
Operational Limits of Near-Infrared Face Recognition: The Critical
Impact of Distance on Identification Accuracy
Raiz Karman
a
, Indrabayu
*
b
and I Putu Wahyu Kusuma
Departement of Informatics Hasanuddin University Makassar, Indonesia
Keywords: Face Recognition, Near-Infrared (NIR), Deep Metric Learning, Triplet.
Abstract: Robust face recognition in low-light conditions is crucial for security, yet the impact of varying stand-off
distances on Near-Infrared (NIR) systems remains underexplored. This study quantifies this impact through
a systematic evaluation of an NIR-to-NIR system. We constructed a dataset of 10 subjects at five controlled
distances (4–20 meters) and implemented an end-to-end deep learning pipeline. Component validation
showed that a Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Network (MTCNN) augmented with selective Contrast
Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) achieved a superior 76.22% detection rate. The
InceptionResNetV2 model, trained with Triplet Loss, achieved 80% overall identification accuracy and
significantly outperformed a classical LBP+LDA baseline. However, performance was critically distance-
dependent, with accuracy dropping from 93% at close ranges to 55% at 20 meters. This degradation highlights
the challenge of Low-Resolution Face Recognition (LRFR), limiting the system's practical range. Future
research should target resolution enhancement via Face Super-Resolution (FSR) and the design of lightweight
architectures for edge devices.
1 INTRODUCTION
Face-based biometric identification has become a
fundamental technology in modern security, driven
by rapid advancements in deep learning. However, its
real-world reliability is often hindered by two primary
challenges: poor lighting and variable acquisition
distances. Low-light or dark environments can render
visible spectrum (VIS) systems ineffective, while
long stand-off distances, typical for surveillance
cameras, produce low-resolution facial images that
lack details crucial for identification (Szeliski, 2022)
Near-Infrared (NIR) imaging has proven highly
effective in addressing illumination issues, enabling
consistent image acquisition regardless of ambient
light (Alhanaee et al., 2021; Schroff et al., 2015).
Beyond recognition, NIR technology also
significantly enhances the preceding step: face
detection. Conventional face detectors operating in
the visible spectrum often fail in adverse lighting, as
shadows and low contrast can obscure facial features.
NIR sensors, being independent of ambient light,
provide images with consistent contrast between
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-3365-1848
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2026-1809
facial skin and the background, leading to more
reliable and robust face detection rates (Jain et al.,
2004). This robustness is critical for surveillance and
security applications that operate continuously.
Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated that
NIR imaging, often combined with deep learning
detectors like YOLO or MTCNN, can effectively
mitigate presentation attacks (spoofing), as the
reflective properties of skin in the NIR spectrum
differ distinctly from materials like paper or screens,
adding a layer of security at the initial detection stage
(Zhou et al., 2023).
Despite these advantages, the adoption of NIR
highlights a significant research gap. Most studies
have focused on Heterogeneous Face Recognition
(HFR)—matching NIR probes to a VIS gallery—
often overlooking an equally critical variable: how
performance within a homogeneous NIR domain
degrades as a function of distance.
This study aims to fill this gap by quantitatively
measuring the impact of acquisition distance on a
deep learning-based NIR face recognition system's
accuracy. By isolating the distance variable, we seek
Karman, R., Indrabayu, and Kusuma, I. P. W.
Operational Limits of Near-Infrared Face Recognition: The Critical Impact of Distance on Identification Accuracy.
DOI: 10.5220/0014269200004928
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology (RITECH 2025), pages 53-60
ISBN: 978-989-758-784-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
53
to define the technology's practical operational limits.
The main contributions include a controlled multi-
distance NIR dataset, a comprehensive pipeline
evaluation that justifies the use of selective CLAHE
through detector comparison, validation of our deep
learning approach against a classical method, and an
analysis linking distance-based performance
degradation to the broader problem of Low-
Resolution Face Recognition (LRFR) (Arafah et al.,
2020).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This research focused on developing a face
recognition system for low-light conditions using a
deep learning pipeline. The research workflow is
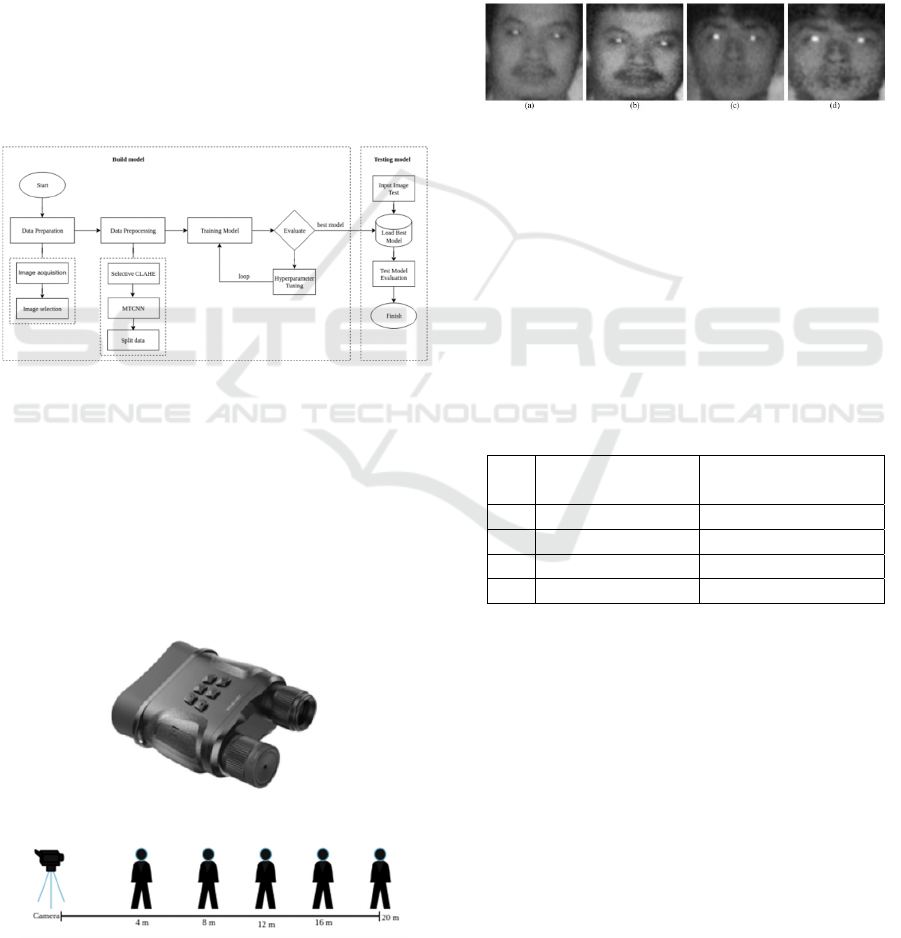
illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Research Process Workflow.
2.1 Data Preparation
This foundational stage involved image acquisition
and selection. Using an Apexel NV001 infrared
camera (Fig. 2), we captured video of 10 subjects at
five distances: 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 meters (Fig. 3).
The videos were processed into frames, and a
meticulous selection process yielded a final dataset of
5,514 representative images.
Figure 2: Camera Apexel NV100.
Figure 3: Illustration of the data collection process.
2.2 Pre-Processing
2.2.1 Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram
Equalization (CLAHE)
To counteract quality loss at a distance, Contrast
Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE)
(Pizer et al., 1987) was selectively applied only to
images captured at 16 m and 20 m. This aligns with
research on the importance of image quality (Sino et
al, 2019) and aims to enhance features in degraded
images, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Comparison of face images at 16 m and 20 m: (a,
c) original, (b, d) with CLAHE.
2.2.2 Multi-Task Convolutional Neural
Network (MTCNN)
A Multi-Task Convolutional Neural Network
(MTCNN) was used to detect and crop faces to
160x160 pixels. To justify our choice of detector and
demonstrate the utility of our selective CLAHE
approach, we conducted a comparative analysis of
four different face detection methods on our dataset.
Table 1: Comparison of Face Detector Performance.
No. Detector
Images Successfully
Detected
1 SSD 54.04%
2 OpenCV 63.42%
3 MTCNN 65.02%
4 MTCNN CLAHE 76.22%
As presented in Table 1, the combination of MTCNN
with selective CLAHE achieved the highest detection
success rate at 76.22%, significantly outperforming
original MTCNN (65.02%) and other common
detectors. This improvement was particularly notable
at the challenging 16 m and 20 m distances, validating
our pre-processing strategy. After detection, a manual
cleaning to remove inaccurate detections reduced the
final dataset by 23.78%. Figure 5 shows examples of
facial images in the dataset at specified distances.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
54
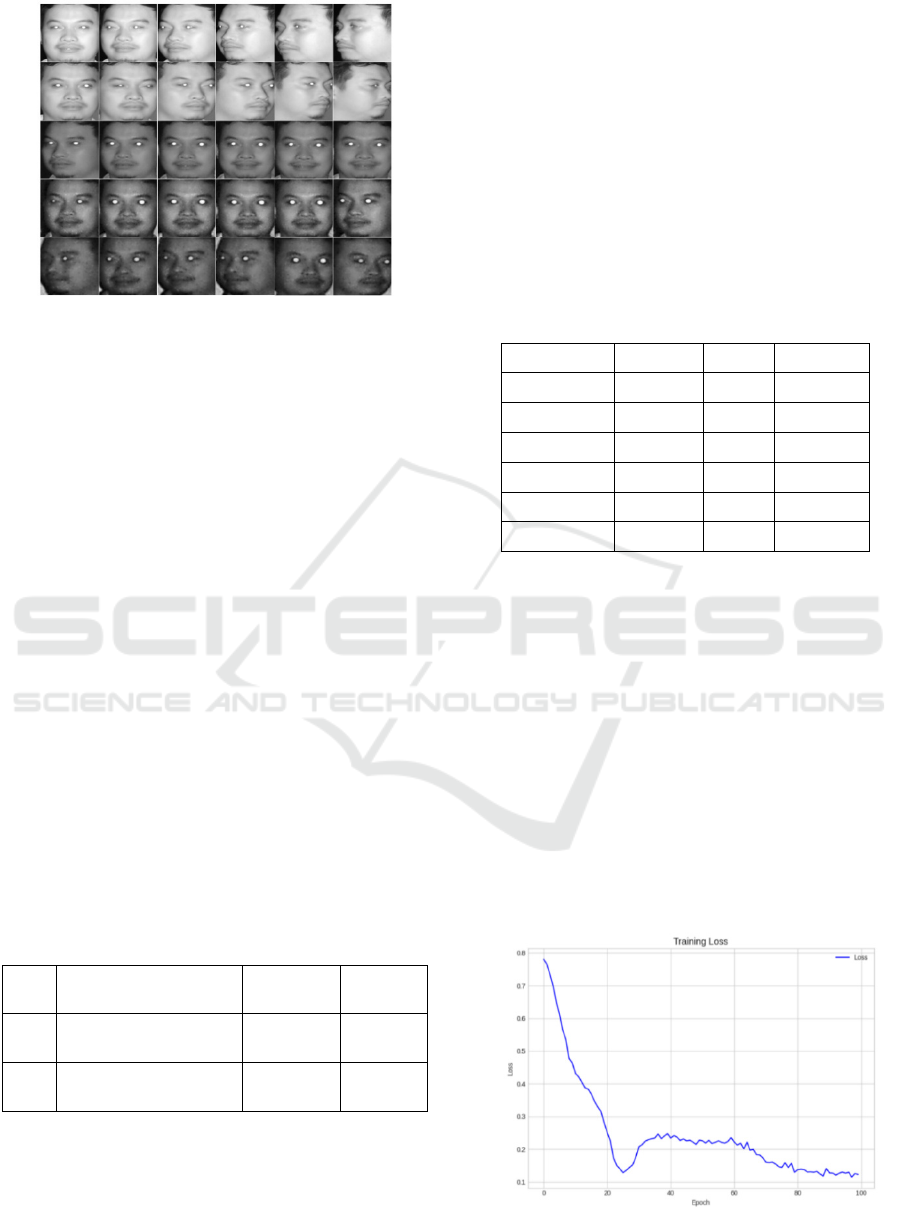
Figure 5: Example of data based on distance
2.2.3 Data Splitting
The dataset was randomly split into 70% for training
and 30% for testing.
2.3 Convolutional Neural Network
(CNN)
We employed the InceptionResNetV2 architecture,
trained using Triplet Loss for deep metric learning.
This method uses triplets (Anchor, Positive,
Negative) to train the model to produce
discriminative feature embeddings. The Triplet Loss
function (Equation 1) aims to minimize the distance
between same-identity pairs and maximize it for
different-identity pairs using Cosine Distance
(Schroff et al., 2015).
𝐿𝑜𝑠𝑠 = max(𝑑
(
𝐴
,𝑃
−𝑑
(
𝐴
,𝑁
+𝛼,0
(1)
Table 2 shows the hyperparameter tuning
configurations used in the model training process. Six
different experimental combinations were run with an
early stopping mechanism (patience=20).
Table 2: Hyperparameter Tuning.
No Trainable Layer Margin
Learning
Rate
1. Block8_6_Branch_0_
Conv2d_1x1
1.0, 1.2,
1.4
0.0001
2. Block8_1_Branch_0_
Conv2d_1x1
1.0, 1.2,
1.4
0.0001
3 RESULTS
3.1 Model Training Performance
A series of experiments was conducted to evaluate the
impact of hyperparameter combinations on model
performance. The primary metrics used for
comparison were the Area Under the Curve (AUC)
and Equal Error Rate (EER), as these metrics directly
reflect the model's ability to separate classes in the
feature space. Table 3 presents a summary of the
results from the six experimental configurations.
Table 3: Summary of Training Result.
Experiment AUC EER Threshold
exp_05 0.846644 0.2472 0.195759
exp_03 0.847407 0.2500 0.256823
exp_06 0.852781 0.2522 0.117221
exp_01 0.853877 0.2562 0.423429
exp_02 0.859016 0.2590 0.302959
exp_04 0.837374 0.2966 0.221290
A quantitative evaluation of the six model
configurations was conducted using the Area Under
the Curve (AUC) and Equal Error Rate (EER) as
primary performance metrics. The results,
summarized in Table 2, reveal a significant trade-off
between the two measures. Experiment 02
demonstrated the highest overall discriminative
capability, achieving a peak AUC of 0.8590.
Conversely, Experiment 05 provided the most
optimal operating point, yielding the lowest EER of
0.2472. This dichotomy underscores that the selection
of the final model is contextual, contingent on
whether the application prioritizes general class
separability (AUC) or a balanced error trade-off at a
specific threshold (EER).
(a)
Operational Limits of Near-Infrared Face Recognition: The Critical Impact of Distance on Identification Accuracy
55
(b)
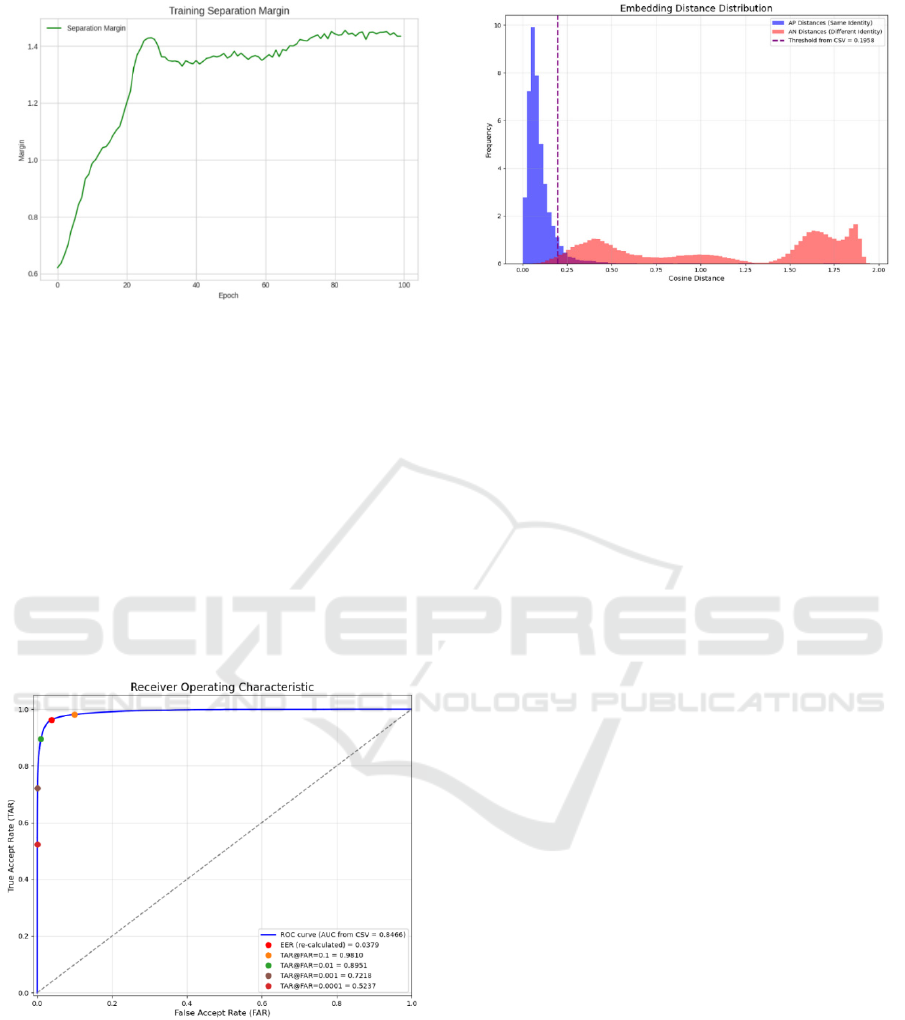
Figure 6: Curve (a) Training Loss, (b) Training Separation
Margin
The model from Experiment 05 was adopted as
the final model for the testing phase after it was
shown to achieve the optimal performance
combination, with the lowest EER of 0.2472. The
convergent and stable training process, as visualized
in Figure 6, confirms the validity of this model. This
decision aligns with the research methodology that
makes the Equal Error Rate (EER) the primary
performance benchmark, an approach consistent with
previous research (Rajasekar et al., 2023) to ensure
the reliability of biometric systems.
(a)
(b)
Figure 7: (a) Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve, (b)
Embedding Distance Distribution Graph
Figure 7(a) shows excellent discriminative
ability, with the curve approaching the top-left corner
and achieving a low Equal Error Rate (EER) of
3.79%, indicating high accuracy. This performance is
visually supported by Figure 7(b), which shows a
clear separation between the cosine distance
distributions for same-identity pairs (anchor-positive)
and different-identity pairs (anchor-negative). This
distinct separation between the two distributions is
the basis for the accurate performance shown by the
ROC curve.
3.2 Face Recognition System Testing
The model was tested using the data_test dataset to
verify its face identification capabilities in realistic
conditions. The testing process was conducted in two
main phases: enrollment, which extracts data using
the trained encoder. The feature extraction results are
stored in a face database used to match during testing.
The second is identification testing, which compares
a new test image against the registered face database.
The system calculates the distance between the test
image (probe) feature vector and the registered image
(anchor). If the distance is less than the specified
threshold, the test image is considered a match to the
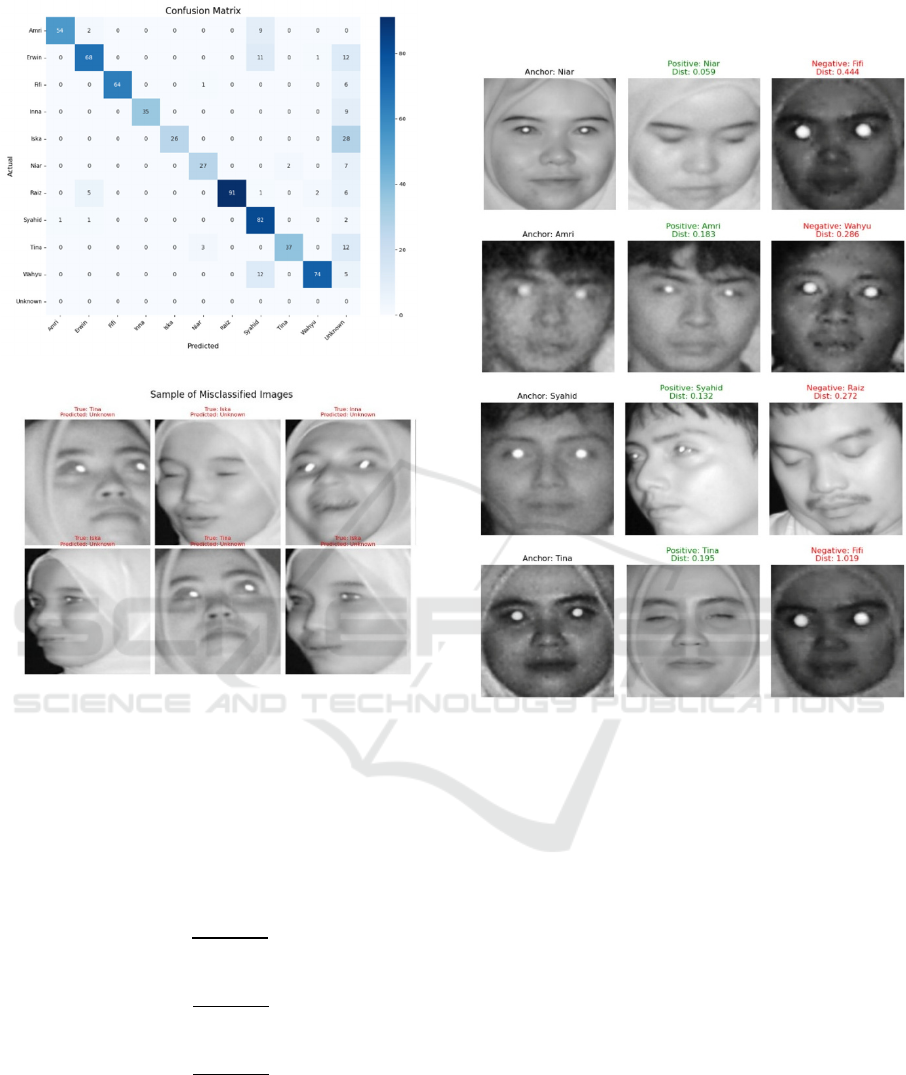
registered identity. Figure 8(a) shows the confusion
matrix, which provides a detailed visualization of the
model's classification results on the data_test set,
consisting of 10 different individual classes. Overall,
the model achieved an Accuracy of 80%, Precision of
93%, Recall of 80%, and an F1-Score of 85%.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
56
(a)
(b)
Figure 8: (a) Confusion Matrix, (b) Sample of Misclassified
Images
From the data in Figure 8(a), the TAR (True
Acceptance Rate), FAR (False Acceptance Rate), and
FRR (False Rejection Rate) can be calculated to
measure and evaluate the performance of the face
recognition mode
𝑇𝐴𝑅 =
𝑇𝑃
𝑇𝑃
+
𝐹𝑁
(2)
𝐹𝐴𝑅 =
𝐹𝑃
𝐹𝑃
+
𝑇𝑁
(3)
𝐹𝑅𝑅 =
𝐹𝑁
𝑇𝑃
+
𝐹𝑁
(4)
Where TP is True Positive, FN is False Negative, FP
is False Positive, and TN is True Negative. Based on
the calculations, the system achieved a True
Acceptance Rate (TAR) of 81.3%, a False Acceptance
Rate (FAR) of 2.1%, and a False Rejection Rate
(FRR) of 18.7%. Figure 8(b) shows examples of
misclassified data, where the model incorrectly
predicted the true identity as "Unknown".
Figure 9: Visualization of Anchor-Positive-Negative
Triplet
The visualization in Figure 9 confirms that the
system successfully applied the 0.1958 threshold to
effectively distinguish between image pairs of the
same and different individuals.
3.3 System Testing Based on Distance
This study evaluated the model's performance at five
predetermined distances: 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 meters.
The results are presented in Figures 10(a) and 10(b).
At distances of 4 and 8 meters, the system's accuracy
was 93%, indicating excellent performance.
However, as the distance increased, the accuracy
declined to 92% at 12 meters. A significant drop
occurred at greater distances, 16 and 20 meters, where
accuracy plummeted to 68% and 55%, respectively.
This decline illustrates the system's difficulty in
maintaining face recognition quality at longer
distances, caused by reduced image resolution and the
loss of important facial feature details. This is
Operational Limits of Near-Infrared Face Recognition: The Critical Impact of Distance on Identification Accuracy
57
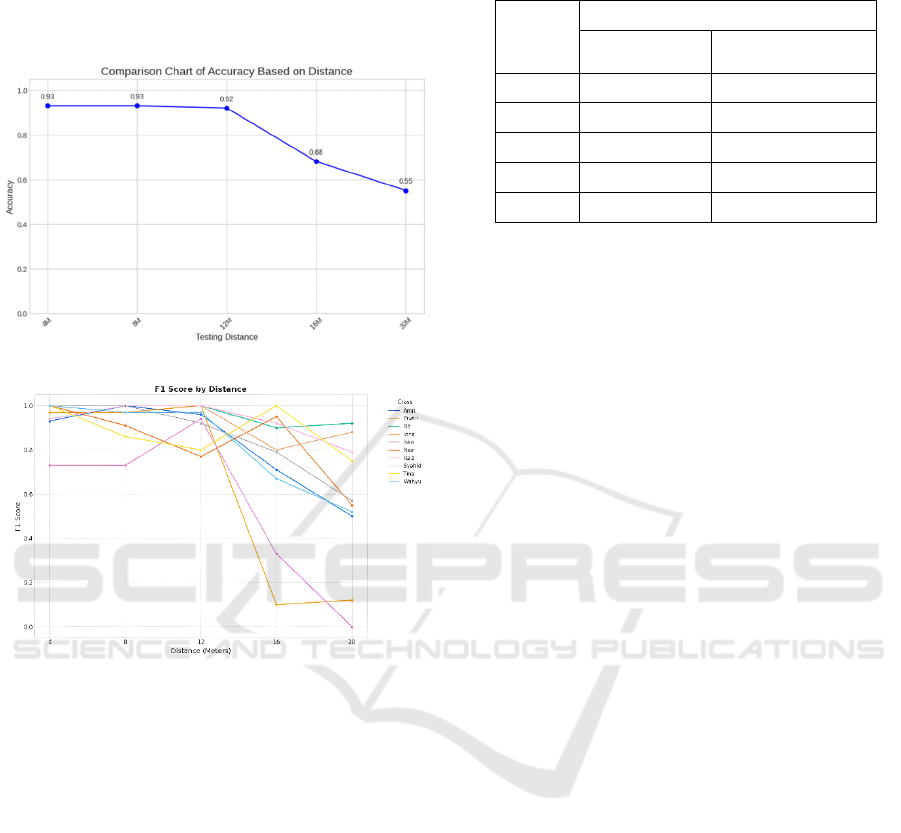
consistent with previous research findings that the
performance of face recognition systems is heavily
influenced by testing distance (Wang et al., 2014). A
similar trend was also observed in the F1-Score
metric, which decreased as the distance increased.
(a)
(b)
Figure 10: (a) Accuracy by Distance, (b) F1 Score by
Distance
To measure the effectiveness of the deep learning
approach, a comparison of accuracy performance was
conducted with the classic LBP+LDA-based face
recognition method at various distances. Table 4
presents the comparative results, showing that the
CNN (InceptionResNetV2) method consistently
outperforms LBP+LDA in all distance scenarios
tested. While the LBP+LDA method experiences a
sharp degradation in performance as the distance
increases, the CNN model shows much higher
stability, with only a moderate decrease in accuracy
at 16 meters (68%) and 20 meters (55%). These
findings confirm that the feature representations
learned by convolutional neural networks are superior
to manual feature descriptors.
Table 4: Accuracy Comparison: CNN vs. LBP+LDA by
Distance.
Distance
(m)
Accuracy (%)
LBP + LDA
CNN
InceptionResNetV2
4 58 93
8 45 93
12 43 92
16 41 68
20 39 55
4 DISCUSSIONS
The most significant insight from this study is the
confirmation that stand-off distance is a critical
performance degradation factor. The sharp accuracy
declines from 93% to 55% reframes the challenge as
a fundamental problem of Low-Resolution Face
Recognition (LRFR) (Szeliski, 2022). Increasing
distance inherently reduces the effective resolution,
leading to the loss of high-frequency details crucial
for the CNN to generate discriminative embeddings.
Our findings are consistent with trends reported
in the broader literature on long-distance and low-
resolution face recognition. For instance, recent work
by Dandekar et al. (2024) also documented a severe
performance drop when facial resolution fell below
40x40 pixels, a threshold easily crossed in our 16m
and 20m scenarios. While our system achieved 55%
accuracy at 20 meters, other studies focusing
specifically on resolution enhancement have shown
promising results. Research utilizing Generative
Adversarial Networks (GANs) for Face Super-
Resolution (FSR) before recognition has managed to
boost accuracy by up to 20 percentage points on
similar low-quality images (Chen et al., 2018; Ledig
et al., 2017). Furthermore, advancements in feature
extraction networks designed for scale invariance,
such as those incorporating feature pyramid networks
or attention mechanisms, have demonstrated
improved robustness against resolution changes
(Deng et al., 2019). A study by Boutros et al. (2022)
using an attention-based lightweight network
reported maintaining over 70% accuracy at distances
comparable to our 16m test, suggesting a promising
direction for future architectural improvements. This
comparative context situates our results as a realistic
baseline for NIR systems without specialized
resolution compensation, while highlighting FSR and
advanced network architectures as essential future
research avenues.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
58

The superior performance of our CNN model
over LBP+LDA (Table 4) underscores the robustness
of deep learning-based feature extraction. However,
the computational complexity of InceptionResNetV2
remains a limitation for deployment on edge devices.
Therefore, future research must focus on two strategic
paths: directly tackling the LRFR problem by
integrating FSR modules (Ledig et al., 2017) and
migrating to lightweight CNN architectures like
MobileFaceNet (Chen et al., 2018), ShuffleFaceNet
(Martindez-Diaz et al., 2019), or the more recent
EdgeFace (George et al., 2024), which are optimized
for resource-constrained environments (Rajasekar et
al., 2023).
5 CONCLUSIONS
This study quantitatively demonstrates that
acquisition distance is the most critical limiting factor
in NIR-based face recognition systems, effectively
reframing the challenge as a problem of Low-
Resolution Face Recognition (LRFR). The key
finding reveals an unavoidable trade-off between
operational range and identification reliability:
system accuracy plummeted from 93% at close range
to 55% at 20 meters. Although NIR technology
successfully overcomes illumination challenges, its
practical utility is severely constrained by distance.
Therefore, future research efforts must
simultaneously target solutions for resolution
degradation, such as the integration of Face Super-
Resolution (FSR), and for computational efficiency
through the adoption of lightweight model
architectures (e.g., MobileFaceNet) to create systems
that are truly reliable and deployable on real-world
edge devices.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful to the AIMP Thematic
Research Group, Faculty of Engineering, Hasanuddin
University, for providing the support and facilities
necessary for this study. During the preparation of
this manuscript, the authors utilized generative AI
tools to assist with improving language, grammar,
and readability. All content, including the core ideas,
analyses, and conclusions, was conceived and
critically reviewed by the authors to ensure scientific
accuracy and originality.
REFERENCES
Alhanaee, K., Alhammadi, M., Almenhali, N., & Shatnawi,
M. (2021). Face recognition smart attendance system
using deep transfer learning. Procedia Computer
Science, 192, 4093-4102.
Arafah, M., Achmad, A., Indrabayu, & Areni, I. S. (2020,
December). Face identification system using
convolutional neural network for low resolution image.
In 2020 IEEE International Conference on
Communication, Networks and Satellite (Comnetsat)
(pp. 55-60). IEEE.
Boutros, F., Siebke, P., Klemt, M., Damer, N.,
Kirchbuchner, F., & Kuijper, A. (2022). Pocketnet:
Extreme lightweight face recognition network using
neural architecture search and multistep knowledge
distillation. IEEE access, 10, 46823-46833.
Chen, S., Liu, Y., Gao, X., & Han, Z. (2018).
Mobilefacenets: Efficient cnns for accurate real-time
face verification on mobile devices. In Chinese
conference on biometric recognition (pp. 428-438).
Springer International Publishing.
Chen, Y., Tai, Y., Liu, X., Shen, C., & Yang, J. (2018).
FSRNet: End-to-end learning face super-resolution
with facial priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
(pp. 2492-2501).
Dandekar, P., Aote, S. S., & Raipurkar, A. (2024). Low-
resolution face recognition: Review, challenges and
research directions. Computers and Electrical
Engineering, 120, 109846.
Deng, J., Guo, J., Xue, N., & Zafeiriou, S. (2019). ArcFace:
Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4690-
4699).
George, A., Ecabert, C., Shahreza, H. O., Kotwal, K., &
Marcel, S. (2024). Edgeface: Efficient face recognition
model for edge devices. IEEE Transactions on
Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 6(2), 158-
168.
Jain, A. K., Ross, A., & Prabhakar, S. (2004). An
introduction to biometric recognition. IEEE
Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology, 14(1), 4-20.
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham,
A., Acosta, A., ... & Shi, W. (2017). Photo-realistic
single image super-resolution using a generative
adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recognition
(pp. 4681-4690).
Martindez-Diaz, Y., Luevano, L. S., Mendez-Vazquez, H.,
Nicolas-Diaz, M., Chang, L., & Gonzalez-Mendoza, M.
(2019). Shufflefacenet: A lightweight face architecture
for efficient and highly-accurate face recognition. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference
on computer vision workshops (pp. 0-0).
Pizer, S. M., Amburn, E. P., Austin, J. D., Cromartie, R.,
Geselowitz, A., Greer, T., ... & Zuiderveld, K. (1987).
Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations.
Operational Limits of Near-Infrared Face Recognition: The Critical Impact of Distance on Identification Accuracy
59

Computer vision, graphics, and image processing,
39(3), 355-368.
Rajasekar, V., Saracevic, M., Hassaballah, M.,
Karabasevic, D., Stanujkic, D., Zajmovic, M., ... &
Jayapaul, P. (2023). Efficient multimodal biometric
recognition for secure authentication based on deep
learning approach. International Journal on Artificial
Intelligence Tools, 32(03), 2340017.
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., & Philbin, J. (2015).
Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and
clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 815-823).
Sino, H. W., Indrabayu, & Areni, I. S. (2019, March). Face
recognition of low-resolution video using Gabor filter
& adaptive histogram equalization. In 2019
International Conference of Artificial Intelligence and
Information Technology (ICAIIT) (pp. 417-421).
IEEE.
Szeliski, R. (2022). Computer vision: Algorithms and
applications. Springer Nature.
Wang, Z., Miao, Z., Jonathan Wu, Q. M., Wan, Y., & Tang,
Z. (2014). Low-resolution face recognition: a review.
The Visual Computer, 30(4), 359-386.
Zhou, Y., Li, X., & Zhang, H. (2023). Monocular facial
presentation attack detection: Classifying near-infrared
reflectance patterns. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1987.
https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031987.
RITECH 2025 - The International Conference on Research and Innovations in Information and Engineering Technology
60
