
Comparative Performance Analysis of Ensemble and Attention-Based
Deep Learning Methods for Depression Classification
Nur Sultan Yüce
1,* a
, Abdullah Ammar Karcioğlu
2b
and Mesut Karabacak
1c
1
Department of Applied Mathematics, Institute of Science, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Turkey
2
Department of Software Engineering, Institute of Science, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Turkey
*
Keywords: Depression Prediction, Ensemble Learning, Deep Neural Networks, LightGBM, TabNet.
Abstract: Depression is a globally prevalent psychological disorder that significantly impairs individuals' quality of life.
Early diagnosis and timely intervention are essential for effective treatment and societal reintegration. This
study conducts a comparative performance analysis of ensemble learning methods including XGBoost,
Random Forest, LightGBM, Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM), and CatBoost and deep learning models
such as Deep Neural Networks (DNN) and TabNet for depression prediction. Using a publicly available
dataset, we applied various preprocessing and hyperparameter optimization techniques to enhance model
performance and mitigate overfitting. Experimental results demonstrate that the LightGBM model achieves
the highest classification accuracy (92.77%) and ROC-AUC (0.976), outperforming other models. These
findings indicate that ensemble-based approaches are highly effective for early depression detection and hold
promise for integration into data-driven clinical decision support systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
Depression is one of the most prevalent mental health
disorders worldwide. According to the World Health
Organization (2019), approximately 5% of adults
experience depression. In Turkey, the 2019 Health
Survey conducted by TurkStat reported that 9% of
individuals experienced depression-related
symptoms in the preceding 12 months (Kurutkan &
Kara, 2021).
Characterized by persistent mood disturbances,
depression often leads individuals to withdraw from
their surroundings and disengage socially and
emotionally (Johnson & Indvik, 1997). Common
symptoms include pessimism, feelings of
worthlessness, helplessness, hopelessness, impaired
social functioning, cognitive difficulties, and suicidal
ideation (Yıldız et al., 2024).
The impact of depression extends beyond
personal mental health, adversely affecting
individuals’ academic and occupational performance
and, on a larger scale, influencing societal
productivity and economic systems (Başoğul &
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-8593-7225
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0907-751X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0057-8115
Buldukoğlu, 2015). A longitudinal study in the
United States estimated the annual economic burden
of depression between 1996 and 2013 to range from
$188 billion to $200 billion (Mrazek et al., 2014),
while a 2013 European study reported a cost of
approximately €113 billion (Olesen et al., 2012).
Given its substantial socioeconomic
consequences, early detection and accurate diagnosis
of depression are critical at both the individual and
public health levels (Deveci, Ulutaşdemir, & Açık,
2013). Timely identification of at-risk individuals can
prevent long-term harm and facilitate access to
appropriate interventions.
With the rapid advancement of artificial
intelligence (AI) technologies, the healthcare sector
has seen growing interest in leveraging machine
learning algorithms to enhance diagnostic accuracy
(Jiang et al., 2017). AI methods have demonstrated
potential in analyzing multidimensional data—such
as socio-demographic attributes, family history, and
academic performance to detect depressive patterns
with high precision.
100
Yüce, N. S., Karcio
ˇ
glu, A. A. and Karabacak, M.
Comparative Performance Analysis of Ensemble and Attention-Based Deep Learning Methods for Depression Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0014363500004848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences (ICEEECS 2025), pages 100-105
ISBN: 978-989-758-783-2
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
This study aims to predict individuals’ depression
status using 20 socio-demographic and behavioral
features through various machine learning and deep
learning models. The primary objective is to compare
the predictive performance of ensemble-based and
attention-based models, contributing to the
development of interpretable and reliable AI-driven
tools for mental health assessment.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In this section, the ensemble learning and deep
learning methods used in the study are described in
detail.
2.1 Ensemble Learning Methods
Ensemble learning is a machine learning paradigm
that combines multiple models to enhance
classification performance and mitigate common
issues such as high variance or bias. In the literature,
such techniques are also referred to as meta-learning
(Brazdil & Giraud-Carrier, 2010; Fan et al., 2023).
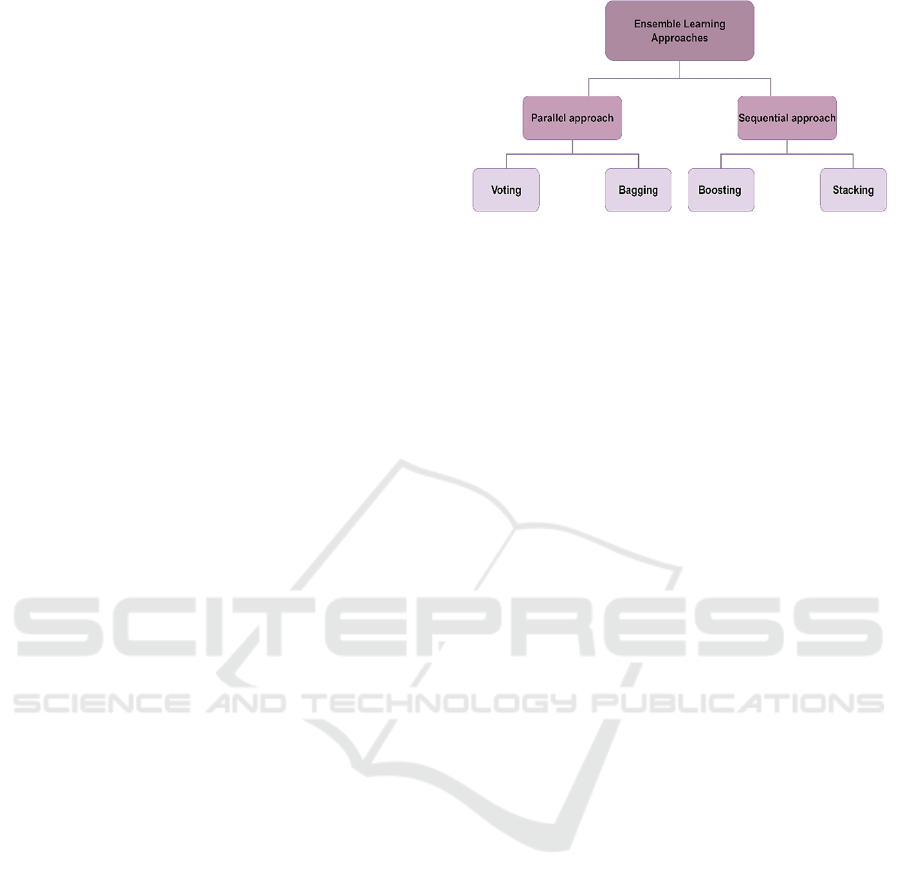
The main ensemble techniques employed in this study
include voting, bagging, boosting, and stacking.
In Voting, all models are trained on the same
dataset, and their predictions are combined through
majority or weighted voting. Bagging (Bootstrap
Aggregating) divides the training data into random
subsets, trains separate models on each, and
aggregates their outputs. Boosting builds models
sequentially, with each new model attempting to
correct the errors of its predecessor. Stacking
involves training several base models and using their
outputs as inputs to a meta-model, which learns to
combine them for improved performance. These
techniques are widely adopted due to their consistent
ability to outperform single-model approaches
(Mienye & Sun, 2022).
These methods are commonly used in academic
studies because they often provide better performance
than using a single model alone. These ensemble
learning methods are visually classified and
summarized in the diagram presented in Figure 1.
2.2 Deep Learning Approaches
In recent years, deep learning has become prominent
for its superior performance in various complex tasks.
Figure 1: Classification of ensemble learning methods.
Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep
learning models can handle large-scale datasets,
automatically extract features, and model intricate
data patterns (Schmidhuber, 2015). Artificial Neural
Networks (ANNs), inspired by biological neurons,
are the core components of deep learning
architectures. They aim to learn input-output
mappings by adjusting their internal parameters based
on data (LeCun et al., 2015).
A Deep Neural Network (DNN) typically consists
of an input layer, multiple hidden layers, and an output
layer. It utilizes forward propagation to generate
predictions and backpropagation to optimize weights.
DNNs often incorporate activation functions such as
ReLU, Tanh, or Sigmoid, and regularization
techniques like Dropout to prevent overfitting
(Schmidhuber, 2015).
One of the deep learning models used in this study is
TabNet, a neural network architecture introduced by
Arik and Pfister (2021) specifically designed for
tabular data. TabNet integrates an attention
mechanism to dynamically select which features to
focus on at each decision step. It combines the end-
to-end learning and representation power of deep
learning with interpretability and feature selection
capabilities commonly associated with tree-based
models.
The TabNet architecture comprises three core
components:
Feature Transformer. Converts each data instance
into a feature representation via fully connected layers
with batch normalization and ReLU activations.
Attention Transformer. Determines the importance
of features at each step using Sparsemax, a sparsity-
inducing activation function.
Decision Steps & Aggregation. Aggregates
decisions over multiple steps to form the final output
representation.
In this study, both ensemble learning methods and
deep learning models are employed to construct a
classification model for depression prediction. Prior
Comparative Performance Analysis of Ensemble and Attention-Based Deep Learning Methods for Depression Classification
101
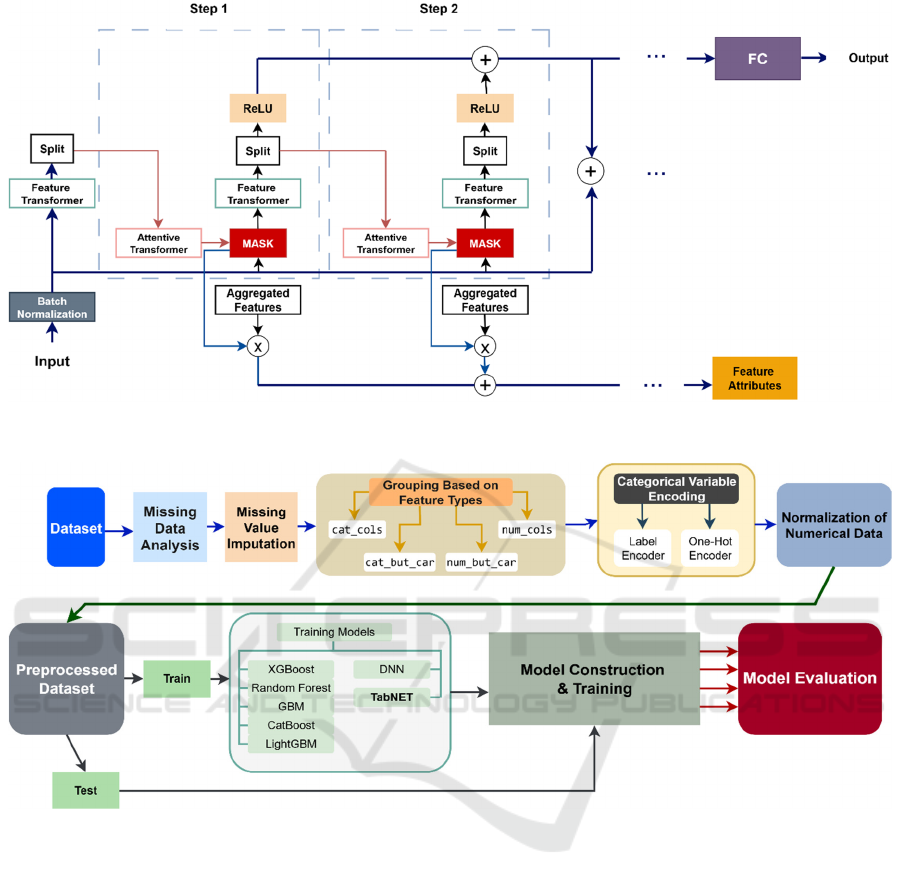
Figure 2. TabNet Architecture (Adapted from Arik & Pfister, 2021).
Figure 3. Data Preprocessing and Modeling Steps.
research in this domain has predominantly relied on
traditional machine learning algorithms. The use of
TabNet, which emphasizes interpretability and
adaptive feature selection through attention,
represents a novel contribution. Therefore, this study
aims to offer added value to the literature in terms of
both predictive performance and the transparency of
the model’s decision-making process.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection and Data Set
In this study, data on individuals with and without
depression
were
obtained
from
Kaggle,
an
open-
source platform.
The dataset consists of 49,976 observations and
includes 20 variables covering demographic
characteristics related to depression, academic and
occupational status, lifestyle habits, and various
psychological indicators. It is suitable for binary
classification, with the target variable divided into
two classes: depression present (1) and absent (0).
The dataset exhibits a balanced distribution between
these classes.
Some variables, such as Profession, Academic
Pressure, CGPA, and Study Satisfaction, contained a
high proportion of missing data. These missing values
were handled using appropriate imputation
techniques prior to modeling. The overall data
preprocessing and modeling pipeline is illustrated in
Figure 3.
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
102
3.2 Data Preprocessing
During preprocessing, columns with more than 60%
missing data (Academic Pressure, CGPA, and Study
Satisfaction) were removed. Additionally, non-
informative columns such as "id" and "Name" were
excluded from both training and test sets. For the
remaining missing data in variables like Profession,
Job Satisfaction, and Work Pressure, numerical
features were imputed using the median, while
categorical features were imputed with the mode of
the respective columns. This approach helped prevent
data leakage between training and test sets.
Variables were categorized as categorical columns
(cat_cols), numerical columns (num_cols),
categorical columns with high cardinality
(cat_but_car), and numerical columns with
categorical appearance (num_but_car). To ensure
consistency during modeling, categorical variables
were encoded in two stages: binary categorical
variables with LabelEncoder, and multiclass
variables with One-Hot Encoding. Numerical
variables were standardized using StandardScaler to
prevent bias due to differing feature scales. The
dataset was split into 80% training and 20% testing
subsets.
3.3 Model Selection and
Hyperparameter Optimization
Different machine learning and deep learning
algorithms were compared for depression
classification, including Random Forest, TabNet,
CatBoost, XGBoost, LightGBM, Gradient Boosting
Machine (GBM), and Deep Neural Networks (DNN).
Early signs of overfitting were observed in some
models, such as Random Forest and XGBoost, which
were mitigated through hyperparameter tuning using
RandomizedSearchCV and GridSearchCV.
Optimized models were further combined using a
stacking approach to construct the final ensemble.
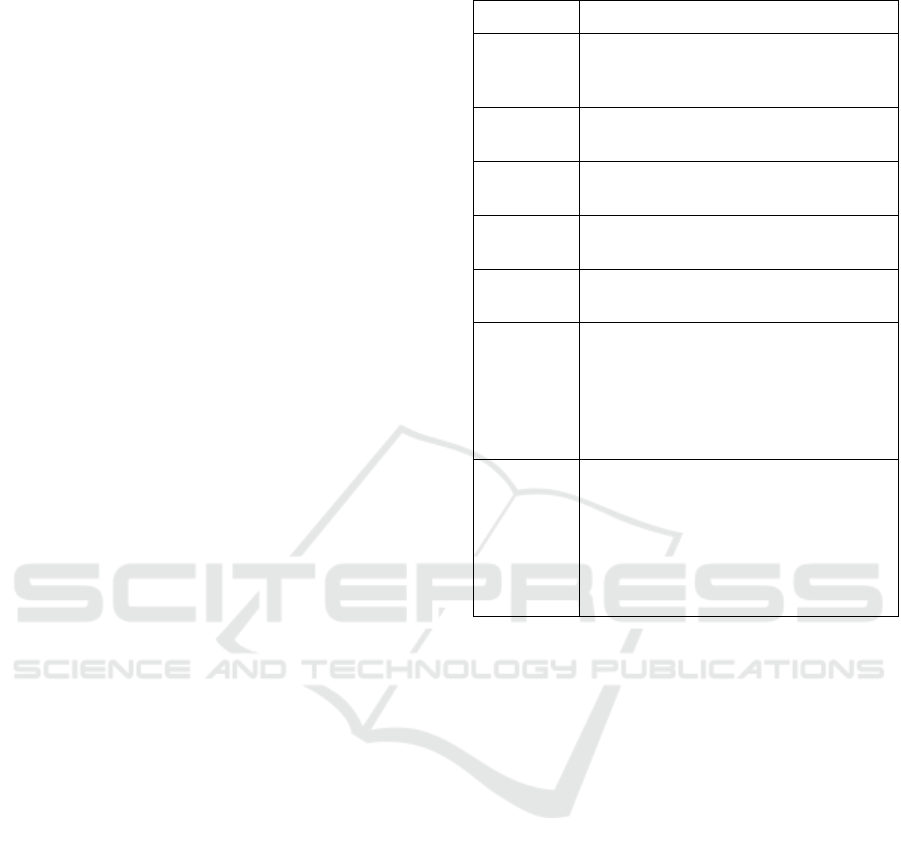
Hyperparameter optimization for TabNet was
performed using the ParameterGrid method. The best
hyperparameter values for all models are presented in
Table 1.
3.4 Performance Evaluation Metrics
Model performance was evaluated using commonly
used classification metrics, including Accuracy,
Precision, Recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC. These
metrics provided a comprehensive assessment of the
models' effectiveness in depression classification
(Obi, 2023).
Table 1. Optimal Hyperparameters per Model.
Model Best Hyperparamete
r
LightGBM colsample_bytree=0.8,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=200
Random
Forest
max_depth=20,
min
_
sam
p
les
_
s
p
lit=10,n
_
estimators=300
CatBoost depth=5, iterations=500,
learnin
g_
rate=0.05
Gradient
Boosting
learning_rate=0.1, max_depth=3,
n_estimators=500,subsample=0.7
XGBoost learning_rate=0.1, max_depth=3,
n
_
estimators=300
TabNet Optimizer: Adam, Batch Size: 128,
Learning Rate: 0.01, Virtual Batch: 16,
Weight Decay: 1e-3,
Mask Type: entmax,
Batch Normalization: Yes,
E
p
och: 100 ,
(
Earl
y
Sto
pp
in
g
: 10
)
DNN Optimizer: Adam,
Learning Rate:0.002
Rightarrow: 0.001,
Weight Decay: 0.001 (L2),
Batch Size: 32, Dropout: 0.5, 0.4,
Batch Normalization: No,
Epoch: 50 ,(EarlyStopping: 3)
4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
LightGBM, Random Forest, XGBoost, Gradient
Boosting Machine (GBM), and CatBoost were
employed as ensemble learning models in this study.
These models were selected due to their high
classification accuracy, flexibility, and widespread
use in various machine learning tasks.
For initial hyperparameter optimization,
RandomizedSearchCV was applied to conduct a
broad search over a wide range of parameter values.
However, after optimization, a substantial gap in
accuracy between training and test sets—particularly
in XGBoost and Random Forest—indicated a
tendency toward overfitting. To address this issue,
more refined hyperparameter tuning was performed
using GridSearchCV. These additional optimizations
successfully mitigated overfitting and improved the
models’ generalization performance.
Following the hyperparameter tuning process, a
Voting Classifier was constructed using the soft
voting strategy to combine the strengths of individual
models. This ensemble approach was aimed at
producing more balanced and robust classification
Comparative Performance Analysis of Ensemble and Attention-Based Deep Learning Methods for Depression Classification
103
results compared to relying on a single model.The
accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC
metrics used to evaluate the classification
performance of the ensemble learning models are
summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 . Performance Comparison of Ensemble Learning
Models.
Model Accuracy F1 Precision Recall ROC
CatBoost %91.33 %89.9 %90.97 %88.9 0.96
Random
Forest
%90.05 %88.4 %88.17 %88.6 0.96
GBM %91.44 %90.1 %91.01 %89.6 0.96
LGBM %92.77 %89.9 %90.14 %89.4 0.97
XGBoost %91.10 %90.0 %89.89 %89.6 0.96
The Deep Neural Network (DNN) model was
selected for its capability to learn robust feature
representations from large datasets, whereas the
TabNet model was chosen for its effectiveness in
processing both numerical and categorical data
simultaneously.
For optimizing the DNN, various experiments
were conducted on hyperparameters such as the
number of layers, number of neurons, and learning
rate. Furthermore, regularization techniques
including early stopping and dropout were employed
to mitigate overfitting. Hyperparameter tuning for the
TabNet model was performed using GridSearchCV.
Additionally, early stopping, dropout (similar to the
DNN), and weight decay were applied to further
reduce the risk of overfitting.
The classification performance metrics—
including accuracy, recall, precision, and F1-score—
of the DNN and TabNet models are summarized in
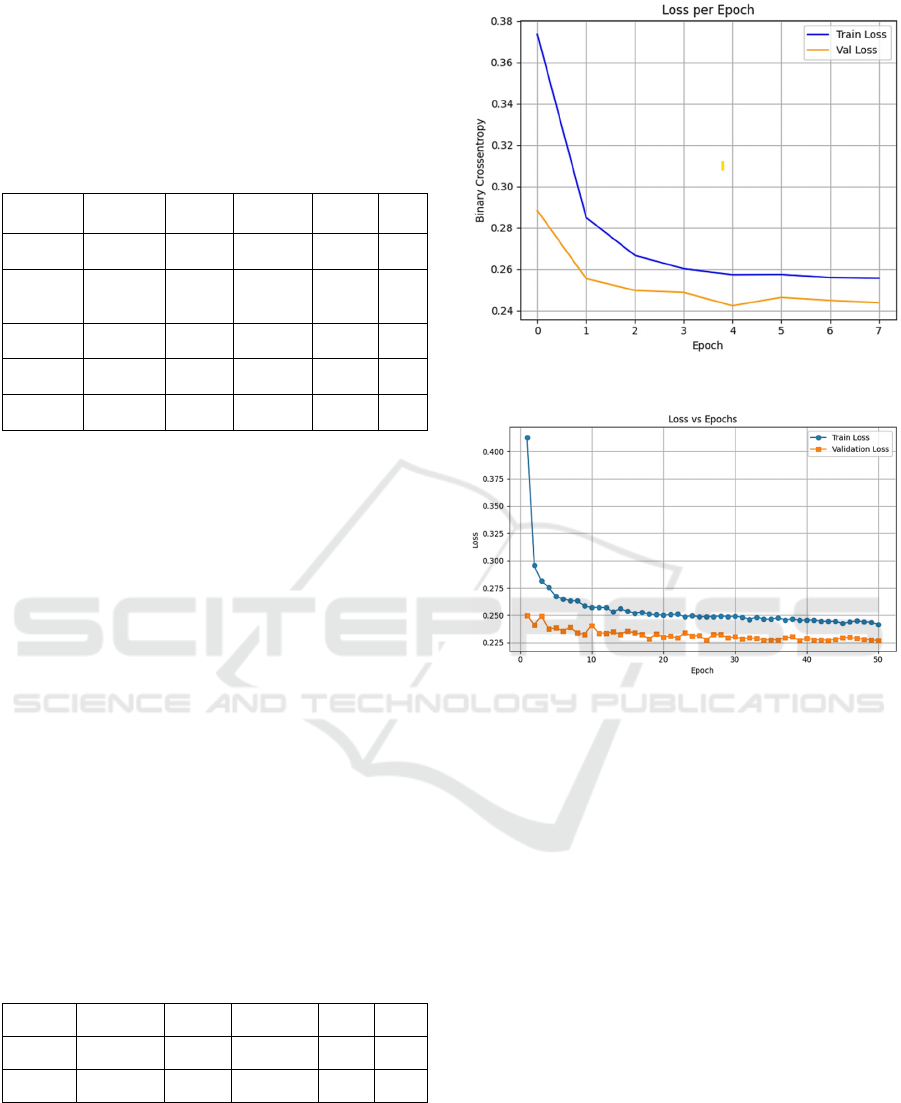
Table 3. The corresponding loss curves are illustrated
in Figures 4 and 5.
Table 3 : Performance Comparison of Deep Learning
Models.
Model Accurac
y
F1 Precision ROC Loss
DNN %90.9 %89.4 %89.0 0.96 0.24
TabNet %91.9 %91.2 %90.9 0.96 0.22
Figure 4: DNN Loss Curve.
Figure 5: TabNeT Loss Curve.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this study, various machine learning and deep
learning algorithms were evaluated and compared on
a dataset for predicting depression. Ensemble
learning-based tree models including CatBoost,
LightGBM, GBM, XGBoost, and Random Forest, as
well as deep learning models such as a conventional
deep neural network (DNN) and TabNet, were
employed. Unlike traditional tree-based models,
TabNet was included due to its attention-based
architecture, which enables effective processing of
numeric and categorical data simultaneously.
Overall, all models performed comparably well,
achieving high levels of accuracy. Among the
ensemble models, LightGBM demonstrated the
highest classification performance with an accuracy
of 92.77%, an F1-score of 89.93%, and an ROC AUC
of 0.976. Among deep learning approaches, TabNet
outperformed the conventional DNN, achieving an
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
104

accuracy of 91.9% and an F1-score of 91.2%. In this
regard, TabNet shows promise as a deep neural
network model that combines the interpretability of
classical tree-based methods with the representational
power of deep learning.
The performance of the models largely depends
on the quality and size of the dataset. Therefore,
addressing missing data through appropriate
imputation methods, incorporating new diagnosis-
specific features, and applying further feature
engineering techniques on existing data could
improve model performance.
In the healthcare domain, early diagnosis is
crucial, particularly for conditions like depression
that significantly impact both individual quality of
life and public health. When supported by expert
clinical supervision, such models can provide
valuable assistance in clinical decision-making
processes.
REFERENCES
Arik, S. O., & Pfister, T. (2021). TabNet: Attentive
interpretable tabular learning. Proceedings of the AAAI
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 35(8), 6679–
6687. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i8.16826
Başoğul, C., & Buldukoğlu, K. (2015). Depresif
bozukluklarda psikososyal girişimler. Psikiyatride
Güncel Yaklaşımlar - Current Approaches in
Psychiatry, 7(1), 1–15.
https://doi.org/10.5455/cap.20140426072955
Brazdil, P. B., Giraud-Carrier, C. G., Kononenko, I., &
Vilalta, R. (2010). A survey of metalearning for
classification. Artificial Intelligence Review, 33(4),
269–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-010-9236-5
Deveci, S. E., Ulutaşdemir, N., & Açık, Y. (2013). Bir
sağlık yüksekokulu öğrencilerinde depresyon
belirtilerinin görülme sıklığı ve etkileyen faktörler.
Fırat Tıp Dergisi, 18(2), 98–102.
Fan, Z., Yu, Z., Yang, K., Chen, W., Liu, X., Li, G., Yang,
X., & Chen, C. L. P. (2023). Diverse models, united
goal: A comprehensive survey of ensemble learning.
Computing and Intelligence Technology (CIT), 17(3),
123–156. https://doi.org/10.1049/cit2.70030
Jiang, F., Jiang, Y., Zhi, H., Dong, Y., Li, H., Ma, S., …
Wang, Y. (2017). Artificial intelligence in healthcare:
Past, present and future. Stroke and Vascular
Neurology, 2(4), 230–243. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-
2017-000101
Johnson, P. R., & Indvik, J. (1997). The boomer blues:
Depression in the workplace. Public Personnel
Management, 26(3), 359–365.
https://doi.org/10.1177/009102609702600305
Kurutkan, M. N., & Kara, O. (2021). Depresyonlu
bireylerde sosyo-demografik faktörlerin diyet
kalitesine etkileri: Türkiye Sağlık Araştırması
verilerinden analitik kanıtlar. In 3rd International
Symposium on Critical Analytical Thinking, Ankara,
Türkiye. https://doi.org/10.33793/acperpro.05.01.39
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning.
Nature, 521, 436–444.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Mrazek, D. A., Hornberger, J. C., Altar, C. A., & Degtiar,
I. (2014). A review of the clinical, economic, and
societal burden of treatment-resistant depression:
1996–2013. Psychiatric Services, 65(8), 977–987.
https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ps.201300059
Olesen, J., Gustavsson, A., Svensson, M., Wittchen, H.-U.,
Jönsson, B., & European Brain Council. (2012). The
economic cost of brain disorders in Europe. European
Journal of Neurology, 19(1), 155–162.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03590.x
Schmidhuber, J. (2015). Deep learning in neural networks:
An overview. Neural Networks, 61, 85–117.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.001
Yıldız, N. G., Aydın, K., Aydın, H., Phiri, Y., & Yıldız, H.
(2024). Türkiye’de depresyonun yaygınlığı ile ilişkili
faktörler: Nüfusa dayalı bir çalışma. Türk Psikiyatri
Dergisi, 35(3), 167–177.
I.D. Mienye and Y. Sun, "A Survey of Ensemble Learning:
Concepts, Algorithms, Applications, and Prospects,"
IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 97039–97063, 2022,
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.320727
J. C. Obi, “A Comparative Study of Several Classification
Metrics and Their Performances on Data,” World
Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology and
Sciences, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 308–314, Feb. 2023, doi:
https://doi.org/10.30574/wjaets.2023.8.1.0054
Comparative Performance Analysis of Ensemble and Attention-Based Deep Learning Methods for Depression Classification
105
