
Research on the Factors Contributing to Change in Housing Price in
California
Ziyu Li
Social Sciences College, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, 92697, U.S.A.
Keywords: Housing Value, Correlation Coefficient, Linear Regression Model.
Abstract: Housing price is always the popular topic in the current market. To predict the alternation in housing price, it
is necessary to initially forecast the trend of those influencing factors. This article aims to investigate the
potential factors that influence alternation in housing prices. 20,640 samples from a dataset of California’s
housing group by 1990 will be conducted in this essay to complete further analysis. Then, this research will
measure correlation coefficients and employ linear regression model based on the eight variables shown from
the dataset. By searching for coefficient, unstandardized beta and variance inflation factor (VIF) value, this
research can conclude the most significant causes to affect housing prices. Finally, the research indicates that
income level is the main feature, other causes including housing ages, location as well as population can also
affect prices in some aspects. The data and purpose outcomes can provide households and housing agencies
direction regarding the trend of housing market.
1 INTRODUCTION
Housing price is one of the most pivotal indicators in
today’s society, affecting the entire economy and
people life. As housing acting as one of the
fundamental properties for people to require
maintaining normal life, it is the criteria to measure
people’s well-being and individual health, which
means lots to human beings (Rolfe et al, 2020). Due
to the extensive demand for shelters, property values
are now a controversial topic among academics and
the public. The importance of researching house
prices is further emphasized by the fact that real estate
is frequently seen as a worthwhile financial asset.
Housing prices in the United States have increased
rapidly and even dramatically over the last few
decades. Nowadays, house prices have become one of
the economies that employed adults care about the
most. Its price trend determines when people will
choose to buy or sell houses. Between 2020 and 2023,
California recorded its first population decline since
becoming a state in 1850 (Batdorf, 2024). This
unprecedented demographic change because of
multiple causes including high living expenses,
increasing remote work flexibility, family
considerations and potential economic challenges.
These shifts have highlighted the complex
relationship between changing population trends and
housing affordability in the state.
While, forecasting the price trends and
comprehending their wider economic impact require
a grasp of the elements that affect house values. This
study will examine and conclude home prices
according to existing housing data from California.
Besides, this research will also analyse the factors
influencing change in housing prices.
The housing price is definitely determined by
multiple features that surrounding housing itself,
housing locations and the entire society. From the
past, the theme has attracted by several researchers to
explore into. Those existing research offers extensive
theoretical models and empirical evidence examining
the key factors influencing housing prices. In the
research by Li and Yang, they employed a multiple
linear programming tool to analyse the key features.
By examining the linear relationship between a
dependent variable and multiple independent
variables, the model estimates regression
coefficients, and minimizes the difference between
the actual observed values and the values predicted by
the model. By comparison of different variable
combinations, the study aimed to identify the optimal
model for accurate housing prices forecasting (Li and
Yang, 2024).
468
Li, Z.
Research on the Factors Contributing to Change in Housing Price in California.
DOI: 10.5220/0014361300004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 468-473
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
Mao and Yao conducted a similar study using
the King County House Sales dataset to investigate
how geographic features impact housing price. In the
research, they apply multiple linear regression
(MLR) combined with 10-fold cross-validation to
assess model performance. The findings highlight
that factors including the number of bedrooms,
latitude, and longitude significantly affect. Their
predictive summary is both methodologically sound
and interpretable, offering detailed views into the
relationship between these variables and property
values (Mao and Yao, 2020). Additionally, Lau
analysed how population alternation and
homeownership rates impact California housing
prices from 2020-2022 potentially using county-level
data. This study applied time-series analysis and
correlation theory to measure relationships between
these variables, with results indicating positive,
negative, or neutral associations (Lau, 2024).
Yu applied the same linear regression analysis, the
common statistic method in order to predict the target
variable by linear combination of characteristic
variables. Evaluation of these models through
different matrixes such as mean square error is the
strategy she used to determine the accuracy of model,
which is indeed understandable and precise (Yu,
2024). Similarly, Yan also conducted excel to build
up a multi-regression model, aiming to research on
influencing factors of housing value in New York in
a comprehensive aspect (Yan, 2022). There are some
other researchers adopt different strategies to figure
out those potential causes. Zoppi et al. attempted to
employ Hedonic models to analyze environmental
and structural features which affects housing market
in Cagliari (Zoppi et al, 2015). Huang et al. conducted
models to study and collect those data of unusual
variation in housing prices (Huang et al., 2010). In
summary, this study will properly conduct the
combination of two strategies, correlation module and
linear regression, in order to investigate the potential
features that influencing change in housing prices in
California.
2 METHODS
2.1 Data Source
In this research, a dataset focuses on housing price
from Kaggle website will be adopted. This dataset
offers a practical starting point for exploring machine
learning techniques. It covers housing information
from the 1990 California census, measuring various
homes across different districts. This dataset includes
region-level statistics such as population, median
income and housing characteristics, providing an
understandable and clear background for building and
evaluating machine learning models. From the
original dataset, there were several missing values in
the total_bedrooms column. To deal with this issue,
the missing entries were occupied using the median
value. From the full set inputs, a random sample of
20640 records was selected for this research. Then,
the updated dataset now includes nine features-
longitude, latitude, housing median age, total rooms,
total bedrooms, population, households, median
income and ocean proximity, along with the target
variable, median house value.
2.2 Variables Explanation
In order to present the further model, the study needs
to initially list out all the dependent variables and the
independent variable that investigating in the dataset.
These variables cover longitude, latitude, housing
age, total rooms, total bedrooms, population,
households, income level, and the house value.
Therefore, the research lists out a relevant variables
table, as shown in Table 1.
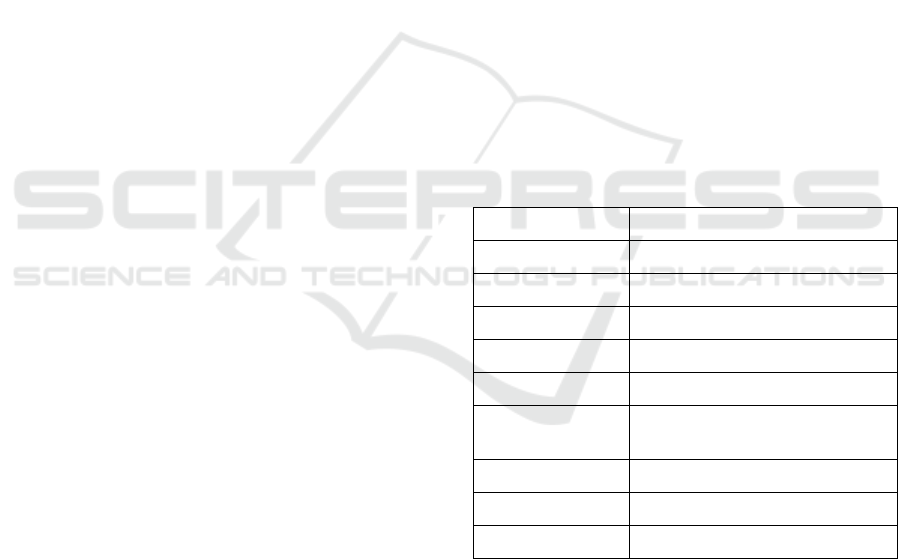
Table 1: Variables introduction
Variables Description
Lon
g
itude House distance to the west
Latitude House distance to the north
Housin
g
A
g
e Median a
g
e of a house
Total Rooms Total room numbe
r
Total Bedrooms Total bedroom numbe
r
Population Total number of residents living
in a house
Households Total household numbe
r
Income Income level for households
House Value Median House
p
rice
2.3 Method Introduction
In this analysis, both correlation and linear regression
methods are used to investigate the potential factors
influencing housing prices in California. The initial
step is data cleaning, referring to handling missing
values, such as replacing null numbers in total
bedrooms with the median calculation as well as
dropping irrelevant columns like ocean proximity,
since it doesn’t change throughout the whole dataset.
Research on the Factors Contributing to Change in Housing Price in California
469
The correlation between median house value and
variables including longitude, latitude, housing
median age, total rooms, total bedrooms, population,
households, and median income is calculated, helping
determine which variables have relatively stronger
relationships with the house price.
After identifying those relevant variables through
correlation approach, this paper builds a multiple
linear regression model based on these indicators.
This model not only quantifies the influence of each
variable but also eliminate errors, for example two
variables are highly correlated, which may distort the
model accuracy. This research uses statistical tests
including p-values and R² scores in order to evaluate
the significance and explanatory power of the model.
In this study, the combination of correlation and
regression model provides a clearer understanding of
how those different features relate to housing prices
in California.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Correlation Analysis
To investigate the relationship between housing value
and those potential influencing factors, this paper
attempts to conduct Pearson correlation analysis,
referring to a calculation measuring linear
relationship between two continuous variables. The
correlation coefficient is a result of ratio between
the covariance of two variables and the product of
their standard deviations (Asuero et al., 2007). Those
coefficients always are ranging from -1 to 1, a
positive value represents a direct relationship while a
negative value implies an inverse relationship.
After the implement of regression correlation
model, the standard deviation and mean of each
variable are figured out. Plugging those data into the
formula mentioned before, then this paper obtains the
correlation coefficient between each pair of two
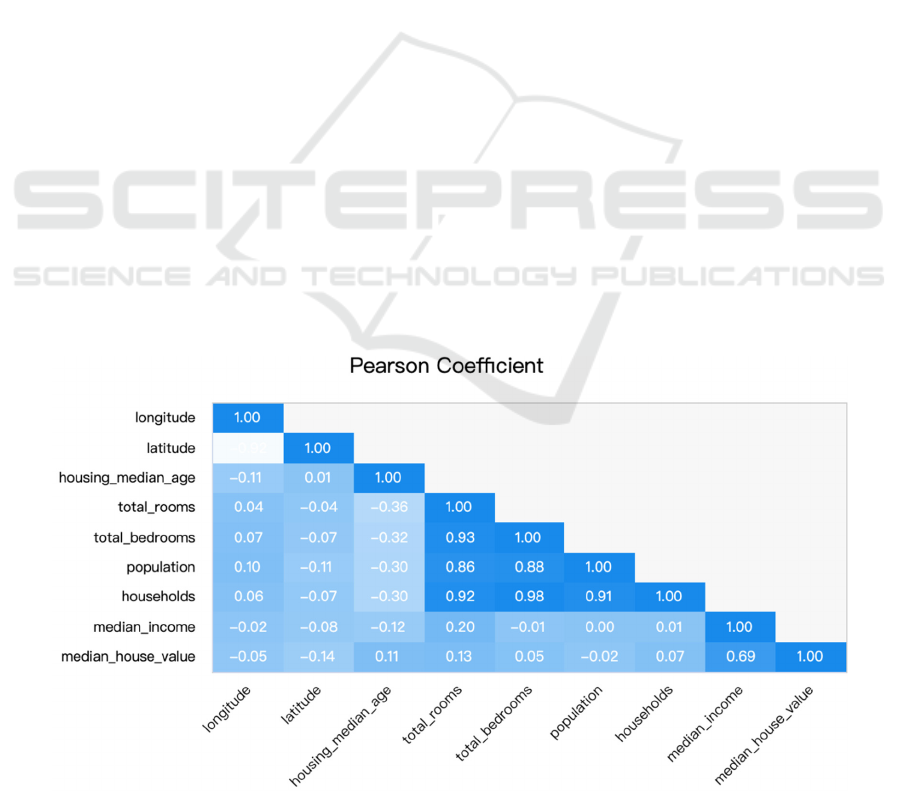
variables among those listed elements. Figure 1
shows the all the combinations; it indicates the
indexes of linear relationship between those factors
directly. From the figure 1, it is intuitive to determine
which pairs of variables maintain a strong correlation.
The diagram presents a strong relationship
between households and total bedrooms (0.98), total
rooms and total bedrooms (0.93), as well as total
rooms and population (0.92). These suggest that
families with more households require greater
amount of rooms and bedrooms, which is obvious.
Although using all the combination is direct to see
each variable, this study should focus more on the
factors influencing the housing value. Therefore, this
paper wipes off the other variables being target
variables in order to receive an updated correlation
diagram.
Figure 1: Pearson Coefficient Table for Variables (Picture credit: Original).
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
470

Figure 2: Pearson Coefficient Table for Median Housing Value (Picture credit: Original).
From Figure 2, it is much more direct to witness the
potential causes to affect change in housing value.
Looking at the chart, the strongest relationship is
between income and house value. The correlation
coefficient between median_income and
median_house_value reaches to 0.69, which is a
relatively strong positive figure. That is probably
because households with higher income will prefer
houses in a higher price to satisfy their requirement of
higher living standard. Besides, wealthy people
always pursue shelters with superb location and
greater size, these factors will also impact a higher
housing price. Therefore, it’s reasonable that income
level is the most strongly and positively linked factor
to housing value.
Other factors like the number of rooms in a house
(total_rooms) and the age of the house
(housing_median_age) maintain weaker positive
relationships with housing prices. Sometimes housing
age cannot be a determination of housing prices as
new houses built in current years can be sold in a high
price because of its brand-new infrastructure and
novel layout. Consumers are likely to be attracted by
those factors, thus larger consumer groups increase its
demand, causing increase in price. However, aged
homes can also be set in a high price. Those homes
are often found in well-established neighborhoods
and hold a larger land size because land was cheaper
and more accessible at that time. Therefore, these
historical houses may also be popular among
consumers. Housing value, as well as can be properly
impacted by the room amounts, while it is reasonable
that room sizes should take into account when it
comes to the number.
Some variables including total bedrooms,
population as well as the households don’t seem to
affect house prices significantly, they maintain
correlation coefficients very close to zero. This
suggests that numbers of households and bedrooms
cannot be the determinations that influencing housing
value.
Finally, location, especially latitude, seems to
matter relatively. Latitude and longitude have small
negative correlations with house prices. This may
indicate that those houses located relatively inland or
farther north in California tend to become slightly
cheaper. As those homes are located far away from
main cities or the coast, the transportation could be
more inconvenient and time-consuming, therefore
demand on those houses will reduce, causing decline
in housing prices of homes.
3.2 Linear Model Results
After calculation of correlation coefficients, the linear
regression model should be conducted for the further
analysis and conclusion. This is a model that
estimates the relationship between dependent
variables and independent variables. As seen from
table 2, those eight dependent variables for linear
regression have established a model combined with
value of beta of each variable to calculate the housing
value.
Research on the Factors Contributing to Change in Housing Price in California
471
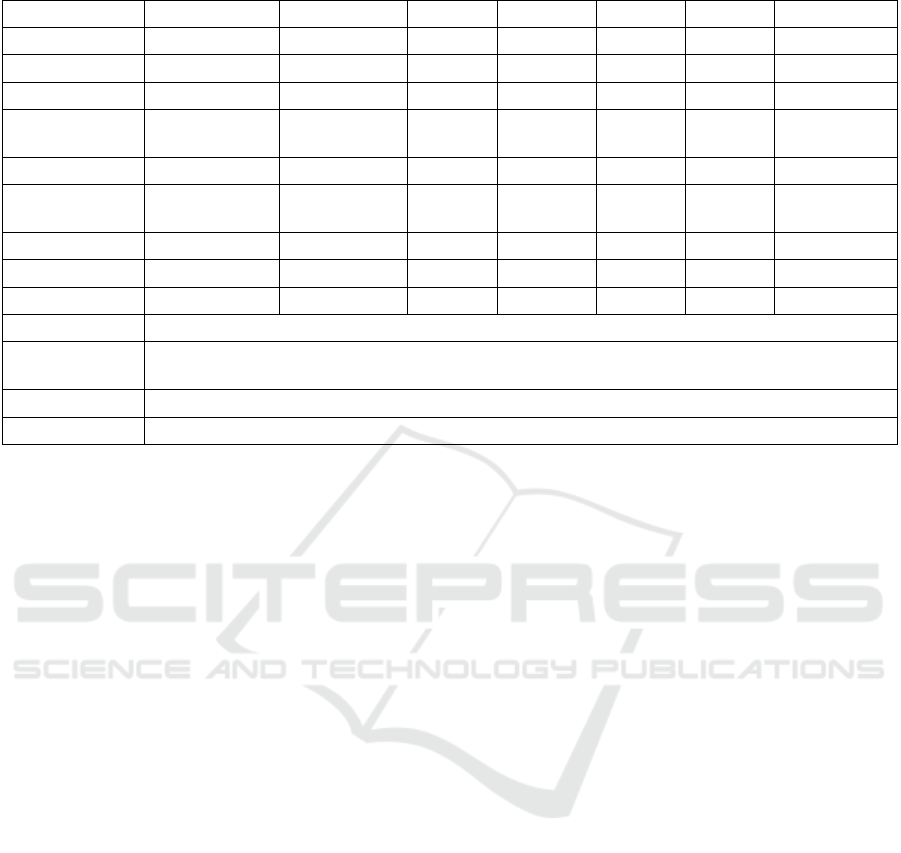
Table 2: Linear Regression Table
BSt
d
. E
r
ro
r
Beta t P value VIF Tolerance
Constant -3585395.747 62900.543 - -57.001 0.000 - -
Longitude -42730.120 717.087 -0.742 -59.588 0.000 8.714 0.115
Latitude -42509.737 676.952 -0.787 -62.796 0.000 8.829 0.113
Housing median
a
g
e
1157.900 43.389 0.126 26.687 0.000 1.260 0.794
Rooms numbe
r
-8.250 0.794 -0.156 -10.387 0.000 12.717 0.079
Bedroom
numbe
r
113.821 6.931 0.415 16.423 0.000 36.004 0.028
Po
p
ulation -38.386 1.084 -0.377 -35.407 0.000 6.371 0.157
Househol
d
47.701 7.547 0.158 6.321 0.000 35.136 0.028
Income 40297.522 337.207 0.663 119.504 0.000 1.732 0.578
R-square
d
0.637
Adjust R-
square
d
0.637
F Test F
(
8, 20424
)
= 4478.347,
p
=0.000
D-W 0.975
Then, R- squared value and adjusted R-squared value
are both 0.637, implying that these several variables
can entirely bring about 63.7% of the change in
median house price, which is powerful result to
display.
From the calculation and the table, it is obvious
that median income keeps the most significant
positive implications on house value with a
standardized Beta of 0.663 and a significant
unstandardized coefficient of 40297.52. This
represents that if other variables constant, an increase
in household income will probably bring a dramatic
increase in housing price. This is also consistent with
the idea that wealthy areas tend to develop more
expensive housing markets and wealthy consumers.
In addition, the location in terms of latitude and
longitude, both possess strong negative effects on
house value, which standardized betas are -0.787 and
-0.742 respectively. Housing median age has a
positive relationship with housing value, with beta of
1157.90.
While it is quite surprising that total rooms display
a negative coefficient, which B equals to -8.25 and β
equals to -0.156, but the total bedrooms show a
positive one (β = 0.415). This suggests
multicollinearity and an overlapping influence.
Indeed, their Variance Inflation Factors (VIF) are
both high, showing 12.717 for total rooms and 36.004
for total bedrooms, which indicates that there may be
a risk of collinearity and potential distortion in terms
of estimates.
4 CONCLUSION
This research randomly selected 20640 samples from
California Census dataset collected by the US Census
Bureau in 1990. By using correlation and regression
analysis as combination of strategies, this study
investigates this potential feature causing alternation
in housing value.
Through the analysis, it is obvious that
households’ income level is always the most
influential feature regarding the housing value
through both size of correlation coefficient and
regression model. Besides, from further regression
analysis, it is known that factors of location and
housing age will cause limited effect on housing
value, and other variables such as room numbers and
households don’t affect significantly.
This outcome provides a relatively clear direction
regarding potential factors which influencing housing
prices, which is useful for households, real estate
agencies as well as the government to determine
future trend on housing markets. Households ought to
select appropriate housings based on their own wealth
level and personal purchasing budget. However, the
conclusion still cannot be the accurate result about
this issue, as the sample size covers only 20000
approximately and the time for research is relatively
outdated, which may affect the conclusion accuracy
and reality.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
472

REFERENCES
Asuero, A.G., Sayago, A., Gonzalez, A. G., (2007). The
Correlation Coefficient: An Overview. Critical
Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 36(1), 41-59.
Batdorf, E., (2024). Where it takes Americans the most (and
least) time to save for a home. Forbes, 3.
Huang, B., Wu, B., Barry, M., (2010). Geographically and
temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-
temporal variation in house prices. International
Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24(3),
383-401.
Lau, J., (2024). California Housing Crisis: Exploring the
Link Between Population Shifts and Housing
Prices. UC Office of the President: UC Center
Sacramento. International Journal of Geographical
Information Science.
Li, T., Yang, X., (2024). The research on factors
influencing house value-take California as an example.
Theoretical and Natural Science, 39, 96-102.
Mao, Y., Yao, R., (2020). A Geographic Feature Integrated
Multivariate Linear Regression Method for House Price
Prediction. 2020 3rd International Conference on
Humanities Education and Social Sciences.
Rolfe, S., et al. (2020). Housing as a social determinant of
health and wellbeing: developing an empirically-
informed realist theoretical framework. BMC Public
Health, 20, 1138.
Yan, Y., (2022). Influencing factors of housing price in
New-York-analysis: Based on excel multi-regression
model. In Proceedings of the International Conference
on Big Data Economy and Digital Management, 1,
1005-1009.
Yu, J., (2024). A Multivariate Regression Analysis of
Factors Influencing California Housing Prices. ICMML
'23: Proceedings of the International Conference on
Mathematics and Machine Learning, 165-169.
Zoppi, C., Argiolas, M., Lai, S., (2015). Factors influencing
the value of houses: Estimates for the city of Cagliari,
Italy. Land Use Policy, 42, 367-380.
Research on the Factors Contributing to Change in Housing Price in California
473
