
Multimodal EEG Seizure Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning
Siyu Chen
Leeds Joint School, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China
Keywords: Multimodal EEG, Seizure Prediction, Deep Learning.
Abstract: Epileptic seizure prediction has become a critical area of research due to its vital role in ensuring patient safety
and improving quality of life. Electroencephalography (EEG), as a non-invasive tool with high temporal
resolution, is significant in monitoring seizures. However, traditional EEG-based methods are constrained by
the complexity of signals and the reliance on manual feature extraction, limiting their accuracy and scalability.
The advent of deep learning has introduced automated feature extraction and end-to-end learning,
significantly enhancing seizure prediction capabilities. Nonetheless, single-modality EEG approaches often
fail to capture the diverse physiological changes associated with seizures. Multimodal methods have emerged
to address this limitation. These methods integrate EEG with other physiological signals, such as
electrocardiograms (ECG) and electrodermal activity (EDA), offering improved accuracy. This paper
provides a systematic review of deep learning-based multimodal seizure prediction methods. It discusses the
role of EEG and advances in deep learning, highlights the advantages of multimodal approaches in integrating
multiple signals, and examines challenges such as data synchronization, computational efficiency, and
practical deployment. The findings demonstrate the transformative potential of multimodal deep learning
frameworks in achieving accurate real-time seizure prediction. Through comprehensive analysis, this research
provides valuable insights for developing scalable seizure detection systems, thereby advancing both clinical
practice and real-world applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, EEG has emerged as a critical tool for
the monitoring and diagnosis of brain disorders due
to its high temporal resolution and ability to directly
measure electrical activity in the brain. EEG signals,
which are primarily generated by the synchronized
activity of cortical neurons, provide valuable insights
into brain function, particularly in understanding
epileptic seizures (Müller-Putz, 2020). Epileptic
seizures result from abnormal, excessive electrical
discharges in specific regions of the brain, and EEG
is particularly effective in capturing these events. As
reported by the World Health Organization (WHO),
approximately 50 million individuals globally suffer
from epilepsy, making it one of the most common and
impactful neurological disorders (Ein Shoka et al.,
2023). Despite its importance, traditional seizure
detection methods based on manual feature extraction
face significant challenges due to the inherent
complexity and variability of EEG signals, as well as
the reliance on expert knowledge for signal
interpretation (Boonyakitanont et al., 2020).
Consequently, there has been a growing interest in
automating seizure detection and prediction using
advanced computational techniques.
The advent of deep learning has significantly
advanced EEG signal analysis by automating feature
extraction and enabling end-to-end learning from raw
data. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and
recurrent neural networks (RNNs), as powerful deep
learning models, excel in modeling spatial and
temporal dependencies in EEG signals for seizure
prediction tasks (Dissanayake et al., 2021). However,
single-modality EEG analysis is often limited in
capturing the full range of physiological changes that
occur during seizures, as they are multifaceted events
that may involve other physiological signals, such as
ECG, electrodermal activity, and accelerometer data.
Recent research has shifted towards multimodal
approaches that integrate multiple signal types,
thereby enhancing seizure prediction accuracy
through complementary information.
This paper presents a comprehensive review of
deep learning-based multimodal EEG seizure
10
Chen, S.
Multimodal EEG Seizure Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0014299200004933
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Food Science (BEFS 2025), pages 10-15
ISBN: 978-989-758-789-4
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
prediction methodologies. It emphasizes the
integration of EEG with complementary
physiological signals to capture a more
comprehensive range of features, thereby enhancing
the accuracy of seizure prediction systems. The
review examines recent deep learning architectures
designed for multimodal signal fusion, critically
analyzing their strengths and limitations.
Additionally, it explores practical aspects of
deploying these systems in real-time applications,
focusing on wearable devices for continuous seizure
monitoring. The paper also outlines key challenges,
such as the need for more scalable models, the
importance of high-quality and diverse datasets, and
the difficulties inherent in the real-world
implementation of multimodal systems.
2 MULTIMODAL EEG SEIZURE
PREDICTION METHOD
EEG signals are electrophysiological recordings that
reflect the electrical activity of the brain and are
widely utilized in epilepsy research and management
due to their high temporal resolution and direct
representation of brain activity (Boonyakitanont et
al., 2020). EEG signal analysis typically involves
extracting features from the time domain, frequency
domain, and nonlinear features (Daoud and Bayoumi,
2019). Time-domain features are derived from raw or
pre-processed EEG signals and capture spike
morphology and amplitude variations. Frequency-
domain features, obtained through the discrete
Fourier transform, provide insights into the power
spectral density of specific frequency bands
(Boonyakitanont et al., 2020). Nonlinear features
combine temporal and spectral information, offering
a more comprehensive representation of transient
brain activities (Boonyakitanont et al., 2020). These
features form the backbone of EEG-based seizure
prediction frameworks, enabling models to
characterize the complex spatiotemporal dynamics of
the brain.
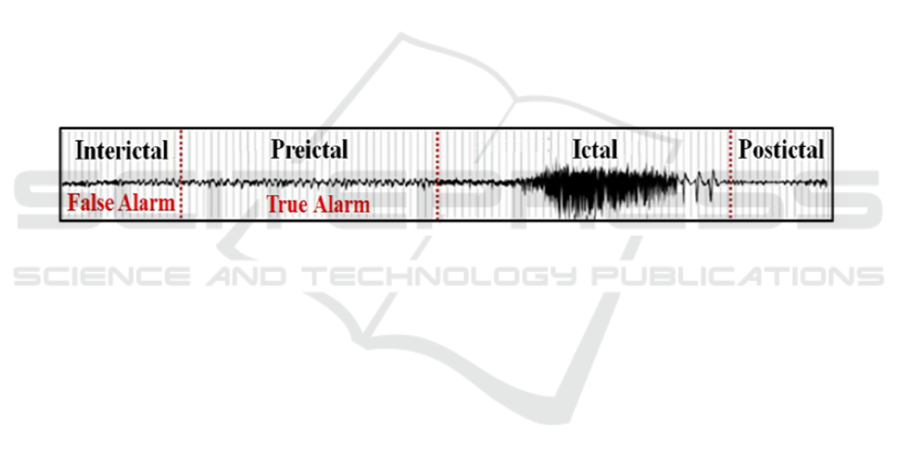
Figure 1: Brain States in a Typical Epileptic EEG Recording (Daoud and Bayoumi, 2019).
Epileptic seizures are associated with distinct
changes in brain activity, which can be observed in
EEG signals. As shown in Figure 1, EEG signals of
epileptic patients are categorized into four major
brain states: Preictal, Ictal, Postictal, and Interictal.
Among these, the Preictal state, which occurs
immediately before seizure onset, is the most critical
for seizure prediction (Daoud and Bayoumi, 2019).
Early detection of this state allows for timely
intervention, significantly improving patient safety
and quality of life.
Given the time-consuming nature and low
accuracy of manual EEG detection, deep learning-
based methods for epilepsy prediction have emerged
as a preferred approach. Traditional seizure
prediction approaches rely on manually engineered
features and machine learning classifiers, such as
support vector machines (SVMs) or random forests,
which separate feature extraction and classification
stages (Daoud and Bayoumi, 2019). However, these
methods are limited by their dependence on
handcrafted features, often failing to capture the
complexity and variability of EEG signals.
Deep learning models overcome these limitations
by automating feature extraction and enbling end-to-
end learning from raw EEG data. CNNs effectively
model spatial patterns, while RNNs capture temporal
dependencies, making them particularly suited for
EEG analysis (Dissanayake et al., 2021). By
integrating time, frequency, and time-frequency
features, deep learning models eliminate the need for
manual feature engineering, offering more accurate
solutions to the inherent challenges of EEG signal
variability in seizure prediction. Recent research has
expanded beyond EEG-based models to integrate
multimodal data, addressing the limitations of single-
modality analysis in deep learning approaches.
Multimodal approaches involve combining various
types of signal data to capture complementary
information from different sources. In epilepsy
detection and prediction, multimodal methods
integrate signals such as EEG, ECG, accelerometers
Multimodal EEG Seizure Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning
11
(ACM), and EDA to comprehensively analyze
physiological and behavioral features (Chen et al.,
2022). Multimodal methods provide more accurate
detection and prediction than unimodal approaches
by analyzing multiple physiological systems affected
during seizure events (Chen et al., 2022).
The evolution of multimodal approaches in seizure
detection and prediction highlights the continuous
refinement of methods from static analyses to
dynamic, real-time applications and advanced deep
learning frameworks. Early work by Memarian et al.
established the foundation for integrating multimodal
data in epilepsy studies by combining EEG, structural
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and clinical
features to predict surgical outcomes in mesial
temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) (Memarian et al.,
2015). Using traditional machine learning techniques,
such as Least Square Support Vector Machines (LS-
SVM) and maximum relevance minimum
redundancy (mRMR) for feature selection, the study
achieved an impressive prediction accuracy of 95%
(Memarian et al., 2015). This work demonstrated two
key findings: the potential of leveraging
complementary data sources and the identification of
crucial predictors like ictal EEG onset patterns and
gray matter thickness reductions. However, it also
highlighted limitations inherent to traditional
methods, including a reliance on handcrafted features
and offline static analyses, which limit scalability to
real-time and dynamic applications (Memarian et al.,
2015).
Building on this foundation, Chen et al. extended
the application of multimodal methods to wearable
and portable technologies, enabling real-time seizure
detection and prediction. As illustrated in Figure 2,
their framework effectively combined EEG with non-
electrophysiological signals including ECG, ACM,
and EDA to capture the multisystem physiological
changes associated with seizures. The system features
a channel-aware module that dynamically selects
relevant signal channels, reducing noise and focusing
on critical information, while short-time Fourier
transform (STFT) is used for feature extraction to
convert raw signals into time-frequency
representations (Chen et al., 2022). This design
automates the process of multimodal signal
integration through deep learning. Testing on the
CHB-MIT dataset demonstrated that combining EEG
and ECG signals achieved over 90% sensitivity, far
outperforming unimodal approaches (Chen et al.,
2022). This study addressed the practicality of
applying multimodal systems in real-world contexts
while also highlighting challenges such as signal
alignment, computational complexity, and hardware
limitations in wearable devices (Chen et al., 2022).
Figure 2: Multimodal Real-Time Seizure Detection
Framework Integrating EEG and Peripheral Physiological
Signals (Chen et al., 2022).
Recent advances in multimodal methods have been
exemplified by Ilias et al., who proposed a state-of-
the-art end-to-end deep learning framework to further
optimize multimodal seizure detection. Their
architecture integrated raw EEG signals and their
STFT spectrogram representations through dual
feature extraction pathways. The framework
consisted of two pathways: a CNN-based pathway for
temporal and frequency feature extraction from raw
EEG, and a pretrained EfficientNet-B7 pathway for
spectrogram image analysis (Ilias and Psarras, 2023).
A Gated Multimodal Unit was introduced to
dynamically assign weights to each modality,
suppressing irrelevant information and enhancing
BEFS 2025 - International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Food Science
12
fusion. This novel framework eliminated the need for
handcrafted features and achieved an accuracy of
97% on the University of Bonn EEG dataset,
surpassing previous methods. By demonstrating the
effectiveness of multimodal end-to-end solutions, this
study marked a significant milestone in seizure
prediction research, particularly in overcoming
information redundancy and improving detection
robustness.
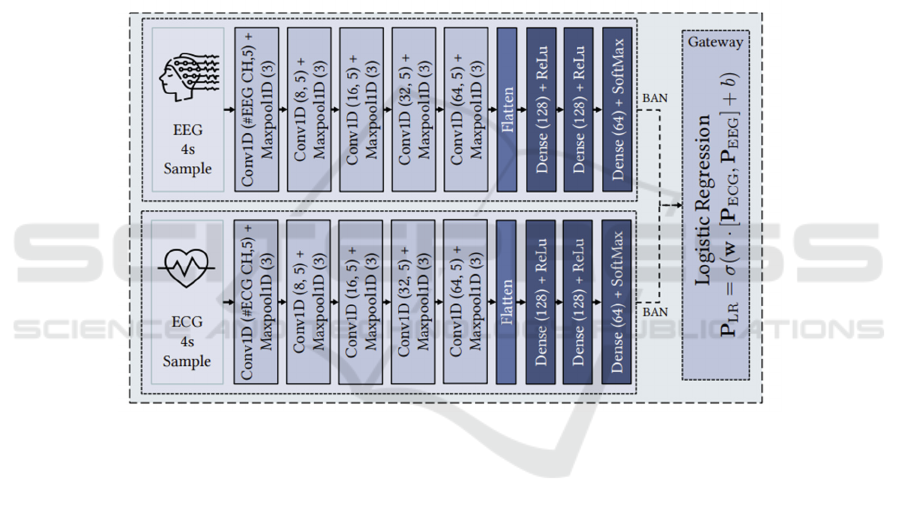
Expanding on the use of multimodal signals for
real-time seizure prediction, Saeizadeh et al.
proposed a progressive prediction framework
combining EEG and ECG signals. The system, as
illustrated in Figure 3, employs a 1D-CNN
architecture for feature extraction followed by
logistic regression techniques to achieve optimal
signal fusion. Unlike prior studies focusing solely on
real-time detection, this framework introduces
progressive prediction, providing seizure warnings at
15-minute intervals, with up to 1-hour anticipation
(Hosseini et al., 2020). This approach addresses
challenges in real-time multimodal integration by
optimizing computational efficiency and leveraging a
low-power body area network. Additionally, their
combiner model mitigates data imbalance issues by
weighting predictions from individual modalities
dynamically (Hosseini et al., 2020). This work
demonstrates the feasibility of integrating multimodal
deep learning frameworks into wearable devices
while highlighting key challenges in real-world
deployment.
Figure 3: Deep Learning Model and Prediction System Structure (Hosseini et al., 2020).
In addition to advancements in dynamic detection,
multimodal approaches have also been explored in
more complex medical imaging contexts, as
demonstrated by (Hosseini et al., 2020). To analyze
functional connectivity within epileptic networks and
localize seizure foci, their study integrated EEG data
with resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI)
(Saeizadeh et al., 2024). By leveraging CNNs for
EEG feature extraction and Long Short-Term
Memory networks (LSTMs) for integrating spatial
and temporal features, the framework provided a
solution for combining high temporal resolution from
EEG and spatial information from rs-fMRI
(Saeizadeh et al., 2024). Furthermore, the integration
of an edge computing framework allowed for reduced
latency and enhanced real-time capabilities. Tested
on clinical datasets, this approach achieved high
accuracy (98%) and sensitivity (96%) in predicting
seizures and localizing epileptogenic zones
(Saeizadeh et al., 2024). While the study focused
more on the clinical application of multimodal
systems for brain network analysis, it highlighted the
scalability of multimodal methods in addressing both
diagnostic and predictive challenges in epilepsy
research.
Multimodal seizure prediction has evolved
significantly, progressing from static analysis to real-
time and wearable applications by integrating diverse
signals and optimizing deep learning frameworks.
However, several limitations and challenges remain.
The synchronization and alignment of multimodal
data, particularly with signals of varying temporal
Multimodal EEG Seizure Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning
13

and spatial resolutions, pose significant difficulties
(Chen et al., 2022) (Saeizadeh et al., 2024). Real-time
processing requires substantial computational
resources, which can hinder the scalability of such
systems, especially in low-power wearable devices
(Chen et al., 2022) (Hosseini et al., 2020).
Additionally, data imbalance and the scarcity of high-
quality, labeled multimodal datasets complicate
model training and generalization (Hosseini et al.,
2020). Despite their powerful capabilities, deep
learning models face limited clinical acceptance due
to their lack of interpretability (Hosseini et al., 2020)
(Saeizadeh et al., 2024).
Furthermore, the transition from research to
clinical application demands user-friendly systems
that integrate seamlessly into medical workflows
while addressing patient compliance and ethical
concerns (Chen et al., 2022) (Saeizadeh et al., 2024).
Overcoming these limitations represents a critical
step toward realizing the full potential of deep
learning-based multimodal seizure prediction
systems in clinical applications.
3 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the integration of deep learning with
multimodal data has made significant advancements
in epileptic seizure prediction, improving both the
accuracy and real-time detection capabilities. By
combining EEG with physiological signals like ECG,
ACM, and EDA, recent approaches have successfully
automated feature extraction, eliminating the need for
manual engineering. This progress has led to more
comprehensive systems capable of capturing
complex physiological interactions and offering
enhanced prediction accuracy.
The transition from conventional, static analysis to
dynamic, real-time applications signifies a substantial
shift in the deployment of seizure prediction systems.
This transition directly improves patient care through
wearable technologies, enabling continuous
monitoring and rapid interventions. These systems
are becoming increasingly practical and accessible.
The real-time insights they provide markedly enhance
patient safety through early detection, a critical
component of effective seizure management.
However, challenges persist, including the
alignment of multimodal data, the efficiency of real-
time processing, and the necessity for high-quality
labelled datasets. Future research directions should
focus on three key areas: improving data alignment,
reducing model complexity, and enhancing system
scalability for wearable devices. Additionally, the
interpretability of deep learning models must be
addressed to facilitate clinical adoption. The
continued evolution of multimodal approaches and
deep learning techniques points toward the
development of more personalised, efficient, and
reliable seizure prediction systems. These
advancements will revolutionize epilepsy
management through proactive interventions and
personalized care strategies.
REFERENCES
Boonyakitanont, P., Lek-uthai, A., Chomtho, K., &
Songsiri, J. 2020. A review of feature extraction and
performance evaluation in epileptic seizure detection
using EEG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control
57:101702.
Chen, F., Chen, I., Zafar, M., Sinha, S. R., & Hu, X. 2022.
Seizures detection using multimodal signals: a scoping
review. Physiological Measurement 43(7):07TR01.
Daoud, H., & Bayoumi, M. A. 2019. Efficient epileptic
seizure prediction based on deep learning. IEEE
Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems
13(5):804–813.
Dissanayake, T., Fernando, T., Denman, S., Sridharan, S.,
& Fookes, C. 2021. Deep learning for patient-
independent epileptic seizure prediction using scalp
EEG signals. IEEE Sensors Journal 21(7):9377–9388.
Ein-Shoka, A. A., Dessouky, M. M., El-Sayed, A., &
Hemdan, E. E.-D. 2023. EEG seizure detection:
concepts, techniques, challenges, and future trends.
Multimedia Tools and Applications 82(27):42021–
42051.
Hosseini, M.-P., Tran, T. X., Pompili, D., Elisevich, K., &
Soltanian-Zadeh, H. 2020. Multimodal data analysis of
epileptic EEG and rs-fMRI via deep learning and edge
computing. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
104:101813.
Ilias, L., Askounis, D., & Psarras, J. 2023. Multimodal
detection of epilepsy with deep neural networks. Expert
Systems with Applications 213:119010.
Memarian, N., Kim, S., Dewar, S., Engel, J., & Staba, R. J.
2015. Multimodal data and machine learning for
surgery outcome prediction in complicated cases of
mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Computers in Biology
and Medicine 64:67–78.
Müller-Putz, G. R. 2020. Electroencephalography.
Handbook of Clinical Neurology 168:249–262.
Saeizadeh, A., Schonholtz, D., Neimat, J. S., Johari, P., &
Melodia, T. 2024. A multi-modal non-invasive deep
learning framework for progressive prediction of
BEFS 2025 - International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Food Science
14

seizures. IEEE 20th International Conference on Body
Sensor Networks (BSN):1–4.
Multimodal EEG Seizure Prediction Method Based on Deep Learning
15
