
A Study on the Influence of Language Training Courses on New
Media Platforms on Students' Purchase Intention: From the
Perspective of Planned Behavior Theory
Yihan Dong
1
, Ruixi Wu
2
, Yufei Wu
3
and Yibo Yang
4
1
College of Communication, Liaoning University, Shenyang, 110000, China
2
Broadcasting and Hosting Art, Communication University of China Nanjing, Nanjing, 210000, China
3
Journalism and Communication, NanJing XiaoZhuang University, Nanjing, 210000, China
4
Art Studies Music Performance, Inner Mongolia Arts University, Hohhot, 010000, China
Keywords: Language Training Courses, New Media Platforms, Students' Purchase Intention, TPB.
Abstract: In the globalized social context, studying abroad becomes a significant path for students seeking academic
and career advancement. The proliferation of new media platforms has facilitated access to information on
language training for study abroad. Using the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), this study examines
students' information seeking (IS) behaviors on new media platforms and their impact on attitudes towards
purchasing language courses abroad via a questionnaire. It investigates how attitudes (ATT), subjective norms
(SN), and perceived behavioral control (PBC) jointly have effect on students' purchase intention. The study
concludes that IS on new media positively correlates with purchasing ATT, which further positively influence
purchase willingness. SN and PB control also positively relate to purchase willingness. This research aids
language training organizations in developing precise and effective strategies, enhancing student satisfaction
and facilitating a more convenient and efficient course selection experience.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the deepening of globalization, more and more
students choose to study abroad in order to expand
their international horizons and obtain a wider range
of educational resources. In this process, language
proficiency has become a major challenge that
international students must face. As a result, there is
a growing demand for language training courses for
studying abroad, especially on new media platforms,
where the dissemination and reception of information
about such courses have become particularly
convenient. When it comes to the course sales of
CCtalk Online School: between 2015 and 2017, the
number of student visits to CCtalk Online School's
paid courses was 204,686, 232,583 and 293,557
separately. The unit prices for customers also
increased to 1966.1 yuan, 2836.4 yuan, and 3170.1
yuan. Individual bloggers such as "Uncle Bao Talks
About Studying Abroad" and study abroad
organizations such as "New Oriental IELTS" reached
4,534,000 followers and 140,000 followers
respectively, introducing study abroad language
training courses on Tiktok platform. The above data
shows that more and more students are interested in
purchasing study abroad audio training courses.
Given the preceding discussion, based on the TPB
model, this study aims to explore the influence of new
media platform language training courses on students'
purchase intention, which is coded for students with
different regions, genders, ages, and education levels
who have the intention to study abroad. By deeply
analyzing the information seeking and attention
behaviors of the study abroad population on new
media platforms and how these behaviors affect
students' attitudes, subjective norms (SN) and
perceived behavioral control (PBC) of the courses,
the present study this paper can further study the
factors that influence their purchase intention.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESIS OF THE
PRESENT STUDY
The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), developed
by Icek Ajzen in 1985, serves as a framework for
predicting and elucidating human behavior.
576
Dong, Y., Wu, R., Wu, Y. and Yang, Y.
A study on the Influence of Language Training Courses on New Media Platforms on Students’ Purchase Intention: From the Perspective of Planned Behavior Theory.
DOI: 10.5220/0014003600004912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development (IESD 2025), pages 576-582
ISBN: 978-989-758-779-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

According to the TPB model, the behavioral intention
(BI) of an individual is a direct determinant of their
behavior, which is influenced by three primary
factors: ATT, SN, and PBC. Drawing on the TPB, this
study investigates the impact of language training
courses on the purchase intention of students using
new media platforms.
Chen Qi (2023) think, IS is the process of using
the Internet to search, browse, obtain, evaluate, use
and other behaviors to meet one's own needs.
Mihyang Park (2011) believed that information
attitudes are diversified, and people will have a
positive or negative attitude in the process of
searching for certain information on new media
platforms. This study explores the impact of IS on
attitude of language training courses for studying
abroad. With the increase of search volume, students
can obtain more comprehensive information, so as to
better understand the course content, teaching quality
and course effect. This more comprehensive
understanding information can enhance students' trust
in the course and thus enhance their purchasing
attitude. Through a large amount of IS, students can
reduce the uncertainty and anxiety about course
selection. With the increase of search volume,
individuals' grasp of information will tend to be
comprehensive, which may be conducive to the
formation of a more positive attitude, there is the
following assumptions around "IS":
H1: Information seeking on language training
courses for studying abroad on the new media
platform will be positively related to the attitude of
students buying language courses (Fig. 1).
ATT has long been an important field of
psychological research (Fretz et al. 1989). So this
branch of this study is aimed at people who actively
search for information about language training
courses for studying abroad on new media platforms
to study the impact of IS on course purchase attitudes.
Psychological research shows that positive emotional
experience enhances motivation and intention. For
example, when students have positive emotions and
expectations for language courses, they are more
motivated to buy courses. This study speculates that
students' positive attitude towards purchasing
language courses may significantly enhance their
intention to purchase language courses. This is an
attitude based on the theory of planning behavio, a
positive attitude usually includes positive emotions
for the course, positive cognitive evaluation, and the
behavioral tendency to buy the course. Students'
positive attitude towards language courses may
translate into stronger purchase intentions. Therefore,
there is the following assumptions around attitude:
H2: The attitude of students buying language
courses is positively related to the student's intention
to buy language courses (Fig. 1).
SN, derived from the TPB, refers to the social
pressure individuals perceive regarding whether to
engage in a specific behavior, and SN will affect the
individual's behavioral decisions, when taking the
TPB as the starting point, discussing its applicability
in the study of consumer BI. The study points out that
other people's views on consumer consumption
behavior are positively related to consumption
intentions, the more others encourage consumption
behavior, the stronger their intention to buy the
product (Li & Wang, 2009). However, most of the
existing studies focus on the relationship between SN
and consumer behavior, there is still little research on
SN and educational selection behaviors. Do students
perceive expectations and support from important
people such as family, friends, teachers, etc. affect
their willingness to buy courses? From this, the
following assumptions can be put forward:
H3: Subjective norms will be positively related to
students' willingness to buy language courses (Fig. 1).
PBC is a fundamental variable in the TPB, after
speculation, perceptual behavior control may
significantly increase students' willingness to
purchase language courses. This is based on the PBC.
PBC is considered to directly affect behavioral intent.
If students can perceive their ability and resources to
complete language courses, they may show a stronger
willingness to buy. This not only depends on the
accurate perception of students' behavior and needs,
it also relies on providing a personalized, interactive
and efficient learning experience through decision-
making and control mechanisms. Do students think
they have the ability and resources to purchase and
successfully participate in these courses? Do they feel
obstacles in course fees, scheduling, technical
support, etc? The following assumptions can be put
forward:
H4: Perceptual behavior control is positively
related to students' willingness to purchase language
courses (Fig. 1).
Through the above analysis, this study will be
based on the PBC, comprehensively explore the
impact of language training courses on students'
willingness to buy on the new media platform, and by
verifying the above assumptions. The study deeply
understand the key factors that affect students'
willingness to buy. Based on four assumptions, the
following models have been made (Fig. 1).
A study on the Influence of Language Training Courses on New Media Platforms on Students’ Purchase Intention: From the Perspective of
Planned Behavior Theory
577
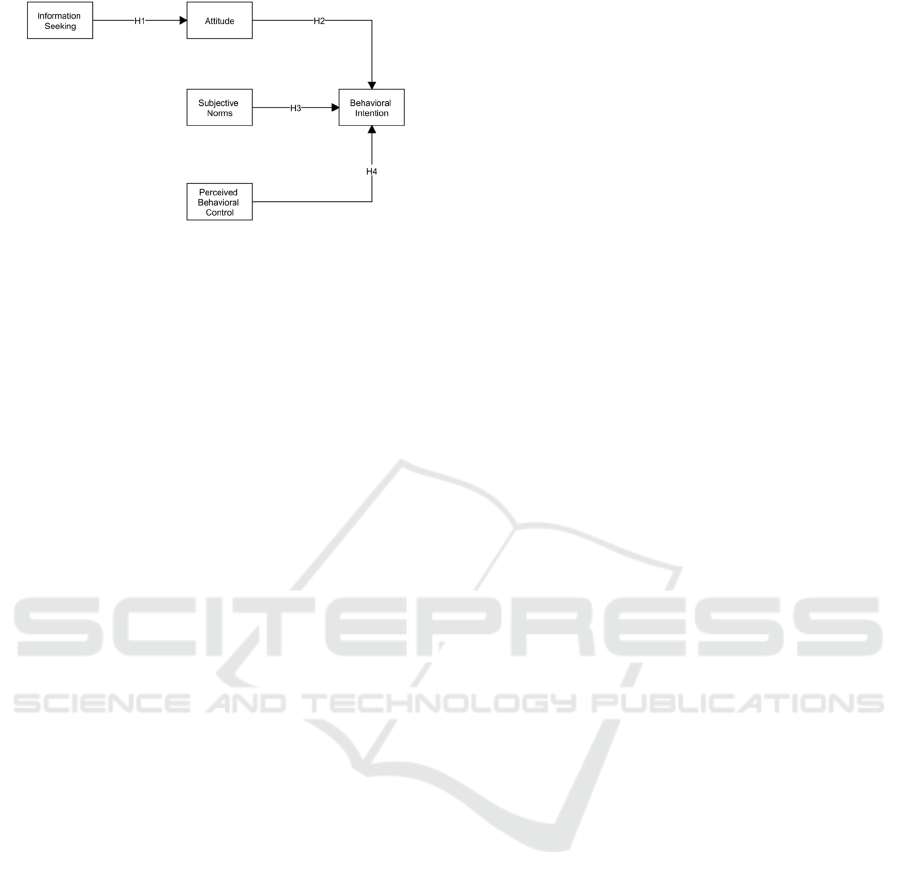
Figure 1: The impact model of overseas language training
course information seeking on students' purchase intention.
3 METHOD
3.1 Data Collection
An online survey carried out from June 24th to July
12th, 2024, on the online questionnaire platform of
WenJuanXing. Participants were divided into
regions, including North China, Central China, South
China, East China, West China, Northeast China. The
sample was taken from some universities. By July
12th, 2024, 867 participants had completed the survey
questionnaire. The survey results were composed of
students from East China (n=149, 17.79%), Central
China (n=125, 14.42%), West China (n=157,
18.11%), South China (n=127, 14.65%), North China
(n=157, 18.11%) and Northeast China (n=152,
17.53%). Since this study targets students who have a
demand for language courses for studying abroad, the
effective questionnaire was 858.
3.2 Measures
3.2.1 Demographic Variables
Demographic variables include gender, age, degree,
education background and location.
Among the 858 participants, 55.36% were female
and 44.64% were male. The age of participants was
concentrated under 25 years old, with 60.78% of them
being undergraduates and 13.73% being high school
graduates or below, and 25.49% being postgraduates
or above. The educational level was relatively
balanced, with 27.68% of them being ordinary
undergraduates.
3.2.2 Independent Variables
For the measurement of Information Seeking, Wilson
(2000) first proposed the concept of information
seeking behavior, which refers to the user's
purposeful search for information to meet their
personal needs. The research team replaced Kahlor L.
(2010)'s “Health Information" in the scale of Health
Information Seeking Behavior with "Studying abroad
language courses and their promotional information"
to measure the frequency of students' proactive search
for information behavior. The study used the Likert
scale (1=rarely, 5=always) to synthesize the
questionnaire, with a Cronbach's alpha value of 0.79
(Table 1).
In the TPB, "ATT" is a critical factor that
influences an individual's BI, referring to the
individual's positive or negative behavior’s
assessment. This study used the scale developed by
Yeon Ho et al. (2020) to measure Attitude.
Participants were asked to answer two questions: "Do
you think it is valuable to purchase studying abroad
language training courses on new media platforms?"
and "Do you find these studying abroad language
training courses on new media platforms attractive?"
The Likert scale (1=strongly disagree, 5=strongly
agree) was used. The higher the score, the more
positive the participant's attitude were in buying the
course, with a Cronbach's alpha value of 0.76 (Table 1)
SN refers to the social pressure an individual feels
about whether or not to engage in a certain behavior,
which may impact on their behavioral decisions. This
study used the scale developed by Yeon Ho et al.
(2020) to analyze Subjective norms. The study used
The Likert scale (1=strongly disagree, 5=strongly
agree). The higher the score, the greater the
individual's willingness to purchase the course is
influenced by SN, with a Cronbach's alpha value of
0.79(Table 1).
PBC refers to an individual's perception of how
easy it is to perform a particular behavior. The Likert
scale (1=strongly disagree, 5=strongly agree) was
utilized for measurement. A higher score indicates
that the individual's intention to purchase the course
is more influenced by their perceived behavioral
control. The synthesized questionnaire demonstrated
a Cronbach’s alpha value of 0.79 (Table 1).
3.2.3 Dependent Variables
In this study, ATT also functions as the dependent
variable in the initial stage.
Behavioral Intention reflects an individual's
readiness to engage in a specific behavior. In this
case, the intention to purchase language training
courses for studying abroad. The Cronbach’s alpha
value for the synthesized questionnaire was found to
be 0.71 (Table 1).
IESD 2025 - International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development
578
3.3 Analysis
This study conducted a linear regression analysis
using SPSS on two sets of data. The first analysis,
with Attitude as the dependent variable and
Information Seeking as the independent variable, was
conducted as the first layer of research. The second
analysis, with BI as the dependent variable and ATT,
SN and PBC as the independent variables, was
conducted as the second layer of research. The
reliability of the independent and dependent variables
was analyzed separately, and it was found that the
Cronbach's alpha values for both sets of variables
were greater than 0.7, indicating that the scale
composite reliability was acceptable. The two sets of
variables were then processed separately for linear
regression analysis, and the results of the study were
obtained.
4 RESULTS
Using the SPSS model for linear regression analysis,
the first study found a positive correlation between
students' search for information on language training
courses through new media platforms and their
attitude towards purchasing these courses, confirming
H1(β= 0.19, p < 0.05)(Table 2). Age was positively
correlated with students’ willingness to purchase
language training courses (β=0.22, p<0.05), while
educational background demonstrated a negative
correlation with this willingness (β=-0.17, p<0.05).
Gender, education level, and location did not show
significant relationships with students' willingness to
purchase language training courses.
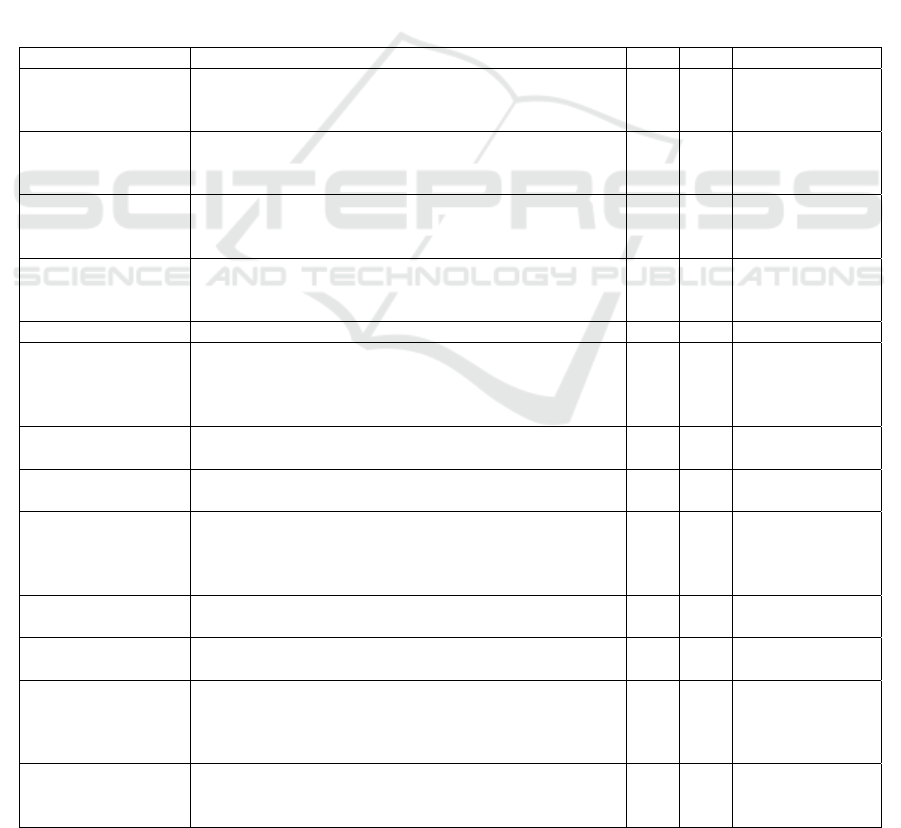
Table 1: Composite reliability and validity of variables.
Variables Survey items M SD Cronbach’s alpha
X1 a Information
seeking behavior
(Kahlor L. ,2010)
The frequency at which you proactively browse and search
for language courses and promotional information for
study abroad online
3.70 1.02 0.79
The frequency at which you actively search for language
courses and promotional information for study abroad
online
The frequency at which you consistently follow up on
language courses and promotional information for study
abroad online
X1b Attitude
(Yeon Ho Shin et
al.,2020
)
Unpleasant: Pleasant
3.75 1.04 0.76
Unattractive: Attractive
X2b
Subjective norms
(Yeon Ho Shin et
al.,2020
)
It is important to me that the people I care about think I
should take a language training course for study abroad.
3.71 1.01 0.79
The people I care about would want me to take a language
trainin
g
course for stud
y
abroad.
The people I care about would hope that I take a language
training course for study abroad.
X3b Perceived
behavioral control
(Yeon Ho Shin et
al.,2020
)
I have the ability to find language training courses on new
media platforms.
3.71 1.02 0.79
I have the financial ability to purchase a language training
course for stud
y
abroa
d
.
I have the time to purchase and study a language training
course for study abroad.
Y1b Behavioral
Intention
(Yeon Ho Shin et
al.,2020)
After searching for language courses and promotional
information for study abroad, I plan to purchase the
course.
3.73 1.04 0.71
After searching for language courses and promotional
information for study abroad, I will invest effort to
p
urchase it.
A study on the Influence of Language Training Courses on New Media Platforms on Students’ Purchase Intention: From the Perspective of
Planned Behavior Theory
579
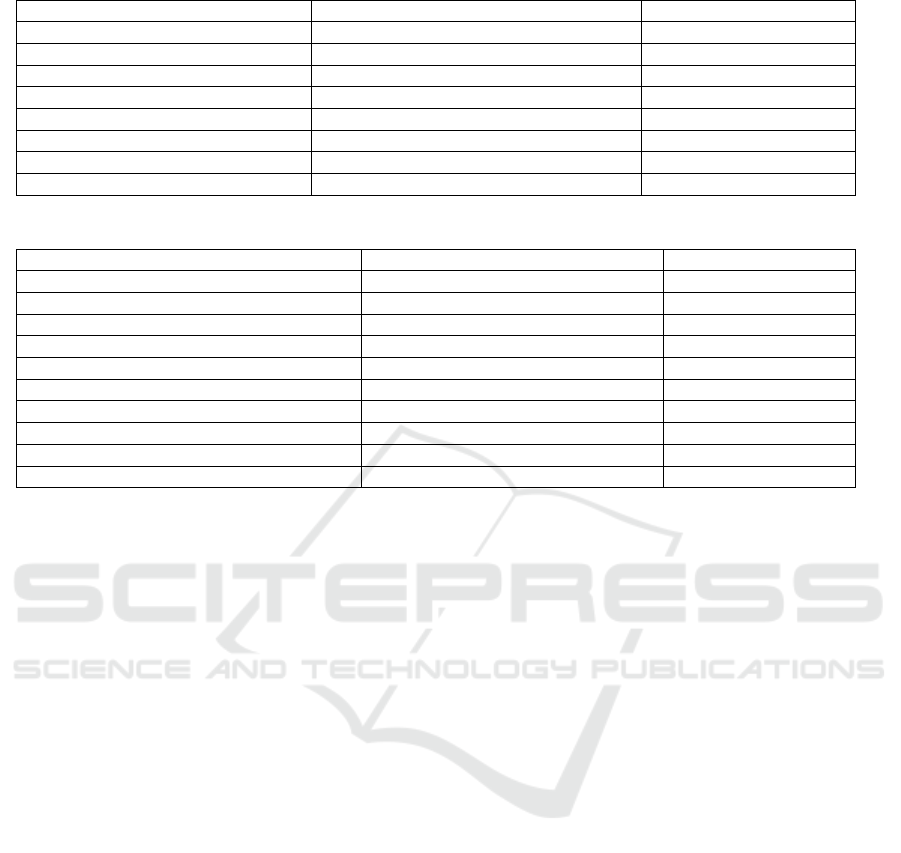
Table 2: Relation between IS and ATT.
Standardized Coefficients Beta Si
g
.
Block1:Demo
g
ra
p
hic variables
Gender
(
1=male,2=female
)
0.036 0.235
Age 0.216 0.000
Degree 0.043 0.341
Education Background -0.168 0.000
Location 0.016 0.599
Block2
IS 0.189 0.000
Table 3: Linear regression analysis to predict the purchase intention of language training courses.
Standardized Coefficients Beta Si
g
.
Block1:Demo
g
ra
p
hic variables
Gender(1=male,2=female) 0.059 0.845
Age 0.084 0.001
Degree 0.072 0.084
Education Back
g
round 0.029 0.001
Location 0.017 0.983
Block2 Theor
y
of Planned Behavio
r
ATT 0.158 0.000
SN 0.131 0.000
PBC 0.159 0.000
Additionally, students' attitudes towards
purchasing language training courses were positively
correlated with their intention to make a purchase,
supporting H2 (β=0.16, p<0.05). Subjective norm
also exhibited a positive correlation with students’
willingness to purchase language courses, supporting
H3 (β=0.13, p<0.05). Finally perceived behavioral
control was positively correlated with student’s
willingness to buy language training course,
confirming that H4 is valid (β=0.16, p<0.05). Age
was positively correlated with student's willingness to
buy language training course (β=0.08, p<0.05) and
educational background was positively related as well
(β=0.03, p<0.05)(Table 3). Gender, education level
and location had no significant relationship with
student’ s willingness to buy language training course
5 DISCUSSION
The purpose of this study is to explore the influence
of language training courses on new media platforms
on students' purchase intention according to TPB.
First of all, this study shows that students' search
for language training course information on new
media platforms is positively correlated with their
attitude towards course purchase, and those who
frequently search course information are more likely
to purchase language courses. This is consistent with
existing research that shows a positive correlation
between consumer search behavior and purchase
behavior (Wang, 2020).
In addition, ATT is also an important regulating
factor of students' willingness to buy courses. In terms
of ATT, the present research found that students'
attitude towards purchasing overseas language
training courses had a significant positive correlation
with their purchasing behavior intention. Some
previous studies have shown similar findings,
suggesting that Consumers from Gen Z who hold a
positive attitude toward fast fashion are more likely
to purchase these products (Wojdyla & Chi, 2024).
More studies related to attitude and consumer
behavior also reveal an important phenomenon, that
is, consumers' attitude not only to the product itself,
but also to media advertising, can affect their
consumer behavior to a certain extent (Zheng, 2012).
Although this study mainly focuses on the variable
measurement of product attitude and recognizes the
potential difference between this variable and
consumers' attitude toward media advertising, it
should not be ignored that media advertising, as an
important channel of product information
transmission, often indirectly affects consumer
behavior by shaping or strengthening consumers'
cognition and attitude toward products.
IESD 2025 - International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development
580

SN refers to the social pressure that individuals
perceive when they perform a certain behavior or not.
This variable mainly reflects the influence of
important people or organizations around the
surveyed group on their decisions. According to the
survey results, subjective norms are positively
correlated with students' willingness to buy language
courses. In other words, individuals are more likely to
buy study abroad courses if their significant others
want to buy them. The results are also consistent with
studies showing, for example, that when adolescents
perceive that people or organizations with whom they
interact closely, such as family and friends, are more
supportive of their participation in soccer activities,
they are more likely to participate in soccer activities
(Li, 2019).
The results of the study on perceived behavioral
control show that there is a positive correlation
between an individual's subjective assessment of the
ability to successfully carry out the purchase of a
language course abroad and whether or not to
purchase the course. This discovery indicates that a
person's belief in their capability to successfully
finalize a purchase plays an important role in actually
acting on it. This is consistent with most previous
studies, for example, that perceived behavioral
control is an important driver of vitamin D
supplement consumption because individuals are
more likely to consume a supplement if they find it
easy to take it (Chen, 2022). For another example,
perceived behavioral control directly affects the
purchase behavior of hairy crabs, indicating that
consumers' confidence in their successful purchase
behavior and more objective conditions can
determine whether consumers buy hairy crabs to a
certain extent (Wang, 2019).
However, the limitations of the current study
should be noted. One of the first is the potential
problem of sample selection bias, where current
studies may focus only on a specific type of student
population (such as students at a certain college, a
certain age group, or students with a specific
academic background) or a specific language course
(such as a beginner's course in English as a second
language), thus limiting the general applicability of
the conclusions. In order to make up for this
deficiency, future studies should focus on expanding
the diversity and breadth of samples. Specifically,
students from different places of origin (such as urban
and rural differences, regional cultural differences)
can be included to examine the impact of regional
background on learning outcomes; At the same time,
students with different family backgrounds (such as
socioeconomic status, parental education level,
family language environment, etc.) should also be
included to analyze how family environment plays a
role in the learning process. Not only can such a
design enhance the comprehensiveness and depth of
research results, but it can also offer a more precise
reference foundation for developing educational
policies to guarantee the rational distribution of
educational resources and the effective
implementation of teaching methods.
Second, this study only focuses on the relationship
between IS, ATT, SN, PBC and BI, without
considering the influence of other factors. Future
research could explore other potential factors, such as
individual motivation, external environmental
factors, to better understand the formation process of
willingness to consume. In addition, this study used a
self-reported approach to assess perceived behavioral
control and purchase intention, which may be subject
to subjectivity and memory bias. Future studies could
be combined with objective data or experimental
design to obtain more accurate results.
Based on the research results, there are some
suggestions for different subjects (consumers,
merchants). For consumers, they can better
understand their purchase intentions and rationally
evaluate their behavior control ability to avoid being
affected by overconfidence. For the merchants of
overseas study language courses, they can provide a
more attractive purchasing environment, convenient
purchasing methods and publicize the importance of
overseas study language learning to increase
consumers' purchase willingness.
In conclusion, the study needs to further explore
and improve the research methods to obtain more
comprehensive and accurate conclusions, and make
corresponding recommendations to guide practical
applications.
6 CONCLUSION
This study explored the influencing factors of
language training courses on new media platforms on
students' course purchase intention, and provides
empirical evidence for TPB through the research
method of questionnaire survey. The results of the
study on attitudes towards purchasing online
language courses and information seeking highlight
that TPB is a promising theoretical framework for
studying individual consumption behavior.
Emphasizing the significance of psychological
drive as a central factor influencing behavioral
intention, this study suggests that the goal of studying
abroad plays an important role in influencing
A study on the Influence of Language Training Courses on New Media Platforms on Students’ Purchase Intention: From the Perspective of
Planned Behavior Theory
581

consumers' decision to purchase language courses.
Furthermore, the study underscores the intricate
nature of consumer decision-making processes and
demonstrates the independent influence of
information access and personal attitudes on
intentions that influence consumer behavior. By
examining theoretical models, this research lays the
groundwork for future investigations into the
underlying mechanisms that influence consumer
behavior in the overseas language course market,
ultimately enhancing the theoretical comprehension
of consumer decision-making.
The research has practical significance. Overall,
the results of the study are very important for the
study abroad language course industry. The research
results can stimulate the information delivery of new
media platforms in this field. At the same time, the
relevant organizations can also make people have a
positive attitude towards the study abroad language
courses in the first place, and have a positive impact
on the course sales of the study abroad language
training institutions.
Based on samples of different backgrounds,
opinions and perceptions, future studies can test the
universality of the conclusions of this study.
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTION
All the authors contributed equally and their names
were listed in alphabetical order.
REFERENCES
Chang, C., Lin, C., Chen, Y., & Chin, Y. 2009. Predicting
information‐seeking intention in academic digital li-
braries. The Electronic Library, 27(3): 448-460.
Chen, Y. H., Chao, S. L., & Chu, Y. W. 2022. Effects of
Perceived Benefit on Vitamin D Supplementation In-
tention: A Theory of Planned Behaviour Perspective.
International Journal of Environmental Research and
Public Health, 19(4): 1952.
Ekaningtyas, S. W. 2023. Factors Influencing Organic Food
Purchase Intention and The Effect of Attitude towards
Organic Food. KINFORMS.
Huimei, L., & Li, W. 2009. The application of the Theory
of Planned Behavior in the study of consumer behavior
intention. Journal of Sichuan Education Institute,
25(9): 18-20.
Lee, J. K., & Kim, E. 2017. Incidental exposure to news:
Predictors in the social media setting and effects on in-
formation gain online. Computers in Human Behavior,
75: 1008-1015.
Li, Y. 2019. Research on youth soccer participation behav-
ior based on TPB theory. World of Sports: Academic
Edition, 80-82+94.
Mihyang Park, & Jiyeon Lee. 2011. An Empirical Study of
the Everyday Life Information Seeking Behavior of the
Baby-boomers as Pre-retirees. Journal of Information
Management, 28(2): 195-208.
Shin, Y. H., Im, J., Jung, S. E., & Severt, K. 2018. The the-
ory of planned behavior and the norm activation model
approach to consumer behavior regarding organic
menus. International Journal of Hospitality Manage-
ment, 69: 21-29.
Wang, J., & Che, B. 2019. Study on the buying behavior of
hairy crab consumers based on TPB model. Chinese
Fishery Economy, 102-110.
Wang, L. 2020. Analysis of influencing factors of consumer
search and purchase behavior. Cooperative Economy
and Technology, 74-75.
Wang, L., Wong, P. P. W., Narayanan Alagas, E., & Chee,
W. M. 2018. Green Hotel Selection of Chinese Con-
sumers: A Planned Behavior Perspective. Journal of
China Tourism Research, 15(2): 192-212.
Wojdyla, W., & Chi, T. 2024. Decoding the Fashion Quo-
tient: An Empirical Study of Key Factors Influencing
U.S. Generation Z’s Purchase Intention toward Fast
Fashion. Sustainability, 16(12): 5116.
Zheng, Y. H. 2012. Research on the influence of consumer
media advertising attitude on consumer behavior. Com-
mercial Economic Research, Business Times, 24-25.
IESD 2025 - International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development
582
