
Market Strategy Evolution and Business Model Transformation of
Marvel Studios: An Analysis Based on Porter's Five Forces Model
Siao Zhai
Faculty of Arts & Science, University of Toronto, Canada
Keywords: Marvel Studios, Superhero Films, Streaming Media, Media Transformation, IP Development.
Abstract: As a crucial component of the global film industry, superhero films have profoundly influenced contemporary
popular culture. Post-9/11 American society's collective desire for security and heroic archetypes catalyzed
unprecedented growth in superhero-themed media. However, while achieving periodic success, the Marvel
Cinematic Universe faces both internal and external industry challenges and pressure to transform its business
model. This paper employs Porter's Five Forces Model as an analytical framework and utilizes authoritative
institutional data to analyze Marvel Studios' market strategies over the two decades following Spider-Man's
2002 release. The research demonstrates that Marvel maintains its competitive advantage through several key
factors: the development of diverse characters and effective audience expectation management. In response
to streaming platform competition, Marvel's integration with Disney has strengthened its market position
through synergistic offline experiences and expanded distribution channels. The studio has controlled
production costs by experimenting with new film genres and casting new actors. In the post-pandemic market,
Marvel has adapted to new consumption scenarios by combining traditional theatrical releases with streaming
platforms. Furthermore, Marvel needs to increase investment in emerging technologies such as Virtual Reality
(VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) to address potential future challenges.
1 INTRODUCTION
On May 3, 2002, a New York high school student
named Peter Parker appeared on 7,500 screens across
North America, breaking records with an opening-
day box office of $43.62 million and reaching $100
million in its first weekend. The film eventually
became the highest-grossing release of the year.
Behind this success, Spider-Man reflected post-9/11
American society’s desire for security and individual
heroism. It told the story of an ordinary teenager
gaining extraordinary abilities and learning to
manage power while balancing social responsibility
with personal emotions and relationships. This film
portrays the transformation of an ordinary individual
into a superhero from the millennial generation's
perspective. In 2016, Marvel integrated Spider-Man
into their superhero universe, establishing a mentor-
paternal relationship with the franchise star Iron Man,
becoming a crucial link connecting different
superhero films.
Although Marvel's first comic book adaptation,
Blade (1998), achieved significant box office success,
audiences found deeper resonance with Peter Parker’s
struggles. His internal conflict between identity,
responsibility, and personal growth made the
character more relatable, attracting non-traditional
comic book fans. This humanized narrative not only
broadened the audience but also paved the way for the
release of subsequent films.
Today, Marvel films continue to serve as valuable
case in both commercial and cultural fields. This
paper focuses on the market strategies employed by
Marvel over the 20 years following Spider-Man's
release. It examines how Marvel managed its core
intellectual property (IP) to maintain continuous
growth in value, fostered fan engagement and
community interaction to enhance participation and
loyalty, and collaborated with media giants such as
Sony and Disney to expand product boundaries and
achieve cross-cultural reach. Additionally, it will
explore Marvel’s strategic adaptation in the post-
pandemic era, combining traditional cinema with
streaming platforms to respond effectively to
audience feedback.
The insights and recommendations presented in
this study aim to assist brand owners in formulating
comprehensive market strategies and making
informed business decisions at critical points within
the entertainment industry.
Zhai, S.
Market Strategy Evolution and Business Model Transformation of Marvel Studios: An Analysis Based on Porter’s Five Forces Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0014051700004942
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management (APMM 2025), pages 5-11
ISBN: 978-989-758-791-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
5

2 BRIEF HISTORY OF MARVEL
COMICS AND MARVEL
STUDIOS
Every successful Marvel character reflects the
prevailing themes of its time. Captain America,
introduced during World War II, symbolized
resistance against tyranny and the pursuit of peace
abroad, while embodying patriotic values and self-
sacrifice at home. In the 1960s, Stan Lee’s Fantastic
Four introduced the concept of a shared superhero
universe, reflecting Cold War-era ideals of scientific
exploration and teamwork. However, during the
1990s, the rapid expansion of Marvel’s comic book
catalog led to market saturation, causing company
financial difficulties. Marvel sold the film rights to
many of its key characters to Hollywood studios.
The 2000s marked a resurgence of these IPs
through the success of comic-based films such as
Blade, X-Men, and Spider-Man, bringing Marvel
characters back into public spotlight. The release of
Iron Man in 2008, which depicted the use of
technological innovation to combat terrorism,
mirrored contemporary societal concerns, particularly
Silicon Valley’s technological boom and the global
fight against terrorism in the Middle East (Yang and
Peng, 2022). In 2019, Avengers: Endgame served as a
culmination of Marvel’s narrative arc, integrating 20
years of storytelling into a unified cultural and
commercial milestone that elevated the Marvel brand
to unprecedented heights.
In response to the disruptions caused by the
COVID-19 pandemic, Marvel implemented strategic
shifts, exploring hybrid distribution models that
combined theatrical releases with streaming
platforms. This transition not only maintained
audience engagement but also expanded the acces-
sibility of Marvel content, paving the way for Phase
Four’s development across multiple media platforms.
3 THE ANALYSIS OF THE
MARVEL BRAND USING
PORTER’S FIVE FORCES
MODEL
3.1 Porter's Five Forces Model:An
External Analysis Tool for
Competitive Advantage
An enterprise's competitive advantage arises not only
from internal resources and capabilities but is also
profoundly influenced by the external industry
structure. In the 1970s, following the development of
SWOT analysis, Professor Michael Porter introduced
the Five Forces Model in 1979, grounded in the
“Structure-Conduct-Performance” (SCP) paradigm
of industrial economics. This analytical tool assists
firms in understanding the impact of five primary
competitive forces on their profitability, thereby
enabling systematic analysis of the external
competitive environment to identify strategic
opportunities that can enhance their competitiveness.
3.2 Industry Rivalry
As the production company behind Marvel films,
Marvel Studios has, since the release of Iron Man in
2008, produced a total of 31 films, creating the
Marvel Cinematic Universe (MCU). In 2009, Marvel
Studios was acquired by Disney for $4.2 billion.
Leveraging Disney’s expansive distribution network,
Marvel rapidly dominated the superhero film niche
market. Today, Marvel has almost become
synonymous with superhero movies.
Marvel’s primary competitor within the superhero
domain is DC Comics. Founded in 1934, DC Comics
initially captured the American public's imagination
with the character "Superman," establishing the
archetype of a superhero. Marvel, meanwhile,
capitalized on the sociopolitical climate of World
War II by introducing "Captain America," gaining
widespread recognition. In 1969, DC Comics was
acquired by Warner Bros., which took responsibility
for adapting and distributing its intellectual
properties. However, it was not until 2013, following
the completion of the first phase of the MCU, that
Warner Bros. released Man of Steel, the inaugural
film in the DC Extended Universe (DCEU), which
grossed $670 million worldwide (Qi, 2024). By this
point, Marvel had already laid the groundwork for the
Avengers storyline through seven films featuring
characters like Iron Man and Captain America.
Although DC and Marvel each have unique
characteristics and audiences in comic creation, DC's
adaptations into films gained fame and achieved
success later than Marvel's.
To compete effectively, Warner Bros. adopted a
differentiated competitive strategy for DC. From a
character development perspective, DC focused on
crafting powerful, godlike characters and exploring
philosophical themes such as sacrifice and justice
through human conflict, thereby appealing to an adult
audience. However, the grand narrative may, to some
extent, make the characters feel distant to audiences,
making it challenging for them to empathize with the
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
6
characters. Conversely, Marvel emphasized themes
of resilience, teamwork, and everyday challenges
faced by families and adolescents, resonating with a
broader demographic. As a market pioneer, Marvel
established a lighthearted and humorous style for
superhero films. Although unique, the dark and
serious tone of DC films does not appeal to audiences
who seek purely entertainment from movies, thereby
limiting the audience base for DC films (Qi, 2024).
In terms of cinematic style, Warner Bros grants
directors’ greater creative freedom, with Zack
Snyder’s serious style and James Gunn’s
entertainment style successively shaping the
development of the DC Extended Universe (DCEU).
This has led to significant stylistic differences across
films, affecting the coherence of the series. Under
Kevin Feige’s centralized management, Marvel
maintained a cohesive visual aesthetic to ensure
consistent character portrayals within its cinematic
universe. This coherence in visual and narrative
elements allows for smoother character and plot
development, strengthens brand recognition and
loyalty, and sets clear expectations for future
installments, helping attract a stable audience and
boosting box office performance.
DC often relies on director interviews and behind-
the-scenes documentaries to attract fans by offering
insights into the creative process, reinforcing the
importance of directors within the franchise and
fostering fan loyalty. In contrast, Marvel uses post-
credit scenes to spark discussions about upcoming
storylines, generating secondary promotion on social
media. This approach not only builds interest in future
films but also effectively manages audience
expectations and encourages broader engagement.
The differences in box office performance
between Marvel and DC can be attributed to their
varying approaches in four key areas: market entry
timing, film style and tone, director creative control,
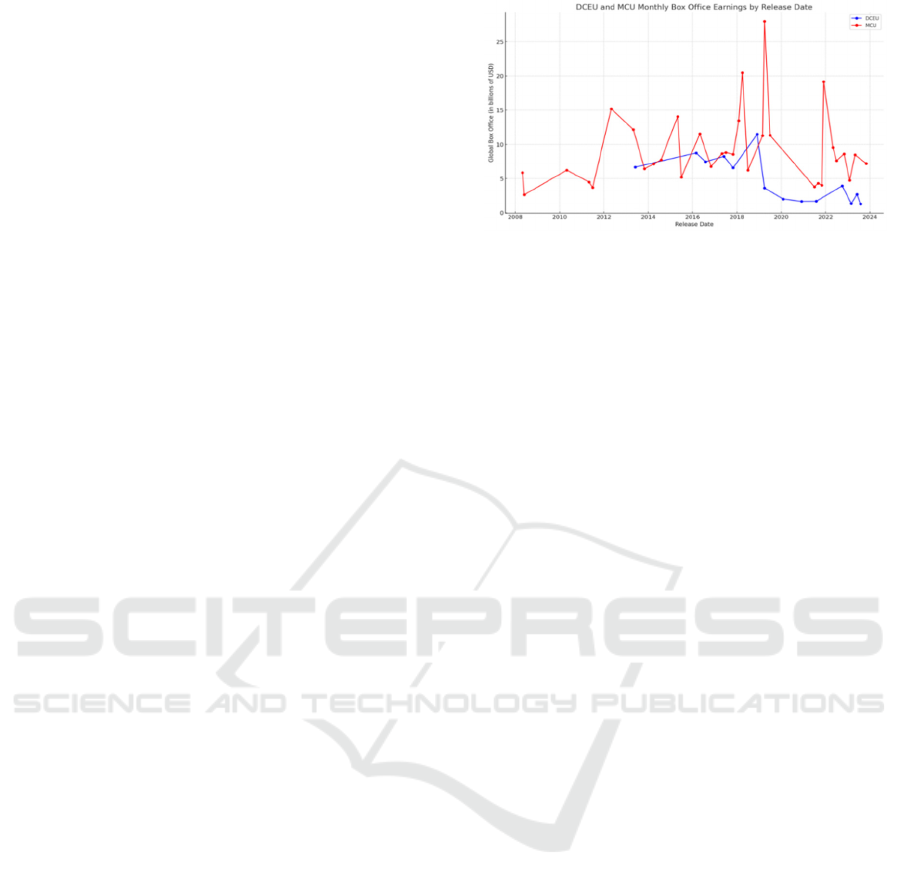
and audience expectation management. As of October
31, 2024, the Marvel Cinematic Universe has
achieved a total box office gross of $30.8 billion,
while the DCEU has earned $6 billion (see Fig. 1). By
leveraging its first-mover advantage, straightforward
and coherent storytelling, and extensive marketing
reach, Marvel has attracted more substantial audience
base.
Figure 1. DCEU and MCU1 Monthly Box Office Earnings
by Release Date (Photo/Picture credit: Original). Note: Box
office data sourced from Box Office Mojo.
3.3 Threat of New Entrants
Streaming services offer a convenient viewing option,
allowing audiences to watch the latest films at home
at any time, leading to a diversion of cinema
audiences and a decline in box office revenue, which
is particularly impactful for blockbuster studios like
Marvel that rely heavily on box office earnings. The
growth of streaming has also driven a reduction in
theatrical release windows and shifted consumer
behavior, as viewers have become accustomed to
accessing new films quickly through a subscription-
based content library, without needing to monitor
theater schedules or seating availability.
Additionally, streaming platforms leverage big data
analytics to accurately gauge audience preferences,
enabling them to respond to market demand more
swiftly than traditional production companies.
In the wake of the pandemic, tech giants from
Silicon Valley have increasingly ventured into the
media landscape by promoting and developing their
streaming platforms. Amazon’s Prime Video, for
example, launched The Boys in 2019, a series that
quickly became the platform's most-watched show
thanks to its anti-hero narrative and darkly satirical
tone. Season two in 2020 saw an 89% increase in
viewership, while seasons three (2022) and four
(2024) achieved 17% and 21% growth respectively,
substantially boosting the platform's paid
subscription base.
Netflix took a different approach, collaborating
with Marvel to release street-level superhero series
such as Daredevil and Jessica Jones. Daredevil's third
season recorded approximately 30 million hours of
view time in its debut week, while Jessica Jones's first
season amassed 20 million hours.
Unlike traditional film studios, streaming
platforms are free from cinema screening costs and
schedule constraints, offering users a wider variety of
content choices. Digital distribution eliminates the
Market Strategy Evolution and Business Model Transformation of Marvel Studios: An Analysis Based on Porter’s Five Forces Model
7

need for physical media transportation and reduces
promotional expenses. Platforms also have access to
user data, including Viewing Behavior Data and
Content Performance Data which helps in directing
content development and enables targeted
advertising, particularly on social media, reducing
marketing expenses eventually (Ulker-Demirel et al.,
2018). Additionally, the subscription model provides
a stable cash flow, freeing content creators from the
need to rely on single blockbuster successes. A
diversified content library helps mitigate risks
associated with underperforming titles. In 2021,
Marvel released the film Black Widow
simultaneously in theaters and on the Disney+
streaming platform as an exploration of a new
distribution model and a response to new entrants in
the industry.
3.4 Supplier Bargaining Power
In Marvel's production budget, director and actor
salaries constitute a substantial portion. The
production cost for Avengers: Endgame was
approximately $356 million, with salaries for actors
and crew members totaling $175 million,
representing 49% of the overall cost. Robert Downey
Jr., who played Iron Man, earned around $75 million
in pay and profit-sharing for Endgame, a stark
contrast to his initial $500,000 salary for the first Iron
Man film in 2008 (Ulker-Demirel et al., 2018). The
film required over 3,000 Visual Effects (VFX) shots,
necessitating the involvement of 12 VFX companies
and thousands of artists. According to a report by
Mordor Intelligence, the global VFX market size is
projected to reach $179.78 billion by 2024 and
$311.46 billion by 2029 (data from Mordor
Intelligence), with an annual growth rate of 9.43%.
For Marvel, this indicates a significant increase in
production costs.
Fortunately, Marvel still holds numerous high-
value character rights and has reached a mutually
beneficial agreement with Sony, the rights holder for
Spider-Man, allowing both parties to capitalize on the
character's exposure and brand value.
3.5 Bargaining Power of Buyers
The rise of streaming platforms has shifted the
landscape, with theaters no longer serving as the
exclusive venue for blockbuster releases. However,
for Marvel films, theaters offer more than just an
immersive viewing experience; they provide social
and interactive elements as well. According to the
2023 Theatrical and Home Entertainment Market
Environment Report released by the Motion Picture
Association (MPA), total theatrical admissions in the
United States and Canada reached 850 million in
2023, representing a 30% increase from the 650
million admissions recorded in 2022. However, this
figure remains below the 1.3 billion admissions seen
in 2019. In 2023, the average number of films
watched per person was four, an increase from 3.2 in
2022, but still lower than the 4.6 average in 2019.
This data suggests that, while the pandemic has
altered the viewing habits of some audience
members, the rate of recovery is accelerating.
Nevertheless, theaters continue to rely on blockbuster
films to support rising labor and rental costs, a
pressure that has led owners to increase ticket prices,
thereby impacting the willingness of price-sensitive
audiences to step into theaters. From 2019 to 2023,
the average ticket price for Marvel movies in the
United States has steadily increased (Tu, 2016).
Notably, in 2023, the average ticket price for Ant-
Man and the Wasp: Quantumania reached $13.89,
marking a 15.4% increase compared to the 2019 price
of $12.04. In the short term, rising ticket prices may
lead to a decline in the number of moviegoers, while
in the long term, this trend could suggest a shift in
viewing habits, encouraging audiences to subscribe to
streaming platforms.
Audience feedback through reviews, social
media, and word-of-mouth has become increasingly
influential on a film’s revenue. According to the 2021
Chinese Film Audience Survey published by China
Film News, 61.4% of moviegoers primarily obtain
film information through short video platforms such
as Douyin and Kuaishou. Additionally, 51.4% use
ticketing platforms like Maoyan and Taopiaopiao for
film-related information, while 48.7% rely on social
media platforms such as Weibo and WeChat.
Audiences are increasingly placing value on a film's
reputation, pre-selecting content by their interests.
Audience feedback circulates widely on the internet,
impacting both the box office performance of films
and the long-term value of intellectual property (Su
and Su, 2020). Film distributors must consider how to
understand user preferences in order to develop
targeted marketing strategies.
Influencers, whether serving as information
sources or engaging in secondary creative content, are
effective in attracting their respective audiences to
movies. Prior to the release of Avengers: Endgame,
Marvel collaborated with numerous prominent
influencers, inviting them to attend premieres and
behind-the-scenes events. These influencers shared
their experiences on social media, boosting audience
anticipation. However, when influencers provide
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
8

negative reviews, the negative discussions on social
media can diminish audience expectations,
potentially leading to a decrease in box office
revenue (Zhang, 2023).
3.6 Threat of Substitutes
Within the industry, DC Extended Universe (DCEU)
poses the most significant threat to Marvel, with
iconic characters such as Batman and Superman
possessing immense IP value. DCEU films like
"Aquaman" and "Joker" have achieved remarkable
global box office success, grossing $1.148 billion and
$1.074 billion respectively. Additionally,
independent superhero movies like the "Hellboy"
trilogy from Dark Horse Comics have earned $303
million in total, potentially diverting Marvel's
audience.
Outside the industry, science fiction films such as
"Star Wars" and "Avatar," as well as fantasy films
like "The Lord of the Rings" and "Harry Potter," serve
as substitutes for Marvel movies, boasting vast and
unique worldviews and stunning visual effects
(Richter, 2016). Furthermore, action-oriented film
series like "Mission: Impossible" and "Fast and
Furious" along with high-budget historical dramas
and disaster movies, also compete for audience
attention.
Looking to the future, Virtual Reality (VR) and
Augmented Reality (AR) technologies present
challenges to the traditional film industry in terms of
content creation and presentation. By wearing
specialized devices, users can immerse themselves in
virtual environments and actively interact with the
content, offering an unparalleled sense of presence
that traditional cinema screens cannot match (Junius,
2015). Other studies also emphasize the importance
of VR technique in marketing and film industry
(Wijayanto and Putra, 2021 & Talafubieke et al.,
2021). This poses a particular challenge for Marvel
movies, which are known for creating visual
spectacles on screen. As hardware costs decrease and
5G technology advances, new content based on VR
and AR will continuously emerge. According to a
report by market research company Grand View
Research, the global VR device market size reached
$7.9 billion in 2021, and the global VR and AR
device market is expected to reach $127.4 billion by
2028, potentially becoming the next major content
platform after PCs and smartphones.
4 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
STRENGTHENING MARVEL’S
COMPETITIVE POSITION
USING PORTER’S FIVE
FORCES
4.1 Industry Rivalry
Following the conclusion of Avengers: Endgame,
Marvel has continued to introduce films such as
Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings and
Eternals, portraying the growth of a new generation
heroes and laying the groundwork for subsequent
explorations of the multiverse concept. Concurrently,
Marvel has launched series like Wanda Vision, Loki,
and The Falcon and the Winter Soldier on Disney+,
allowing for a deeper exploration of existing
characters. In support of the multiverse-focused
storyline in Phase 5, Marvel has committed to
releasing numerous films and series annually,
integrating the storylines of both new and legacy
characters, and anchoring them within larger
crossover events, thereby aiming to replicate the
success of the Avengers franchise.
On the one hand, Marvel needs to delve deeply
into the internal conflicts and growth of its characters,
crafting more complex personalities to foster
audience empathy. Emphasis could be placed on
minority, female, and LGBTQ+ characters to broaden
the appeal and attract diverse audience. On the other
hand, Marvel should expedite the release of films that
serve as pivotal “node” events, like The Avengers, to
unify its characters and deliver impactful “ensemble
moments” that heighten audience anticipation for
future multiverse developments.
4.2 Threat of New Entrants
Disney’s collaboration with Marvel primarily
manifests in resource integration and platform
support. Disney’s substantial financial power ensures
the high-quality production of Marvel content and
enables the creation of themed experiences like the
Avengers Campus in California, which enhances fan
engagement and expands the offline retail channels
for merchandise. Through annual events such as D23
and theme park interactions, Disney strengthens fan
engagement and boosts anticipation for Marvel’s
films and series. The synergy between online and
offline experiences amplifies the brand’s reach and
recognition. In contrast, platforms like Amazon and
Market Strategy Evolution and Business Model Transformation of Marvel Studios: An Analysis Based on Porter’s Five Forces Model
9

Netflix primarily rely on online marketing, lacking
the immersive experience and emotional connection
provided by offline settings.
4.3 Supplier Bargaining Power
Introducing capable new actors not only appeals to
audiences across age groups and cultural
backgrounds, as seen with the Asian creative team
behind Shang-Chi and the Legend of the Ten Rings,
and the character Kamala Khan in Ms. Marvel, which
resonates with young viewers from Muslim
backgrounds. It also aids in controlling production
costs, as these actors are likely to appear in multiple
upcoming movie series.
4.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
Furthermore, Marvel recognizes the value of
influencer marketing in its promotional campaigns.
By collaborating with influencers whose followers
align with the film’s target audience, Marvel can
precisely reach viewers of specific ages, interests, and
regions. Influencers’ previews or analyses of movie
trailers can foster curiosity, and personal
endorsements are more likely to elicit positive
attitudes toward the film watching. Such marketing is
generally cost-effective and benefits from the high
engagement and trust that influencers’ followers
have.
4.5 Threat of Substitutes
In terms of media formats, VR and AR possess the
potential to partially replace the visual and auditory
experiences offered by Marvel’s film and streaming
content, due to their immersive nature, interactive
features, and robust storytelling capabilities.
Although there are currently no comparable
competitors in the market, Marvel Studios could
explore the development of interactive content for VR
and AR devices, establishing an early presence in
these sectors.
5 CONCLUSION
This study examined Marvel Studios' market
strategies over two decades through Porter's Five
Forces analysis framework. The research
demonstrates Marvel's successful evolution from a
comic book company to a global entertainment
powerhouse, achieved through strategic intellectual
property management, innovative distribution
models, and adaptive market positioning.
The findings illuminate several critical factors
affecting Marvel's market position. First, Marvel's
competitive advantage over DC originates from its
early market entry and narrative consistency, which
fostered robust brand recognition and audience
loyalty. Second, the emergence of streaming
platforms presents substantial challenges to Marvel's
conventional theatrical distribution paradigm. Third,
escalating production costs are driven by premium
actor compensation and increasing dependence on
sophisticated visual effects technology. Fourth, the
post-pandemic theatrical sector maintains
considerable bargaining power, while the influencers
wield substantial impact on film reception.
Additionally, technological advancements in VR and
AR potentially offer immersive experiences that
could surpass traditional theatrical superhero film
presentations.
Based on these findings, several strategic
recommendations emerge for entertainment industry
stakeholders. Companies should prioritize diverse
character development to broaden audience appeal,
implement strategic release timing to maximize
market impact, and explore emerging technologies
like VR and AR to stay ahead of technological
disruption.
This research contributes to the broader
understanding of entertainment industry dynamics
and provides valuable insights for media companies
navigating similar challenges in intellectual property
management and market adaptation. Future research
could explore the long-term implications of streaming
platforms on traditional theatrical distribution models
and the potential impact of emerging technologies on
content creation and consumption patterns.
REFERENCES
C. H. Yang, K. Peng, Cross-boundary Integration: an
analysis of industrial and cultural mechanisms of
marvel cinematic universe. World Cinema. 2, 59
(2022)
P. X. Qi, A comparative analysis of Dc and Marvel films
from an industrial perspective. comedy world. 4, 75
(2024)
E. Ulker-Demirel, A. Akyol, G. G. Simsek, Marketing and
consumption of art products: the movie industry. Arts
Mark. 8, 80 (2018)
Y. Tu, Analysis on the model innovation of Marvel film IP
industry chain. Mod. Bus. 33, 37 (2016)
J. C. Su, H. Y. Su, Research on Marvel's brand strategy.
China Mark. 27, 127 (2020)
APMM 2025 - International Conference on Applied Psychology and Marketing Management
10

Y. Zhang, Market advantages and artistic patterns of
marvel's genre-based film production. Study Explor.
3, 168 (2023)
Á. Richter, The Marvel cinematic universe as a transmedia
narrative. AMERICANA E-J. Am. Stud. 12, 1 (2016)
W. Y. Junius, A Time Series Study on Marvel from 2000-
2009: Marvel's Movies Impact Relative to Stock
Price. J. Glob. Bus. 4(1). 6-10 (2015)
S. Wijayanto, J.C.P. Putra, Effectiveness of a virtual reality
marketing video on the desire to buy a product. JOIV:
Int. J. Inf. Vis. 5, 360–365 (2021).
M. Talafubieke, S. Mai, N. Xialifuhan, Evaluation of the
virtual economic effect of tourism product emotional
marketing based on virtual reality. Front. Psychol. 12,
759268 (2021).
Market Strategy Evolution and Business Model Transformation of Marvel Studios: An Analysis Based on Porter’s Five Forces Model
11
