
Research Progress of Pressure Sensors: Structure, Principle,
Application
Erli Zhang
a
School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology,
Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, 510000, China
Keywords: Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor, Capacitive Pressure Sensor, Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors.
Abstract: With the advancement of technology, the application of pressure sensors has gradually become more
widespread. Flexible pressure sensors have attracted people's attention because they can adapt to more
complex and changeable characteristics. The article reviews the structure, principle and application of
piezoelectric pressure sensors, capacitive pressure sensors and piezoresistive pressure sensors, and the article
provides researchers with relevant research materials for developing and improving flexible pressure sensors.
In addition, this article briefly discusses the development challenges that will be faced in the transition from
traditional rigid sensors to flexible pressure sensors in terms of future applications of pressure sensors. For
example, materials will be selected based on the application environment and accuracy requirements of future
sensors. The popularization and application of flexible sensors is bound to be the general trend. Therefore,
studying novel flexible pressure sensors sensing mechanisms and finding new multifunctional materials to
meet more application needs are major issues and challenges for future research.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid innovation of the Internet of Things
(IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and the continuous
development of the concept of intelligent
manufacturing (Duan et al,2022). Pressure sensors
are gradually being widely used in many fields. At the
same time, with the diversification of application
fields, the types of pressure sensors are gradually
increasing to suit different tasks. Since traditional
rigid pressure sensors cannot be applied to more
complex environments, flexible sensors have become
an important research field in recent years. Flexible
sensors can be stretched, compressed, and folded,
allowing them to change into different shapes to fit
onto irregular surfaces, greatly expanding their
application areas (Liu et al,2023).
Although flexible pressure sensors have made a
lot of progress and development, they still face many
challenges. One of the challenges is that as the
pressure increases and exceeds a certain limit, the
sensitivity of the flexible pressure sensor decreases.
Under high pressure, the sensor material will affect
sensitivity due to hyperelasticity and boundary
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6999-3990
limitations. In order to solve the problems are
mentioned above, researchers need to constantly
optimize the micro-geometry of the sensor and the
elasticity, dielectric properties and other properties of
the material (Yuan et al,2024).
The article will list the structure, principle and
application of piezoelectric pressure sensors,
capacitive pressure sensors and piezoresistive
pressure sensors. Meanwhile, this article can provide
research data and give some optimization suggestions
for future pressure sensors for researchers who study
pressure sensors mentioned above.
2 THE STRUCTURE, PRINCIPLE
AND APPLICATION OF
PRESSURE SENSORS
2.1 Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor
Piezoelectric sensors are composed of piezoelectric
materials, and they are active sensors that do not need
external
energy
to
obtain
output
signals
(Gautschi,
Zhang, E.
Research Progress of Pressure Sensors: Str ucture, Principle, Application.
DOI: 10.5220/0014320700004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 79-83
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
79
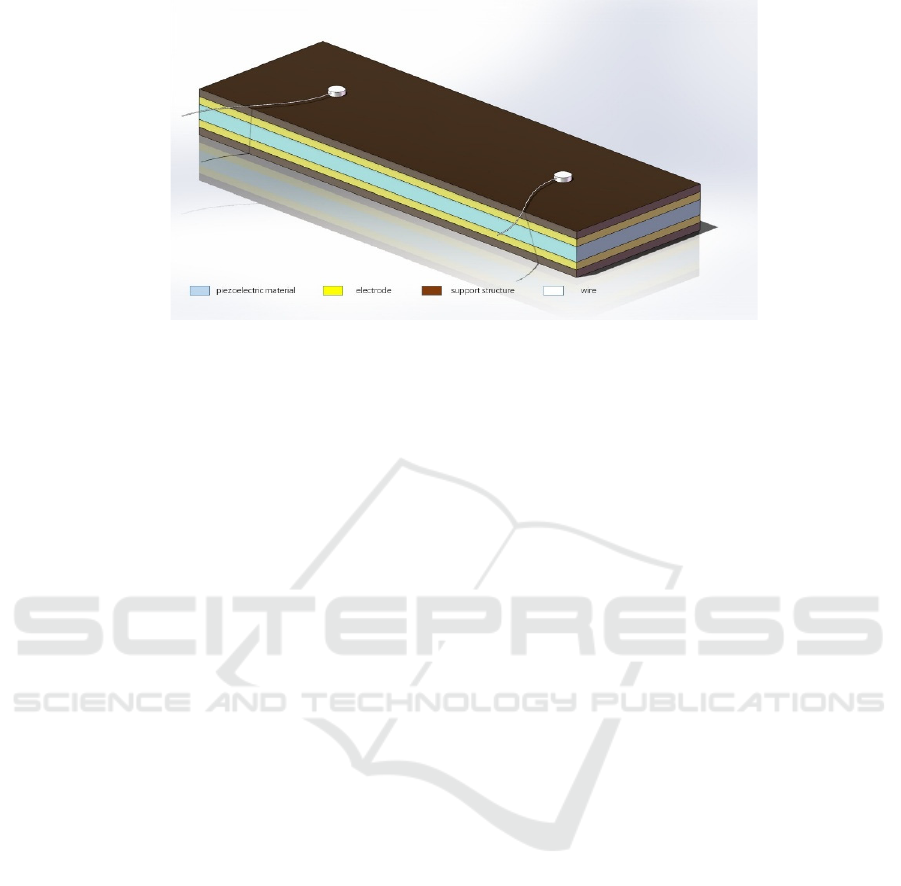
Figure 1: Piezoelectric pressure sensor device structure (Picture credit : Original).
2002). Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensors usually
consist of four parts: piezoelectric material, electrode,
support structure, and wire, as shown in Figure 1. The
piezoelectric effect produced by piezoelectric
materials is the working basis of piezoelectric sensors.
Electrodes are the medium through which the sensor
transfers charge. The support structure is the
packaging protection structure of the sensor. It has a
suitable Young's modulus and can provide a flexible
environment. In addition, the support structure is
usually made of some polymers, such as polyimide
(PI), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), polyethylene
terephthalate (PET), etc. Therefore, the supporting
structure usually has the characteristics of insulation,
stretchability and corrosion resistance, which makes
the packaging structure better protect other
components in the sensor. The wire is used to connect
the piezoelectric pressure sensor to external
instruments and transmit electrical signals (Ma,2024).
Due to their exceptional stretchability and other
characteristics that extend their service life, flexible
piezoelectric pressure sensors are frequently utilized.
The working principle of the piezoelectric
pressure sensor is the piezoelectric effect. The
piezoelectric effect is that when a piezoelectric
material is subjected to external pressure, alternating
charges are generated on the surfaces of both ends of
the piezoelectric material, thereby forming a voltage
at both ends of the piezoelectric material (Wang et al,
2010). The voltage signal generated by the
piezoelectric material will be exported by the
electrode, and will be amplified, filtered, and
processed by the signal conditioning circuit and
transformed into a standard electrical signal output.
The processed standard electrical signal is
proportional to the externally applied pressure, so the
pressure can be calculated by measuring the size of
the standard electrical signal.
Piezoelectric pressure sensors have wide
frequency and high dynamic performance, so they
have significant advantages in measuring transient
dynamic parameters (Tan et al,2006). The values that
show how the system reacts and evolves in response
to quickly shifting external stimuli are known as
transient dynamic parameters. The parameter is very
important when used to analyze and design the
dynamic performance of the system to guarantee that
the system is able to react steadily and quickly under
transient conditions. Piezoelectric pressure sensors
also have the characteristics of good stability.
Because of the relatively stable nature of the
piezoelectric effect of its working principle, it has a
strong ability to resist external interference. Therefore,
piezoelectric pressure sensors are usually used in
long-term monitoring of the environment or the
automation field. Stable data results can be obtained
without frequent recalibration of the sensor.
Furthermore, piezoelectric pressure sensors have a
long service life because they use a design
mechanism without moving parts, which greatly
reduces the negative effects of mechanical wear or
component fatigue. In some industrial environments
and aerospace fields, piezoelectric pressure sensors
have become their first choice due to the harsh
application environment of sensors and the inability
to frequently replace sensors. In addition,
piezoelectric pressure sensors are universally utilized
in mechanical mechanisms of industrial production
and even in medical equipment such as ventilators.
2.2 Capacitive Pressure Sensor
Capacitive pressure sensors are typically consist of a
dielectric layer and parallel plates with electrodes on
both ends of the dielectric layer. Usually one of the
two parallel plates will be fixed, and the other parallel
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
80

Figure 2: Capacitive pressure sensor device structure (Picture credit: Original).
plate will have the ability of mechanical sensing, as
shown in Figure 2 (Mishra et al,2021). In the
production and manufacturing of traditional
capacitive pressure sensors, metal materials such as
copper and silver are often selected as the
manufacturing materials of electrodes. The electrodes
of the flexible capacitive pressure sensor are required
for good conformability so that the flexible sensor can
bend, stretch and have other properties (Mishra et
al,2021). With the advancement of science, it has
become easier to manufacture electrodes that meet the
performance requirements of soft sensors. Electrodes
made of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are flexible,
stretchable and transparent (Mishra et al,2021). In
addition, the electrode material can also choose some
composite materials to satisfy the diverse needs of
applications in practice.
The capacitive pressure sensor can be regarded as
a parallel plate capacitor, and the data of sensor's
detection is reflected by the capacitance change of the
parallel plate capacitor. The value of capacitance
depends mainly on the relative distance between the
two parallel electrode plates and the dielectric
constant. The relative distance between the two
parallel plates changes with the external pressure, and
the two are inversely proportional. The dielectric
constant is usually associated with the material in the
dielectric layer and the temperature.
Capacitive pressure sensors have excellent
sensitivity and can remain stable to changes in
ambient temperature. Therefore, capacitive pressure
sensors are often used in the medical field. In the last
few years, cuff electrodes have been frequently
utilized to monitor neural signals. However, the
radius of the nerve is much larger than that of the cuff
electrode, so the cuff electrode may cause excessive
pressure on the nerve tissue. Therefore, an elliptical
electrode with the ability to flatten the nerve trunk and
increase the contact zone between the nerve trunk and
the electrode was proposed. Therefore, the capacitive
pressure sensor with elliptical electrodes can better
detect the pressure between the nerve stem and the
electrodes, thereby detecting people's nerve health
(Chiang et al,2007). The application of capacitive
pressure sensors in the medical field often requires
changing the material, shape and other characteristics
of the electrode according to the situation to cope with
different environments. Capacitive pressure sensors
can be integrated into most medical devices because
they can be made very small. During surgical
operations, piezoelectric pressure sensors are
integrated into minimally invasive catheter surgeries
to monitor patients’ blood pressure and other
conditions. In addition, capacitive pressure sensors
are used in environments that are in direct contact
with medical drugs, such as infusion pumps and
ventilators, because of their strong corrosion
resistance. Many features of capacitive pressure
sensors can satisfy their use in the medical field, and
the development of flexible capacitive pressure
sensors can further expand their application range.
2.3 Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors
Piezoresistive resistors and diaphragms are the core
parts of the piezoresistive pressure sensor structure
(Tran et al,2018). The structure diagram of the
traditional piezoresistive pressure sensor is shown in
Figure 3. The most important step in the manufacture
of piezoresistive pressure sensors is the design of the
sensing diaphragm. The design area of a conventional
square flat diaphragm is typically separated into two
levels, with the upper layer being variable and the
bottom layer being fixed, as seen in Figure 4. In
addition, the edges of the diaphragm will be fixed.
Because of this double-layer sensing diaphragm
structure, the sensitivity and linearity can be
improved (Tran et al,2018). When manufacturing
piezoresistive pressure sensors, different structures
and
material choices will affect the sensitivity and
Research Progress of Pressure Sensors: Structure, Principle, Application
81

Figure 3: Piezoresistive pressure sensor device structure (Picture credit: Original).
Figure 4: Traditional square flat diaphragm structure (Picture credit: Original).
linearity of the piezoresistive pressure sensors. A
high-sensitivity pressure sensor with exceptional
linearity in the 0–54 kPa range was predicted
theoretically. It was constructed using a twin
Wheatstone bridge architecture and a diaphragm that
was 7 μm thick. In addition, a graphene-based
resistive pressure sensor has a low linearity but a very
high sensitivity across a broad pressure range (0~100
kPa) (Zhang et al,2018). Consequently, the
performance of the piezoresistive pressure sensor is
somewhat influenced by the choice of material and
structure.
The working principle of piezoresistive pressure
sensor is piezoresistive effect. The piezoresistive
effect refers to the change in resistance when
mechanical strain occurs due to external pressure
(Meti et al,2016). When the piezoresistive pressure
sensor is subjected to external pressure, the sensing
diaphragm will deform and exert bending force on the
piezoresistive resistors. For the varistor device, the
piezoresistive action will cause the resistance value to
fluctuate (Tran et al,2018). The piezoresistive effect
of semiconductor materials is significant and has high
sensitivity. Compared with semiconductor materials,
the piezoresistive effect of metal materials is weaker,
and it mainly causes changes in resistance through
geometric deformation. The piezoresistive device
connected to the upper diaphragm is connected in a
Wheatstone bridge structure. An output voltage
proportionate to the external pressure is produced
from the resistance change brought on by the
piezoresistive effect (Meti et al,2016). The method of
applying an input voltage to a Wheatstone bridge
structure and obtaining a linear output result has the
characteristic of high sensitivity because small
changes in resistance in the piezoresistive effect can
be amplified.
Because of their high sensitivity, ease of
preparation, and ability to provide linear signals,
piezoresistive pressure sensors are widely used.
Piezoresistive pressure sensors have been noticed by
people due to their affordability and ease of
preparation. Since the flexible electronic instruments
are developing rapidly, the demand for piezoresistive
pressure sensors with high sensitivity, long service
life and wide data detection range is gradually
increasing. Flexible electronic devices using
piezoresistive pressure sensors can be used to detect
a range of micro-movements such as heartbeat and
breathing (Cao et al,2021). Detecting tiny movements
requires very high sensitivity of the sensor, so the
piezoresistive pressure sensor is suitable for this
application, and its linearity characteristics can also
clearly reflect the data of tiny changes. Driven by the
rapid development of science and technology,
electronic devices are gradually being integrated into
the medical field. The possibility of using some
piezoresistive graphene sensors with special sawtooth
structures for invasive surgical procedures has been
proposed (Szczerba,2022). For the application of
piezoresistive pressure sensors in the medical field,
the flexible sensor structure can better fit the patient's
skin surface and better detect the patient's relevant
data. Thus, the trend of future sensor advancement
innovation will be the creation of flexible
piezoresistive pressure sensors.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
82

3 CONCLUSION
This article focuses on the structure, principle and
application of piezoelectric pressure sensors,
capacitive pressure sensors and piezoresistive
pressure sensors. With the development and progress
of technology, flexible mechanisms and pressure
sensors are gradually integrated. Flexible pressure
sensors have the characteristics of high sensitivity,
long service life, and can be applied to more
diversified environments. Therefore, the
development of flexible pressure sensors has become
the main trend of future sensor development.
There are several challenges in the way of the
advancement of flexible sensors. The flexible
structure of the flexible pressure sensor and the
selected material often affect the final performance of
the pressure sensor. Different application fields have
different requirements for sensor accuracy and
different application environments. Therefore, the
application field needs to be considered when
designing flexible mechanisms and finding new
functional materials. In addition, the production and
processing of sensors also need to keep up with the
speed of technological development. Finding new
sensing mechanisms is essential for future sensor
development. The article suggests that in the future
development of pressure sensors, attention should be
paid to finding new pressure sensor sensing
mechanisms. This can not only broaden the
application range of sensors, but also provide options
for applications that require higher accuracy, simpler
preparation and lower cost. The advancement of
pressure sensors should be associated with
applications. Further research based on application
requirements is a prerequisite for the advancement of
pressure sensors.
REFERENCES
Cao, M., Su, J., Fan, S., Qiu, H., Su, D., & Li, L. (2021).
Wearable piezoresistive pressure sensors based on 3D
graphene. Chemical Engineering Journal, 406, 126777.
Chiang, C. C., Lin, C. C. K., & Ju, M. S. (2007). An
implantable capacitive pressure sensor for biomedical
applications. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 134(2),
382-388.
Duan, Y., He, S., Wu, J., Su, B., & Wang, Y. (2022). Recent
progress in flexible pressure sensor arrays.
Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2495.
Gautschi, G. (2002). Piezoelectric sensors (pp. 73-91).
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Liu, E., Cai, Z., Ye, Y., Zhou, M., Liao, H., & Yi, Y. (2023).
An overview of flexible sensors: Development,
application, and challenges. Sensors, 23(2), 817.
Ma, R. (2024). Research on flexible piezoelectric pressure
sensor based on hybrid MAPbI3 pressure-sensitive
material, Xidian University.
Meti, S., Balavald, K. B., & Sheeparmatti, B. G. (2016).
MEMS piezoresistive pressure sensor: A survey.
International Journal of Engineering Research and
Applications, 6(4), 23-31.
Mishra, R. B., El-Atab, N., Hussain, A. M., & Hussain, M.
M. (2021). Recent progress on flexible capacitive
pressure sensors: From design and materials to
applications. Advanced Materials Technologies, 6(4),
2001023.
Szczerba, Z., Szczerba, P., & Szczerba, K. (2022).
Sensitivity of piezoresistive pressure sensors to
acceleration. Energies, 15(2), 493.
Tian, H., Lin, Q., & Li, B. (2006). Research on the
application of optical fiber transmission technology of
piezoelectric pressure sensor. Sensors and
Microsystems, 25(2), 3.
Tran, A. V., Zhang, X., & Zhu, B. (2018). Mechanical
structural design of a piezoresistive pressure sensor for
low-pressure measurement: A computational analysis
by increases in the sensor sensitivity. Sensors, 18(7),
2023.
Wang, L., Qin, L., & Li, L. (2010). Piezoelectric dynamic
pressure sensor. 2010 IEEE International Conference
on Information and Automation (pp. 906-911). IEEE.
Yuan, H., Zhang, Q., Zhou, T., Wu, W., Li, H., Yin, Z., ...
& Jiao, T. (2024). Progress and challenges in flexible
capacitive pressure sensors: Microstructure designs and
applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149926.
Zhang, J., Chen, J., Li, M., Ge, Y., Wang, T., Shan, P., &
Mao, X. (2018). Design, fabrication, and
implementation of an array-type MEMS piezoresistive
intelligent pressure sensor system. Micromachines, 9(3),
104.
Research Progress of Pressure Sensors: Structure, Principle, Application
83
