
Design and Implementation of Personalised Learning Support System
Yifei Dou
Information and Computational Science, Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University, Suzhou, China
Keywords: Personalized Learning, System Design, Computer System.
Abstract: Based on the popularity of electronic devices, education is changing from a single learning model to
diversified learning, and the field of education is experiencing a paradigm shift from standardized teaching to
personalized learning. At present, countries are also carrying out the popularization of personalized learning.
This study summarizes the intelligent personalized learning system based on multi-level architecture in view
of the limitations of the traditional education system "one-man", aiming at empowering the education essence
of "teaching students in accordance with their aptitude" through technology. So that students can find a truly
suitable learning mode through the learning system, the system adopts a four-layer architecture design, and
recommends suitable personalized learning systems. Future research will focus on intelligence, explore the
efficiency of personalized learning system, such as solving learning strategy problems through ai, and verify
the usability of personalized learning system, and attract students to accept personalized learning model by
building system innovation. In addition, people's identification and popularization of personalized learning
will also become an important research topic.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the interdisciplinary integration of artificial
intelligence, big data analysis and cognitive science,
the education system has gradually shifted from "one-
to-one" standardized teaching to "people-oriented"
personalized service. This transformation is not only
driven by the development of technology, but also
reflects the return of the essence of education, which
is to respect the individual differences of learners and
realize the goal of teaching students in accordance
with their students' abilities. For learners, finding the
resources that meet their needs from a large number
of learning resources is very important for learning
efficiency and self-study effect (Wang and Gao,
2022).
And with the rapid development of various mobile
devices, such as mobile phones, tablets, laptops,
GPRS technology and Bluetooth technology
popularity, gradually become our main tool for
learning, another new survey conducted by Newzoo's
Global Mobile Market Report 2019 shows that the
popularity of smart phones is high: 82.9% in the UK,
79.9% in Germany, 79.1% in the US, 77.5% in France,
74.3% in Spain, 70.4% in South Korea and 66.3% in
Russia (Bourekkache et al., 2020). In Algeria, the
smartphone penetration rate is 38.1%, which is
considered an important rate (Bourekkache et al.,
2020). Because of the popularity of these devices, it
has become difficult for our study life to leave online
learning, so having an excellent personalized learning
system is essential for learning efficiency. And on a
global scale, The United Nations Educational,
Scientific and Cultural Organization, UNESCO states
that "access to quality education means access to
personalized learning", highly emphasizing the
promise of this approach for addressing uneven
outcomes in school education. As J. Groff puts it,
personalized learning is essential because it is
"entirely consistent with the science of learning"
(Zhao and Wu, 2025).
It is proposed in InfoTech that adaptive resource
recommendations (or building a personalized
learning path) should be made in a dialogue with the
learner, and he should have the possibility to select
some suggested new content or activity. This paper
proposes a knowledge model to ensure adequate
recommendation of dynamically generated learning
paths and to store various approved and well-
annotated learning paths for future reuse (Ivanova,
2023). The architecture design of personalized
learning system is the key to realize personalized
education. An effective personalized learning system
should contain these aspects, including user
Dou, Y.
Design and Implementation of Personalised Learning Support System.
DOI: 10.5220/0014318100004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 49-54
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
49
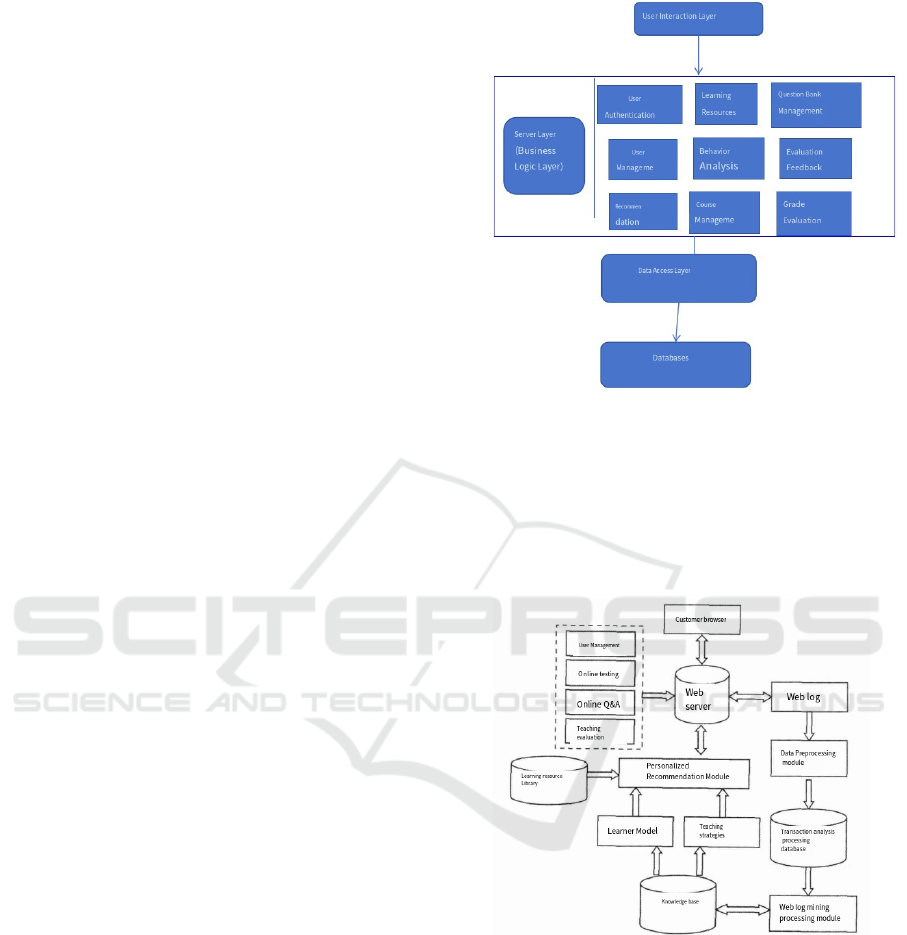
interaction layer, server layer, data access layer,
database layer. The user interaction layer is mainly
responsible for collecting the basic information of
learners, and effectively displaying and
recommending learning resources to students. The
server is mainly responsible for analyzing the user
model and finding a suitable learning path for learners.
The data access layer is mainly responsible for
ensuring the security of data entering the data
database and reviewing whether the data is normal or
not to ensure the security of user data. The database
layer is mainly responsible for storing data and
facilitating learners to call data, and can also give
visual charts for users to view data efficiently and
clearly.
2 THE OVERALL
ARCHITECTURE DESIGN
The user side is responsible for the display and
processing by the web interface, and the interactive
interface directly facing the learner, showing the
graphical interface of the student learning, teacher
monitoring and other modules, as well as the
corresponding security protection. It can intuitively
show the function of the system to the user, provide
users with a convenient and quick experience, but
also consider the user experience, and operation and
maintenance.
The server layer (business logic layer) is the core
area of the system, responsible for receiving and
processing the information transmitted by the user
end, can carry out the centralized management of
complex business, technology selection, code
governance, etc., which may affect the performance.
The database is mainly responsible for providing
an interface for the server to realize the addition,
deletion and modification of data. The use of the
database can make the data more durable and reliable,
and can also make the query and optimization more
efficient, but the problems such as operation and
maintenance complexity and security need to be
solved. Figure 1 shows the overall architecture of
personalized learning.
Figure 1: The overall architecture of personalized learning
(Picture credit: Original).
3 TECHNOLOGY SELECTION
3.1 User Side Development
Figure 2: User-side personalized learning model (Zhang et
al., 2023).
The system is mainly composed of six modules (as
shown in Figure 2): login module, Web log mining
processing module, knowledge base, personalized
recommendation module, regular function module
and learning resource library, as shown in Figure 2
(Zhang et al., 2023). When users log in, they must
first register, and carefully fill in the questionnaire
designed by the system administrator, generate user
personalized information materials, and establish the
initial user interest matrix for resources to avoid the
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
50

cold start problem of the system (Zhang et al., 2023).
In the system have the function of traditional online
learning system, such as user management, learning
resource management, online testing, online
answering questions and teaching evaluation, etc., at
the same time the system also includes a core of
personalized intelligent module - Web log mining
processing module, in order to realize the learners and
page clustering and learners learning rule, the
analysis of learning style. When a user access to the
system, the operation module mainly complete the
following two aspects: first, using the K - Means
clustering algorithm is analyzed, according to the
learners and page two objects according to the
similarity between them is divided into several groups,
constitute a set of similar objects. If some pages are
found to belong to the same group, other pages in the
same group can be recommended to learners when
learners access the pages (Zhang et al., 2023).
Since the user side is directly oriented to learners,
there are many frameworks that can provide a better
experience for users. For example, FeedbackFlow
Dynamics studies the evolution of real-time feedback
systems and user behavior (Devi et al., 2025). It
investigates the impact of information and timed
feedback on user engagement. By allowing users to
modify timing and input types, interfaces become
more interesting and responsive. The EmoFeedback
interaction model incorporates user emotions into the
design process, recognizing their significant impact
on interface usability and aesthetics, by analyzing and
responding to emotional signals, it enhances the user
experience and contributes to the development of
emotionally intelligent interfaces (Devi et al., 2025).
The DynamicAdapt UX framework ensures a more
satisfying, personalized, and contextualized
experience for customers (Devi et al., 2025). Reactive
flow design model assessment in a variety of screen
sizes and optimize the design of the data flow and
equipment (Devi et al., 2025).
At the same time, interface design plays a vital
role in improving user experience and promoting
product development (Qiu, 2024). By implementing
a series of targeted optimization measures, such as
adopting card design, expanding the search bar, and
increasing the user comment section, we successfully
solved the problem of information overload caused by
user feedback. This makes the overall site clear visual
effect is more intuitive, allows the user to quickly find
interested project (Qiu, 2024). These optimizations
not only improve user efficiency, but also
significantly improve user satisfaction and loyalty
(Qiu, 2024).
User experience evaluation in this framework
employs the PrEmo (Product Emotion Measurement)
instrument, a validated psychometric tool for
quantifying affective responses to design stimuli
through 14 discrete emotional dimensions (Jiao,
2022). Grounded in Desmet's theoretical emotion
framework, the methodology operationalizes four
core components: 1) product evaluation protocols, 2)
attentional engagement metrics, 3) appraisal-induced
affective states, and 4) product attribute-emotion
mapping. Participants interact with purpose-designed
product prototypes that embody specific functional
objectives, aesthetic principles, and attention-guiding
features. Affective outcomes are subsequently
quantified through dynamic visual stimulus
presentations using affect-encoded animation
sequences (Jiao, 2022).
3.2 Server Layer
3.2.1 Micro Server Scheme
The combination of using Spring Boot with Spring
Cloud Spring Boot with its "convention over
configuration" design concept, provides developers
with a quick build Spring application convenient tools.
Spring Cloud further spring-based Boot, focusing on
service governance under the micro service
architecture, provides a set of perfect solutions,
covering service routing, registration and discovery,
load balance, monitoring, and many other aspects.
These features make the Spring Cloud micro service
architecture for building the preferred method of
(Chen et al., 2024). The use of microservice cluster
can disintegrate the complex scientific research
management system into a series of independent and
loosely coupled services, which significantly
improves the automation and information level of the
system (Wang, 2024).
3.2.2 Distributed Server Solution
This distributed server architecture employs multiple
nodes to minimize service delays in real-time systems
(Yanase et al., 2021). Under this design, each user
connects to a dedicated server node for event
transmission. The assigned server aggregates user-
generated events, disseminates them across the
network for synchronization, processes all collective
events through coordinated computation, and
ultimately relays the processed results back to
corresponding users for subsequent operations
(Yanase et al., 2021). The maximum number of users
in the server is given in the form of the server capacity,
Design and Implementation of Personalised Learning Support System
51
and to process events in the order in which they occur
at the user side, the delay between the user and the
server and the delay between the servers are corrected
to the maximum delay DU between the user and the
server and the maximum delay DS between the
servers, respectively (Yanase et al., 2021). Therefore,
in the Distributed Server Processing (DSP) approach,
it requires 2DU+DS. Compared with the CP, it will
have an extra step to events with other server
synchronization (Yanase et al., 2021). However,
since the server location is closer, the latency between
the user and the server is lower, so the communication
latency can be reduced (Yanase et al., 2021).
3.3 Data Access Layer
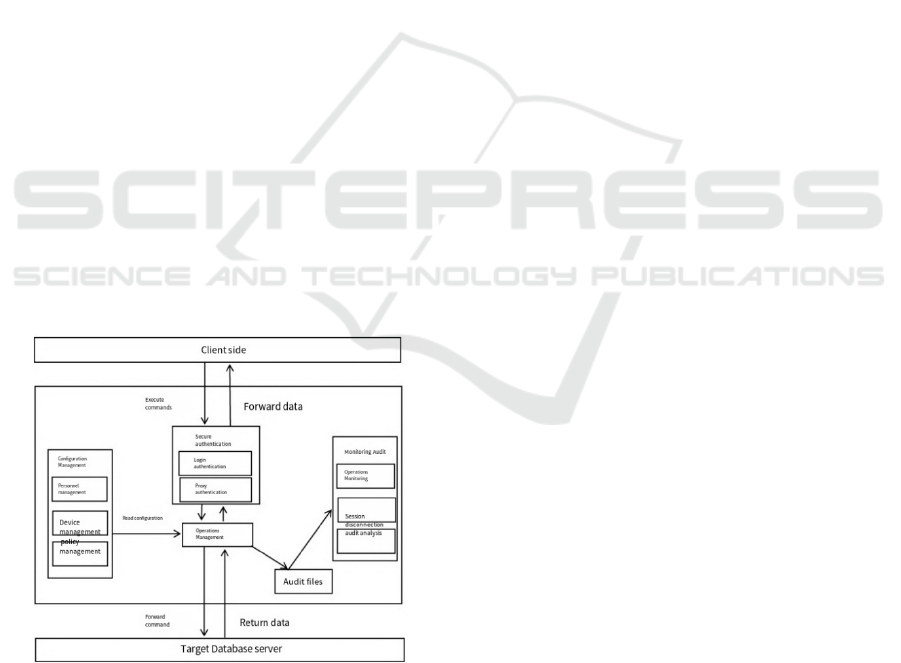
The overall system architecture (as shown in Figure
3) includes three parts, which are the front-end and
back-end management interface, the server and the
client, and the program code is deployed on the server.
The system takes the operation and maintenance
control module as the core, including the access
entrance of safety certification, configuration
management and monitoring and audit functions. The
safety certification covers two sub-modules of login
authentication and proxy authentication, and the
monitoring and accounting page sets up three sub-
modules of operation and maintenance monitoring,
session cutting and audit analysis. The configuration
management page covers three sub-modules of
personnel, equipment and policy management (Jia,
2024).
Figure. 3: Overall architecture of Data access layer (Jia,
2024).
There are many kinds of database security threats,
which need to be paid attention to and protected. The
following article will list the security matters that
need to be paid attention to SQL Injection. This is a
form of attack in which malicious code into the front
end (Web application) and transmitted to the backend
database (Jiao, 2022).
Due to SQL injection, computer attackers have
unrestricted access to all the data contained in the
database. There are two possible types of such code
attacks: SQL injection against standard databases and
NoSQL injection against massive databases (Jiao,
2022).
Database vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
This can also happen when the database is found to
be absolutely inaccessible due to misconfiguration
(Jiao, 2022). Many database systems maintain preset
credentials and setup options by design, a critical
consideration given that malicious actors possess
advanced technical expertise. These cyber attackers
routinely leverage architectural deficiencies and
improper configuration settings as entry points to
compromise organizational networks (Jiao, 2022).
Denial of Service (DoS) incidents specifically
target system availability by overwhelming database
infrastructure, resulting in two primary consequences:
impaired operational efficiency and potential service
interruption that renders critical assets unreachable
(Jiao, 2022). While such attacks preserve data
confidentiality, they force organizations to incur
substantial operational expenses through extended
downtime and remediation efforts (Jiao, 2022).
Ultimately, persistent unavailability of web services
fundamentally undermines the service's core value
proposition, negating its functional purpose despite
maintained data integrity (Jiao, 2022).
Decentralized data management presents critical
security challenges when handling sensitive
information. Organizations frequently maintain
extensive repositories of confidential records without
implementing comprehensive data governance
frameworks, creating attack surface proliferation
through orphaned datasets and legacy storage systems
(Jiao, 2022). Compounding this challenge, the
continuous influx of newly generated critical
information within dynamic data ecosystems makes
systematic monitoring inherently complex. This
operational reality exposes both archival and recently
ingested data assets to potential security breaches
before proper safeguards can be implemented (Jiao,
2022).
Database backup risks. It is best to back up a
proprietary repository within the specified time frame
(Jiao, 2022). Curiously, however, database backup
files are also completely unattacked. As a result,
database backup leaks are a frequent security breach
(Jiao, 2022).
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
52

Excessive privilege allocation in database systems
creates substantial security exposure. While role-
based access differentiation is fundamental to
database operations (Jiao, 2022), three primary
privilege escalation vectors emerge: non-essential
privilege retention (maintaining permissions
exceeding operational requirements), legitimate
access overreach (exploiting authorized privileges for
unauthorized activities), and dormant credential
exploitation (leveraging inactive access rights).
Empirical studies indicate approximately 80% of
corporate network breaches originate from insider
threats, with over-provisioned access rights
significantly increasing attack surface vulnerability
through privilege creep mechanisms (Jiao, 2022).
Malicious software propagation vectors
demonstrate sophisticated attack methodologies
through credential hijacking mechanisms. Advanced
persistent threats typically compromise endpoint
devices to establish command-and-control channels,
subsequently exploiting legitimate user credentials
through three operational phases: session co-option
(hijacking authenticated connections), privilege
escalation (leveraging authorized access levels), and
lateral movement (penetrating enterprise networks
via compromised accounts). Forensic analysis
confirms 62% of such breaches originate from
malicious payloads executing privilege escalation
protocols using authenticated user contexts (Jiao,
2022).
3.4 The Database Layer
Cache operates as an advanced object-oriented
database system, utilizing a multi-dimensional
transaction processing architecture to enable
distributed data management. This system establishes
a consistent data model structure, allowing data
manipulation via standard SQL queries while offering
integrated development utilities to accelerate
database implementation, particularly for web-based
applications. Additionally, the platform features
XML object compatibility and enables cross-
language interoperability through support for .NET,
ActiveX, C++, EJB, Java, JDBC, ODBC, SOAP, Perl,
Python, and XML protocols (Goswami and Sharma,
2021).
Teiid, a data integration technology, supports
virtualization of various types of databases; Through
such virtual databases, data sources such as relational
databases, Web databases, and application software
such as ERP and CRM can be accessed in real time
(Wada et al., 2010). Virtualization technology so that
data analysts or other users can use all ubiquitous
databases as if they were a single database, thus
helping to reduce the workload of users (Wada et al.,
2010).
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the interdisciplinary perspective, this study
summarizes an intelligent personalized learning
system. Through the four-layer architecture of "user
interaction layer, business logic layer, data access
layer and database layer", it integrates a variety of
methods and combines a variety of hot core
technologies to solve the pain points of low resource
adaptability and rigid learning path in traditional
education. The study shows that the learning system
is not only a technology, but also the promotion of
education reform. In the future, the technology will
take the essence of education as the carrier to build a
humanized and intelligent learning ecological model.
There are still many challenges in personalized
learning system, such as data collection and privacy,
algorithm bias, user diversity and effect verification.
In the future, both technology developers and users
will collaborate to solve these challenges.
REFERENCES
Bourekkache, S., Tigane, S., Kazar, O., and Kahloul, L.:
‘Mobile and personalized learning system for computer
science students,’ 2020 Sixth International Conference
on e-Learning (econf), Sakheer, Bahrain, 2020, pp.
189-193
Chen, Z., Wu, J., Ma, F. Z.: ‘Application Development
Research based on microservice architecture’.
Technology News. 2024
Devi, V. S. A. et al.: ‘Designing Intuitive User Interfaces in
Human-Computer Interaction for Enhanced Digital
Experience,’ 2025 International Conference on
Intelligent Control, Computing and Communications
(IC3), Mathura, India, 2025, Pp. 637-643
Goswami, P. K., and Sharma, A.: ‘An Intelligent Shift
Towards High-Performance Database Engines
Including Autonomous Databases Using Derived
Transient Objects from the Persistent at the Runtime,’
2021 IEEE International Conference on Technology,
Research, and Innovation for Betterment of Society
(TRIBES), Raipur, India, 2021, pp. 1-5
Ivanova, T. I.: ‘Knowledge-Based Semi-Automatic
Selection of Personalized Learning Paths,’ 2023
International Conference on Information Technologies
(InfoTech), Varna, Bulgaria, 2023, pp. 1-4
Jia, J. Y.: ‘Application of Big Data Technology and
MySQL Database’. Integrated Circuit Applications.
2024
Design and Implementation of Personalised Learning Support System
53

Jiao, Z.: ‘Research and Application of Human-Computer
Interface Based on User Experience,’ 2022 7th
International Conference on Intelligent Computing and
Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi'an, China, 2022, Pp.
1417-1420
Jiao, Z.: ‘Research and Application of Human-Computer
Interface Based on User Experience,’ 2022 7th
International Conference on Intelligent Computing and
Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi'an, China, 2022, Pp.
1417-1420
Qiu, L.: ‘Application of Deep Learning-Based User Intent
Recognition in Human-Computer Interaction,’ 2024
5th International Conference on Intelligent Computing
and Human-Computer Interaction (ICHCI), Nanchang,
China, 2024, pp. 549-552
Wada, Y., Watanabe, Y., Syoubu, K., Sawamoto, J., and
Katoh, T.: ‘Virtual Database Technology for
Distributed Database,’ 2010 IEEE 24th International
Conference on Advanced Information Networking and
Applications Workshops, Perth, WA, Australia, 2010,
pp.214-219
Wang, H., and Gao, Z.: ‘Research on Personalized Service
Path of Learning Resources by Data Driven,’ 2022
International Symposium on Educational Technology
(ISET), Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2022, pp. 143-147
Wang, Y.: ‘Research on Scientific Research Management
System Based on Microservice Architecture’.
Electronic Engineering and Products World. 2024
Yanase, S., He, F., and Oki, E.: ‘Approximation Algorithms
to Distributed Server Allocation With Preventive Start-
Time Optimization Against Server A Failure’, IEEE
Networking in Letters, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 191-195, Dec.
2021
Zhang, J., Jing, S. Y., Linag, S.: ‘Research on personalized
learning resource recommendation model based on
Web log mining’. 2023 3rd International Conference on
Electronic Information Engineering and Computer
Communication (EIECC). 2023
Zhao, J. Y., Wu, J.: ‘Artificial Intelligence Empowering
Personalized Learning: The Path Analysis of K-12
Education Digitization in the United States’. Journal of
Comparative Education. 2025
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
54
