
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients
Binlu Yang
College of Computer Science and Technology, Hainan University, Haikou, China
Keywords: Epilepsy, Human-Computer Interaction, Brain-Computer Interface, Artificial Intelligence, Smart Wearable
Devices.
Abstract: Epilepsy is one of the most common chronic neurological disorders worldwide. Traditional drug therapies
have limited effectiveness for such patients and long-term use may lead to side effects such as cognitive
impairment and metabolic disorders. In addition, patients face unpredictable seizure risks, traditional nursing
methods have limitations in evaluation and treatment effect, there are many technical aspects of epilepsy
patients that can be optimized, and innovative technological breakthroughs are urgently needed to break
through the existing bottlenecks. This paper reviews the application of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs),
multimodal interaction technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), eye-tracking, and smart wearable devices in
epilepsy management. It also proposes future research directions, including multimodal data integration,
nanoscale brain-computer interface (BCI) development, patient-participatory design, and ethical privacy
protection. These innovations aim to enhance diagnostic accuracy, enable personalized treatment, and
improve daily monitoring for epilepsy patients, thereby boosting their quality of life and advancing the
medical field toward greater intelligence and precision.
1 INTRODUCTION
Epilepsy is a prevalent neurological disorder
affecting approximately 70 million people globally
(Zhao et al., 2020). It is a chronic condition with a
broad impact, recognized by the World Health
Organization as one of the five key neurological and
psychiatric diseases requiring global prevention and
control (Beghi et al., 2019). Patients face challenges
such as seizure-related quality of life issues, reliance
on technological devices, and device design
inadaptability. Advancements in smart devices and
technologies aim to improve patients' lives,
prompting extensive research into epilepsy-specific
human-computer interaction (HCI), particularly in
interface and modality design. BCIs offer closed-loop
neural regulation by decoding brain signals, such as
implantable systems that suppress abnormal
discharges and reduce seizure frequency, and non-
invasive devices like lightweight (1.7g) head-
mounted microscopes that monitor neural activity and
blood oxygen metabolism, capturing pre-ictal
neurovascular signals. The integration of BCIs,
multimodal interaction technologies, and AI provides
new avenues for epilepsy monitoring and
intervention. Multimodal technologies enhance
system adaptability and patient compliance by
combining visual, auditory, and tactile data. For
instance, eye-tracking combined with ear-worn
electroencephalography(EEG) devices enables home
seizure warnings with 99.8% accuracy. AI algorithms
play a key role in multimodal data analysis, predicting
drug responses and optimizing doses through EEG
and genomic data fusion. Additionally, optogenetics
and gene therapy (e.g., adeno-associated virus-
delivered neuropeptide Y) offer molecular-level
seizure control. Despite progress, challenges remain
in multimodal data integration, device
miniaturization, biocompatibility, and ethical and
privacy risks. Future research should focus on
interdisciplinary innovation, such as nano-flexible
electrode development for reduced tissue damage and
long-term BCI implantation, patient-involved design
for improved device comfort and interfaces, and
ethical frameworks for neural data usage regulation.
This paper analyzes existing work, its effects, and
shortcomings, explores the characteristics and needs
of epilepsy patients, and discusses emerging research
directions.
28
Yang, B.
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0014307100004718
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2025), pages 28-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-792-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
2 EXISTING WORK AND ITS
EFFECTS
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence
and machine learning, the collaboration between
computer and medical fields have become
increasingly prominent in epilepsy research (Li et al.,
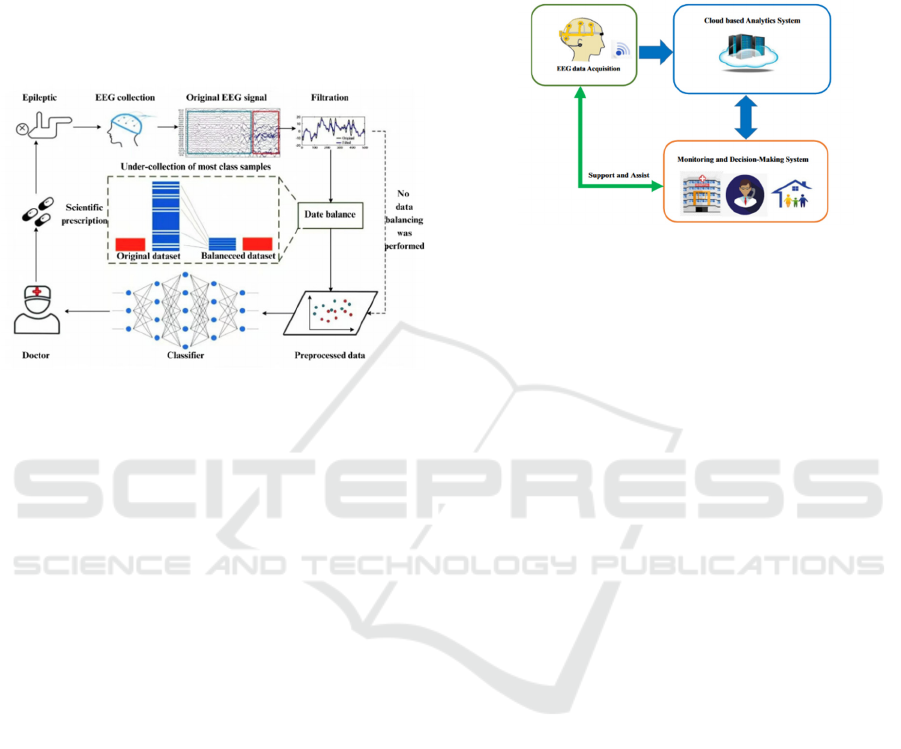
2024), as shown in figure 1.
Figure 1: Computer collaboration process (Li et al., 2024).
2.1 Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
BCI devices collect brain activity data, transmitting it
to computer terminals for decoding algorithm
research. BCIs are highly valuable for real-time
epilepsy monitoring, prediction, and intervention,
offering personalized treatment (Chen, 2025).
Clinical techniques include EEG, magnetic resonance
imaging(MRI), and PET-CT (Zhang, 2022).
Implantable or non-invasive BCI devices (e.g.,
cortical electrodes, EEG headsets) continuously
collect EEG data, using AI algorithms to identify pre-
ictal abnormal discharges. Some BCIs can provide
warnings minutes to hours before seizures, helping
patients take safety measures.
2.2 Multimodal Interaction Technology
This technology combines EEG, EMG
(electromyogram), visual, and auditory data sources
to comprehensively reflect patient behavior,
improving epilepsy monitoring accuracy and severity
assessment. It also aids diagnosis based on seizure
observation and etiology (NICE, 2022). Adaptive
PageRank algorithms assess brain region importance,
considering interactions between regions, while
multi-kernel strategies address data heterogeneity by
integrating connectivity and node information for
classification (Frontiers, 2021). The system
comprises three main modules: EEG data acquisition,
cloud-based analysis, and monitoring/decision
support. EEG data is collected, transmitted wirelessly
to the cloud for analysis using machine learning, and
results are fed back to support treatment planning and
home epilepsy management, as shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2: Basic components of the automatic seizure
detection system (Picture credit: Original).
Epileptic seizure physiological signals exhibit
spatiotemporal heterogeneity, making single-modal
data (e.g., EEG) susceptible to noise and insufficient
for comprehensive condition reflection. Multimodal
technology integrates EEG, EMG, motion sensors
(accelerometers, gyroscopes), visual behavior
analysis (cameras), and other physiological indicators
to build multidimensional feature models. For
example, combining EEG and motion analysis
enhances detection sensitivity for tonic-clonic
seizures to 100% through deep learning algorithms
like convolutional neural networks(CNN) and long
short-term memory networks(LSTM). Synchronized
monitoring of multiple physiological parameters,
such as skin conductance activity (EDA),
electrocardiogram (ECG), and EEG, captures
sympathetic nervous system excitement during
seizures, reducing missed detections (Ein Shoka et
al., 2023). Cross-modal alignment techniques, such as
ResizeNet networks, address cross-species EEG
signal differences and feature distribution shifts,
improving model generalization.
2.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in
Epilepsy Human-Computer
Interaction
AI algorithms play a crucial role in epilepsy
prediction, diagnosis, and rehabilitation. By
integrating EEG, ECG, and genomic data, they
construct personalized treatment models. Deep
learning models (e.g., CNN, LSTM) excel in EEG
signal analysis, identifying pre-ictal sharp waves with
98.72% sensitivity and 91.17% F1 score (Yu, 2021).
Transfer learning frameworks address inter-
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients
29
individual EEG differences, enhancing classification
performance. AI predicts drug responses and
optimizes doses, such as HCN1 channel-based
precision drug design. Google Health's AI model can
predict seizures an hour in advance with 85%
accuracy. AI also provides personalized treatment
plans by analyzing EHRs (electronic health records)
and multimodal data. Lin's team proposed a machine
learning-based prediction model for epilepsy patients
with cognitive impairment (Lin et al., 2021).
The suggested framework consists of three
collaborative stages:
Stage 1: IoT-based wearable medical sensors and
smartphones collect real-time data, connecting to
patients' EEG data collectors.
Stage 2: Cloud computing provides processing and
storage resources, receiving patient data via the
internet for classification and analysis. Abnormalities
are classified based on patient status, and results are
reported to healthcare providers, enabling early drug
intervention and real-time data updates.
Stage 3: Medical staff monitor patient records and
EEG data via cloud-based networks, review reports,
and take appropriate actions. BCI devices collect
brain activity data, transmitting it to computer
terminals for decoding algorithm research.
2.4 Eye-Tracking
Eye-tracking technology controls devices through eye
movement, offering precise input for epilepsy
patients unable to use hands or voice. Eye-trackers are
categorized into head-mounted and desktop types
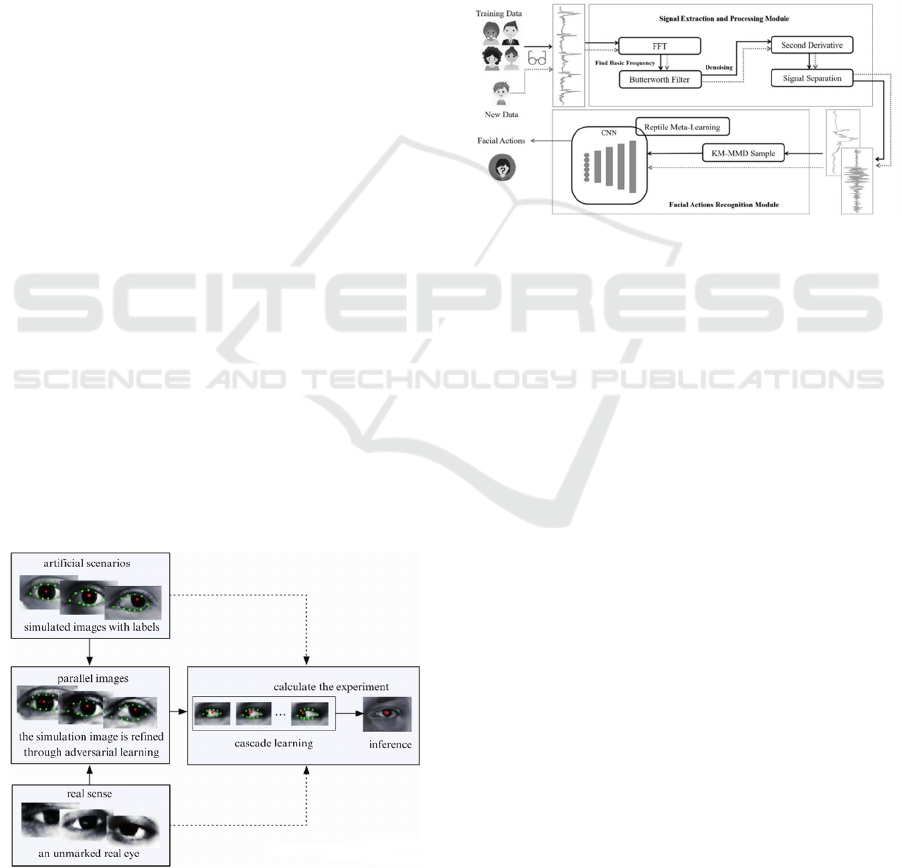
(Zhang, 2022), as shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3: Learning process of eye tracking (Zhang, 2022).
2.5 Smart Wearable Devices
Smart bands, watches, and other wearables record
physiological data like skin conductance,
temperature, pulse, and motion, using LSTM
networks to predict seizures. They provide real-time
monitoring and feedback for self-management. A
facial expression recognition system based on novel
flexible piezoresistive materials captures pressure
signals from facial muscle and skin deformation via
sensors in eyeglass legs, enabling emotion
classification (Zhang & Xing, 2025), as shown in Fig.
4.
Figure 4: The workflow of our system (Zhang & Xing,
2025).
3 SHORTCOMINGS OF
EXISTING TECHNOLOGIES
3.1 Challenges of BCI Systems in
Epilepsy Applications
The spatiotemporal complexity of epileptic
discharges demands high algorithm accuracy for
signal decoding. The imbalance between inter-ictal
and ictal EEG data leads to high accuracy for non-
seizure data but poor recognition of seizure data,
causing false positives and missed detections. Future
algorithms must improve minority sample
recognition (Wang & Zhang, 2022). This imbalance
makes classifiers prone to false positives and missed
detections in practical applications, affecting the
accuracy and reliability of epilepsy seizure
prediction. In the future, more efficient and robust
algorithms need to be designed to address this issue,
enhancing the ability to identify minority class
samples, thereby improving the precision and
reliability of epilepsy seizure prediction (Xiaohui et
al., 2024).
Long-term device stability is also an issue, with
implantable electrodes suffering signal attenuation
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
30

due to tissue encapsulation and non-invasive devices
being prone to motion artifacts. Moreover, individual
differences in seizure foci and types require highly
customized algorithms and stimulation parameters.
Pediatric patients' dynamically developing brains
further complicate BCI parameter adjustment,
necessitating personalized algorithms and timely
parameter updates.
3.2 Challenges in Multimodal Data
Fusion
Multimodal data heterogeneity is a significant
challenge. Differences in time resolution, spatial
features, and semantic associations across modalities
(e.g., EEG, MRI, ECG) complicate data fusion.
Ambiguous semantic links between genomic and
imaging data require complex algorithms, yet current
methods struggle to capture high-order heterogeneity,
risking information loss and poor fusion outcomes. In
clinical settings, modality missingness adaptation is
insufficient. Many multimodal systems rely on
complete data inputs, so missing key modalities due
to privacy, technical, or cost constraints degrades
system performance. This limits clinical application
and adversely affects diagnosis and treatment. Cross-
modal relationship modeling is further complicated
by difficulties in spatiotemporal alignment of
heterogeneous data. Existing algorithms often fail to
capture high-order associations between such data.
For example, structural and functional brain networks
provide different perspectives on epilepsy-related
structural changes, but common fusion models only
integrate information at a single granularity, ignoring
the multi-granular nature of brain networks and
leading to suboptimal fusion effects (Qi et al., 2024).
To address these challenges, researchers are
exploring new methods. For instance, the alternating
single-modal adaptation (MLA) method optimizes
each modality's encoder while integrating cross-
modal information to reduce interference and
enhance fusion performance. For modality
missingness, robust multimodal learning methods
like MoRA are being developed, which insert specific
modules to identify missing modalities and improve
model robustness under extreme missingness
conditions (Xiaohui et al., 2024).
3.3 Limitations of AI Epilepsy Early
Warning Systems
Real-time response delays and data bias/fairness
issues are two major challenges for AI in epilepsy
prediction. AI systems often rely on historical data for
predictions, which limits their ability to respond
dynamically to sudden epileptic events. For example,
epilepsy seizures are often sudden and unpredictable,
yet AI systems require time to process new data and
update models, potentially missing optimal
intervention timing. To enhance real-time
responsiveness, researchers are investigating new
algorithms and architectures, such as deep learning-
based real-time prediction models and edge
computing technologies to accelerate data processing.
Regarding data bias and fairness, training data is
often regionally and demographically skewed, with
most data originating from Western patients. This
results in reduced accuracy and applicability for
specific groups like children and ethnic minorities,
potentially exacerbating healthcare disparities. To
mitigate this, researchers recommend using more
representative datasets and developing adaptive
algorithms. Cross-institutional and international data
sharing can also help create more comprehensive and
balanced training datasets.
3.4 Impact of Different Environments
and Application Scenarios on
Eye-Tracking Effectiveness
Eye-tracking technology faces multiple challenges in
practical applications, including poor environmental
adaptability, insufficient real-time responsiveness,
and interference signals. Under complex
environmental conditions, such as low light or high
reflection, eye-tracking technology often
underperforms. In such cases, single-modal eye-
tracking data struggle to maintain system stability and
accuracy, necessitating multimodal data fusion
technology to enhance overall performance. By
integrating data from different modalities, such as
environmental sensor data or other biometric data, the
shortcomings of single-modal data can be effectively
addressed, improving the adaptability and robustness
of eye-tracking systems in complex environments.
The insufficient real-time responsiveness also
restricts the application of eye-tracking technology in
scenarios demanding high response speeds. For
instance, delays in eye-tracking can degrade user
experience and even pose safety risks in autonomous
driving or real-time interaction systems.
Interference signals are another significant
challenge for eye-tracking technology. Physiological
phenomena like eye jitter and blinking can cause data
interruptions or misjudgments, affecting system
accuracy and reliability. To tackle this issue,
researchers are developing advanced signal
processing algorithms to identify and filter out
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients
31

interference signals. Additionally, improving the
design of eye-tracking devices, such as using more
precise sensors and optimized optical systems, can
help reduce the impact of interference signals.
3.5 Hierarchical Security Protection
and Attack Path Analysis of
Wearable Devices
Missed detection of focal and non-motor seizures,
edge computing bottlenecks, and digital security risks
are key challenges for wearable devices in epilepsy
monitoring.
Wearable devices (e.g., wristbands) are highly
sensitive to tonic-clonic seizures, achieving 100%
detection accuracy when combining EEG and ECG,
but have low recognition rates for complex partial or
absence seizures, with missed detection rates
exceeding 50%. Focal autonomic seizures or absence
seizures lack significant physiological or motor
features, making them hard to detect. Existing devices
are less effective for these seizure types.
Edge computing bottlenecks constrain device
performance. High-precision AI models (e.g.,
Transformers) consume significant power on
wearables, creating a trade-off between performance
and battery life. Researchers are exploring efficient
algorithms and hardware optimizations to reduce
energy consumption and enhance computational
efficiency.
Digital security risks are a concern. Wearable
devices require layered protection from hardware to
application levels. Threats penetrating network
boundaries can compromise hardware and system
layers, jeopardizing application service and data
security. This may lead to digital asset risks and
potential post-attack denial by attackers (Zhao et al.,
2024). Device manufacturers need to strengthen
security measures, such as advanced encryption,
regular security patches, and user education.
4 CHARACTERISTICS AND
NEEDS OF EPILEPSY
PATIENTS
4.1 Disease Characteristics
Epilepsy patients face multiple challenges: seizures
are sudden and unpredictable, with irregular
occurrence and duration, potentially causing transient
loss of consciousness, motor control, or sensory
impairments. This increases the risk and difficulty of
using electronic devices. For instance, patients may
lose control during seizures or be unable to recall
operations afterward. Epilepsy is chronic and
recurrent, requiring lifelong management. About 30%
of patients develop drug-resistant epilepsy,
necessitating surgical or neuromodulation options.
Epileptic symptoms are diverse, including
generalized convulsions and brief loss of
consciousness, with varying impacts on daily life.
4.2 Physical and Cognitive Effects
Epileptic seizures pose significant physical injury
risks, such as falls and suffocation, potentially leading
to fractures or traumatic brain injuries. Frequent
seizures or medication side effects often result in
memory decline and attention deficits, particularly in
children. world health organization (WHO) data
indicates that 40%-60% of epilepsy patients
experience anxiety or depression, facing substantial
psychological and social pressures. Stigma and
psychological burdens lead many to conceal their
condition, while school and workplace discrimination
create additional challenges.
4.3 Core Needs of Epilepsy Patients
The needs of epilepsy patients stem from disease
characteristics and social biases. A comprehensive
support system covering "prevention-treatment-
integration" is required.
Epilepsy management must be multidimensional.
Precision medical support is essential, starting with
early diagnosis and correct classification.
Individualized treatment plans should be developed,
with drug-resistant patients trying alternative
therapies like neurostimulation or the ketogenic diet.
Treatment plans should be dynamically adjusted. For
safety and emergency care, patient environments
should be safety-adapted, and scientific first aid
knowledge should be promoted. Special groups have
unique needs: children require cognitive
rehabilitation and personalized educational support
(e.g., Cambridge University's "EpiSchool" AI
platform for customized learning paths); women of
childbearing age need pregnancy medication
guidance and genetic risk counseling; elderly
patients, often with multiple comorbidities, require
hospital-based comorbidity management and family
monitoring with home safety modifications.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
32

5 DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
5.1 Multimodal Interaction in Home
and Medical Settings
5.1.1 Multimodal Data Integration
Real-time monitoring data from EEG, ECG, EMG,
and wearables (smart bands/clothing). Cameras
capture limb movements, and voice interactions are
recorded. Environmental data such as temperature,
humidity, and intensity of illumination in homes and
public places are also collected. Integrating these data
sources creates a comprehensive patient data profile
throughout the life cycle.
5.1.2 Subjective Feedback
Voice diaries and emotion recognition (via NLP to
detect anxiety/depression) from patients and families.
Combined with genetic data, medication history, and
multimodal monitoring results, dynamic medication
suggestions (e.g., dosage adjustment or drug
switching) are generated. Timely medication
reminders, sleep advice, and seizure trigger
avoidance (e.g., staying up late, strong light
stimulation) are provided to help patients establish
regular routines. Disease causes, first aid measures,
and treatment progress are explained in layman's
terms to alleviate patients' fears stemming from
misunderstandings.
5.1.3 Smart Home Integration
During a seizure, AI systems recognize falling
motions via cameras, automatically shutting off gas,
dimming lights, and activating emergency calls.
Smart home devices provide vibration or voice
prompts to patients ("You are about to erupt. Please
sit down ") and send location information to family
members.
5.2 Emerging Research Directions
5.2.1 Multisensor Fusion for Early Warning
Devices integrate motion sensors (detecting abnormal
convulsions), skin conductance sensors (monitoring
stress levels), and microphones (identifying abnormal
breathing sounds). Edge computing enables real-time
analysis and alarm triggering. Upon detecting
abnormal EEG signals, emergency procedures are
initiated, contacting emergency contacts or medical
institutions automatically. Seizure times and
symptoms are recorded for doctors' reference.
5.2.2 AR/VR + Dialogue Robots for
Rehabilitation Training
AR simulates high-risk scenarios (e.g., crossing
roads) to train patients in self-protection actions upon
recognizing premonitory symptoms. VR provides
relaxing environments to alleviate anxiety (e.g.,
meditation forests) and simulates social interactions
to boost patients' confidence and social engagement.
5.2.3 Doctor-Patient Remote Collaboration
Patients can film seizure videos with their
smartphones. AI automatically marks key frames
(e.g., tonic-clonic phases), enabling doctors to
diagnose quickly combining voice descriptions. This
is applicable for emergency handling and daily
monitoring, reducing safety risks for patients going
out alone and saving time for both doctors and
patients. It also provides more convenient and
equitable medical support for remote patients.
5.2.4 Nano-BCI
Nano-particles or flexible electronics enable non-
invasive, high-precision monitoring, reducing the
immunoreaction to implantable BCIs and increasing
patient acceptance.
5.2.5 Brain-Cloud Interface
Epilepsy patients can upload EEG data to the cloud in
real-time. After verification, the system synchronizes
data to doctors' platforms. Qualified physicians can
access and analyze global patient data online for
monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment.
5.3 Patient-Centered Design
Epilepsy can cause cognitive impairments and
tendencies toward depression and anxiety. It is crucial
not only to enhance technologies for predicting and
diagnosing epilepsy but also to monitor patients'
emotions in real-time to prevent worsening
conditions or impulsive negative behaviors.
Automatically adjusting interaction methods and
feedback based on patients' physiological and
psychological characteristics to provide customized
user experiences represents a future research
challenge.
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients
33

5.3.1 Emotion Recognition and Guidance
Natural Language Processing (NLP) analyzes
anxiety, depression, or loneliness in patients' speech,
offering immediate comfort such as guided
mindfulness exercises, relaxation techniques, or
referrals to professional psychological resources. It is
necessary to train models to distinguish between
pathological and psychological emotional changes to
avoid misjudgments. For patients with social
limitations due to their condition, robots can reduce
loneliness through daily conversations and encourage
emotional expression.
5.3.2 Personalized Adaptation
Customize dialogue content based on patients' age,
severity, and cultural background. Combine voice,
text, and visual interfaces (e.g., animated breathing
guidance) to accommodate different communication
preferences. Incorporate patient feedback during
development to optimize interface and functionality
adaptation.
5.3.3 Affective Computing and AI
Companionship
Voice emotion recognition (e.g., tone, speed) and
facial expression analysis enable AI chatbots to
provide real-time psychological support. Combined
with soothing music, dynamic lighting, and tactile
feedback (e.g., pressure blankets), anxiety levels can
be reduced.
5.4 Ethics and Privacy Protection
Given the global nature of epilepsy patients, data
encryption standards (e.g., EU AI Act) should be
established to build cross-cultural ethical consensus.
5.4.1 Privacy Protection
Encrypt storage of patient health data (e.g., seizure
records, medication information) and biometric data
(e.g., EEG) to comply with medical data regulations
(e.g., HIPAA, GDPR). Studies indicate that EEG
signals collected under identical stimuli can identify
individuals with near 100% accuracy. Leaked
biometric information from such stimuli can still
identify individuals (Ruiz-Blondet et al., 2016). At
the 2012 USENIX Security Symposium, Professor
Ivan Martinovic from Oxford University introduced
"brain spyware" that collects BCI data to steal
information such as addresses, birthdates, credit card
numbers, and acquaintances by analyzing users'
visual stimulation responses (Martinovic et al., 2012).
Hackers may alter BCI data to manipulate external
devices for illegal purposesErro! A origem da
referência não foi encontrada. (Chen, 2025).
5.4.2 Liability Boundaries
Clearly define robots as auxiliary tools, not
substitutes for professional medical advice.This
fundamental distinction is critical to ensuring patient
safety and maintaining the integrity of medical
practice. To underscore this, explicit and prominent
risk warnings must be incorporated into the
operational protocols and user interfaces of these
robotic systems. For instance, a warning such as “In
the event of any discomfort or unwell symptoms,
contact a doctor immediately” should be readily
accessible and visible to users at all times (Schermer,
2009). Such warnings aim to prevent users from over
- relying on the robotic systems and neglecting the
necessity of professional medical diagnosis and
intervention when necessary.
5.4.3 Cultural Sensitivity
Avoid misunderstandings due to cultural differences
(e.g., epilepsy stigmatization in some regions) by
designing inclusive dialogue logic. Cultural
differences can significantly influence how health
conditions are perceived, discussed, and addressed.
For example, in some regions, epilepsy may be
stigmatized due to traditional beliefs, myths, or lack
of awareness about its true nature as a neurological
disorder. Such stigmatization can affect patients'
willingness to seek help, adhere to treatment, and
discuss their condition openly. To address these
challenges, it is crucial to design inclusive dialogue
logic within healthcare technologies. This involves a
thorough understanding of diverse cultural
perspectives, values, and beliefs related to health and
illness. By incorporating this understanding into the
design of conversational interfaces, people can create
more empathetic, appropriate, and effective
interactions that respect cultural differences. By
prioritizing cultural sensitivity in the design of
healthcare technology dialogue logic, people can
reduce the risk of misunderstandings, enhance patient
trust, and improve the overall effectiveness of
healthcare interactions, ultimately contributing to
more equitable and accessible healthcare for diverse
populations.
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
34

5.4.4 Fairness and Inclusiveness
Advocate for the inclusion of advanced devices (e.g.,
BCIs) in medical insurance to reduce the burden on
low-income families. Expand rural coverage through
telemedicine. Prevent predictive failures for specific
groups (e.g., children or ethnic minorities) due to
training data biases.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper systematically reviews the current state,
applications, and future directions of human-
computer interaction technologies for epilepsy
patients. It examines challenges faced by epilepsy
patients, including seizure unpredictability and
limitations of traditional care. It also reviews the
applications and limitations of BCIs, multimodal
interaction technologies, AI, eye-tracking, and smart
wearables in epilepsy monitoring, warning, and
intervention. Furthermore, it proposes future research
directions, including multimodal data integration,
nano-BCI development, patient-centered design, and
ethical and privacy protection. By integrating
technology and humanistic concern, it aims to
establish a comprehensive epilepsy management
ecosystem covering monitoring, intervention, and
feedback, providing full-cycle health management for
patients.
BCIs, multimodal interaction technologies, and
AI offer a transformative path from "passive control"
to "active intervention" in epilepsy treatment,
enhancing monitoring accuracy and intervention
timeliness. However, clinical application challenges
persist, including multimodal data fusion complexity,
device long-term stability, real-time response delays,
and ethical and privacy risks. Human-computer
interaction technologies in epilepsy prediction still
face challenges such as real-time response delays and
data bias/fairness issues. Overcoming these requires
technological innovations like more efficient
algorithms and architectures, as well as social and
policy support, including data sharing and fairness
standard development. With advancements in brain
science and AI, the future promises a safer, more
precise, and inclusive epilepsy management system,
achieving comprehensive support for "prevention-
treatment-integration."
REFERENCES
Beghi, E., Giussani, G., Nichols, E., et al.: 'Global, regional,
and national burden of epilepsy,1990 2016: a
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease
Study 2016', The Lancet Neurology, 2019, 18(4): 357-
375
Chen, T. L.: 'Research on the Use and Protection of Brain-
Computer Interface Data', Journal of Xichang College
(Social Science Edition), 1-11, 2025
Ein Shoka, A.A., Dessouky, M.M., El-Sayed, A., et al.:
'EEG seizure detection: concepts, techniques,
challenges, and future trends', Multimed Tools Appl,
82, 42021-42051, 2023
Frontiers in Neuroscience.: ‘Epilepsy Detection and
Recognition Based on Multimodal Signals’. (IF 3.2)
Pub Date: 2021-09-29
Li, Q., Li, P.F., D., Zhao, Z., et al.: 'An Epileptic EEG
Imbalanced Classification Method Combining
Reinforcement Learning with Swarm Intelligence
Algorithms', Journal of Chongqing University of
Technology (Natural Science), 2024, 38(12): 110-123
Lin, F., Han, J., Xue, T., et al.: 'Predicting cognitive
impairment in outpatients with epilepsy using machine
learning techniques', Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1):
20002
Martinovic, I., Davies, D., Frank, M., et al.: 'On the
feasibility of Side-Channel attacks with Brain-
Computer interfaces', 21st USENIX Security
Symposium (USENIX Security 12), 2012: 143-158
NICE guideline[NG217].Epilepsies in children, young
people and adults[EB/OL](27 April 2022)[9 May
2022].https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng217.
Qi, X. Y., Ding, W. P., Ju, H. R.: 'Seizure recognition
method based on multimodal multi-grain fusion
network', Data Acquisition and Processing, 2024,
39(3): 710-723
Ruiz-Blondet, M.V., Jin, Z., Laszlo, S.: 'CEREBRE: A
novel method for very high accuracy event-related
potential biometric identification', IEEE Transactions
on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(7):
1618-1629
Schermer, M.: 'The mind and the machine: on the
conceptual and moral implications of brain-machine
interaction', Nanoethics, 2009, 3(3): 217-230
Wang, Y., Zhang, L.: 'A novel clustering-based exploratory
SMOTE algorithm', Journal of Chongqing University
of Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 36(04): 187-
195
Xiaohui, Z., Jaehong, Y., Mohit, B.: 'Multimodal
Representation Learning by Alternating Unimodal
Adaptation' arXiv:2311.10707. 2024
Yu, Y. J.: ‘Intelligent Epilepsy Detection and Recognition
Based on Multimodal Signals’. Hangzhou Dianzi
University. 2021
Zhang, H.Y.: 'Research on Eye Movement Signal
Processing and Classification Algorithms for Cognitive
Tasks in Epileptic Patients', University of Chinese
Academy of Sciences (Xi'an Institute of Optics,
Computer Interaction Methods and Modes for Epilepsy Patients
35

Precision Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of
Sciences), 2022
Zhang, J., Xing, X.: 'Smart Glasses Facial Action
Recognition System Using Improved Meta-Learning
Network', Microcomputer Information, 1-10, 2025
Zhao, G., Zheng, Y., Tao, Z. L.: 'System risk assessment
analysis for intelligent wearable devices', Information
Security for Computer Networks, 2024, 24(10): 1595-
1603
Zhao, J., Zhao, D., Shi, L., et al.: 'Multilayer weighted
integrated self-learning algorithm for automatic
diagnosis of epileptic electroencephalogram signals',
Computational Intelligence, 2020, 38(1): 3-19
EMITI 2025 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
36
