
Research on Human-Computer Interaction Behavior and Gesture
Recognition Based on Machine Vision
Yiyuan Zhang
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Tianjin University of Technology, Tianjin, China
Keywords: Achine Vision, Human-Computer Interaction, Neural Networks.
Abstract: At present, significant breakthroughs have been made in human-computer interaction behavior and gesture
recognition technology based on visual perception, which has shown important application value in the fields
of rehabilitation medicine, intelligent furniture and virtual reality systems by capturing human movement
characteristics. In chronological order, this study deeply analyzes the design mechanism and performance
boundaries of typical algorithms at different stages of development. The detection framework of Histogram
(HOG) with Support Vector Machine (SVM) as the core of manual feature engineering of early vision
methods was introduced. The introduction of multimodal data fusion strategies in the mid-stage development
includes the co-architecture of RGB-D sensors and inertial measurement units (IMUs), as well as modern
deep learning methods that break through the limitations of traditional paradigms and include method models
representing end-to-end networks such as Visual Background Extractor (VIBE) and Multimodal Fusion
(MMF). At the same time, the performance of different vision method models on the dataset is compared, and
the future trend and development of the current model are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence
technology, human-computer interaction systems
based on machine vision have become a current
research hotspot and are widely used in daily life.
Machine vision enables computers to acquire, process,
and understand image information by simulating
human visual functions, thereby enabling advanced
functions such as object recognition and scene
understanding. In the field of smart home,
applications such as face recognition unlocking and
gesture control have greatly improved the user
experience; Service robots achieve autonomous
movement and precise operation through visual
navigation and environmental perception; Virtual
reality technology creates immersive experiences
with the help of visual interactions. The intelligent
interaction system breaks through the limitations of
traditional interaction methods, realizes efficient
human-machine collaboration, and promotes the
innovation and development of intelligent
manufacturing, smart medical care and other fields.
At present, significant progress has been made in
research at home and abroad, and the dual-stream
network has performed well on benchmark datasets
such as UCF-101 by separating spatiotemporal
feature processing, but the computational complexity
is high. 3D-CNN can effectively capture timing
features, but it faces the problem of a large number of
parameters. Current research focuses on lightweight
design and multimodal fusion to improve recognition
performance in complex scenarios. However, there
are still challenges in terms of real-time performance,
occlusion processing, and adaptation to viewing angle
changes, and the algorithm architecture and
computational efficiency need to be further optimized
(Zhang & Feng, 2024). Another important trend is the
combination of advanced vision algorithms with
high-precision optical inspection platforms. This
integrated solution not only enables rapid
identification and classification of defects, but also
accurately locates the location of defects, providing a
reliable basis for subsequent quality analysis. A large
number of experimental results show that these
methods show excellent performance in various
defect detection tasks of machined parts, and the
detection accuracy and efficiency are significantly
improved compared with traditional methods
(Abrorov et al., 2025). Emerging signal
decomposition and tensor modeling methods have
improved feature robustness, and hybrid architectures
Zhang, Y.
Research on Human-Computer Interaction Behavior and Gesture Recognition Based on Machine Vision.
DOI: 10.5220/0014318400004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Inter national Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 55-60
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
55

combined with deep learning have enhanced feature
capture capabilities, but cross-domain adaptation for
weightless training is still a key challenge (Chen,
2025).
However, the real-time performance of the system,
environmental adaptability and multimodal fusion
still need to be further explored. In the future, with the
advancement of deep learning algorithms and
hardware technology, human-computer interaction
systems based on machine vision will develop in a
more intelligent and natural direction. For human-
computer interaction tasks, three mainstream
approaches are proposed: feature engineering
methods based on traditional image processing, end-
to-end models based on deep learning, and hybrid
architectures fused with multimodal sensors.
According to relevant studies, the traditional method
has high accuracy but insufficient generalization
ability across scenarios. The deep learning methods
represented by 3D convolutional neural networks are
highly accurate, but difficult to deploy. The emerging
multimodal approach also faces the engineering
problems of sensor heterogeneity and data
synchronization. These performance differences
show the fragmentation of the current research in the
algorithm design and evaluation system.
There are three significant shortcomings in the
existing research: first, the evaluation criteria present
the phenomenon of "data silos", and different papers
use self-built datasets and customized indicators,
resulting in a lack of reproducibility; Second, the
model optimization presents "scene fragmentation",
and the demand characteristics of vertical fields such
as medical and industrial fields are not included in the
general model design. Third, the research on
hardware adaptability is insufficient, and the
inference speed of mainstream algorithms on
embedded devices is generally lower than 30fps,
which is difficult to meet the needs of real-time
interaction. These problems essentially reflect the
imbalance between theoretical innovation and
engineering implementation of HCI vision methods.
In this study, we mainly introduce machine vision
methods in different periods and their respective
advantages and disadvantages, and summarize the
methods to obtain their adaptation range. This
document, saved in the “Word 97-2003” format, is a
guide to using the Manuscript Template. Before
submitting your final paper, check that the format
conforms to this guide. In particular, check the text
to make ensure that the correct referencing style has
been used and that the citations are in numerical order
throughout the text. Your manuscript cannot be
accepted for publication unless all formatting
requirements are met.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Early Machine Vision Methods:
Manual Feature Extraction and
Limitations
Early machine vision methods mainly relied on
manually designed feature extraction algorithms
(Deng et al., 2025), as shown in Figure 1, which
performed well in specific scenarios but were often
not robust enough in complex environments (Safyari
et al., 2024, Guoming & Qinghua, 2022). Background
modeling (e.g., Gaussian mixture model GMM) and
optical flow methods (e.g., Lucas-Kanade algorithm)
were the mainstream techniques at the time for
motion detection and target tracking (Liu et al., 2025).
Background modeling distinguishes foreground and
background by counting pixel changes, which is
suitable for static camera scenes, but is prone to
failure when dynamic background or lighting
changes. The optical flow rule estimates motion by
calculating the pixel displacement between adjacent
frames, but it is sensitive to noise and has a high
computational complexity.
In terms of human pose estimation, the method of
HOG (Directional Gradient Histogram) combined
with SVM (Support Vector Machine) performs well
in static scenes. However, when faced with dynamic
occlusion (e.g., pedestrian staggering, object
blocking), its accuracy drops dramatically, severely
limiting practical applications. In addition, this type
of method relies on artificially set features, which
makes it difficult to adapt to different lighting,
viewing angles, and pose changes.
Still, traditional approaches have advantages in
structured scenarios. For example, in the field of
industrial quality inspection, methods based on edge
detection (such as the Canny operator) and template
matching can stably identify product defects in fixed
patterns. However, as the complexity of the scene
increases (e.g., multi-target, non-uniform lighting),
its performance decreases significantly.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
56
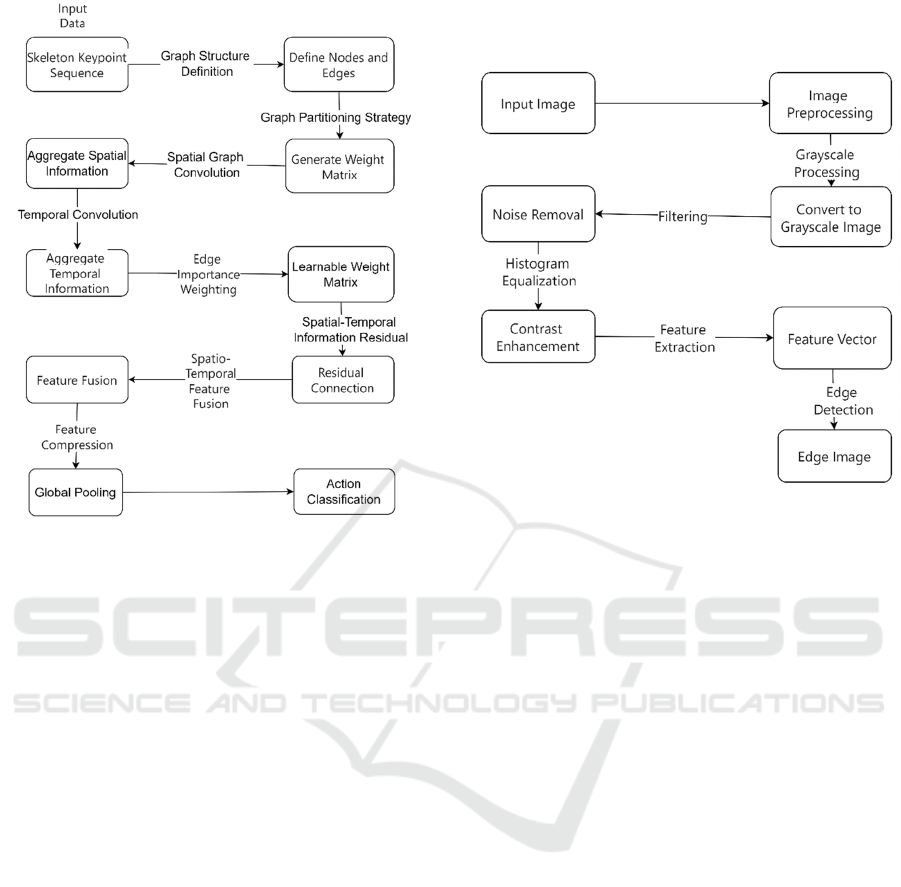
Figure 1: Early machine vision manual extraction method
(Picture credit: Original).
2.2 Medium-Term Development:
Innovation of Two-Stage and
Single-Stage Models
With the rise of deep learning, machine vision has
entered a new stage, and dual-stage (e.g., Faster R-
CNN) and single-stage (e.g., YOLO) models have
greatly improved the accuracy of object detection and
pose estimation. The specific process is shown in
Figure 2. In the field of human pose estimation,
models such as OpenPose use a top-down detection
strategy to locate the human body in the image first,
and then predict the position of the joint point.
Experiments based on the COCO dataset show that
the accuracy of joint point detection (AP@0.5) of
OpenPose can reach 72.1% (Wang et al., 2022),
which is far higher than that of traditional methods.
However, the computational cost of the two-stage
model is high, and it is difficult to meet the real-time
requirements. The inference speed of the two-stage
model is low, while the speed of the single-stage
model is improved, but the accuracy is slightly
reduced. In terms of time series modeling, Graph
Convolutional Network (GCN) is introduced into the
action recognition task, and ST-GCN achieves a high
accuracy rate on the NTU RGB+D dataset. However,
the number of parameters is too high, resulting in high
inference latency on mobile devices, which limits its
application on low-power devices.
Figure 2: Flow chart of the ST-GCN model (Picture credit:
Original).
2.3 Current Trends: Multimodal
Fusion and Transformer
Architecture
In recent years, machine vision has further developed
towards multimodal fusion and Transformer
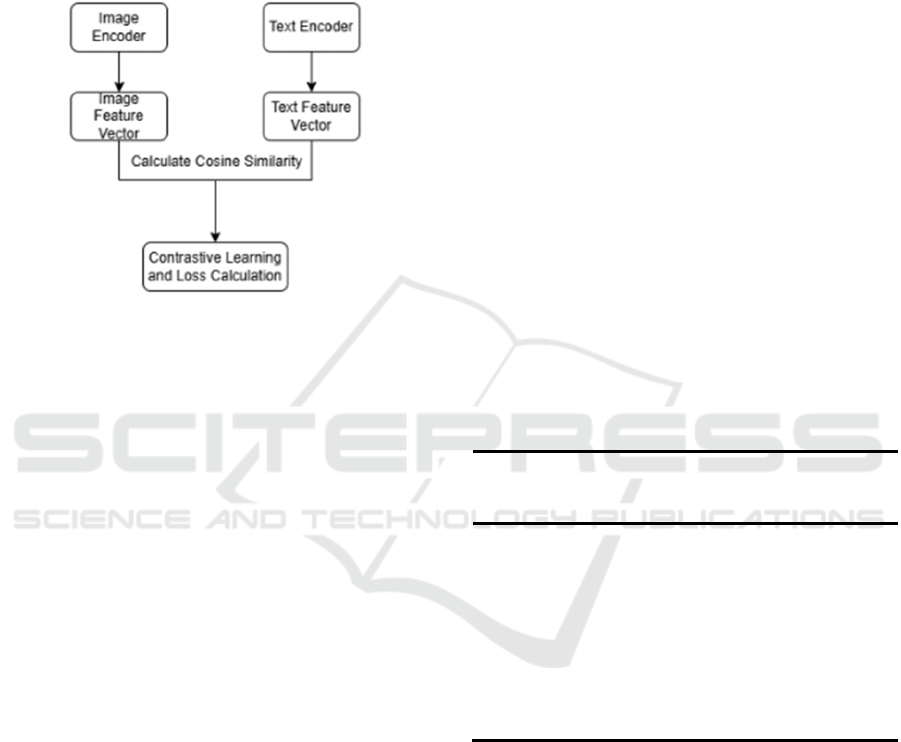
architectures. The specific framework shown in
Figure 3 is that RGB-D sensors (such as Intel
RealSense) combine with inertial measurement unit
(IMU) data to improve accuracy in monocular vision-
constrained scenes. In the fall detection task, the false
alarm rate of traditional monocular vision is high, but
it can be reduced after fusing IMU data. However, if
the synchronization error of multi-source data
exceeds 50ms, it will lead to feature misalignment
and affect the final decision.
The introduction of the Transformer architecture
has driven cross-modal learning. The CLIP model
achieves visual-language alignment through
contrastive learning, and the accuracy of user intent
recognition in VR interactive scenes is improved by
23% (Chen, 2024). However, it is extremely
computationally complex (FLOPs>150G) and
difficult to deploy at the edge. To reduce
computational costs, distillation techniques such as
TinyCLIP are produced, but at the expense of
accuracy.
Research on Human-Computer Interaction Behavior and Gesture Recognition Based on Machine Vision
57
Future directions may include:
Lightweight design: e.g., neural architecture
search (NAS) to optimize model efficiency; Timing
optimization: improve multi-modal data
synchronization and reduce feature misalignment;
Edge computing: Uses quantization, pruning, and
other technologies to adapt to mobile needs.
Figure 3: Diagram of the CLIP unit model (Picture credit:
Original).
3 DISCUSSION OF TEST
METHODS AND RESULTS
3.1 Overview of the Methodology
In the experimental design, three sets of differentiated
datasets, MSCOCO (general scene), MPII (single
posture), and HAA500 (medical rehabilitation), were
selected to compare different methods, and then the
basic performance of algorithms, real-time
capabilities, scene generalization capabilities, and
hardware adaptability of different methods were
detected by using different evaluation indicators, such
as the average accuracy of joint point detection, the
number of frames per second processed on the device
side, the percentage of test accuracy degradation
across datasets, and the running energy consumption
of embedded devices (Yang et al., 2023).
In the experimental configuration, the hardware
platform uses NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier (edge
computing) and RTX 3090 (server-grade GPU) to
compare the performance of the algorithm in a
resource-constrained and high-performance
environment. In the data preprocessing stage, all input
images were uniformly scaled to 256×256 resolution,
and the sampling frequency of time series data was
fixed at 30Hz to ensure that the experimental
conditions were consistent.
Among the evaluation indicators, the experiment
was quantitatively analyzed from four dimensions:
the basic performance of the algorithm: the average
accuracy of joint point detection (AP@0.5) to
measure the accuracy of key point positioning, the
real-time ability: the number of frames per second
(FPS) processed on the device side to evaluate the
inference efficiency, the scene generalization ability:
the percentage of the accuracy of cross-dataset testing
(such as MPII → HAA500) to reflect the model
mobility, and the hardware adaptability: the running
energy consumption of embedded devices (Watt) to
record Jetson Xavier's power consumption.
Experimental comparison of three types of typical
methods: traditional methods: HOG+SVM, optical
flow method; Two-stage model: OpenPose (based on
COCO pre-training); Lightweight model:
MobileNetV3+ST-GCN (parameter < 10 Mbit/s);
3.2 Test Results
The differences between different methods in terms
of accuracy, real-time, generalization ability and
hardware adaptability are reflected in Table 1.
Table 1: The performance of several methods on similar
datasets.
Method
type
mAP@0.5
(MSCOCO)
FPS
(Jetson)
Cross-domain
attenuation
(HAA500→MPII)
HOG+SVM low high high
OpenPose low medium medium
VIBE medium low medium
RGB-
D+IMU
convergence
medium high medium
MMF high low medium
Experimental results show that different
algorithms have significant differences in
performance, and each has its own advantages and
disadvantages. For example, the VIBE method shows
excellent detection accuracy on the server side, with
a mAP@0.5 of 88.9%, which reflects the advantages
of deep learning models in feature extraction and
pattern recognition. However, the real-time
performance of the algorithm on edge computing
devices is not good, and it can only reach the
processing speed of 9FPS, which is difficult to meet
the basic needs of most real-time human-computer
interaction applications (usually requiring ≥ 30FPS).
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
58

In stark contrast, the traditional HOG+SVM method,
although its detection accuracy is reduced by 23.7
percentage points compared with VIBE, the
processing speed on edge devices is increased by 5
times, showing better real-time performance.
This comparison results reveal that the algorithm
selection needs to be weighed according to the needs
of specific application scenarios. In fields that require
extremely high accuracy, such as medical
rehabilitation, such as surgical action recognition and
rehabilitation training evaluation, high-precision
algorithms such as VIBE should be prioritized, even
at the expense of some real-time performance. In
applications that emphasize real-time interaction,
such as smart homes and service robots, algorithms
with better real-time performance such as
HOG+SVM should be selected to ensure that the
system response speed meets the needs of user
experience.
In terms of the comparison of multimodal
methods, the experimental data clearly demonstrate
the advantages of fusing multi-source information.
The RGB-D+IMU fusion method only has an
accuracy attenuation of 15.8% in the cross-domain
test, which is significantly better than the 28.7%
attenuation rate of the pure vision method OpenPose.
This result verifies that multi-source information
fusion can effectively improve the adaptability of the
system in different environments. Especially in
practical applications such as fall detection, the
inertial data provided by the IMU can effectively
compensate for the perception defects of the vision
system in occlusion conditions, and greatly reduce the
false alarm rate from 19.4% to 6.8% of the pure vision
method, which significantly improves the reliability
of the system.
However, there are significant limitations to the
multimodal fusion approach. The first is the issue of
hardware cost, which increases significantly overall
due to the need to deploy additional depth cameras
and inertial measurement units. Secondly, the
problem of multi-source data synchronization has
become a technical bottleneck, and when the time
synchronization error of each sensor data exceeds
50ms, it will lead to feature matching misalignment,
which will seriously affect the system performance.
All these factors limit the large-scale deployment of
multimodal methods in industrial scenarios.
Therefore, when selecting the actual project, it is
necessary to comprehensively consider various
factors such as performance requirements, cost
budget, and deployment conditions to select the most
suitable technical solution.
4 FUTURE AND PROSPECTS
With the continuous evolution of artificial
intelligence technology, human-computer interaction
systems based on machine vision will develop in a
more intelligent and natural direction. At the
algorithm level, the research of lightweight deep
learning architecture will become an important
direction, and the computational efficiency can be
improved while maintaining accuracy through model
compression, knowledge distillation and other
technologies. At the same time, the adaptive
multimodal fusion method is also worthy of further
exploration, especially the mechanism of
dynamically adjusting the weights of each modality
for different scenarios, which is expected to further
improve the environmental adaptability of the system.
Advances in hardware technology will provide
new possibilities for breakthroughs in system
performance. The emergence of new edge computing
chips, the continuous improvement of sensor
accuracy, and the development of low-power design
will effectively alleviate the current real-time and
energy consumption bottlenecks. Of particular
interest is the device-cloud collaborative computing
architecture, which is expected to achieve the best
balance between performance and efficiency by
rationally distributing computing load.
In terms of application scenario expansion, there
is huge room for development in the fields of medical
rehabilitation, intelligent manufacturing, and smart
cities. Future research should pay more attention to
the in-depth optimization of vertical fields and the
development of customized solutions for specific
scenarios. At the same time, with the enhancement of
privacy protection awareness, how to achieve data
security and privacy protection under the premise of
ensuring performance will also become an important
research direction.
From a broader perspective, the ultimate goal of
human-computer interaction systems is to achieve
natural and seamless human-machine collaboration.
This requires deep interdisciplinary integration,
including collaborative innovation in multiple fields
such as computer vision, cognitive science, and
human factors engineering. Future research should
not only focus on the improvement of technical
indicators, but also pay attention to the optimization
of user experience, so as to truly realize the
fundamental purpose of technology serving people.
Research on Human-Computer Interaction Behavior and Gesture Recognition Based on Machine Vision
59

5 CONCLUSION
In this study, the performance of different vision
algorithms in multiple key dimensions was compared
through systematic experiments, and the important
relationship between algorithm selection and scene
requirements was revealed. In terms of algorithm
accuracy, deep learning methods show significant
advantages, and its complex network structure can
effectively capture high-level semantic features,
which is especially suitable for application scenarios
with strict accuracy requirements. However, this
performance gain comes at the expense of real-time
performance, especially on resource-constrained
edge devices. In contrast, although the traditional
method has limited accuracy, its lightweight
computational characteristics make it irreplaceable in
real-time interactive scenarios.
From an engineering practice perspective, the
results of this study emphasize the basic principle that
there is no one-size-fits-all best solution. Algorithm
selection must be based on an in-depth understanding
of the requirements of application scenarios, and
multi-dimensional factors such as accuracy, real-
time, and cost must be comprehensively considered.
Especially in the process of industrial
implementation, it is also necessary to weigh the
relationship between technological advancement,
system reliability and commercial feasibility, which
are often more critical than simple algorithm
indicators.
The experimental results of the multimodal fusion
method highlight the important value of cross-modal
complementarity. By integrating the advantages of
different sensors, the system can overcome the
inherent limitations of a single perception mode and
significantly improve its robustness in complex
environments. This technology path is particularly
suitable for safety-critical applications such as
medical monitoring and industrial testing. However,
it should be pointed out that while multimodal
systems improve performance, they also bring new
technical challenges, including increased hardware
integration complexity and data synchronization
requirements, which need to be carefully considered
in actual deployment.
REFERENCES
Zhang, H., Feng, J. H.: ‘A review on human behavior
recognition based on deep learning methods’,
Journal of Jiyuan Vocational and Technical
College, 2024, 23(04): 62-69
Abrorov, A., Juraev, M., Nodira, K., et al.:
‘Automated Surface Defect Detection in
Machined Parts Using Deep Learning Techniques
and Machine Vision’. Diffusion Foundations and
Materials Applications, 2025, 3827-37
Chen, X.: ‘Cross-domain human activity recognition
using reconstructed Wi-Fi signal.’ Physical
Communication, 2025, 71, 102651-102651
Deng, Y., Qu, H., Leng, A., et al.: ‘Methods and
challenges in computer vision-based livestock
anomaly detection, a systematic review.’
Biosystems Engineering, 2025, 253, 104135-
104135
Safyari, Y., Mahdianpari, M., Shiri, H.: ‘A Review of
Vision-Based Pothole Detection Methods Using
Computer Vision and Machine Learning.’
Sensors, 2024, 24(17): 5652-5652
Guoming, C., Qinghua, L.: ‘Overview of ship image
recognition methods based on computer vision.’
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022,
2387(1)
Liu, H., Gao, X. Y., Su, X. X., et al.: ‘Human posture
tracking method based on computer vision
technology.’ Software Guide,1-11. 2025
Wang, J. T., Pan, C., Yang, L. F., et al.: ‘Fall detection
algorithm based on improved ST-GCN model.’
Information Technology and Informatization,
2022, (02): 69-71+75
Chen, L.: ‘Research on image description algorithm
based on CLIP pre-trained model.’ Chongqing
University of Technology, 2024
Yang, G., Li, L. H., Luo, K., et al.: ‘Journal of
Guizhou University’ (Natural Science Edition),
2023, 40(05): 1-14
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
60
