
Agriculture Optimization Based on Linear Programming and Python
Algorithm: Take Sichuan Province as an Example
Kaiquan Fan
a
SWUFE-UD Institute of Data Science, Southwestern University of Finance and Economy, 610000, China
Keywords: Linear Programming, Machine Language, Optimization, Agriculture.
Abstract: Food is the paramount necessity of the people. Increasing the yield of food is always the most significant
thing for every country in the world. Only those countries that struggle improving their technology in planting
planning obtain achievement and success in the fight against hunger and poverty. Blindly expanding the sown
areas not only unduly takes up labor and land sources, but also may undermine the process of social
industrialization. In this case, the best way to boost yield is to improve the level of resources utilization. Based
on the agricultural data of Sichuan province from 2011 to 2022 and 3 types of crops taken as an example, this
study constructs math model and use machine language to find the optimal solution of planting planning. The
study innovates a universal model to analyze and optimize problems under multi-constrains. With increasingly
more relevant and influential factors added and trained with more detailed data, more accurate and more
mature the model is.
1 INTRODUCTION
Food shortage and hunger have become to a global
problem. According to the report delivered by Food
and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2024, the
numbers of global undernourished population for
2019-2023 are respectively 581.3 million, 669.3
million, 708.7 million, 723.8 million and 733.4
million (Raphael et al., 2014). Even though it has
tended to stabilize in recent 3 years, it had sharply
increased by 26% from 2019 to 2023. Every country
is trying their best to increase the production of food
like using new technology in planting food crops.
Only those countries that spare no effort to innovate
and modernize their agriculture gain success in the
struggle against hunger and poverty (Goncharova and
Merzlyakova, 2021). With the development of some
developing countries, increasingly more domestic
agricultural land is going to be used for
industrialization, blindly expanding the area of
cultivated land is obviously not a proper method (Sofi
et al., 2015).
Under these present circumstances, one of the
most significant factors contributing to increase
production is the optimization of resource usage. The
optimization of land use structure represents a
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-1237-4178
resource allocation approach that holistically
integrates the economic, social, and ecological
benefits of regional land utilization. Through the
adjustment of land distribution in both quantitative
proportions and spatial arrangements, this process
aims to establish a balanced state between the supply
and demand of land resources (Wu and Zhong, 2020).
Traditionally, crop planning was simply based on
the farmers’ thoughts and their own views. However,
with the development of modern research, crop
planning becomes more and more mathematical and
scientific (Jain et al., 2018). France emphasized the
importance of modeling in agriculture (France, 1988).
Levkina highlighted the avail of mathematical
modeling to assess economic benefit and analyze
risks in agriculture (Levkina et al., 2019). Bhatia and
Bhat reviewed that through optimizing farm resource
allocation, the production and production efficiency
shall increase (Bhatia and Bhat, 2020). Dixit and
Tyagi delivered a fuzzy approach to analyze and
handle the linear programming problems in
agriculture, which is an abstract and microscopical
way. Thus, quantization and rigorous analysis in such
problems are still in need (Dixit and Tyagi, 2024).
Algorithm design is also an essential part in solving
linear programming. When making crop planning
Fan, K.
Agriculture Optimization Based on Linear Programming and Python Algorithm: Take Sichuan Province as an Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0014324000004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 157-161
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
157
decisions, regional situations, constraints and the
planning purpose can be constructed into a
mathematical model, which is the core of
optimization. To plan these functions and constraints
as a whole and deal with it, the computer language is
one of the most efficient and the most accurate tool.
In past decades, computer have had a rapid and great
progress, which provided people a convenient and
swift way to solve linear programming problems
(Dantzig, 2020).
In this backdrop, the present article aims to realize
crops pattern optimization, handle the problem of
planting insufficiency and maximize the resource
usage under the given conditions. At theoretical and
academic level, this study is an attempt to enrich the
theoretical system of agricultural planning, deepen
the theoretical integration of interdisciplinary
approaches. And it is also expected to fill some gaps
in the application of refined mathematical theories in
agricultural planting planning, provide new ideas and
methods for the improvement of agricultural planning
theory. Moreover, it can promote the transformation
of agricultural planning from the traditional empirical
type to the scientific and precise type. And at practical
level, it is also an attempt to improve the economic
efficiency of agricultural production and provide the
scientific basis for the formulation of agricultural
policies.
Moreover, it is worth highlighting that this study
designs Python algorithms to build mathematical
models and solve problems. In addition, the study
takes the agricultural planting situations in Sichuan
province as an example to solve. And the actual data
will be taken into calculation. Therefore, readers can
clearly understand the key point and the mode of
analysis in this research, and the real change of
resource and benefit in agriculture through
optimization.
2 METHODS
2.1 Data Source
The Agricultural data used in this paper comes from
BEEDATA platform website, and it was provided by
the official institution China’s National Bureau of
Statistics and Sichuan Provincial Bureau of Statistics.
The data contains the detailed agricultural situation in
Sichuan province during 2011 to 2022.
2.2 Data Introduction
The data used in the article contains 12 variables.
Creating an algorithm to discuss the influence of each
variable and optimize the agricultural structure in
Sichuan province. And the names and explanations of
each variable are shown in Table 1.
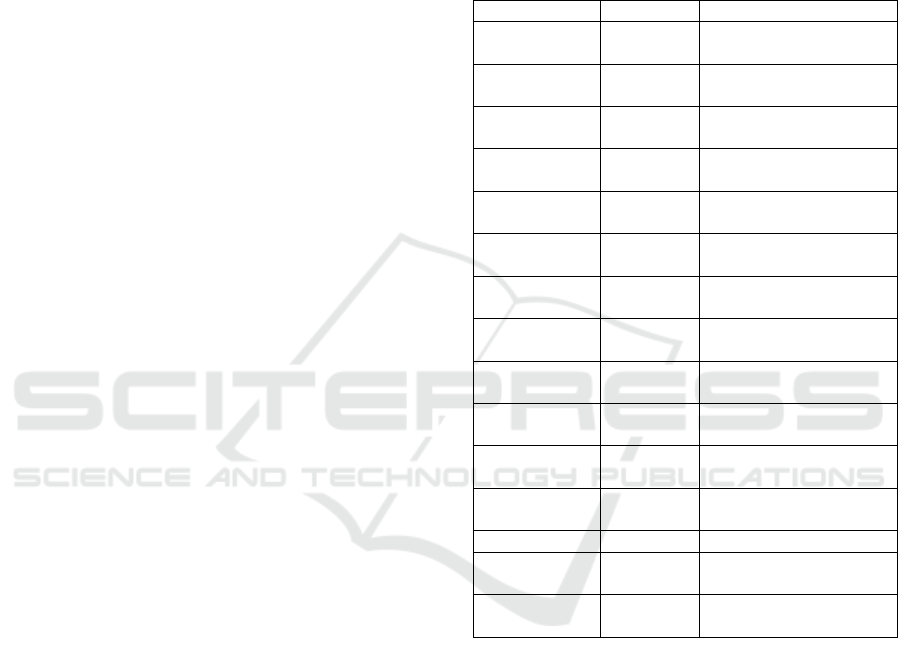
Table 1: Variables used in this article.
Variables Lo
g
o
g
ra
m
Ex
p
lanation
sown_area xi the area of each type of
crop be sown
pesticide_cost cp the cost of pesticide per
kilo
g
ra
m
pesticide_amo
unt
p the usage amount of
p
esticide
pesticide_per_
unit
pu the average usage of
p
esticides per km^2
pesticide_bud
g
et
Bp the budget for
p
urchasin
g
p
esticide
sown_area_of
_
cro
p
s
S the total sown area of
food cro
p
s
unit_plants_o
utput
ui Output of each crop per
km^2
output Y the amount of crops
yiel
d
fertilizer_cost cf the cost of fertilizer per
kilo
g
ra
m
fertilizer_amo
unt
f the usage amount of
fertilize
r
fertilizer_per_
unit
fu the average usage of
fertilizer per km^2
fertilizer_bud
g
et
Bf the budget for
p
urchasin
g
fertilize
r
n_va
r
n the number of variables
demand di the demand quantity of
each food cro
p
sown_area xi the area of each type of
crop be sown
When i = 0, 1, 2, it respectively represents grains,
tubers and beans.
2.3 Method Introduction
The method used in this paper is linear programming
simplex algorithm which is realized by python
language. The main body of this algorithm is the
mathematical model which contains a purpose
function and several constraints. The ultimate goal is
to maximize the output of crops. Therefore, the
objective function to maximize can be built as:
Y=
∑
𝑥
u
(1)
This means the total production (Y) should be
maximized by increasing the production of each type
of crops.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
158
And the conditions to limit this purpose function
are respectively the pesticide:
c
pB
(2)
𝑖. 𝑒. 𝑐
𝑝
∑
𝑥
B
(3)
The cost in pesticide of crops should be less than or
equal to the budget of pesticide (B
).
The total sown area:
∑
𝑥
S (4)
The sum of them should be less than or equal to the
total area used to plant.
The fertilizer:
c
fB
(5)
𝑖. 𝑒. 𝑐
𝑓
∑
𝑥
B
(6)
The cost in fertilizer of crops should be less than or
equal to the budget of fertilizer (B
).
The demand:
x
d
(7)
The production of each type of crops should satisfy
the demand quantity of the public.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Analysis
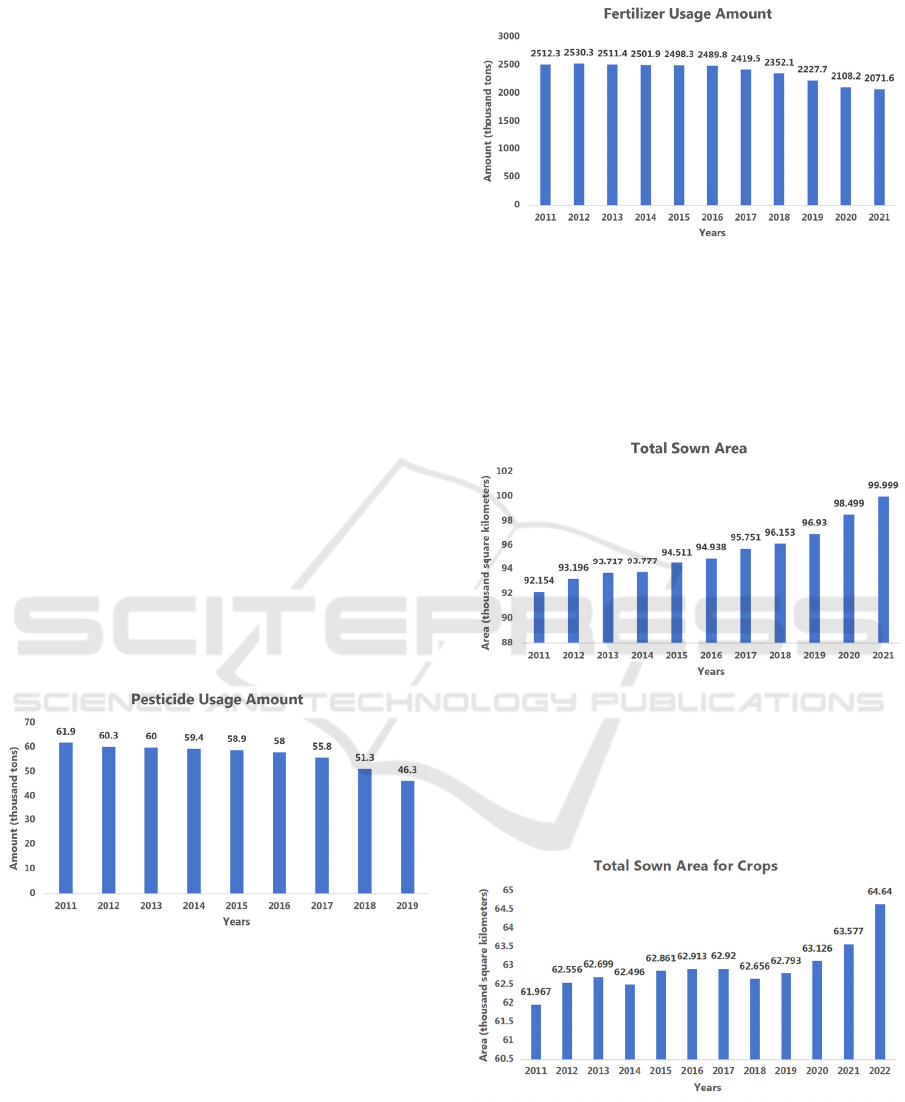
The figure 1 is the histogram of pesticide usage
amount from 2011 to 2019. The amount of pesticide
usage has been decreasing during this period, and the
amount is in the 46-62 thousand tons range. The
average is 56.88 thousand tons.
Figure 1: The histogram of pesticide usage amount
(Picture credit: Original)
The figure 2 is the histogram of fertilizer usage
amount of fertilizer from 2011 to 2021. The usage
amount of fertilizer decreased slowly in this decade.
The amount fluctuates from 2000-2500 thousand tons.
The average is 2383.9 thousand tons.
Figure 2: The histogram of total fertilizer usage amount
(Picture credit: Original).
The figure 3 is the histogram of total sown area from
2011 to 2021. The average is 95.42 thousand square
kilometers. The total sown area has been steadily
increasing in recent years and reached the highest
value, 99.999 thousand 𝑘𝑚
, in 2021.
Figure 3: The histogram of total sown area (Picture credit:
Original).
According to figure 1, 2, and 3, the average usage of
pesticides and fertilizers per square kilometer can be
calculated, which respectively are 0.5961 ton/𝑘𝑚
and 24.9832 ton/𝑘𝑚
.
Figure 4: The histogram of total sown area for crops
(Picture credit: Original).
The figure 4 is the histogram of total sown area for
crops from 2011 to 2022. The amount of total sown
area for crops rose and fell modestly, but there was an
Agriculture Optimization Based on Linear Programming and Python Algorithm: Take Sichuan Province as an Example
159

increasing tendency in total sown area for crops. The
average is 62.934 thousand square kilometers.
Figure 5: The histogram of output of grains, tubers and
beans (Picture credit: Original).
The figure 5 is the histogram of output of grains,
tubers and beans. The average of these three crops are
respectively 27872.8, 5171.3 and 1171.1 thousand
tons. The proportion of the three is approximately
25:5:1. Accordingly the minimum bound of demands
can be set as the 60% of minimum output of all crops,
which are respectively 16053.36, 2833.62 and 610.08
thousand tons.
The figure 6 is the histogram of sown area of grains,
tubers and beans. The average of these three crops are
respectively 45.36, 12.35 and 5.067 thousand square
kilometers.
Figure 6: The histogram of sown area of grains, tubers and
beans (Picture credit: Original).
The minimum demands quantity of each type of crops
are set as the minimum amount in the data, which are
respectively
According to these grams, the output per km
of
each type of crops can be worked out which are
respectively 314.5, 418.7 and 231.1 tons/km
, whose
sown areas are accordingly 85.07, 11.28 and 4.40
thousand km
. In addition, the average cost of
pesticide and fertilizer are respectively 40800 and
2628 yuan/ton.
3.2 Code Implementation
The math model can be translated into machine
language into python. And this algorithm is based on
a computing library of python which is gurobipy.
This algorithm is universal for majority situation.
Once the data have been collected, users can input
them into the code to find the optimal solutions.
The table 2 is the input data for every parameter.
In this problem, the data come from the preceding
analysis of this article. In other situations, users can
only change the detailed values of following
parameters to optimize different problems.
Table 2: The table of the input data for every parameter.
PValueP Value
c
40800
c
2628
p
𝑝
∗x
f
𝑓
* x
𝑝
0.5961
𝑓
24.9832
B
c
∗56880
B
c
*2383900
S 62934 n 3
u
[314.5,418.7,231.1]
d
[16053360,2833620
,610080]
And the objective function is 𝑌 = 𝑠𝑢𝑚𝑥
𝑖 ∗
𝑢
𝑖 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑖 𝑖𝑛 𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛. The table 3 shows 4
constrains that limit this optimization model, which
are respectively pesticide, fertilizer, sown area and
demand.
Table 3: The table of 4 constrains.
Constrain Value
Pesticide
sum(x
[i] for i in range(n)) * 𝑝
* c
<=
B
)
Fertilizer
sum(x
[i] for i in range(n)) *
𝑓
* c
<=
B
)
Sown area sumx
i for i in rangen = S
Deman
d
(x
[i] * u
[i] >= d
[i] for i in range(n)
Through optimization by importing the gurobipy
library, the solution could be found and shown in the
following table 4.
Table 4: The table of output solution.
Parameters Value
x
grains
51044.07 𝑘𝑚
x
tubers
9250.03 𝑘𝑚
x
beans
2639.90 𝑘𝑚
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
160

4 CONCLUSIONS
This study takes many factors which could influence
the actual situation such as the pesticide budget, the
fertilizer budget, the sown areas and demands for
every crop. This article also focuses on the refinement
of planting planning by applying the basic principles
of linear programming. And the design of the
algorithm improves the efficiency and the accuracy of
planting planning. Theoretically and academically,
this research endeavors to strengthen the theoretical
framework of agricultural planning while enhancing
the interdisciplinary theoretical convergence. This is
also an attempt to make agricultural planting planning
more scientific and refined. It also aims to address
existing lacunae in applying refined mathematical
theories to agricultural planting planning, offering
innovative insights and methodologies for advancing
agricultural planning theory. And it may provide a
reference for the official department to formulate
relevant policies. For further research, more relevant
data and relevant factors should be taken into account.
In the actual situation, there are plenty of different
limits and constrains that influences the planning.
More factors, more universal the model is. Trained
with more data, the model will be more mature and
accurate. And the results should be compared and the
model should be adapted by futural training for more
accurate and advanced results.
REFERENCES
Bhatia, M., Bhat, G. M. J. (2020). Linear programming
approach-application in agriculture. J. Emerg. Technol.
Innov. Res, 6(5), 155-157.
Dantzig, G. B. (2020). Impact of linear programming on
computer development. In Computers in Mathematics,
233-240.
Dixit, P., Tyagi, S. L. (2024). A Fuzzy Approach to Linear
Programming in Agriculture Land Allocation. Journal
of Computational Analysis & Applications, 33(6).
France, J. (1988). Mathematical modelling in agricultural
science. Weed Research, 28(6), 419-423.
Goncharova, N. A., Merzlyakova, N. V. (2021). Food
shortages and hunger as a global problem. Food Science
and Technology, 42, e70621.
Jain, R., Malangmeih, L., Raju, S. S., Srivastava, S. K.,
Immaneulraj, K., Kaur, A. P. (2018). Optimization
techniques for crop planning: A review. The Indian
Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 88(12), 1826-1835.
Levkina, R. V., Kravchuk, I. I., Sakhno, I. V., Kramarenko,
K. M., Shevchenko, A. А. (2019). The economic-
mathematical model of risk analysis in agriculture in
conditions of uncertainty. Financial and credit activity
problems of theory and practice, 3(30), 248-255.
Raphael, R. et al., (2014). Optimization of preparation
conditions of activated carbon from agriculture waste
utilizing factorial design. Powder Technology An
International Journal on the Science & Technology of
Wet & Dry Particulate Systems.
Sofi, N. A., Ahmed, A., Ahmad, M., Bhat, B. A. (2015).
Decision making in agriculture: A linear programming
approach. International journal of modern
mathematical sciences, 13(2), 160-169.
Wu, Z. B., Zhong, F., (2020). Investigation on the Land Use
Optimization Path under the Guidance of
Implementation Evaluation: A Case Study of Shangluo
Central City. Financial and credit activity problems of
theory and practice.
Agriculture Optimization Based on Linear Programming and Python Algorithm: Take Sichuan Province as an Example
161
