
Global Promotion Strategy of Social Media Platforms: Take Tik Tok
and RedNote as Examples
Qiyue Miao
Cultural & Media Policy University of Warwick, Coventry, U.K.
Keywords: Social Media, Digital Platforms, New Media, Digital Marketing, Media Globalization.
Abstract: This paper focuses on the globalization strategy of social media, and uses the globalization attempts of TikTok
and RedNote as the main cases to explore the foundation of social media globalization. This paper deeply
studies the advantages and disadvantages of social media globalization. By comparing Chinese and foreign
social media, it analyzes how social media can expand the global market in addition to basic preparations,
combined with past cases and the current context, and what kind of global business and marketing strategies
can be tried. This paper aims to propose that the globalization of social media is a measure that can be taken
in the current era. Social media always needs to adopt corresponding strategies with the environment, maintain
attention to cultural values and cross-cultural relations, and further expand foreign markets on the premise of
ensuring that ideas and content are in line with the mainstream of global background ideas.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technology has brought rapid development to
globalization. People have more convenient and
actionable ways to communicate with each other all
over the world, which led to globalization both
physically and culturally. In order to pursue the trend
brought by the development of technology, many
digital media platforms start to try to reach broader
groups of audience without country restrictions,
whom from different cultures. Focused on Chinese
social media platforms, TikTok was firstly launched
in 2016 in China, called Douyin (Tone, 2018). In
2017, TikTok started to enter the international market
by launched in Indonesia. It quickly became popular
all around the world in the next few years. In January
2025, as TikTok was banned in the US due to political
laws, a large group of audience entered RedNote, a
Chinese social media platform mainly welcomed in
mainland China and used it as the substitute of
TikTok (Pandith & Dixon, 2025). This has brought an
opportunity for RedNote to enter the international
market. This paper will mainly focus on the analysis
of these two media platforms’ globalization decisions
and strategies and evaluate what are the most
appropriate time and effective ways to enter the
global market. In comparison with overseas social
media platforms, Twitter and Instagram, this paper
aims to give advice to social media which would like
to target a larger range of audience around the world
and reach successful globalization.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Reasons for TikTok’s
Popularity
Up until 2025, TikTok gained large groups of users
all around the world. In Figure.1, TikTok has been
popular in Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa and
Latin America. Its monthly active users have reached
over 1,000 million all over the world. TikTok is
welcomed as it matches different users’ needs and
provides diversified content.
380
Miao, Q.
Global Promotion Strategy of Social Media Platforms: Take Tik Tok and RedNote as Examples.
DOI: 10.5220/0013992000004916
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication (PRMC 2025), pages 380-385
ISBN: 978-989-758-778-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
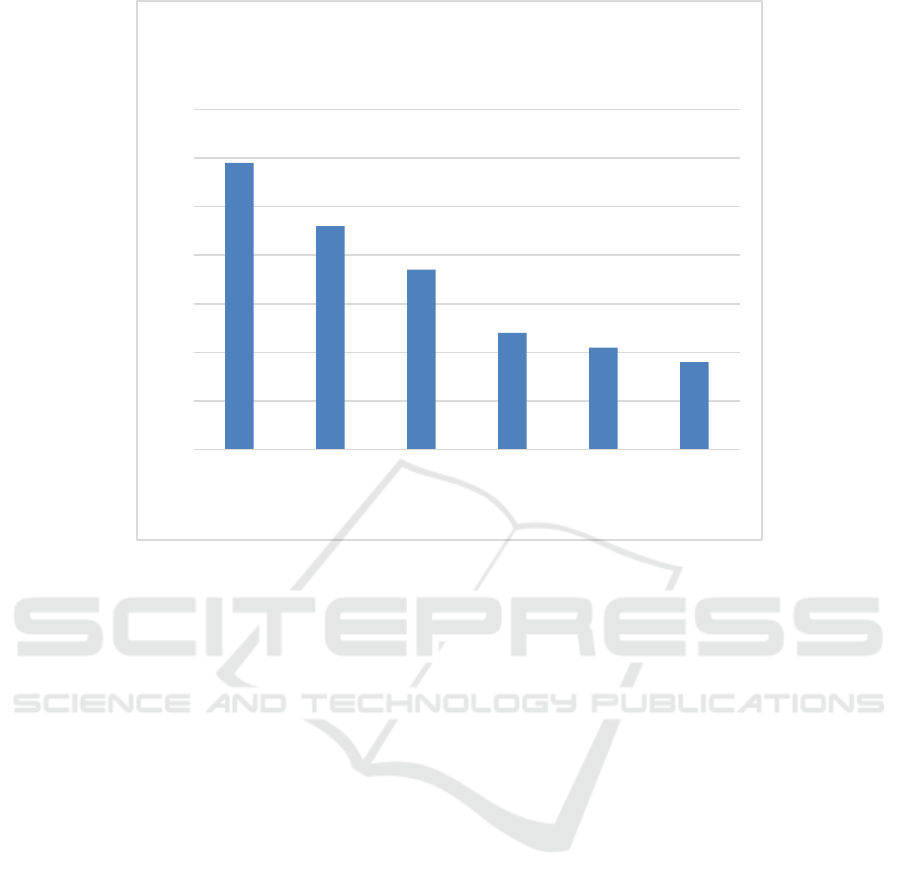
Data Source: Team, B. (2025, March 8).
Alt Text for the figure: The bar chart reflects the monthly active users of Tik Tok in 2025 in six regions.
Figure.1: TikTok Monthly Active Users by Region in Millions, 2025.
In Li ’s study on TikTok’s global rise strategies, a
survey of 150 TikTok users (100 females and 50
males) aged 18-30 in Beijing, China showed Chinese
users’ reflections to TikTok (Li,2022). It was found
that Tik Tok’s rapid growth was attributed to its
effective marketing strategies, strong artificial
intelligence technology, and ability to meet users'
needs. Besides, compared to other short video apps
like Instagram, Snapchat, and YouTube, TikTok
showed its uniqueness in features and contents. It was
very clear about its target audience, which would be
the young users, and it managed to meet the
audience’s needs with easy video creation and
personal recommendations. This has set it apart from
other competitors.
Some scholars examined why TikTok also
achieved success in the US (Boffone,2022). The key
features included personalization, community,
virality, and types of content. It allowed anyone with
a TikTok account to spin out of themselves and give
shape to information, story, music, performance, art-
all cultural phenomena. Along with its explosion,
TikTok started to shape its own new culture. In this
platform, planetary peoples and cultures
reverberative intersected, exchanged, and then
created something new. However, a very realistic and
direct fact was also pointed out. TikTok relied on its
shaping algorithm technology, which was
conservative and in flux, always transcending and
morphing into something new. Aldama (2022)
claimed that as a commercial company, TikTok’s
algorithms and exploitative structures have in some
ways led to more radical institutional communication.
While it must be admitted that this just shows that
TikTok's algorithms and technology have made its
culture extremely influential even abroad.
2.2 The Reasons for RedNote’s
Popularity
Compared with TikTok, RedNote has just started its
globalization journey. Its success can be said to be
more dependent on the context. According to
Figure.2, the number of RedNote mobile app
downloads kept rising in China and the rest of the
world. From quarter 4, 2024, there was a rapid
increase in the number of the United States and the
rest of the world, and the number of downloads in the
US even exceeded that in China, in quarter 1, 2025.
This change was the result of policy towards TikTok
in the US, which forced people to start to find another
substitute for social media like TikTok.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
Asia-Pacific Middle East
and Africa
Latin
America
North
America
Western
Europe
Central and
Eastern
Europe
TikTok Monthly Active Users by Region
(Million)
Global Promotion Strategy of Social Media Platforms: Take Tik Tok and RedNote as Examples
381
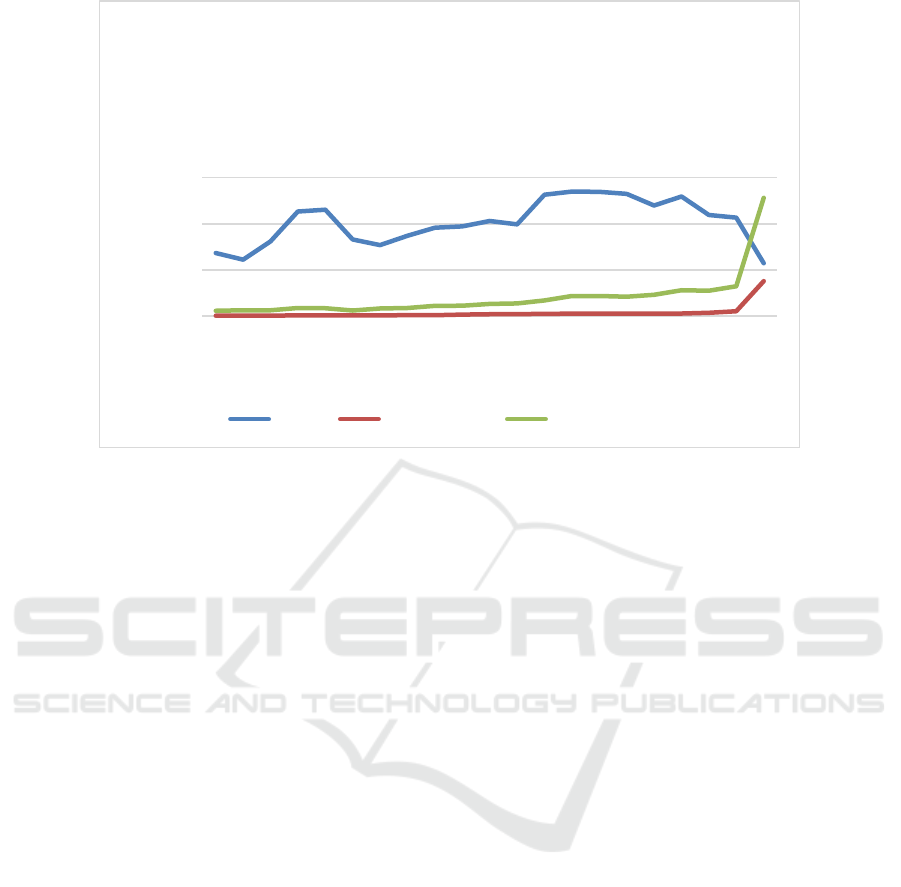
Data Source: Statista.
Alt Text for the figure: The abscissa represents each quarter from 2020 to 2025, the ordinate represents the download volume
of RedNote, and the three broken lines in the figure represent China, the United States and other countries in the world.
Figure.2: Number of quarterly Xiaohongshu (RedNote) mobile app downloads in the United States and China from 2020 to
2025.
Similar to Tik Tok, RedNote also has its algorithm
system and clear target audience. In some studies,
through literature review and analysis of information
and statistics from various sources, the results showed
that RedNote’s content had social features and the
ability to discover and share information about
luxury, fashion, and beauty products (RMMD,2019).
RedNote used user-generated content and influencer
marketing strategies to target users at a specific
demographic of young, urban, and affluent female
consumers in China and has achieved success.
The difference is that RedNote has a feature that
is intended to be liked and frequently used by some
study, which involved quantitative analysis of posts
in RedNote and qualitative interviews with 24 users
of RedNote from different backgrounds, found that
on RedNote, users could regain control of content
distribution and build their own communities on
similar recommendation-driven platforms by
redistributing hashtag dominance (Wan et al. 2025).
Hashtag in RedNote has given users the sense of
belonging and controlling, which becomes another
reason for its popularity in China.
In 2025, ‘TikTok Refugees’ entered RedNote and
started to interact with Chinese users in the platform.
Some scholars used qualitative research methods to
analyze public data on RedNote, including posts and
related comments (Liu et al.,2025). The study focused
on the opportunity that this accident brought to
RedNote, which was to transform from a domestic
social media platform into a vibrant environment for
cross-cultural communication. Users from different
places carried out real interactions and role-exchange
dynamics through platform mediation, creating a
common identity development process guided by the
pursuit of the "global village" imagination.
Up till now, it is hard to evaluate if RedNote has
reached its success in globalization. In some report,
opinions about whether this phenomenon would be
temporary or not were collected (Yang,2025). It was
pointed out that lack of monetization for creators,
issues such as political censorship and lack of data
privacy protection would still need to be solved.
While in another way, if the problems could be
solved, then RedNote would be able to maintain the
users. People’s natural reactions and the authenticity
of the content were the competitive advantages of
RedNote.
2.3 Difference Between Chinese Social
Media Platforms and Local Media
Platforms Overseas
Through previous studies of the reasons for the
popularity of TikTok and RedNote, a clear target
group, a free content creation environment and
precise algorithm technology are the basis for the
0
5000000
10000000
15000000
Q1 2020
Q2 2020
Q3 2020
Q4 2020
Q1 2021
Q2 2021
Q3 2021
Q4 2021
Q1 2022
Q2 2022
Q3 2022
Q4 2022
Q1 2023
Q2 2023
Q3 2023
Q4 2023
Q1 2024
Q2 2024
Q3 2024
Q4 2024
Q1 2025
Number of quarterly Xiaohongshu (RedNote)
mobile app downloads in the United States and
China
from 2020 to 2025
China United States Rest of the world
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
382

popularity of a social media platform. In the process
of globalization attempts, how to create a cultural
environment that is both distinctive and inclusive
through the platform is very important.
Looking at similar social media platforms
overseas like Instagram and Facebook, some
scholars took a cross-sectional survey was
conducted on 396 college students and collected
demographic information (Alhabash and
Ma,2017). The results showed that for these
platforms, the top 2 motivations across all were
entertainment and convenience. This was closely
associated with the U&G framework and had
continued relevance in understanding user
behaviors and motivations in the digital age. The
reasons why people overseas choose social
media platforms can give some inspiration to
domestic media platforms' globalization
attempts. By studying the degree of demand for
entertainment and convenience among overseas
users, domestic media platforms can focus on
them and build target group demographics to
create a new and more comprehensive social
media culture for all users.
3 DISCUSSION
3.1 Possibilities of Globalization
Whether a social media platform can successfully
achieve globalization depends not only on the
improvement of the platform itself, but also on the
identification and analysis of the current context. If
the policy reform against TikTok is an unexpected
opportunity for RedNote, then for more general social
media platforms, it is very significant to analyses
whether the current context is the best time for global
promotion.
Influenced by society and technology, people’s
mindsets keep changing over time. Viewing from
individual changes, people’s ability to accept the
technology and cultures allows this era to be
appropriate for social media’s globalization. In the
most current era, more and more people get in touch
with digital platforms and start to use technology.
Associating with social media has provided people
with new ways to explore self-understanding. In the
past, people’s self-understanding was built on long
histories of written, visual and quantitative modes of
self-representation. While in the digital era,
technology has brought a virtual world with a whole
new system of culture for people to participate,
communicate and create. Using technology to reflect
and see ourselves is another method, and people are
more likely to allow machines to tell us who we are
(Rettberg, 2014). As mentioned above, people will
continue to crave more entertainment and
convenience, which makes the future world closely
related to more advanced technology. For social
media platforms, improving technology and
algorithms will better cater to the preferences of
future audiences and build a solid technical
foundation for globalization.
Moving to the external context, the structural
conditions brought by technology to the world also
provide opportunities for the globalization of social
media platforms. In today's thoughts and cultures of
globalization, the idea of “one world” has become
dominant, and the tend towards the whole is shown as
a structural change. The new structural conditions of
huge, globe-spanning online platforms, fast-
advancing algorithmic culture, and the precariousness
of online labor are formed (Cunningham & Craig,
2016), which has provided an appropriate
environment for social media platforms to explode
overseas and find more possibilities.
In this context of globalization, choices are
offered to social media platforms. The purpose of
explosion should also be considered. Whether to use
this chance to achieve globalization for broader
financial benefits or to build a well-known brand all
over the world, it should be clear about the
advantages and disadvantages of globalization and
take use of them. Sometimes the success of
globalization can not only bring extra economic
income but also show the growth in the ability to
communicate. Take TikTok as an example, it set the
goal of strengthening the nation's prowess in global
communication and fostering the development of
overseas social media platforms, and its success
showed a huge improvement of China's international
communication ability (Hu & Liang, 2023).
Thus, the success of social media’s globalization
can also link to the concept of a nation’s culture and
ability to show its culture, which is closely associated
with soft power. Social media has played a significant
role in the spread of populism and nationalist
narratives, allowing them to bypass mainstream
media and directly engage with their supporters (Flew
& Iosifidis, 2019). In this case, the necessary
conditions for a social media platform to achieve
globalization are emphasized more - unique culture
and strong cultural output capabilities. It can be
concluded as well that if a social media platform can
succeed in globalization, then people must be able to
see its unique cultural integration or its creation of a
new inclusive culture.
A very practical double-side situation is that a
global platform promoted by a nation must contain
Global Promotion Strategy of Social Media Platforms: Take Tik Tok and RedNote as Examples
383

the nation’s unique cultural output. At the same time,
if a social media platform takes "cultural
globalization" as its goal, it will be easier to gain
national support. However, this may lead to another
extreme negative result of cultural imperialism.
Issues like the oversimplification of international
communication flows, the failure to address
"glocalization" strategies by media producers, the
problems with cultural protectionism, and the
inadequacy of the "hypodermic" model of media
effects may occur (Curran, 2007). When the purpose
is too ambitious, it may cause external obstacles in the
process of globalization. Therefore, it is necessary for
platforms to consider the extent of cultural output and
how to create a more inclusive and acceptable social
media culture.
3.2 Suggestions for Globalized
Strategies
In addition to the precise algorithm technology,
accurate positioning target group, and rich and
appropriate content as the basis for globalization, we
can see more that we can learn and improve from past
social media globalization cases. TikTok’s globalized
process showed the basic logic of trying and finding
out what do people really want to see. Take an
overview of TikTok’s growth and development,
TikTok kept implementing its specific business
model. It focused on short-video content, innovative
social networking, and live-streaming commerce,
which catered to the needs of modern users. The core
of this model is TikTok’s ability to innovate, cater to
user preferences, and leverage live-streaming
commerce (He et al., 2021). Besides this useful
business model, TikTok also operated “borderline
practices”. These practices focused on content
transfer (borrowing, remixing, and reposting content)
and algorithmic manipulation (using fake accounts
and organizing content to trick the recommendation
algorithms) (Su & Kaye, 2023). Tik Tok has always
aimed to cater to the market, exploring user
preferences while implementing its business model,
and guiding and utilizing them with its effective
innovation capabilities to gain a wider audience. Its
success could be an inspiration to other social media
platforms, which is to predict market preferences,
obtain user data, and innovate business models.
Except from the successful case of TikTok, we
can also discover new possibilities for globalization
and paths to explore through the differences and
similarities between domestic and international social
media platforms. Viewing from the marketing
campaign strategy of TikTok and similar foreign
social media Instagram, content marketing,
sponsored content, and user-generated content are the
basic strategies in operation. However, a lot of
differences in social identity can be observed.
Different cultural contexts have set up conflicts
between individualism and collectivism, and there are
huge gaps within the evolution of virtual communities
and co-creation (Gao et al., 2012b). This may be the
reason why many social media platforms' attempts to
globalize are difficult to succeed. Behind similar
business models and marketing strategies, users bring
their own different backgrounds, which makes the
content have insurmountable cultural barriers. This
reveals the importance of social media platforms,
understanding user preferences and creating inclusive
communities.
As a content sharing platform with short videos as
the mainstream, TikTok has penetrated the world
with its business model, while another type of social
media platform that mainly shares pictures and texts
seems to be difficult to achieve globalization. The
form of microblogging is missing from the currently
globalized social media platforms. By analyzing and
comparing the user behaviors of the domestic social
media platform Sina Weibo and the similar foreign
social media platform Twitter, it is found that there
are significant differences in the microblogging
behavior on Sina Weibo and Twitter. The user's
behavior can be analyzed through multilingual and
culture-aware user modeling based on microblogging
data, thereby obtaining a more accurate user profile,
and making accurate content push and community
division (Gao et al., 2012a). This has provided new
ideas for simulating user preferences in different
regions and also brings new ideas to social media
platforms: in the process of making up for the lack of
globalized microblogging, user behaviors can be
guided through language and cultural perception to
create a global common community.
While social media platforms are implementing
technology upgrades and global promotion strategies,
it should also be always paid attention to the current
era and mainstream thinking. At present, in the
context of an open and inclusive global environment,
social media can take global actions. In the process of
globalization, social media platforms should take into
account the cultural values, new cultural identities,
intercultural relationships, intercultural adaptation,
and intercultural conflict of current users (Chen,
2012). In operations, the media should understand
that users with different cultural values have different
motivations for using social media. As mentioned
above, on foreign social media platforms, the two
main motivations for people to use social media
platforms are entertainment and convenience. People
in different places may have different rankings.
Social media should find the main motivations for
different groups of people around the world to use
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
384

social media. Based on this, social media can create a
new online space by weakening or strengthening
people's connections with the community, allowing
new cultural identities to emerge. At the same time, it
should be aware of the errors that cultural differences
may cause in expression and understanding and try to
avoid misunderstandings caused by cultural
differences that lead to a decline in reputation.
4 CONCLUSION
Taking Tik Tok and RedNote as cases, this paper
expounds the globalization promotion strategy of
social media. In general, the globalization of social
media needs to consider the current situation and
formulate corresponding strategies for the
environment of the times. The current open and
inclusive global context allows social media to carry
out the globalization process. Social media that wants
to complete globalization should have precise
algorithm technology, accurate target groups, rich
and inclusive content as a foundation, and at the same
time need to have innovative user preference
inference capabilities to create a new and inclusive
cultural identity on the platform. Social media needs
to pay attention to cultural values and the problems
that may arise from cultural differences and be
prepared to deal with them.
In addition, this paper still has some limitations.
The analysis of social media globalization strategies
mainly focuses on Chinese social media, with TikTok
and RedNote as the key analysis platforms, and
foreign social media that adopt globalization are not
selected and analyzed. At the same time, the context
mentioned in the paper mainly uses the Chinese
background and the American background as two
representative cultural environments in cases, mainly
discussing how social media platforms in Chinese
context can try to integrate into foreign cultures
represented by the United States, to achieve
globalization.
REFERENCES
Alhabash, S., & Ma, M. 2017. A tale of four platforms:
motivations and uses of Facebook, Twitter, Instagram,
and Snapchat among college students? Social Media +
Society 3(1).
Boffone, T. 2022. TikTok cultures in the United States. In
Routledge eBooks.
Chen, G. 2012. The Impact of New Media on Intercultural
Communication in Global Context. China Media
Research 8(2): 1–10.
Cunningham, S., & Craig, D. 2016. Online entertainment:
A new wave of media globalization? International
Journal of Communication.
Curran, J. 2007. Media and cultural theory. In Routledge
eBooks.
Flew, T., & Iosifidis, P. 2019. Populism, globalisation and
social media. International Communication Gazette
82(1): 7–25.
Gao, Q., Abel, F., Houben, G., & Yu, Y. 2012a. A
comparative study of users’ microblogging behavior on
Sina Weibo and Twitter. In Lecture notes in computer
science 88–101.
He, X., Hua, K., Ji, C., Lin, H., Ren, Z., & Zhang, W. 2021.
Overview on the growth and development of TikTok’s
globalization. Advances in Economics, Business and
Management Research.
Hu, J., & Liang, R. 2023. The overseas social media
platform and the improvement of China’s international
communication Ability—Taking TikTok as an
example. International Journal of Frontiers in
Sociology 5(16).
Li, Z. 2022. Strategies behind Tik Tok’s global rise.
Advances in Social Science, Education and Humanities
Research.
Liu, G.L., Zhao, X., & Feng, M.T. 2025. TikTok Refugees,
Digital Migration, and the Expanding Affordances of
XiaoHongshu (RedNote) for informal language
learning. International Journal of TESOL Studies.
Pandith, F., & Dixon, R. 2025. With “TikTok refugees”
fleeing to RedNote, China is beating the U.S. at soft
diplomacy. US News & World Report.
Rettberg, J.W. 2014. Seeing ourselves through technology:
how we use selfies, blogs and wearable devices to see
and shape ourselves.
RMMD, P. 2019. Impact of Xiaohongshu on its User based
and Society: A review. ICONIC RESEARCH AND
ENGINEERING JOURNALS 2(11): 285–294.
Statista. 2025. Xiaohongshu (RedNote) quarterly China,
U.S. downloads 2015-2025.
Su, C., & Kaye, B.V. 2023. Borderline practices on Douyin/
TikTok: Content transfer and algorithmic manipulation.
Media, Culture & Society: 1–16.
Team, B. 2025. TikTok Statistics You need to know.
Backlinko.
Tik Tok, a global music video platform and social network,
launches in Indonesia-PR Newswire APAC. 2017.
Tone, S. 2018. The app that launched a thousand memes.
#SixthTone.
Wan, R., Tong, L., Knearem, T., Li, T.J.-J., Huang, T.-H.
“Kenneth,” & Wu, Q. 2025. Hashtag Re-Appropriation
for Audience control on Recommendation-Driven
Social Media Xiaohongshu (Rednote). arXiv.
Global Promotion Strategy of Social Media Platforms: Take Tik Tok and RedNote as Examples
385
