
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep
Learning Integration
Serli Marlina
1a
, Jamillah Binti Mohd Basir
2b
, Amalia Husna
1c
and Siti Hafifah
1
1
Universitas Negeri Padang, Indonesia
2
Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, Indonesia
Keywords: Interactive Games, Deep Learning, Prosocial.
Abstract: This research was motivated by the lack of development of deep learning-based social games as integrated,
meaningful, and enjoyable games for children aged 5-6 years. At present, educators routinely employ
commercially produced games, which adversely affects the engagement levels of the educational process and
can frequently lead to a decline in attentiveness among students. The primary aim was to assess social games
founded on deep learning methodologies to promote prosocial behaviors in children aged 5 to 6 years. The
conceptualization and evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games that integrate Deep Learning methodologies
were conducted utilizing the ADDIE Model, which consists of five discrete stages: analysis, design,
development, implementation, and evaluation. The interactive game design was tailored to teachers' needs in
using games for prosocial stimulation. The games were designed to emphasize children's developmental
characteristics and prosocial skills, as assessed based on evaluations of child development, the number of
children, school conditions, and teachers' skills in using technology. The results showed that SERLI
Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration demonstrated a significant increase in prosocial skills (p <
0.01) and high user satisfaction. This investigation significantly advances the field of adaptive educational
gaming and the implementation of deep learning methodologies within the educational sector.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development and growth of early childhood is
one of the most important things to pay attention to,
from when the child is in the womb until they are born
into the world. Early childhood encompasses the
developmental stage of human beings from the
moment of birth until the age of eight years.
According to (Suryana, 2021), this specific age range
represents an exceptionally pivotal phase in the
holistic growth and maturation of individuals.
Therefore, the provision of appropriate attention and
stimulation throughout this formative period is
imperative for promoting optimal developmental
outcomes in children. This perspective is reinforced
by (Windayani et al., 2021), who assert that early
childhood is the period when the foundation of a
child's personality is formed, which will shape their
experiences in the future. Thus, during this period, it
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1336-5071
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-8573-7291
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-7033-4892
is crucial to monitor every aspect of their growth and
development and identify their potential to ensure the
achievement of all aspects of their future
development.
In the scholarly conversation regarding the
various dimensions of early childhood maturation and
progression, the sphere of social development
surfaces as a critical element that necessitates
meticulous examination. According to (Khadijah &
Jf, 2021), social development in early childhood is a
form of maturity in interacting with people around
them through the social relationships they form. This
developmental maturity is manifest in the manner in
which children comprehend the existence of their
peers, engage in communication, and exhibit
collaborative conduct across a multitude of contexts.
In agreement with (Kaffa et al., 2021), it is added that
social development is characterized by a child's
ability to socialize, adapt to the social environment,
Marlina, S., Basir, J. B. M., Husna, A. and Hafifah, S.
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration.
DOI: 10.5220/0014068500004935
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Early Childhood Education (ICECE 2025) - Meaningful, Mindful, and Joyful Learning in Early Childhood Education, pages 155-163
ISBN: 978-989-758-788-7; ISSN: 3051-7702
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
155

and adjust to the norms and values prevailing in their
group. Children demonstrating social development
typically forge advantageous interpersonal
connections with increased facility, possess the
ability to conform to societal norms, and display
empathy and compassion towards their peers.
Furthermore, (Harianja et al., 2023) explain that
children's social development is an important and
ongoing process in which children learn to understand
their identity, form interpersonal relationships, and
manage and express their emotions in various social
contexts. This protocol encompasses not only the
capability for interpersonal interaction but also
incorporates an understanding of social norms,
empathetic engagement, cooperative endeavors, and
the competence to resolve conflicts in a constructive
fashion.
According to Vygotsky and Bandura's views,
which are known through social learning theory that
focuses on cognitive development (Hurlock, 1995),
children aged 4–6 years have begun to show progress
in social development. The social development of
children comprises various significant dimensions,
which include: the capacity for self-recognition and
self-regulation (self-awareness), comprehension of
obligations towards oneself and others, and the
exhibition of prosocial behaviors such as sharing,
cooperation, and respect for others. Furthermore,
children initiate the cultivation of communication
competencies, the ability to constructively resolve
conflicts, and the capacity for empathy towards the
emotions of others. Additionally, children begin to
form a social identity as part of a group and learn to
manage their emotions healthily in various situations
(Harianja et al., 2023).
A pivotal aspect of social advancement that
requires deliberate scrutiny relates to prosocial
conduct. Prosocial behavior refers to positive actions
voluntarily undertaken by an individual to provide
assistance to others, whether in the form of physical
or psychological support, without any element of
coercion (Suparmi & Sumijati, 2021).This behavior
not only reflects concern for others but also serves as
the foundation for building healthy and harmonious
social relationships from an early age. In line with
(Saharani et al., 2021), prosocial behavior can be
delineated as a classification of actions that enhance
interpersonal engagement, cooperation, and selfless
support among individuals without the expectation of
reciprocal advantages. This conduct exerts a positive
impact on social dynamics as it fosters an atmosphere
typified by concord and serenity, while concurrently
promoting mutual regard and affection among
members of the community.
Indicators that reflect social development include:
(1) children begin to understand basic rules both
within the family environment and when playing; (2)
children begin to show compliance with these rules;
(3) the emergence of awareness of the rights and
interests of others; and (4) children begin to be able
to engage in games with peers and gradually expand
their social interactions with adults around them (N.
Fuadia, 2022). This is evident in children's ability to
engage in group activities or interact in peer group
contexts through play and games. Moreover, the
trajectory of social development in children is
characterized by both gradual advancement and
individual specificity. Each child demonstrates a
unique developmental pace, and their social skills are
likely to continue evolving over time, dependent upon
the availability of appropriate support and stimulation
from their educational environments.
However, observations indicate that the lack of
development of deep learning-based social games has
limited stimulation of social skills in children aged 5–
6 years. Educators persist in employing commercially
produced games that do not explicitly aim to cultivate
prosocial behaviors such as cooperation, sharing, and
empathy. Consequently, children frequently
demonstrate diminished engagement in social
interactions, a tendency towards conflicts, and
difficulties in group adaptation. Moreover, non-
contextual games undermine the overall educational
experience, resulting in diminished attention spans
and low levels of social participation among children.
This underscores the pressing need for games that are
thoughtfully designed to effectively enhance the
optimal social development of children.
With the advancement of technology, digital
learning media has begun to be used in early
childhood education (PAUD), one of the significant
transformations being the use of interactive
educational games based on applications as a medium
for stimulating children's development. Research by
(Firanti et al., 2024) indicates that the use of
interactive technology such as tablets, learning apps,
and educational games significantly contributes to
enhancing young children's social-emotional skills,
particularly in aspects such as empathy, emotional
regulation, and the ability to resolve social conflicts
peacefully. Support for these findings is reinforced by
(Elyakim et al., 2024), who state that technology-
based learning models can create a conducive
learning environment for building social skills, such
as cooperation, sharing, and effective communication
among children. In the realm of digital collaborative
learning, children cultivate the ability to articulate
their thoughts, engage in active listening with their
ICECE 2025 - The International Conference on Early Childhood Education
156
peers, and partake in turn-taking while utilizing
devices through the interactive components present in
educational games. This highlights the significant
capacity of technology not only to enhance
educational pursuits but also to improve social skills
in a way that is both flexible and pertinent to specific
contexts.
In light of the extensive possibilities inherent in
technology to facilitate social learning, the advent of
interactive educational games has transformed into
one of the most prominent pedagogical strategies
within the domain of early childhood education. A
particularly noteworthy facet that continues to evolve
is the utilization of technology-based media, as
illustrated by interactive games. Games represent a
crucial element of children's experiential learning and
play an essential role in their developmental
progression. According to (Suryana et al., 2023),
interactive games in an educational context offer an
enjoyable approach for children by combining the
concept of learning through play and serving as an
effective learning medium for conveying content
while also providing an engaging form of
entertainment, thereby enhancing children's
motivation and engagement in the learning process.
(Fajar & Zega, 2023) argue that interactive games
designed with the appropriate approach can provide
significant brain stimulation and support early
childhood learning more optimally.
Regarding interactive games, a number of
previous researchers have studied them for
application in children. One study conducted by
(Andi Saputri et al., 2024) used innovative interactive
learning media to improve six key social-emotional
skills in children, namely empathy, emotional
regulation, cooperation, communication, conflict
resolution, and self-awareness. Meanwhile, (Elyakim
et al., 2024) investigated the impact of using
educational app-based games on children aged 4–6
years. The results of the investigation suggested that
children who were exposed to sufficient time and
supervision demonstrated superior advancement in
the areas of empathy, emotional understanding, and
social conflict resolution skills when compared to
their peers who did not engage in interactive gaming
experiences.
Consistent with preceding research that elucidates
the capacity of interactive media to facilitate the
social-emotional growth of children, the investigators
in this study intend to devise educational media in the
form of technology-driven interactive games as a
mechanism for fostering prosocial behaviors during
early childhood development. The main difference
from previous studies lies in the technological
approach used, namely through the application of an
adaptive deep learning system that enables the media
to respond to children's behavior in real-time.
Therefore, this study aims to examine the “Design
and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with
Deep Learning Integration.”
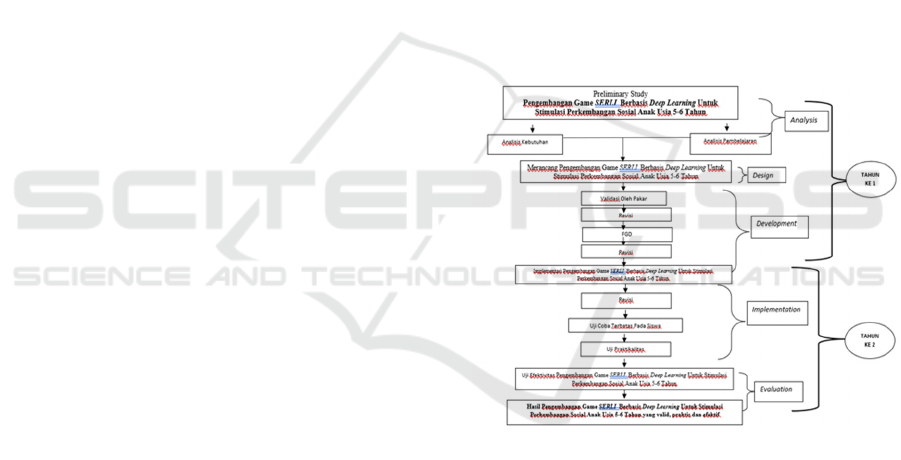
2 METHOD
This research is a research and development (R&D)
study. The development model used is the ADDIE
model. This model was chosen because its steps are
practical and suitable for the development of the
SERLI game based on deep learning for stimulating
the social development of children aged 5-6 years.
The ADDIE framework is comprised of five distinct
phases: analysis, design, development,
implementation, and evaluation. The ADDIE
development procedure and activities to be carried
out at each stage:
Chart 1: SERLI Game Development Procedure Based
on
Deep
Learning.
The subjects of this study were students in Group
B at the UNP Development Kindergarten and the
Pertiwi Kindergarten at the Padang Governor's
Office. The selection of these early childhood
education institutions as the central subjects of the
study was based on their congruence with the
research aims. The information necessary for this
investigation included both quantitative and
qualitative aspects, which comprised data from the
preliminary study (analytical findings) as well as
results from product evaluations. The data from the
preliminary study consists of information related to
needs assessment, curriculum development,
pedagogical strategies, teacher training, and student
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration
157
achievement outcomes; conversely, the product
evaluation data includes analyses of the model's
validity, feasibility, and effectiveness.
The instruments to be used in this study consist of
(1) interview guidelines; (2) observation guidelines;
(3) model validity test sheets and learning tools by
experts; (4) model practicality test sheets; and social
development measurement scales to test the
practicality of the model. The data to be collected are
quantitative and qualitative. Data from the validity
and practicality tests will be analyzed using the
Cohen's Kappa formula, while data on practicality
from the implementation aspect will be analyzed
using percentage and achievement level techniques.
Quantitative data from the effectiveness test will be
processed using the t-test statistic. Qualitative data
acquired from interviews and observational studies
will undergo procedures involving data reduction,
data presentation, and the formulation of conclusions.
The research product trial will be conducted at the
UNP Labor Development Kindergarten, with
kindergarten B children as the trial subjects.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
To strengthen the results of the development of
SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning
Integration, researchers also conducted in-depth
interviews with several early childhood education
(PAUD) teachers to gain a contextual understanding
of children's social, motor, and literacy development
over the past three years. These interviews aimed to
obtain qualitative data to support the effectiveness of
the developed media and to explore real-world needs
related to technology-based learning for early
childhood. The following is a summary of the
interview results:
Table 1: Teacher Needs Analysis.
Question
Answer
How has
the child's
social
develop-
ment been
over the
past three
years?
Children's social development over the past
three years (2022–2025) has shown
considerable progress and is in line with their
age group, although challenges remain. n the
year 2022, subsequent to the COVID-19
pandemic, numerous children encountered
social developmental delays attributable to
restricted face-to-face interactions and a
heightened reliance on electronic devices.
These children displayed a proclivity towards
fostering enhanced attachment to their
caregivers, exhibited a deficiency in self-
confidence within unfamiliar environments,
and encountered challenges in collaborative
behaviors including sharing, turn-taking, and
conflict resolution. The linguistic constructs
employed by these children at times
reflected adult vernacular as a result of the
omnipresent impact of digital media,
notwithstanding their partial grasp of the
fundamental significances. As we enter
2023, children are beginning to adapt and
recover their social skills through direct
interaction at school and group activities
such as playing together, collaborative
projects, and field trips. Teachers and
parents actively provide social interaction
exercises such as role-playing and
discussions about emotions. By 2024–2025,
children's social development becomes
more stable: they are more confident in
communicating, demonstrate indepen-
dence, understand social rules, and are able
to share and resolve minor conflicts with
guidance. Furthermore, children
commenced displaying a sense of ease
within expansive social networks, fostering
close interpersonal relationships, and
demonstrating nascent indications of
empathy—evidenced by their solicitude for
peers experiencing distress, as exemplified
by the observation of a companion in tears.
Although some children still struggle to
control their emotions or adapt to new
environments, overall they are able to
socialize well, no longer rely on their parents
at school, and actively play and share with
their peers.
In what
ways has
the motor
developm
ent of
your child
evolved
over the
preceding
three
years?
The motor development of children over the
past three years (2022–2025) has generally
shown positive progress and is in line with
their age stages, both in terms of gross
motor skills and fine motor skills. Following
the global health crisis in 2022, a substantial
number of children exhibited delays in
motor development attributable to the
constrained physical activity experienced
during the period of lockdown. The
prospects for children to participate in
physical activities such as running, jumping,
and engaging in outdoor play have been
significantly curtailed, which has
subsequently resulted in constraints
regarding their gross motor skills,
encompassing balance and the coordination
of physical movements. Nevertheless, with
the reopening of educational institutions
and recreational facilities, a significant
improvement in motor skills has been
documented. Children have initiated active
ICECE 2025 - The International Conference on Early Childhood Education
158
participation in a variety of activities,
including cycling, ball games, gymnastics,
climbing, and jumping, which have
facilitated the strengthening of their large
muscle groups. Simultaneously, there has
been a significant advancement in fine
motor development, predominantly due to
the heightened involvement in tactile
activities within educational environments,
such as drawing, cutting, folding, stringing,
and writing. Children have started to exhibit
improved hand-eye coordination and
increased manual dexterity. However, a
segment of children continues to experience
delays in motor development, potentially
influenced by the widespread utilization of
digital devices or other factors such as
inadequate stimulation, nutritional
insufficiencies, or health-related challenges.
Although the progress is not homogeneous
across the population, the majority of
children now exhibit a heightened
enthusiasm for engaging in various motor
activities orchestrated by educators and
demonstrate significant advancements in
both their physical capabilities and
coordination skills.
How has
children's
literacy
developed
over the
past three
years?
The development of literacy among
children aged 4–6 years over the past three
years has shown positive progress in line
with their age group, although it has been
uneven. Children have begun to develop
from simply recognizing letters to being
able to understand simple texts and write
with guidance. This phenomenon has been
shaped by a diverse array of engaging
pedagogical approaches, including the
practice of reading aloud, which facilitates
children's ability to narrate stories utilizing
their own linguistic expressions. Reading
interest is also beginning to grow,
especially among children who receive
support from home and school and have
access to adequate literacy media. Certain
children exhibit the capability to identify
individuals, inanimate items, and various
species, while also adhering to
uncomplicated directives. Furthermore,
they are commencing to discern letters,
numerals, and lexical items with increasing
proficiency. However, this development is
not yet uniform—there are still children
who show slow development, even
experiencing speech delays, especially
those who are more frequently exposed to
gadgets than books. Determinants such as
the caliber of cognitive engagement within
the home environment, the proactive
involvement of caregivers, and the
availability of enriching educational
resources serve as pivotal influences on the
literacy achievements of children. Not
withstanding, an overarching analysis of
the trajectory of children's literacy
advancement over the preceding three
years indicates a favorable and encouraging
progression.
What types
of games
have
educators
implemente
d to
enhance the
social
developmen
t of
children?
A diverse array of games incorporated into
early childhood educational practices
during the preceding three years has
demonstrated efficacy in facilitating both
social and cognitive growth. The games
used include traditional games such as
hide-and-seek, hopscotch, congklak, snake
and ladder, marbles, and jump rope, as well
as modern games involving group or team
activities, such as ball relay, building towers
together, playing ball in a circle, and races.
Additionally, role-playing games like
“marketplace,” “doctor and patient,”
“family,” and becoming a merchant, buyer,
teacher, or student are highly popular
among children because they provide
opportunities for self-expression, commu-
nication, taking turns, and understanding
social roles in daily life. Activities like
playing shop and queuing at the cashier
also develop social skills and discipline.
Teachers actively create variations of
games, including storytelling, drawing, and
question-and-answer games that enrich
children's imagination and strengthen
social interaction. Daily school activities like
cleaning the environment together are also
turned into collaborative games that instill
values of cooperation and responsibility. All
variants of these games, encompassing
traditional, contemporary, or role-playing
formats, confer substantial advantages in
the enhancement of children's social
competencies, communicative abilities,
empathy, and collaborative skills.
What
categories
of games
have
educators
employed
to enhance
the motor
develop-
ment of
children?
Diverse categories of games and physical
endeavors have been persistently
employed to facilitate the advancement of
gross and fine motor skills in early
childhood over the preceding three years.
Gross motor activities include games such
as jumping rope, jumping over shapes or
colors, walking on a balance beam, relay
races, playing ball (kicking, throwing,
catching), tug-of-war, swimming, hide-and-
seek, tag, and obstacle courses that involve
crawling, jumping, and walking along a line.
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration
159
Additionally, endeavors encompassing
cognitive intermissions, physical exercises,
dance, and music-based movements are
pivotal in augmenting children's agility,
bodily coordination, and rhythmic
locomotion. Simultaneously, fine motor
competencies are fostered through
activities such as construction with building
blocks, engagement with puzzles,
manipulation of playdough or modeling
clay, clipping and affixing images, threading
beads, drawing, coloring, inserting buttons
or sticks into openings, and tearing paper.
Furthermore, children are provided with
the opportunity to engage in role-playing
scenarios themed around environments
such as marketplaces, healthcare facilities,
or educational institutions, which promotes
the cultivation of social competencies,
empathy, and the integration of manual
and cognitive functions. Tasks such as
color-sorting of spheres and the
transference of water into a receptacle
exemplify activities that enhance hand-eye
coordination. This synthesis of traditional
and modern games has evidenced
effectiveness in promoting children's motor
development in a comprehensive manner,
while concurrently delivering enjoyment
and aligning with their playful contexts.
What
varieties of
games have
educators
employed
to enhance
the literacy
developme
nt of
children?
A diverse array of activities and games have
been utilized to foster early childhood
literacy advancement in a manner that is
both engaging and interactive. Initiatives
such as read-aloud sessions, digital
storytelling, and collaborative storytelling
events function as effective instruments for
nurturing children's enthusiasm for
narratives and linguistic articulation.
Morning storytelling sessions, during which
children take turns narrating stories and
their peers are given the opportunity to ask
questions, further facilitate the
enhancement of verbal and auditory
competencies. Additionally, various
educational games such as word guessing,
chain messages, picture story boxes,
picture word cards, letter and number
cards, and picture guessing encourage
children to learn vocabulary, initial letter
sounds, and word structure in a fun way.
Other games like “What's My Name?”,
matching pictures with their initial letters,
and a hidden letter hunt in the classroom
reinforce letter recognition and improve
children's memory and concentration.
Young learners are also encouraged to
engage with enchanted containers,
decipher characters, formulate lexemes,
and organize alphabetical or lexical cards,
all of which contribute positively to the
enhancement of creativity, systematic
cognitive abilities, and acquaintance with
the alphabet. Physical games such as
carrying plastic spoons filled with letters to
select matching pictures also train
coordination and literacy. All such
endeavors—be they conventional or
contemporary games, musical compo-
sitions, pedagogical videos, or dramatized
interactions-thoroughly facilitate the
advancement of literacy skills in children
from a nascent stage in an innovative and
purposeful manner.
Have
educators
historically
conceptuali
zed games
aimed at
enhancing
children's
social,
motor, and
literacy
competenci
es? If
affirmative,
what
categories
of games
do they
encompass
and what
are their
respective
titles?
The majority of educators specializing in
early childhood development possess
proficiency in the formulation and
execution of integrated play activities
aimed at concurrently enhancing multiple
dimensions of child development, including
social interaction, motor skills, and literacy
competencies. These games are often
tailored to weekly themes or learning
projects in the classroom. Instances
encompass Market Play or Role Play, in
which children assume the roles of vendors
and consumers utilizing toys, repurposed
materials, or self-constructed props.
Children learn to read price labels, write
shopping lists, and perform simple
transactions, which simultaneously
stimulate social skills (cooperation, taking
turns, politeness), motor skills (writing,
carrying bags, holding toy money), and
literacy skills (reading text and product
labels). Games like Word Market, Smart
Mat, or Snake and Ladder searching for
letters and numbers are also examples of
fun and effective integrated activities. In
these educational activities, children have
the opportunity to acquire knowledge of
letters, words, or numerical concepts,
concurrently enhancing their cognitive
abilities, motor skills, and social interaction
competencies with their peers. Some
teachers even combine physical games like
relay races moving word cards or simple
dramas with literacy and social elements.
Although some have never tried it, most
teachers report frequently conducting
these activities because they are highly
beneficial in developing children's various
skills comprehensively and enjoyably.
ICECE 2025 - The International Conference on Early Childhood Education
160

In the event
that a game
amalgamates
technological
advance-
ments with
traditional
gaming
formats
grounded in
deep learning
methodologie
s, do you
believe it is
imperative to
foster social,
motor, and
literacy
a
dvancement
s
? If so, what
kind of game
is needed?
Games that combine technology with
physical and conventional activities are
considered highly promising and necessary
in stimulating children's social, motor, and
literacy development in a comprehensive
manner. Various educators have utilized
technology such as interactive applications
that provide guidance or instructions
during learning, as well as digital-based
games that encourage children to move
and express themselves actively. Examples
include picture guessing games, puzzles,
sound recognition, and educational games
based on deep learning such as “Smart
Thematic Puzzle,” where children assemble
physical puzzles, then scan the results into
an application to hear stories and answer
interactive questions. These participatory
activities facilitate the advancement of
literacy skills (through the understanding of
narratives and the refinement of
storytelling abilities), augment fine motor
skills (through the construction of puzzles),
and encourage social skills (through
cooperative engagement and the sharing of
roles). Furthermore, hybrid gaming
frameworks that amalgamate tangible
tools with adaptive artificial intelligence, in
conjunction with augmented reality
applications such as nature exploration
games, incentivize children to engage in
physical movement within real-world
contexts while gaining insights into their
environment. Activities of this kind are not
merely engaging and enjoyable; they also
enhance children's cognitive abilities for
conceptualization while engaged in play.
Most critically, digital games ought to be
constructed with a contextual framework
that resonates with children’s real-world
experiences—incorporating physical
movement, social engagement, and tactile
interactions—thereby ensuring that they
do not supplant but, rather, enhance their
recreational activities.
This study raises the important issue of stimulating
the social development of children aged 5-6 years
through SERLI Interactive Games that integrate deep
learning technology. The findings of the research
indicate that interactive games employing deep
learning techniques have a significant impact (p <
0.01) on the improvement of prosocial skills in
children. The aspects of socio-emotional
development that were scrutinized in this study
produced encouraging results, especially concerning
the enhancement of prosocial behaviors such as
cooperation, empathy, and compliance with social
norms. This is in line with the view (N. N. Fuadia,
2022) who stated that children's socio-emotional
development can be effectively stimulated through
specially designed games, where children can learn to
interact, share, and show empathy in a fun context.
These findings align with (Hafsania, 2021), it has
been posited that fostering social and emotional
growth in early childhood through play constitutes an
exceptionally efficacious approach, as play serves as
the inherent medium through which children
articulate their emotions and engage with their
environment.
The qualitative interviews conducted in this
research elucidated noteworthy advancements in the
social development of children subsequent to the
COVID-19 pandemic. Empirical data indicates that in
the year 2022, a significant number of children
encountered social delays attributable to restricted
face-to-face interactions and a heightened reliance on
electronic devices. Early childhood social
development is the process of forming social
relationships with their environment, but this process
often encounters various issues that impact children's
social development. This situation reinforces the
urgency of developing SERLI Interactive Games as
an alternative solution that can bridge the need for
technology and stimulate social development.
According to (Rakhmawati, 2022), Efficacious
educational games ought to possess the capacity to
simultaneously enhance various aspects of child
development. These educational games are carefully
engineered to operate as pedagogical tools that
reinforce educational pursuits, aid instructors in
delivering instructional content, and facilitate the
comprehensive development of children. SERLI
Interactive Games fulfills these criteria by integrating
social, motor, and literacy stimulation in a single,
adaptive platform. This SERLI research brings
innovation by integrating deep learning technology
that enables real-time adaptation to children's
behavior. These findings align with the view of
(Setiawan et al., 2019) who stated that digital
educational games can serve as effective learning
tools for early childhood by incorporating fun
learning concepts. Similar research by (Dewi &
Agung, 2021) also shows that interactive multimedia-
based educational games can maximize child
development, particularly in social aspects through an
innovative approach.
The use of the ADDIE model in the development
of SERLI games has proven effective in creating
adaptive learning media that is tailored to teacher
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration
161

needs and child characteristics. This is supported by
research (Irawati, 2012) which shows that developing
educational games using the ADDIE model can
improve children's learning abilities through well-
integrated games. Furthermore, (Handayani, 2018) it
was underscored that meticulously crafted
educational games possess the potential to enhance
the social development of children, as play constitutes
a realm that is intimately familiar to them.
Moreover, the principal advancement of this study
is encapsulated in the application of deep learning
methodologies, which facilitate the game’s capacity
to adjust dynamically in response to the behavioral
patterns exhibited by children. This differs from
previous studies, which generally used static games.
The development of a treasure hunt game based on
paintings to facilitate the social and emotional
development of early childhood children is highly
feasible for use in learning, but has not yet integrated
adaptive technology like that developed in SERLI.
Overall, this investigation provides a substantial
advancement in the formulation of adaptive
educational games and the implementation of deep
learning methodologies within the realm of early
childhood education. The SERLI game is not only
statistically proven to be effective but also relevant to
the needs of education in the digital age, where
technology must be utilized to support children's
holistic development while maintaining the natural
and enjoyable essence of play.
This research further corroborates earlier
conclusions indicating that unsuitable educational
play materials can engender novel difficulties for
children, thereby rendering social development an
essential component. SERLI's interactive games
address this issue with designs tailored to the
developmental characteristics of 5-6-year-olds and
the needs of early childhood education curricula.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This research elucidates that the advancement of
SERLI Interactive Games, grounded in deep learning
methodologies, exerts a beneficial influence on the
enhancement of prosocial competencies in children
within the age bracket of 5 to 6 years. Employing the
ADDIE instructional design framework, this game
was adeptly developed in a manner that is responsive
to the requirements of educators, the distinctive
attributes of young learners, and the contextual
elements pertinent to early childhood pedagogy. The
evaluative findings indicate that the deployment of
this game significantly augments children's abilities
in collaboration, empathy, and compliance with
social norms (p < 0.01), while also producing
heightened levels of user satisfaction among both
educators and learners. Additionally, the game
integrates stimulation of children's social, motor, and
literacy aspects, addressing post-pandemic learning
challenges and overcoming the limitations of
conventional games. Therefore, SERLI Interactive
Games is an effective and relevant educational
innovation to support the development of young
children in the digital age.
REFERENCES
Andi Saputri, H., Regina Putri, A., Ningsih, L., & Fitrah
Andikos, A. (2024). Improving Early Childhood Social
Interaction through Learning Models Technology
Based. Journal of Asian Primary Education (JoAPE),
1(2), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.59966/joape.v1i2.1338
Dewi, N. P. A. P., & Agung, A. A. G. (2021). Game
Education Berbasis Multimedia Interaktif pada Aspek
Bahasa Anak Usia Dini. Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia
Dini Undiksha, 9(2), 149–157.
Elyakim, V. A., Firanti, A., Harahap, L. H., Mawardani, M.
A., & Perangin-angin, D. (2024). Peningkatan
Teknologi Interaktif terhadap Pengembangan Sosial
dan Emosional Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini (PAUD).
Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat Bidang Sains Dan
Teknologi, 3(4), 281–289.
Fajar, R., & Zega, W. (2023). Manfaat Penggunaan
Permainan Edukatif dalam Pembelajaran Anak Usia
Dini. PRESCHOOL: Jurnal Pendidikan Islam Anak
Usia Dini, 4(2), 53–64.
Firanti, A., Harahap, L. H., Mawardani, M. A., & Perangin-
angin, D. (2024). Peningkatan Teknologi Interaktif
terhadap Pengembangan Sosial dan Emosional
Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini (PAUD). ABDIKAN:
Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat Bidang Sains Dan
Teknologi, 3(4), 281–289.
Fuadia, N. (2022). Perkembangan Sosial Emosi Pada Anak
Usia Dini. Wawasan: Jurnal Kediklatan Balai Diklat
Keagamaan Jakarta, 3(1), 31–47. https://doi.org/10.
53800/wawasan.v3i1.131
Fuadia, N. N. (2022). Perkembangan Sosial Emosi Pada
Anak Usia Dini. Wawasan: Jurnal Kediklatan Balai
Diklat Keagamaan Jakarta, 3(1), 31–47.
Hafsania, N. (2021). Pengembangan Permainan Berburu
Harta karun Berbasis Karya Seni Lukis untuk
Memfasilitasi Perkembangan Sosial Emosional Anak
Usia Dini. Edukatif: Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan, 4(3).
Handayani, R. (2018). Pengembangan Permainan Edukatif
untuk Stimulasi Perkembangan Kognitif Anak Usia
Dini. Jurnal Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran, 25(3), 134–
142.
Harianja, A. L., Siregar, R., & Lubis, J. N. (2023). Upaya
meningkatkan perkembangan sosial emosional anak
ICECE 2025 - The International Conference on Early Childhood Education
162

usia dini melalui bermain peran. Jurnal Obsesi: Jurnal
Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini, 7(4), 4871–4880.
Hurlock, E. B. (1995). Perkembangan Anak (Edisi Keen).
Irawati, S. (2012). Pengembangan Game Edukasi
Menggunakan Model ADDIE untuk Meningkatkan
Kemampuan Belajar Anak. Urnal Teknologi
Pendidikan, 14(2), 67–75.
Kaffa, Z., Neviyarni, I., & Map, M. A. P. (2021). Analisis
Perkembangan Sosial Anak. Jurnal Pendidikan
Tambusai, 5(2), 2612–2616.
Khadijah, M. A., & Jf, N. Z. (2021). Perkembangan sosial
anak usia dini teori dan strateginya. Merdeka kreasi
group.
Rakhmawati, R. (2022). Alat Permainan Edukatif (APE)
untuk Meningkatkan Perkembangan Sosial Emosional
Anak Usia Dini. Bulletin of Counseling and
Psychotherapy, 4(2), 381–387.
Saharani, S., Iriyanto, T., & Anisa, N. (2021).
Perkembangan Perilaku Prososial Anak Usia 4-5 Tahun
Di TK Mardi Putra 01 Kota Batu. JP2KG AUD (Jurnal
Pendidikan, Pengasuhan, Kesehatan Dan Gizi Anak
Usia Dini), 2(1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.26740/jp2k
gaud.2021.2.1.19-30
Setiawan, A., Praherdhiono, H., & Sulthoni, S. (2019).
Penggunaan game edukasi digital sebagai sarana
pembelajaran anak usia dini. Jurnal Inovasi Dan
Teknologi Pembelajaran, 6(1), 39–44.
Suparmi, S., & Sumijati, S. (2021). Pelatihan Empati dan
Perilaku Prososial pada Anak Usia Sekolah Dasar.
Psikodimensia: Kajian Ilmiah Psikologi, 20(1), 46–58.
Suryana, D. (2021). Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini Teori dan
Praktik Pembelajaran. KENCANA.
Suryana, D., Karmila, D., & Mahyuddin, N. (2023).
Pengembangan Game Interaktif dalam Meningkatkan
Kecerdasan Matematika Anak di Taman Kanak-Kanak.
Jurnal Obsesi : Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini, 7(3),
3084–3096. https://doi.org/10.31004/obsesi.v7i3.3934
Windayani, N. L. I., Dewi, N. W. R., Yuliantini, S.,
Widyasanti, N. P., Ariyana, I. K. S., Keban, Y. B.,
Mahartini, K. T., & Suparman. (2021). Teori dan
Aplikasi Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini. Yayasan Penerbit
Muhammad Zaini.
Design and Evaluation of SERLI Interactive Games with Deep Learning Integration
163
