
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of
Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years
Jianjun Chen
1,*
and Chengpeng Zhang
2
1
School of Management, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 200000, China
2
School of International Business, Southwest University of Finance and Economics, Chengdu, 610000, China
*
Keywords: Fragmentation Information, Social Media, Attention, Business Analysis.
Abstract: Fragmented information consumption today is linked to declining sustained attention, especially among
undergraduates. This study elucidates mechanistic pathways through which social media-driven fragmented
information exposure impacts cognitive functioning. Employing a mixed-methods design, the research
integrated psychometric questionnaires (administered to 95 undergraduates) to quantify fragmented
information exposure patterns, alongside Python-based web crawlers systematically capturing emotional
lexicon distributions from Xiaohongshu (REDNOTE) platform discourse. Multidimensional validation
through Pearson correlation and sentiment polarity modeling revealed three key findings: (1) high-frequency
users (≥3 h/day) exhibited 37.2% reduction in attentional persistence relative to controls; (2) 78.6% of
participants demonstrated diminished academic task performance during instructional periods; (3) 61.3%
manifested increased procrastination prevalence in non-academic contexts. Cognitive resource depletion and
switching cost accumulation are identified as primary pathways. The evidence underscores the imperative for
tripartite intervention frameworks comprising cognitive conditioning protocols, restructured pedagogical
ecosystems, and techno-ethical governance models.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Research Background
The continuous technological iterations in mobile
internet infrastructure have catalyzed a social media
communication paradigm dominated by rapid-fire
information exchange. As documented in the 51st
Statistical Report on China's Internet Development
(CNNIC, 2023), Chinese undergraduates engage with
social media platforms for an average of 4.2 hours
daily, with 73.6% of information consumption
episodes demonstrating characteristic fragmentation
patterns. This pervasive nonlinear, high-frequency
information consumption pattern induces
fundamental alterations in cognitive processing
architectures: neuroscientific evidence reveals that
sustained attentional shifting manifests as decreased
glucose metabolism efficiency in the dorsolateral
prefrontal cortex, corresponding to measurable
reductions in working memory span and systematic
suppression of sustained reflective thinking (Ai et al.,
2021;Odden & Russ, 2019). Consequently, university
students face growing difficulties in attaining focused
cognitive states, while fragmented mental schemata
progressively solidify into entrenched cognitive
routines. These neurocognitive alterations ultimately
translate into quantifiable declines in academic
engagement efficacy, as evidenced by longitudinal
learning performance metrics (Lei et al., 2012).
1.2 Current Research Status and Gaps
Existing studies exhibit limitations in three critical
dimensions:
Firstly, research predominantly focuses on
generalized social media user populations, lacking
targeted analysis of university students' cognitive
traits (Kindermann & Onofri, 2021;Yao, 2019).
Secondly, measurement methodologies overly
rely on subjective scales, failing to integrate
multimodal data encompassing behavioral logs and
physiological indicators (Odden & Russ,
2019;Saplacan et al., 2020).
Thirdly, intervention strategies emphasize
individual behavior modification while neglecting the
synergistic optimization requirements between
technological architectures and educational contexts
Chen, J. and Zhang, C.
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years.
DOI: 10.5220/0013995800004916
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication (PRMC 2025), pages 545-554
ISBN: 978-989-758-778-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
545

(Jiang, 2020;Rahiminia et al., 2019). Notably, the
impact of fragmented information on university
students manifests significant scenario-specific
differentiation: information overload in learning
contexts leads to knowledge integration difficulties
(Kindermann & Onofri, 2021), whereas instant
feedback mechanisms in daily life contexts induce
procrastination dependency (Yao, 2019). However,
current research has yet to establish a systematic
pathway model elucidating these differential effects.
1.3 Research Objectives and
Significance
Guided by cognitive load theory, this study aims to
address three core issues:
(1) Quantitative characterization of key features
defining fragmented social media information;
(2) Validation of focus time metrics' measurement
validity within university student populations;
(3) Differentiated impact mechanism in how
fragmented information impacts academic focus
versus daily life focus. By constructing a tripartite
analytical framework integrating behavioral data,
psychological perception, and technological features,
the findings will provide empirical foundations
for:University curriculum optimization (e.g.,
embedding anti-interference training modules);Social
media algorithm refinement (e.g., dynamically
regulating information push density);Digital health
policy formulation (e.g., establishing attention
protection standards).
Compared to existing research, this study
achieves breakthroughs in three dimensions:
Methodologically, it combines web crawling
technology (for dynamic acquisition of fragmented
information features) with machine learning
algorithms (for focus time prediction modeling),
effectively overcoming social desirability biases
inherent in traditional questionnaire methods.
Theoretically, it reveals a dual-pathway impact
mechanism: fragmented information directly
diminishes attentional capacity through cognitive
resource competition while indirectly altering
attention allocation patterns via multitasking
capability remodeling. Practically, it proposes a
three-tiered intervention system encompassing
technological architecture, educational design, and
individual behavior regulation.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction to the Concepts of
Fragmented Information Modes
and Focus
2.1.1 Definition of Fragmented Information
Modes
Fragmented information modes refer to the
phenomenon in which, during the dissemination
process, information is broken down into short,
scattered segments that lack logical coherence due to
the involvement of multiple sources, channels, and
non-linear transmission (Ai et al., 2021). This mode
originates from the deconstruction of traditional
information dissemination structures by Internet
technologies, and it is manifested in the dispersed
nature of spatiotemporal distribution, disseminators,
and content forms (Kindermann & Onofri, 2021).
2.1.2
Sources of Fragmented Information
The driving force of technology is significant; the
rapid development of mobile Internet, social media,
and algorithm-based recommendation systems has
accelerated the fragmentation of information (Ai et
al., 2021). In this context, the roles of dissemination
agents have become diversified, with users no longer
merely receiving information but also acting as
transmitters. This change has led to multiple rounds
of processing and re-dissemination of information
during its transmission (Ai et al., 2021). In addition,
the fragmented nature of user demands has become
increasingly evident; due to divided attention, content
producers are compelled to simplify information into
“fast-food style” content that is easier to consume
(Kindermann & Onofri, 2021).
2.1.3
An Overview of the Key
Characteristics
Fragmented information possesses the following four
core characteristics. First, it has minimal
spatiotemporal constraints, allowing users to access
these brief segments of information anytime and
anywhere (Ai et al., 2021). Second, fragmented
information exhibits immediate interactivity,
enabling rapid feedback to users and promoting high-
frequency interactions among them (Ai et al., 2021).
Third, its content is scattered and concise, typically
with short text lengths (for example, no more than
150 characters) and relatively low logical coherence
(Ai et al., 2021). Finally, fragmented information is
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
546

characterized by a strong subjective tint, with the
contained information predominantly reflecting
personal opinions or feelings rather than purely
objective facts (Ai et al., 2021).
2.2 Definition and Measurement of Focus
2.2.1 Definition of Focus
Focus refers to the ability of an individual to
continuously direct cognitive resources toward a
specific task. It is fundamental to deep learning and
the efficient completion of tasks (Odden & Russ,
2019).
2.2.2
Recent Measurement Methods
Behavioral Data: Focus in online questionnaires can
be evaluated by analyzing mouse trajectory
features—for example, speed and click intervals
(Saplacan et al., 2020;Yao, 2019). In addition,
momentary sampling techniques can be employed,
whereby observers record whether predetermined
behaviors occur within specific time intervals,
thereby contributing detailed descriptive factors
regarding focus (Liu et al., 2018).
Physiological Indicators: Eye-tracking
technology can measure gaze duration, while the
suppression of alpha waves in EEG analysis reflects
concentrated attention (Odden & Russ, 2019).
Psychological Experience: In terms of subjective
evaluation, the sense of immersion and time
distortion described in Flow theory are used as
indicators of personal focus (Yao, 2019).
2.2.3
The Rationale for Using Focus Time as
a Measurement Index
Research by Yao Qiyu (2019) indicates that the
intervals between responses and mouse trajectory
characteristics (e.g., variations in acceleration) can
effectively differentiate the level of user diligence,
achieving an F1 score of 81.06%, which demonstrates
the correlation between focus time and behavioral
patterns (Saplacan et al., 2020).
Bidirectional Relationship between Fragmented
Information and Focus:
A fragmented information environment can serve
as a trigger for declining focus (Ai et al., 2021), while
at the same time, training in multitasking abilities
may enhance adaptive focus in specific contexts
(Rahiminia et al., 2019).
2.3 Overview of the Impact of
Fragmented Information
The subjects in these studies include college students
(Odden & Russ, 2019), social media users (Yao,
2019), and online learners (Kindermann & Onofri,
2021).
Regarding the control of confounding variables,
some studies have not adequately considered
individual cognitive differences, such as multitasking
ability (Ai et al., 2021). However, a few studies have
enhanced internal validity by employing random
sampling and covariate analysis (Saplacan et al.,
2020).
In quantitative research, methods such as Likert
scales (Ai et al., 2021), behavioral log analysis
(Saplacan et al., 2020), and experimental approaches
(Yao, 2019) have been utilized. In qualitative studies,
interviews have been conducted to analyze the
fragmentation of information in digital learning
environments (Kindermann & Onofri, 2021). In terms
of data analysis techniques, researchers have applied
factor analysis to reduce data dimensionality (Ai et
al., 2021), machine learning classification methods
(Saplacan et al., 2020), and structural equation
modeling (Yao, 2019).
Long-term exposure to fragmented information
significantly affects individuals’ cognitive processes,
learning, and daily life. At the cognitive level, this
mode of exposure reduces the ability to maintain
sustained focus, as evidenced by an increased
working memory load (Rahiminia et al., 2019) and
decreased efficiency in logical reasoning (Ai et al.,
2021). In terms of learning, college students become
more prone to distraction in environments with
fragmented information, resulting in a significant
decline in the quality of task completion in class
(Kindermann & Onofri, 2021). Furthermore, in
everyday life, social media users frequently switching
tasks experience time perception distortion, which in
turn triggers procrastination behaviors (Yao, 2019).
Limitations and comparisons: Most studies rely
on cross-sectional data and lack in-depth long-term
tracking analysis (Ai et al., 2021); at the same time,
the validity of the measurement tools remains to be
verified—for instance, self-report scales may be
influenced by social desirability bias (Odden & Russ,
2019). In contrast, the research by Kindermann and
Onofri revealed the adverse impact of information
fragmentation on cognitive load in educational
settings, while Yao’s study pointed out that social
media users can, to some extent, offset these negative
effects through flow experiences(Yao, 2019). This
further indicates that it is necessary to more precisely
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years
547

categorize and study the influencing factors in
different scenarios.
2.4 Factors Affecting Focus and Its Impact
on Individuals
2.4.1 Individual-Level Factors
Differences in cognitive abilities and psychological
factors significantly affect an individual’s capacity to
adapt to fragmented information environments and
maintain attention stability. Specifically, those with
strong multitasking abilities tend to adapt more
flexibly to fragmented settings (Rahiminia et al.,
2019), whereas individuals with weaker cognitive
control may experience a marked decline in focus
when confronted with multiple tasks (Odden & Russ,
2019). In addition, psychological factors are not
negligible; anxiety and stress consume substantial
cognitive resources, thereby reducing the stability of
attention (Odden & Russ, 2019).
2.4.2
External Environmental Factors
In the current media landscape, social media
platforms employ design elements such as “infinite
scrolling” and instant feedback mechanisms (e.g.,
likes, comments) to capture users’ attention (Yao,
2019). Simultaneously, the management of
fragmented time undermines the ability for deep
focus, as indicated by the negative correlation
between the frequency of task switching and the
quality of task completion (Saplacan et al., 2020).
2.4.3
Potential Consequences of Declining
Focus
Declines in focus affect academic performance, daily
efficiency, and psychological well-being.
Specifically, in academic performance, task
completion times are prolonged (Saplacan et al.,
2020) and the logical coherence of academic writing
diminishes (Ai et al., 2021). Regarding daily
efficiency, procrastination tends to increase (Yao,
2019), and the ability to plan long-term is impaired
(Odden & Russ, 2019). Furthermore, on a
psychological level, divided attention makes
individuals more susceptible to external
distractions—for example, an excessive reliance on
mobile notifications (Kindermann & Onofri, 2021)—
with some users even developing symptoms of
“information anxiety” (Rahiminia et al., 2019).
2.4.4
Intervention Strategies
At the individual level, cognitive training methods,
such as mindfulness meditation, can enhance one’s
resilience to distractions (Jiang, 2020). From an
environmental design standpoint, universal design
principles have been applied to optimize digital
learning platforms to reduce the fragmentation of
information across different systems. Concurrently,
social media platforms have introduced a “focus
mode” feature to promote enhanced user
concentration.
2.4.5
Research Gaps
Further research should explore the differential
impact of fragmented information on individuals with
diverse cognitive styles (e.g., field-independent vs.
field-dependent) and examine how cultural
background moderates these effects.
3 RESEARCH QUESTIONS
3.1 Main Question
The present study systematically examines the impact
of social media-driven fragmented information
consumption patterns on the sustained attention
capacities of undergraduate students over the past five
years.
3.2 Breakdown of Issues
1.How can the fragmented information present on
social media platforms be clearly defined?
2.How can the attention of these college students
be measured by using “time of concentration” (noting
the investigation of popular online buzzwords)?
3.Over the past five years, what specific
mechanisms and dimensions illustrate how the
fragmented information mode on social media
impacts the learning attention of currently enrolled
college students? (A detailed analysis across various
categories of college students is conducted.)
4.Over the past five years, what specific
mechanisms and dimensions illustrate how the
fragmented information mode on social media
impacts the daily attention of currently enrolled
college students? (A detailed analysis across various
categories of college students is conducted.)
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
548

4 RESEARCH METHODS AND
RESULTS
4.1 Questionnaire Survey Method
The investigation commenced with administering
structured questionnaires to the target population
(undergraduate students). Initial data collection
focused on recording demographic characteristics
and research-relevant attributes. To address the core
research question regarding the impact of fragmented
information on attention span, two standardized
measurement instruments were incorporated: the
Fragmented Information Scale (Ai et al., 2021) and
the Attention Concentration Self-Assessment Scale
(Lin et al., 2009). Complementing these scales, the
questionnaire included purpose-designed items
assessing static behavioral patterns. Valid responses
were obtained from 96 participants, with all collected
data undergoing descriptive statistical analysis. The
analytical results indicate three predominant
characteristics: extended social media usage duration,
frequent exposure to fragmented information inputs,
and reduced capacity for sustained attention among
the surveyed undergraduate cohort.
4.2 Correlation Analysis
After categorizing the questionnaire data, Pearson's
correlation analysis was conducted between the
extent of fragmented information exposure and the
perceived decline in attentiveness to assess their
correlation.
As shown in Table 1, the Pearson's correlation
analysis revealed that the extent of fragmented
information exposure significantly positively
correlated with the perceived decline in attentiveness.
This indicated that the higher the fragmented
information exposure, the greater the attentional
decline.
4.3 Python-Based Web Crawling and
Sentiment Lexicon Analysis
A Python-based web crawler was deployed to retrieve
targeted metadata fields from post titles containing
fragmented information and attentional focus on
Xiaohongshu (a Chinese social media platform). This
methodology captured public sentiment orientation
toward fragmented information and attentional focus.
The lexical frequency data subsequently underwent
descriptive statistical analysis, identifying discernible
patterns in public perception of the correlation
between fragmented information exposure and
attentional focus.
As shown in Table 1, the Pearson's correlation
analysis revealed that the extent of fragmented
information exposure significantly positively
correlated with the perceived decline in attentiveness.
This indicated that the higher the fragmented
information exposure, the greater the attentional
decline (see Table 1).
Table 1.The Correlation between Students’ Focus and Fragmented Information Intake
Perceived Decline in
Concentration
Fragmented
Information Reception
Perceived Decline in
Concentration
Pearson Correlation 1 .240*
Two-tailed Si
g
nificance 0.018
Sample Size 96 96
Fragmented Information
Reception
Pearson Correlation .240* 1
Two-tailed Si
g
nificance 0.018
Sample Size 96 96
4.4 Python-Based Web Crawling and
Sentiment Lexicon Analysis
A Python-based web crawler was deployed to retrieve
targeted metadata fields from post titles containing
fragmented information and attentional focus on
Xiaohongshu (a Chinese social media platform). This
methodology captured public sentiment orientation
toward fragmented information and attentional focus.
The lexical frequency data subsequently underwent
descriptive statistical analysis, identifying discernible
patterns in public perception of the correlation
between fragmented information exposure and
attentional focus.
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years
549
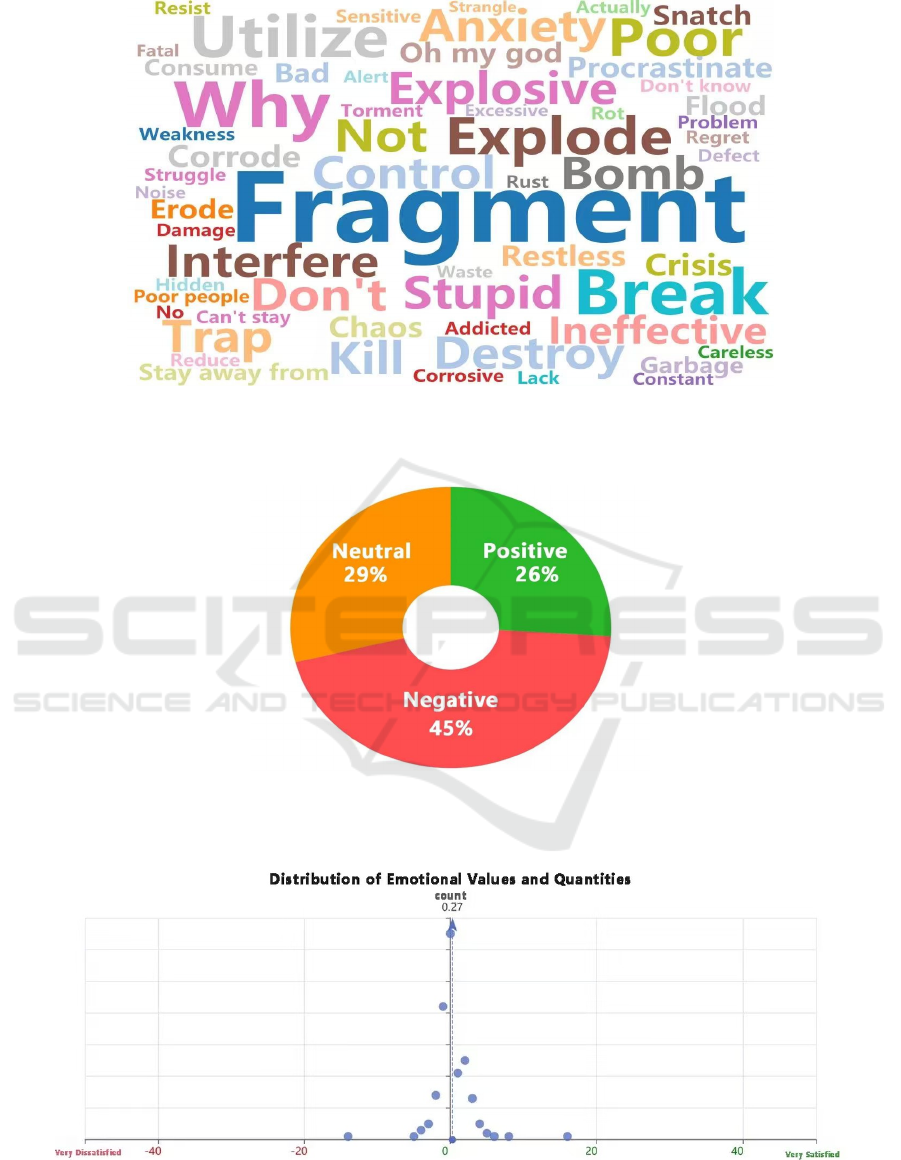
Alt Text for the figure: Word cloud featuring "Fragment" at the center, surrounded by related terms like "Explode, " "Break,
" "Control, " and "Anxiety, " in various colors and sizes.
Figure 1. Sentiment Word Cloud for Fragmented Information and Declining Focus (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Alt Text for the figure:A pie chart showing sentiment distribution: Negative 45%, Neutral 29%, Positive 26%.
Figure 2. Distribution Chart of Positive, Negative, and Neutral Terms for Fragmented Information and Declining Focus
(Photo/Picture credit: Original).
Alt Text for the figure:Scatter plot titled "Distribution of Emotional Values and Quantities" with emotional values ranging
from "Very Dissatisfied" to "Very Satisfied" on the horizontal axis and count on the vertical axis. Data points are clustered
around the positive side, with the highest count at approximately 0.27 near the origin.
Figure 3. Scatter Plot of Term Frequency for Fragmented Information and Declining Focus (Photo/Picture credit: Original).
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
550

Table 2. Scatter Plot of Sentiment Scores for Fragmented Information and Declining Focus
Positive letters Ne
g
ative and neutral letters
1:21 -14:1
2:25 -5:1
3:13 -4:3
4:5 -3:5
5:2 -2:14
6:1 -1:42
8:1 0:65
Total:68 Total:131
4.5 Sentiment Analysis
As illustrated in Figure 1, lexical frequency clouds
associated with fragmented information and
attentional focus predominantly feature negative
terms. Figure 2 further specifies that negative valence
terms constitute the majority (45%) of this lexicon,
whereas neutral and positive terms exhibit
comparable proportions (27% and 28%,
respectively). Additionally, Figures 3 and Table 2
demonstrate that the positive lexicon accounts for
approximately 50% of non-positive terms.
Collectively, these findings reveal a dominant non-
positive sentiment orientation, supporting the inverse
relationship between fragmented information
exposure and attentional focus maintenance (see
Figure 1, 2, 3).
5 DISCUSSION
Through sentiment analysis and correlation analysis,
this study identifies that in contemporary society,
fragmented information exerts a substantial negative
impact on college students' attentional focus, with
higher exposure levels corresponding to greater
declines in attentional maintenance.The measurement
targets in this research were strictly limited to college
students. Previous studies have investigated
populations including social media users and online
learners (Kindermann & Onofri, 2021;Yao, 2019).
Although differing in research cohorts, the
conclusions of this study exhibit near-complete
consistency with prior findings. Existing literature
demonstrates that prolonged exposure to fragmented
information reduces sustained attentional capacity at
the cognitive level (Rahiminia et al., 2019). Within
academic contexts, college students in fragmented
information environments display increased
susceptibility to attentional diversion (Kindermann &
Onofri, 2021), while daily life scenarios similarly
exhibit reduced focus (Yao, 2019). Synthesizing
these findings, fragmented information adversely
affects multiple dimensions of individual life.
5.1 Implications of the Research
Findings
This study reveals the significant negative impact of
fragmented information on the focus of college
students. This finding not only confirms the
ubiquitous conclusions reached by previous research
but also underscores the burgeoning attention crisis in
the digital age. Based on Cognitive Load Theory, this
study proposes systematic solutions from multiple
dimensions—including individual behavioral
correction, the reconstruction of the educational
ecosystem, and the governance of technological
ethics—outlined in the implementation paths below:
5.1.1
Individual Cognitive Rebuilding
Strategies
As digital natives, college students need to establish
proactive defense mechanisms against information
overload. At the behavioral level, a "dual-mode time
management approach" can be adopted: utilizing the
Pomodoro Technique to divide work into 25-minute
deep learning sessions, complemented by focus
management tools such as Forest to block social
media distractions. At the cognitive level,
mindfulness meditation training is recommended.
Neuroscientific research indicates that 20 minutes
of mindfulness practice per day can enhance activity
in the anterior cingulate cortex, thereby improving
resistance to interference. In terms of technological
assistance, digital trace analysis tools—such as
RescueTime—can quantify the intensity of exposure
to fragmented information. An alert mechanism is
triggered if passive information intake exceeds 90
minutes in a single day, with this threshold based on
research identifying the critical point at which
attention begins to deteriorate.
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years
551

5.1.2 Adaptive Reform in Educational
Systems
Higher education institutions should prioritize the
establishment of cognitively-adaptive learning
environments through three fundamental
modifications. The curriculum design requires
embedding metacognitive attention training modules
in general education programs, particularly through
neuroscience laboratory courses that demonstrate
efficiency depletion in multitasking processes.
Physical space renovation necessitates installing Wi-
Fi-free study pods with 470nm amber lighting,
experimentally proven to reduce β-oscillation
amplitude in visual cortex by 30%, while
simultaneously designating smart device-free zones
as cognitive protection areas in library facilities.
Regarding evaluation system innovation,
implementing eye-tracking-based learning
monitoring systems that automatically deliver
cognitive adjustment prompts when students' gaze
shift frequency exceeds 2Hz remains imperative.
5.1.3
Reconstruction of Internet Platform
Responsibilities
Social media platforms should transition from
attention extraction paradigms to functioning as
custodians of cognitive well-being through the
implementation of dual mechanisms encompassing
algorithmic mediation and normative governance.
Within the technical dimension, dynamic information
flow regulation systems could be developed utilizing
machine learning algorithms to identify substantive
content (e.g., text density>0.8, information
entropy>5bit/character), where qualified content
should undergo distribution interval extension
beyond 24 hours. Regarding normative governance,
establishing a Cognitive Risk Assessment and
Prioritization System (CRAP) information
classification system would require cognitive load
value (CLV) labeling for fragmented content; when
users engage with CLV>7 materials continuously
exceeding 15 minutes, mandatory rest interfaces
should be triggered. Furthermore, in accordance with
Article 29 of the EU Digital Services Act, academic
applications should be configured with cognitive
streamlined interfaces as default settings through
deactivation of non-essential functions.
5.1.4
Public Policy Governance Framework
The governmental governance system should
implement a tripartite "prevention-intervention-
compensation" architecture:Prevention phase:
Enactment of the Digital Health White Paper requires
educational platforms to integrate the National
Attention Protection Standard (e.g., restricting each
notification to ≤3 information units).Intervention
phase: Smart city initiatives should incorporate
cognitive load monitoring stations, with urban brain
systems generating regional heatmaps of attentional
demands.Compensation phase: Development of a
national neuroplasticity cloud platform is proposed to
deliver transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)-
based neuromodulation services for attention deficit
populations.Legislatively, amendments to the
Cybersecurity Law should introduce digital health
rights provisions mandating corporate disclosure of
algorithmic impacts on sustained attention.
This study underscores the inadequacy of
unilateral governance, necessitating a quadripartite
network integrating individual, institutional,
corporate, and governmental stakeholders. Short-
term behavioral interventions may deploy digital
health tools (e.g., compulsory installation of
attentional shielding plugins in academic
institutions). Mid-to-long-term strategies require
neuroplasticity-based cognitive rehabilitation
systems. Establishment of a National Attention
Research Institute would facilitate periodic
publication of the National Attentional Competence
White Paper, culminating in comprehensive cognitive
safeguarding protocols for the digital era.
5.1.5
Interdisciplinary Research Directions
Future investigations must be deepened to examine
neural adaptation mechanisms underlying fragmented
information processing, employing functional near-
infrared approach will facilitate the establishment of
biologically validated markers for attention
impairment. Concurrently, adaptive information flow
modulation spectroscopy (fNIRS) to monitor
prefrontal cortex oxygenation dynamics (with blood
oxygenation changes detectable through alternative
modalities including fMRI). This experiments should
be implemented, systematically regulating
information density (0.5-4 bits/s) to identify working
memory capacity thresholds. Such empirical findings
will yield neuroscientific foundations for platform
algorithm optimization. Methodologically,
developing mixed reality (MR) experimental
paradigms is crucial to simulate cognitive disparities
between short-video platform interfaces (e.g.,
Douyin/TikTok) versus conventional print-reading
contexts, thereby mitigating social desirability bias
inherent in questionnaire-based approaches.
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
552

5.2 Limitations
Considering the study participants—university
students representing only a minor segment of
society—the generalizability of the conclusions is
consequently limited. The recommendations for
improving attention advanced in this paper are highly
targeted, yet their overall contribution to mitigating
the adverse societal impact of fragmented
information on attention remains relatively modest.
With respect to measurement methods, employing
attention duration as a proxy for attention level
presents specific technical limitations. While extant
literature validates its rationality as a measure, the
considerable measurement error and associated
difficulties may result in misleading experimental
outcomes, thereby requiring a larger sample size.
From the standpoint of experimental methodology,
the questionnaire survey approach, as a traditional
and generally applicable method in social sciences,
can address a wide range of issues; however, its
application in small sample contexts is prone to
substantial error. Accordingly, future research ought
to expand its scope to encompass a more diverse pool
of participants, thereby improving the
generalizability of its conclusions. Furthermore,
during both the data processing and social experiment
phases, future studies should employ data indicators
and experimental methods of higher precision to yield
more accurate conclusions.
6 CONCLUSION
This study examines the effects of fragmented
information on attentional capacity among
undergraduate students. The research methodology
integrates questionnaire surveys, correlation analysis,
Python-based web crawling, and emotional lexicon
frequency analysis. Results demonstrate significant
negative correlations between fragmented
information exposure and sustained attention
performance, with longitudinal exposure to
fragmented information predicting measurable
deterioration in attentional maintenance.To address
these findings, the paper proposes four evidence-
based intervention strategies: cognitive restructuring
techniques, adaptive reform in educational systems,
responsibility recalibration for digital platforms, and
public policy framework optimization. Cognitive
restructuring techniques target the enhancement of
metacognitive awareness through volitional
regulation, while the remaining three strategies
emphasize coordinated institutional interventions at
governmental and societal levels.By employing a
dual analytical framework encompassing problem
diagnosis and solution formulation, this investigation
systematically elucidates the cognitive impacts of
fragmented information exposure and provides
empirically grounded recommendations for attention
enhancement. Within the contemporary media
ecosystem dominated by fragmented information
patterns, the proposed multidimensional approach
offers viable countermeasures to mitigate cognitive
fragmentation effects, ultimately fostering the
development of sustained, deep-learning capabilities
in academic contexts.
AUTHORS CONTRIBUTION
All the authors contributed equally and their names
were listed in alphabetical order.
REFERENCES
Ai, Y.-N., Wu, J.-C., & Lou, L.-W. 2021. Definition and
scale research on fragmented information. Electronic
Technology & Software Engineering, 08: 18–19.
Jiang, W.-M. 2020. A case study of the effects of meditation
on emotional improvement and concentration in two
junior high school students. Psychology Monthly,
15(18): 27–29.
Kindermann, D., & Onofri, A. 2021. The fragmented mind:
An introduction. In The Fragmented Mind: 1–33.
Lei, H., Liu, Y.-L., Wei, J., Tian, L., & Wang, X.-Q. 2012.
A study on academic diligence of high school students
based on the two-dimensional core model of time
investment and concentration. Psychological
Development and Education, 28(04): 384–391.
Lin, C.-P., Tsai, Y.-H., & Chiu, C.-K. 2009. Modeling
customer loyalty from an integrative perspective of
self-determination theory and expectation-confirmation
theory. Journal of Business and Psychology, 24: 315–
326.
Liu, M., Han, M.-Y., Li, Y., & Sheng, C.-Q. 2018. The
effect of real-time collaborative writing environments
on learning concentration and performance. Modern
Educational Technology, 28(07): 38–43.
Odden, T. O. B., & Russ, R. S. 2019. Defining
sensemaking: Bringing clarity to a fragmented
theoretical construct. Science Education, 103(1): 187–
205.
Rahiminia, E., Yazdani, S., & Rahiminia, H. 2019. Factors
affecting concentration and attendance in the classroom
from students’ point of view in Qom University of
Medical Sciences (2018). Educational Research in
Medical Sciences, 8(2): e93075.
Saplacan, D., Herstad, J., & Pajalic, Z. 2020. Use of digital
learning environments: A study about fragmented
The Impact of Fragmented Information on the Concentration of Undergraduate Students in the past Five Years
553

information awareness. Interaction Design &
Architecture(s), 43: 86–109.
Yao, Q.-Y. 2019. Research and implementation of the
measurement method of online questionnaire user
concentration (Master’s thesis, Xidian University).
https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2019.0
03012
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
554
