
Investment Financial Risk Assessment in Fuyao Glass'
Internationalization Process
Zitao Wang
School of Accountancy, Tianjin University of Commerce, Guangrong Road 409, Beichen District Tianjin, China
Keywords: Fuyao Glass, Investment Risk, Multinational Enterprises, Manufacturing Industry.
Abstract: This study investigates the financial risk management challenges faced by Fuyao Glass during its international
expansion, with a focus on its U.S. investments from 2014 to 2020. By analyzing the company's financial
data, the research highlights two major risks: exchange rate volatility and structural market risks, which
significantly impacted Fuyao's profitability. The findings reveal large fluctuations in foreign exchange gains
and losses (ranging from ¥459 million in profits to ¥422 million in losses), underscoring the company's
exposure to currency risks despite its growing overseas revenue (55–65% of total income). The study applies
Miller's (1996) risk classification framework to assess Fuyao's strategies, demonstrating that while the
company successfully transitioned from trade to local manufacturing, its risk mitigation measures, particularly
in financial hedging, remained underdeveloped. Based on these insights, the paper proposes an integrated risk
management approach combining strategic financial tools, dynamic asset-liability matching, and specialized
team training. This research contributes to the understanding of financial risks in emerging-market
multinationals and offers practical recommendations for manufacturing firms expanding globally.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Risk Identification Research
Scholars have developed a systematic theoretical
framework for classifying cross-border investment
risks. Miller (1996) pioneered a risk classification
system based on three dimensions: macro-
environmental risks, industry-specific risks, and
internal corporate risks, laying the foundation for
subsequent studies. Xu Hui and Yu Juan (2007)
expanded on Miller's framework by incorporating 15
key risk factors through empirical analysis, defining
investment risk as the potential losses arising from
uncertainties in cross-border operations, including
economic setbacks or investment failures. Chen Ning
(2011) further refined the classification logic by
proposing a "macro-meso-micro" three-dimensional
risk analysis model, enhancing the theoretical
inclusivity of risk categorization. This evolution
reflects the deepening academic understanding of
cross-border investment risks.
In macro-level research, scholars have focused on
political, legal, and financial risks in host countries.
Usher (1965) was among the first to highlight the
impact of political instability on foreign investments.
Liu Hongxia (2006) expanded this perspective by
categorizing political risks into three dimensions:
regulatory and service risks, overseas protection risks,
and investment environment risks, thereby extending
the analysis to include both home and host country
dynamics.
In the economic risk domain, Pantzalis et al. (2001)
explored the relationship between multinational
enterprises' geographic dispersion and risk exposure,
finding that broader subsidiary distribution reduces
exchange rate risk. Liao Wangke (2011) introduced
the concept of "country risk," emphasizing unique
challenges in cross-border economic activities. Yang
Da (2020) further classified risks into economic and
non-economic categories, demonstrating the
significant impact of RMB exchange rate fluctuations
on Chinese outbound investments.
At the meso level, scholars like Liang Yingying
(2014) and Cai Chengbin (2019) examined industry-
specific risks, particularly tax rates and cost structures.
Micro-level research, represented by Zhang Youtang
and Huang Yang (2011), highlighted internal risks
such as unfamiliarity with foreign financing policies
and overlooked factors like corporate social
Wang, Z.
Investment Financial Risk Assessment in Fuyao Glass’ Internationalization Process.
DOI: 10.5220/0014350500004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Inter national Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 259-265
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
259

responsibility and environmental standards (Zhu
Xinglong, 2016).
1.2 Risk Mitigation Measures
After identifying risks, effective mitigation strategies
are crucial. Scholars have proposed approaches
ranging from risk early-warning systems to tailored
policies for different investment stages.
Tyebjee and Bruno pioneered a combination of
qualitative analysis and quantitative research to first
identify key risk factors, and then used a
questionnaire survey method to construct a risk
project evaluation model suitable for the US market.
Their research results indicate that a company's
operational management capabilities and risk
resilience significantly influence the expected level of
risk (Tyebjee & Bruno, 1984). Huang Li and Li
Wanchao adopted case study and statistical analysis
methods, selecting eight industrial enterprises as
research samples. They screened out eight core
financial indicators, including the quick ratio and
equity ratio, using a significance T-test, and
successfully constructed an enterprise financial early
warning system using principal component analysis
(Huang Li & Li Wanchao, 2003). These studies
demonstrate the methodological evolution from
qualitative identification to quantitative modeling,
providing diversified analytical tools for assessing
risks in cross-border investments.
(1) Preventive measures based on different
investment stages
Zhang Liulu innovatively divides the cross-border
investment process into three key stages and proposes
differentiated risk management strategies tailored to
the characteristics of each stage: During the
investment decision-making phase, the focus is on
conducting a systematic analysis of project feasibility
and risk sources to provide a basis for investment
evaluation; during the investment implementation
phase, the emphasis is on dynamically adjusting
investment strategies based on actual operational
performance; and during the investment recovery
phase, the primary focus is on political risk factors,
conducting a comprehensive assessment of project
sustainability and ensuring the safe recovery of
investment costs (Zhang Liulu, 1997). The
introduction of this phased risk management
framework not only enhances the theoretical
framework of transnational investment risk
management but also provides enterprises with
comprehensive risk prevention and control guidance
throughout the entire lifecycle of cross-border
investment decisions in practice.
1.3 Research Objectives
This study aims to analyze the financial risks
involved in Fuyao Glass's internationalization
process, with a focus on the impact of exchange rate
fluctuations and market structure risks on its cross-
border investments. By evaluating Fuyao's financial
data from its investments in the United States
between 2014 and 2020, the study identifies
shortcomings in its risk management system and
proposes an integrated risk management framework
combining strategic planning, financial tool
application, and organizational optimization. This
framework provides theoretical insights and practical
recommendations for the globalization practices of
Chinese manufacturing enterprises.
2 FUYAO GLASS INVESTMENT
CASE STUDY
2.1 About Fuyao
Fuyao Glass Industry Group Co., Ltd. (hereinafter
referred to as Fuyao Glass) was established in Fuzhou,
Fujian Province, China in 1987. It is mainly engaged
in the manufacture of automotive glass, float glass,
and other industrial glass, and provides a full range of
services including research and development, design,
manufacturing, sales and distribution, and after-sales
service. It is currently the largest global glass
manufacturing enterprise in China.
2.2 History of Investment in the United
States
As shown in Table 1, in terms of investment scale, the
combined registered capital of all subsidiaries reached
US$173 million in 2014. The actual operational scale
expanded even more significantly: the total revenue of
the three companies reached RMB 233 million in 2014,
surged to RMB 1.3 billion in 2015 due to the
commencement of operations at Fuyao USA, and
stabilized at around RMB 1.5 billion thereafter.
Among these, Fuyao America contributed the
majority of revenue (977 million RMB), while the
North American subsidiary also achieved rapid
growth (from 174 million RMB to 522 million RMB).
This development trajectory reflects Fuyao's strategic
upgrade from exploratory trade to deep localization in
manufacturing, achieving internationalization through
substantial capital investment to establish a complete
domestic supply chain system in the United States.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
260
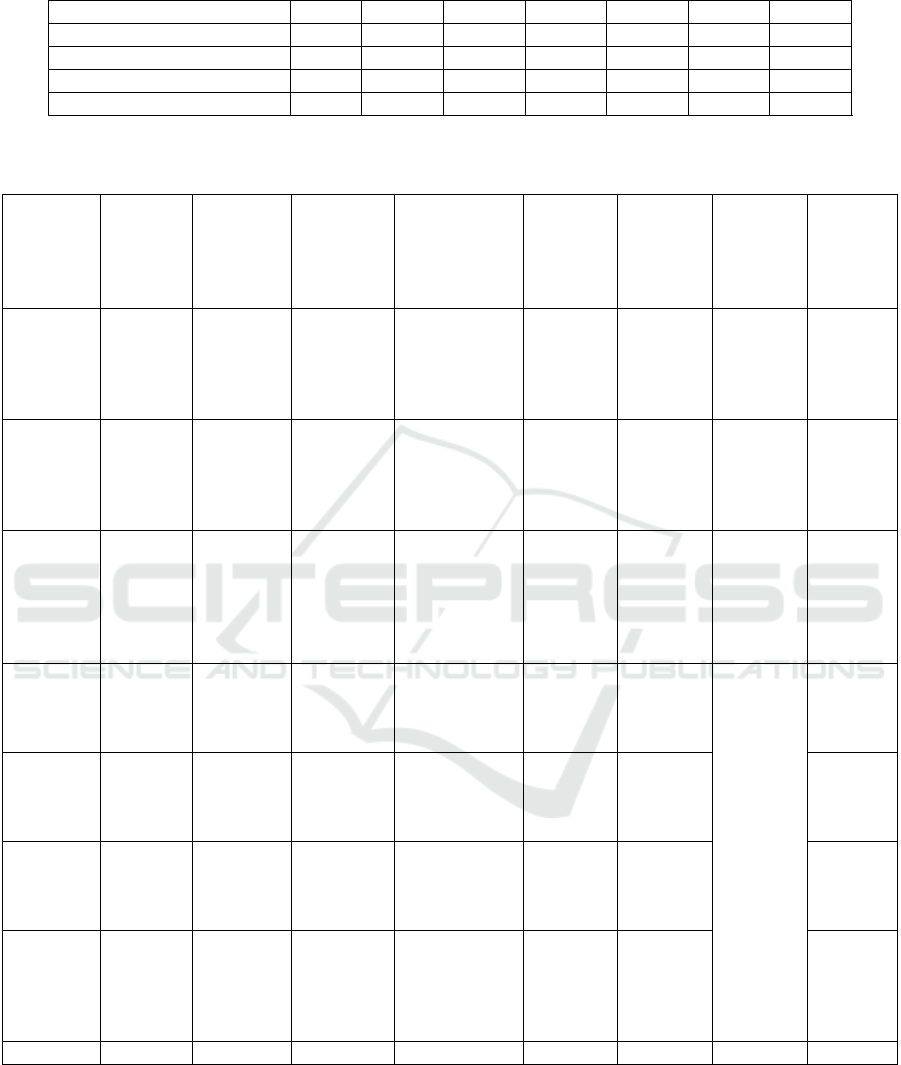
Table 1: Balance of Fuyao Glass’ long-term equity investment in U.S. subsidiaries(in millions of dollars)
Company/Time 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Fuyao America 71700 97704 97704 97704 97704 97704 97704
North American Package 17367 33074 33074 45657 52162 52162 52162
Fuyao North America 5885 5885 5885 5885 5885 5885 5885
ADD UP THE TOTAL 23258 120955 136662 149246 155751 155751 155751
Data source: Fuyao Glass Annual Report
Table 2: Formation of Fuyao Glass U.S. subsidiaries.
NAME OF
SUBSIDIA
RY
ACRONY
MS
REGISTER
ED
CAPITAL
(US$
MILLION)
INVESTME
NT TIME
COMMISSION
ING TIME
MIAN
AREAS
OF
BUSINES
S
NATURE
OF
BUSINES
S
SERVICE ACQUISI
TI ON
METHOD
American
Green
Banyan
(liquidated
in 2010)
—— 426 1994 American commercia
l enterprise
Automotiv
e glass
sales
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Fuyao
Northern
Glass
Industry
Co., Ltd.
Fuyao
North
290 2004 South
Carolina,
United
States
commercia
l enterprise
Automotiv
e glass
sales
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Fuyao
Glass North
America
Co., Ltd.
North
American
accessories
600 2010 2011 Michigan,
USA
manufactur
ing
company
Automotiv
e glass
processing
and sales
Business
combinati
ons under
non-
common
control
Fuyao
Glass
America,
Inc.
Fuyao
USA
16000 2014 2016 Ohio,
United
States
manufactur
ing
company
Automotiv
e glass
manufactur
ing and
sales
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Fuyao
Glass
Illinois,
Inc.
Fuyao
Illinois
0.1 2014 2015 Illinois,Uni
ted States
manufactur
ing
company
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Fuyao
America C
Asset
Company
US C
Assets
0.08 2014 Illinois,Uni
ted States
commercia
l enterprise
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Fuyao
America
Asset
Company
A
Asset A in
the United
States
0.08 2014 Ohio,
United
States
commercia
l enterprise
Investmen
t
establishm
ent
Total 17316.26
Data source: Fuyao Glass Annual Report Summary
As shown in Table 2, Fuyao Glass' investment
strategy in the U.S. market has followed a clear
evolutionary path and expansion trajectory. From an
investment perspective, the company has undergone
a transformation from trade to manufacturing through
three distinct phases since its initial entry into the U.S.
market in 1994: the initial phase (1994–2010) focused
primarily on establishing trading companies,
including the establishment of Fuyao North America
Glass
Industry Co., Ltd. with a registered capital of
Investment Financial Risk Assessment in Fuyao Glass’ Internationalization Process
261
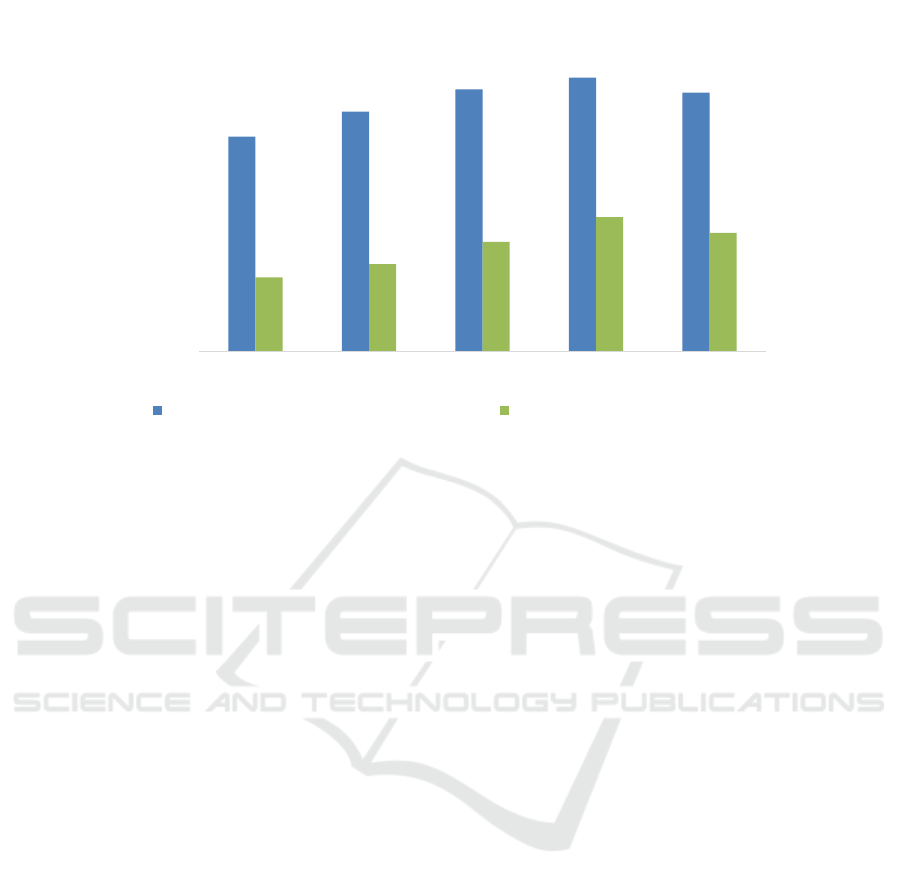
Data source: Fuyao Glass Annual Report Summary
Figure 1: Fuyao Glass Foreign Operating Income Percentage,2016-2020
USD 2.9 million; the intermediate phase (2010–2014)
saw a shift toward production-oriented investments,
such as the establishment of North America
Supporting Company in 2010 through a corporate
merger with a registered capital of USD 6 million;
and the later phase (starting in 2014) marked the
entry into a large-scale capacity expansion phase,
with an investment of USD 160 million to establish
Fuyao Glass USA Co., Ltd. and the establishment of
production bases in Ohio and Illinois.
3 FUYAO COMPANY RISK
IDENTIFICATION AND
MANAGEMENT MEASURES
3.1 Risk Identification at Fuyao
Company
When beginning to analyze Fuyao's risk
identification, Fuyao's unique corporate
characteristics determine its specific risks. In line
with the theme of this article, this section will
analyze Fuyao's current risks from the perspective of
internal financial risks.
Fuyao Glass's financial data from 2016 to 2020,
as shown in Figure 1, reveals the significant
exchange rate risks and market structural risks it
faces in its cross-border operations. From the
perspective of revenue structure, although the
proportion of domestic revenue increased from 34.47%
in 2016 to 45.73% in 2020, domestic revenue
experienced a negative growth rate of 11.84% in
2020, reflecting the substantial impact of overseas
market fluctuations on the company's overall
revenue. More notably, exchange rate risk exposure
is highlighted. Figure 2 shows exchange losses of
388 million yuan and 422 million yuan in 2017 and
2020, respectively, with corresponding foreign
currency statement translation differences of -295
million yuan and -495 million yuan for the respective
years. This significant two-way volatility (foreign
exchange gains of 459 million yuan in 2016 and 259
million yuan in 2018) indicates that the company's
foreign exchange risk management system has room
for improvement. Notably, exchange rate
fluctuations and revenue regional structure form a
dual risk overlap—even when domestic revenue
accounted for nearly 50% (in 2019), the company
still faced financial performance instability caused
by exchange rate fluctuations, indicating that Fuyao's
internationalization strategy has not yet established
an effective exchange rate risk hedging mechanism.
This financial risk characteristic typifies the core
challenges faced by manufacturing multinational
corporations in their global expansion: while seeking
to expand overseas markets to achieve revenue
diversification, they must also address the resulting
currency mismatch and exchange rate volatility risks.
The magnitude of data fluctuations indicates that
exchange rate factors have substantively impacted
the
stability of corporate profits, necessitating
0
500000
1000000
1500000
2000000
2500000
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Total operating revenue (in ten thousand yuan) Revenue from overseas operations
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
262
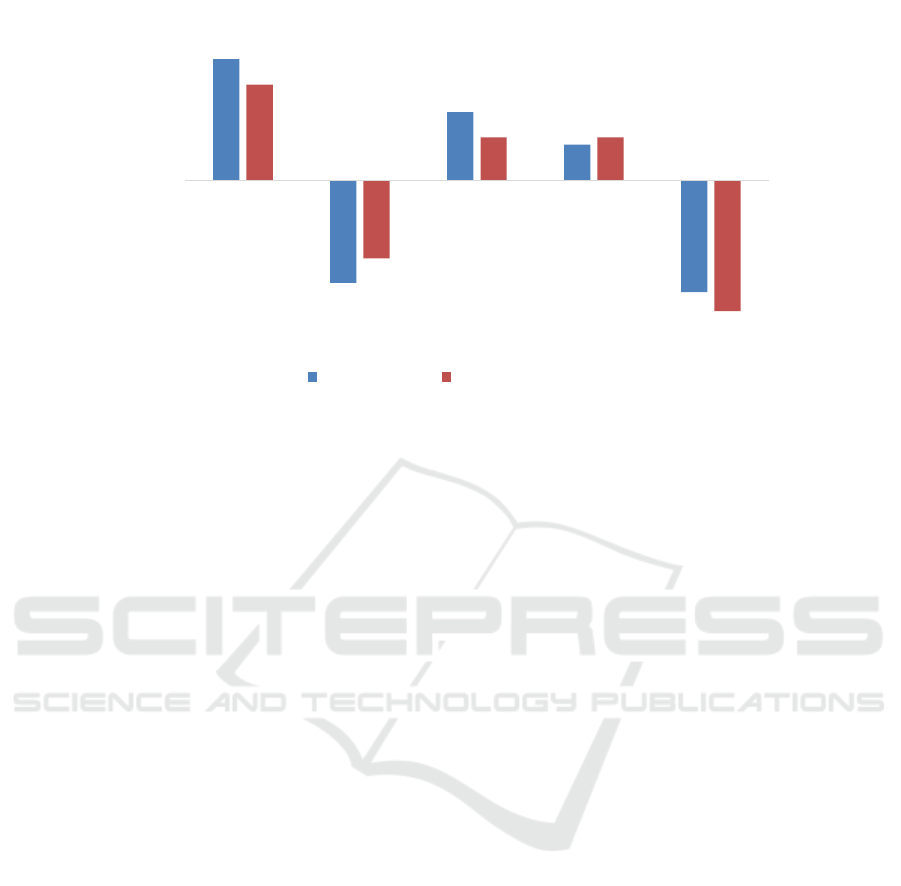
Data source: Fuyao Glass Annual Report Summary
Figure 2: Fuyao Glass Exchange Gains and Foreign Currency Financial Statement Translation Differences,2016-2020.
enhanced utilization of financial instruments such as
forward foreign exchange contracts and optimization
of currency matching in overseas asset-liability
structures.
3.2 Fuyao Company's Cross-border
Investment Risk Management
As a multinational corporation, Fuyao Glass is
susceptible to the impact of exchange rate and
economic fluctuations, and its foreign exchange risk
management strategy urgently needs systematic
optimization. Facing the new normal of two-way
fluctuations in the RMB exchange rate after 2014, the
company should improve its risk management system
from three aspects: dynamic monitoring, use of
financial instruments, and team building.
3.2.1 Establish a Dynamic Exchange Rate
Risk Monitoring System
Companies need to establish a real-time, efficient
foreign exchange risk monitoring mechanism.
Specifically, they should integrate multi-dimensional
data sources: obtain real-time exchange rate data
through professional foreign exchange trading
platforms such as Bloomberg and Reuters; track
macroeconomic indicators using international
financial data terminals such as Wind and CEIC; and
combine this with detailed data on foreign currency
assets and liabilities from the company's internal
financial system to ensure data comprehensiveness.
In terms of monitoring frequency, foreign currency
asset and liability scales should be updated daily, risk
exposure reports should be generated weekly, and
monthly analyses should be conducted using
economic reports from authoritative institutions such
as the IMF and central banks to scientifically predict
exchange rate trends and provide data support for
decision-making.
3.2.2 Strategies for the Refined Use of
Financial Instruments
Companies should select financial derivatives
appropriately based on the characteristics of their risk
exposure and develop differentiated operational
strategies. First, currency swaps can be used for
hedging the risks associated with long-term foreign
currency debt, such as long-term liabilities in
overseas project financing or cross-border mergers
and acquisitions. When implementing such strategies,
it is essential to select compliant counterparties (such
as international banks), negotiate terms including
principal amounts, exchange rates, and tenors, and
conduct regular cash flow exchanges. The advantage
lies in locking in long-term exchange rates to
effectively mitigate volatility risks; however, it is
important to note the drawbacks of higher transaction
costs and lower flexibility. Second, forward foreign
exchange contracts are suitable for future foreign
currency receipts and payments with known amounts,
such as import/export trade receivables. Companies
can enter into contracts with banks to agree on future
exchange rates and amounts, with settlement at the
contract rate upon maturity. Its advantages include
-60000
-40000
-20000
0
20000
40000
60000
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
exchange gain converted difference
Investment Financial Risk Assessment in Fuyao Glass’ Internationalization Process
263

simplicity and lower costs, but businesses must be
vigilant about the risk of adverse market exchange
rate movements at contract maturity. Third, foreign
exchange option management. Foreign exchange
options are suitable for high-uncertainty foreign
currency receipts and payments, such as potential
income from bidding on overseas projects.
Businesses pay an option premium to purchase call or
put options, gaining the right, not the obligation, to
trade at the agreed-upon exchange rate. The primary
advantage is controllable risk (with losses capped at
the option premium), but the higher cost of options
must be balanced against this benefit.
3.2.3 Strengthen Professional Team
Building and Process Optimization
Companies should establish a professional foreign
exchange management team, with members holding
qualifications such as CFA or FRM, and undergo
regular training in derivatives operations and risk
management. Additionally, a comprehensive
assessment mechanism should be established: prior to
transactions, develop hedging strategies based on risk
exposure, clearly define tool selection and
proportions (e.g., hedging ratios not exceeding 80%);
during transactions, dynamically monitor market
changes and adjust positions in a timely manner; post-
transaction, conduct monthly assessments of hedging
effectiveness, utilize VaR models for quantitative
analysis, and continuously optimize strategies. By
leveraging currency matching, dynamically adjusting
risk exposure, and employing financial tools with
precision, Fuyao Glass can establish a three-pronged
foreign exchange risk management system to
effectively mitigate the impact of exchange rate
fluctuations on operational outcomes. This
optimization approach aligns with the practical needs
of multinational corporations while also aligning with
the macro trend of exchange rate marketization
reforms.
4 CONCLUSION
First, Fuyao Glass's internationalization development
path exhibits the typical three-stage characteristics of
“trade-led, manufacturing-rooted, and supply chain
integration.” This evolutionary process validates the
core tenets of the stepping-stone theory, which posits
that emerging market enterprises can achieve rapid
globalization through resource leverage and
continuous leaps. However, as internationalization
deepens, the financial risks faced by enterprises also
exhibit increasingly complex characteristics,
particularly the compounding effects of exchange rate
risks and market structural risks.
Second, according to data analysis, Fuyao Glass's
exposure to exchange rate risks was relatively high
between 2016 and 2020, with fluctuations in foreign
exchange gains and losses reaching 880 million yuan
(from a gain of 459 million yuan to a loss of 422
million yuan), and fluctuations in foreign currency
statement translation differences reaching 860
million yuan. Such significant fluctuations not only
directly impact the stability of corporate profits but
also reflect the inadequacies of the current foreign
exchange risk management system. Notably, even as
domestic revenue accounted for over 45% of total
revenue, exchange rate fluctuations still significantly
impacted corporate performance, indicating that
business regional diversification alone cannot
automatically mitigate exchange rate risks. Third,
there are three key areas for improvement in risk
management: first, the use of financial derivatives is
relatively conservative, failing to fully leverage risk
hedging functions; second, the currency matching of
overseas assets and liabilities needs to be improved;
third, there is a lack of specialized foreign exchange
risk management teams and systematic risk
assessment mechanisms. These issues make it
difficult for companies to effectively respond to the
new normal of two-way fluctuations in the RMB
exchange rate.
Based on the above findings, this study
recommends that multinational manufacturing
enterprises should establish a “three-in-one” risk
management system: at the strategic level, establish a
risk preference framework aligned with the
internationalization process; at the operational level,
improve the combination of tools such as forward
contracts and currency swaps; and at the
organizational level, cultivate a specialized risk
management team. Additionally, it is particularly
important to integrate risk management into the entire
process of internationalization strategy to achieve
synergistic development between risk control and
business expansion. The theoretical value of this
study lies in combining traditional investment risk
theory with emerging market corporate practices,
thereby enriching the research perspective on cross-
border investment risk management. Practically, it
provides a referenceable risk management framework
for the globalization process of Chinese
manufacturing enterprises. Future research could
further explore the application of new risk
management tools in the context of the digital
economy, as well as the mechanisms through which
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
264

geopolitical factors influence cross-border
investment risks.
REFERENCES
Cai, C. (2019). The impact of host country economic risks
on Chinese enterprises' overseas investment: An
analysis based on two dimensions of China's outward
direct investment and engineering project investment.
Macroeconomic Research, (04), 107-115.
Chen, N. (2011). Risk prevention in cross - border
operations of small and medium - sized enterprises from
the perspective of stakeholders. Modern Finance, (1),
54-59.
Huang, L., & Li, W. (2003). Application of principal
component analysis in empirical research on financial
forecasting. Statistics and Information Forum, (05), 83-
86.
Liang, Y. (2014). A study on the determinants and
strategies of China's outward direct investment. Nankai
University. (04), 93-95.
Liao, W. (2011). Response matrix analysis method for
transnational investment risk assessment. Technology
and Economy, (01), 56-63.
Liu, H. (2006). Research on the risks of Chinese overseas
investment and their prevention. Journal of Central
University of Finance and Economics, (03), 63-67.
Miller, K. D. (1996). A framework for integrated risk
management in the international business. Journal of
International Business Studies, (2), 311-331.
Pantzalis, C., Simkins, B., & Lluch, P. (2001). Operational
hedges and the foreign exchange exposure of U.S.
multinational corporations. Journal of International
Business Studies, 32(4), 793-812.
Tyebjee, T. T., & Bruno, A. V. (1984). A model of venture
capitalist investment activity. Management Science,
30(9), 300-330.
Usher, D. (1965). Political risk. Economic Development
and Cultural Change, 13(4).
Xu, H. (2004). Interactive research on risk perception and
international market entry strategy decision - making:
With a discussion on risk prevention in Chinese
enterprises' transnational operations. Exploration of
Economic Issues, (10), 10-12.
Xu, H., & Yu, J. (2007). A study on the identification of key
risks in enterprise internationalization. Nankai
Management Review, (04), 92-97.
Yang, D. (2020). The impact of RMB exchange rate
fluctuations on the risk of Chinese enterprises' outward
direct investment. Journal of Northeastern University
(Social Sciences Edition), 22(06), 24-30.
Zhang, L. (1997). Risks and prevention measures for
Chinese overseas investment. Journal of Henan
University (Social Sciences Edition), (03), 63 - 66+129.
Zhang, Y., & Huang, Y. (2011). Research on risk warning
and regional positioning of transnational investment by
enterprises. Accounting and Finance Bulletin, (31), 17-
20.
Zhu, X. (2016). Research on the risks of China's outward
direct investment and its prevention system. Wuhan
University. (06), 12-18.
Investment Financial Risk Assessment in Fuyao Glass’ Internationalization Process
265
