
Internal Audit Effectiveness on Corporate Governance and Financial
Fraudulent Risk: Evidence from Kangmei Pharmaceutical
Yunjiao Wu
Rotman Commerce, University of Toronto, 27 King's College Circle, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Keywords: Kangmei Pharmaceutical, Financial Fraud, Internal Audit Quality, Corporate Governance, Internal Control.
Abstract: Over the last decade, financial fraud has occurred more frequently as it has become increasingly complicated,
organized, and systematic, given the rapid growth of small and medium-sized enterprises. Due to the sudden
economic downturn post-pandemic, firms facing extensive financial pressure tend to act more aggressively,
eventually leading to the incentive to commit fraud. Thus, the research on financial fraud and its relationship
with firms’ corporate mechanisms is of great significance in helping the public better conduct control samples
for future fraud prevention. Applying Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s financial fraud case as a recent example,
given the current accounting system and theoretical framework of fraud, by analyzing its internal audit quality
and corporate governance, this article provides insight into how internal audit quality and corporate
governance will ultimately contribute to the overall fraud risk.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the development of the global economy and the
international market, growing attention from the
public has been focused on financial fraud associated
with financial statement misconduct and audit failure.
The U.S. Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of
the Treadway Commission’s financial statement
fraud study from 1897 to 1997 in U.S. public
companies revealed that approximately 40% of
financial fraud occurred in industries including
technology, healthcare, and financial services
(Beasley, Carcello, Hermanson, & Lapides, 2000).
This astonishing finding indicates a growing risk of
violations in selected industries. However, many
previous studies conducted in the last century did not
fairly present any fraud control samples, emphasizing
the effectiveness of the firm’s audit committee and
functions of its corporate governance mechanisms
(Beasley et al., 2000), which raised public concerns
about the validity and universality of their results.
Hence, further investigation should be conducted
among the selected industries to determine the degree
of the mentioned fraud control samples in mitigating
financial fraud in public companies, using the recent
fraud example of Kangmei Pharmaceutical as a case
study illustration.
A focus on Kangmei Pharmaceutical is
appropriate for many reasons. First, this incident
occurred after a series of financial frauds in Chinese
listed companies such as Lantian Corporation, Wanfu
Biotechnology, Green Earth, Zhangzi Island, Kangde
Xin, etc., which means the fraudulent behaviour
persists despite repeated bans as the Chinese capital
market has grown rapidly in recent years (Zhang,
2023). The disturbing trends warn public stakeholders
to pay more attention to the relevant industry.
Meanwhile, the repetitive occurrence of such
incidents also indicates a lack of enforcement of the
regulations, which is also a crucial factor beyond low
public awareness. Under such circumstances, the
revelation and analysis of Kangmei Pharmaceutical
fraud are critical to understanding the formulation of
financial fraud in enterprises and how fraud control
samples failed to prevent it.
Second, when examining Kangmei
Pharmaceutical’s detailed ownership structure, a
disturbing discovery is made: the company is solely
controlled by a single person, Ma Xingtian, with his
wife as an affiliated person (Li, 2024). As a result, the
imbalanced ownership structure contributed to
Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s vulnerable internal
control and offered opportunities for the Ma couple,
as the top management, to commit fraud.
Finally, according to the China Securities
Regulatory Commission (CSRC) release, the audit
partner, Zhengzhong the Pearl River, failed to detect
material misstatements presented in Kangmei
Pharmaceutical’s financial statements and issued
standard unqualified opinions on the 2016 and 2017
144
Wu, Y.
Internal Audit Effectiveness on Corporate Governance and Financial Fraudulent Risk: Evidence from Kangmei Pharmaceutical.
DOI: 10.5220/0013987500004916
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication (PRMC 2025), pages 144-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-778-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
annual reports, which led to the serious audit failure
and subsequent financial fraud (Ye, Bai, & Xue,
2022). Therefore, Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s
financial fraud is a typical example of a firm’s
misconduct due to weak corporate governance and
auditors’ misconduct. This paper will examine the
relationship between the internal audit quality and the
control effectiveness of Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s
corporate governance and potential enterprises’
fraudulent behaviours.
2 DEFINE INTERNAL AUDIT
AND FINANCIAL FRAUD
2.1 Internal Audit Quality and Audit
Committee Functions
With growing concern regarding a series of financial
frauds in the Chinese enterprise market within the
past decades, the role of internal audit (IA) has
evolved and expanded into massive activities
associated with corporate governance, as it provides
effective internal control systems, which makes a
strong corporate governance mechanism and enables
greater trust from the external auditors in internal
settings (Ferrari, Cunha, &Boff, 2023). Based on the
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
requirements, all listed companies should form an
Audit Committee involving key components that at
least three members presented in the committee, all
members are independent executives, and at least one
member obtains financial expertise (Krishnan, 2005).
Per IFRS, public companies must appoint an audit
committee to hire external auditors who obtain a
Certified Public Accountant (CPA) license to become
audit partners and conduct financial statement audits
to convince investors and stakeholders to trust the
firm's financial conditions.
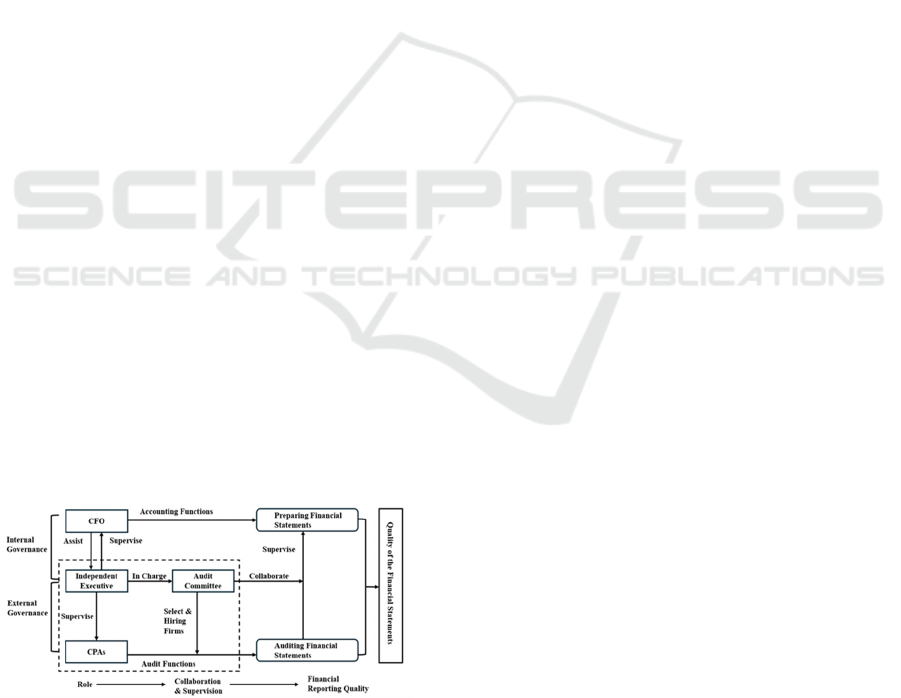
Alt Text for Graphical Figure: A diagram showing the
complete accounting system involving accounting and
auditing functions from the internal and external
governance angles.
Figure 1: Theoretical Framework of Firms’ Effective
Accounting System (Ye et al., 2022).
Figure 1 shows that firms can enhance financial
statement quality only when internal and external
governance cooperate well in the circled area. As a
key functional department involving internal and
external governance, the effectiveness of the audit
committee is critical.
2.2 Financial Fraud Theories
The theoretical approach mainly includes the Fraud
Triangle Theory and the GONE Theory. Of all three
factors contributing to potential fraud, pressure is the
majority cause due to firms’ need to meet the
financial forecasting, compensation and incentive
structures, external financing, or poor performance
(Hogan, Rezaee, Riley, & Velury, 2008), while weak
internal control will offer opportunities for top
management to manipulate revenues and earnings to
attract more investors. Besides, justification factors
allow some excuses to justify themselves as
“reasonable” when committing fraud. In contrast, the
GONE theory supposes individuals are profit-
seeking, and their behavior is rational; if there is an
opportunity and they believe it will be difficult to be
exposed in the future, they will inevitably engage in
fraudulent actions (Luo, 2020).
2.3 The Relationship Between IA
Quality and Financial Fraud
Compared to companies without fraud, companies
that commit fraud typically have either no audit
committee present or the members of the audit
committee are not entirely independent directors who
receive financial benefits such as stock options from
the company (Beasley et al., 2000). Furthermore, a
larger audit committee involving more independent
directors would have more expertise in terms of
diversity to provide more objected decision-making
and enhance accountability and oversight since more
independent members in the audit committee also
reflect more time, finances, and administrative
support (Pasko, Zhang, Pyzhikova, & Mykhailova,
2024). The hypothesis test shows that the two distinct
but important aspects of the internal audit function,
competence and independence, jointly strongly
improve financial reporting quality (Abbott,
Daugherty, Parker, & Peters, 2016), supporting the
above finding. Moreover, firms with a well-organized
audit committee typically have strong internal control
and IA quality, as mentioned above, which enhance
corporate governance to reduce the incentive for
fraud. For this reason, high IA quality greatly reduces
the opportunity fraud factors and helps organizations
construct a healthy corporate environment.
Internal Audit Effectiveness on Corporate Governance and Financial Fraudulent Risk: Evidence from Kangmei Pharmaceutical
145
3 EVIDENCE FROM KANGMEI
PHARMACEUTICAL
3.1 Company Background
Kangmei Pharmaceutical was founded in 1997 by Xu
Yanjun and Xu Dongjin. However, Xu’s spouse, Ma
Xingtian, physically controlled the company as the
sole director. In 2001, the company successfully went
public and was listed on the Shanghai Stock
Exchange. During the past two decades, Kangmei
Pharmaceutical has mainly produced and sold
traditional Chinese medicine, chemical drugs, health
food, purchased products, and Chinese medicinal
materials. As of 2018, 154 companies were included
in its consolidated financial statements, with 46
newly included, 33 newly formed and 13 newly
merged (Luo, 2020), making the company one of the
major operators in China’s pharmaceutical industry.
However, in October 2018, Kangmei was accused by
several financial analysts and journalists of
manipulating and falsifying its operating revenue,
stock inventories, cash and other current assets.
As shown in Table 1, a series of investigations
was launched, leading to a tremendous fraud
sequence.
Table 1: Timeline of Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s Fraud (Ye et al., 2022).
Sta
g
e Timeline Si
g
nificant Event
Stage I October 2018
– December 2018
The financial analysis article questioning Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s
fraud has been released, and the firm’s stock price has declined
significantly. On Dec 28
th
, 2018, the CSRC investigated Kangmei
Pharmaceutical’s violation of information disclosure regulations.
Stage II April 2019 Kangmei Pharmaceutical has released its 2018 annual report and
announcement on correcting accounting errors in the previous period,
with nearl
y
30 billion
y
uan of funds missin
g
.
Stage III May 2019
–
November 2021
The Shanghai Stock Exchange issued a letter of inquiry in May
2019, and the CSRC issued a notice of investigation to Zhengzhong
Pearl River. On May 14
th
, 2020, the CSRC issued the "Administrative
Penalty Decision" and "Market Ban Decision" to Kangmei
Pharmaceutical. On Nov 12
th
, 2021, the Guangzhou Intermediate
People’s Court made a firs
t
-trial
j
ud
g
ment on the class action lawsuit.
The audit partner of Kangmei Pharmaceutical
since 2001 is Zhengzhong Pearl River Accounting
Firm. Zhengzhong Pearl River, founded in 2000 and
registered in Guangzhou, is one of the earliest
accounting firms in China. In 2013, the firm switched
from a limited liability partnership (LLP) to a general
partnership (GPP). Since then, Zhengzhong Pearl
River has ranked 22nd in the "2018 Top 100
Accounting Firms by Business Revenue" released by
the China Association of Certified Public
Accountants (CACPA) and obtained 91 clients by the
end of 2018 (Luo, 2020). However, such a famous
CPA firm fails to detect the abnormal transactions in
Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s 2016-2018 annual report,
thus consequently being blamed by CSRC for the
other party responsible for Kangmei’s financial fraud.
Therefore, the following sections will analyze the
details of Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s fraud from both
IA and governance perspectives and follow the fraud
risk factors to determine the ultimate cause and the
aftermath of this incident.
3.2 Assessment of the IA Quality
First, since Zhengzhong Pearl River failed to detect
the falsified financial statement prepared by Kangmei
Pharmaceutical, the primary focus is on Kangmei’s
internal audit department to determine whether they
adequately oversee the board and monitor the external
audit. When examining the company’s board
structure and the audit committee, the first concerning
factor is the threat of independence. The three audit
committee members, Luo Jiaqian, Ma Huanzhou, and
Wen Shaoqian, all have management positions within
the company, which means they are not independent
executives, causing the audit committee to lose its
independence completely (Zhang, 2023).
Additionally, two of these executives are of senior
age (Zhang, 2023), making people question their
competence to adequately monitor the company’s
accounting department and provide sufficient
supervision to the IA. On the other hand, Zhengzhong
Pearl River has been Kangmei’s audit partner for 17
years, making the external auditors also face the
familiarity risk, in which auditors become too
familiar with the client’s transactions to detect any
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
146

material misstatements. The reason why Kangmei
Pharmaceutical was reluctant to switch partners may
be due to the consideration of lowering the audit fee
because auditors are risk-oriented; when companies
experience increasing risks, such as rapid growth,
organizational instability, and financial complexity,
the audit cost will increase due to the extra work
performed by the auditors (Bentley, Omer, & Sharp,
2013). Based on the information above, Kangmei
Pharmaceutical has the above characteristics since it
grew rapidly as of 2018, and in that single year, it also
had complex transactions such as consolidations.
Hence, the management had incentives to reduce the
audit cost for not switching audit partners for a long
time, even though the accounting industry
recommends that firms regularly switch audit
partners every five to ten years to avoid familiarity
risk. Since Zhengzhong Pearl River has been
Kangmei’s audit partners for almost twice the
recommended time frame, their audit failure is
foreseeable. Therefore, the external audit failure is
another vital evidence that the IA quality of Kangmei
Pharmaceutical is seriously inadequate, as the audit
committee should have monitored and prevented such
events by notifying the board beforehand.
3.3 Assessment of the Corporate
Governance and Internal Control
Subsequently, susceptors also point out that the
controller of Kangmei Pharmaceutical deliberately
selected those who were too old to maintain sufficient
supervision and empowerment to be the audit
committee members to undercut its function when
committing fraud, leading to questions about
Kangmei’s corporate governance and control. In
1999, The Blue Ribbon Commission (BRC) listed
various factors from the board’s characteristics that
could affect the audit committee’s effectiveness, such
as composition, independence, knowledge and
expertise, effectiveness, power, duties and
responsibilities, and the association between board
characteristics and earnings manipulation and fraud
(Cohen, Krishnamoorthy, & Wright, 2004). By
closely investigating Kangmei’s board structures,
there is a high functional overlap between the
controllers and the top management. The board
chairman, Ma Xingtian, also worked as the
company's CEO, with his wife, Xu Dongjin, the top
manager, meaning they monitored their own work.
Compared to the Ma couple, none of the other
shareholders own more than 5% of the company
shares, which means Ma has dominant control over
the decision-making and financial forecasting of the
entire company, and other executives cannot
counteract his irrational movements (Li, 2024).
Furthermore, the ownership structure has created
conditions for the Ma couple, as major shareholders,
to fully control the board decisions. Since they have
authority over the appointment, removal, and
compensation of members of the supervisory board
and audit committee through the shareholders’
meeting, the audit committee virtually have no
supervisory to effectively constrain the Ma couple as
they were not independent directors (Liang, 2021),
which led to serious internal control deficiencies and
a lack of corporate governance within the company.
Another indication is that the three audit committee
members held positions in Kangmei Pharmaceutical,
which significantly deteriorated the independence, a
crucial factor in the audit committee’s ability to
confront management and effectively collaborate
with external auditors (Cohen et al., 2004),
consequently minimizing control effectiveness.
3.4 Assessment of the Fraud Risk
Eventually, from the theoretical framework, these
control weaknesses provide board incentives and
opportunities for the Ma couple to manipulate the
company’s earnings and falsify the financial
statements over many years.
Applying the fraud triangle theory, the external
incentives mainly came from the financial pressure
since the company was rapidly growing. By the end
of the second quarter of 2018, Kangmei
Pharmaceutical had tripled its total assets compared
to five years ago through investment. As of December
31, 2018, the company had borrowed nearly 29.1
billion Chinese yuan (CNY), and the top ten
shareholders of Kangmei almost pledged all their
shares (Wang, 2021). As a result, pressures to obtain
more funds for its operating activities and debt
covenant is the Ma couple’s primary incentive for
financial fraud. On the other hand, the opportunity
factors are also displayed internally. According to the
previous analysis, a malfunctioned internal audit team
lacking effective corporate governance and control
opens the gate to misrepresentations in financial
statements since neither the internal supervision nor
the external audit detection was very effective in this
case. Finally, the Ma couple also had a fluke mind in
that they justified their misconduct to external factors
like the company’s rapid growth rather than their
incentives, while the executives from the audit
committee also had similar accuse as the extreme
ownership and equity structures did not provide them
enough motivation to perform their duties (Wang,
2021). Ultimately, all three factors contribute to a
series of Kangmei’s financial fraud.
Likewise, under the GONE theory, the Ma
couple’s excuses could be easily punctured since the
company's rapid growth is not a natural movement.
Internal Audit Effectiveness on Corporate Governance and Financial Fraudulent Risk: Evidence from Kangmei Pharmaceutical
147

Instead, as the controller, they made rapid expansion
and aggressive financial movements to satisfy greed
in their mind. Meanwhile, market opportunity factors
also played a role since managers have incentives to
misstate earnings to maintain a higher stock price
(Dechow, Ge, Larson, & Sloan, 2011), exactly what
the Ma couple did when engaging in fraud. In
addition, the pressure factors also explain the need for
them to conduct fraudulent activities because of their
urgent request for funds to fulfill the company’s cash
flow gaps. Lastly, internal opportunities, such as
insufficient supervision and regulatory enforcement,
increase the overall exposure to fraud risk from an
unsound system (Li, 2024).
4 REVELATIONS OF
KANGMEI’S FRAUD SCANDAL
In Kangmei’s financial fraud case, the Chief
Financial Officer (CFO), independent executives, and
the audit partners each committed dereliction of duty,
together proving that the entire enterprise mechanism
between all three was a total system failure. However,
this case also provides valuable lessons to the Chinese
and global enterprises market, especially high-risk
industries, to avoid the same mistake. Hence, several
recommendations and enforcement have been made
by the CSRC.
4.1 Improving the Corporate
Governance Structure
The primary reason for Kangmei’s fraud was that the
unbalanced ownership structure gave the Ma couple
too much authority as the board chairman. The
succession directors should allocate the equity
structure more reasonably and distribute the shares
evenly to all board members to avoid a single
shareholder dominating the entire board's decisions.
Moreover, the newly established board should ensure
that an odd number of directors are present on the
board, for instance, five executives before the fraud
incident. In that case, a majority vote should be
introduced to ensure the board decision is made in
favour of the majority shareholder groups so that their
decision.
4.2 Standardizing Financial Reporting
Procedures
During the CSRC’s investigation, there was a
sequence of financial misconduct in the CFO’s
representation and Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s
financial statement presentation, meaning that the
staff in its accounting department did not perform
their duties per IFRS requirements and under
accounting conceptual frameworks. Thus, the
company should also increase staff training to ensure
they have adequate financial expertise to follow the
required accounting procedures when preparing
financial statements. Ethical training should also be
introduced on a staff working basis to increase the
moral status of financial employees and reduce the
likelihood of fraud. At the same time, extra attention
should be paid to external auditors’ independence and
competence to avoid the case of Zhengzhong Pearl
River’s corruption with Kangmei’s top management
and violating the professional code of conduct as a
CPA.
4.3 Enhancing the Audit Committee’s
Functions to Improve IA Quality
While notable action was taken to improve the
external auditor’s expertise, the IA department should
be emphasized more when reconstructing the
corporate environment. Without internal audits’
unique efforts and expertise in companies’
organizational operations, the organization would
experience significantly more disclosures of material
weaknesses and revelations of financial
noncompliance (Holt & DeZoort, 2009), which
heavily reduces the effectiveness and efficiency of
external auditors. The U.S. Security Exchange
Commission (SEC) officials have repeatedly
emphasized the importance of the internal audit
function to the success of a company’s fraud
prevention and financial statement fair representation
(Holt & DeZoort, 2009). Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s
newly elected board should take subsequent actions
to reconstruct the audit committee by ensuring that at
least three members of the board’s independent
directors regularly perform their duties with at least
one obtained financial expertise.
4.4 Establishing a Comprehensive
System for Corporate Mechanisms
Cross-Monitoring One Another
Accordingly, the ultimate cause of Kangmei
Pharmaceutical’s fraud was a chain of reactions of
complex system failure when all three components
regarding the corporate governance, IA, and external
auditors simultaneously failed in the corporate
mechanism as a whole. The company should redesign
its corporate mechanisms to let all three pieces
function independently from each other but
collaborate well through cross-checking. Besides,
external effort should also help reduce the chances of
fraud and prompt companies to establish a more
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
148

functional and transparent corporate mechanism. Law
enforcement departments, such as the CSRC, should
tighten relevant regulations to eliminate any
loopholes for potential fraud and better direct
enforcement.
5 CONCLUSION
This article uses Kangmei Pharmaceutical’s financial
fraud as an illustrative example to conduct a detailed
analysis of its IA quality and corporate governance
and apply the fraud theories to determine how these
factors contribute to Kangmei’s significant financial
fraud. Based on extensive research and analysis, the
IA quality will positively influence the company’s
internal control and corporate governance since an
effective audit committee will monitor the company's
financial activities, enabling the management to act in
the shareholder’s interests. The audit committee can
also collaborate with the external auditors, as the
internal control is strong, and the external auditors
will perform less audit work. They can focus more on
the risky account to improve both the effectiveness
and efficiency of the overall audit work. At the same
time, since the audit committee members are
independent board executives, they also provide the
board oversight and help prevent financial fraud
internally by monitoring the external auditors’ work
and potential fraudulent behaviors conducted by top
management. Regarding the case study, Kangmei
Pharmaceutical demonstrated the exact opposite side
by showing its chaotic corporate governance, making
single shareholders dominate the entire board,
significantly weakening the effectiveness of IA
quality. Without the independent audit committee
member providing sufficient supervision, the top
management also corrupts its audit partner and leads
to serious misrepresentation in financial reporting and
subsequent audit failure, making all three parties
liable for committing fraud.
The revelation from Kangmei Pharmaceutical
also provides the industry with valuable insights to
help reduce the likelihood of financial fraud from
multiple perspectives. The internal approach should
focus on enhancing the staff qualifications (the CPA
competence and independence) and the function of
the IA Committee to improve internal control, which
helps eliminate the opportunity factors for
committing fraud. The board should also reinforce the
ethical code of conduct and corporate by-laws to its
management and employees. By improving their
moral status, the corporate environment is eventually
healthier. External enforcement should tighten the
regulations for industries obtaining a higher inherent
risk of fraud, for instance, introducing harsh
punishments and joint liabilities for all parties
engaging in fraud activities or negligent duties, as the
CRSC did for consequences made by Kangmei
Pharmaceutical’s directors and the in-charge external
auditors to reduce the top management’s incentives
for fraud.
Finally, this case study contains limitations in that
it is a single example from the Chinese capital market.
As the healthcare industry naturally involves a higher
inherent risk for financial fraud, the results generated
by Kangmei Pharmaceutical may not be fully
representative and generalized to all companies and
industries. In future research, more data should be
obtained from multinational-based firms to help
compare the fraud trend across countries. Equally
important, more case analyses through different
companies should be conducted cross-industries
when comparing the IA quality and corporate
governance to validate the study result.
REFERENCES
Abbott, L. J., Daugherty, B., Parker, S., & Peters, G. F.
2016. Internal audit and financial reporting quality: The
joint importance of independence and
competence. Journal of Accounting Research 54(1): 3-
40.
Beasley, M. S., Carcello, J. V., Hermanson, D. R., &
Lapides, P. D. 2000. Fraudulent financial reporting:
Consideration of industry traits and corporate
governance mechanisms. Accounting Horizons 14(4):
441-454.
Bentley, K. A., Omer, T. C., & Sharp, N. Y. 2013. Business
strategy, financial reporting irregularities, and audit
effort. Contemporary Accounting Research 30(2): 780-
817.
Cohen, J. R., Krishnamoorthy, G., & Wright, A. 2004. The
corporate governance mosaic and financial reporting
quality. Journal of Accounting Literature 87-152.
Dechow, P. M., Ge, W., Larson, C. R., & Sloan, R. G. 2011.
Predicting material accounting
misstatements. Contemporary Accounting
Research 28(1): 17-82.
Ferrari, A., Cunha, P. R. D., & Boff, M. 2023. Management
style in internal audit: influence between personal
factors and role conflict. Revista Contabilidade &
Finanças 34(92): e1710.
Hogan, C. E., Rezaee, Z., Riley Jr, R. A., & Velury, U. K.
(2008). Financial statement fraud: Insights from the
academic literature. Auditing: A Journal of Practice &
Theory, 27(2), 231-252.
Holt, T. P., & DeZoort, T. 2009. The effects of internal
audit report disclosure on investor confidence and
investment decisions. International Journal of
Auditing 13(1): 61-77.
Internal Audit Effectiveness on Corporate Governance and Financial Fraudulent Risk: Evidence from Kangmei Pharmaceutical
149

Krishnan, J. 2005. Audit committee quality and internal
control: An empirical analysis. The Accounting
Review 80(2): 649-675.
Li, S. 2024. A study on financial fraud at Kangmei
Pharmaceutical based on the GONE theory. Advances
in Economics, Management and Political Sciences 70:
231-240.
Liang, C. 2021. Analysis of financial fraud in Kangmei
Pharmaceutical: based on the perspective of internal
control. Marketing of Time-Honored Brands (10):83-
84.
Luo, L. 2020. Research on the identification and prevention
of financial fraud in Kangmei Pharmaceutical
Company. Zhongnan University of Economics and
Law.
Pasko, O., Zhang, L., Proskurina, N., Ryzhikova, N., &
Mykhailova, Y. (2024). Does internal audit matter?
Audit committee, its attributes, and corporate social
responsibility reporting quality. Investment
Management & Financial Innovations 21(2): 70.
Wang, H. 2021. Research on financial fraud of Kangmei
Pharmaceutical based on the fraud triangle theory.
China Storage and Transportation (12): 102-103.
Ye, X., Bai, X., & Xue, Y. 2022. Financial directors,
independent directors, and certified public accountants
improve the quality of financial reports: thoughts on the
financial fraud incident of Kangmei Pharmaceutical.
Finance Research (06): 14-23.
Zhang, R. 2023. Research on the corporate governance
system of Kangmei Pharmaceutical. Accounting for
Township Enterprises in China (03): 135-137
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
150
