
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation,
and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News
Texts
Dilara Adıgüzel
1a
, Burcu Yalçıner
2b
and Işıl Karabey Aksakallı
1c
¹Department of Computer Engineering, Erzurum Technical University, Erzurum, Turkey
²Department of Computer Engineering, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey
Keywords: Automatic Topic Labeling, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, Zero-Shot Classification, TF-IDF, Coherence Score,
BART, DeBERTa-v3.
Abstract: This study presents a comparative analysis of supervised and unsupervised methods for automatic topic
labeling in news articles, emphasizing models that work with unlabeled data. The Reuters-21578 dataset was
used to evaluate three distinct approaches: topic modeling, zero-shot classification (ZSC), and similarity-
based classification. In the first phase, topic modeling was performed using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
on 6,440 documents. Fifteen topics were extracted, and the best coherence score achieved was 0.5122 when
the number of topics was set to 15. The second phase involved zero-shot classification without labeled training
data. Two pre-trained natural language inference (NLI) models—BART-large-MNLI and DeBERTa-v3-
MNLI-FEVER—were employed. This approach yielded 63.06% accuracy, 74.12% precision, 63.06% recall,
and an F1-score of 66.15%. Three-fold stratified cross-validation produced a consistent average F1-score of
67.96 ± 1.24%, demonstrating good generalization. In the final phase, similarity-based classification was
performed using vector representations derived from Term Frequency—Inverse Document Frequency (TF-
IDF), Bag-of-Words (BoW), and Word2Vec embeddings. Among these techniques, the TF-IDF-based
approach demonstrated the highest performance, achieving 94.47% accuracy and 97.03% precision. The
findings reveal the relative strengths and limitations of each approach under different conditions, providing
practical insights for real-world applications that involve unlabeled or weakly labeled text data. This work
serves as a practical guide for researchers and practitioners seeking effective solutions for automatic topic
classification in resource-constrained scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Topic classification is one of the fundamental tasks in
the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP),
enabling the automatic labeling of unstructured text
under specific thematic categories. This process plays
a critical role in enhancing the effectiveness of
various applications such as information retrieval,
content filtering, document clustering, and
summarization across diverse text types including
news articles, customer reviews, academic
publications, and social media posts
(Minaee et al.,
2020).
A wide range of methods have been developed to
a
https://orcid.org/ 0009-0009-5248-9593
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5799-530X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4156-9098
address this task, each tailored to different data
characteristics and application scenarios. Among
these, LDA stands out as a widely adopted
probabilistic model based on soft clustering, which
allows documents to be simultaneously associated
with multiple topics. LDA has proven especially
valuable in unsupervised learning settings and topic
discovery tasks. However, in contexts requiring
multi-label classification or fine-grained semantic
understanding, LDA often falls short due to its limited
flexibility and lack of contextual awareness.
To overcome these limitations, ZSC approaches have
gained traction for their ability to perform
classification without any labeled training data. ZSC
74
Adıgüzel, D., Yalçıner, B. and Karabey Aksakallı, I.
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News Texts.
DOI: 10.5220/0014363100004848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences (ICEEECS 2025), pages 74-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-783-2
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

leverages large-scale pre-trained language models
such as Bidirectional and Auto-Regressive
Transformers (BART) and Decoding-enhanced
BERT with Disentangled Attention (DeBERTa) fine-
tuned on NLI tasks to infer the semantic relationship
between input text and target labels. This enables the
model to generalize even to unseen categories. ZSC
is particularly effective in scenarios involving a high
number of classes or severe class imbalance, offering
scalable and robust alternatives to traditional
supervised methods. In contrast, similarity-based
classification methods represent texts as numerical
vectors (e.g., using TF-IDF or Word2Vec) and assign
labels based on the conceptual proximity between
document and class representations. These methods
are often favored for their low computational cost,
interpretability, and adaptability. Although traditional
vectorization techniques such as TF-IDF can deliver
strong discriminative power at scale, embedding-
based models such as Word2Vec provide richer
semantic context and often enhance classification
accuracy.
In summary, LDA, ZSC and similarity-based
classification represent three complementary
approaches to the topic classification problem, each
grounded in different theoretical foundations:
unsupervised topic discovery, inference-based
generalization, and semantic similarity respectively.
A systematic examination of these methods provides
valuable insights into designing effective
classification strategies, particularly in large-scale,
unlabeled data environments. The remainder of the
paper is organized as follows: Section 2 reviews the
related literature, Section 3 outlines the objectives of
the study, Section 4 presents the dataset and
methodology, Section 5 reports the experimental
results, and Sections 6 and 7 provide the discussion
and conclusion, respectively.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Li et al. (2024) proposed a classification model
designed to address multi-label text classification
tasks in scenarios involving unlabeled or weakly
labeled data. Their approach is grounded in ZSC and
relies on vector representations of class labels
generated through Sentence-BERT (SBERT)
embeddings. The semantic similarity between
documents and labels is computed using cosine
similarity, allowing the model to infer associations
even when class instances have never been seen
during training. The model also features a flexible
architecture capable of handling previously unseen
classes, making it particularly suitable for real-world
applications with limited annotated data. Although
the study does not specify the dataset used, its
contributions to the domain of weakly supervised
multi-label classification with zero shot are
significant. Conceptually, this study aligns with the
ZSC and similarity-based classification paradigms
explored in our study. However, our work
distinguishes itself by offering a comparative analysis
of these methods alongside LDA, providing a more
holistic evaluation of topic-labeling strategies.
Similarly, Schopf et al.
(2022) conducted a
comparative performance evaluation of ZSC and
similarity-based classification techniques, utilizing
state-of-the-art embedding models such as Simple
Contrastive Sentence Embedding (SimCSE) and
Sentence Bidirectional Encoder Representations from
Transformers (SBERT). Their analysis focused on
accuracy-driven metrics, without employing
threshold-based decision mechanisms. Unlike our
study, LDA or other topic modeling techniques were
not incorporated, and the dataset used was not
disclosed. In contrast, this study integrates both
threshold-based decision strategies and traditional
topic modeling, enabling a more comprehensive
assessment of modern and classical approaches in a
unified framework. In a related study, Lakshmi and
Baskar
(2021) introduced novel similarity metrics to
improve the performance of clustering algorithms in
text document grouping tasks. Their work highlights
the critical role of similarity functions in
unsupervised learning, particularly for semantic
grouping. While the dataset used was not specified,
the methodological foundation laid by their research
contributes theoretical grounding to the similarity-
based classification component of this study.
Finally, Yadav et al.
(2025) developed a hybrid
topic modeling framework that integrates traditional
LDA with the contextual word embedding
capabilities of BERT to address the semantic
limitations of conventional topic models. Their
approach is further enhanced through the use of
clustering and dimensionality reduction techniques
and has been validated on multiple text datasets. The
integration of statistical and contextual
representations in this hybrid model enables the
generation of more coherent and interpretable topic
clusters. Our study similarly explores the
complementary strengths of LDA and embedding-
based methods, making this work a relevant and
influential reference within the broader literature.
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News
Texts
75

3 OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
The primary objective of this study is to conduct a
systematic comparison of three distinct approaches to
topic labeling in news texts: ZSC, LDA, and
similarity-based classification. Within this
framework, each method is analyzed in terms of its
classification performance, scalability, data
dependency, and interpretability, offering a
comprehensive view of their respective strengths and
limitations. Notably, the evaluation focuses on three
contrasting paradigms:
1. ZSC which enables learning from unlabeled
data through pre-trained language inference
models,
2. LDA, a traditional probabilistic topic
modeling technique that operates in an
unsupervised setting, and
3. similarity-based approaches that rely on
semantic proximity between documents and
category representations.
These methods are assessed under diverse pre-
processing strategies and decision-making structures,
highlighting their practical adaptability and
theoretical underpinnings. The evaluation is
grounded in empirical experimentation using the
Reuters-21578 dataset, which poses a realistic multi-
label text classification challenge. The analysis
critically examines the suitability of each approach
for real-world applications, particularly in scenarios
characterized by limited or imbalanced labeled data.
3.1 Contribution of the study
This study presents a comprehensive and systematic
comparison of three distinct methodological
approaches which are ZSC, LDA and similarity-
based classification on a common dataset, providing
in-depth insights into the advantages, limitations, and
practical applicability of each method.
The analysis places particular emphasis on the
impact of class imbalance on model performance,
offering a relative evaluation of each approach under
varying data conditions. While highlighting the
potential of Zero-Shot methods to operate effectively
in the absence of labeled data, the study also
demonstrates that traditional representation
techniques such as TF-IDF can yield high
performance under specific circumstances.
Furthermore, the structural strengths and constraints
of LDA within the context of topic modeling are
critically examined, leading to meaningful
conclusions regarding its practical utility in multi-
label text classification tasks.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Reuters-21578 Dataset
The Reuters-21578 dataset is one of the most widely
used and standardized large-scale benchmark
collections in the field of text classification. The news
articles included in this dataset were originally
published by the Reuters news agency in 1987. The
annotation process was carried out collaboratively by
Carnegie Group Inc. and Reuters Ltd. In 1990, the
dataset was transferred to the Information Retrieval
Laboratory at the University of Massachusetts
Amherst for research purposes. Its formatting into
Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)
was completed by David D. Lewis and Stephen
Harding. The final standardized version of the dataset
was released in 1996 during the Special Interest
Group on Information Retrieval (SIGIR) conference
and comprises 21,578 documents.
The Reuters-21578 collection consists of 22
SGML files, each containing news articles labeled
with <REUTERS> tags. These labels were assigned
manually by human indexers, based on the contextual
content of the articles. As a result, documents can be
assigned to multiple categories, making the dataset
inherently multi-label in structure. Among the
available labeling schemes, the TOPICS category is
by far the most frequently used and cited subset in the
text classification literature due to its clarity and
broad coverage.
To support various experimental setups, the
dataset has been distributed with several predefined
data splits. The most commonly used configuration
includes 9,603 documents as a training set, 3,299
documents for testing, and 8,676 documents as an
unlabeled or auxiliary set, which is not used in
standard training or evaluation procedures
(Lewis,
1997). This design enables the dataset to serve as a
valuable benchmark for both supervised and semi-
supervised learning scenarios, and continues to
provide a consistent basis for comparative studies
across the research community.
4.2 Topic Modelling
4.2.1 Data Pre-Processing
To enable the effective application of LDA-based
topic modeling, a multi-stage and carefully structured
data pre-processing pipeline was executed on the
Reuters-21578 dataset. In the initial phase, SGML
and HTML formatting tags were systematically
removed, ensuring that only semantically meaningful
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
76

raw text remained. This refinement was essential to
allow the algorithm to learn solely from content-
bearing components of the documents, thereby
forming a robust foundation for accurate topic
discovery.
Subsequently, all textual data were converted to
lowercase to ensure format consistency. Punctuation
marks, numerals, and special characters were stripped
from the text corpus. In addition, non-informative
tokens which are commonly referred to as stop words
were filtered out to reduce noise and enhance the
discriminative power of document representations
(Kowsari et al., 2020).
Considering the multi-label nature of the Reuters-
21578 collection, each document was assigned its
most frequent category label to satisfy LDA's
requirement for single-topic representation
(Lewis,
1997). To manage class imbalance, only categories
with at least 10 associated documents were included
in the analysis. This constraint improved the model's
semantic coherence while ensuring statistically
reliable outcomes.
4.2.2 ModApte Split
For the training and evaluation phases, the widely
accepted ModApte Split was employed to partition
the dataset. This strategy utilizes the LEWISSPLIT
attribute in the Reuters-21578 corpus to separate the
documents into predefined TRAIN and TEST
subsets. While the training set supports model
learning, the test set is reserved exclusively for
performance evaluation.
This data partitioning technique not only ensures
fair comparison across different methods but also
contributes to the reproducibility of the experimental
framework. Moreover, the use of a predefined split
functions as a safeguard against overfitting, thereby
enhancing the generalizability of the results
(Lewis,
1997).
4.2.3 LDA Model and Coherence Score
LDA is a probabilistic topic modeling technique
based on the assumption of mixed membership,
whereby documents may be simultaneously
associated with multiple topics. Unlike traditional
classification models that enforce a single-label
constraint, LDA adopts a soft clustering approach that
captures the multidimensional nature of thematic
content. This makes it particularly useful for
extracting latent structures in large-scale textual
corpora.
To assess the semantic validity of topics generated
by the model, the Coherence Score—a widely
recognized evaluation metric—was utilized. This
score reflects the degree of semantic similarity or co-
occurrence among the top-N words most
representative of each topic. A higher coherence
score typically indicates that the topic is more
interpretable and better aligned with human judgment
(Zvornicanin, 2025).
Interpreting the coherence score depends
significantly on the characteristics of the dataset;
thus, no universal threshold exists for determining
what constitutes a "good" score. Nevertheless, a
general upward trend in coherence values often
accompanies increases in the number of topics, until
a saturation point is reached, after which performance
may plateau or decline. A common strategy for
selecting the optimal number of topics involves
plotting coherence scores against topic counts and
identifying the point where semantic richness and
internal consistency are maximized. This process
plays a critical role in ensuring that the model yields
interpretable and meaningful results without over-
fragmenting the content space.
4.2.4 Zero-Shot Classification
Zero-shot text classification refers to the task of
assigning appropriate category labels to textual data
without requiring any labeled training examples for
the target classes, relying instead on the semantic
relationships between labels and input texts
(Yin et
al., 2019).
In this study, the Zero-Shot classification
approach leverages large-scale pre-trained language
models originally fine-tuned on Natural Language
Inference (NLI) tasks. Two advanced models were
utilized:
• BART-large-MNLI, a transformer-based
encoder-decoder model fine-tuned on the
Multi-Genre NLI (MNLI) dataset, and
• DeBERTa-v3-large-MNLI-FEVER-ANLI-
Ling-Wanli, an enhanced model variant
trained across multiple NLI datasets,
including FEVER and ANLI, offering
deeper contextual understanding and
generalization capabilities.
In the classification process, each document is
treated as a premise, while a set of hypothesis
statements is generated to represent each candidate
class label. For instance, to determine whether a given
news article belongs to the "politics" category, a
corresponding hypothesis such as "This text is about
politics." is formulated. The model then evaluates the
semantic entailment between the premise and each
hypothesis, and classifies the input based on the
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News
Texts
77
likelihood of entailment versus contradiction.
This strategy enables multi-label classification
without relying on labeled data and provides a
flexible, scalable solution for tasks involving
dynamic or high-cardinality label sets
(Facebook AI,
2025). Furthermore, predictions from multiple
models are aggregated using a confidence-weighted
voting mechanism, enhancing the reliability and
robustness of final decisions. Performance evaluation
is carried out through three-fold stratified cross-
validation, and all misclassifications are
systematically logged for in-depth error analysis and
future refinement.
4.2.5 Similarity Based Classification
Similarity-based classification approaches enable the
categorization of textual data by representing
documents as numerical vectors and computing
similarity or distance measures between them.
Among the most widely adopted representation
techniques are TF-IDF and BoW. TF-IDF assigns
discriminative weights to terms by balancing their
frequency within a document against their frequency
across the entire corpus, thereby highlighting features
that are both relevant and distinctive for classification
tasks
(Ramos, 2003). In contrast, the BoW model
represents documents based solely on term
occurrence frequencies, offering a simple yet
effective baseline for many text processing
applications. Advanced embedding-based models
such as Word2Vec enhance these representations by
capturing both syntactic and semantic relationships
among words. These embeddings provide richer
semantic information by learning from word co-
occurrence patterns within a given context. However,
Word2Vec has notable limitations: it struggles with
polysemous words—those with multiple meanings—
and is unable to generate vector representations for
out-of-vocabulary (OOV) terms not seen during
training
(Kowsari et al., 2020). A commonly used
method during the classification stage is the centroid-
based approach, where the vector average (centroid)
of documents assigned to each class is computed.
New documents are classified by measuring cosine
similarity between their vector representations and
the centroids of each class. This method is
particularly valued in the literature for its low
computational cost and ease of implementation.
Furthermore, incorporating a similarity threshold
allows for more robust decision-making by ensuring
that documents are only assigned to a class if their
similarity score exceeds a predefined confidence
level.
The similarity-based threshold classification
method offers flexibility, particularly in multi-label
and hierarchical classification scenarios. It
contributes to greater transparency and
interpretability of classification outcomes. In this
framework, a document is assigned to a class only if
the similarity score between its vector and the class
representation surpasses a set threshold. For instance,
in text classification tasks, cosine similarity is
calculated between document vectors and class
centroids; classification occurs when this score
exceeds the threshold. Choosing an appropriate
threshold is crucial for balancing model accuracy,
recall, and precision, and often requires dataset-
specific empirical tuning. Despite its conceptual
simplicity, similarity-based classification remains a
highly effective solution across a broad range of NLP
applications.
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
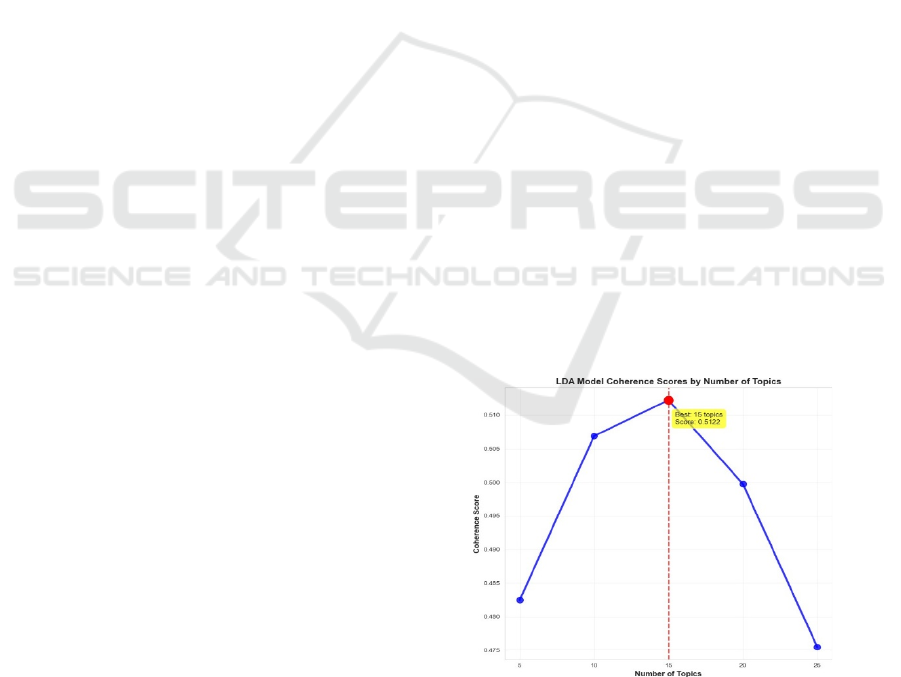
In this study, topic modeling was performed using
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) method on Reuters-
21578 news dataset. On the comprehensive corpus of
6,440 documents selected for analysis, 15 different
topics were identified and the performance of the
model was evaluated with the coherence score. The
highest success was achieved with 15 topics and a
coherence score of 0.5122. This score shows that the
model is able to capture the topic structure in a
meaningful and consistent manner. The line and bar
graph of the coherence scores was shown in Figure 1
and Figure 2 respectively.
Figure 1: Line graph of coherence scores changing with
increasing number of topics.
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
78
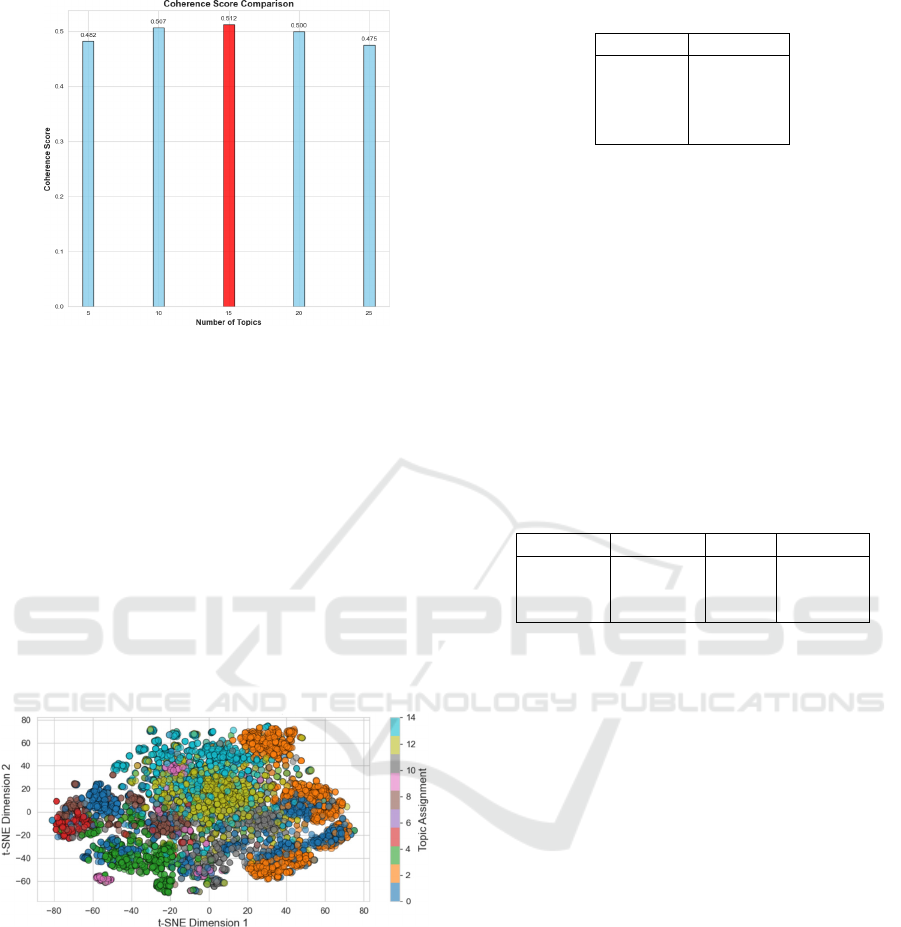
Figure 2: Bar graph of coherence scores for a given number
of topics.
In the analysis of high-dimensional datasets,
traditional visualization methods are insufficient and
therefore dimension reduction techniques are used.
Van der Maaten and Hinton (2017) developed t-
distributed Stochastic Neighborhood Embedding (t-
SNE), an effective nonlinear dimensionality
reduction method that allows intuitive understanding
of high-dimensional data in low-dimensional planes
by positioning similar items close and dissimilar
items far away. In this study, this method was used to
visualize topic distributions and Visualization of the
topics obtained with the LDA model with the t-SNE
method was shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Visualization of the LDA topic distributions using
the t-SNE method.
This visualization method enables visual analysis
of how clusters of topics are decomposed in space and
of uncertainties. The experiments conducted in this
paper show that the proposed ensemble-based ZSC
method achieves 63.06% accuracy, 74.12% precision,
63.06% sensitivity and 66.15% F1-score on the
Reuters-21578 dataset shown in Table 1.
Table 1: General classification performance metrics.
Metric Value (%)
Accurac
y
63.06
Precision 74.12
Recall 63.06
F1-Score 66.15
Cross-validation results shown in Table 2
indicates that the model performs consistently and has
a good generalization ability with an F1-score of
67.96% ± 1.24%. However, the class-based
performance analysis reveals that the model shows
significant classification success only on the three
dominant categories of "business", 'finance' and
"trade", while it is almost unable to assign documents
to the other minority categories. This is a natural
consequence of the class imbalance in the dataset,
with the categories "business" (4,485 documents),
'trade' (2,235 documents) and "finance" (1,036
documents) clearly dominating over the others.
Table 2: Classification performance according to some
different categories.
Category Precision Recall F1-Score
Business 0.786 0.696 0.738
Finance 0.446 0.802 0.573
Trade 0.791 0.423 0.551
Confidence analysis of the model's predictions
showed a high model confidence of 91.40% on
average across all classification results. This indicates
that the model is confident in its predictions, but may
have limitations in distinguishing subtle semantic
differences.
This paper presents a comprehensive evaluation
of the ensemble-based ZSC method on the Reuters-
21578 dataset. Based on the obtained F1-score of
66.15% and consistent performance in cross-
validation, it can be concluded that the system
provides competitive and reliable results. While the
model successfully classifies documents in dominant
categories, it is observed that class imbalance is a
significant barrier to effective detection of minority
categories. The misclassification analysis revealed
that the semantic overlap of the categories "business",
'finance' and "trade" is inherent in financial news,
which increases classification difficulties. While the
high average model confidence confirms the
consistency of the learned representations, it shows
that this representational power is not sufficient to
discriminate in fine detail. Therefore, in future
studies, eliminating the class imbalance and
providing more detailed semantic discriminations are
critical for improving performance.
In this section, the results of centroid-based
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News
Texts
79
classification experiments using three different text
representation approaches, TF-IDF, Bag-of-Words
(BoW) and Word2Vec embeddings, show that the
TF-IDF representation outperforms the other methods
in all evaluation metrics. In particular, the
classification reliability increases significantly with a
higher threshold, but there is a natural decrease in the
coverage rate as shown in Table 3.
Table 3: Classification Performance Comparison with
Threshold Value for TF-IDF.
Threshold
Value
Accuracy
(%)
F1-Score
(%)
Coverage
(%)
0.1 76.68 79.83 99.51
0.3 81.62 85.18 61.67
0.5 94.47 94.82 27.13
These results increase the preferability of TF-IDF,
especially in situations requiring high accuracy. The
BoW representation showed a lower but stable
performance compared to TF-IDF. BoW's focus on
word presence rather than word frequencies resulted
in its inability to adequately reflect term importance
across the corpus. Table 4 shows the performance of
BoW at different thresholds.
Table 4: Classification Performance with Different
Thresholds for BoW.
Threshold
Value
Accuracy
(%)
F1-Score
(%)
Coverage
(%)
0.1 72.69 75.58 99.82
0.3 76.13 78.30 90.91
0.5 82.22 83.59 48.88
Document representations generated with
Word2Vec embeddings produced lower accuracy and
F1-scores compared to other methods. Regardless of
the thresholds, similarity scores were high for almost
all test documents, which limited the discriminative
power of the model as shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Comparison of classification performance for
Word2Vec.
Method
State
Accuracy
(%)
F1-Score
(%)
Coverage
(%)
All thresholds 63.65 69.50 100.00
These results suggest that while Word2Vec
provides good representations at the word level,
averaged representations at the document level fail to
adequately reflect meaningful differences. This
weakness is particularly pronounced for short or
semantically sparse documents.
6 DISCUSSION
This paper presents important findings by
systematically comparing the performance of Zero-
Shot, LDA and similarity-based approaches for text
classification. However, the results should be
considered with some methodological and dataset-
based limitations.
6.1 Limitations of the Study
The Reuters-21578 dataset used in the study consists
of news texts from year 1987. This results in a text
structure that is far from current natural language
structures and may be insufficient to accurately
reflect the performance of modern language models.
In addition, the documents in the dataset are mostly
short and information-dense, which may lead to the
failure of context-based models (e.g. DeBERTa) to
develop the expected level of contextual
discrimination.
Despite the specific advantages of each method
used in the study, there are various limitations. ZSC
can perform classification without requiring labeled
data; however, it performs poorly for classes with few
samples, and the linguistic naturalness of hypothesis
sentences can affect performance. LDA, due to its
reliance on word distribution, may struggle to
distinguish between semantically similar but
superficially different texts; moreover, the
subjectivity in parameter selection affects the model's
stability. Similarity-based methods, on the other
hand, rely solely on surface-level similarity,
disregarding contextual meaning, which leads to
performance loss in documents that are semantically
close but differ in wording.
The apparent class imbalance in the Reuters-
21578 dataset resulted in poor performance of the
classification models in minority classes. While the
Zero-Shot model was successful in the dominant
classes, it was unable to classify documents
belonging to low-frequency topics. In particular, the
underrepresentation of semantically related but low-
example categories suggests that contextual richness
and data balance need to be considered together.
7 CONCLUSION
This study comparatively investigates ZSC, LDA and
similarity-based classification methods on the
Reuters-21578 dataset, revealing their strengths and
weaknesses in text classification tasks. Experimental
ICEEECS 2025 - International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronics, Energy, and Computer Sciences
80

findings show that the ZSC model offers the
flexibility to work with unlabeled data and is
particularly successful with high-frequency
categories. However, class imbalance led to
performance loss in minority classes. While TF-IDF
based similarity methods stand out with their high
accuracy and F1-scores, Word2Vec-based
approaches are insufficient in document separation
despite semantic representation. Although LDA can
model general trends, its flexibility is limited due to
its context-independent nature. In conclusion, ZSC
models are considered as a strong option in scenarios
where working with unlabeled data is at the forefront,
but their success is closely related to data distribution
and semantic discreteness.
In future studies, the impact of sampling and data
augmentation techniques on improving ZSC
performance in the face of class imbalance will be
explored, and the effectiveness of semantic
similarity-based models will be enhanced by
employing more powerful contextual embedding
methods instead of Word2Vec. Experiments will also
be conducted across different languages and data
structures to evaluate the generalizability of the
approach. Moreover, integrating multilingual pre-
trained models to improve the performance of ZSC
models in low-resource languages presents a
promising direction for further research.
REFERENCES
Minaee, S., Kalchbrenner, N., Cambria, E., Nikzad, N.,
Chenaghlu, M. and Gao, J. (2020). Deep learning based
text classification: A comprehensive review. arXiv
preprint arXiv:2004.03705.
Lewis, D. D. (1997). Reuters-21578 text categorization test
collection – Distribution 1.0. README file v1.2.
AT&T Labs – Research.
Zvornicanin, E. (2025). Topic Modeling and Coherence
Score. Baeldung.
Yin, W., Hay, J. and Roth, D. (2019). Benchmarking Zero-
shot Text Classification: Datasets, Evaluation and
Entailment Approach. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.00161.
Facebook AI (2025). BART Large MNLI. Hugging Face.
Ramos, J. (2003). Using TF-IDF to Determine Word
Relevance in Document Queries. Department of
Computer Science, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ,
Tech. Rep.
Kowsari, K., Jafari Meimandi, K., Heidarysafa, M., Mendu,
S., Barnes, L. and Brown, D. (2020). Text
Classification Algorithms: A Survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1904.08067.
Li, X., Jiang, J., Dharmani, R., Srinivasa, J., Liu, G. and
Shang, J. (2024). Open-world Multi-label Text
Classification with Extremely Weak Supervision. In
Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami,
Florida, USA, pp. 15084–15096.
Schopf, T., Braun, D. and Matthes, F. (2022). Evaluating
Unsupervised Text Classification: Zero-shot and
Similarity-based Approaches. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2211.16285.
Lakshmi, R. and Baskar, S. (2021). Efficient text document
clustering with new similarity measures. International
Journal of Business Intelligence and Data Mining, vol.
16, no. 1, pp. 49–72.
Yadav, A. K., Gupta, T., Kumar, M. and Yadav, D. (2025).
A Hybrid Model Integrating LDA, BERT, and
Clustering for Enhanced Topic Modeling. Quality &
Quantity.
Linderman, G. C. and Steinerberger, S. (2017). Clustering
with t-SNE, provably. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1706.02582.
Comparative Evaluation of Zero-Shot, Latent Dirichlet Allocation, and Similarity-Based Methods for Automatic Topic Labeling in News
Texts
81
