
The Construction and Representation of Digital Identities: The
Impact of Social Media on Consumer Thinking
Wanqing Yin
City Culture and Communication College, Suzhou City University, 215104 Jiangsu, China
Keywords: Digital Identity Construction, Social Media Influence, Consumer Behavior Patterns, User-Generated Content.
Abstract: As social platforms grow and the number of users increases, users are forming unique digital identities on the
platforms, while at the same time new trends in brand marketing strategies are changing consumer thinking.
The aim of this study is to analyse the impact of social media on the construction and representation of
consumers' digital identities and examine how it changes consumer thinking and behaviour. In this study, data
were collected through a questionnaire, using methods such as descriptive statistics and cross-tabulation to
classify and analyse the behavioural patterns of social media users from different backgrounds. The results of
the study show that young users under the age of 18 are highly active on various social media platforms. They
mainly focus on user reviews and brand storytelling. Meanwhile, users aged 26 to 34 showed a stronger
interest in visual content. Generally speaking, consumers shape and present their digital identities through
social media. This process not only reflects the differences in the concerns of different age groups, but also
plays an important role in driving consumer behaviour.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern digital field, social platforms are
growing rapidly and diversifying. Along with the
popularity of mobile internet which has increased the
number of users, social media has penetrated into
people's daily lives. As of December 2023, the number
of active users across the network has reached 1.438
billion, with a growth rate of between 2.4% and 3.4%
over the past year. Billions of people use various
social platforms for information exchange, social
interaction, and entertainment. These platforms have
not only become an important link for people to
connect with each other, and even it has become a
powerful hub for information dissemination.
These ‘preferences’ and ‘habits’ on social
platforms gradually shape users’ unique online
“digital identities”. Symbolic existence has become
the dominant paradigm in the age of smart media, and
mimetic spaces provide a place for anonymised
identity interaction. Digital Identity as a Critical
Infrastructure for Higher-Order Forms of Social Being
Catalysed by Digital Technology, has the objective
necessity of constructing and generating. Social media
users display their personalities, values and lifestyles
by posting content, engaging in interactions, etc. They
construct a digital image that is related to, but different
from, the real self.
In the China Brand Marketing Innovation and
Consumption Trend Insight Report 2024, it is
mentioned that brand marketing is shifting towards
segmented groups and precise targeting. The
traditional one-way communication marketing model
is gradually being replaced by interactive and
personalised marketing. Brands are increasingly
focusing on deeper engagement with consumers
through social media, to understand their needs,
preferences and consumption habits to develop more
precise marketing strategies.
Looking at the evolving situation of today's social
platforms and new trends in brand marketing, this
study aims to analyse the impact of social media on
the construction and performance of consumers'
digital identities. And exploring how this influence
changes consumer ideas and behaviour is important
for both theory and practice.
Users shape their unique virtual selves through
verbal actions and interactive exchanges on social
media platforms. Social tools have a profound impact
on users' perceptions, changing the way they view and
evaluate products and brands, and this change in
perception is directly related to purchasing behaviour,
resulting in new characteristics and patterns of
consumption. Focusing on this area, this paper
494
Yin, W.
The Construction and Representation of Digital Identities: The Impact of Social Media on Consumer Thinking.
DOI: 10.5220/0014137000004942
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management (APMM 2025), pages 494-500
ISBN: 978-989-758-791-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

provides insights into how social media influences
consumers’ digital identity construction, cognitive
processes, and purchasing activities, whether different
types of platform content make a difference to users’
consumer mindsets, and what is the correlation
between the frequency and quality of online
interactions and shifts in consumer mindsets. On a
more granular level, delve into how the algorithmic
recommendation models of different social platforms
lead users to present specific areas of the self and how
the social norms of these platforms limit or facilitate
the development of digital identities. Also, to analyse
the mechanisms by which social media influences
consumer behaviour such as purchase decisions and
consumption tendencies.
This study utilises the questionnaire method, a
technique that has the advantage of being able to parse
user groups on social media platforms. The
questionnaire, which covered the frequency of social
media use, preferences and ways of presenting digital
identities, was disseminated through multiple
platforms such as Weibo and Xiaohongshu to ensure
a wide coverage of different groups of people. At the
same time, descriptive statistical analysis was used to
understand the basic behavioural characteristics of
consumers on social media, and cross-tabulation
statistics were used to explore the relationship
between different variables, such as the link between
different age levels and their consumption patterns, so
as to examine the impact of social media on
consumers in depth, which helped to carry out the
study successfully.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Research Related to Digital Identity
Construction
In the last two years, more research on digital identity
construction has focused on how individuals shape
and represent themselves in digital environments.
Zhao Shuangge and Xunsha explored the wandering
regulation of simulacra in the age of intellectual
media, and the value definition and meaning reshaping
of prosaic reality (Zhao & Xun, 2024). Their research
highlights the fluidity and malleability of personal
identity in the digital environment. Huang Jiakang, on
the other hand, explores the logic of digital identity
formation, the difficulties in constructing it and the
ways to solve the difficulties from the perspective of
youth, revealing that young people face the problems
of losing themselves and the proliferation of false
identities when constructing their identities in the
digital world (Huang, 2024). Zegang Liu's research
focuses on the formation of digital identities in the age
of artificial intelligence, emphasising the importance
of technological advances to the identity building
process (Liu, 2024). Yan Guohua and Han Shuo and
Xu Qiang, on the other hand, explored the identity
construction of youth groups in virtual existence from
the perspective of semiotics and identity theory (Yan
& Han, 2024; Xu, 2023). They see this development
as encompassing multiple dimensions of self-
expression and social recognition. However, they also
pointed out that some young people may overly pursue
online identity to the detriment of real-life issues.
Zhang Zheng and Liu Chenxu's study focuses on the
new identity practices of Generation Z youth in digital
image consumption, emphasising the construction of
digital self-consciousness (Zhang & Liu, 2023).
Masiero S and Bailur S examine the importance of
digital identity in social development, analysing its
role in promoting social inclusion, enhancing the
efficiency of public services and fostering economic
development. They provide an important perspective
for understanding the value of digital identity plurality
and contribute to emphasising the social benefits of
digital identity (Masiero & Bailur, 2021). Contributed
to this study in emphasising the social value of digital
identity. However, the study discusses less about the
specific implementation techniques and application
environments, and thus appears to be less
comprehensive.
These studies provide multi-layered insights into
digital identity formation in the context of a
combination of individual and societal factors,
contributing to the understanding of the phenomenon.
However, they often ignore individual differences
across cultural and social contexts, as well as the long-
term effects of technological advances on identity
construction. Some studies have dealt less with the
changes in digital identities as they are established; in
fact, digital identities are constantly evolving and
adapting to personal development and social contexts.
This paper will analyse the age perspective and
compare the different age groups in order to fill the
current research gap.
2.2 Research Related to Algorithmic
Intervention in Identity
Classification
Along with the development of the Internet and
computing tools, algorithms play an important role in
digital identity. Hong Jiewen and Chang Jingyi
constructed a digital identity for the youths of Station
B by studying their algorithmic identity construction
The Construction and Representation of Digital Identities: The Impact of Social Media on Consumer Thinking
495

by analysing and mining the user behavioural data and
attaching specific labels to the users (Hong & Chang,
2023). This study reveals how platform algorithms
affect individual identity presentation and self-
identification. However, this study is less involved in
exploring the potential risks posed by algorithmic
categorisation and does not analyse in depth the issues
of bias and discrimination that may arise. Lun Li and
Yuying Sun fill this gap by pointing out that the design
and operation of algorithms are often influenced by
the developer's values, cognitive limitations, and data
bias (Li & Sun, 2023). This can lead to unfairly
categorised assessments of certain groups. This
research makes an important contribution to shedding
light on the problems of algorithmic discrimination,
but specific options for addressing these problems are
not explored in sufficient detail.
In addition, the opacity of the algorithms
exacerbates the risk of bias and discrimination. Users
are often unaware of how algorithms categorise and
evaluate them, and it is difficult to monitor and
intervene in the algorithms' decision-making process.
Xu Qiang points out that this trait may make users feel
that their digital identity is arbitrarily defined and
manipulated, leading to confusion and anxiety about
self-identity (Xu, 2023). When discussing
psychological impacts, Xu Qiang's research is
valuable, but improvements are still needed in terms
of specific regulatory measures and increased
transparency.
Frederico Schardon and Ricardo Custódio
conducted a systematic review, mapping and
categorisation study of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI).
They comprehensively sorted out the relevant
literature on SSI and constructed a detailed
classification system of SSI, which provided an
important theoretical foundation and research
framework for understanding the concepts, technical
implementations, and challenges faced by SSI, and
made important contributions to the theoretical
construction of the SSI field (Schardong & Custódio,
2022). However, the study mainly focuses on the
technical level and theoretical discussion of SSI, and
involves less about the specific performance and
mechanism of SSI's influence on consumer thinking in
practical application scenarios, especially in the social
media environment, and the content study is not
comprehensive enough.
These studies emphasise the impact of algorithmic
interventions on users‘ digital identities, while hinting
at the problems of bias and injustice that can result
from algorithms’ lack of ethical journalistic
awareness. There is still a lack of research on how to
properly address these issues, especially in areas such
as enhancing algorithmic regulation and increasing
algorithmic transparency. In this paper, we will
conduct an in-depth discussion from the perspective of
parsing algorithm intervention to complement the
existing research deficiency and provide theoretical
basis and practical guidance for the fair and reasonable
construction of maintaining users' digital identities.
2.3 A Study of the Impact of Social
Media on Consumer Philosophy
The impact of social media on consumer thinking and
behaviors is multifaceted. Wang Yonggui et al.
provided a macro perspective of social media
marketing research by comprehensively analysing
Web of Science core databases and CNKI databases
(Wang et al., 2024). Chen Chong explored how social
interactions influence residents' consumption from the
perspective of demonstration and cognitive effects,
highlighting the role of social media content
dissemination in shaping consumption behaviors
(Chen, 2023). Lu Xinyuan and other scholars have
analysed how social comparisons in social media
affect users' purchasing behaviors from the social
consumption interpretation, and revealed its far-
reaching effect on the complexity of shopping
decisions (Lu et al., 2023).
Knoll J states that individuals are more favoured
when they possess positive evaluative traits (e.g., good
behaviors), display social or positive non-verbal
actions (e.g., assisting others), and are perceived by
consumers as being similar or meeting expectations
(Knoll et al., 2015). JIN Fei proposed, suggesting that
social media sharing cues play an important role in
consumer decision making, influencing consumer
judgement and choice (Jin, 2022). Such as adding
sharing buttons to the product interface, adding
themed hashtags on major social platforms, or just
using advertising slogans with sharing incentives. Joy
A and others discuss future trends in digital
transformation for luxury brands, including the use of
meta-universes, digital fashion and non-homogenised
tokens NFT. The study states that these emerging
technologies present new opportunities and challenges
for luxury brands, and that brands need to continue to
innovate to meet the needs of consumers in the digital
age (Joy et al.,2022). This exploration provides
forward-looking insights into marketing and digital
strategies, but consumer acceptance and consumption
habits of these emerging digital products and services
remain under-analyses.
These studies provide this paper with a key insight
into how social networks influence consumer
behaviors. In addition, there is still a dearth of research
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
496
on how social media shapes consumer perceptions.
Some studies ignore platform characteristics. For
example, Xiaohongshu focuses on recommendation
and sharing, while Weibo emphasises rapid
information dissemination and topic discussion. This
is an area that has been under-represented in existing
research, as different features may create different
feelings in consumers. From another perspective, the
impact of social media on consumer perceptions
ignores consumer group differences. Consumers of
different generations, genders and economic status
differ in their behavioural performance and
purchasing philosophies on social platforms.
However, most studies have failed to explore these
differences in depth and their conclusions have limited
applicability.
3 METHOD
This study used a questionnaire survey method,
distributed questionnaires through microblogging,
the Rednote and WeChat platforms, and collected
data on the questionnaire star platform, with a total of
106 valid questionnaires recovered. The
questionnaire was designed to cover respondents'
basic information (e.g., gender, age, education level,
etc.), social media usage habits (e.g., frequency of
use, purpose, content posting, etc.), and the impact of
social media on consumption decisions. By analysing
these data, this study aims to reveal the impact of
social media on consumers' digital identity
construction and consumer thinking through
descriptive statistical analysis and cross-statistical
analysis.
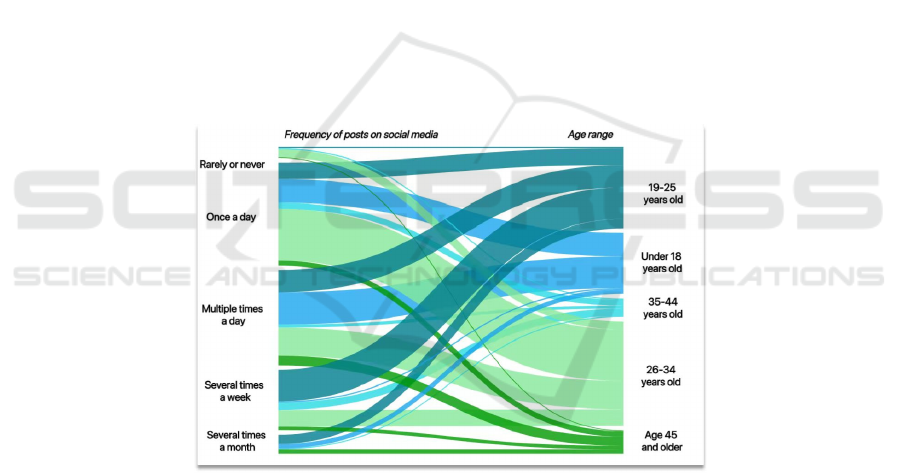
As shown in figure 1, heavy social media user groups
were identified through cross-tabulation analysis
based on the frequency of social media use and
content posting habits of the respondents. Meanwhile,
an in-depth analysis was conducted for the user
groups under 18 and 26-34 years old to reveal the
consumer thinking and behavioral patterns of their
groups, and to explore whether they are
representative and significant.
Figure 1. Social media posting frequency and age hierarchy. (Picture credit : Original)
4 RESULTS
For the young user group under the age of 18, as
shown in Table 1. through cross-tabulation analysis,
their behavioural patterns on social media are clearly
characterised by heavy use. A high percentage of users
in this group post content multiple times a day or at
least once a day, showing how active they are on social
media. When it comes to content publishing, this age
group places a high value on user reviews/ratings, with
the highest average score of 0.565. In addition, the
influence of KOL/Netflix recommendations on this
group cannot be ignored, with an average score of
0.522. These findings suggest that targeting young
users under the age of 18 on social media platforms,
trend adjustments may influence consumer purchasing
preferences to a certain extent, especially for fashion
and trend-sensitive consumers. Adolescent self-
presentation practices may be less guided by social
feedback, as most adolescents do not care about the
number of followers or likes, and they are increasingly
inclined to be guided by creative tendencies towards
authenticity (Hernández-Serrano et al., 2022). Brands
The Construction and Representation of Digital Identities: The Impact of Social Media on Consumer Thinking
497
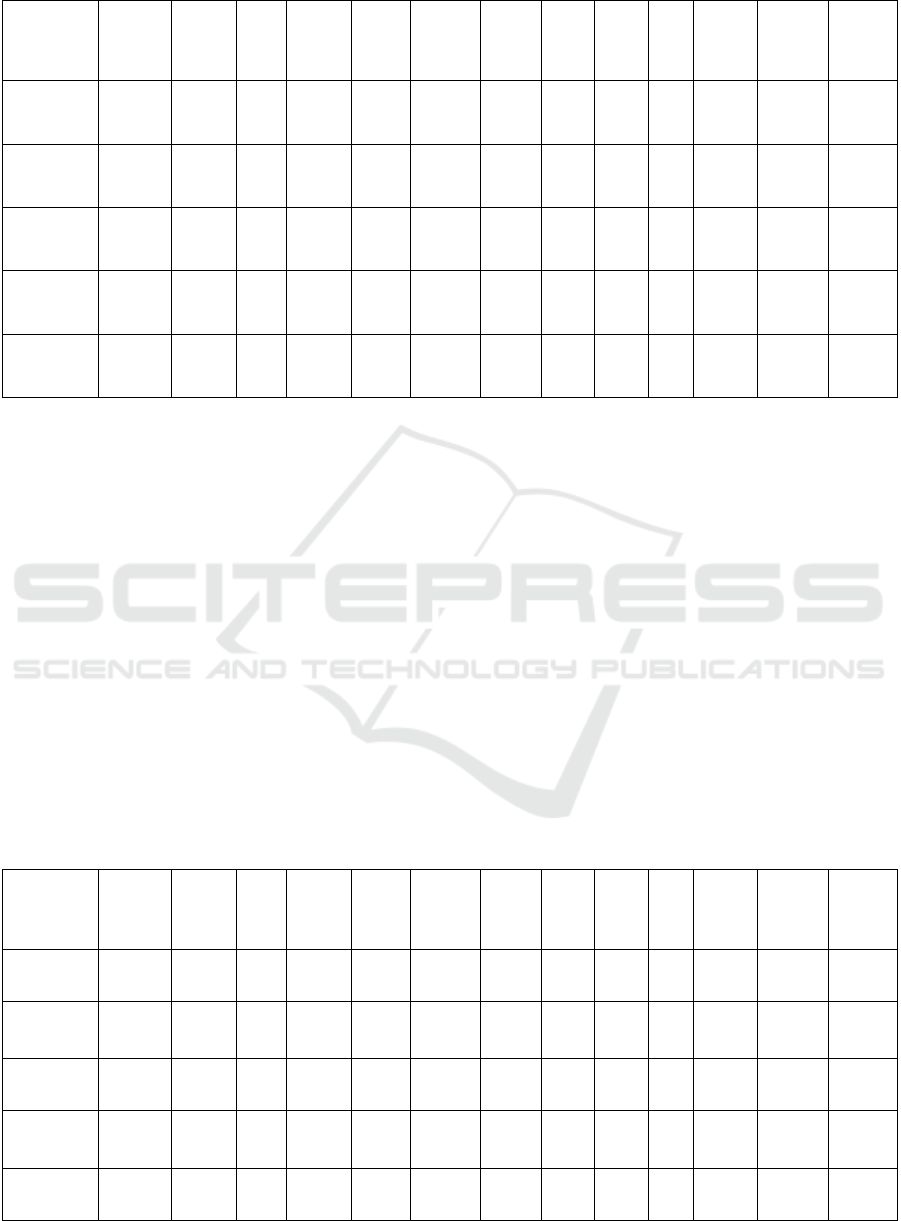
Table 1. Factors that attract attention to brands and products. (Under 18 years old).
Name
The
mean ±
standard
deviation
Varianc
e
Sum
25th
percenti
le
Media
n
75th
percentil
e
Standa
rd
error
Mean
95%
CI(LL
)
Mean
95%
CI(UL
)
IQR
Kurtosi
s
Skewnes
s
Coefficie
nt (CV)
User
reviews/rating
s
0.565±0.5
07
0.257
13.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.106 0.358 0.772
1.00
0
-2.113 -0.282 89.677%
KOL/influenc
er
recommendat
ion
0.522±0.5
11
0.261
12.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.106 0.313 0.730
1.00
0
-2.190 -0.093 97.895%
Offer/Discoun
t Information
0.261±0.4
49
0.202 6.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 0.094 0.077 0.444
1.00
0
-0.709 1.167
172.108
%
Engaging
visual content
(images,
videos)
0.261±0.4
49
0.202 6.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 0.094 0.077 0.444
1.00
0
-0.709 1.167
172.108
%
Brand
Story/Values
0.391±0.4
99
0.249 9.000 0.000 0.000 1.000 0.104 0.187 0.595
1.00
0
-1.951 0.477
127.525
%
should consider actively displaying user reviews and
ratings on social media, as well as telling engaging and
innovative brand stories, and actively communicating
and collaborating with KOLs in order to strengthen
their connection with young users.
For the 26-34 years old user group, as shown in
Table 2, this study further reveals the unique
behavioural patterns of this group on social media.
Also for ‘Factors that attract attention to a brand or
product’, this age group ranked first for ‘User
reviews/ratings’ and ‘KOL/Netflix
recommendations’, ‘Attractive visual content
(images, videos)’, the three options tied for first place,
also at 0.618, as important factors influencing their
attention to a brand or product. As shown in Table 3,
for further research, in terms of ‘factors influencing
consumer decision-making’, the same group is more
favourable to recommendations from family and
friends, with an average score of 0.735, and is less
concerned about the social responsibility or value of
the brand, and is less attracted to information about
discounts than other factors. This suggests that for the
26-34 years old user group in the actual consumer
decision-making, more reliance on positive reviews,
price, product quality and other real factors, more
inclined to use it for professional development or
information acquisition, thus investing differently in
image management, and not blindly pursuing fashion
trends. Brands are able to continue to capture their
attention through visual content and KOL
partnerships, while enhancing community outreach to
achieve the goal of influencing the consumer mindset
of this group.
Table 2. Factors that attract attention to brands and products. (26-34 years old).
Name
The
mean ±
standard
deviation
Varianc
e
Sum
25th
percenti
le
Media
n
75th
percentil
e
Standa
rd
error
Mean
95%
CI(LL
)
Mean
95%
CI(UL
)
IQR
Kurtosi
s
Skewnes
s
Coefficie
nt (CV)
User
reviews/rating
s
0.618±0.4
93
0.243
21.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.085 0.452 0.783
1.00
0
-1.856 -0.507 79.863%
KOL/influenc
er
recommendat
ion
0.618±0.4
93
0.243
21.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.085 0.452 0.783
1.00
0
-1.856 -0.507 79.863%
Offer/Discoun
t Information
0.618±0.4
93
0.243
21.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.085 0.452 0.783
1.00
0
-1.856 -0.507 79.863%
Engaging
visual content
(images,
videos)
0.353±0.4
85
0.235
12.00
0
0.000 0.000 1.000 0.083 0.190 0.516
1.00
0
-1.688 0.644
137.437
%
Brand
Story/Values
0.412±0.5
00
0.250
14.00
0
0.000 0.000 1.000 0.086 0.244 0.580
1.00
0
-1.979 0.375
121.320
%
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
498
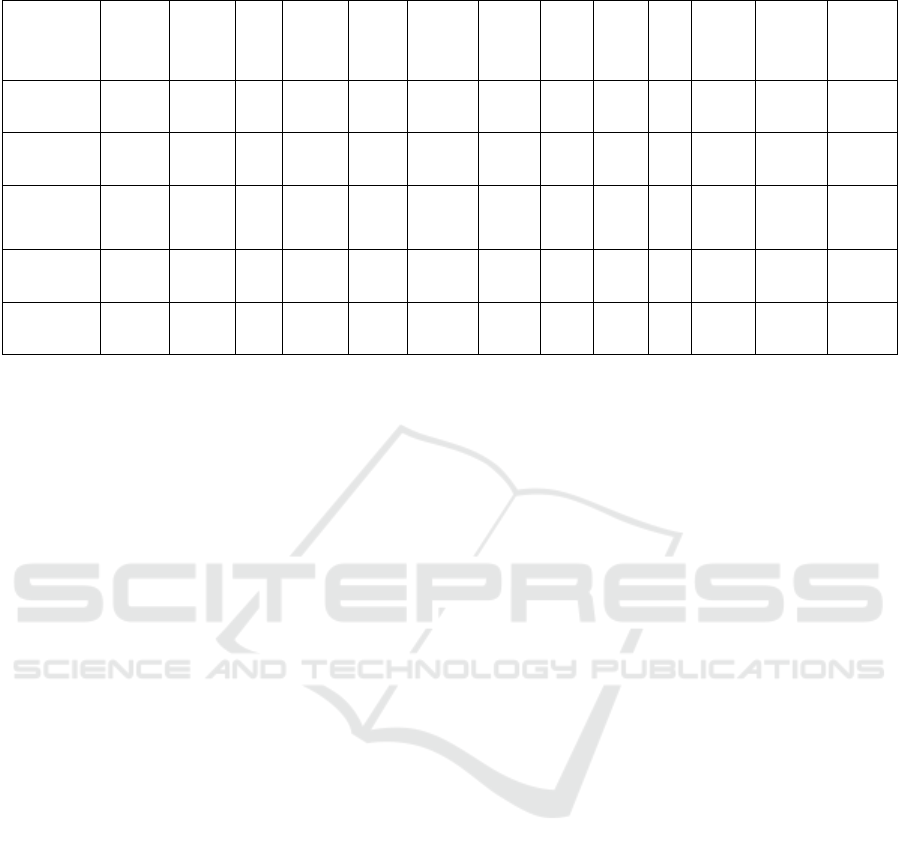
Table 3. Factors influencing consumption decisions. (26-34 years old).
Name
The
mean ±
standard
deviatio
n
Varianc
e
Sum
25th
percenti
le
Media
n
75th
percentil
e
Standa
rd
error
Mean
95%
CI(LL)
Mean
95%
CI(UL
)
IQR
Kurtosi
s
Skewnes
s
Coefficie
nt (CV)
Recommendati
ons from
friends/family
0.735±0.4
48
0.201
25.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.077 0.585 0.886
1.00
0
-0.804 -1.117 60.902%
Discussion/wor
d-of-mouth
within the
community
0.647±0.4
85
0.235
22.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.083 0.484 0.810
1.00
0
-1.688 -0.644 74.966%
The degree to
which personal
interests and
needs are
matched
0.618±0.4
93
0.243
21.00
0
0.000 1.000 1.000 0.085 0.452 0.783
1.00
0
-1.856 -0.507 79.863%
The brand's
sense of social
responsibility
or value
0.500±0.5
08
0.258
17.00
0
0.000 0.500 1.000 0.087 0.329 0.671
1.00
0
-2.129 0.000 101.504%
Frequency and
creativity of the
advertisement
0.176±0.3
87
0.150 6.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.066 0.046 0.307
0.00
0
1.225 1.777 219.273%
5 DISCUSSION
In today's information age, social networks have
served as a central place for platform users to
construct and display their digital identities, and the
ways in which they influence consumer perceptions
deserve in-depth study. The findings reveal that the
distinctive behavioural styles exhibited by users of
different age groups on social platforms are closely
related to digital identity shaping and consumption
philosophy.
From the perspective of digital identity
construction, social media provides a rich and diverse
range of platforms and tools that enable consumers to
shape their digital image in a personalised way, which
is particularly evident among the youth population.
Digital identity is a subjective product driven by the
personal development aspirations of youth groups
(Yan et al., 2024). Young users between the ages of
18 and 34, for example, show a high level of activity
on social media, posting frequent content and actively
participating in interactions. The process by which
individuals present themselves to others is the process
by which individuals present images and identities
that conform to their self-perceptions and shape
others' impressions of their individual selves during
social interactions (Li & Sun, 2023). They gradually
form a recognisable ‘self’ in the virtual world by
sharing their life, hobbies and views on various
things. This process of digital identity construction is
the result of their interaction and communication with
others in the social media space, as well as an
expression of their perception and positioning of
themselves.
The mechanism of social media's influence on
consumer thinking is multifaceted. On the one hand,
social media marketing can motivate consumers to
participate in marketing activities and influence their
consumption behaviour (Wang et al., 2024). Social
media is changing the way consumers access
information. In the traditional model, advertisements
and brochures are the main channels to learn about
products and brands. Nowadays, platforms offer a
rich source of information, including product reviews
and brand stories. This content influences perceptions
and shapes consumer thinking. On the other hand, the
social interaction feature of social media enhances the
connection and communication between consumers.
Consumers use the platform to share their shopping
experiences, discuss consumer opinions, and interact
with friends, family and other users. Such interactions
both satisfy social needs and influence the mindset of
individual users; they are influenced by the behaviour
and perceptions of others in their interactions, thus
shaping their personal consumption patterns and
paths of thought.
In addition, the algorithmic recommendation
systems of social media have also influenced
consumer thinking and behaviour to some extent.
Algorithmic recommendation systems recommend
personalised content and products for users based on
their browsing history, interests and other
information. Such personalised recommendations
make it easier for consumers to access information
about products that match their interests and needs,
thus influencing their consumption decisions. In the
future, as social media continues to grow and evolve,
its impact on consumer digital identity construction
and consumer thinking will be even more profound.
The Construction and Representation of Digital Identities: The Impact of Social Media on Consumer Thinking
499

6 CONCLUSION
This study found that social media plays a key role in
the construction of consumers' digital identities. The
rapid expansion of social platforms has led to the
gradual creation of unique digital identities out of the
habits of users' activities. Different generations of
people display a variety of different digital images. At
the same time, as an important way of information
dissemination, social media provides consumers with
a large amount of product information, and influences
consumer decisions through user feedback and brand
culture stories and other content.
This research informs the future development of
algorithms in the field of communication, especially
as reflected in brand marketing practices. For brands,
this means they need to focus more on social media
marketing, which is particularly important in shaping
digital identities and influencing consumer spending
choices. The study provides brands with valuable
insights to help better understand and reach their
target groups and gain an edge in the competitive
marketplace. At the same time, this paper analyses the
differences in the behaviour of different groups on
social platforms and points out their importance for
accurate and personalised promotion strategies.
Adjusting content and activities according to users'
interests and action patterns can increase user
engagement and loyalty.
REFERENCES
A. Joy, Y. Zhu, C. Peña, et al., Digital future of luxury
brands: Metaverse, digital fashion, and non-fungible
tokens. Strateg. Change 337-343 (2022)
C. Chen, The influence of social interaction on
consumption in the perspective of demonstration effect
and cognitive effect. Bus. Econ. Res. 56-60 (2023)
F. Jin, How sharing on social media influences consumer
choices. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 1785 (2022)
F. Schardong, R. Custódio, Self-sovereign identity: A
systematic review, mapping and taxonomy. Sensors
5641 (2022)
G. H. Yan, S. Han, Digital identity: Construction and
reflection of virtual survival symbols of youth groups.
China Youth Res. 44-51 (2024)
J. Knoll, H. Schramm, C. Schallhorn, et al., Good guy vs.
bad guy: The influence of parasocial interactions with
media characters on brand placement effects. Int. J.
Advert. 720-743 (2015)
J. L. Huang, The logic of generating, constructing and
cracking youth digital identity. J. Theory 82-87 (2024)
J. W. Hong, J. Y. Chang, Between ‘intentional’ and
‘unintentional’: A study on the construction of
algorithmic identities of youth in B station. Journalist
39-52 (2023)
L. Li, Y. Y. Sun, Discourse-power-presentation: The
generative logic of digital identity. J. Soc. Sci. Hunan
Norm. Univ. 32-38 (2023)
M. J. Hernández-Serrano, B. Jones, P. Renés-Arellano, et
al., Analysis of digital self-presentation practices and
profiles of Spanish adolescents on Instagram and
TikTok. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 49-63 (2022)
Q. Xu, Identity landscape: Digital identity and its
identification in the real and imaginary. Shandong Soc.
Sci. 113-119+144 (2023)
S. G. Zhao, S. Xun, The wandering regulation of mimesis:
The value definition and meaning reshaping of
proximate reality in the age of intellectual media. Media
Watch 68-77 (2024)
S. Masiero, S. Bailur, Digital identity for development: The
quest for justice and a research agenda. Inform. Technol.
Dev. 1-12 (2021)
X. Y. Lu, J. A. Zhang, H. Meng, F. F. Ren, How social
comparison in social media affects users' consumption
behaviour — An explanation based on social
consumption. Modern Intell. 39-50 (2023)
Y. G. Wang, H. Y. Wang, J. L. Yang, J. Q. Liu, Social
media marketing research and prospect — A
comprehensive analysis based on Web of Science core
database and CNKI database. Manag. Rev. 146-160
(2024)
Z. G. Liu, Points, bases and difficulties in the construction
of digital citizenship in the era of artificial intelligence.
Law Rev. 105-119 (2024)
Z. Zhang, C. H. Liu, Constructing digital self-
consciousness: New identity practices in the
consumption of digital images by ‘Generation Z’ youth.
Fujian Forum (Hum. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 30-39 (2023)
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
500
