
How 6G Will Transform Augmented and Virtual Reality in
Healthcare, Education, and Entertainment: Opportunities and
Challenges
Muhammad Irawan Agung and Zulkifli Tahir
Department of Informatics, Hasanuddin University, Indonesia
Keywords: 6G, Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality, Latency, High-Speed Connectivity.
Abstract: The Advent of 6G technology is poised to revolutionize several industries, particularly healthcare, education,
and entertainment, through the enhancement of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
applications. With its increased data transfer speeds, ultra-low latency, and expanded network capacity, 6G
promises to deliver more immersive and real-time AR/VR experiences. In healthcare, 6G can enable advance
applications like remote diagnosis and therapy via VR-based telemedicine and real-time patient monitoring
through AR. In education, it will create more engaging interactive virtual learning environments, allowing for
highly personalized experience through AR/VR simulations. Meanwhile, in entertainment, 6G will redefine
how users engage with digital content, offering more immersive and collaborative experience through the
metaverse and VR-based games. However, realizing this potential come with challenges, including the need
for robust infrastructure, ensuring data privacy and security, and addressing the hardware limitations required
to support such sophisticated AR/VR systems. This paper explores both the opportunities and the hurdles that
must be overcome to fully leverage 6G technology for AR/VR applications in these key sectors.
1 INTRODUCTION
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and
Virtual Reality (VR) has progressed significantly
across multiple domains, with a particular emphasis
on medical education. Studies suggest that
incorporating AR and VR in medical training can
greatly enhance procedural proficiency, student
involvement, and long-term knowledge retention
(Tene et al., 2024; Al-Ansi et al., 2023a). These
technologies enable learners to rehearse medical
procedures in a controlled, risk-free environment, a
benefit that traditional techniques often lack.
However, despite the evident advantages, existing
technologies encounter challenges, primarily related
to network latency and bandwidth, which impede the
large-scale adoption of AR and VR, particularly in
real-time applications like surgical training or
diagnostic exercises (Jilani Saudagar et al., 2024).
With the advent of 6G technology, these barriers
are expected to be significantly reduced. 6G offers
extremely low latency, high data transfer speeds, and
increased network capacity, making it a game-
changer for AR and VR applications. This technology
is set to open up vast new possibilities for enhancing
training in medical fields, education, and
entertainment, providing smoother and more
immersive real-time experiences (Zawish et al., 2024;
Yang et al., 2022).
Expanding upon prior studies, the incorporation
of AR and VR into medical education has
demonstrated considerable potential, especially in
offering practical experience with medical
simulations, surgical procedures, and healthcare
interventions (Sharma et al., 2024; Porambage et al.,
2023; Nguyen et al., 2022). Additionally, this
research emphasizes how AR and VR can play a
crucial role in remote diagnostics and treatment,
enabling patients with disabilities to access medical
care from the convenience of their own homes.
Data analysis of 28 studies shows that while VR
positively impacts medical training, it was used to
measure "performance" more frequently (16 times)
than AR (4 times). However, a chi-square test found
this relationship was not statistically significant (p =
0.052). This indicates that further research with larger
sample sizes and improved methodologies is needed
to establish the technology's full effectiveness.
A descriptive analysis shows a largely favorable
impact of AR/VR on learner performance, with a
164
Agung, M. I. and Tahir, Z.
How 6G Will Transform Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare, Education, and Entertainment: Oppor tunities and Challenges.
DOI: 10.5220/0014276100004928
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology (RITECH 2025), pages 164-170
ISBN: 978-989-758-784-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

majority (57.14%) reporting a significant positive
effect and another portion (35.71%) also showing
positive results. However, with a small fraction
(3.57%) being neutral or unevaluated, the findings are
not entirely uniform. This inconsistency highlights a
critical need for future research using more robust
methodologies (Cui et al., 2023).
In healthcare, VR offers medical professionals
efficient, risk-free, and repeatable skills training for
surgical procedures. In education, AR and VR
provide personalized, interactive learning by
simulating complex scientific and historical concepts
that are impractical for traditional classrooms (Guo et
al., 2022).
In the entertainment sector, 6G is set to open new
opportunities for more immersive and realistic
gaming experiences. The integration of AR/VR into
entertainment, supported by 6G’s fast, low-latency
connectivity, will enable users to interact more deeply
with virtual worlds, offering a more engaging
experience than ever before.
While the potential of 6G to improve AR and VR
applications is vast, challenges such as the need for
specialized hardware, data security issues, and
scalable infrastructure cannot be overlooked. Thus, it
is essential to explore how 6G can be leveraged to
enhance the use of AR and VR in these key sectors
and to identify the hurdles that need to be overcome
for large-scale adoption of this transformative
technology.
2 RELATED STUDIES
The progression of wireless communication
technologies, particularly 5G and the upcoming 6G,
has led to extensive studies aimed at enhancing the
performance and dependability of data-heavy
applications like AR and VR. These applications
require extremely low latency and high data
throughput to ensure smooth and immersive user
experiences.
Numerous studies have explored how different
modulation schemes influence network performance
(Gupta et al., 2020). Examined QPSK, 16-QAM, and
64-QAM in the context of 5G systems, focusing on
their impact on bit error rate (BER) and signal-to-
noise ratio (Lee et al., 2020). Investigated the BER
performance under Rician and Rayleigh fading
channels, which are essential for simulating real-
world wireless environments.
With 6G on the horizon, new wireless
architectures and signal processing methods are being
explored (Zhang et al., 2019). Outlined the
requirements for 6G networks to support AR/VR
applications, emphasizing enhanced reliability and
reduced latency (Wang and Mao., 2020). Surveyed
the future directions of wireless communications for
immersive technologies.
In addition to modulation and channel modeling,
noise reduction has been a focus for improving signal
quality (Zhao et al., 2021). Demonstrated how
advanced channel coding and denoising methods can
reduce BER in 5G networks, improving AR/VR
performance.
Deep learning approaches have also been
explored to optimize wireless communication (Chen
et al., 2020). Reviewed deep learning techniques for
adaptive modulation, channel estimation, and
denoising, which are essential for next-gen network
performance.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Dataset Description and
Preprocessing
The dataset used in this study consists of wireless
communication signals captured under various
modulation schemes, specifically QPSK, 16-QAM,
and 64-QAM, and transmitted through different
channel models, including Rayleigh and Rician
fading. The dataset contains raw received signals and
denoised signals stored as complex number strings,
alongside key metrics such as Signal-to-Noise Ratio
(SNR) and Bit Error Rate (BER), measured both
before and after applying denoising techniques (Tariq
et al., 2021).
3.1.1 Data Preprocessing
To preprocess the data, complex-valued strings from
the signal columns were parsed, and their real and
imaginary components were extracted. These
component lists were then averaged to convert the
vector data into scalar features for each sample
simplifying further analysis. The data for this study
was simulated using controlled wireless
communication models. These simulations emulate
real-world conditions that a 5G/6G network might
encounter, with different SNR levels and various
fading channel models (Rayleigh and Rician). The
dataset was generated by applying noise at different
levels and then applying denoising techniques to
remove the noise and assess the improvements in
BER and SNR. vector data into scalar features for
each sample, simplifying further analysis.
How 6G Will Transform Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare, Education, and Entertainment: Opportunities and Challenges
165
To ensure numerical stability, Min-Max
normalization was applied to the extracted real and
imaginary components, scaling all features to a range
of 0 to 1. This normalization ensures that the data is
standardized for further statistical analysis and
machine learning tasks. Missing values in the dataset
were imputed with zeros to maintain dataset integrity
(
Siriwardhana et al
., 2021).
3.1.2 Denoising Techniques
Wavelet-based denoising was the primary technique
used to reduce BER and improve signal quality. The
process involved using a Discrete Wavelet Transform
(DWT) to decompose the signal into frequency
bands, allowing for the removal of high-frequency
components representing noise. This method is
effective because it removes noise while preserving
the signal's original low-frequency components (Liu
et al., 2022).
In addition to wavelet-based denoising, a median
filter was applied to further clean the signal. This
filter is effective at removing impulsive noise by
replacing each signal point with the median of
neighboring points, enhancing signal clarity.
3
.1.3 Dataset Analys
After preprocessing and denoising, the mean,
standard deviation, minimum, and maximum values
of the normalized real and imaginary components
were calculated. This descriptive analysis of the
dataset helps in understanding the distribution of the
data and the effectiveness of the denoising process.
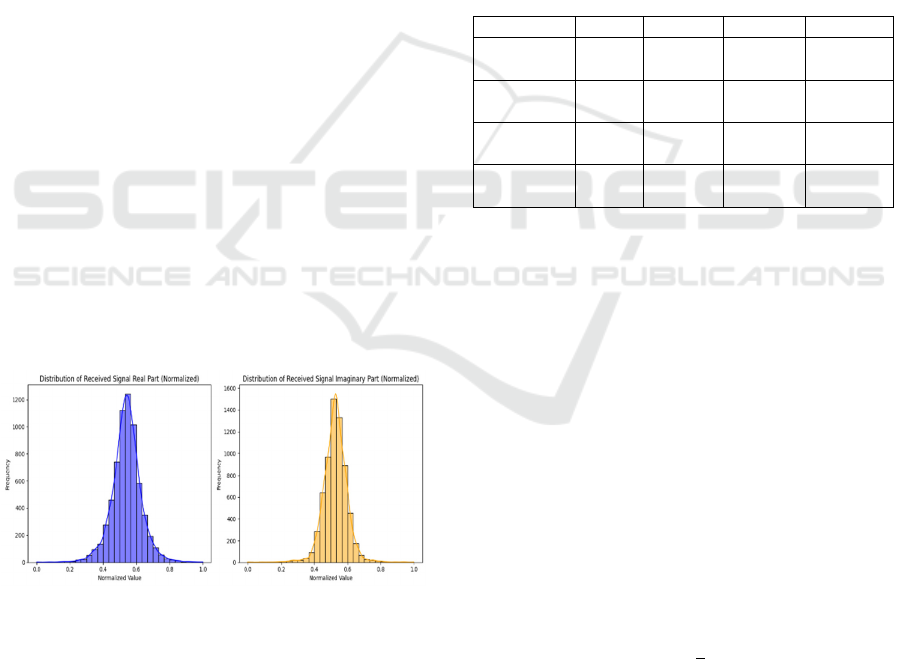
Figure 1: Distribution of Normalized Real and
Imaginary Components of Received Wireless Signals.
Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of the
normalized real and imaginary components of the
received signals. The histograms supplemented by
Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) curves reveal that
both the real and imaginary parts of the received
signals are symmetrically distributed, centered
around a value of approximately 0.5, with no
significant skewness or bias (Vameghestahbanati et
al., 2023).
3.1.4 Statistical Summary of Normalized
Signal Features
Table 1 provides a comprehensive summary of the
descriptive statistics for the normalized signal
features, including the mean, standard deviation,
minimum, and maximum values for both the received
and denoised signals. The relatively low standard
deviations (approximately 0.07 to 0.09) reflect a
moderate spread in the data, consistent with the
smooth distributions observed in Figure 1 (Zhang et
al., 2022).
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of Normalized Real and
Imaginary Signal
Features for Received and Denoised
Signals.
Feature Mean Std. Dev Minimum Maximum
Received
Signal Real
0.5412 0.0883 0.0 1.0
Received
Si
g
nal Ima
g
0.5264 0.0701 0.0 1.0
Denoised
Si
g
nal Real
0.5243 0.0965 0.0 1.0
Denoised
Signal Imag
0.5262 0.0701 0.0 1.0
3.2 Performance Analysis
Performance evaluation in this study is focused on Bit
Error Rate (BER), a key metric for assessing the
integrity of signal transmission. BER quantifies the
ratio of erroneous bits received to the total bits
transmitted and serves as a direct indicator of signal
quality and network reliability.
The effectiveness of denoising techniques was
evaluated by measuring BER both before and after
denoising across three modulation schemes: QPSK,
16-QAM, and 64-QAM. These modulation schemes
represent common configurations in modern wireless
networks, including 5G and the emerging 6G
systems.
The mean BER values were calculated for each
modulation scheme using Equation (1):
𝑀𝑒𝑎𝑛𝐵𝐸𝑅
∑
𝐵𝐸𝑅
(1)
Where:
• MeanBER represents the mean Bit Error Rate.
• 𝐵𝐸𝑅
denotes the Bit Error Rate of the i-
th
sample.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
166

• n represents the total number of samples tested
for each type of modulation.
The average BER values for each modulation
scheme were computed as follows:
Table 2: Average Bit Error Rate (BER) Before and After
Denoising for Different Modulation Schemes.
Modulation
Mean BER
Before
Mean BER
Afte
r
QPS
K
0.1991 0.1196
16-QAM 0.1993 0.1200
64-QAM 0.1989 0.1192
The results indicate a significant reduction in BER
after applying denoising, confirming the
effectiveness of the denoising algorithms in
mitigating noise and enhancing signal fidelity. This
reduction is critical for applications like Augmented
Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), which rely on
high-quality, low-latency data transmission.
Enhanced signal quality ensures a more reliable and
immersive AR/VR experience by reducing
transmission errors and latency.
This improvement in BER is crucial for latency-
sensitive and high-data-rate applications such as
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR),
where data integrity directly influences the user
experience. Enhanced signal quality through effective
noise reduction contributes to lower latency, fewer
transmission errors, and ultimately more reliable and
immersive AR/VR interactions.
Figure X illustrates the comparative mean BER
values before and after denoising for each modulation
type, visually affirming the quantitative findings. In
conclusion, the performance analysis confirms that
advanced signal processing techniques, particularly
denoising, play a vital role in optimizing wireless
communication systems for next-generation
applications.
3.3 Correlation Analysis Between SNR
and BER
To understand how variations in network conditions
influence signal quality, a correlation analysis
between Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and Bit Error
Rate (BER) was performed. SNR, which is a key
metric for measuring signal quality, reflects the ratio
of signal power to noise power. BER, on the other
hand, quantifies the number of incorrect bits received
compared to the total bits transmitted.
Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used to
quantify the linear relationship between SNR and
BER. The formula for Pearson's correlation is as
follows (2):
r=
∑
SNR
i
-SNR
BER
i
-BER
∑
SNR
i
-SNR
2
∑
BER
i
-BER
2
Where 𝑆𝑁𝑅
and 𝐵𝐸𝑅
represent
individual observations for 𝑆𝑁𝑅
and 𝐵𝐸𝑅, and
𝑆𝑁𝑅
and 𝐵𝐸𝑅 represent the mean values of SNR
and BER.
The correlation analysis showed a strong negative
correlation between SNR and BER, both before and
after applying the denoising techniques. This
indicates that as SNR increases, BER decreases,
meaning that higher signal quality (higher SNR) leads
to fewer transmission errors (lower BER).
Results of the Correlation Analysis:
The Pearson correlation coefficients between SNR
and BER are summarized below:
Table 3: Pearson Correlation Coefficients Between Signal-
to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and BER.
Condition Pearson Correlation Coefficient
Before
Denoisin
g
0.953
After
Denoising
0.890
These negative correlation values confirm that
improving SNR directly improves BER, which is
crucial for AR/VR applications that require high-
quality data transmission with low error rates. The
negative correlation between SNR and BER also
supports the effectiveness of denoising in reducing
transmission errors and enhancing signal fidelity.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Impact of 6G on AR/VR
Applications
The incorporation of 6G technology is expected to
greatly enhance AR and VR applications, primarily
by offering extremely low latency, faster data transfer
rates, and increased network capacity. These
improvements facilitate real-time, immersive
experiences, which are crucial for applications in
sectors such as medical education, training, and
entertainment.
The performance analysis demonstrated a
significant reduction in BER and improvement in
(2)
How 6G Will Transform Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare, Education, and Entertainment: Opportunities and Challenges
167

signal quality after the application of denoising
techniques. This improvement is crucial for AR/VR
applications that rely on low latency and high data
throughput to provide seamless, immersive
experiences.
Like any major technological advancement, 6G
introduces several non-technical obstacles that need
to be overcome for its successful deployment. These
include issues related to data security, privacy, and
the constraints of current hardware infrastructure
.
4.2 Non-Technical Challenges in 6G-
Driven AR/VR Applications
While 6G holds significant promise for enhancing
AR/VR applications, several non-technical issues
pose challenges that could impede wide-scale
adoption. The integration of 6G with AR/VR
applications significantly increases the generation of
sensitive personal data, such as biometrics, medical
records, and real-time location information. While
beneficial, 6G's high-speed data transfer also elevates
the risk of exposing this data to cyberattacks and leaks
if not properly secured. Therefore, implementing
robust security measures like encryption, secure data
transfer, and user authentication is essential to protect
user privacy and build trust in these advanced
technologies. (Al-Ansi et al., 2023; Nguyen et al.,
2021).
Privacy in 6G-powered AR/VR is a major
concern, as the real-time capture of sensitive data in
fields like healthcare and education raises ethical and
legal questions. This necessitates clear privacy
regulations to protect users from data exploitation
without consent. Ultimately, balancing user
experience with robust privacy protection remains a
critical challenge for the expansion of 6G networks
(
Chowdhury et al., 2022; He et al., 2023).
Hardware limitations present a significant non-
technical challenge to leveraging 6G for AR/VR.
Despite 6G's high-speed capabilities, necessary
devices like AR glasses and VR headsets are still
constrained by issues of affordability, accessibility,
and processing power. Furthermore, a major hurdle in
hardware design is the need for these devices to be
both lightweight and energy-efficient to fully utilize
6G's potential (
Khan et al., 2022; Porambage et al.,
2022).
The infrastructure for widespread 6G network
deployment remains underdeveloped, especially in
rural and technologically limited regions. Achieving
universal adoption with equitable access will require
significant infrastructure investment and global
cooperation (
Saad et al., 2021; Dogra et al., 2021).
4.3 Addressing Non-Technical
Challenges for Future Research
To overcome these non-technical barriers, several
actions are required:
• Data privacy and security protocols need to be
further developed to protect users in AR/VR
environments. This includes end-to-end
encryption, anonymization techniques, and
secure cloud storage solutions.
• Regulations governing the use of personal data
in AR/VR applications must be updated to
reflect the advanced capabilities of 6G and its
ability to handle large volumes of sensitive data
• Hardware development must focus on creating
affordable, energy-efficient, and high-
performance devices that are capable of fully
utilizing 6G networks without compromising
the user experience.
• Governments, industries, and researchers
should collaborate on developing scalable 6G
infrastructure to ensure that the benefits of
AR/VR technologies are accessible to all,
including in underserved regions.
4.4 Conclusion of Discussion
While 6G presents significant opportunities for
enhancing AR/VR applications, the non-technical
challenges—such as data security, privacy concerns,
and hardware limitations—must not be overlooked.
Addressing these
challenges is crucial to ensure
that AR/VR experiences in sectors like healthcare,
education, and entertainment are not only
transformative but also secure, private, and accessible
to a global audience. Future research should focus on
overcoming these hurdles through policy
development, technological innovation, and
collaborative efforts from all stakeholders.
Key findings include:
• QPSK performs well in low SNR conditions,
while 64-QAM offers higher data throughput in
ideal conditions.
• Denoising consistently reduced BER, enhancing
signal quality across all modulation schemes,
which is crucial for AR/VR applications that rely
on high-quality, low-latency data transmission.
• There is a strong negative correlation between
SNR and BER, highlighting the importance of
improving SNR for better AR/VR performance.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
168

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the members of the
Distributed Intelligence Research Group at
Hasanuddin University for their insightful
discussions and collaborative environment which
greatly supported this research
REFERENCES
Al-Ansi, A., Al-Ansi, H., Kardi, N., Al-Banna, A., and
Muthanna, A. (2023a). 6G for unleashing the full
potential of metaverse: Challenges and future
directions. IEEE Access.
Al-Ansi, A., Kardi, N., Al-Banna, A., and Muthanna, A.
(2023b). A survey on security and privacy challenges in
6G networks. IEEE Access.
Chen, M., Hao, Y., and Hwang, K. (2020). Deep learning
for wireless communications and networking: A
survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials,
vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 2571-2612.
Chowdhury, M. Z., Shahjalal, M., Ahmed, S., and Jang, Y.
M. (2022). 6G wireless communication systems: A
comprehensive survey on security and privacy. Journal
of Network and Computer Applications.
Cui, J., Wang, Y., and Ding, Z. (2023). A survey on AI for
6G: From a signal processing perspective. IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
Dogra, A., Jha, R. K., and Jain, S. (2021). A survey on 6G
architecture, applications, and technologies.
Telecommunication Systems.
Guo, F., Yu, F. R., Zhang, H., Li, X., Ji, H., and Leung, V.
C. M. (2022). Deep learning for physical layer
communications in 6G: A survey. IEEE Wireless
Communications.
Gupta, A., Khurana, R., and Kumar, P. (2020). Performance
analysis of modulation techniques for 5G wireless
systems. IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 56789-56798.
He, Y., Zhang, Z., and Yu, F. R. (2023). Hardware
limitations and co-design for 6G communication
systems: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys &
Tutorials.
Jilani Saudagar, A.K., Kumar, A., and Khan, M.B. (2024).
Mediverse beyond boundaries: A comprehensive
analysis of AR and VR integration in medical education
for diverse abilities. Journal of Disability Research,
vol. 3, pp. 3-15.
Khan, L. U., Saad, W., Niyato, D., Han, Z., and Hong, C.
S. (2022). A survey on metaverse: The state-of-the-art,
taxonomy, and open research challenges. IEEE Access.
Lee, J., Kim, Y., and Park, J. (2020). Bit error rate analysis
for Rician and Rayleigh fading channels in 5G systems.
IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 69,
no. 3, pp. 3342-3351.
Liu, Y., Wang, X., and You, X. (2022). Deep denoising for
wireless signal processing in 6G networks. IEEE
Transactions on Wireless Communications.
Nguyen, D. C., Ding, M., Pathirana, P. N., Seneviratne, A.,
Li, J., Niyato, D., Dobre, O., and Poor, H. V. (2021).
6G-enabled security and privacy for smart healthcare:
A survey. EURASIP Journal on Wireless
Communications and Networking.
Nguyen, D. C., Pham, Q. V., Pathirana, P. N., Ding, M.,
Seneviratne, A., Lin, Z., Dobre, O., and Hwang, W. J.
(2022). 6G and the metaverse: A promising symbiosis.
IEEE Communications Standards Magazine.
Porambage, P., Gür, G., Osorio, D. P. M., Liyanage, M.,
and Ylianttila, M. (2022). A survey on security and
privacy of 5G/6G enabled drones. IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
Porambage, P., Gür, G., Osorio, D. P. M., Liyanage, M.,
Gurtov, A., and Ylianttila, M. (2023). The roadmap to
6G: A survey on tends and future directions. IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
Saad, W., Bennis, M., & Chen, M. (2021). A vision of 6G
wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies,
and open research problems. IEEE Network.
Sharma, S., Popli, R., Singh, S., Chhabra, G., Saini, G.S.,
Singh, M., Sandhu, A., Sharma, A., and Kumar, R.
(2024). The role of 6G technologies in advancing smart
city applications: Opportunities and challenges.
Sustainability, vol. 16, 7039.
Siriwardhana, Y., Porambage, P., Liyanage, M., and
Ylianttila, M. (2021). A survey on mobile augmented
reality with 5G mobile edge computing: Architectures,
applications, and technical aspects. IEEE
Communications Surveys & Tutorials.
Tariq, F., Khandaker, M. R. A., Wong, K. K., Imran, M. A.,
Bennis, M., and Debbah, M. (2021). A speculative
study on 6G: A survey on key technologies, use cases,
and challenges. IEEE Open Journal of the
Communications Society.
Tene, T., Vique López, D.F., Valverde Aguirre, P.E., Orna
Puente, L.M., and Gomez, C.V. (2024). Virtual reality
and augmented reality in medical education: an
umbrella review. Frontiers in Digital Health, vol. 6,
1365345.
Vameghestahbanati, M., Arum, S. C., Berggren, F., and
Jäntti, R. (2023). Waveform design for 6G: A survey
and vision. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications
Society.
Wang, Y., and Mao, S. (2020). A survey on 5G and beyond:
Architectures, applications, and future directions. IEEE
Access, vol. 8, pp. 111273-111289.
Yang, P., Xiao, Y., Xiao, M., and Li, S. (2022). 6G for
connected sky, ground, and ocean: A communications,
computing, and intelligence integration perspective.
IEEE Network.
Zawish, M., Dharejo, F.A., Khowaja, S.W., Raza, S., Davy,
S., Dev, K., and Bellavista, P. (2024). AI and 6G into
the metaverse: Fundamentals, challenges and future
research trends. In IEEE Open Journal of the
Communication Society.
Zhang, C., Patras, P., and Li, H. (2022). Joint denoising and
channel estimation for 6G using deep learning. IEEE
Wireless Communications Letters.
How 6G Will Transform Augmented and Virtual Reality in Healthcare, Education, and Entertainment: Opportunities and Challenges
169

Zhang, Z., Xiao, Y., Ma, Z., Xiao, M., Ding, Z., Lei, X.,
Karagiannidis, G. K., and Fan, P. (2019). 6G wireless
networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key
technologies. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine,
vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 28-41.
Zhao, R., Wang, Q., Wang, T., and Liu, S. (2021).
Performance improvement of AR/VR applications over
5G networks using advanced channel coding and
denoising techniques. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas
in Communications, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 1703-1717.
Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., Yu, G., and Chen, S. (2022). A survey
of 6G wireless communications: New technologies, use
cases, and challenges. Journal of Communications and
Information Networks.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
170
