
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on
Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement
Ruotong Zhao
Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Complementary Skills, Human Resource Management.
Abstract: This study focuses on the dual impact of the use of AI tools in the workplace on employees' skills and emotions.
It explores the degradation of skills and emotional connection caused by over-reliance on AI tools while
enhancing employees' work efficiency. Through the literature research method, we constructed a model of
Skill Complementarity - Emotional Connection to explore the dual impact of the use of AI tools on employees
and the dynamic feedback mechanism. It is found that although AI tools can improve the processing efficiency
of complex tasks, excessive use of AI tools can weaken employees' autonomy and lead to negative impacts.
Therefore, companies should provide differentiated training according to different employee groups, establish
a dynamic assessment mechanism to adjust the degree of intervention of AI tools, and improve employees'
acceptance of AI tools through training to avoid the potential risks associated with their over-reliance on AI
tools.
1 INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence has become a necessary tool to
help human beings improve productivity in modern
society, and with the emergence of various types of
AI tools, some of the employees have begun to worry
about whether AI will lead to unemployment of
human beings. As a matter of fact, human resources
are still the most important resource in enterprises in
today's society, but in the context of increased
competition in contemporary society, human beings
must follow the trend of the times and dare to adopt
more flexible and innovative productivity tools, and
combine and apply AI tools with human resources, in
order to promote the iteration of technology and
advance social progress and development.
Although there are already colleges and
universities combining AI with other majors to derive
composite majors, the existing AI applications are
still in the primary stage, and some studies have
concluded that AI is accompanied by a series of
negative psychological problems while bringing
about an increase in the ability of employees (Shi &
Liu, 2025). Therefore, management needs to pay
attention to the impact of timely AI tools on
employees in terms of emotional connection, and HR
should help employees use AI tools reasonably. At
the same time as the use of AI for employees to bring
more convenient and efficient help to reduce
cognitive load to improve the quality of life and work
efficiency at the same time, employees on the AI tools
to produce a sense of dependence on the employee's
future development will also cause a series of impacts
(Zhang & Shen, 2024).
The public generally believes that AI can enhance
human skills, but dependence on AI tools may lead to
skill degradation. To maximize the positive impact of
AI tools in an organization, they should be used
strategically to complement human abilities, with
clear guidelines and training provided to employees
on how to leverage AI effectively while maintaining
and developing their own core competencies. In the
era of AI, exploring these questions cannot only help
corporate managers or human resources practitioners
to improve their human resources management,
training and development capabilities, but also allow
employees to re-examine this special relationship,
adjust unreasonable usage, and avoid emotional ties
that may lead to unhealthy development. This study
is based on an extensive review of domestic and
international literature on AI tools.
130
Zhao, R.
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement.
DOI: 10.5220/0013987200004916
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication (PRMC 2025), pages 130-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-778-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Current Status
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence
technology, AI tools are increasingly applied in the
workplace. Their use in organizations evolves
through three stages: technology embedding, process
reconstruction, and value creation. AI is transforming
employees' work methods and workflows, from
human resource management to daily office tasks.
For example, the application of AI technology in the
recruitment process has become very common,
through natural language processing and machine
learning, AI can quickly screen resumes, identify
potential candidates, and conduct preliminary
interviews, thus significantly improving recruitment
efficiency (Hmoud & Laszlo, 2019). At the strategic
level it is even able to construct employee
competency growth curves through deep learning-
driven predictive analytics systems, increasing the
accuracy of talent retention decisions by 28.6%.
Meanwhile for other industry sectors it is worth
noting that the application of AI tools shows
significant industry heterogeneity: the financial
industry focuses on risk prediction models, while the
manufacturing industry focuses on IoT-driven device
co-optimization. Meanwhile, AI tools are not limited
to recruitment but also play an important role in
training and employee development. With
personalized training modules and real-time
feedback, AI can help employees improve their skills
and adapt to changing work environments. AI is also
increasingly used in performance management today,
where through data analysis and predictive
modelling, AI can provide more accurate
performance appraisals and help employees improve
their performance.
However, existing research still has some
limitations. Based on research related to various
aspects of business, some studies can tend to be
technologically deterministic, with Tiwari noting that
78% of the literature overestimates the technological
efficacy of AI tools and ignores the rigid constraints
of organizational practices. For example, small and
medium-sized manufacturing enterprises have a
23.7% misjudgment rate of AI quality control
systems due to the lack of standardized processes
(Tiwari et al., 2021). At the same time, existing
evaluations mostly use unidimensional efficiency
indicators (e.g., man-hour compression rate),
ignoring hidden values such as knowledge spillover
effects.
Meanwhile, the update of AI tools also has some
impact on the research results, Zhang, J. found that
the performance leap of ChatGPT from version 3.5 to
4.0 led to the extension of the average adaptation
cycle of employees to 4.2 months, which incurred a
significant skill replacement cost. Nowadays, when
AI updates are very fast and iterative, the impact of
model updates on various aspects cannot be ignored.
2.2 AI Tools
It has been shown that AI tools have significant
effects in enhancing employee skills. For example, by
using AI-driven training platforms, employees can
learn new skills more efficiently, reduce learning
time, and improve learning outcomes (Singh &
Shaurya, 2021). AI tools can also help employees
better master complex tasks by simulating real-life
work scenarios and providing practice opportunities
(Qamar et al., 2021).
However, the use of AI tools also brings some
negative psychological problems. For example,
employees may feel less autonomous and have
concerns about skill degradation due to over-reliance
on AI tools. In addition, the use of AI tools may
trigger anxiety and stress in employees, especially if
the feedback from AI tools is not clear or fair enough.
Empirical studies show that AI-assisted software
engineers have significant improvements in code
quality and development efficiency, but there is an
obvious ability compensation gradient effect: the
benefit rate of junior employees is significantly
higher than that of senior employees, which reflects
the barriers to the absorption of new technologies in
the existing knowledge system.
2.3 Impact of AI Tools
The use of AI tools in the workplace not only affects
employees' skill improvement but also has a profound
impact on their emotional connection. Research has
shown that employees' emotional connection to AI
tools may affect their job satisfaction and work
engagement. For example, when employees feel that
AI tools provide support and assistance, they are more
likely to have a positive affective connection to the
AI tool, which leads to increased job satisfaction
(Tang et al., 2022). Emotional connection research
presents a dialectical relationship of technological
empowerment-psychological depletion. In the
positive dimension, AI tools enhance the stickiness of
using them through emotional design (e.g.,
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement
131

anthropomorphic interaction interface), and increase
the job satisfaction of telecommuting employees.
Particularly in high-pressure work scenarios,
intelligent stress management systems have led to a
significant increase in team cohesion index through
real-time emotion recognition and intervention
(Qamar et al., 2021).
However, the implicit expansion of algorithmic
power is triggering a systemic crisis in the
organizational emotional ecosystem: nearly half of
employee’s report that AI performance monitoring
has led them to experience the Panopticon Effect.
Algorithmic bias may even trigger a crisis of
perceived fairness - one multinational company's AI
recruitment system reduced female hiring by 12.4%
due to gender discrimination, leading to a 19.3% drop
in employee commitment (Vrontis et al., 2022). In
addition, employees' dependence on and excessive
trust in AI tools can also have an impact on their
subsequent career development.
All in all, over-reliance on AI tools may lead to
excessive emotional connection of employees,
affecting their autonomy and creativity. When AI
tools play an overly important role in decision-
making, employees may rely less on their own
judgement, leading to reduced decision-making
ability. In addition, incorrect or unfair feedback from
AI tools may trigger negative emotions in employees,
reducing job satisfaction and work engagement.
2.4 Shortcomings of Current Research
Although existing studies have made some progress
in the area of AI tools on employees' skill
enhancement and emotional connection, there are still
some shortcomings. Firstly, most studies have
focused on the short-term impact of AI tools, while
fewer studies have examined the long-term impact.
Whether the long-term use of AI tools will lead to a
sustained improvement in employee skills or trigger
a more serious degradation of skills still requires
further research.
Second, existing studies have less research on the
impact of AI tools in different cultural and
organizational contexts. Different cultural and
organizational contexts may have a significant impact
on the acceptance and usage of AI tools, thus
affecting their skill enhancement and emotional
connection effects on employees. Managers need to
pay attention to the mental health and skill
development of their employees to ensure that the use
of AI tools truly promotes employee growth and
organizational development rather than leading
employees astray.
3 ANALYSIS
3.1 The Implementations
Compared with the systematic literature review that
relies on a predefined framework of questions, this
method chooses a more open research paradigm that
avoids the limitations of quantitative tools and meets
the needs of exploratory theoretical research.
3.1.1 Literature Search and Screening
Taking EBSCO, Web of Science, CNKI and other
databases as the core, using keywords such as AI tool
use, employee skills, emotional connection and other
keyword combinations in Chinese and English, we
screened journal articles, monographs and industry
reports published in the fields of management and
psychology during 2018-2024, focusing on the
inclusion of SSCI/CSSCI source literature.
3.1.2 Theoretical Framework Construction
In terms of theoretical framework construction, this
study is based on the MRD structure, which is
methodology, results and discussion, which
integrates two major theoretical axes. The first is the
theory of skill complementarity, which draws on the
three-quadrant model of human-computer ability
complementarity proposed by Man Tang et al. to
deeply analyze the skill compensation mechanism
achieved by AI tools through task offloading,
decision-making enhancement and cognitive
expansion. The second is the emotional connection
theory, which combines the cognitive dependency of
AI proposed by Zhang and Shen to reveal the
dynamic evolution path of emotional response.
Through the theoretical coupling, we construct the
Skill Complementation and Emotional Connection
analysis matrix, forming a multi-dimensional
explanation framework, which provides a solid
theoretical foundation for the in-depth analysis of the
impact of AI tools on employees' skills and emotions.
3.1.3 Critical Analysis
Contradiction analysis is used to deconstruct
opposing views in literature. For example, in terms of
the paradox of efficiency gain and alienation, Qamar
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
132

et al. confirm the efficiency gain of AI in recruitment,
while Shi and Liu reveal that over-reliance on AI
leads to an increase in the incidence of ethical excuses,
in terms of the gradient effect of skill compensation,
Man Tang et al. find that the rate of skill enhancement
for junior employees is significantly higher than that
for senior employees, which is attributed to the
difference between knowledge inertia and technology
absorption, in terms of the two-way regulation of
affective connection's bidirectional moderation, some
scholars noted that employees in collectivist cultures
are more tolerant of AI monitoring, but did not
quantify the moderating effect of the power distance
index (PDI). These comparisons reveal the core
research blind spot: the absence of an interaction
mechanism between skill compensation and affective
alienation.
3.2 Theoretical Research
Existing studies do not have a combined analysis of
skill complementarity and affective connection
aspects generated using AI tools on employees.
Current research mostly explores the single impact of
AI tools on employees' skills or emotions in isolation,
failing to reveal the dynamic interaction mechanism
between the two. Skill complementarity theory
emphasizes that AI improves efficiency through task
division but ignores the inhibitory effect of the
emotional connection between employees and AI
tools on employee skill transformation. For example,
although AI-assisted programming improves code
output, the black-boxing of algorithms may weaken
developers' understanding of technical principles,
leading to the skill compensation illusion.
Meanwhile, the effective connection theory focuses
on anxiety but fails to explain how affective
fluctuations can be counteracted in skill acquisition.
It is worth considering how to utilize the relationship
between affective connection and complementary
skills to train and assist employees. The potential
cause is a lack of interdisciplinary dialogue due to
disciplinary barriers leading to theoretical
fragmentation, with management favoring efficiency
analysis and psychology focusing on emotional
mechanisms.
The limitations of the current research
methodology are mainly due to insufficient empirical
evidence for longitudinal tracking and cross-cultural
comparisons. Current research relies on cross-
sectional data and lacks tracking of the long-term
impact of AI tools. Qamar et al. validated the
immediate effects of AI training but did not assess
whether employees' ability to iterate their skills
would decline after 3 years because of AI
dependency. Cross-cultural comparative studies are
similarly scarce, with employees in collectivist
cultures more likely to embrace AI tools but failing to
quantify the moderating effect of different cultural
dimensions on technology adoption thresholds.
Initial speculation was that longitudinal studies
were costly and time-consuming due to academics'
preference for short-term results. Cross-country data
access was limited by corporate confidentiality
agreements and cultural sensitivities, leading to
homogenized samples (more than 80% of the market
is between Europe, the US and China) (Vrontis et al.,
2022). Methodologically, existing scales (e.g., the
Technology Anxiety Scale) have not been adapted to
the characteristics of different AI tools and their
validity is questionable.
3.3 Practical Disconnect
There is a synergistic imbalance between the help of
AI tools to organizations and the presence of ethical
constraints on employees. There is a general tendency
to emphasize technology over management in
enterprise practice, and many enterprises do not carry
out human-computer collaboration training after
introducing AI tools, resulting in employees' anxiety
due to the skills gap. This shows that when enterprises
invest in technology, they often neglect supporting
management measures, such as training and skills
upgrading programs, thus affecting the ability of
employees to adapt to new technologies.
In terms of ethical governance, the correction of
algorithmic bias also remains at the technological
level, lacking a synergistic framework of technology-
institution-culture. Shi and Liu's study found that the
incidence of employees' moral excuses was 37%
higher in enterprises that did not have an ethical
review mechanism in place (Shi & Liu, 2025). This
highlights the fact that it is not enough for enterprises
to rely only on technological means to correct
algorithmic bias in the process of technology
application and that they also need to build a
comprehensive ethical governance framework at the
institutional and cultural levels to reduce the ethical
risks in the application of technology.
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement
133

4 RESULTS
By integrating the existing literature, this study found
that the application of AI tools in the workplace
presents a complex bidirectional dynamic
relationship between employees' skills and emotions.
In terms of skill complementarity, AI tools
significantly improve employees' efficiency in
handling complex tasks through task decomposition
and cognitive support. Junior employees can quickly
master standardized operations assisted by the tools,
but long-term over-reliance may lead to the gradual
degradation of core skills. For example, when the
degree of AI intervention exceeds a certain threshold,
the ability of employees to solve problems on their
own may be implicitly weakened, forming a tool
substitution trap - behind the surface of the efficiency
improvement, it is the loss of innovative thinking and
depth of technical understanding.
At the level of emotional connection, the
interaction design of AI tools directly affects the
psychological state of employees. Transparent and
explainable feedback mechanisms (e.g., clear
progress reminders and decision-making basis) can
enhance employees' trust in the tool, thus establishing
positive emotional dependence. On the contrary,
black-boxing or excessive monitoring of algorithms
can easily trigger anxiety and alienation and even
trigger resistance to technological control. It is worth
noting that employees with different skill levels
respond differently to affective stimuli: high-skilled
employees are more concerned about the limitations
of AI tools on professional autonomy, while low-
skilled employees may be caught in a cycle of passive
adaptation due to increased tool dependency.
Analyzed in conjunction with the model diagram
(Skill Complementarity-Emotional Connection
Model), it was found that the two do not act in
isolation but form dynamic feedback through self-
efficacy. When employees accumulate successful
experiences with the help of AI, their self-efficacy
will further stimulate their willingness to learn
actively, forming a positive cycle of skill
enhancement and confidence reinforcement. On the
other hand, if the use of tools weakens employees'
perceptions of their own abilities, it will lead to a
vicious interaction of increased anxiety and skill
stagnation. As shown in Figure 1, this mechanism
manifests itself differently in different organizational
environments: hierarchical organizations are more
receptive to AI monitoring, but employees become
emotionally drained faster, whereas in flat teams, the
flexibility of tool use may mitigate emotional
conflict, but there is a risk of homogenization of
skills.
5 DISCUSSION
After logically analyzing and extrapolating the
literature in related fields, this paper focuses on two
major academic sections, psychology and
management, and examines the use of AI tools in
today's hot topic of exploration, drawing relevant
conclusions about the ability to assist in human
resource management.
5.1 Main Findings
The core finding of this study reveals that the use of
AI tools in the workplace brings positive as well as
negative impacts to employees, which can be reduced
by managers through training: while enhancing
employees' skills, AI tools may trigger a complex
evolution of emotional connections. The main finding
suggests that AI tools significantly increase
employees’ efficiency in handling complex tasks
through a skill complementation mechanism, but this
efficiency gain comes with a potential risk - when AI
tools are used beyond a reasonable threshold,
employees’ reduced autonomy will lead to a
degradation of their skills and trigger negative
affective associations. This finding validates the
tension between perceived usefulness and perceived
risk in the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM).
This suggests that the realization of the value of AI
tools needs to be based on a dynamic equilibrium.
Secondly, due to inter-individual differences (the
acceptance of AI tools by highly ethically sensitive
employees was significantly lower than that of the
general group, which stemmed from their higher
demand for their own task completion and higher
sense of ethical standards 0. This result challenges the
assumption of established research that technology
acceptance is solely attributed to tool effectiveness,
and the author analyses the need for organizations to
establish a differentiated training system, such as
designing pre-training courses such as psychological
counselling for employees with high ethical senses
before conducting formal AI operation courses
(defining employees' adaptability to the use of AI
tools can be done by designing measurement
questionnaires to categorize the groups.
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
134
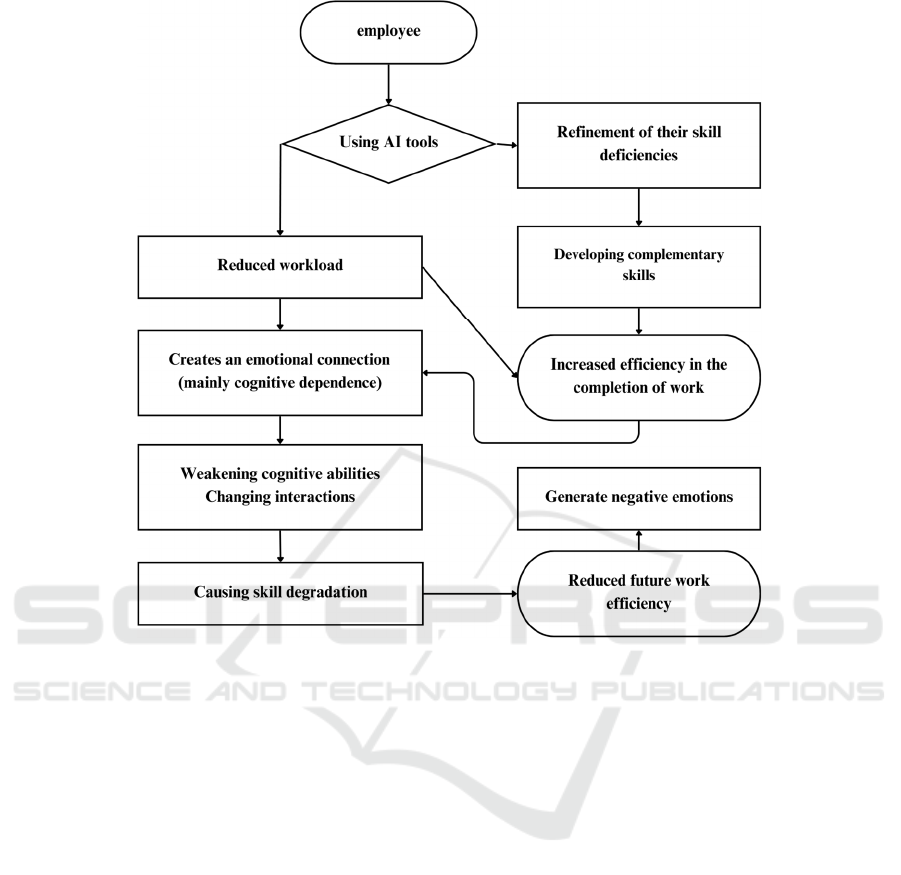
Alt Text for Figure: Steps towards achieving complementary skills and emotional connection of employees using
AI tools for employees in organizations.
Figure 1: Skills Complementarity-Emotional Connection Model Diagram.
5.2 Theoretical Breakthroughs
Existing research has long been fragmented by
disciplinary perspectives - management scholars
focus on technology effectiveness and productivity
improvement, while psychologists focus on mood
swings and mental health, resulting in a fragmented
explanation of the skill-emotion interaction
mechanism. The theory of skill complementarity
emphasizes that AI tools optimize efficiency through
task division, yet it does not reveal the inhibitory
effect of emotional depletion on skill transformation;
the study of affective connection portrays the path of
anxiety generation but overlooks the moderating
effect of skill level on affective response (Morandini
et al., 2023). This split essentially stems from
methodological differences: quantitative studies
prefer measurable efficiency indicators, while
qualitative studies are more concerned with in-depth
descriptions of subjective experiences.
By integrating complementarity theory and
affective connection theory, this study constructed the
Skills Complementarity Model, which realizes three
levels of theoretical innovation. Firstly, From the
perspective of dynamic interaction, the study reveals
that skill enhancement and emotional depletion are
not independent processes but form a feedback loop
through self-efficacy. Skill degradation can erode
employees' confidence in their own abilities, which in
turn increases technical anxiety, which in turn inhibits
the active acquisition of new skills. Secondly,
expanding on the ethical dimension to include the
impact of emotional connection on employees’
behaviors using AI tools in employee training and
development considerations, concluding that
classifying different employees before training will
increase employees’ acceptance of AI tool use and
reduce cognitive dependence and negative emotions
caused by inappropriate AI use. Lastly, constructing
an interdisciplinary explanatory framework that
combines the emotional connection between AI and
human beings studied in the field of psychology with
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement
135

the impact of AI tools on the skill aspects mastered
by employees studied in the field of management
from the perspective of the discipline of human
resources, to point out the direction for organizations
to train their employees related to the use of AI
(Azeem et al., 2024).
5.3 Theoretical and Practical
Extensions
The core value of this study is that it breaks through
the interpretative limitations of a single discipline and
provides an integrative analytical framework for
human-computer collaborative management in the
digital workplace. At the theoretical level, the
proposed model bridges the gap in existing literature
on the skill-emotion interaction mechanism and
provides a testable hypothesis system for subsequent
research. At the practical level, the findings of the
study provide a threefold message to business
managers (Krishnan et al., 2024). Organizations
should consider the boundaries of using AI tools in
work tasks, establish a dynamic evaluation
mechanism, and adjust the degree of AI intervention
according to the complexity of the task and the ability
level of the employee, to avoid the degradation of
skills caused by over-reliance on AI tools. The
enterprise needs to have an emotional support system,
incorporate AI ethics training into the regular
management system, enhance employees' awareness
of the limitations of the technology through
workshops, case studies and other forms, and reduce
the trust crisis caused by algorithmic errors
(Natarajan & Gombolay, 2020). Organizations can
differentiate their capacity building by designing a
technical-psychological dual-track training program
for highly ethically sensitive employees, which
enhances their critical examination of algorithmic
decision-making while improving their tool operating
skills.
5.4 Research Limitations and Future
Directions
Due to the limitations of secondary data and data
acquisition methods, this study was unable to track
the cumulative effects of long-term AI tool use on
employees' career development. For example, skill
degradation may exhibit progressive characteristics,
the tipping point of which is difficult to capture
through cross-sectional data. In addition, the samples
mainly come from technology-intensive industries
that have been well studied in literature, and the
interaction patterns between AI tools and employee
competencies in traditional industries (e.g.,
manufacturing, education) remain to be explored
(Yang & Yan, 2024).
Future research can be deepened in three
directions: first, adopting a mixed research
methodology to reveal the trajectory of skill evolution
through tracking experiments and in-depth interviews.
Second, conducting cross-cultural comparisons to test
the mitigating effect of organizational training on the
emergence of employees' technological anxiety
across different cultures, and third, focusing on the
impact of generative AI (e.g., big language models)
knowledge workers, especially the relationship
between technological dependency and creativity's
paradoxical relationship (Fang et al., 2024).
6 CONCLUSION
The widespread use of AI tools in the workplace
opens new paths for employee skill enhancement but
also brings potential risks of emotional detachment
and capability degradation. This study systematically
reveals the double-edged sword effect of AI tools:
while significantly improving efficiency through task
division and skill complementation, over-reliance
will weaken employee autonomy, triggering skill
degradation and negative emotional connection.
Especially in the highly ethically sensitive group,
concerns about the fairness of algorithms
significantly reduce the acceptance of the technology,
highlighting the critical impact of individual
differences on the effectiveness of AI applications.AI
tools can cause emotional bonding phenomena while
improving the skills of employees, suggesting that the
inappropriate use of AI tools can lead to skill
degradation and re-establishment of negative
affective bonding. Whereas the proper use of AI tools
can greatly improve efficiency, highly ethical
employees are less receptive to AI tools, so
companies that need to use AI as aid in the modern
era should provide different training for different
groups of employees. Research shows that the
efficiency of AI tools stems from their data
processing and automation advantages, but the
rapidity of technology iteration also forces employees
to adapt frequently, resulting in hidden skill reset
costs. In addition, the complexity of the emotional
connection is reflected in the co-existence of tool
dependence and psychological alienation - the lack of
algorithmic transparency exacerbates employee
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
136

mistrust, while the imbalance of technological
enablement may inhibit innovation. In conclusion,
managers should pay attention to employee
psychology, conduct regular sniffing or checking to
ensure that employees are using AI tools correctly,
and continually train employees in line with
organizational goals.
REFERENCES
Afzal, I, Shohan A H N, Siddiqui S, et al. 2023. Application
of AI on Human Resource Management: A Review[J].
Journal of HRM 26(1).
Azeem, M. M., Febriyanto, U., Nurhadi, F. A., & Halid, H.
2024. Unlocking the Values of Artificial Intelligence
(AI) in Human Resource Management (HRM) in
Enhancing Employee Retention. Global Business &
Management Research.
Hmoud, B., & Laszlo, V. 2019. Will artificial intelligence
take over human resources recruitment and selection.
Network Intelligence Studies 7(13), 21–30.
Krishnan, L. R. K., Praveen, K., & Poorani, S. 2024.
Artificial intelligence in human resource management:
Enhancing efficiency & transforming employee
experience.
Man Tang, P., Koopman, J., & McClean, S. 2022. When
conscientious employees meet intelligent machines: An
integrative approach inspired by complementarity
theory and role theory. Academy of Management
Journal 65(3), 1019–1054.
Morandini, S., Fraboni, F., De Angelis, M., Puzzo, G.,
Giusino, D., & Pietrantoni, L. 2023. The impact of
artificial intelligence on workers’ skills: Upskilling
and reskilling in organisations. Informing Science 26,
39-68.
Natarajan, M., & Gombolay, M. 2020. Effects of
anthropomorphism and accountability on trust in
human robot interaction. In Proceedings of the 2020
ACM/IEEE international conference on human-robot
interaction.
Qamar, Y., Agrawal, R.K., Samad, T.A., & Jabbour, C.J.C.
2021. When technology meets people: the interplay of
artificial intelligence and human resource management.
Journal of Enterprise Information Management 34(5):
1339–1370.
Shi, Q., & Liu, P. 2025. Team Intelligence Reliance, Moral
Disengagement and Time Theft Behavior. Journal of
Shanxi University of Finance and Economics 24(1):
45–52.
Singh, A., & Shaurya, A. 2021. Impact of Artificial
Intelligence on HR practices in the UAE. Humanities
and Social Sciences Communications 8(1): 1–9.
Tiwari, P., Pandey, R., Garg, V., & Singhal, A. 2021.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Human
Resource Management Practices. 2021 11th
International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data
Science & Engineering (Confluence), IEEE.
Vrontis, D., Christofi, M., Pereira, V., Tarba, S., Makrides,
A., & Trichina, E. 2022. Artificial intelligence,
robotics, advanced technologies and human resource
management: a systematic review. International Journal
of Human Resource Management 33(6): 1237–1266.
Yang, X., & Yan, S. 2024. Encourage or Reject Employee
Involvement: Value Creation in Human Resource
Management in the AI Era— An Evolutionary Game
Analysis of Enterprises and Employees. Behavioral
Sciences 14(12): 1220.
Yanyan Fang, Xiaoyun Xie & Junqi Shi. 2024. A new
species of the genus Pterostilbene (Coleoptera,
Staphylinidae, Staphylininae) from China. Research on
generative artificial intelligence and human resource
management: a workflow analysis perspective. Chinese
Science Foundation (05): 820-830.
Zhang, J., & Shen, Y. 2024. The Impact of AI Tools on
Employees' Skills and Emotions. Journal of
Management Sciences in China 31(2): 188–195.
Balancing Efficiency and Dependency: The Impact of AI Tools on Employee Skills and Emotional Engagement
137
