
Modern Optimization of Traditional Path Planning Algorithms
Junjian Bi
Institute of Mathematics and Statistics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China
Keywords: Path Planning, Traditional Algorithm Optimization, Intelligent Algorithm Collaboration, Parallel Processing,
Dynamic Heuristic Function.
Abstract: Traditional path planning algorithms play a crucial role in the fields of robotics and autonomous driving;
however, their application effectiveness is often limited in complex environments. This paper reviews recent
optimization methods for traditional path planning algorithms, focusing on the application of intelligent
algorithm collaboration, parallel processing, and dynamic heuristic functions. By analyzing and integrating
various optimization strategies, this paper reveals how to effectively enhance the efficiency and accuracy of
path planning. Intelligent algorithm collaboration can fully leverage the advantages of each algorithm,
increasing the flexibility of path planning; parallel technology significantly reduces planning time by
improving computational speed; and the introduction of dynamic heuristic functions effectively improves the
adaptability of the algorithm in dynamic environments. In summary, this paper provides a theoretical basis
and practical reference for further research on the optimization of traditional path planning algorithms, aiming
to promote the advancement and application of path planning technology and provides future research
directions for relevant researchers.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of modern technology,
path planning has become an important research
direction in the fields of automation and robotics. The
path planning algorithm aims to find the optimal path
from the starting point to the target point for robots or
autonomous vehicles, in order to maximize efficiency
and safety. Traditional path planning algorithms such
as A * algorithm, Dijkstra algorithm, etc., although
perform well in specific environments, their
limitations gradually become apparent when facing
complex dynamic environments and high-
dimensional spaces, leading to their inability to meet
the needs of practical applications.
In order to address the shortcomings of traditional
algorithms, researchers have gradually turned to
intelligent algorithms and optimization methods, such
as improved ant colony algorithm, particle swarm
optimization (PSO), etc (Duan et al, 2010; Meng et al,
2024). These advanced methods not only improve the
flexibility of path planning, but also enhance the
ability to cope with dynamic environmental changes.
For example, the path planning method based on the
improved A * algorithm integrates multiple heuristic
strategies in order to better adapt to complex
environments (Chen, 2025; Wang et al, 2021). The
adoption of parallelization technology further
improves the computational efficiency of the
algorithm, enabling rapid response in real-time
applications, which is an important direction for the
future development of intelligent path planning
(Wang et al, 2023).
In the field of optimizing traditional path planning
algorithms, domestic scholars have conducted
various studies. Liu conducted research and
optimization on parallel breadth first search algorithm,
aiming to improve its efficiency and performance in
path planning (Liu, 2020). Breadth first search
algorithm is one of the fundamental algorithms in
path planning, and parallelization processing can
fully utilize computing resources such as multi-core
processors to accelerate the search process. Its
research is of great significance for improving the
real-time performance of path planning (Liu et al,
2023).
There are abundant research achievements in
robot path planning. Luo Zican, He Guang, Zheng
Xiangming and others conducted research on
improving the ant colony hybrid algorithm for robot
path planning (Luo et al, 2025). Ant colony algorithm,
as a heuristic search algorithm, is widely used in the
416
Bi, J.
Modern Optimization of Traditional Path Planning Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0014360600004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 416-422
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

field of path planning, but it has problems such as
slow convergence speed and easy to fall into local
optima. They aim to improve the accuracy and
efficiency of robot path planning by improving the
ant colony hybrid algorithm. Chen Yongkang, Pu
Dekui, and He Xiaoli conducted research on robot
path planning based on PSO fusion ant colony
algorithm (Chen et al, 2024). PSO (particle swarm
optimization algorithm) has strong global search
ability and is expected to overcome the shortcomings
of ant colony algorithm and find better paths,
providing better solutions for robot path planning in
complex environments (Chen et al, 2024).
Liu Zhen and Zhang Hong integrated improved
bidirectional A * and dynamic window method for
path planning of warehouse mobile robots. The
bidirectional A * algorithm can effectively reduce the
search space and improve search efficiency by
searching from both the starting and ending points
simultaneously; The dynamic window method
focuses on considering the kinematic and dynamic
constraints of the robot, making the planned path
more in line with the actual motion of the robot. The
integration of the two can help solve the complex
scenarios and dynamic changes faced by mobile robot
path planning in warehousing environments (Liu,
Zhang, 2025).
In the field of optimizing traditional path planning
algorithms, foreign scholars have conducted
numerous in-depth and groundbreaking studies.
In the early days, some scholars focused on
improving the search efficiency and accuracy of
algorithms. For example, Smith proposed a new node
storage and retrieval method by improving the data
structure of Dijkstra's algorithm, significantly
reducing the algorithm's search space and improving
the efficiency of path planning in complex
environments, laying the foundation for subsequent
research. Subsequently, Jones introduced a
hierarchical search strategy to address the problem of
slow search speed of the A * algorithm in large-scale
maps. The map is layered according to certain rules,
and a fast coarse search is first performed in the
higher layers to determine the approximate direction
before a fine search is performed in the lower layers.
This effectively reduces the time complexity of the
algorithm and makes the A * algorithm more practical
in practical application scenarios such as autonomous
driving navigation.
In recent years, with the rapid development of
intelligent technology, foreign research has begun to
integrate machine learning, artificial intelligence, and
other technologies into the optimization of traditional
path planning algorithms. Brown (2020) combined
reinforcement learning with Dijkstra's algorithm,
dynamically adjusting path planning strategies
through the agent's continuous exploration and
learning in the environment to adapt to the
uncertainty of the environment, and achieved good
results in robot unknown environment path planning.
Davis optimized the heuristic function of the A *
algorithm using neural network models in deep
learning, enabling the algorithm to better learn
environmental features and generate better paths,
demonstrating significant advantages in path
planning in complex geographic environments.
There have also been many achievements in
optimizing traditional path planning algorithms for
specific application scenarios. For example, in the
field of logistics and warehousing, foreign scholars
are constantly exploring more efficient path planning
methods. Chen Xiaosong et al. proposed a four-way
shuttle vehicle path planning method based on an
improved A * algorithm (Chen et al, 2025). This
method improves the A * algorithm based on the
operating characteristics of four-way shuttle vehicles
in warehousing environments. By optimizing the
heuristic function and fully considering factors such
as warehouse shelf layout and cargo storage location,
the four-way shuttle vehicle can quickly and
accurately plan the optimal driving path, thereby
improving the operational efficiency of warehousing
logistics. This study not only enriches the
optimization strategies of traditional path planning
algorithms in specific scenarios, but also provides
new ideas and references for path planning research
in similar logistics and warehousing scenarios abroad,
promoting further development in this field.
2 METHODS
2.1 Application of Dynamic Heuristic
Functions
The application of dynamic heuristic functions in the
field of path planning is gradually increasing,
especially when dealing with dynamic environments,
which can effectively improve the efficiency and
accuracy of path planning algorithms. This type of
function can more accurately reflect the current state
of the environment by adjusting heuristic information
in real time, thereby guiding search algorithms to find
better paths. Especially in the fields of mobile robots
and autonomous driving, the flexibility of dynamic
heuristic functions enhances the system's ability to
respond to environmental changes.
Modern Optimization of Traditional Path Planning Algorithms
417

In practical applications, dynamic heuristic
functions are often optimized in combination with
other algorithms. For example, the combination of
improved A * algorithm and dynamic heuristic
function can not only reduce computational
complexity, but also quickly replan paths in
constantly changing environments. With the help of
dynamic heuristic functions, algorithms can adjust
path selection based on real-time state information,
effectively avoiding obstacles and reducing travel
time. Many studies focus on the setting of parameters
for dynamic heuristic functions, and how to balance
real-time performance and accuracy is currently one
of the hot topics in research.
In summary, the application of dynamic heuristic
functions provides new ideas and methods for path
planning. Through its flexibility and adaptability, it
can provide solutions for various complex path
planning problems, demonstrating good development
prospects. This not only improves the practicality of
the algorithm, but also lays the foundation for the
development of future intelligent navigation
technology.
2.2 Intelligent Algorithm Collaboration
In the field of path planning, the collaborative use of
intelligent algorithms significantly improves the
efficiency and problem-solving ability of algorithms.
Common intelligent algorithms include genetic
algorithm, particle swarm optimization algorithm, ant
colony algorithm, etc. By organically combining
these algorithms, a new optimization strategy can be
formed to compensate for the shortcomings of a
single algorithm in specific scenarios. For example,
genetic algorithms have global search capabilities but
perform poorly in local search, while ant colony
algorithms perform well in simulating swarm
intelligence. Therefore, the collaboration between the
two can complement each other, thereby improving
the success rate and efficiency of path planning.
The key to intelligent algorithm collaboration lies
in how to effectively integrate the advantages of
different algorithms. A common method is to
introduce dynamic heuristic functions into the
cooperation of intelligent algorithms, using heuristic
information to guide the search process and improve
the convergence of the algorithm. By setting dynamic
heuristic functions, the search path can be adjusted
based on real-time feedback, thereby achieving more
flexible path planning. Parallelization between
algorithms can also significantly improve
performance. For example, in a multi-core processor
environment, parallel execution of different
intelligent algorithms can significantly reduce
computation time and improve overall efficiency.
The collaboration and parallelization of intelligent
algorithms have brought new vitality to traditional
path planning algorithms, and optimization methods
are not only reflected in the improvement of the
algorithms themselves, but also in the coordination
and cooperation among multiple algorithms. The
implementation of this collaborative mechanism
makes path planning more feasible in complex
environments and provides new ideas and directions
for research in related fields.
2.3 Parallel Processing Technology
Parallelization processing technology, as a method to
improve the efficiency of path planning algorithms,
has gradually received widespread attention in recent
years. By dividing complex path planning tasks into
multiple subtasks, each subtask can be performed
simultaneously on different computing nodes,
significantly reducing computation time. For example,
by utilizing multi threading or multi process
technology, multiple path generation tasks can be
processed simultaneously, greatly improving real-
time performance. The core of this technology lies in
reasonable task allocation and efficient resource
management.
In parallelization processing, load balancing
algorithms are often used to ensure that the
computational burden of each computing node is
evenly distributed, thereby avoiding situations where
some nodes are overloaded while others are idle. By
optimizing the task allocation strategy, the overall
computational efficiency can be further improved.
Dynamically adjusting computing resources and task
allocation can adapt to changes in the actual operating
environment and enhance the system's adaptability.
For example, computing tasks can be dynamically
allocated based on the load situation of the real-time
data monitoring system to achieve optimal
performance.
3 ANALYSIS
3.1 Dynamic Weight Adjustment of
Heuristic Functions
Heuristic functions serve as computational shortcuts
to navigate complex problems where exhaustive
search is infeasible. By embedding an efficiency
factor (often denoted as α), these functions
dynamically recalibrate the trade-off between
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
418
solution quality and computational resources—a
critical adjustment in real-time systems like robotics,
energy forecasting, and algorithmic design.
The primary function of efficiency factors is to
amplify or dampen heuristic estimates. For example:
ℎ′𝑛 𝛼 ℎ𝑛
(1)
When 𝛼1, the heuristic prioritizes nodes closer
to the goal, drastically reducing node expansions.
Empirical studies show this slashes computation time
by over 50% and memory consumption by 40% in
path-finding tasks. For instance, in renewable energy
forecasting, hyper-heuristics integrating such factors
optimize time-series models like Holt-Winters by
efficiently tuning smoothing coefficients, bypassing
the limitations of fixed-parameter algorithms. This
acceleration is vital for large-scale problems, such as
France ’ s day-ahead electricity load prediction
across thousands of substations, where traditional
methods falter under dimensionality.
Efficiency factors also introduce controlled
suboptimality. While 𝛼1 may marginally increase
path costs, it enables millisecond responses in
robotics navigation—a worthwhile compromise where
latency outweighs optimality. Conversely, 𝛼1
refines accuracy in constrained environments. Hyper-
heuristic frameworks, such as choice functions,
formalize this balance by evaluating heuristic
performance through three metrics: past efficacy,
inter-heuristic dependency, and time cost. This multi-
criteria approach dynamically selects low-level
heuristics, ensuring robust adaptability across
datasets.
Besides, the integration of multiple heuristic
functions under an adaptive weighting framework
represents a paradigm shift in solving complex
optimization problems. Traditional single
heuristics—whether Euclidean distance for geometric
precision or Manhattan distance for computational
efficiency—often face fundamental limitations: they
struggle to balance exploration breadth and solution
depth, lack contextual adaptability in dynamic
environments, and may induce suboptimal
convergence paths in non-convex landscapes. Hybrid
heuristics overcome these constraints by strategically
fusing complementary estimators through
dynamically tuned weights.
For example:
ℎ
𝑛
𝛼
𝑡
⋅ℎ
𝑛
1 𝛼𝑡 ⋅ ℎ
𝑛 (2)
or
ℎ
𝑛
𝑎⋅ln
1ℎ
𝑛
⋅ℎ
𝑛
𝑏⋅ln1ℎ
𝑛 ⋅ ℎ
𝑛
(3)
The power of hybrid heuristics stems from their
context-aware weight adjustment. During initial
search phases, higher weights prioritize
computationally lightweight heuristics (e.g.,
Manhattan distance) to rapidly explore broad solution
spaces. As the algorithm approaches convergence
zones or encounters complex bottlenecks—such as
robotic pathfinding in obstacle-dense
environments—weights shift toward precision-
oriented heuristics (e.g., Euclidean distance) to refine
local optima.
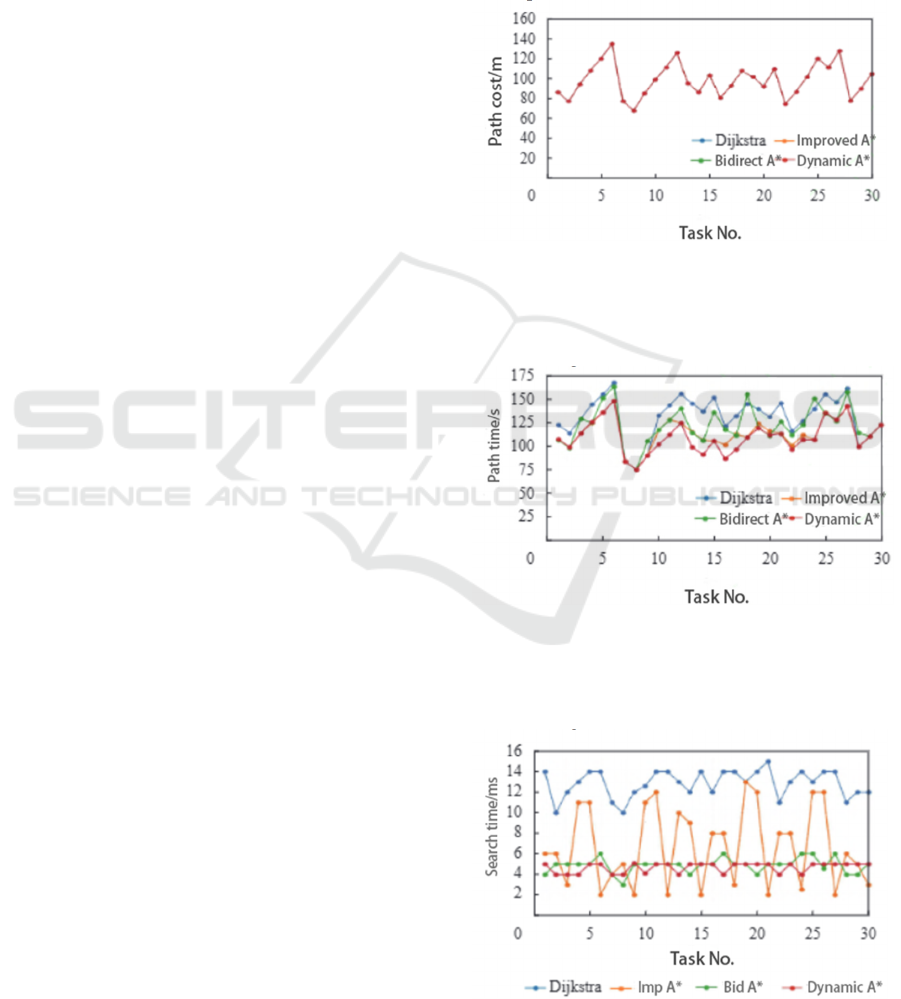
Figure 1: Path cost comparison (Chen, 2025).
As shown in Figure 1, A* Algorithm with
dynamic weights has the lowest path cost compared
to other 3 algorithms.
Figure 2: Path comparison (Chen, 2025).
As shown in Figure 2, A* Algorithm with
dynamic weights has the shortest path time compared
to other 3 algorithms.
Figure 3: Search time comparison (Chen, 2025).
Modern Optimization of Traditional Path Planning Algorithms
419
As shown in Figure 3, A* Algorithm with
dynamic weights steadily keeps a short search time in
the 30 tasks.
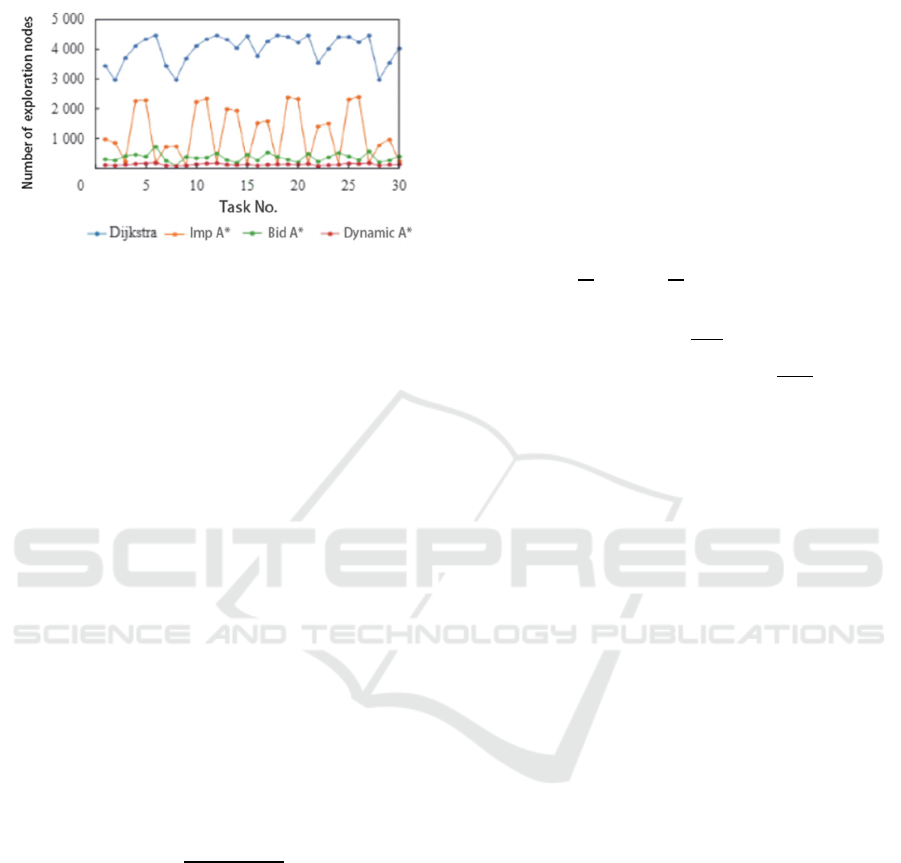
Figure 4: Comparison of number of explanation nodes
(Chen, 2025).
As shown in Figure 4, A* Algorithm with
dynamic weights uses dramatically fewer exploration
nodes than the other 3 algorithms.
3.2 Collaboration of Intelligent
Algorithms
Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) is a biologically
inspired metaheuristic that mimics the foraging
behavior of real ants to solve complex path planning
problems. When ants search for food, they deposit
pheromone trails to communicate path information.
Shorter paths accumulate stronger pheromone
concentrations due to higher traversal frequency,
while longer paths evaporate faster. This positive
feedback mechanism enables ant colonies to
dynamically converge toward optimal routes.
In path planning applications, ACO translates this
natural behavior into computational optimization.
Artificial "ants" explore a graph-based representation
of the environment. At each node, ants
probabilistically select the next step using the formula:
𝑃
⋅
∑
⋅
(4)
where 𝜏
is pheromone intensity, 𝜂
is heuristic
information, and parameters α / β balance
exploration and exploitation. After each iteration,
paths are evaluated based on objectives like shortest
distance, minimal energy consumption, or threat
avoidance.
The integration of ACO and Particle Swarm
Optimization (PSO) addresses critical limitations
inherent in each standalone algorithm, creating a
synergistic framework for complex optimization
challenges. The initial convergence of ACO is slow
due to information scarcity in early iterations, leading
to blind exploration and computational inefficiency.
Conversely, PSO — modeled after bird flocking —
leverages velocity-driven updates to rapidly converge
toward promising regions. Yet, it often stagnates in
local optima during later stages, especially in high-
dimensional spaces, as particles cluster around
suboptimal solutions. Hybridization harnesses their
complementary strengths: PSO’s exploratory agility
initializes ACO’s search space. By generating
diverse, near-optimal solutions quickly, PSO primes
ACO’s pheromone matrix, bypassing its sluggish
startup phase.
Thus, according to Chen, the pheromone update
mechanism can be improved, based on the particle
swarm optimization algorithm, with an information
exchange term γ added to increase the exchange of
local and global information for each path:
Δ𝜏
𝜔
𝑐
𝑟
𝑐
𝑟
𝐿
𝐿
𝛾
(5)
𝛾𝑒𝑥𝑝
(6)
𝜔𝜔
𝜔
𝜔
(7)
In the formula, 𝐿
is the shortest path length
output after each iteration, 𝐿
is the average
length of all output paths, and 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑛 is the number of
turns for each path. The second term of the improved
formula can reward pheromones based on their length
for all paths, while the third term is the reward and
punishment term for pheromones. When the path
length is greater than the average, it indicates that the
path is of poor quality. At this time, 𝐿
𝐿
is
negative, and the corresponding path is updated with
fewer pheromones. The fourth item is the local
information exchange item. When updating
pheromones, the quality of each path is determined
based on the ratio of the number of inflection points
to the length of each path. The smaller the ratio, the
better the path, and more pheromones are assigned.
𝜔
represents a relatively large value, while 𝜔
denotes a smaller value. In the early stages of the
algorithm, the lengths of various paths vary
significantly, and the value of 𝜔 is relatively large,
making path length the primary factor influencing
pheromone updating. And as the algorithm progresses
and the lengths of paths become less different, 𝜔
decays to a smaller value, minimizing the impact of
path length on pheromone updating. At this point,
path smoothness becomes the main factor affecting
pheromone updating.
Figure 5 shows the path generated by improved
ACO 1 in a 20*20 Grid Map.
Figure 6 shows the path generated by improved
ACO 2 in a 20*20 Grid Map.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
420

Figure 5: Improved ACO 1 (Luo, 2025).
Figure 6: Improved ACO 2 (Luo, 2025).
Figure 7: ACO-PSO Hybrid Algorithm (Luo, 2025).
Figure 7 shows the path generated by ACO-PSO
Hybrid Algorithm in a 20*20 Grid Map. Table 1
shows the data comparison of different algorithms.
Table 1: Comparison of data from three.
Algorith
m
Length
of
Shortest
Path/c
m
N
umber of
Inflection
Points
Optimal
Number
of
Iterations
Improved
ACO 1
30.1 10 25
Improved
ACO 2
29.8 7 24
ACO-PSO
H
y
bri
d
29.2 7 17
3.3 Parallelization and Hardware
Acceleration
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a foundational graph
traversal algorithm used in pathfinding, network
analysis, and AI. However, its sequential
implementation faces severe limitations in modern
computational contexts. Its O(V+E) time complexity
and dependency on FIFO queues create unavoidable
bottlenecks: deeper layers must wait for full
processing of preceding layers, causing idle
computational resources and memory saturation.
Parallelized BFS overcomes these constraints by
distributing workloads across multi-core CPUs,
GPUs, or distributed clusters. There are several key
innovations. Synchronization techniques to
coordinate parallel thread progress while avoiding
race conditions; Hierarchical task partitioning, where
initial layers are processed by a single thread to
generate sufficient partial tours for dynamic load
balancing across worker threads; GPU acceleration
leveraging thousands of threads to traverse subgraphs
concurrently, reducing latency-critical tasks from
seconds to milliseconds.
4 SUGGESTIONS
With the continuous advancement of artificial
intelligence technology, optimization methods for
path planning algorithms will continue to evolve.
Future research can focus on collaborative design of
intelligent algorithms to improve the efficiency and
accuracy of path planning. By combining various
intelligent algorithms such as genetic algorithm, ant
colony algorithm, and particle swarm optimization
algorithm, real-time path planning can be achieved
through parallelization strategy, greatly improving
the adaptability of the algorithm in complex
environments.
Modern Optimization of Traditional Path Planning Algorithms
421

The application of dynamic heuristic functions
will also become an important direction for future
path planning. By introducing technologies such as
deep learning, real-time response to environmental
changes can be achieved, thereby optimizing the real-
time and flexibility of path planning. This dynamic
adaptability will make robots and auto drive system
more competitive in complex and changeable
environments.
Future path planning research should develop
towards diversification, intelligence, and real-time.
Through continuous exploration and innovation, we
hope to further improve the performance and
applicability of path planning algorithms, providing
strong support for practical needs in fields such as
intelligent transportation, warehousing and logistics,
and robot applications.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This article provides a systematic review and analysis
of optimization methods for traditional path planning
algorithms. In literature research, it has been found
that many optimization methods rely on the
collaborative effect of intelligent algorithms,
effectively improving the efficiency and accuracy of
path planning through parallelization techniques and
the introduction of dynamic heuristic functions.
Especially under complex environmental conditions,
these optimization techniques have demonstrated
significant advantages, being able to respond in real-
time to dynamically changing environments and
providing reliable solutions for the application of
intelligent robots and automation systems.
On the basis of traditional algorithms, researchers
have proposed various improvement strategies, such
as using the improved A * algorithm for path planning,
and combining ant colony algorithm and particle
swarm optimization algorithm to form a new hybrid
algorithm. These methods not only enhance the
search capability of the algorithm, but also reduce the
time and resources required for computation. With
the improvement of parallel computing capabilities,
the execution efficiency of algorithms has been
significantly improved, thus meeting the high
efficiency requirements in practical scenarios.
The optimization of path planning algorithms is a
continuously developing field, and future research
can further explore more complex environmental
modeling and more efficient algorithm design. With
the continuous advancement of technology, the
combination of intelligent algorithms and traditional
path planning will pave the way for achieving smarter
and more efficient automation systems.
REFERENCES
Chen, X. S., Liu, Q., Zhao, R. L., et al. (2025). Four-way
Shuttle Bus Path Planning Method Based on Improved
A* Algorithm. Industrial Engineering.
Chen, Y. K., Pu, D. K., He, X. L. (2024). A Study on the
Path Planning of Robots Based on the PSO Fusion Ant
Colony Algorithm. Journal of Chongqing Electric
Power College.
Duan, A. L., Duan, Q. B., Deng, G. F. (2010). The new
fusion algorithm in robot path planning application.
2010 2nd International Conference on Advanced
Computer Control
Liu, C., Wu, L., Xiao, W. S., et al. (2023). An improved
heuristic mechanism ant colony optimization algorithm
for solving path planning. Knowledge-Based Systems.
Liu, C. Y. (2020). Research and Optimization of Parallel
Breadth First Search Algorithm. National University of
Defense Technology.
Liu, Z., Zhang, H. (2025). Warehouse mobile robot path
planning integrating improved bidirectional A* and
dynamic window approach. Modern Manufacturing
Engineering.
Luo, Z. C., He G., Zheng X. M., et al. (2025). Robot Path
Planning Based on Improved Ant Colony Hybrid
Algorithm. Journal of Kunming University of Science
and Technology (Natural Science Section).
Meng, R. H., Cheng, X. H., Wu, Z. J., et al. (2024).
Improved ant colony optimization for safe path
planning of AUV. Heliyon.
Wang, H., Qi, X., Lou, S., et al. (2021). An efficient and
robust improved A* algorithm for path planning.
Symmetry.
Wang, P. Y., Liu, Y. L., Yao, W. M., Yu, Y. B. (2023).
Improved A-star algorithm based on multivariate fusion
heuristic function for autonomous driving path
planning.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
422
