activation functions.
The architecture of this method comprises three
layers:
An input layer: This layer is connected to a hidden
layer of GK neurons to provide a linear output.
The non-linear mapping of inputs: higher
dimensional space in the hidden layer of the network
takes place where summation takes place.
The RBFNN output can be mathematically expressed
as:
𝑓(𝑥) =
∑
𝑤
⋅𝜙
(‖
𝑥−𝑐
‖)
‖ (2)
where 𝑓(𝑥 is the predicted output, 𝑤
is the output
weight, 𝜙 is the radial basis function (commonly
Gaussian), 𝑐
is the center of the RBF unit, and 𝑁 is
the number of hidden neurons.
2.3 Performance Indices
Five standard evaluation metrics, including Root
Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error
(MAE), coefficient of determination (R2), Scatter
Index (SI), and Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE),
were utilized to assess the accuracy and performance
of the suggested and employed model. The
mathematical expressions for these statistical
measures are as follows:
𝑅𝑀𝑆𝐸 =
∑
𝐸𝑇
−𝐸𝑇
(3)
𝑀𝐴𝐸 =
∑
𝐸𝑇
−𝐸𝑇
(4)
𝑅
=1−
∑
(
)
∑
(
)
(5)
𝑆𝐼 =
∑
𝐸𝑇
−𝐸𝑇
/𝐸𝑇
× 100%
(6)
𝑁𝑆𝐸 = 1 −
∑
∑
(7)
where the subscripts "pre" and "obs" denote
predictions and observations, respectively, and the
superscript n signifies the total number of data points.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this research, the outcomes of the proposed two
regression models, CGSVM and RBFNN, are
evaluated. The authors investigated the performance
and effectiveness of these models by comparing their
prediction accuracy and R2 values, which they
compute based on the prediction features from the
initial training phase.
3.1 Prediction Outcomes of CGSVM
and RBFNN Models
As shown in Figure 2, actual daily rainfall values
compare with the estimated values using the CGSVM
and RBFNN approaches. The Figure Analysis shows
that both models are usually able to reproduce the
overall trends in data, especially during periods of
low-to-moderate precipitation. RBFNN seems to
produce more stable predictions than the other two.
This is especially true for sections with denser and
less variable data. However, both models appear to be
limited in simulating pronounced spike-type rainfall.
These sudden peaks that coincide with high-intensity
rain are only partly traced by the models. This is often
the case with data-driven rainfall estimation.
Generally, there is a reasonable agreement between
the predictions and the actual measurements using
both models, indicating the potential applicability of
both models in Mediterranean climates.
A Machine Learning Model for Estimating Daily Rainfall in Mediterranean Climate
297
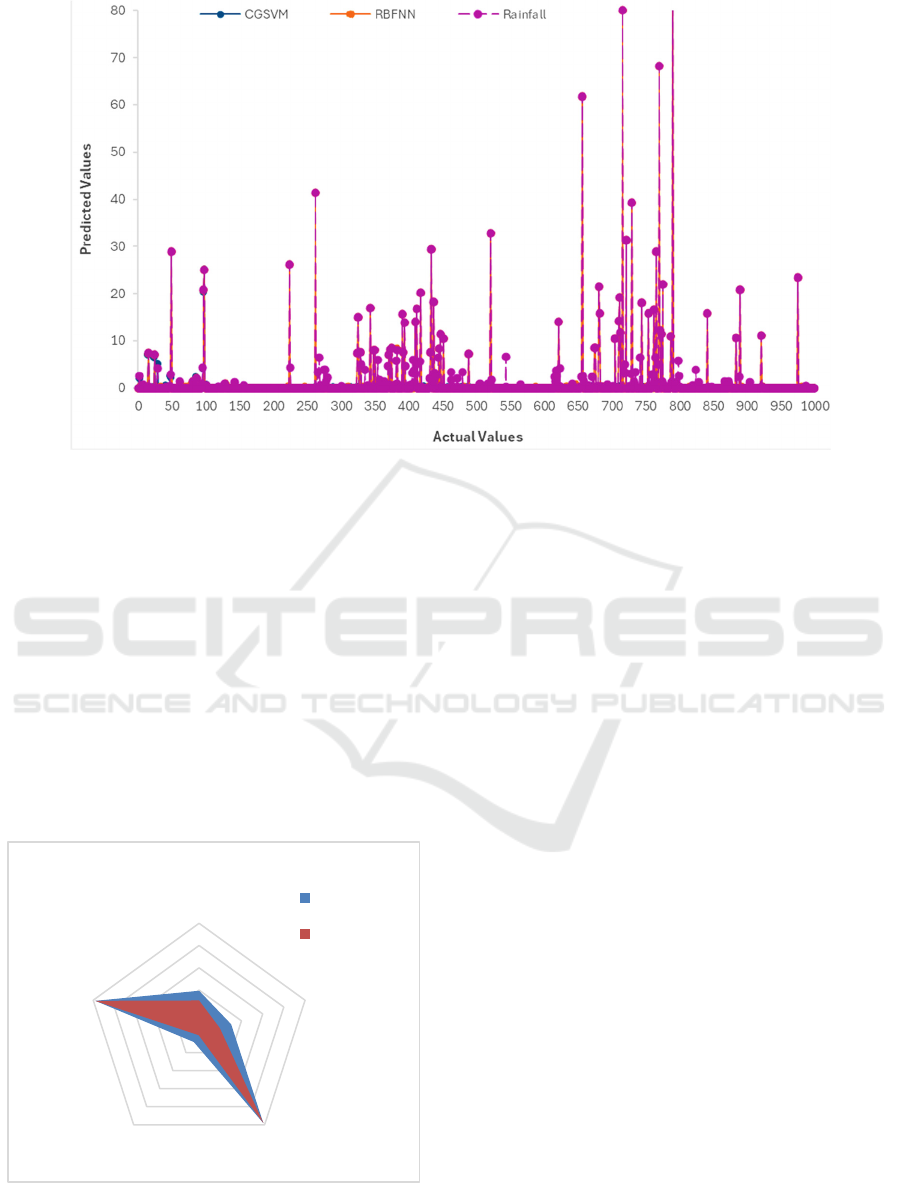
Figure 2: Comparison of actual and predicted daily rainfall values using CGSVM and RBFNN models
3.2 Metric Assessment Outcomes
Figure 3 presents a spider chart to compare the
performance of CGSVM and RBFNN by using five
evaluation metrics: RMSE, MAE, R2, NSE, and SI.
The Figure reveals that both models perform similarly
across most metrics, yet subtle distinctions can be
observed. The RBFNN model slightly outperforms
CGSVM in terms of RMSE and MAE, indicating a
marginally lower average error and tighter overall fit.
This suggests that the RBFNN's architecture may be
better suited for capturing the nonlinear behavior of
rainfall data. In contrast, CGSVM shows a slight
advantage in the SI and R2 metrics, implying slightly
Figure 3: Comparative radar chart of evaluation metrics for
CGSVM and RBFNN models.
better variance explanation and normalized error
performance. However, the difference between the
two models is not substantial across any single metric,
suggesting that their overall regression capabilities are
comparably effective. The NSE values for both
models remain moderate, reinforcing the earlier
observation that while the models are proficient in
capturing general trends, their ability to predict peak
rainfall events remains limited.
4 CONCLUSION
This study explored the potential of two classical
regression models—Coarse Gaussian Support Vector
Machine (CGSVM) and Radial Basis Function
Neural Network (RBFNN)—for estimating daily
rainfall in a Mediterranean climate, using data from
Bozcaada station, Türkiye. Both models were
evaluated not only in terms of visual agreement with
observed rainfall patterns but also through a set of
standard performance metrics, including RMSE,
MAE, NSE, SI, and R2. The findings indicate that
while both CGSVM and RBFNN were reasonably
effective in capturing the overall structure of daily
rainfall, RBFNN demonstrated slightly more
consistent accuracy, particularly for moderate rainfall
events. However, both models exhibited limitations
in predicting high-intensity rainfall, which is often
sparse and highly irregular. This underlines an
ongoing challenge in precipitation modeling—
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
RMSE
MAE
R2SI
NSE
Metric Evaluation Result
CGSVM
RBFNN
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
298

achieving a balance between general pattern
recognition and responsiveness to extreme values.
Although the RBFNN had a slight edge in error
reduction, the overall difference between the two
approaches was relatively small, suggesting that both
can serve as viable tools for rainfall estimation in
similar climatic settings. Future studies should
consider integrating ensemble techniques or multi-
source data fusion to enhance model reliability in
Mediterranean regions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Turkish State
Meteorological Service for providing access to the
weather station data.
REFERENCES
Abdel Azeem, M., Dev, S., (2024) A performance and
interpretability assessment of machine learning models
for rainfall prediction in the Republic of Ireland,
Decision Analytics Journal 12, 100515,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2024.100515
Ananth, J., (2020) MapReduce and optimized deep network
for rainfall prediction in agriculture, Comput. J., 63 (6),
900–912.
Baig, F., Ali, L., Faiz, M.A., Chen, H., Sherif, M. (2024)
How accurate are the machine learning models in
improving monthly rainfall prediction in hyper arid
environment?, Journal of Hydrology 633, 131040,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.131040
Farooq, R., Imteaz, M.A., Shangguan, D., Hlavčová, K.,
(2024) Machine learning algorithms to forecast wet-
period rainfall using climate indices in Northern
Territory of Australia, Science Talks 12, 100397,
https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.sctalk.2024.100397
Gharehbaghi, A., Afaridegan, E., Kaya, B., Adhami, M.
(2024) Calibration and evaluation of various reference
evapotranspiration estimation methods in a humid
subtropical climate: A case study in Samsun Province,
Türkiye, Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts
A/B/C, 136, 103734,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2024.103734.
Gharehbaghi, A., Kaya, B., (2022) Calibration and
evaluation of six popular evapotranspiration formula
based on the Penman-Monteith model for continental
climate in Turkey. Phys. Chem. Earth, Parts A/B/C 127,
103190. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.pce.2022.103190.
Karah Bash AA, and Khail, AA (2025) Advanced multi-
layer deep learning model for accurate estimation of
heat transfer and flow designing parameters across
diverse dataset configurations. Engineering
Applications of Artificial Intelligence 151: 110723.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2025.110723
Liyew C.M. and Melese, H.A. (2021) Machine learning
techniques to predict daily rainfall amount, Journal of
Big Data 8:153, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-
00545-4
Mesta, B., Akgun, B., Kentel, E., (2024) Improving
precipitation estimates for Turkey with multimodel
ensemble: a comparison of nonlinear artificial neural
network method with linear methods, Neural
Computing and Applications, 36:10219–10238,
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-09598-x
Ojo, O.O., Ogunjo, S.T., (2022) Machine learning models
for prediction of rainfall over Nigeria, Scientific
African, 16, e01246,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01246
Rajput, J., Singh, M., Lal, K., Khanna, M., Sarangi, A.,
Mukherjee, J., Singh, Sh, 2023. Performance evaluation
of soft computing techniques for forecasting daily
reference evapotranspiration. Journal of Water and
Climate Change 14 (1), 350. https://doi.
org/10.2166/wcc.2022.385.
A Machine Learning Model for Estimating Daily Rainfall in Mediterranean Climate
299
