
Multi-Robot Collaborative Interaction in Children’s Education
Jian Huang
a
School of Computing and Data Science, Xiamen University Malaysia, Jalan Sunsuria, Bandar Sunsuria, 43900 Sepang,
Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
Keywords: Human-Computer Interaction, Multi-Robot Collaborative System, Children’s Education, Emotion
Recognition, Adaptive Strategy.
Abstract: With the development of artificial intelligence and robotics technology, multi-robot collaboration systems
have shown great potential in children's education. This review introduces the concepts of human-computer
interaction, multi-robot collaborative systems, and children's emotional states in the field of education. It
explains the limitations of single-modal technology and emphasizes the advantages of multimodal technology
by comparing and analysing single-modal and multimodal technologies. In addition, this review discusses the
task division, dynamic role allocation, and interaction regulation strategies of multi-robot systems in the
classroom. Finally, it points out that real-time response and child privacy protection still remain challenges
that need to be addressed urgently. It is recommended to optimize the system architecture through means such
as model pruning, introduce federated learning and build a complete privacy protection protocol to ensure the
security of children's data. This review provides theoretical and technical references for the future application
of multi-robots and multimodal perception technologies in personalized education.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid advancement of technology, robotics
has emerged as a significant area of interest. In
contemporary times, robotics extends beyond the
realm of industrial automation and is increasingly
recognized for its potential in children's education. A
study conducted by Kay et al. on an international
scale revealed that during interactions with the
Cozmo robot, children not only exhibited a wide
range of playful behaviours but also regarded the
robot as a "brother" or a "pet" (Kay et al., 2023). In
another study, Yang et al. implemented the NAO
robot in classroom settings for children with autism
and observed substantial improvements in attention,
classroom communication, and positive emotional
expression (Yang et al., 2024). In conclusion, these
studies have demonstrated that the application of
robots in the field of children's education has a
promising future.
However, most educational robots today operate
as single-robot systems, limiting their ability to
provide personalized instruction. This limitation
restricts their effectiveness in delivering personalized
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6281-6385
instruction and the capacity to execute multiple tasks.
Multi-robot cooperative systems, which leverage
coordinated behaviours across multiple robots,
efficient data transmission, and a low rate of
information errors, have emerged as a focal point in
contemporary research. The collaboration of multiple
robots can perform certain tasks that a single robot
cannot accomplish, such as dynamic role allocation
and communication collaboration. Wu and Suh
highlighted in their research that integrating learning
mechanisms into multi-robot cooperative systems
facilitates achievements such as collaborative
decision-making, task decomposition, and situational
awareness (Wu & Suh, 2024). By systematically
reviewing various robot learning methods (including
reinforcement learning, imitation learning, and
transfer learning), they concluded that robots still
possess a certain degree of universality in the current
complex educational environment.
Currently, although multi-robot collaborative
systems have demonstrated great potential in
education, they still face issues regarding the
reliability and accuracy of identifying children's
emotional states. The personalized interaction ability
Huang, J.
Multi-Robot Collaborative Interaction in Children’s Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0014355500004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 365-370
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
365

of educational robots largely depends on the precise
identification of children's cognitive states.
The multi-robot collaborative system, with multi-
source data sharing and multi-angle monitoring, can
intelligently adjust learning strategies based on
children's cognitive states and emotional changes,
thereby providing more flexible teaching support.
Research shows that even with simple adaptive
strategies based on rules (such as time management
and task reminders), robots can significantly enhance
children's learning effectiveness and engagement
(Rosenberg-Kima et al., 2020).
This study mainly explores how a multi-robot
collaborative system can work in real time and
achieve adaptive adjustments in an educational
environment. The research will first introduce the
core concepts in this field. Then, it will compare and
analyse the application of single-modal technology
and multimodal technology in emotion recognition.
Next, the study focuses on how robots can achieve
adaptive interaction technologies such as task
division and dynamic role allocation in the field of
education. Finally, this study identified the
limitations of current technologies and envisioned the
potential of educational robots to enhance children's
learning experience in the future. It is hoped that this
paper can provide theoretical support and technical
references for the promotion of robots in education in
the future.
2 CORE CONCEPTS
2.1 Children's Emotions and Education
The emotional state of children is a key factor in the
quality of robot-assisted education. The robot system
can make personalized adjustments to teaching based
on these identifications of children's emotional states,
thereby enhancing learning outcomes and increasing
students' acceptance. Beck et al. combined facial
expressions, gaze patterns, and deep learning models
to construct a multimodal emotion recognition system
for early education (Beck et al., 2023). The
experimental results of Laban et al. showed that
participants expressed emotions more naturally and
used richer language under the guidance of robots
with cameras and voice interaction, and their
cognitive control ability over negative emotions
significantly improved. Although the research
subjects were college students, it still has reference
value for children's education robot systems (Laban
et al., 2025).
2.2 Multi-Robot Collaboration System
In a multi-robot collaborative system, multiple robots
can work together in the same environment to
complete tasks. Compared to a single-robot system,
the multi-robot collaborative system has greater
scalability, fault tolerance, and flexibility. The robots
in this system can communicate and collaborate
through various mechanisms, such as wireless
network communication, distributed protocols,
collaborative algorithms and models, etc. The
research by Wu and Suh indicates that the multi-robot
collaborative system not only performs well in
dynamic environments such as search and rescue,
logistics, etc. but also its real-time role switching and
behaviour adjustment capabilities are applicable to
classroom scenarios (Wu & Suh, 2024). In addition,
this research points out that the application of hybrid
learning methods is the mainstream of future multi-
robot collaborative systems. By combining
reinforcement learning with imitation learning, the
system can accurately respond in real-time capturing
the learner's state and environmental changes.
2.3 Human-Computer Interaction in
Children's Education
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is an
interdisciplinary field. It aims to enhance the usability
and user-friendliness of systems by studying the
interaction between systems and users. In the field of
children's education, HCI has evolved from initial
screen projections and smart whiteboards to today's
educational robots. These robots not only facilitate
the transmission of knowledge, but also can
understand the emotions of children and adjust the
teaching pace accordingly. Yang et al.'s experiment,
found that through regular waving and LED eye
contact methods, the online attention duration of
autistic children increased by 29.22%. The rate of
children's smiling responses triggered by the robot's
praise behaviour reached 62.17%, which was 37%
higher than that in a regular classroom (Yang et al.,
2024). This immersive interactive classroom based on
emotional feedback helps maintain students'
concentration and enhance their learning interests.
3 EMOTIONAL PERCEPTION
TECHNOLOGY
Emotion perception is the core capability for
educational robots to achieve dynamic adjustment
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
366

and personalized interaction. Only by establishing
real-time and precise perception capabilities can the
system achieve dynamic adjustment and thereby
enhance learning effectiveness. Currently, emotion
perception technology is mainly divided into single-
modal and multi-modal types.
3.1 Single-Modal Technology
Single-Modal technology refers to the technique that
relies solely on a single signal source for emotion
recognition. Common approaches include facial
expressions and speech.
The research by Xu et al. specifically constructed
a CNN model (Figure 1) to identify and process facial
expressions (Xu et al., 2024). The input of this model
is a 48×48 grayscale face image. The model consists
of three convolutional layers (using 32, 64, and 128
convolutional kernels respectively). After each
convolutional layer, there is a 2×2 max pooling
operation, which is used to compress the feature maps
and retain key information. Finally, through a fully
connected layer and a classifier, the image is
classified into one of the six emotions (Happy,
Confused, Bored, Claim, Excited, Anxious).
Experimental results show that the recognition
accuracy of this model for all six emotions is above
80%, with an average accuracy of 85%. This indicates
that CNN has strong capabilities for extracting and
classifying complex facial expressions, and can be
more accurate in emotion recognition for children.
Figure 1: CNN Model (Xu et al., 2024)
In order to better understand the emotional
characteristics in speech, researchers usually use Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models to analyse
language. Xu et al. also constructed an LSTM-based
system (Figure 2) in the part of speech emotion
recognition (Xu et al., 2024). This model first extracts
Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) of each
speech segment as input features, then sends these data
to two LSTM layers (with 128 and 64 units
respectively), and finally classifies them into one of
the six previous emotions through a fully connected
layer and a classifier. This experiment result, found
that the recognition accuracy of each emotion by the
LSTM model is slightly higher than that of the CNN
model, with an average recognition accuracy of 87%.
This indicates that LSTM has greater robustness when
dealing with scenarios involving frequent language
communication such as education.
Figure 2: LSTM Model (Xu et al., 2024)
Single-modal models such as CNN and LSTM
achieved relatively high accuracy rates in ideal
experimental conditions for emotion recognition.
However, in real educational scenarios, the situation is
far more complex than in experiments, and their
accuracy rates may decrease in real environments.
Firstly, if only analysing from one direction and
directly drawing conclusions, it is prone to cause the
model to misjudge the emotional status of students.
For instance, some students may choose to remain
silent even if they have doubts during learning.
Secondly, external environmental factors (such as
light, noise, etc.) also affect the recognition effect.
Therefore, in order to more accurately identify users'
emotions, need to analyse them from multiple
dimensions.
3.2 Multimodal Technology
Conversely, multimodal technology benefits from its
integration of information from multiple distinct
sensory channels (such as vision, voice, brain waves,
etc.). It enhances the accuracy and robustness of
recognition, enabling the system to more
comprehensively capture the user's emotional state. It
also enables better understanding and adaptation to
different contexts and situations, thereby allowing for
more flexible adjustment of teaching strategies.
Multi-Robot Collaborative Interaction in Children’s Education
367
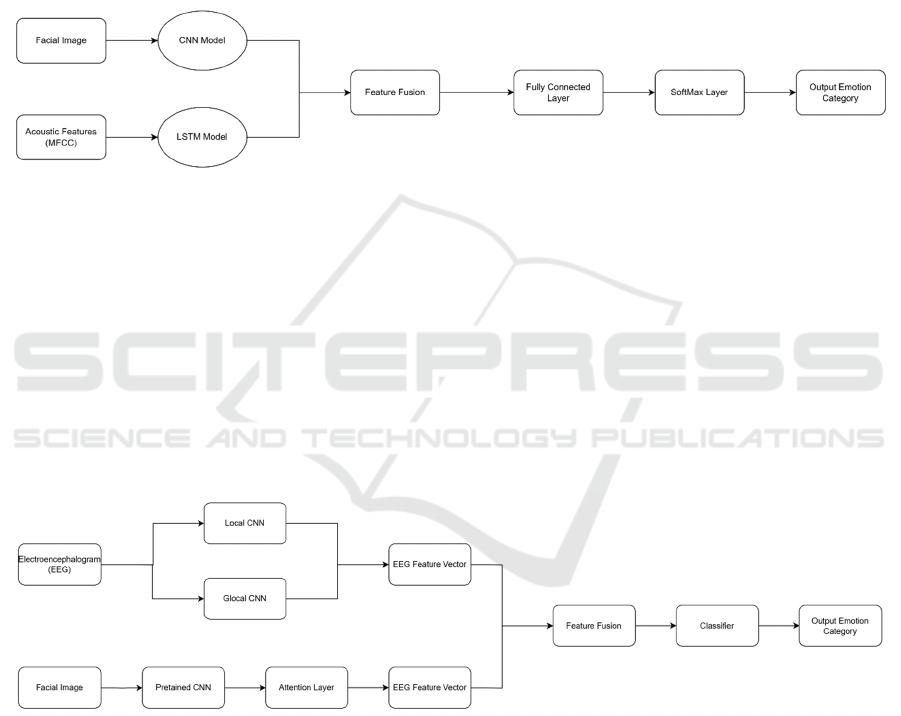
CNN-LSTM is a typical multimodal fusion
model. In the experiments conducted by Xu et al.,
they proposed a multimodal emotion recognition
model (Figure 3) that combines CNN and LSTM (Xu
et al., 2024). It extracts the facial image features and
acoustic features of users in accordance with the
previous path and processes them in parallel.
However, before entering the fully connected layer,
the features extracted in both directions will be
concatenated together. Finally, the emotion
classification is completed through the classification
layer. Compared with the experimental data of the
previous single-modal models, the CNN-LSTM
model has higher recognition accuracy in each
emotion category than the single-modal model. Its
average recognition accuracy even reaches 90%.
Moreover, this model can reduce the task completion
time of users by 14.3% and the error rate by 50%.
This indicates that the multimodal fusion model of
CNN-LSTM for emotion recognition is not only
technically effective but also has practical
educational application value.
Figure 3: CNN-LSTM Model (Xu et al., 2024)
Another multimodal model (Figure 4) was
developed by the Wang team, which combines
electroencephalogram (EEG) signals and facial
expressions for recognition (Wang et al., 2023). The
team first uses a pre-trained convolutional neural
network to extract image features from facial videos.
Besides, they also introduce an "attention
mechanism". This is used to highlight those moments
of facial expressions that better reflect the true
emotions. Meanwhile, another convolutional neural
network structure extracts spatial features from EEG
signals. Ultimately, these features, after being
integrated, will be sent to the classifier for emotion
determination. This integration method can better
capture the subtle changes in human complex
emotions, thereby revealing the "emotional disguise"
of children. In actual tests, the accuracy rate of
emotion classification of this model reached over
96%, significantly surpassing the traditional methods
that only use a single modality. However, due to the
high cost of the equipment required by this model,
this may limit its promotion in ordinary schools.
Figure 4: Deep Learning Model (Wang et al., 2023)
4 ADAPTIVE MULTI-ROBOT
COLLABORATION IN
CHILDREN’S EDUCATION
The multi-robot collaborative system has great
potential in enhancing children's learning experience.
Due to its ability to enable multiple robots to perform
tasks such as task allocation and role-playing, in the
face of complex and ever-changing educational
environments, the system can quickly make adaptive
adjustments. This is of great help for personalized
teaching and creating an immersive experience for
children.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
368

4.1 Task Division and Dynamic Role
Allocation
Just as Park et al. have verified in the multi-robot task
allocation, efficient task allocation and dynamic role
switching are the key factors for enhancing the
collaborative ability of the system (Park et al., 2021).
In the classroom, robots can be assigned to either
explain the course progress or promptly identify the
emotional states of the children. By transmitting the
emotional data to the teaching robot, the robot can
adjust the teaching pace according to the emotions.
The ability of dynamic role switching enables the
robots to switch tasks according to the needs of the
classroom. When students face a classroom test, the
robot will transform into a "supervisor" for
inspection. The functions of task allocation and
dynamic role switching help enhance the classroom
immersion of each child and improve their learning
experience.
4.2 Strategy Learning and Adaptive
Mechanism
The adaptive strategy refers to the mechanism by
which robots can continuously provide feedback and
adjust their own behaviours based on the real-time
emotional states of children. Through reinforcement
learning or imitation learning, robots can
continuously optimize their teaching decisions. Take
the experiment by Rosenberg-Kima et al. as an
example (Rosenberg-Kima et al., 2020). In this
experiment, the NAO robot could detect the activity
level of group members' discussions and the
completion degree of tasks to adjust the frequency of
the robot's questioning, encouragement, and time
reminders in real time. From the results, it can be seen
that these interactive behaviours have significantly
improved the quality and participation level of the
group's meeting discussions. Similarly, in the context
of children's education, robots can continuously
improve their teaching decision-making models
through the cycle of teaching and learning.
4.3 Emotional Perception and
Interaction Regulation Strategies
Accurate emotion perception is the prerequisite for
interactive regulation. Robots need to identify
children's emotions from multimodal data and then
execute corresponding strategies. For instance, when
it detects expressions of "confusion" or "anxiety", the
robot can simplify the explanation content. When
encountering "depressed" emotions, the robot can
offer encouragement or suggestions for rest. This
mechanism helps maintain children's interest in the
class and provides a more immersive learning
experience.
5 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
5.1 Challenge
5.1.1 Theory Challenge
There are still some challenges in the application of
multi-robot collaborative systems in the field of
children's education. The review by Dahiya et al.
summarizes that the system mainly faces
requirements for real-time performance and accuracy
in theory (Dahiya et al., 2022). The current models
make it difficult to provide feedback at the
millisecond or even microsecond level. In an
educational environment, if the delay is too large, it
may lead to a "dead silence" situation. Secondly, if
the robot's accuracy in recognizing children's
emotions or behaviours is insufficient, it may cause
incorrect strategy judgments and execute incorrect
teaching actions. This will exacerbate the children's
confusion.
5.1.2 Data Challenge
Data challenge is also a major problem that needs to
be considered in the field of children's education. The
recognition of children's emotions by robots requires
the collection of their characteristic signals. This
often faces dual challenges of privacy and ethics.
Berson et al. emphasized in their review that the
existing systems still have deficiencies in protecting
children's sensitive data (Berson et al., 2025). This
may lead to risks such as the leakage of children's
data, the commercialization of children's data, and so
on.
5.2 Future Directions
Future educational robots should mainly adopt multi-
robot collaborative systems and incorporate adaptive
strategy mechanisms. A multimodal model is used to
more accurately identify children's emotions and
issue appropriate decisions. The system can optimize
the algorithm through methods such as model pruning
to meet the low latency requirements. The adaptive
closed-loop model and continuous learning
mechanism are utilized to continuously optimize the
robot's role division and collaboration capabilities. In
Multi-Robot Collaborative Interaction in Children’s Education
369

addition, the system can also introduce federated
learning. This method trains models locally on the
school end and the home end, and only aggregates
and encrypts parameters to the central server (Hridi et
al., 2024). This can effectively prevent the leakage of
children's data and improve the fairness of the model.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper systematically reviews the potential of
multi-robot collaboration systems in the field of
children's education. Multi-robot collaboration
systems can utilize advanced emotion recognition
technology and adaptive interaction strategies to
enhance flexibility and personalization in the
classroom environment. This article first introduces
the relevant concepts, emphasizes that the multi-robot
collaborative system has a promising future in the
field of children's education, and explains the
limitations of the single-robot system.
Then, this paper compares and analyses single-
modal and multimodal recognition technologies.
Although CNN and LSTM can achieve relatively
accurate recognition in experimental environments,
they are still prone to be affected by noise and
complex emotional states in real-world environments.
The multimodal models such as the CNN-LSTM
model and the EEG-facial fusion model combine
visual, auditory and neural signals, which can achieve
higher recognition accuracy.
After that, this paper explores the application of
adaptive strategies in the classroom environment. In
the future, robots can continuously optimize the
classroom rhythm and adjust their interaction
behaviours with children based on an adaptive closed-
loop model.
Finally, this paper summarizes some of the
remaining challenges in this field. For instance, the
demand for high real-time performance and accuracy
in the classroom environment, the risk of sensitive
data leakage of children, and ethical security. Future
research should focus on model optimization to build
a system architecture capable of achieving
millisecond-level response. Additionally, encryption
mechanisms such as federated learning should be
introduced and a comprehensive privacy protection
protocol should be established to ensure the data
security of children.
In conclusion, this field still needs to conduct
empirical research in real classroom settings to collect
more data. Only on the basis of interdisciplinary
collaboration and regulatory guarantees, the multi-
robot collaborative system can truly achieve
sustainable promotion in the education field and
provide personalized and effective learning support
for more children.
REFERENCES
Beck, E., Bockelmann, C., & Dekorsy, A. (2023). Semantic
information recovery in wireless networks. Sensors,
23(14), Article 6347.
Berson, I. R., Berson, M. J., & Luo, W. (2025, March).
Innovating responsibly: Ethical considerations for AI in
early childhood education. AI Brain Child, 1(1), 2.
Dahiya, A., Aroyo, A. M., Dautenhahn, K., & Smith, S. L.
(2023). A survey of multi-agent human–robot
interaction systems. Robotics and Autonomous
Systems, 161, 104335.
Hridi, A. P., Sahay, R., Hosseinalipour, S., & Akram, B.
(2024, May). Revolutionizing AI‑assisted education
with federated learning: A pathway to distributed,
privacy‑preserving, and debiased learning ecosystems.
AAAI Student Symposium, 3(1), 297–303.
Kay, L., Brandsen, S., Jacques, C., Stocco, F., & Zaffaroni,
L. G. (2023). Children’s digital and non‑digital play
practices with Cozmo, the toy robot. M/C Journal,
26(2).
Laban, G., Wang, J., & Gunes, H. (2025). A robot-led
intervention for emotion regulation: From expression to
reappraisal. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.18243.
Park, B., Kang, C., & Choi, J. (2021). Cooperative
multi‑robot task allocation with reinforcement learning.
Applied Sciences, 12(1), Article 272.
Rosenberg‑Kima, R. B., Koren, Y., & Gordon, G. (2020).
Robot‑supported collaborative learning (RSCL): Social
robots as teaching assistants for higher education small
group facilitation. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 6, 148.
Wang, S., Qu, J., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2023).
Multimodal emotion recognition from EEG signals and
facial expressions. IEEE Access, 11, 33061–33068.
Wu, B., & Suh, C. S. (2024). State-of-the-art in robot
learning for multi-robot collaboration: A
comprehensive survey. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2408.11822.
Xu, Y., Lin, Y.-S., Zhou, X., & Shan, X. (2024, June).
Utilizing emotion recognition technology to enhance
user experience in real‑time. Computers and Artificial
Intelligence, 2(1), 1388.
Yang, Q., Lu, H., Liang, D., Gong, S., & Feng, H. (2024).
Surprising performances of students with autism in
classroom with NAO robot. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2407.12014.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
370
