
The Reconstruction of Image Aesthetics Driven by the Development
of Artificial Intelligence Technology
Chengze Li
a
Beijing 101 High School, Beijing, China
Keywords: AI, Deep Learning, Datasets, Aesthetics.
Abstract: The remarkable growth of artificial intelligence (AI) has deeply affected contemporary art creation. Image
generation, as a result of the merging of AI and art, is reshaping the boundaries of art creation through a
distinctive method of creation and infinite potential. This paper reviews the technological changes in machine
learning and deep learning and their impact on the popularization of AI art creation. From the perspective of
painting production, relevant mainstream datasets, algorithms, and models are introduced, including
convolutional neural network models, generative adversarial network models, and diffusion models. This
paper further analyzes key element recognition in AI painting and image aesthetic quality assessment. AI not
only challenges the position of the subject in artistic creation but also brings about revolutionary changes in
artistic aesthetic standards and evaluative criteria. As artificial intelligence technology continues to develop,
its integration with art can effectively promote interdisciplinary collaboration and open up new possibilities
for innovation, expression, and cultural exchange in the digital age.
1 INTRODUCTION
Artificial intelligence (AI) is propelling a
technological revolution unprecedented in human
history. As pointed out by Paul Doherty, human
society is entering an era of coexistence and
symbiosis with machines (Doherty & Wilson, 2018).
In this revolution, the development of generative AI
art has achieved the transformation of AI from
imitation to innovative creation. Early computer
graphics laid the foundation for AI art, and in recent
years, breakthroughs in technologies such as deep
learning, convolutional neural networks (CNNs),
generative adversarial networks (GANs), and
diffusion models (DMs) have led to significant
progress in AI art in terms of creative means, style
expression, and aesthetics. While these works not
only introduce an unprecedented visual sensation to
people, they also inspire profound contemplation of
aesthetic concepts and artistic expression. As a
multidimensional perceptual cognitive activity, art
appreciation involves aesthetic judgment, semantic
perception, and emotional resonance, and AI is
gradually approaching it with computational models.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-8181-8556
This article first reviews the evolution of artificial
intelligence technology, especially the application of
machine learning and deep learning in artistic
creation; then sorts out the commonly used datasets,
algorithms and models in AI art creation; then
discusses the specific application of technologies
such as convolutional neural networks, generative
adversarial networks, and diffusion models in image
generation; finally, analyzes the performance of AI
art in aesthetic reconstruction. This article attempts to
explore the mainstream technologies and cases at the
intersection of AI and art, and to outline future
technological prospects by integrating computer
science and aesthetics.
2 AI TECHNOLOGY CHANGES
AND ART
American philosopher John Searle divides the
development of AI into three stages: weak AI, strong
AI, and super AI (Searle, 1980). The mainstream
view holds that technology is still in the stage of weak
AI. In 1950, Alan Turing proposed the famous
Li, C.
The Reconstruction of Image Aesthetics Driven by the Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology.
DOI: 10.5220/0014362300004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Inter national Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 527-534
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
527

"Turing Test," marking the beginning of the AI era.
Over the next 75 years, various AI technologies have
tried to pass this test (Mitchell, 2024). From 1950 to
1989, AI was in its early stages of exploration, with
technical models mainly being knowledge-driven
symbolic models and focused on narrow tasks.
Painting techniques were associated with simple,
rule-based symbols and geometry, such as in software
like Photoshop. Between 1990 and 1999, AI entered
the application stage, establishing data-driven image
models and early shallow statistical methods, such as
those used by Google. From 2000 onward, AI entered
the deep learning stage, where technical models
driven by knowledge, data, algorithms, and
computing power generated content, such as CNNs
and GANs. Since 2020, artificial intelligence has
entered the stage of large-scale training, as seen in the
emergence of the GPT series.
2.1 Machine Learning
Machine learning is a method by which computer
systems learn to perform a task using data to improve
at it. The history of machine learning, from 1950 to
1960 till now, has been punctuated by various
milestones like the invention of the Perceptron, a
graphic recognition machine designed to simulate
human neural control systems that gave birth to
neural networks. Machine learning development
benefits from three key ingredients: compute, data
and algorithms. Machine learning has made
tremendous progress in recent decades. In particular,
breakthroughs in natural language processing, e.g.,
the birth of ChatGPT, have enabled a new age for AI.
The theory of Artificial Systems, Computational
Experiments, and Parallel Execution (ACP) was
proposed by Li and others from the Chinese Academy
of Sciences. This approach proposes human
participation in control and learning, enhancing the
efficiency and fairness of machine learning, and
achieving closed-loop learning and optimization
results (Li et al., 2021).
If ACP is placed in the realm of art, human artists
(PA), virtual machine artists (MC), and physical
machine artists (MP) can collaborate on artworks
together. The PA is the starting point and criterion in
the process of artistic creation. The MC mimics the
PA's creation in virtual space, and the MP completes
the art in the real physical world under the MC's
guidance; its work is judged by the PA to optimize the
intelligent painting system. Under this framework,
artistic creation is no longer confined to individual
talent but rather the result of the collaborative wisdom
of humans, machines, and algorithms.
2.2 Deep Learning
Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning,
which is a technique based on artificial neural
networks. It utilizes a multi-layer network structure to
learn high-level features of data and has achieved
tremendous success in image recognition, speech
recognition, and natural language processing. The
key technologies of deep learning include CNN,
GAN, etc.
CNNs and GANs are representatives of the use of
deep learning in the field of AI art. CNNs are key
deep learning models for image recognition and
classification. They can automatically learn image
feature representations and are widely used in tasks
such as image classification and object detection.
GANs comprise a generator and a discriminator,
which can produce new data samples through
adversarial training, enabling applications in image
generation and style transfer. Image recognition and
classification are the most popular applications of
deep learning, but they have limitations, such as high
data requirements and a potential for incorrect
interpretation.
Painting style transfer is an interesting research
task in computer vision. The algorithm based on deep
learning realizes style transfer by training neural
network models, and its core is two loss functions,
namely content loss and style loss. Content loss
quantifies how the content image differs from the
generated image, while style loss quantifies how the
style image differs from the generated image.
Minimization of both content loss and style loss leads
to the generation of stylized images that are both
content-wise similar to the target image and style-
wise similar to the target style image.
3 DATA, ALGORITHMS,
MODELS AND AI ART
The training data serves as the raw material for
training AI models. A significant amount of data is
needed for training the AI models, which are usually
gathered from online image databases, digital
collections from museums, user-uploaded images,
etc. Trained with large-scale data, the model is
capable of identifying and learning features and
patterns. For the models that create artworks, the
trained model learns about different artists' styles,
color palettes, composition, etc. During training, the
model continuously updates its parameters so that
higher quality and a higher similarity between the
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
528

generated images and the corresponding ground truth
are achieved.
3.1 Datasets
The implementation of AI art features requires high-
quality datasets. Images in high-quality datasets
typically have high resolution, low noise, and rich
details, which are crucial for generating high-quality
artworks, while low-quality data can result in blurry
or distorted generated images.
After obtaining the original datasets, it is often
necessary to do some data cleaning work on the data
before model training begins. Data cleaning involves
removing duplicate, erroneous, or low-quality data.
The cleaned datasets ensure that the model is not
affected by useless or harmful data during training. In
addition to data cleaning, the data also needs to be
labeled. The labeled dataset can help the model better
understand the content of the data. When Madhu et al.
studied the dataset of ancient Greek vase paintings,
they added the bounding boxes of the figures and the
corresponding key points of body postures to the
original dataset. Ultimately, in the style transfer
process, compared with unlabeled datasets, the mean
average precision and mean average recall rate have
improved significantly by more than 6% (Madhu et
al., 2022).
Fairness and unbiasedness are important metrics
of a quality model, which can ensure the diversity and
representativeness of the datasets and also reduce the
bias of the model's generated works. Including works
of art from different genders, races, and cultural
backgrounds can prevent the generated works from
having a single perspective or discriminatory
misinterpretation. By July 2025, Wikiart had
collected around 250,000 artworks, including works
by more than 3,000 artists, but with a bias towards the
West, with half of them from Western Europe. If this
were the way to develop the global art model, there
would inevitably be deviations. Researchers need to
adjust and optimize the content of the dataset in a
timely manner to meet the requirements.
Wang, working on an algorithm model based on
an improved NTS network, was unable to obtain
feature evidence from existing public datasets and
relied on self-collection and organization to build a
new dataset. Eventually, his model achieved a
recognition rate of 95.1% for Thangka art style
effects. The model's recognition effect on the Oil
Painting dataset was only 73.8% (Wang, 2022).
3.2 Algorithms and Models
In the field of AI, there are two closely linked but
different notions: algorithms and models. An
algorithm is a series of clear and orderly steps and
principles for solving a specific problem and
completing a specific task. It can be an algorithm or a
program. A model is a mathematical model or
calculation framework formed by learning from
training data with a specific algorithm. A model is the
output of running an algorithm on training data,
which captures the characteristics of the data and can
be used for prediction, classification, or data
generation. Frequently used models include the linear
regression model, decision tree model, CNN, GAN,
diffusion model (DM), variational autoencoder
(VAE), etc.
3.2.1 Convolutional Neural Network Models
CNNs are the core model in deep learning for
processing grid-structured data and have developed
into a variety of classic architectures over the years.
Some of CNN's classic models are widely used in the
field of AI art, such as the VGG model, ResNet
model, InceptionNet model, etc. The VGG model,
proposed by the Visual Geometry Group at the
University of Oxford, is characterized by "small
convolution kernels + great depth". By stacking
convolutional layers with multiple 3×3 small
convolutional kernels and 2×2 max pooling layers to
build a deep architecture, it can automatically and
efficiently extract features from lower to higher levels
of the image (Simonyan & Zisserman, 2014).
VGGNet performs well in tasks such as image
classification. It can apply the style of one image to
another, generating works with specific artistic styles.
The ResNet model, proposed by Microsoft,
addresses the vanishing gradient problem in deep
networks through "residual connections" and, for the
first time, increases network depth to over a hundred
layers, solving the degradation problem of deep
networks and enabling the training of extremely deep
networks. Versions such as ResNet50 are often used
for classifying artworks. By learning the features of
paintings of different styles, it can classify and
recognize artworks and also provide a feature
extraction basis for style generation in artistic
creation.
The InceptionNet model was proposed by Google.
In 2015, Google introduced DeepDream, a deep
learning-based image processing technology based
on pre-trained Inception series models, which
amplifies specific features in images through
The Reconstruction of Image Aesthetics Driven by the Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology
529
techniques such as gradient ascent to generate images
with a fantastical and surreal style.
Researchers have been optimizing the model. The
Valentin model, based on the ResNet architecture,
was trained on 40,000 images. It improved
classification quality through a variety of methods,
including data augmentation, scheduler optimization,
parameter selection, and loss function tuning. At the
same time, analytical preprocessing was carried out
on the existing painting image dataset. The model
achieved a classification accuracy of 51.5% for five
types of paintings. To reduce overfitting and
computational time, the authors truncated the weight
parameters of the neural network. For categories with
significant differences, the model accuracy improved
significantly to 91.25% (Kovalev & Shishkin, 2020).
In the comparative study by Sethi et al. on the
architectures of VGG-16 and VGG-19, the
comparison of different performance parameters was
discussed, which shows which parameter is more
convenient to use for which particular use case. The
study results show that after 1,000 iterations, the style
loss of VGG-16 and VGG-19 has almost similar
performance, but the difference in the value of
content loss is 73.1%; however, VGG-19 performs
better because it minimizes both content loss and
style loss (Sethi et al., 2022).
Yin et al. combined the historical experience of
CNNs and proposed an algorithm for DeepInversion,
reusing pre-trained mature CNN architectures such as
ResNet50, VGG16, and InceptionV3 as knowledge
sources. This is a data-free knowledge transfer
method, with an accuracy improvement of more than
10% compared to the original model (Yin et al.,
2020).
3.2.2 Generative Adversarial Network
Models
GANs are an algorithmic model involving adversarial
training between a generator and a discriminator.
They are a machine learning model proposed by
Goodfellow et al. (Goodfellow et al., 2014). The
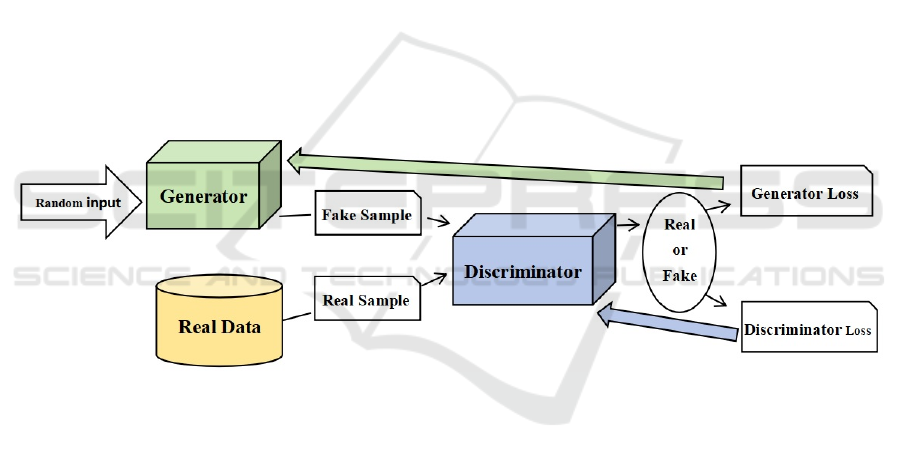
technical framework of GANs is shown in Figure 1.
GANs are based on the unsupervised learning of two
artificial neural networks called the generator and the
discriminator, both of which are trained under the
concept of adversarial learning.
Figure 1: GAN infrastructure (Goodfellow et al., 2014).
In the art of aesthetics, GANs can be modeled as
two confronting artists and critics interacting with
each other to improve the art itself and to make the
work extremely realistic. In GANs, the generator tries
to generate new data so that it appears to be real data
without knowing how the real data is generated;
however, it aims at making the generated data
realistic as if they are actually real and hard to
discriminate. At the same time, the discriminator
behaves like a connoisseur.
Liu et al. adopt the structure of GANs to study
visual effects created by the seamless merge of
Unity3D. The generator and the discriminator both
utilize the Transformer model, which handles
sequential data and long-range correlations
effectively. The obtained experimental results
indicate that the inception score (IS) is 8.95, with the
Frechet Inception Distance (FID) being 20.1,
showing good diversity and image quality (Liu et al.,
2025).
3.2.3 Diffusion Models
In the machine learning domain, DMs are generative
models that can produce new data similar to the
training data. The main idea lies in using random
processes to start from a simple and manageable state
and gradually introduce increasingly complex
structures through some process, thereby generating
data similar to the target data.
The extended model can be thought of in art as
creating an artwork from nothing, bringing structure,
details, etc., little by little from a chaotic, unordered
mess to the piece itself. This is commonly done in
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
530
several steps or "time steps," beginning from a state
that is always simple and introducing some
randomization with control at each time step, so that
the final data gradually takes on a structure
resembling the target data. DMs are similar to an
artist's step-by-step iteration in the creative process:
starting with a simple initial thought, through
continuous adjustment and addition of details, and
finally rendering a beautiful work.
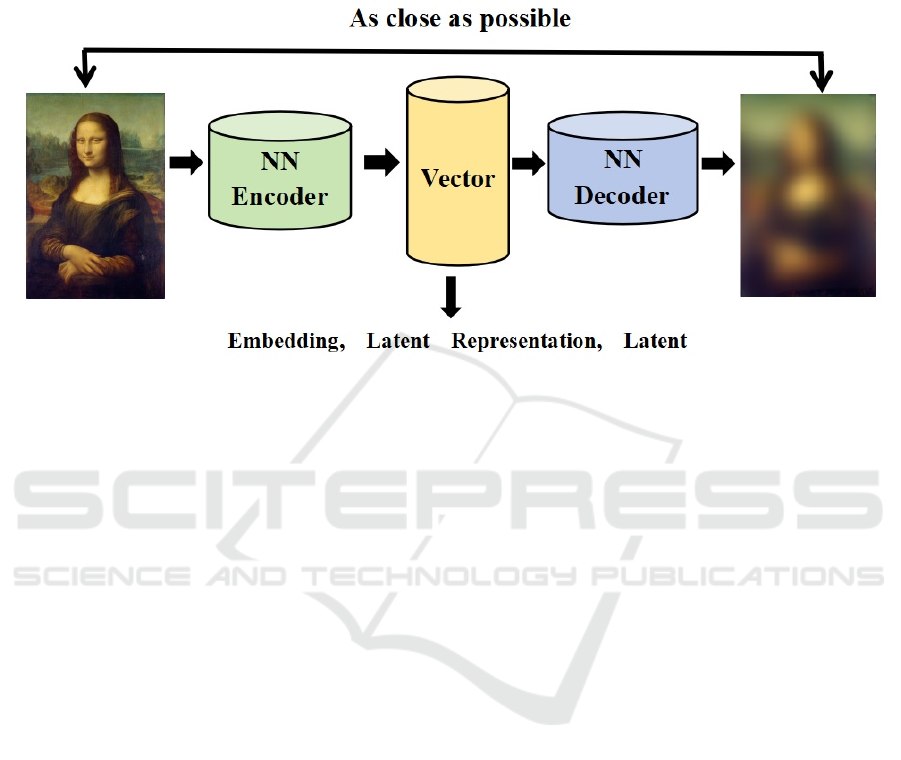
Figure 2: Data mapping of pixel space to Latent space (Rombach et al., 2022)
4 AESTHETIC
RECONSTRUCTION OF AI
ART
In the traditional sense, aesthetics usually refers to the
aesthetic experience, emotion, and evaluation of the
object of aesthetic appreciation. The emergence of AI
art has raised a series of aesthetic questions and
controversies. AI is both a connoisseur and a creator.
It integrates technologies such as computer vision,
machine learning, and deep learning to perform
feature analysis, style recognition, emotion
interpretation, and value assessment on a vast number
of artistic paintings, while generating a large number
of works. The 20th-century thinker Benjamin once
believed that the contemporary era was the "age of
mechanical replication" of art, and the "aura" of
artworks was vanishing (Benjamin, 1936). However,
the advancement of AI technology is unstoppable,
and the quality of its works even surpasses that of
human-created ones. Théâtre D'opéra Spatial (Spatial
Opera Theater), a painting by Jason Allen, was
generated by the AI drawing tool Midjourney and
retouched in Photoshop. This award-winning work
has sparked discussions about the subject of art, and
the boundaries of artistic creation are constantly
expanding and blurring.
4.1 Identification of Key Elements
The Stable Diffusion Model is one of the most
popular AI painting base models today. The latent
method on which the Stable Diffusion Model is based
is the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM). It was
proposed by Robin Rombach and Patrick Esser of AI
video company Runway, who are also important
participants in the subsequent development of Stable
Diffusion. The technical structure of LDM is shown
in Figure 2. Its near-optimal balance between
reducing complexity and retaining details
significantly enhances visual fidelity (Rombach et al.,
2022). From an artistic perspective, if a painter is
creating a watercolor painting, through the diffusion
model, it is like the painter constantly adding ink and
noise, making the painting appear somewhat blurry.
At this point, the stable diffusion model acts as a
protective layer that moves the image from the pixel
space to the latent space, and then adds ink and noise
to the latent space. This protective layer ensures that
the changes do not have an irreversible impact on the
painter's work. Ultimately, it makes the presentation
of the painting orderly.
The Reconstruction of Image Aesthetics Driven by the Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology
531

Figure 3: Common Classic painting styles
The complexity of painting, which is the diversity
of styles and the various tools, materials, and media
chosen by different artists, makes it one of the most
challenging tasks in computer vision. The AI model
integrates several key dimensions for style
recognition. Among the color features, classicism has
low-saturation tones, such as the blue-gold palette in
The Rape of Europa (Figure 3). Impressionism
features high contrast and vivid colors. Modernism,
on the other hand, has bold, pure tones. Post-
impressionism features collages and mixed colors. In
stroke analysis, CNNs analyze the direction,
intensity, and pattern of strokes, such as short strokes
with high rotation relative to the smooth texture of
realism. The ResNet model distinguishes between
Expressionist rough strokes and Impressionist loose
strokes. In terms of composition, classicism
emphasizes symmetrical order, while Impressionism
emphasizes natural spontaneity. Modernism is
characterized by perspective subversion, while post-
impressionism is characterized by fragmented
recombination. In semantic features, classicism
includes mythological figures, while postmodernism
features popular symbols. Technically, the dot-stroke
features of Impressionism enhance the accuracy of
style classification. In Warhol's Marilyn Diptych, AI
detects repeated print blocks that link it to 20th-
century screen printing, in line with postmodernist
diversity, fragmentation, and anti-traditionalism.
For the oil painting style classification task,
researchers first extract the painting features and then
model and classify the features. Folego et al., in their
research on the authenticity of Van Gogh's paintings,
divide each painting into nonoverlapping image
blocks, keeping 196.3 pixels per inch. They use a
multimodal fusion method that combines manual
features with CNN features. In analyzing artistic
style, short and fast brushstroke direction features can
provide the most useful information to identify Van
Gogh's works, while high-saturation contrasting color
features provide more discriminative ability to
distinguish between Van Gogh's different artistic
periods. This method achieved an accuracy rate of
92.3% in distinguishing Van Gogh's works,
performing better than traditional methods that only
used color or brushstrokes (Folego et al., 2016).
4.2 Aesthetic Evaluation of Images in
the Context of AI
Mainstream models such as GANs and DMs still have
problems such as distorted detail rendering and
mechanical
style transfer, making it difficult to
Figure 4: A postmodernist makeover of the Mona Lisa by an AI called Dreamina
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
532

accurately capture the deep emotional expression of
artworks. When AI stares at The Rape of Europa, it is
unable to distinguish mythological implications from
chaotic pixels. When it stares at Warhol's Marilyn
Monroe, it sees repetition rather than an attack on
consumerism. Figure 4 shows a similar style
transformation of the Mona Lisa after the style of
Marilyn Diptych was identified using an AI called
Dreamina. Although the work retains postmodernist
features, the new work has problems such as
mechanical replication and incomplete composition.
Image Aesthetic Quality Assessment (IAQA) is a
computer vision topic that consists of multi-
disciplinary knowledge. Essentially, it aims to
approximate human subjective judgment of an
image's "aesthetics" through algorithms to realize
automated analysis and assessment of an image's
aesthetic quality. It makes the abstract concept of
aesthetics measurable and computable. The
mainstream method is the deep learning method,
where convolutional neural networks such as
VGG/ResNet automatically learn the deep aesthetic
features of images; with a trained model using a
labeled large-scale training dataset, the models learn
humans' aesthetic preferences from the training data.
Chounchenani et al. summarized the research on
IAQA in input-processing-output deep learning over
the past decade. Based on the Atomic Visual Actions
dataset, the experiment compared different deep
learning methods, including ResNet-50, VGG-16,
InceptionNet-V3, and others, in image aesthetic
quality assessment, with the evaluation method
achieving the highest accuracy rate of 91.5%. It is
noted that deep learning models still need further
improvement (Chounchenani et al., 2025).
The integration of IAQA and style transfer aims
to apply the "aesthetic judgment capability" of IAQA
to achieve better generation effects in style transfer.
Before style transfer, IAQA analyzes the aesthetic
defects of the original image, such as imbalanced
composition and lack of contrast, to clarify the
optimization targets of the style transfer algorithm.
IAQA can also act as an aesthetic supervisor to
constrain style parameters after style transfer.
Additionally, IAQA can learn different users'
aesthetic preferences, thus enabling style transfer to
generate results that conform to specific users'
aesthetic preferences.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This article summarizes AI technologies and
applications related to painting art, including machine
learning, deep learning, etc. It further analyzes
mainstream datasets, algorithms, and models based
on AI in the field of painting. Finally, this paper
describes AI's style transfer and aesthetic
reconstruction in painting art. Although AI shows
great potential, existing technologies still have much
room for improvement in terms of data quality, model
interpretability, and practical application. There are
three levels of room for technological progress. The
first is the optimization of existing AI datasets,
computing power, and models. The second is the
cross-integration and application of multiple models
to enhance big data training capabilities. The third is
the integration of AI with other technological fields.
Technological advancements in the field of AI art can
combine knowledge from both technical and artistic
fields, and drive AI's advancement in the field of art
based on "aesthetic" target requirements.
REFERENCES
Benjamin, W. (1936). The work of art in the age of
mechanical reproduction. New York.
Chounchenani, M. D., Shahbahrami, A., Hassanpour, R., &
Gaydadjiev, G. (2025). Deep learning based image
aesthetic quality assessment: A review. ACM
Computing Surveys, 57(7), Article 183.
Daugherty, P. R., & Wilson, H. J. (2018). Human +
machine: Reimagining work in the age of AI. Harvard
Business Review Press.
Folego, G., Gomes, O., & Rocha, A. (2016). From
impressionism to expressionism: Automatically
identifying van Gogh's paintings. In 2016 IEEE
International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP)
(pp. 141–145). IEEE.
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., ... & Bengio, Y. (2014).
Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 27.
Kovalev, V. Y., & Shishkin, A. G. (2020). Painting style
classification using deep neural networks. In 2020
IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computer and
Communication Engineering Technology (CCET) (pp.
334–337). IEEE.
Li, S., Wang, Y., Wang, X., & Wang, F. (2021). Mechanical
design paradigm based on ACP method in parallel
manufacturing. In 2021 IEEE 1st International
Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence
(DTPI) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Liu, Q., Li, J., & Hu, W. (2025). Exploration of cross-modal
AIGC integration in Unity3D for game art creation.
Electronics, 14(6), 1101.
Madhu, P., Villar-Corrales, A., et al. (2022). Enhancing
human pose estimation in ancient vase paintings via
perceptually-grounded style transfer learning. ACM
The Reconstruction of Image Aesthetics Driven by the Development of Artificial Intelligence Technology
533

Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage, 16(1),
Article 16, 12–17.
Mitchell, M. (2024). The Turing test and our shifting
conceptions of intelligence. Science, 385(6710).
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., &
Ommer, B. (2022). High-resolution image synthesis
with latent diffusion models. In 2022 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR) (pp. 10674–10685). IEEE.
Searle, J. R. (1980). Minds, brains, and programs. The
Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 3, 417–457.
Sethi, P., Bhardwaj, R., Sharma, N., Sharma, D. K., &
Srivastava, G. (n.d.). A deep learning-based neural style
transfer optimization approach. Intelligent Data
Analysis, 29(2), 320–331.
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep
convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition. CoRR, abs/1409.1556.
Wang, H. (2022). Research on painting image style
classification and application based on deep learning
(Master's thesis). Qinghai University.
Yin, H., Molchanov, P., Alvarez, J. M., Li, Z., & Kautz, J.
(2020). Dreaming to distill: Data-free knowledge
transfer via DeepInversion. In 2020 IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition (CVPR) (pp. 8712–8721). IEEE.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
534
