
A Correlation Analysis Between Gamification Design of Online
Learning Resources and Foreign Language Enjoyment: Take the
Duolingo App as An Example
Yuting Xu
School of Chinese Language and Literature, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Keywords: Online Learning, Positive Emotion, Gamification Design.
Abstract: With the development of Internet technology, the influence of gamification learning design on the learning
effect has been widely noticed, but there is a lack of in-depth exploration of its relationship with foreign
language enjoyment. Therefore, this paper takes Duolingo APP as an example to explore the relationship
between the two. This paper finds that gamification design has a significant positive correlation and influence
on enhancing learners' foreign language enjoyment, but also has obvious individual differences. Based on
this, this paper proposes some suggestions for designing foreign language learning materials, closely integrat-
ing gamification elements with learning content while paying attention to learners' differences.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, applying Positive Psychology (PP) in
the field of Foreign Language Acquisition (FLA) has
attracted extensive attention from scholars. One of the
most popular positive emotions is foreign language
enjoyment, which is regarded as a key factor in
improving learners' overall cognitive level and
increasing learners' communicative willingness in the
process of foreign language acquisition (Dong, 2022).
Existing studies have proved that, through classroom
games, teachers can create a relaxing atmosphere,
reduce tension and pressure, and trigger students'
pleasure emotions.
However, current research mainly focuses on the
design of teaching games in traditional physical
classrooms and pays insufficient attention to the
learning resources of online platforms. With the
development of modern network technology, it is
more and more common for language learners to use
online learning platforms for self-study, therefore, the
game-based learning design of learning resources on
online learning platforms has also become a concern.
Based on this, this study, from the perspective of PP,
takes Duolingo APP as an example to explore the
relationship between game-based learning design of
learning resources and foreign language enjoyment,
to provide suggestions for the design of materials or
learning methods of other foreign language learning.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Foreign Language Acquisition from
a Positive Psychology Perspective
In 2012, PP was introduced into the field of foreign
language acquisition, and its key emotion theory,
Broaden-and-Build Theory, was first introduced
(Fredrickson, 2001; MacIntyre & Gregersen, 2012).
The theory discusses the effects of positive emotions
on individual psychology and behavior, suggesting
that positive emotions have two core functions:
instantaneous broaden function and long-term build
function. Through the two functions, positive
emotions can promote the accumulation of resources
while further enhancing the positive emotions, and
ultimately increase the overall sense of well-being. In
addition, the introduction of the Control-Value
Theory in the field of educational psychology has also
played a theoretical guiding role in the field of foreign
language acquisition (Pekrun, 2006). The theory
discusses emotions from three dimensions: titer
(positivity and negativity), activeness (arousal level),
and definite object (arousal object). It argues that
pleasure is a positive high-arousal emotion, which is
closely related to an individual's sense of control over
the learning activity or outcome and value
recognition. In recent years, many scholars have
conducted empirical studies, and the results generally
show that there is a significant positive correlation
548
Xu, Y.
A Correlation Analysis Between Gamification Design of Online Learning Resources and Foreign Language Enjoyment: Take the Duolingo App as An Example.
DOI: 10.5220/0014003100004912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development (IESD 2025), pages 548-553
ISBN: 978-989-758-779-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

between foreign language enjoyment and the learning
effectiveness of language learners (Li & Han, 2022).
2.2 Game-Based Learning
Gamification refers to the application of game
elements to non-game scenarios. Most Gamification
systems include three elements: points, badges, and
leaderboards (PBL), which are the three standard
features of gamification (Kevin & Dan, 2014).
Richard Landers proposed the game-based learning
theory in 2014, which explores how gamified features
can improve learning effect by influencing learners'
behaviors and attitudes. The theory suggests that
gamified features can improve the learning effect
through two kinds of processes: mediation and
regulation, with learners' learning attitude as the
intermediary or by the method of improving their
learning attitude. In addition, the flow theory is also
applied to gamified learning. Gamification features
can encourage learners to enter the "flow state", that
is the psychological state of being fully immersed,
feeling excited, happy, and focused, which will
stimulate learners' positive emotions and lead to a
new state of mind-flow, so that the flow experience
runs through the whole process, and ultimately
produce better learning results. Empirical studies
have found that the game elements and feedback
mechanisms integrated into the learning environment
can trigger learners' emotional experiences such as
pleasure, tension, or immersion, which can further
stimulate learners' intrinsic motivation (Zhang &
Shang, 2018).
However, most of the existing studies focus on the
effect of gamified learning, and pleasant emotions are
only involved as part of the effect, and the
relationship between the two has not been discussed
in depth. Moreover, most of the existing empirical
studies focus on the gamification design of the
physical classroom and pay less attention to the
game-based design of the learning resources of the
online learning platform. Based on this, this study
chooses Duolingo, an online learning platform with
the core concept of the combination of gamification
and learning, as an example to explore the
relationship between the gamification design of
Duolingo's learning resources and the sense of
pleasure in foreign language acquisition.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Study Design
The purpose of this study is to collect and analyze the
data through the online questionnaire to explore the
relationship between the gamification design of
learning resources in the Duolingo app and the
pleasure of foreign language learning, and thus
provide new methods and suggestions for foreign
language learning.
Game-based learning is the application of game
elements in learning situations. This theory has been
applied to the teaching of foreign language
acquisition with the development of Internet
technology. Garris et al. proposed an input-
processing-output model for teaching games and
foreign language acquisition, which illustrated the
acceptance process of the gamification of foreign
language acquisition (Garris et al., 2002). Previous
studies have also proved that game-based learning has
a significant positive influence on foreign language
subjects, which can stimulate students' interest and
enthusiasm for learning, and promote the
improvement of the learning effect (Li et al., 2019).
Combined with existing research, gamification
system theory, and the actual situation of the
gamification design of APP learning resources in
Duolingo, this study selected the typical gamification
elements therein and analyzed them in the following
four dimensions: points, badges, leaderboards, and
friends quest.
3.1.1 Points
Duolingo's point design is a core component of its
gamification learning mechanism. The basic point
system awards experience points (XP) based on the
user's performance in completing courses, missions,
and other activities, and maintaining a winning streak
provides additional points to bind users for long-term
use. In addition to the basic system, users can earn
points by participating in time-limited activities and
challenges, improving their leaderboard rankings,
and completing missions of friend quests. The
acquisition of points is an intuitive reflection of the
user's learning progress and provides instant feedback
on the user's learning outcomes quantitatively. The
clear task objectives make users feel controllable so
can reduce their anxiety during learning. Interesting
game design and instant feedback can make learners
feel a sense of achievement and improve their
individual value evaluation, which in turn can
A Correlation Analysis Between Gamification Design of Online Learning Resources and Foreign Language Enjoyment: Take the Duolingo
App as An Example
549

encourage users to have pleasant emotions.
Accordingly, the following assumptions are
proposed:
H1: The point design will positively promote
learners' pleasure.
3.1.2 Badges
Duolingo provides users with a wide variety of
reward badges. The badges are awarded based on the
learner's achievements and performance. For
example, learners can earn "Winning Streak" badges
for completing learning tasks for several days in a
row, or "Diligence" badges for completing a specific
number of lessons, and so on. In addition to mainline
learning, Duolingo also offers a special daily task
function, and students can get the monthly badge after
they insist on completing it.
From the perspective of Control-Value Theory,
badges, as a visual sign of achievement, enable users
to feel their progress and ability enhancement. At the
same time, they are also combined with social
functions, which can be shown to friends in their
profiles to gain recognition and appreciation from
others, to increase the users' recognition of the value
of the learning activities, thus providing motivation
for continuous learning. Accordingly, the following
assumptions are proposed:
H2: Badge design will positively promote
learners' pleasure.
3.1.3 Leaderboards
Duolingo motivates users to learn and compete with
each other through the Leaderboard system. The
system is open once a week for seven days, users are
ranked with 30 people of the same level by points, and
they can improve their ranking by completing
learning tasks and gaining experience value. The
leaderboard is updated every day, which enables
users to see their progress and others' scores in time.
After the weekly settlement, users at the top of the list
will be promoted to a higher level, while those at the
bottom of the list will be relegated to a lower level,
ranging from bronze to diamond. This design also
makes users feel that they are part of a learning
community in Duolingo, which enhances their sense
of belonging and identity, thus increasing their
participation and activity and making them enjoy the
learning process more. Accordingly, the following
assumptions are proposed:
H3: The leaderboard design will positively
promote learners' pleasure
.
3.1.4 Friends Quest
In addition to the three main game elements, the
community features of Duolingo--Friends Quest,
Classes, etc., also have significant gamification
features. The Friends Quest sets clear tasks for users,
as well as interactive reminders, achievement sharing,
and other functions. Through this, users can
encourage and urge each other with their friends to
complete the task goals together. The class system
allows users to join or create a class, and the organizer
will help class members set common learning goals
so that the users can feel the collective atmosphere of
learning through completing the class tasks and
sharing progress. The design of community function
can stimulate users' social motivation and
achievement motivation, to enhance their sense of
self-worth and obtain a pleasant emotional
experience. Accordingly, the following assumptions
are proposed:
H4: The Friends Quest design will positively
promote learners' pleasure.
In summary, this study proposes the above four
assumptions based on PP's Control-Value Theory,
combined with gamification elements and gamified
learning theory, and will test and revise the
assumptions through quantitative research.
3.2 Issuance and Recovery
3.2.1 Research Tools
This study conducted a quantitative study through a
combined questionnaire with the following
measurement tools:
First, this study refers to the Game User
Experience Satisfaction Scale (GUESS) and
combines the theory of the gamification system and
the actual situation of the gamification design of APP
learning resources in Duolingo to prepare the scale. It
is divided into 4 dimensions, including points,
badges, leaderboards, and friends' quests with a total
of 8 measurement items, which is a 5-level Likert
Scale. The scale has high reliability (Cronbach's
α=0.869) and validity, proving to be a reliable and
valid scale for the sense of experience of gamification
design.
In addition, this study was compiled concerning
the Chinese version of the Foreign Language
Enjoyment Scale (CFLES). The original scale was a
5-level Likert scale, which was adapted by Li et al.
based on a sample of Chinese high school students
from the Foreign Language Enjoyment Scale. To
meet the needs of this study, the original question
IESD 2025 - International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development
550
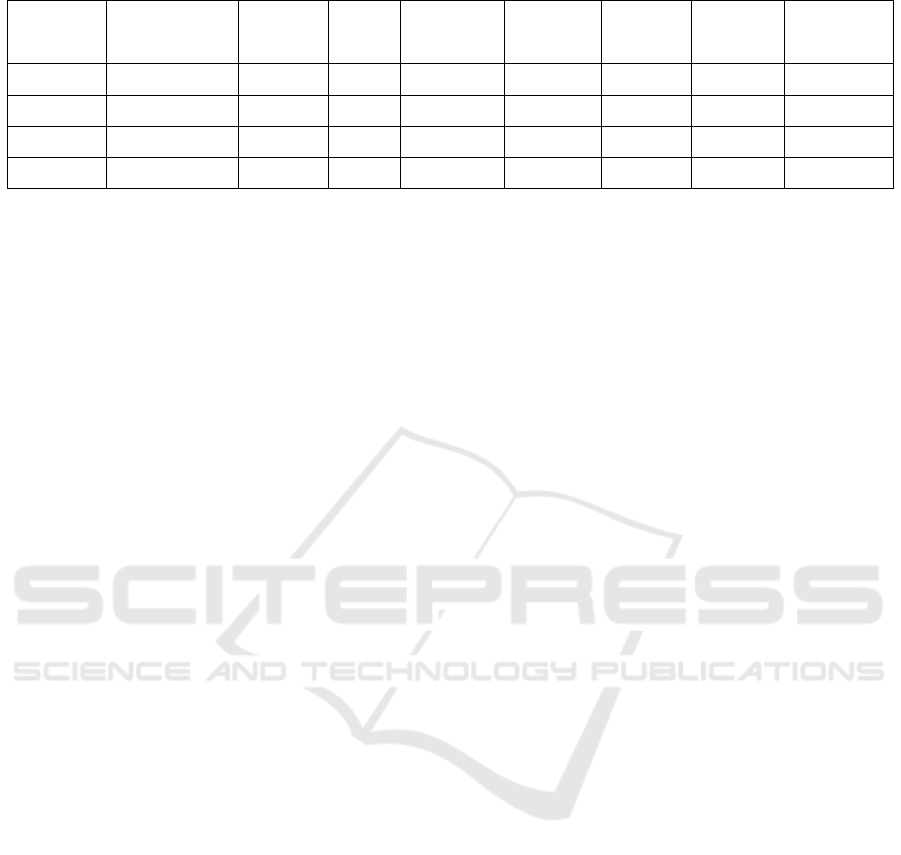
Table 1: Gamification design of learning resources and foreign language enjoyment.
Variant Mean ± standard
deviation
Variance Median Minimum
value
Maximum
values
Kurtosis Skewness Coefficient
of Variation
(CV)
point 3.745±0.969 0.940 4.000 1.000 5.000 0.409 -1.048 25.884%
badges 3.775±0.939 0.881 4.000 1.000 5.000 0.784 -1.091 24.868%
leaderboards 3.688±1.038 1.076 4.000 1.000 5.000 0.186 -0.968 28.137%
Friends quest 3.737±0.996 0.992 4.000 1.000 5.000 0.211 -1.037 26.653%
item scenario was set to the Duolingo online platform,
and the questions were adapted to form three
dimensions, including personal foreign language
pleasure, Duolingo's gamification-design-related
foreign language pleasure, and Duolingo's
community-interaction-related foreign language
pleasure, with a total of eleven measurement items.
The adapted scale has high reliability (Cronbach's
α=0.888) and validity and proved to be a reliable and
valid foreign language pleasure scale.
3.2.2 Distribution and Collection of
Questionnaires
This study was conducted by distributing the
questionnaires through the online platform. In this
study, 20 questionnaires were firstly distributed for
pre-survey, the reliability and validity of the
questionnaire were tested according to the collected
data, and the questionnaire was formally distributed
after some of the items were reasonably adjusted
according to the feedback from the subjects. In this
study, convenient sampling was used to select non-
English major undergraduates who use the Duolingo
App for online English learning as the research
subjects. Finally, a total of 200 valid questionnaires
were obtained. After the questionnaires were
collected, with the help of SPSS 22.0, the data were
analyzed by descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation
test, and linear regression analysis.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Overall Sense of Gamification
Design Experience in Duolingo
This study first used SPSS 22.0 to make descriptive
statistics on each variable. The results are shown in
Table 1.
Table 1 shows that foreign language learners'
experience of gamification design is at a medium-
high level with individual differences. The average
values of all variables are between 3.688 and 3.796,
and the median is 4, indicating that their central trends
are similar and tend to be high, which suggests that
the overall performance of foreign language learners'
sense of experience with gamification design is
relatively positive, and generally at a high level. At
the same time, the skewness of all variables is
negative and the data distribution is skewed to the
left, indicating that there are extremely low values in
the data, and the data distribution is skewed to the left,
suggesting that a few subjects have different
experiences in the game design of learning resources
and foreign language pleasure.
On the whole, learners' overall acceptance of
game design is high, but there was individual
variability in the learners' sense of experience and the
resulting pleasurable emotions. For example, among
the four important elements, each variable has a high
average value and a low coefficient of variation, but
the variability of the leaderboard is the largest,
indicating that learners' acceptance and experience of
this element are significantly different, making its
impact more complex. This reflects that the design of
the leaderboard should be more careful, fully
considering the individual differences and
psychological needs of users to further optimize the
design
.
4.2 Correlation Between Gamification
Design of Learning Resources and
Foreign Language Enjoyment
Based on the descriptive statistics results in Table 1,
this study used SPSS 22.0 for Pearson correlation
analysis and linear regression analysis. Table 2 shows
that there is a significant positive correlation between
foreign language pleasure and the four gamification
elements: points, badges, leaderboards, and friends
quest. The correlation analysis data all showed a
significant level of 0.01, and the correlation values
were high, showing a significant positive correlation.
This suggests that in the context of foreign language
learning, learners are more likely to feel more
A Correlation Analysis Between Gamification Design of Online Learning Resources and Foreign Language Enjoyment: Take the Duolingo
App as An Example
551
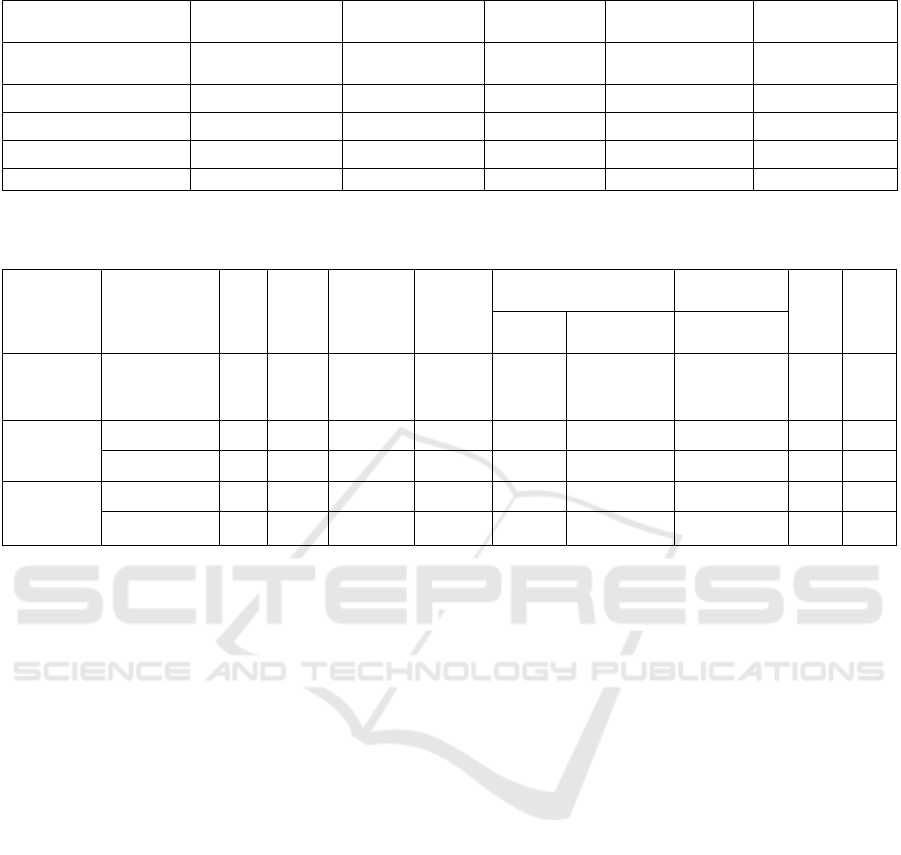
Table 2: Correlation matrix between gamification design of learning resources and foreign language enjoyment.
Foreign Language
Pleasure
Check Numbers Coat of Arms
Charts
(
of best-sellers
)
Friendly Alliance
Foreign Language
Pleasure
1
Point 0.778** 1
Badges 0.748** 0.631** 1
Leaderboards 0.755** 0.657** 0.629** 1
Friends
q
uest 0.763** 0.652** 0.634** 0.592** 1
* p<0.05 ** p<0.01
Table 3: The role of gamification design of learning resources on foreign language enjoyment.
Variant R R² Adjusted
R²
F (4,195)
Non-Standardized
Coefficient
Standardized
Coefficient
t VIF
B standard
erro
r
Beta
Implicit
Variable
Foreign
Language
Pleasure
0.894 0.800 0.796 195.044
Independen
t Variable
Point 0.230** 0.040 0.278 5.734 2.292
Badges 0.196** 0.040 0.229 4.922 2.118
Leaderboards 0.202** 0.036 0.261 5.639 2.096
Friends quest 0.226** 0.037 0.282 6.077 2.092
* p<0.05 ** p<0.01
pleasure and enjoyment in the process of language
learning if they obtain higher points, more badges,
higher leaderboard rankings, and more active
performances in their friend's quest on the game-
based learning platform.
Based on Table 2, taking points, badges,
leaderboards, and friends' League as independent
variables and foreign language pleasure as dependent
variables, linear regression analysis shows that all
four gamification elements have a significant positive
effect on foreign language enjoyment and that the
model was well fitted. Table 3 shows that the
regression coefficients are good, in addition, the
multilinear test found that the model does not have a
covariance problem (VIF<5) and the D-W value is
around the number 2, which indicates that the model
is not autocorrelated and the model is significant. This
indicates that the gamification design can effectively
enhance the foreign language pleasure of foreign
language learners and have a positive impact on them.
Among them, the regression coefficients of points
and friends quest are slightly higher than those of
badges and leaderboards, indicating that points and
friends quest are more influential on foreign language
pleasure.
It can be seen that the gamification design of
learning resources in Duolingo has a significant
positive correlation and impact on enhancing learners'
foreign language enjoyment. However, due to the
significant differences in users' experience of
different elements, the existing design still needs to
be optimized.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Overall Sense of Gamification
Design Experience in Duolingo
The average value of the four dimensions (Table 1)
reflects the foreign language learners' experience of
the game learning elements of Duolingo. On the
whole, foreign language learners can obtain a sense
of foreign language enjoyment through game-based
learning, which improves the learning effect. But at
the same time, this sense of experience has individual
variability, and some elements may put pressure on
some learners, especially the element of leaderboards
with the greatest variability. Therefore, when
designing the leaderboard, students can set a variety
of ranking methods, such as single skill ranking, as
well as privacy options, allowing learners to choose
whether to disclose their ranking information or not,
to reduce learners' anxiety and pressure.
IESD 2025 - International Conference on Innovative Education and Social Development
552

5.2 Correlation Between Gamification
Design of Learning Resources and
Foreign Language Enjoyment
As shown in Tables 2 and 3, the gamification design
elements have a positive effect on enhancing learners'
foreign language pleasure. When designing other
foreign language learning materials, it can learn from
the design ideas of Duolingo, and closely combine
gamification elements with learning content to
improve students' learning pleasure. At the same
time, it should pay attention to individual differences,
provide diversified learning paths, meet the needs of
different learners by setting up different learning
modules, intelligent recommendation functions, etc.,
and dynamically optimize and improve them
according to the progress and feedback of the
learners, to achieve the purpose of promoting
continuous learning (Landers & Landers, 2014; Jiang,
2020).
6 CONCLUSION
Taking the Duolingo App as an example, this study
explores the relationship between the gamification
design of learning resources and foreign language
enjoyment from four dimensions: points, badges,
leaderboards, and friend quests. Overall, the
gamification elements have a strong positive effect on
foreign language pleasure, which can promote the
generation of foreign language pleasure emotions and
thus improve the learning effect, which provides an
empirical basis for future foreign language teaching
and learning design. Meanwhile, this study also
reminds designers to fully consider learners'
individual differences and psychological needs, and
make targeted improvements and optimization of
gamification strategies to provide language learners
with a better learning experience.
REFERENCES
Dong, L. 2022. Predictive effects of control-value apprais-
als on foreign language classroom anxiety and enjoy-
ment. Foreign Language World (03): 79-88.
Fredrickson, B. L. 2001. The role of positive emotions in
positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of
positive emotions. American Psychologist 56(3), 218.
Garris, R., Ahlers, R. H., Driskell, J. E. 2002. Games, mo-
tivation, and learning: A research and practice model.
Simulation & Gaming 33: 441-467.
Jiang, Y. 2020. An investigation of the effect of teachers on
Chinese university students' foreign language enjoy-
ment. Foreign Language World (01): 60-68.
Kevin, W., & Dan, H. 2014. For the win: How game think-
ing can revolutionize your business. Zhejiang People's
Publishing House.
Landers, R. N., & Landers, A. K. 2014. An empirical test
of the theory of gamified learning: The effect of leader-
boards on time-on-task and academic performance.
Simulation and Gaming 45(6): 769-785.
Li, C., & Han, Y. 2022. The predictive effects of foreign
language enjoyment, anxiety, and boredom on learning
outcomes in online English classrooms. Modern For-
eign Languages (02): 207-219.
Li, Y., Song, J., & Yao, Q. 2019. Research on the influence
of gamification learning method on students' learning
effect: Meta-analysis Based on 35 experiments and
quasi-experimental Studies. E-Education Research
(11): 56-62.
MacIntyre, P. D., & Gregersen, T. 2012. Emotions that fa-
cilitate language learning: The positive-broadening
power of the imagination. Studies in Second Language
Learning and Teaching 2: 193-213.
Pekrun, R. 2006. The control-value theory of achievement
emotions: assumptions, corollaries, and implications
for educational research and practice. Educational Psy-
chology Review 18: 315-341.
Zhang, L., & Shang, J. 2018. A theoretical study on game-
based learning from the perspective of learning experi-
ences. E-Education Research (06): 11-20+26.
A Correlation Analysis Between Gamification Design of Online Learning Resources and Foreign Language Enjoyment: Take the Duolingo
App as An Example
553
