
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development
to Lower Development Barriers
Gejian Zhu
Department of Design, Goldsmiths, University of London, London, U.K.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Digital Media Interaction, Low-Code Tools, Creative Technology, User
Experimentation.
Abstract: With the widespread adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) tools in digital media creation, whether AI tools
have lowered the technical barrier for non-professionals is worth questioning. Taking open source AI
platforms ml5.js and Ready Player Me as examples, this study examines whether non-programming users can
independently achieve interactive media effects, such as gesture recognition and virtual character control,
without conventional programming skills. Experimental observations on two design students were used to
assess task completion, perceived usability of the tools, and understanding of system logic. The experimental
results show that although participants finished the task successfully, their knowledge of the internal operation
of the tool was comparatively more limited. This study suggests that the AI platform significantly lowers the
threshold for development at the operational level but does not fully compensate for the gap in users'
perception of the system. This study provides a practical reference for creative technology education and AI
tool development and points out the possible risk of "black box usage".
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid development of Artificial Intelligence
technology has resulted in a growing use of AI tools
in the digital media industry, especially in key
technical fields like image synthesis, speech
recognition, gesture tracking, and motion capture. AI
is increasingly replacing the traditional manual
modeling approach and programming development
process. In recent years, there has been a large
number of open-source or low-threshold AI
platforms, like ml5.js, MediaPipe, and Ready Player
Me, that have made interactive media content, which
previously required specialist programming skills,
available to people without technical backgrounds
(Billinghurst et al., 2015). This changing trend raises
a fundamental question: has AI technology truly
lowered the threshold for developing interactive
digital media technologies?
The creation of traditional interactive digital
media, especially with regard to complex
functionalities like mixed reality (MR), gesture
recognition, or the manipulation of virtual characters,
is often reliant on advanced computer vision
algorithms, sensor data processing, and skills in
object-oriented programming. For non-professionals,
the threshold to building such systems is usually high.
However, the development of artificial intelligence
technologies has somewhat changed this situation.
For example, ml5.js provides a modular gesture
recognition model, allowing for image input and
recognition processes to be completed with a few
lines of code; similarly, Ready Player Me provides for
the quick generation of 3D virtual characters from
photos, making it possible to integrate them into
interactive environments, thereby empowering "non-
programmers" to create interactive experiences.
These technologies make it possible for "non-
programmers" to participate in the creation of
interactive experiences.
However, systematic research to confirm the
competence and experience of non-professional users
in creating digital media interactions with the
assistance of AI tools remains scarce. The objective
of this research is to examine whether AI technology
has significantly reduced the threshold of digital
media technology development through empirical
experiments based on the observation of the process
and feedback of participants with non-programming
backgrounds in utilizing AI tools (e.g., ml5.js and
Ready Player Me) to accomplish basic interactive
tasks.
556
Zhu, G.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development to Lower Development Barriers.
DOI: 10.5220/0014362800004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 556-564
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

This research will aim to respond to the following
inquiries:
1. Can nonspecialist users utilize AI tools to
accomplish interaction tasks within a fairly short
time?
2. Do they have to depend on programming skills
while using?
3. What are the implications of the usability and
cognitive barriers present in AI tools for users from
varied backgrounds?
The importance of this research is not merely to
learn about the influence of AI on digital media's
technical threshold, but also to offer a practical
foundation for digital media education and tool
design in the future.
2 DEVELOPMENT STATUS OF
DIGITAL MEDIA
TECHNOLOGY
2.1 Developmental Threshold Levels
and Technological Challenges
Involving Digital Media Interaction
Technologies
With the passage of time, the development of
interactive technologies involving digital media like
virtual character animation, gesture recognition, and
mixed reality (MR) has called for the development of
advanced-level algorithms and complex system
architectures, and hence posed a serious technical
barrier to innovation. During previous eras, for
example, systems for gesture recognition normally
relied on tools like OpenCV, Kinect, or depth-sensing
cameras, together with computer vision approaches to
image processing, machine learning, and feature
abstraction, as a bid to create recognition systems
(Wachs et al., 2011). The development of MR
systems involves a form of programming and
platform technologies, ranging from Unity, C#, and
spatial map algorithms, as demanded by the
programmers (Billinghurst et al., 2015). Such a high-
level technical barrier has, on numerous occasions,
locked out nontechnical persons from the production
environment of interactive media content, leading to
a situation where content producers are mostly
engineers or development groups, as opposed to
mostly individual artists or designers.
2.2 AI-Powered Platform Development
and the Movement Towards
Low-Code Development
During the last decade, progress made on Artificial
Intelligence (AI) has gone a long way towards
fuelling the growth of "low-code" and "zero-code"
projects on digital media production. Several
platforms on AI have revolutionized conventional
methods, thereby reducing costs associated with
learning the abilities needed to construct complex
systems. For one:
The ml5.js library includes a range of pre-trained
models, including image classification, gesture
classification, and audio classification, that can be
easily used on the web using JavaScript in
applications that do not call for engineering skills,
including educational and interactive art solutions
(McCarthy, L., 2019).
MediaPipe thus supports end-to-end computer
vision solutions developed by Google that include
gesture recognition, face tracking, and detection of
human skeletal features, and is available on web and
mobile platforms (Lugaresi et al., 2019).
Virtual characters' platforms, such as Ready
Player Me, combine technologies such as three-
dimensional modeling, motion capture, animation
binding, and export procedures. Such combinations
allow a user to create interactive characters that can
be used on different platforms without needing to use
Blender or Maya (Wolf3D, 2021).
In recent years, low-code and no-code platforms
have emerged as a significant trend in software and
digital media development, substantially enhancing
the ability of “non-experts” to build applications
independently. Yan notes that such platforms enable
non-technical users to rapidly construct required
systems through visual components and drag-and-
drop logic, thus shortening development cycles and
reducing technical barriers (Yan, Z., 2021). Similarly,
Upadhyaya demonstrates that low-code tools play a
critical role in accelerating innovation, enabling faster
delivery, and supporting in-house solution
development in small and medium-sized enterprises
(Upadhyaya, 2023). These findings reinforce the
positioning of AI platforms in this study as “creator-
friendly tools” and provide a theoretical foundation
for their application in the field of digital media
interaction.
The arrival of these tools heralds a blurring of the
boundary between "technology-creation" and digital
media development, which is no longer exclusively
the domain of programmers, but has become a
creator-oriented platform design.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development to Lower Development Barriers
557

2.3 The Extent to Which AI Empowers
Nontechnical Creators: Synthesis of
Research
Despite the claim that tools of artificial intelligence
are actually made to reduce development barriers,
researchers are divided on the issue of empowerment
of the "non-professionals." Certain researchers
believe that AI tools increase the autonomy of
designers and foster interdisciplinary approaches
(Manovich, 2020); e.g., tools allow artists to combine
pictures and transform styles without the requirement
for programming knowledge, as shown through
applications such as RunwayML or DALL-E.
However, other researchers refute this notion,
declaring that systems of artificial intelligence can
cause a new form of a "black-box problem," where,
on the one hand, the models are easy to use but, on
the other, the essential mechanisms and logic on
which the outputs are based remain inaccessible to the
users, thereby limiting the system control exercised
by them (Burrell, 2016).
Additionally, educational technology experts
examined studies on the future use of artificial
intelligence when teaching digital media. More
specifically, Lee and Ko (2022) recognized that
integrating AI tools in interaction design classes can
significantly contribute to the value of student
outputs; nonetheless, a number of the students found
themselves challenged when altering the parameters
of the model and setting up file paths (Lee & Ko,
2022). As a result, although usability is improved
through the use of AI tools, a gap is observed between
usability and comprehensibility.
Previous literature suggests a movement from a
traditionally "expertise-oriented" development style
to a "creation-friendly" one aided by tools of artificial
intelligence, but empirical evidence is needed to
validate significant impacts on non-proficient
audiences. More particularly, the issue of whether or
not platforms based on AI allow for "de-
technicalized" development in domains where the
barrier to entry is very high, as is the case for gesture
recognition and mixed reality interaction, has yet to
be adequately examined based on actual behavior and
attitudes towards use. The experimental portion of
this work takes this as its starting point to assess to
what degree platforms based on AI allow non-
proficient end-users to create interactive media.
3 EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
3.1 Purpose of the Experiment
The aim of the current study is to evaluate non-
experts' skill in making efficient use of core digital
media interaction functionalities through empirical
examinations of tools aided by artificial intelligence,
including ml5.js and Ready Player Me. The empirical
examinations are carried out to find out whether the
current AI tools have actually mitigated the problem
faced during the practical use of digital media
technologies. The core areas of interest include:
completion of tasks, understanding of the tools,
reliance on knowledge from previous programming,
and individual intuitions and perceptions met during
use.
3.2 Experiment Participants
This paper recruited two participants without any
prior experience in program development, who were
both digital media design and interaction design
students. They had a bit of creative knowledge but no
formal training in developing programs
systematically. Before the experiment started, all
participants filled out a background form to check on
their programming knowledge, experience with the
use of AI tools, and knowledge of digital media
interaction principles. The whole experiment was
video-recorded, and oral permission was obtained
from all participants.
3.3 Tool Platform Description
So that the experimental study is carried out on a
sustainable scale, two well-known open-source
platforms concerning artificial intelligence were
selected:
ml5. A client-side machine learning library meant
for progressive developers, featuring pre-trained
models that can be used for functions like gesture
recognition and image classification. The library
itself can be called from HTML and JavaScript.
Invocation by these technologies is simple, making it
suitable for the creation of interactive demos in a
browser environment.
Prepared Player Me. A cross-platform virtual
character generation tool that supports custom avatar
and animation binding. Users can upload selfies to
generate 3D character models and can realize simple
animation control in Unity and other platforms
through the web interface, which is suitable for MR
and virtual interactive scene construction.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
558

3.4 Experimental Task Design
Members are obliged to engage in the following two
activities:
Task 1 (based on ml5.js): Create a gesture
recognition interaction prototype aimed at starting or
stopping video playback by waving the hand.
Task 1 (using ml5.js): create a prototype that is
operable via hand movement interaction- i.e.,
"waving a hand to play/stop video playback."
Task 2 from Ready Player Me: Create a digital
avatar that can modify its behaviors, like waving or
nodding, on a web page based on users' interactions,
as when a button is clicked.
Character generation, loading, and the associated
logic that drives actions are illustrated and
incorporated via a friendly web interface.
In order to reduce information interference,
participants only received absolutely necessary
training materials and legitimate platform links; no
encrypted templates were provided, and participants
were expected to figure out the rationale themselves
for making use of the tools.
3.5 Methods for Collecting and
Assessing Data
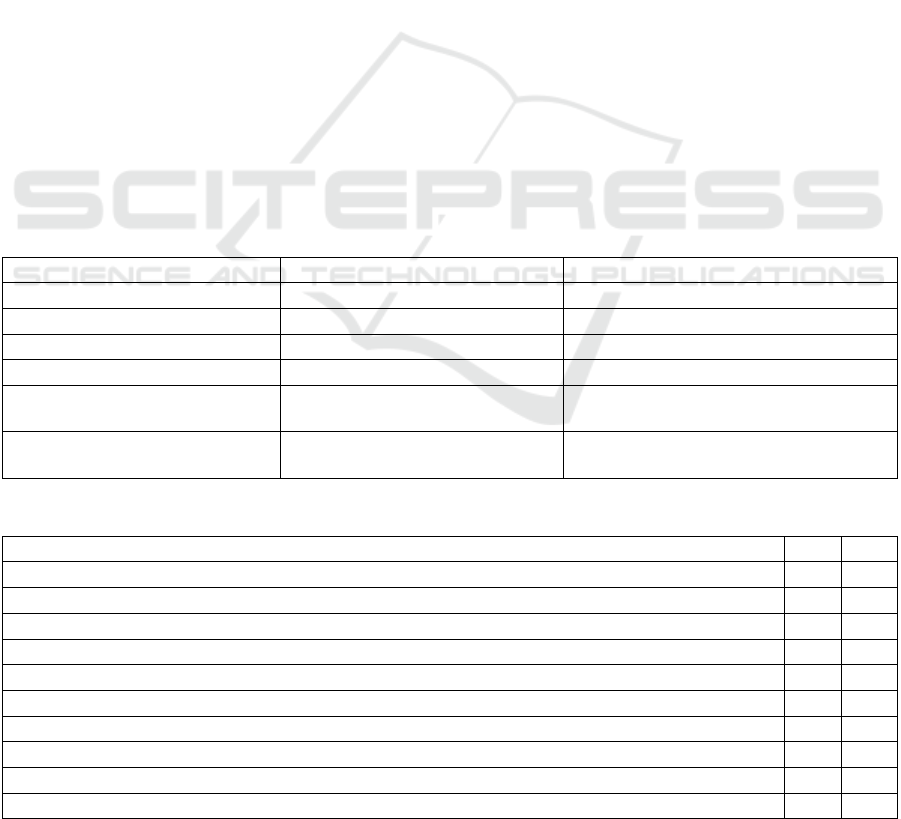
Table 1 shows the empirical information will be
collected and analyzed using the following
methodologies
Table 1: Empirical Data Collection and Analysis Methods.
Data Collection
Tools
Recorded/Measured Content Instructions Example Questions/Variables
Measurement
Methods
Observation
Chart Sheet
Time to complete tasks -
Problems encountered - Help
needed - Frequency of
debu
gg
in
g
incidents
Researchers
recorded the
experiment in
real time.
"Task 1 took 35 minutes" "I
encountered a model loading
error"
Process
observation +
record sheet
Participant
Survey (Post-
experiment
Questionnaire)
Using a five-point Likert
scale (1 = strongly disagree, 5
= strongly agree), measures:
1. Tool effectiveness 2.
Understanding of operating
procedures 3. Necessity of
programming 4. Perceived
creative freedom 5. Overall
satisfaction with AI tools
Quantitatively
measured
participants'
subjective
feelings.
"I was able to complete the
task successfully" "I
understood how the
interactive features work"
Questionnaire
(5-point Likert
scale)
Semi-Structured
Interviews
Deepen understanding of user
experience and perception
The recordings
were
transcribed and
coded for
analysis.
Which components were the
most difficult? Which areas
were the most challenging?
What was the main problem
that was effectively solved?
Have you noticed a decrease
in the technical barrier to
entry? Are you willing to
continue using AI tools in the
future?
Face-to-
face/online
interviews +
qualitative
analysis
A mixed-methods design will be utilized,
combining both quantitative and qualitative data
analysis methods.
Quantitative evaluation:
Compare the data for task completion time and the
self-assessment scale for the two participants.
Recognize the key aspects, such as the assignment
fulfillment, use of the code, and the level of
independence observed when carrying out the task.
Qualitative analysis:
Coding interviews aim to detect essential issues,
misconceptions concerning thought processes, and
positive assessments.
Assessing the validity of people's beliefs related
to the claim that "AI diminishes barriers to progress."
Its purpose is to assess the performance of AI-
assisted tools for first-time programmers through the
analysis of participants' actions and self-assessment.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development to Lower Development Barriers
559
4 ANALYSIS OF EMPIRICAL
RESULTS (FINDINGS AND
RATIONALE)
4.1 Brief Description of the
Experimental Methodology
This paper recruited two participants with no formal
programming backgrounds (hereafter referred to as
P1 and P2), one of whom was studying digital media
and the other graphic design; neither of the
participants had received any formal programming
training. After a questionnaire was used to collect
basic background information, the participants each
went through a step-by-step procedure involving two
experimental tasks:
First is using ml5.js to enable gesture recognition
for the control of video playback on a web page;
Second is creating virtual characters using Ready
Player Me and controlling their actions with web
buttons.
4.2 User Task Completion
Table 2 shows the task Completion and Support
Requirements of Participants. Observations revealed
that both participants completed the tasks on
assignment within the duration; however, Participant
2 had rational challenges (like setting up the resource
file path) getting through to Ready Player Me, but
managed to complete the task with a gentle push from
the researcher.
4.3 Analysis of Questionnaire Results
As shown in Table 3, the average score trend graph
illustrates that:
Has a high overall satisfaction and ease of use
rating (mean value 4.4), indicating that AI tools are
effective in reducing the burden of operation.
Has the lowest rating for "understanding of
system principles" (mean value 2.5), reflecting that
the black-box phenomenon of "only using but not
understanding" is common among non-professional
users. The lowest rating for "understanding of system
principles" (mean value 2.5) reflects that non-
professional users generally have the black box
phenomenon of "only using but not understanding".
Table 2: Task Completion and Support Requirements of Participants
Indicator P1 P2
Did Task 1 (Gesture Recognition) independently completed Independently completed
Did Task 2 (Virtual Characters) independently completed Required some technical assistance
Time spent on Task 1 (min) 35 min 45 min
Time spent on Task 2 (min) 40 min 60 min
Need to write code
(call predefined APIs + modify
parameters)
(Try to copy the code and debug the
structure.)
Need Documentation or guidance
required
Documentation consulted 1 time
Multiple times and in consultation with the
researcher
Table 3: The following are the Likert scale scores (1-5, higher means higher agreement)
Questionnaire items P1 P2
Q1: I was able to complete the main functions of the system independently 5 4
Q2: The difficulty of the task was within my understanding 4 3
Q3: I basically didn't need to write any code 5 4
Q4: The tool interface is user-friendly and quick to get started 4 4
Q5: It's easier than the traditional way 5 5
Q6: I understood how the interactive functions work 3 2
Q7: I was satisfied with the results 4 4
Q8: I'm willing to continue to use it in the future 5 4
Q9: I think that the AI tool lowered the technical threshold 5 4
Q10: I am uncomfortable with the “black box” mechanism 2 3
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
560
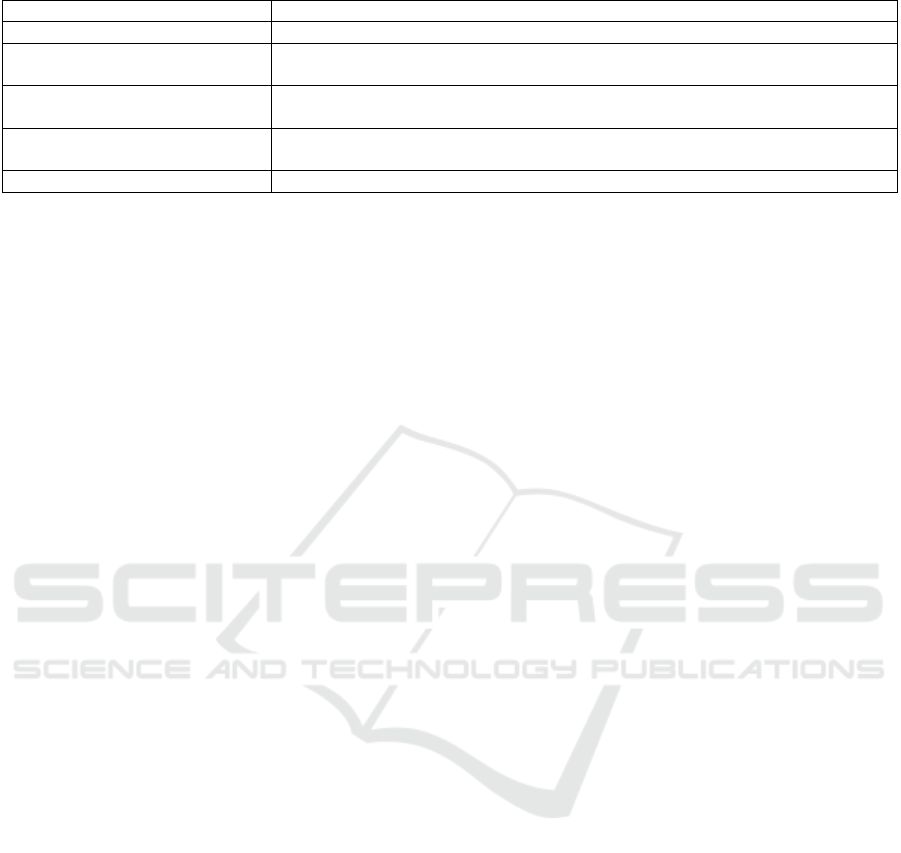
Table 4: The following key findings were compiled from the semi-structured interviews.
To
p
ics Excer
p
ts from user feedbac
k
Ease of use of the tool "It's like
p
uttin
g
to
g
ether buildin
g
blocks, as lon
g
as
y
ou know which
p
ieces work."
Main difficulties "I'm stuck not knowing how to get the model to load."The Documentation is too
long, I don't want to read it."
Need to write code "Although I copied a few lines of code, I didn't write it; I just followed the tutorial
and changed the path."
Sense of control and
understandin
g
"The functionality works, but I don't quite know why it works."
Willin
g
ness to use in the future "Ver
y
p
ractical! I'd like to use it a
g
ain in a class
p
ro
j
ect later."
4.4 Generalization of Interviews
Table 4 shows the following key findings were
compiled from the semi-structured interviews.
Overall, the interviews showed that AI tools have
good “task accessibility,” but users generally view
them as ‘toolboxes’ rather than “development
platforms,” and lack a deep understanding of model
parameters and system logic. However, users
generally viewed it as a “toolbox” rather than a
“development platform” and lacked a deep
understanding of the model parameters and system
logic
4.5 Testing
Research findings show that those who do not hold
specialized knowledge can use tools powered by AI
without human intervention to perform simple tasks
involving interaction. Additionally, resolutions can
be achieved for simple problems by reading
Documentation or collecting information from others.
Artificial intelligence tools have significantly
reduced the accessibility hurdles of coding and
system development, especially in the areas of
gesture recognition and virtual character creation.
However, the participants showed limited
awareness of the basic principles and logic governing
interactions, which is characteristic of an orthodox
"black-box use" practice.
AI tools perform well in the aspect of “assisted
creation”, but the participants' understanding of the
interaction logic and technical principles is still weak;
AI tools perform well in the aspect of “assisted
creation”, but the participants' understanding of the
interaction logic and technical principles is still weak.
AI tools perform well in “assisting creation”, but
there is still room for improvement in “technical
education”.
5 DISCUSSION AND
IMPLICATIONS (DISCUSSION
AND IMPLICATIONS)
5.1 Whether AI Tools Truly Lower the
Threshold of Digital Media
Development
Experiment outcomes show that users who had no
prior experience with programming were able to
successfully run virtual character control and gesture
recognition tasks within a short period. This result
suggests that artificial intelligence libraries like
ml5.js and Ready Player Me have meaningfully
reduced the barriers to the use of digital media
interaction technologies. In the past, acting out
similar functions required a high level of expertise in
image recognition algorithms, 3D modeling, and
script programming; however, in this case,
participants could carry out basic functionalities
using built-in APIs and graphical interfaces.
However, empirical data and findings from
interviews revealed one other dimension: while
participants cited greater convenience when using the
tool, they mostly lacked understanding from the
ground up of the principles regulating its function,
and a lack of information on the motivation behind
the inclusion of certain functionalities. Thus, this
suggests that tools driven by artificial intelligence
mainly reduce the 'barrier to creating superficial
results,' but the 'barrier to understanding and learning
the technology' endures.
5.2 Usability and Its Connection to the
Black Box Problem
The questionnaire results show that a significant
percentage of respondents view AI tools as” user-
friendly, quick," and significantly better than
traditional development methods, since the mean
response for question 5 was 5. For question 6,
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development to Lower Development Barriers
561

however, which asked about the statement “I
understand how the interaction functions work,” the
mean responses were significantly lower at 2.5. This
difference highlights the widespread “black box
problem” in AI tools: people can use sophisticated
models without having an idea of the underlying
principles and limitations that drive them.
One promising pathway to addressing the black-
box problem is the adoption of Explainable Artificial
Intelligence (XAI). Mathew emphasizes that XAI is
evolving toward enhancing model interpretability and
user cognitive understanding, with the primary aim of
making model decision-making processes more
transparent (Mathew, 2025). Bauer further finds that
providing feature-based explanations significantly
improves users’ comprehension and information-
building capabilities, thereby altering their trust and
usage attitudes toward AI systems. These insights
suggest that integrating XAI elements into AI-driven
media tools, such as ml5.js and Ready Player Me,
could not only improve usability but also strengthen
users’ cognitive control and trust in the creative
process (Bauer, K., 2023).
The imbalance between the "enthusiasm for
application" and the "lack of awareness" can lead to
greater adoption of the technology by creators and, in
the process, compromise their capacity to apply the
required changes for reasons of either complex
demands or restrictions from the tools. It is important
to recognize this point in both educational and
professional environments.
5.3 the Implications for Digital Media
Education
Results from this experiment show two major
implications for pedagogical procedures:
First is artificial intelligence tools could provide
an accelerated verification system for teaching
methods and learning experiences.
People who have minimal experience or
backgrounds other than engineering can make use of
tools involving artificial intelligence to expedite the
construction of interactive prototypes over a short
period, shortening the amount of time normally
needed, indeed, a factor of significant value for
innovation and discovery work.
Second is the continuation of the dimension of
"technical understanding" is also critical.
Over-reliance upon the use of tools reduces the
ability of experienced users to cope with complex
technical nuances. Therefore, it becomes necessary
for machine learning tools to include unambiguous
explanations of algorithmic concepts in pedagogical
environments so that learners can grasp essential
recognition processes and data-flow reasoning and
thus develop into effective "system designers" and
not just as "tool operators."
5.4 Considerations for Future Tool
Development and Industry Practice
Relative to industry procedures, the fading barriers to
the use of tools for artificial intelligence will
increasingly promote the democratization of design
procedures, consequently making a larger audience
for nontechnical creatives to work on projects focused
on digital media and interaction design. The
development is expected to promote a revolution in
team dynamics, where artists and designers handle
tasks concerning prototyping, and tech creators focus
on refining complex systems.
However, the situation requires additional
requirements in the creation of artificial intelligence
tools:
Improving transparency: Increased visual
feedback during model runs is crucial for supporting
users in understanding the underlying functional
principles of the tool.
Modularization involves providing "plug-and-
play" modules suited for beginners, as well as for
others who already have a grounding, to tune
parameters with increased specificity. Educational
congruity: Convey pedagogical examples and first-
hand activities focused on developing innovative
learning to minimize the learning process duration.
5.5 Constraints and Potential
Directions for Future Research
The constraints on the results are the comparatively
small sample size, comprising only two nonspecialist
participants, and the relatively simple tasks used. As
a future direction, possible expansion can be made in
a number of different ways:
Recruiting more diverse user groups (e.g.,
different professional backgrounds or age groups);
Including increasingly complex task scenarios,
which involve multimodal interaction and interaction
in mixed reality environments;
Integration of vast observations is needed to study
the learning trajectories and competencies
development of the users while working on tools
embedded with artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence technology has greatly
reduced the obstacles to the initial creation of digital
media interactive technologies, but this feeling of
"empowerment" is limited, since it mostly focuses on
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
562

rapid implementation and prototyping. While AI is a
solid helper for creators, it by no means eliminates the
need for technical reasoning and creative control.
Educators and tool developers need to strike a balance
between "user-friendliness" and "transparency."
6 CONCLUSION AND
PROSPECTS FOR FURTHER
RESEARCH
6.1 Research Summary
This study investigated whether non-experts can
effectively use AI tools, specifically ml5.js and Ready
Player Me, to lower development barriers in digital
media interaction. Two participants without
programming backgrounds were asked to complete
gesture recognition and virtual character control
tasks, with data collected through observation,
surveys, and semi-structured interviews. The results
show that AI tools significantly reduced the difficulty
of implementing these functions, allowing
participants to complete tasks—typically requiring
advanced technical skills—quickly and without
substantial external support. However, despite their
operational success, participants demonstrated
limited understanding of the underlying system
principles and tended to treat the tools as "black
boxes." This indicates that AI tools reduce the
operational threshold but not the cognitive threshold,
and thus do not fully replace the need for technical
comprehension.
6.2 Responding to the Research
Questions
The findings respond directly to the three research
questions. First, non-experts could complete gesture
recognition and virtual character tasks independently
or with minimal assistance, confirming that AI tools
can support productive outcomes without deep
technical skills. Second, while most functions were
accessible through graphical interfaces and API calls,
basic programming knowledge was still required to
understand parameter structures and logical
workflows. Third, participants rated the tools highly
in usability but low in comprehension of underlying
model logic, suggesting a gap between functional use
and conceptual understanding.
6.3 Significance and Practical
Application of Research
This study provides empirical evidence to address the
scholarly question of how AI empowers nontechnical
creators. For education, AI tools can serve as
effective entry points for beginners in interaction
design, provided they are accompanied by instruction
in basic technical reasoning to maintain users'
creative control. The results highlight tool developers'
need to design platforms with more precise feedback
mechanisms and greater model transparency to
enhance users' cognitive control. The findings
suggest that future workflows may increasingly adopt
a "creator × tool platform" model in the creative
industries. AI tools function as collaborative partners,
reshaping production processes and expanding
participation.
6.4 Research Limitations and Future
Directions
Several limitations must be acknowledged. The small
sample size limits the generalizability of the findings,
and the tasks designed for this study were
intentionally simplified, excluding more complex
scenarios involving multimodal interaction,
collaborative networks, or persistent data handling.
Furthermore, the study was short-term and did not
assess participants' skill development over time.
Future research should address these gaps by
expanding the sample size and diversity, introducing
tasks of greater complexity, and conducting
longitudinal studies to explore the long-term effects
of AI tool use on technical competence, learning
motivation, and creativity. Additionally, further work
could investigate the integration of speech
recognition, natural language processing, and other
multimodal AI technologies to extend the scope of
AI-assisted digital media interaction.
7 CONCLUSIONS
The advent of technological innovations fueled by
artificial intelligence is drastically transforming the
ground of digital media creation from a developer-
centric model to a creator-centric model. This has
significantly reduced the technical barriers that once
restricted new creators, enabling them to use
sophisticated interactive media technologies without
requiring in-depth programming knowledge. The
findings of this study suggest that AI-augmented tools
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence Tools in Digital Media Development to Lower Development Barriers
563

not only enhance creativity horizons but also enhance
efficiency at all stages of development, thus enabling
users to focus more on design thinking and creating
innovative content.
Despite these advantages, a considerable gap
exists between usability and a thorough cognitive
understanding of the underlying technologies. This
means that while artificial intelligence tools have the
potential to supplement the skills of authors, they
need to go hand-in-hand with pedagogical efforts
focused on enhancing technical and critical literacy.
In short, this research highlights the importance of
working with AI-powered tools as an insightful
turning point and not a definitive result. Introducing
such tools to real-world applications and teaching
methodologies might develop a more diverse and
creative environment for creativity and foster further
experimentation, interdisciplinarity, and the
continuous evolution of interactive digital media.
Future research activity could investigate the
long-term effects of outputs from artificial
intelligence on the development of user
competencies, independence, and novel
methodologies. Comparison of studies across
different cultural and disciplinary backgrounds could
produce a more sophisticated understanding of these
tools' reception, adoption, and reinterpretation across
broad user populations.
REFERENCES
Bauer, K., von Zahn, M., & Hinz, O. (2023). Expl (AI) ned:
The impact of explainable artificial intelligence on
users’ information processing. Information Systems
Research, 34(4), 1582-1602.
Billinghurst, M., Clark, A., & Lee, G. (2015). A survey of
augmented reality. Foundations and Trends® in
Human–Computer Interaction, 8(2-3), 73-272.
Burrell, J. (2016). How the machine ‘thinks’:
Understanding opacity in machine learning algorithms.
Big Data & Society, 3(1), 2053951715622512.
Lee, H., & Ko, Y. (2022). Integrating AI tools in design
education: Opportunities and challenges. International
Journal of Art & Design Education, 41(1), 122–135.
Lugaresi, C., Tang, J., Nash, H., McClanahan, C., Uboweja,
E., Hays, M., ... & Grundmann, M. (2019). Mediapipe:
A framework for building perception pipelines. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1906.08172.
Manovich, L. (2020). AI and the future of creativity. AI &
Society, 35(2), 173–182. Retrieved from
https://api.pageplace.de/preview/DT0400.9781000924
787_A46597486/preview-
9781000924787_A46597486.pdf
Mathew, D. E., Ebem, D. U., Ikegwu, A. C., Ukeoma, P. E.,
& Dibiaezue, N. F. (2025). Recent emerging techniques
in explainable artificial intelligence to enhance the
interpretable and understanding of AI models for
human. Neural Processing Letters, 57(1), 16.
McCarthy, L. (2019). ml5.js: Friendly Machine Learning
for the Web. Retrieved from https://ml5js.org
[Accessed 7 Aug. 2025].
Upadhyaya, N. (2023). Low-Code/No-Code platforms and
their impact on traditional software development: A
literature review. No-Code Platforms and Their Impact
on Traditional Software Development: A Literature
Review (March 21, 2023).
Wachs, J. P., Kölsch, M., Stern, H., & Edan, Y. (2011).
Vision-based hand-gesture applications.
Communications of the ACM, 54(2), 60-71.
Wolf3D. (2021). Ready Player Me: Cross-game Avatar
Platform. Retrieved from https://readyplayer.me
[Accessed 7 Aug. 2025].
Yan, Z. (2021). The impacts of low/no-code development
on digital transformation and software development.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.14073.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
564
