
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant
Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
Omer Ba Faqas
1
, Necati Aksoy
1
and Oğuz Mısır
2
1
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Bursa Technical University, Bursa, Turkey
2
Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Bursa Technical University, Bursa, Turkey
Keywords: Path Planning, A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, Ant Colony Optimization, Autonomous Navigation,
Comparative Analysis.
Abstract: This paper presents a comparative performance evaluation of four distinct path planning algorithms A*,
Rapidly-exploring Random Tree Star (RRT*), Genetic Algorithm (GA), and Ant Colony Optimization (ACO)
for autonomous navigation in static, grid-based environments. We assessed each algorithm's efficacy based
on path optimality, computational efficiency, and success rate across maps with varying obstacle densities.
Empirical results show that the A* algorithm provides optimal paths with the lowest computation time in low-
to-moderate complexity environments. RRT* demonstrates superior flexibility in more complex topologies,
while the metaheuristic GA and ACO approaches can solve highly complex problems but at a significant
computational cost and with high sensitivity to parameter tuning. These findings establish an environment-
contingent framework for algorithm selection, underscoring the trade-off between path optimality and
computational resources.
1 INTRODUCTION
Path planning remains a cornerstone of autonomous
robotics and intelligent systems, with extensive
research spanning from medical applications to
mobile robotics and autonomous driving. A
comprehensive survey in (Zhang et al., 2025) reviews
algorithms for steerable flexible needles (SFNs) in
minimally invasive surgery, classifying them into
mathematical, inverse kinematics, sampling, and
intelligence-based approaches, while (Ugwoke et al.,
2025) presents a simulation-driven review of classical,
heuristic, and metaheuristic algorithms for
autonomous robots, outlining their principles,
applications, and challenges. Similarly, (Reda et al.,
2024) analyzes 275 papers on autonomous driving
systems, with particular attention to 162 works on
path planning, and categorizes methods into
traditional, learning-based, and metaheuristic
techniques, highlighting their advantages and
limitations. General overviews, such as (Sánchez-
Ibáñez et al., 2021) and (L. Liu et al., 2023), provide
broad classifications of global and local planning
strategies ranging from cell decomposition and
roadmaps to intelligent methods like fuzzy logic,
neural networks, and evolutionary algorithms—while
also pointing to emerging trends and future prospects.
Beyond reviews, several studies offer comparative
analyses and methodological innovations. The work in
(Noreen et al., 2016) evaluates RRT variants (RRT,
RRT*, RRT*-Smart) under different performance
criteria, while (Aksoy et al., 2024) compares A*,
Dijkstra, RRT*, and PRM in multi-level indoor
environments using metrics such as computation time,
memory, and path length. To standardize evaluation,
(Hsueh et al., 2022) introduces PathBench, a
benchmarking framework enabling systematic
integration and comparison of algorithms. Hybrid and
improved approaches have also been proposed: (Li et
al., 2025) combines Dijkstra with the Timed Elastic
Band (TEB) algorithm to generate smoother and safer
paths, [(Elshamli et al., 2004) applies genetic
algorithms for adaptive planning in dynamic
environments, and (J. Liu et al., 2016) enhances ant
colony optimization with pheromone diffusion and
geometric local optimization for faster convergence
and better path quality. Collectively, these works
underscore the diversity of path planning approaches,
182
Faqas, O. B., Aksoy, N. and Mısır, O.
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in Obstacle-Dense Maps.
DOI: 10.5220/0014368000004848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences (ICEEECS 2025), pages 182-191
ISBN: 978-989-758-783-2
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

the importance of benchmarking, and the ongoing
shift toward intelligent and hybrid solutions for
increasingly complex environments.
In this study, one representative algorithm was
selected from each of the first two categories, while
an additional collective-intelligence-based method
(ACO) was also included, resulting in four algorithms
being evaluated in detail. The algorithms were
applied on fixed-size grid environments and analyzed
across five map scenarios with different levels of
structural complexity. This enabled the assessment of
their respective advantages, disadvantages, and
overall performance under specific environmental
conditions. Throughout the study, the structure,
working principles, and results of the algorithms are
supported by visualizations and comparative graphics,
providing not only theoretical insights but also
practical guidance for algorithm selection in
engineering applications.
2 PRELIMINARIES
The core challenge in autonomous robot navigation is
determining an optimal or feasible trajectory from a
start point to a goal within an environment
constrained by obstacles. The selection of a path
planning algorithm is a critical design decision,
heavily influenced by the nature of the environment,
the required solution quality, and the available
computational resources. This study provides a
rigorous comparative analysis of four distinct
algorithmic paradigms: the deterministic A* search,
the probabilistic sampling-based RRT*, and the
metaheuristic approaches of GA and ACO. This
section delineates the foundational principles,
mathematical formalisms, and critical operational
parameters of each algorithm, establishing the
theoretical basis for their subsequent empirical
evaluation in complex, obstacle-dense environments.
2.1 A* Algorithm
The A* algorithm is a cornerstone of deterministic
graph search path planning. It efficiently combines
the systematic completeness of Dijkstra's algorithm
with the directed search of a Best-First Search
through a heuristic function, guaranteeing an optimal
path provided one exists.
The algorithm's core mechanism involves the
minimization of a cost function for each node,
expressed in Eq.1.
𝑓(𝑛) = 𝑔(𝑛) + ℎ(𝑛) (1)
where g(n) represents the exact cumulative cost
from the start node to the current node n, and h(n)
denotes a heuristic estimate of the cost from n to the
goal. For the solution to be optimal, the heuristic
function must be admissible, meaning it never
overestimates the true cost, and consistent, ensuring
monotonicity. The Euclidean distance is a common
choice for a consistent heuristic in continuous spaces.
The performance of A* is heavily influenced by
several key parameters. The selection of the heuristic
function, such as Euclidean or Manhattan distance,
directly impacts search efficiency. A common tuning
technique involves using a weighted heuristic,
formulated as f(n) = g(n) + ε · h(n) with ε > 1, which
can significantly expedite the search at the expense of
optimality, transforming the algorithm into a
suboptimal but highly efficient variant. Furthermore,
strategies for breaking ties between nodes with
identical f(n) values can affect the number of node
expansions; favoring nodes with a higher g(n) value
often leads to expansions closer to the goal,
potentially improving overall efficiency. The
underlying graph representation, whether a 4-
connected or 8-connected grid, also influences the
algorithm's branching factor and the smoothness of
the resulting path.
2.2 RRT* Algorithm
The RRT* algorithm addresses the scalability
limitations of graph-based search in high-
dimensional continuous spaces. As an extension of
the Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT), RRT is
probabilistically complete, meaning the probability of
finding a feasible path approaches one as the number
of iterations increases (Noreen et al., 2016).
Crucially, it is also asymptotically optimal,
guaranteeing that its solution will converge to the true
optimum as computational time approaches infinity.
RRT* differs from the classical RRT algorithm in that
it rewires the tree after each new node is added to
minimize the path cost, thereby asymptotically
converging toward an optimal (shortest or least-cost)
solution.
The algorithm operates by incrementally building
a tree structure rooted at the start configuration. For
each randomly sampled point in the configuration
space, the algorithm executes a series of steps. It then
generates a new node by moving from this nearest
node towards the random sample by a predefined step
size. The central innovation of RRT* over RRT lies
in the subsequent steps: it identifies a set of neighbor
nodes within a certain radius of the new node and then
connects the new node to the neighbor that provides
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
183

the lowest cumulative cost from the start according to
the cost-minimization criterion. The expression
𝑥
shown in Eq.2 determines the most suitable
parent for the newly generated node 𝑥
. This
selection is made by choosing the node among the
neighbors that minimizes the total path cost from the
starting point.
𝑥
=arg𝑚𝑖𝑛
∈
(
)
𝑐
(
𝑥
,𝑥
)
+ 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡
(
𝑥
)
(2)
Finally, it rewires the tree, checking if the new
node can serve as a better parent for any of its
neighbors, thereby continuously optimizing the tree
structure and reducing path costs over time. The
RRT* algorithm rewires the tree to determine
whether the newly added node can serve as a better
parent for its neighbors, continuously optimizing the
structure and reducing path costs. Its performance
depends on key parameters such as step size,
neighborhood radius, and goal bias. The step size
balances exploration speed and precision, while the
neighborhood radius decreases with node density to
ensure asymptotic convergence and computational
efficiency. The goal bias allows occasional direct
sampling of the goal to accelerate convergence but
must be used carefully to avoid local minima in
complex environments.
2.3 Genetic Algorithm (GA)
Genetic Algorithms (GA) belong to a class of
stochastic, population-based metaheuristic methods
inspired by the principles of Darwinian evolution.
These algorithms operate on a population of
candidate solutions, referred to as “chromosomes.”
The population evolves over successive generations
through processes such as selection, crossover, and
mutation(Elshamli et al., 2004). In this evolutionary
process, each new generation aims to produce better
solutions those with higher fitness values than the
previous one.
In the context of path planning, a chromosome
typically represents a potential route encoded as a
sequence of waypoints or actions. Each chromosome
corresponds to a possible trajectory that enables the
robot to move from its starting position to the goal.
The driving force of evolution, known as the fitness
function, quantitatively evaluates how good each path
is. This evaluation may consider factors such as path
length, the number of obstacle collisions, energy
consumption, or the smoothness of motion.
As shown in Eq. (3) a standard fitness function in
genetic algorithms can be defined to evaluate and
guide the optimization process.
𝑂𝑏𝑗
(
𝑝
)
=
(
)
()
(3)
𝑃𝑎𝑡ℎ(𝑃) represents the total length of the path,
while 𝑂𝑏𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑐𝑙𝑒(𝑃) is a penalty term calculated
based on the degree of collision between the path and
obstacles. The coefficients 𝑤₁ and 𝑤₂ are weighting
factors that determine the relative importance of these
two components in the optimization process. A higher
w₂ value prioritizes obstacle avoidance, whereas
increasing w₁ emphasizes the selection of shorter
paths. Consequently, the genetic algorithm is guided
to generate paths that are both short and safe.
2.4 Ant Colony Optimization(ACO)
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a swarm
intelligence–based metaheuristic inspired by the
collective foraging behavior of real ant colonies. In
nature, ants find the shortest path between their nest
and a food source by depositing and sensing chemical
pheromones along their routes (J. Liu et al., 2016).
This decentralized communication mechanism,
known as stigmergy, enables the colony to
collectively adapt and optimize its behavior over
time. In computational analogues, artificial ants
cooperatively construct solutions, with each ant
representing a potential path. The colony then
reinforces high-quality solutions through pheromone
updates, allowing the algorithm to converge toward
near-optimal routes.
The probability that an artificial ant located at
node i will move to node j at time t depends on two
main factors: (1) the pheromone intensity 𝑇
(𝑡) on
the edge connecting nodes i and j, and (2) the heuristic
desirability 𝜂
which typically represents the inverse
of the distance between the nodes 𝜂
=
. This
probability is given in Eq.4
𝑃
=
∑
(
)
∈
(4)
where 𝛼 and β are weighting parameters controlling
the influence of pheromone and heuristic information,
and 𝑁
is the set of feasible neighboring nodes. This
rule ensures that paths with higher pheromone
intensity and shorter distance are more likely to be
selected. After all ants complete their tours,
pheromone trails are updated in Eq. 5.
𝑇
(
𝑡+1
)
=
(
1−𝜌
)
𝑇
(
𝑡
)
+∆𝑇
(5)
where 𝜌 is the pheromone evaporation rate and ∆𝑇
is the pheromone deposited, typically defined as
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
184

∆𝑇
=
if the k-th ant used edge (i, j), where 𝑄 is a
constant and 𝐿
is the path length.
Parameter tuning strongly influences ACO
performance. A higher α increases dependence on
pheromone trails (exploitation), whereas a higher β
emphasizes heuristic guidance (exploration). A large
evaporation rate ρ\rhoρ accelerates the search for new
paths but may slow convergence. The number of ants
determines the number of solutions generated per
iteration, balancing search diversity and computation
time.
Through this dynamic balance of pheromone
reinforcement, heuristic influence, and evaporation,
ACO efficiently discovers near-optimal paths in
complex environments.
3 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF
THE METHODS
In this section, four algorithms A*, RRT*, GA, and
ACO were tested on five grid environments of
varying difficulty levels. Each algorithm was
executed under identical experimental conditions,
with the same start and goal positions, and with
specific parameter settings to ensure fairness. For
each grid, the results were compared in terms of
several metrics, including path length, execution
time, success rate, visual quality of the generated
path, and algorithmic stability. Screenshots and visual
outputs were also provided for each test, and the
analyses were supported by numerical data.
The experiments were conducted on a computer
with the following specifications: Intel 12th Gen
Core™ i5-12500H 3.10 GHz processor, 8 GB DDR4
RAM, and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 Ti GPU.
All algorithms were implemented in Python and
executed within the same operating system and
programming environment to ensure consistency in
comparison.
To allow a comprehensive performance
evaluation, all four algorithms were tested on the
same set of grid maps under identical conditions. The
test scenarios were designed with different structural
complexities, enabling detailed analysis of algorithm
performance across multiple environments. In this
study, the paths obtained from deterministic and
probabilistic methods are analyzed and compared
across Map 1, Map 2, Map 3, and Map 4.
3.1 Map 1: Medium-Density Obstacle
Structure and Performance
Analysis
In this scenario, the performance of four algorithms
was evaluated within a grid environment containing
medium-density obstacles. The workspace was
defined as a 25×50 grid, with the start point set at
(0,0) and the goal point at (6,31). Obstacles were
strategically positioned along the horizontal and
vertical axes to partially block the direct line toward
the goal. This configuration was designed to assess
the algorithms’ capabilities in obstacle detection,
environmental awareness, and alternative path
generation.
Each algorithm was configured according to its
methodological principles. The A* algorithm
employed the Manhattan distance heuristic and four-
directional movement, generating fast and optimal
paths. The RRT* algorithm was executed with 800
iterations, a step size of 1 unit, and a neighborhood
radius of 4 units, enabling rapid exploration of the
environment through random sampling. The Genetic
Algorithm (GA) utilized a population of 300
individuals, a maximum path length of 80 steps, 500
generations, and a mutation rate of 10%, ensuring
population diversity and guiding the search toward
near-optimal solutions. The Ant Colony Optimization
(ACO) algorithm was run with 60 artificial ants over
200 iterations, applying a 60% pheromone
evaporation rate and parameters of α = 1 and β = 2,
thereby integrating pheromone-based reinforcement
with heuristic guidance.
The results revealed clear differences among the
four methods. The A* algorithm consistently
produced the shortest and smoothest paths with the
lowest execution time, achieving a 100% success rate
across all trials. The RRT* algorithm also reached the
goal in every run; however, due to its sampling-based
nature, its paths were more irregular and
computationally more expensive compared to A*.
The Genetic Algorithm achieved a similarly high
success rate but required significantly longer
computation times. The ACO algorithm successfully
generated feasible paths in all tests, though its routes
occasionally included indirect detours, and its
execution time was higher than that of the other
methods.
Overall, the results for Map 1 indicate that the A*
algorithm is the most efficient and stable method for
environments with medium obstacle density.
Although RRT* achieved a comparable success rate,
it exhibited lower efficiency in terms of path
smoothness and computation time. Both GA and
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
185
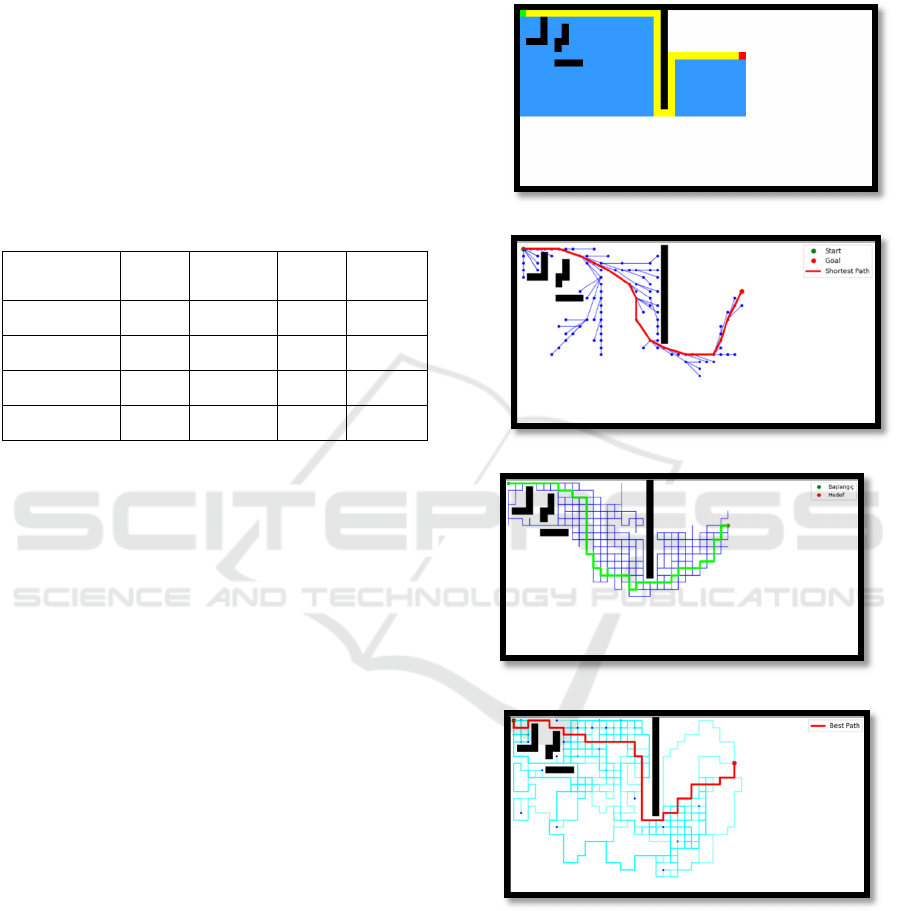
ACO successfully reached the goal but, due to their
population-based and pheromone-based nature,
tended to explore a broader solution space before
converging. Consequently, both algorithms incurred
higher computational costs and longer convergence
times. Figure 1 shows the path planning of the
compared algorithms on Grid 1. A* algorithm
provided the fastest, most stable, and shortest path
solutions in this environment, whereas RRT*, GA,
and ACO demonstrated greater flexibility and
adaptability but were limited by their computational
overhead. A comparative summary of algorithmic
performance on Map 1 is presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Performance Analysis on Grid 1
Algorithm
Path
Length
(ste
p
s)
Execution
Time (ms)
Success
Rate
Stability
A* 54 0.9 100% High
RRT* 52.5 1.9 100% Medium
Genetic
Algorithm
57 3386 100% Medium
Ant Colony
Optimization
57 16553 100% Medium
3.2 Map 2: High-Density Obstacle
Structure and Performance
Analysis
In this test scenario, the performance of four path
planning algorithms was evaluated in a complex
environment with high obstacle density. The grid was
designed with 25 rows and 50 columns, with the start
point located at (1,1) and the goal at (23,48).
Obstacles were strategically positioned to form
narrow passages and maze-like barriers, creating
bottlenecks and obstacle clusters that made direct
routes impossible. This configuration was
specifically designed to test not only the ability of the
algorithms to find short paths but also their capacity
to develop robust strategies in highly constrained
environments. Each algorithm was tested under
carefully selected parameter settings appropriate to its
structure. The A* algorithm used four-directional
neighborhood and the Manhattan heuristic,
maintaining simplicity and speed while producing
efficient routes in the cluttered space.
RRT* was applied with a step size of 1 unit, a
neighborhood radius of 4 units, and a maximum of
800 iterations, expanding its branching structure to
search for feasible solutions. The Genetic Algorithm
was executed with an initial population of 800
individuals, a maximum path length of 170 steps, 700
generations,
and a mutation rate of 10%, allowing a
A) A* Algorithm
B) RTT* Algorithm
C) Genatic Algorithm
D) Ant Colony Algorithm
Figure 1: Performance Analysis on Grid 1.
diverse exploration of more complex routes. The Ant
Colony Optimization method was tested with 60 ants,
200 iterations, a pheromone evaporation rate of 60%,
and parameter values of α=1 and β=2, ensuring a
balance between pheromone reinforcement and
heuristic guidance.
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
186

The results demonstrated that all four algorithms
achieved a 100% success rate in this high-density
grid; however, significant differences were observed
in computation time and path quality. The A*
algorithm once again produced short and stable paths,
while RRT* found even shorter solutions but required
noticeably longer runtimes. Figure 2 shows the path
planning of the compared algorithms on Grid 2. The
Genetic Algorithm successfully reached the goal but
incurred very high computational costs and generated
paths that were zigzagged and indirect due to the
complexity of the environment. Similarly, Ant
Colony Optimization produced valid solutions but at
a considerable computational expense.
RRT* was applied with a step size of 1 unit, a
neighborhood radius of 4 units, and a maximum of
800 iterations, expanding its branching structure to
search for feasible solutions. The Genetic Algorithm
was executed with an initial population of 800
individuals, a maximum path length of 170 steps, 700
generations, and a mutation rate of 10%, allowing a
diverse exploration of more complex routes. The Ant
Colony Optimization method was tested with 60 ants,
200 iterations, a pheromone evaporation rate of 60%,
and parameter values of α=1 and β=2, ensuring a
balance between pheromone reinforcement and
heuristic guidance.
The results demonstrated that all four algorithms
achieved a 100% success rate in this high-density grid;
however, significant differences were observed in
computation time and path quality. The A* search for
feasible solutions. The Genetic Algorithm was
executed with an initial population of 800 individuals,
a maximum path length of 170 steps, 700 generations,
and a mutation rate of 10%, allowing a diverse
exploration of more complex routes. The Ant Colony
Optimization method was tested with 60 ants, 200
iterations, a pheromone evaporation rate of 60%,
algorithm once again produced short and stable paths,
while RRT* found even shorter solutions but required
noticeably longer runtimes. The Genetic Algorithm
successfully reached the goal but incurred very high
computational costs and generated paths that were
zigzagged and indirect due to the complexity of the
environment. Similarly, Ant Colony Optimization
produced valid solutions but at a considerable
computational expense. A comparative summary of
the performance results on Grid 2 is presented in Table
2. The results obtained from this test demonstrate that
in highly cluttered environments, deterministic
methods (particularly A*) exhibit more consistent
performance in terms of speed and accuracy, while
sampling-based and intelligence inspired approaches
require
significantly longer computation times and
A) A* Algorithm
B) RTT* Algorithm
C) Genatic Algorithm
D) Ant Colony Algorthm
Figure 2: Performance Analysis on Grid 2.
tend to generate more complex paths. Nevertheless,
these methods can still be considered as valuable
alternatives due to their capability to cope with highly
complex structures.
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
187
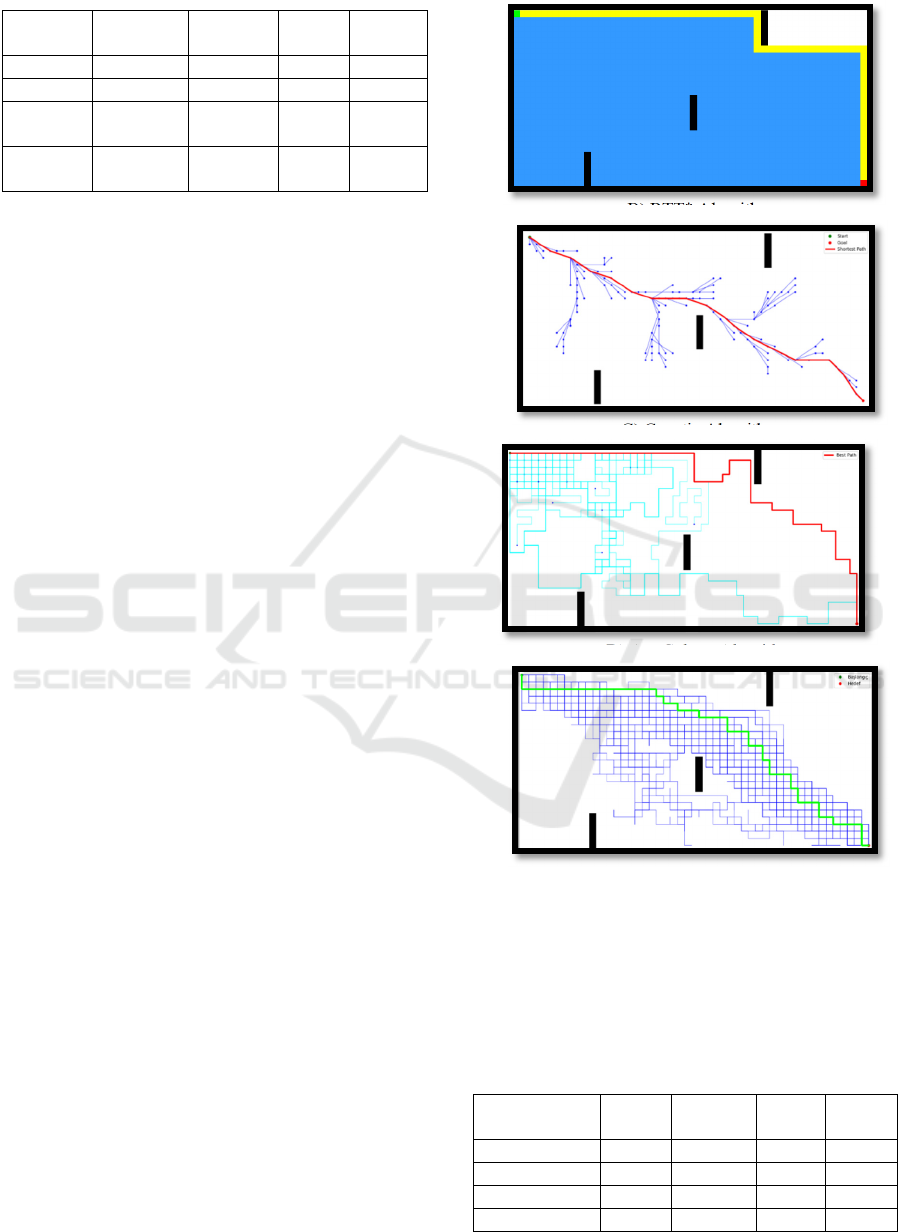
Table 2. Performance Analysis on Grid 2.
Algorithm
Path Length
(steps)
Execution
Time (ms)
Success
Rate
Stability
A* 70 2.5 100% High
RRT* 66.3 14.2 100% Medium
Genetic
Algorithm
134.9 17,551 100% Medium
Ant Colony
Optimization
79 13,885 100% Medium
3.3 Map 3: Low-Density Obstacle
Structure and Performance
Analysis
In this test, the performance of four different path
planning algorithms was evaluated on a grid with low
obstacle density. The grid consists of 25 rows and 50
columns, with the start point at (0, 0) and the goal
point at (24, 49). Obstacles were sparsely placed,
leaving wide open areas across the grid. The purpose
of this structure is to assess the ability of the
algorithms to generate the shortest and most accurate
paths in free spaces. Specifically, the obstacles were
positioned to partially block the direct route, allowing
observation of whether the algorithms could
effectively utilize open spaces to find efficient paths.
Each algorithm was executed with parameters
tailored to its principles. In A*, the Manhattan
distance heuristic with four-directional neighborhood
connectivity was employed. RRT* was run with a step
size of 1 unit, a neighborhood radius of 4 units, and an
iteration limit of 800. For the Genetic Algorithm,
anticipating the possibility of longer paths in this
structure, a population of 300 individuals was
initialized, the maximum step length was increased to
110, and evolution was performed over 500
generations with a mutation rate of 10%. In the Ant
Colony Optimization algorithm, 60 artificial ants and
200 iterations were used, with a pheromone
evaporation rate of 60%, and α = 1, β = 2 parameters.
These values allowed the ants to balance the
exploitation of previously successful paths with
proximity to the goal. According to the test results, all
algorithms achieved the target with a 100% success
rate. The A* algorithm once again produced the
shortest and most stable paths with high speed, while
the RRT* algorithm, despite its randomized sampling
nature, generated efficient paths that were even
slightly shorter. The Genetic Algorithm successfully
reached the goal but required significantly longer
computation times compared to the other methods.
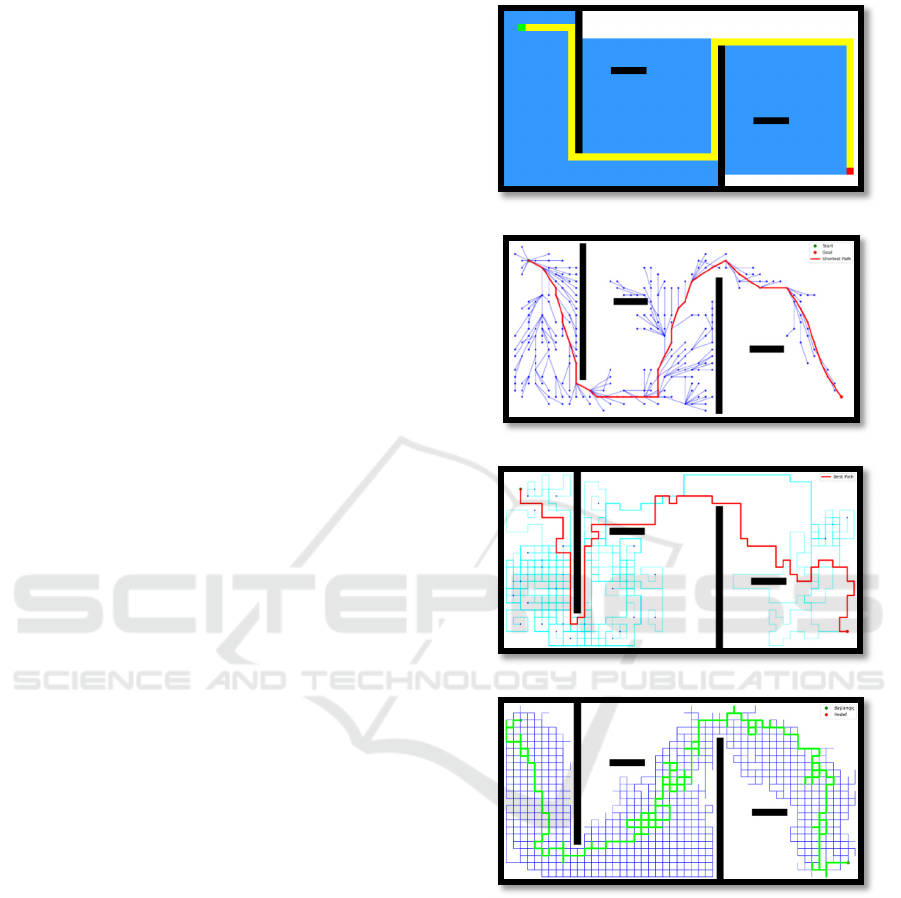
Figure 3 shows the path planning of the compared
algorithms on Grid 3. The Ant Colony Optimization
algorithm
was the slowest method in
this
scenario, as
A) A* Algorithm
B) RTT* Algorithm
C) Genatic Algorithm
D) Ant Colony Algorithm
Figure 3: Performance Analysis on Grid 3
wider free areas demanded more exploration and
pheromone accumulation, resulting in higher iteration
counts and longer execution times. A comparative
summary of the performance results on Grid 3 is
presented in Table 3.
Table 3. Performance Analysis on Grid 3.
Algorithm
Path
Length
Execution
Time (ms)
Success
Rate
Stability
A* 74 steps 3.0 ms 100% High
RRT* 65.4 steps 3.19 ms 70% Medium
Genetic Algorithm 74 steps 6395 ms 80% Medium
Ant Colony 81.2 steps 11629 ms 100% Medium
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
188
These results indicate that in environments with
sparse obstacles and large open spaces, deterministic
methods (particularly A*) are capable of producing
high-quality paths in a very short time. RRT* has
shown a tendency to generate efficient paths in free
regions due to its sampling-based exploration. On the
other hand, Genetic Algorithm and Ant Colony
Optimization required significantly longer execution
times because of their exploration and optimization
processes. It is clearly observed that in such spacious
and low-obstacle environments, deterministic
algorithms provide a direct advantage.
3.4 Map 4: Vertical Barriers and
Performance of Path Planning
Algorithms
This test scenario was conducted on an environment
where vertical barriers were densely placed, making
direct passage more difficult. The grid consisted of 25
rows and 50 columns, with the start point defined as
(2, 2) and the target point as (22, 48). Vertical
obstacles were positioned to block large areas of the
grid, requiring the algorithms to identify feasible
routes through narrow corridors. This structure was
specifically designed to evaluate the algorithms’
ability to navigate confined passages and optimize
path planning under restrictive conditions.
All algorithms were executed using fixed
parameters suitable for their respective characteristics.
The A* algorithm employed
four-directional
connectivity and the Manhattan heuristic to ensure fast
and stable path generation. The RRT* algorithm was
run with a step size of 1 unit, a neighborhood radius of
4 units, and an iteration limit of 800, aiming to
discover feasible paths through random sampling and
rewiring processes. The Genetic Algorithm was tested
with an initial population of 800 individuals, a
maximum step limit of 500, and 500 generations,
while maintaining solution diversity with a 10%
mutation rate. The Ant Colony Optimization (ACO)
method was implemented with 100 ants, 300
iterations, a pheromone evaporation rate of 50%, α =
1, β = 2, and a reinforcement of 200 pheromone units
for each successful path.
The results revealed that the A* algorithm
consistently produced reliable, short, and fast
solutions, even in this complex configuration. The
RRT* algorithm achieved a 100% success rate and
generated path lengths comparable to A*, but with
noticeably higher computation time. The Genetic
Algorithm successfully produced valid paths in 75%
of the tests; however, both the path length and
execution
time remained relatively high. The Ant
A) A* Algorithm
B) RTT* Algorithm
C) Genatic Algorithm
D) Ant Colony Algorthm
Figure 4: Performance Analysis on Grid 4.
Colony Optimization method achieved success in all
runs, but generated the longest and most
computationally expensive paths. Nevertheless, the
routes produced by ACO displayed smooth navigation
through obstacles, albeit via indirect detours. Figure 4
shows the path planning of the compared algorithms
on Grid 4.
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
189
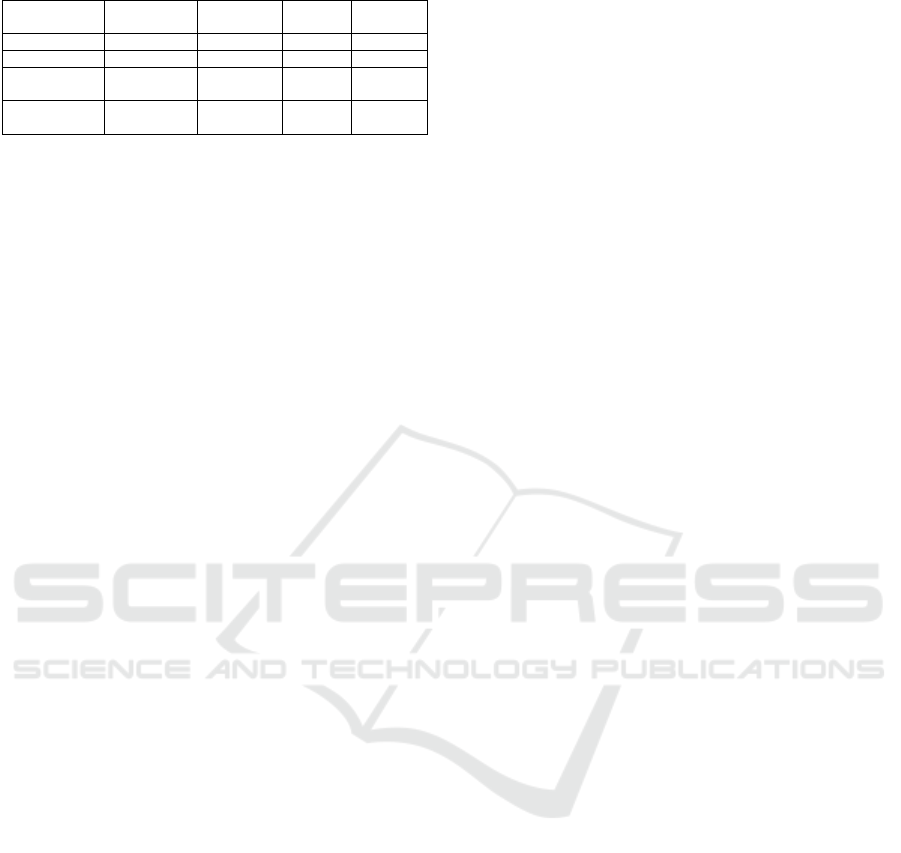
Table 4. Performance Analysis for Grid 4.
Algorithm
Path
Len
g
th(ste
p
s)
Execution
Time (ms)
Success
Rate
Stability
A* 99 2.5 ms 100% Hi
g
h
RRT* 96.6 17.2 ms 100% Mediu
m
Genetic
Algorith
m
171.2 26,537 ms 75% Medium
Ant Colony
O
p
timization
102.33 25,316 ms 100% Medium
This test demonstrates that in complex
environments with dense vertical obstacles,
deterministic methods (particularly the A* algorithm)
still provide a strong and reliable solution, while
sampling-based and intelligence-inspired approaches
are more costly in terms of computation time and path
length. Nevertheless, these methods remain valuable
alternatives due to their flexibility in generating
feasible and alternative routes through obstacle-rich
areas
.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, the performance of four widely used
path planning algorithms for autonomous robot
navigation A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant
Colony Optimization was thoroughly compared
across four different grid environments. The
algorithms were evaluated based on key performance
metrics such as path length, computation time, and
success rate. Additionally, they were conceptually
categorized into search-based, sampling-based, and
intelligence-inspired methods for further
interpretation.
Among the search-based methods, the A*
algorithm consistently found the shortest or near-
shortest paths across all tested grids while achieving
the lowest computation times. Particularly in grids
with low and medium obstacle density, A*
demonstrated a 100% success rate, producing reliable
and well-structured paths. However, in environments
with higher complexity and dense vertical barriers,
the path length and computation time increased,
although the success rate remained high. This
indicates that while A* benefits from its systematic
search and heuristic-driven guidance, the
computational cost grows with the expansion of the
search space in complex environments.
The RRT* algorithm, representing the sampling-
based category, exhibited flexibility in complex
scenarios due to its random sampling and rewiring
principles. It successfully generated feasible paths in
all tested grids; however, the path quality and
computation time varied significantly. In highly
cluttered environments with narrow passages, RRT*
produced shorter paths compared to A*, but at the
expense of higher computation times. The
performance of RRT* was strongly influenced by
parameter settings such as iteration count and step
size.
Within the intelligence-inspired methods, the
Genetic Algorithm demonstrated a capacity to
explore alternative solutions, particularly in highly
complex environments. Nevertheless, its
performance was more sensitive to parameter tuning
compared to the other methods. With properly set
population size, number of generations, and mutation
rate, feasible and reasonable paths could be obtained.
However, in most cases, GA incurred the highest
computational costs in terms of both path length and
execution time. Its success rate also tended to
decrease in complex structures, and the generated
paths were often indirect.
The Ant Colony Optimization algorithm,
leveraging pheromone-based exploration and
exploitation mechanisms, achieved near-perfect
success rates across all grids. However, it was one of
the most computationally expensive methods in terms
of execution time and path quality. Although
increasing the number of ants and iterations improved
performance, it also significantly raised
computational costs. ACO showed a tendency to
generate feasible yet indirect paths, particularly in
wider grids with multiple alternative passages.
Overall, this study highlights the critical
importance of algorithm selection depending on the
application conditions. For low to moderately
difficult environments, the A* algorithm emerges as
the most advantageous solution in terms of both speed
and accuracy. In contrast, RRT* and Ant Colony
Optimization provide flexible alternatives in more
complex structures with narrow corridors, while the
Genetic Algorithm requires extensive parameter
tuning and remains the most computationally
demanding method. These findings suggest that
instead of relying on fixed algorithms, hybrid and
adaptive approaches may offer more effective
solutions for future autonomous robot navigation
tasks. Furthermore, parametric optimization and
learning-based adaptation mechanisms represent
promising directions for improving the performance
of existing algorithms.
5 CONCLUSION
This study's empirical investigation of A*, RRT*,
Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
190

confirms that the optimal path planning algorithm is
intrinsically linked to the operational environment's
complexity. A fundamental trade-off exists between
computational efficiency and solution robustness.
The A* algorithm consistently demonstrated superior
speed and optimality in low-to-medium complexity
environments, establishing it as a benchmark for
structured spaces. In contrast, RRT* offered greater
flexibility in navigating intricate, non-convex
topographies, while the metaheuristic GA and ACO
approaches proved capable of solving the most
complex scenarios, albeit at a significant
computational cost and with high sensitivity to
parameter tuning.
Future research should prioritize the development
of hybrid methodologies that synergistically combine
the deterministic efficiency of algorithms like A*
with the exploratory strengths of RRT* or ACO.
Furthermore, extending this comparative analysis to
dynamic and three-dimensional environments,
alongside integrating machine learning for adaptive
parameterization, remains a critical next step for
advancing autonomous navigation systems.
REFERENCES
Aksoy, N., Cakil, F., & Tekdemir, I. G. (2024).
Performance Analysis of Deterministic and
Probabilistic Path Planning Algorithms in Complex
Environments. 2024 Innovations in Intelligent Systems
and Applications C, ASYU
2024.https://doi.org/10.1109/ASYU62119.2024.10757
028
Elshamli, A., Abdullah, H. A., & Areibi, S. (2004). Genetic
algorithm for dynamic path planning. Canadian
Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering,
2, 0677–0680.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE.2004.1345203
Hsueh, H. Y., Toma, A. I., Ali Jaafar, H., Stow, E., Murai,
R., Kelly, P. H. J., & Saeedi, S. (2022). Systematic
comparison of path planning algorithms using
PathBench. Advanced Robotics, 36(11), 566–581.
https://doi.org/10.1080/01691864.2022.2062259
Li, B., Li, B., Ni, K., Zhou, F., Li, Y., Huang, W., Jiang, H.,
Liu, F., Ni, K., Zhou, F., Li, Y., Huang, W., Jiang, H.,
& Liu, F. (2025). Research on robot path planning
based on fused Dijkstra and TEB algorithms. Journal of
Mechanical Science and Technology 2025 39:8, 39(8),
4651–4660. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12206-025-
0738-8
Liu, J., Yang, J., Liu, H., Tian, X., & Gao, M. (2016). An
improved ant colony algorithm for robot path planning.
Soft Computing 2016 21:19, 21(19), 5829–5839.
https://doi.org/10.1007/S00500-016-2161-7
Liu, L., Wang, X., Yang, X., Liu, H., Li, J., & Wang, P.
(2023). Path planning techniques for mobile robots:
Review and prospect. Expert Systems with
Applications, 227, 120254.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2023.120254
Noreen, I., Khan, A., & Habib, Z. (2016). A Comparison of
RRT, RRT* and RRT*-Smart Path Planning
Algorithms. IJCSNS International Journal of Computer
Science and Network Security, 16(10), 20–27.
http://cloud.politala.ac.id/politala/1. Jurusan/Teknik
Informatika/19. e-journal/Jurnal Internasional
TI/IJCSNS/2016 Vol. 16 No. 10/20161004_A Compar
ison of RRT, RRT and RRT - Smart Path Planning
Algorithms.pdf
Reda, M., Onsy, A., Ghanbari, A., & Haikal, A. Y. (2024).
Path planning algorithms in the autonomous driving
system: A comprehensive review. Robotics and
Autonomous Systems,
174,104630.https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ROBOT.2024.10
4630
Sánchez-Ibáñez, J. R., Pérez-Del-pulgar, C. J., & García-
Cerezo, A. (2021). Path Planning for Autonomous
Mobile Robots: A Review. Sensors 2021, Vol. 21, Page
7898, 21(23), 7898. https://doi.org/10.3390/S21237898
Ugwoke, K. C., Nnanna, N. A., & Abdullahi, S. E. Y.
(2025). Simulation-based review of classical, heuristic,
and metaheuristic path planning algorithms. Scientific
Reports 2025 15:1, 15
(1), 12643-.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-96614-2
Zhang, H., Zhao, Y. J., Jin, Y. X., & Duan, H. L. (2025).
Path planning algorithm of steerable flexible needle: A
review. Expert Systems with Applications, 287, 128270.
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2025.128270
Simulation-Based Analysis of A*, RRT*, Genetic Algorithm, and Ant Colony Optimization for Autonomous Robot Path Planning in
Obstacle-Dense Maps
191
