
Sino-US Electric Vehicle Policy Coordination and Cooperation Under
the Goal of Carbon Neutrality
Yujing Zhang
Zhangzhou Number3 Middle School, Zhangzhou, China
Keywords: Global Green Economy, Zero Emission, Reduce Trade Barriers, The Transformation of the Global Green
Economy, The Realization of Carbon Neutrality Goals.
Abstract: In the context of increasingly severe global climate change and environmental problems, the goal of carbon
neutrality has become the core policy orientation of various countries. With its significant advantage of "zero
emission", electric vehicles (EV, Electric Vehicle) have become an important tool to promote the
transformation of the green economy. As the two largest economies and major carbon emitters in the world,
China and the United States, the coordination and cooperation of their electric vehicle policies have important
leading and demonstration significance for realizing the global carbon neutrality goal. Based on the
background of global climate change, this article deeply discusses the current situation of electric vehicle
policies between China and the United States, analyzes the necessity and feasibility of policy coordination
between China and the United States, and proposes paths and policy suggestions to promote cooperation
between the two countries. Research results show that policy coordination between China and the United
States in the field of electric vehicles has accelerated the widespread promotion of green technologies around
the world, providing examples and references for the global response to climate change.
1 INTRODUCTION
Global climate change has caused major threats to the
human living environment and ecosystems. Rising
temperatures, rising sea levels, and frequent extreme
weather events have intensified the frequency and
severity of natural disasters. According to a report by
the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(IPCC), a subsidiary of the United Nations Panel on
Climate Change, if effective emission reduction
measures are not taken, the global average
temperature may rise by more than 2°C by 2100. It is
predicted that it will directly lead to serious damage
to the ecological balance, mass extinction of species,
and profound socioeconomic crisis (Qu, 2008). The
concept of carbon neutrality was proposed to deal
with climate problems caused by greenhouse gas
emissions. Carbon neutrality refers to achieving "net
zero emissions" of greenhouse gases by reducing
carbon emissions and increasing carbon sinks within
a certain period. In 2020, China made a commitment
to “peak carbon emissions in 2030 and achieve
carbon neutrality in 2060” (Wu, 2022). The United
States has committed to achieving carbon neutrality
by 2050. This goal promotes industrial
transformation in China and the United States and
provides a clear direction for the development of the
global green economy. Electric vehicles are
considered a key means to reduce carbon emissions
and achieve green travel. The emissions of traditional
internal combustion engine vehicles account for 20%-
30% of global greenhouse gas emissions, while
electric vehicles have become the preferred choice for
green travel due to their "zero emission"
characteristics. The popularization of electric
vehicles can also reduce air pollution, reduce energy
dependence, optimize the energy structure, and
promote the use of clean energy. As the world's
largest producers and consumers of electric vehicles,
policy coordination between China and the United
States will directly affect the stability of the global
electric vehicle industry chain and the development
direction of the market.
In summary, the coordination and cooperation
between China and the United States on electric
vehicle policies will help promote the research
development, and application of electric vehicle
technology, promote the construction of a global
green transportation system, and promote the
standardization and integrated development of the
18
Zhang, Y.
Sino-US Electric Vehicle Policy Coordination and Cooperation Under the Goal of Carbon Neutrality.
DOI: 10.5220/0013985200004916
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication (PRMC 2025), pages 18-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-778-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
global market. Sino-US cooperation will help
accelerate the market penetration of electric vehicles,
reduce greenhouse gas emissions, help achieve the
temperature control goals set out in the Paris
Agreement, and provide feasible cooperation
examples and paths to address climate change.
This article aims to analyze the current situation
of electric vehicle policies in China and the United
States, sort out the policy framework, incentive
measures, and market development status of China
and the United States in the field of electric vehicles,
and clarify the similarities and differences between
the two sides' policies and the entry point for
coordination. On this basis, this article discusses the
necessity and feasibility of policy coordination,
analyzes the key interests of China and the United
States in policy coordination, explores the possibility
and cooperation paths of policy docking between
China and the United States, and proposes policies for
cooperation between China and the United States in
the field of electric vehicles. suggestion.
2 ANALYSIS OF THE CURRENT
SITUATION OF ELECTRIC
VEHICLE POLICIES IN CHINA
AND THE UNITED STATES
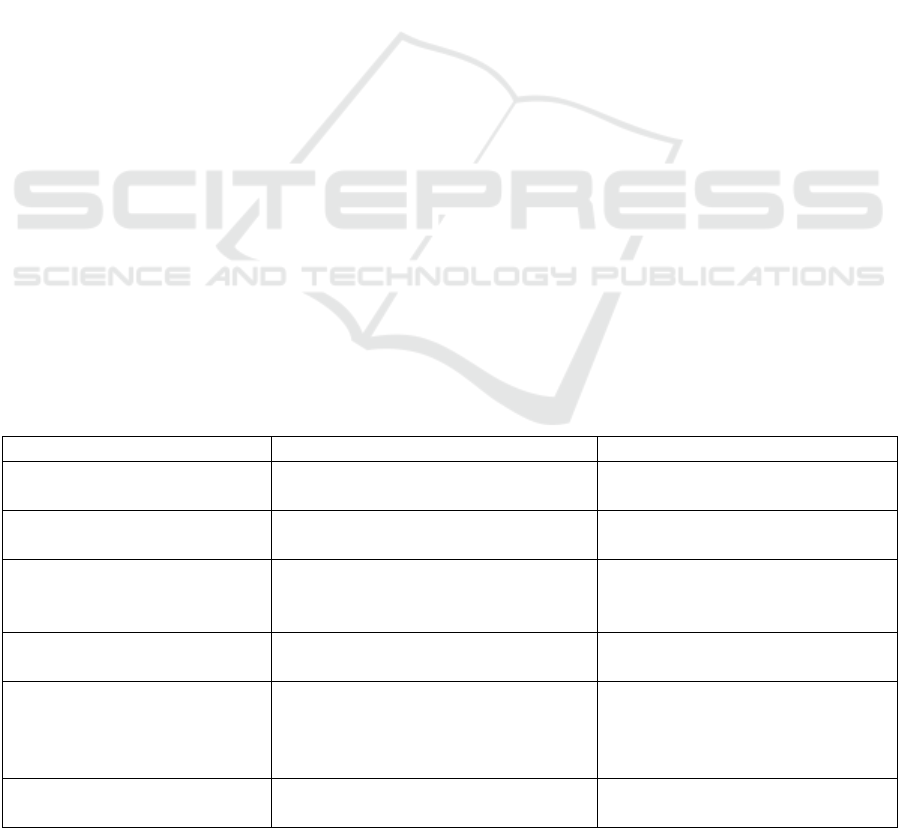
Table 1 compares the current status of electric vehicle
policies in China and the United States, covering six
key elements: policy objectives, incentives,
infrastructure construction, market supervision,
technical support, and representative companies.
Both countries attach great importance to the
development of electric vehicles, have formulated
clear policy goals and incentives, and at the same time
promote technological innovation. Among them, the
United States' target was achieved five years earlier
than China's, showing the United States' urgency to
accelerate the promotion of electric vehicles. Both
China and the United States have set "50%" as the
target ratio, showing that they attach equal
importance to the development of electric vehicles.
The focus of incentives between China and the United
States is different. China's incentives cover car
purchases and technology research and development,
while the United States focuses on direct economic
subsidies, with clear and highly targeted tax
incentives. China's construction direction is more
inclined to privatization and diversification (such as
power replacement), while the United States is biased
toward public facilities and power grid upgrades. In
terms of supervision, China directly intervenes in the
market through the "double points" policy to force
companies to meet the proportion of new energy
vehicles; the United States is relatively flexible and
indirectly encourages the development of electric
vehicles by improving fuel economy. In terms of
technical support, China focuses on improving the
performance of core components of electric vehicles;
the United States focuses on future trends, such as the
Internet of Vehicles and autonomous driving. Both
Chinese and American companies have world-
renowned brands in the field of electric vehicles.
Chinese companies focus more on battery production
and emerging brands, while the United States focuses
on the transformation of traditional automobile giants
and Tesla.
Table 1. Current status of electric vehicle policies in China and the United States
policy elements China USA
policy objectives
New energy vehicles will account
for 50% of new car sales in 2035
By 2030, electric vehicles will
account for 50% of new car sales
Incentives
Car purchase subsidies, purchase
taxes, R&D subsidies, etc
$7,500 car purchase tax
credit,infrastructure subsidies
infrastructure construction
Vigorously build public and
private point piles and promote the
power exchange model
Build 500,000 charging piles
and upgrade power grid facilities
market supervision
Implement a “double points”
policy for new energy vehicles
Improve fuel economy and
emissions standards
Technical support
Support the research and
development of batteries, battery
replacement and networking
technologies
Support innovation in
intelligent networking and
autonomous driving technologies
Representative enterprise BYD, Future, Xiaomi Auto, etc.
Tesla,Ford, General Motors,
etc.
Sino-US Electric Vehicle Policy Coordination and Cooperation Under the Goal of Carbon Neutrality
19

2.1 China’s Electric Vehicle Policy
Focusing on the national strategic goal of "carbon
peaking in 2030 and carbon neutrality in 2060",
China's electric vehicle policy focuses on promoting
the popularity and technological innovation of
electric vehicles through policy incentives, market
supervision, and technical support. The Chinese
government has adopted a variety of policy tools to
promote the development of the electric vehicle
market. First, China’s car purchase subsidy policy
played a key role in the early stages. Although
subsidies are gradually declining, tax exemptions and
operating subsidies are still important incentives for
the electric vehicle market. The reduction of purchase
tax has made the price advantage of electric vehicles
more prominent and increased consumers'
willingness to purchase. Secondly, China’s “double
points policy” has become an important means to
promote the transformation of automobile companies.
(Hu, 2024) According to this policy, car companies
must achieve a balance of points in the sales of new
energy vehicles and fuel vehicles, and companies that
do not meet the standards need to purchase the surplus
points of other companies to form a market-oriented
incentive mechanism. Finally, China strongly
supports the construction of electric vehicle
infrastructure, especially the construction of charging
piles and battery swap stations. In terms of
technological innovation, China's power battery
industry has demonstrated global competitive
advantages, with companies such as CATL and BYD
leading the world in market share in the field of power
batteries.
2.2 Electric Vehicle Policy in the
United States
The electric vehicle policy in the United States is
mainly oriented towards market incentives and
technological innovation, with the federal and state
governments jointly promoting the development of
the electric vehicle market. In 2022, the United States
passed the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), providing
comprehensive policy support for the production and
consumption of electric vehicles. First, on the
consumer side, the United States has implemented a
car purchase tax credit policy, and consumers can
enjoy tax credits of up to US$7,500 for purchasing
qualified electric vehicles. (Xiao, 2018) Secondly, the
US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act plans to
invest US$7.5 billion to build a network of 500,000
charging piles nationwide. Different from China's
"battery swap model", the United States mainly
improves the convenience of using electric vehicles
through the construction of fast charging networks. In
addition, zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) policies have
been actively promoted in California, New York, and
other states in the United States. These states have set
stricter electric vehicle sales targets for car companies
and mandated car companies to sell electric vehicles
within a certain period. The sales ratio of cars has
increased to a certain level. The United States also
leads the world in electric vehicle technological
innovation. Tesla, Ford, General Motors, and other
companies have technological advantages in
intelligent driving, autonomous driving, and Internet
of Vehicles technologies.
2.3 Comparison of Electric Vehicles
Between China and the United
States
There are some commonalities between China and the
United States in the formulation of electric vehicle
policies, but there are also significant differences in
policy objectives, market supervision methods,
incentives, and market environment. In terms of
policy goals, both China and the United States have
set clear goals for the popularization of electric
vehicles. China's goal is to achieve 50% of new car
sales with new energy vehicles (including electric
vehicles) by 2035 and to achieve full electrification.
The United States has proposed a goal of electric
vehicles accounting for 50% of new car sales by
2030. (Wei, 2022) In terms of market supervision,
China’s “dual-point policy” requires car companies to
sell a certain proportion of electric vehicle points, and
companies that do not meet the standards need to
purchase points. The "Zero Emission Vehicle Policy
(ZEV)" in the United States requires car companies to
achieve a certain proportion of electric vehicle sales
in specific states, otherwise, they will face high fines.
In terms of incentives, China's electric vehicle
purchase subsidies have gradually declined, but
purchase tax exemptions and corporate research and
development subsidies continue. The tax credit policy
in the United States is more direct. Consumers who
purchase compliant electric vehicles can receive tax
credits of up to $7,500 (Xiao, 2018). In addition, the
US subsidy policy focuses more on supporting the
local manufacturing of power batteries and the
localization of the industrial chain of electric vehicles
(Wang, 2022). In terms of market environment,
China's electric vehicle market is policy-led, the
market environment is driven by policies, and the
supportive policies of local governments have also
promoted the rapid development of the local market.
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
20

The market environment in the United States is more
market-oriented, and companies have a more
dominant position in the market.
3 PATHS FOR SINO-US
ELECTRIC VEHICLE POLICY
COORDINATION AND
COOPERATION
3.1 Current Status of Tariff Policy
The Sino-US trade friction has caused the import and
export of electric vehicles and related parts to face
high tariff barriers. In 2018, the United States
imposed high tariffs on electric vehicles and their
parts exported from China, and China also adopted
reciprocal tariff countermeasures on auto parts
imported from the United States. The increase in
these tariffs not only increases the cost of electric
vehicles but also inhibits the mutual circulation of the
Chinese and American electric vehicle markets,
affecting the stability of the global electric vehicle
supply chain. China and the United States each have
advantages in key technical fields of electric vehicles.
China is in a leading position in power batteries,
battery replacement technology, and intelligent
network connectivity. Companies such as CATL and
BYD have significant international competitiveness
in the field of power battery technology (Ou, 2016).
The United States has a leading position in
autonomous driving, the Internet of Vehicles, and
control software. Tesla and Google's Waymo have
achieved world-leading technological breakthroughs
in autonomous driving and intelligent driving
systems. However, technological cooperation
between China and the United States still faces issues
such as "technical barriers" and "data sovereignty",
especially when it comes to the transfer of key
technologies, and the policies of both parties are
inconsistent. The Sino-US trade friction has led to
rising tariffs on electric vehicles and their parts,
which has directly affected the stability of the supply
chain and the market access of companies. To reduce
barriers to the circulation of electric vehicle parts,
China and the United States can negotiate to reduce
tariffs on electric vehicles and their core components,
especially in key areas such as power batteries, chips,
and electronic control systems. By establishing the
"China-U.S. Electric Vehicle Tariff Coordination
Mechanism", the two sides can launch policy
dialogues on multilateral platforms (such as the G20
and APEC), reduce trade barriers, and ensure the
stability of the supply chain.
3.2 Technical Cooperation and
Research and Development
The complementary advantages between China and
the United States in key electric vehicle technologies
provide the possibility for technical cooperation
between the two parties. China has competitive
advantages in power batteries, intelligent
connectivity, and battery swapping technologies,
while the United States has outstanding performance
in the fields of autonomous driving and electric
vehicle software control (Fu, 2023). By establishing
the "China-US Electric Vehicle Technology
Cooperation Platform", the two parties can carry out
joint research and development in areas such as
power batteries, autonomous driving, and the Internet
of Vehicles, and promote the unification of technical
standards. In addition, the two parties can establish an
"electric vehicle big data sharing platform" to realize
the sharing of autonomous driving data and
algorithms, reduce research and development time,
and optimize the path of technological innovation.
Driven by the goal of carbon neutrality, technical
cooperation and R&D cooperation on electric
vehicles between China and the United States have
become an important direction for the coordinated
development of both parties (Wu, 2016). Technical
cooperation pays more attention to the "now" and
mainly solves the current bottlenecks in market
promotion. For example, China and the United States
can reduce barriers to technology adaptation by
unifying charging pile interfaces and battery
standards, thereby accelerating market penetration. In
addition, by integrating the existing technologies and
resources of both parties, companies can significantly
reduce development costs and achieve rapid
application of existing technologies. R&D
cooperation focuses on the “future” and aims to
promote technological breakthroughs and
innovations (Zhang, 2021). The two countries can
jointly solve technical problems in the industry and
seize the forefront of the global electric vehicle
market through cooperation in the research and
development of high-efficiency batteries, new energy
technologies and intelligent vehicle systems.
Technical cooperation focuses on efficiency and
short-term results, while R&D cooperation is based
on the long term and seeks technological
breakthroughs. The combination of the two will make
China and the United States more competitive in the
global electric vehicle field, while also making an
Sino-US Electric Vehicle Policy Coordination and Cooperation Under the Goal of Carbon Neutrality
21

important contribution to the realization of the carbon
neutrality goal. This dual-path collaboration not only
promotes the accelerated development of green
industries in both countries but also provides a
reference for global sustainable development.
3.3 Market Access and Mutual
Recognition of Standards
There are large differences in market access standards
for electric vehicles between China and the United
States, especially in terms of power battery
certification, battery replacement technology
standards, and vehicle safety testing standards. To
solve this problem, China and the United States can
negotiate and sign the "Mutual Recognition
Agreement on Electric Vehicle Market Access" to
achieve certification docking of electric vehicle
products and reduce market entry costs for
companies. In addition, China and the United States
can also unify the technical standards of charging
interfaces to ensure the compatibility of charging
networks for electric vehicles in the Chinese and
American markets and reduce the adaptation costs of
enterprises.
Coordinated path for market access; broad market
access for new energy vehicle industries in China and
the United States requires path adjustments from
three perspectives. First, in the bilateral agreement on
mutual market recognition, China and the United
States can negotiate and sign the "Mutual
Recognition Agreement on Electric Vehicle Markets"
to promote the simplification of the certification
process for electric vehicles and reduce the testing
process before products enter the market. Second, in
unifying electric vehicle certification and testing
standards, China and the United States should
establish unified certification and testing standards in
terms of charging pile interface standards, power
battery testing standards, and vehicle operating
system compatibility to reduce market barriers. At the
same time, it is also very important to strengthen
policy communication and dialogue mechanisms.
China and the United States should establish a
"China-US Electric Vehicle Market Dialogue Group"
in multilateral cooperation platforms such as the G20
and APEC to regularly coordinate electric vehicle
market access standards to ensure the docking and
integration of standards. consistency.
As shown in table 2, the policy coordination path
of China and the United States on electric vehicles is
specifically reflected in tariff adjustment, technical
cooperation, market access, and multilateral
cooperation. China and the United States can save a
lot of costs for enterprises by reducing tariffs on
electric vehicles and parts, especially those with high
dependence on production and exports. This measure
will directly improve the circulation efficiency of the
market and allow more electric vehicles to enter each
other's markets. By establishing a "zero tariff zone",
the two countries can also encourage more companies
to participate in cross-border trade and promote the
further integration of the electric vehicle-related
industrial chain. Such adjustments are not only
directly beneficial to enterprises but also help expand
the global market share of electric vehicles. At the
same time, China and the United States can jointly
establish a joint R&D center to concentrate on solving
technical problems in the field of electric vehicles.
Under this cooperation model, the two countries can
share key technical data and jointly explore core areas
such as battery performance optimization, charging
efficiency improvement, and vehicle networking
technology. This technical cooperation will further
promote the standardization of technology and make
Chinese and American companies more competitive
in the global market. Through resource integration,
the two sides can take advantage of each other's
strengths, accelerate technology iteration, and
contribute to the global upgrade of electric vehicle
technology. China and the United States can simplify
the certification process for enterprises to enter each
other's markets through market mutual recognition
agreements. Such measures can not only significantly
reduce the operating costs of enterprises, but also
shorten the time to market for products and help
technology land faster. The two countries can also
eliminate technical barriers caused by differences in
standards by coordinating testing standards. This
facilitation of market access will promote the deep
integration of the electric vehicle markets of China
and the United States, while also providing
consumers with more choices. China and the United
States can establish a special electric vehicle policy
dialogue mechanism on international platforms such
as the G20 and APEC. In international cooperation,
the cooperation between China and the United States
will not only help strengthen the leadership of the two
countries in the field of new energy, but also promote
the sustainable development of the electric vehicle
industry by formulating a global policy framework.
Through such multilateral cooperation, China and the
United States can further strengthen their voice and
influence in the international arena.
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
22
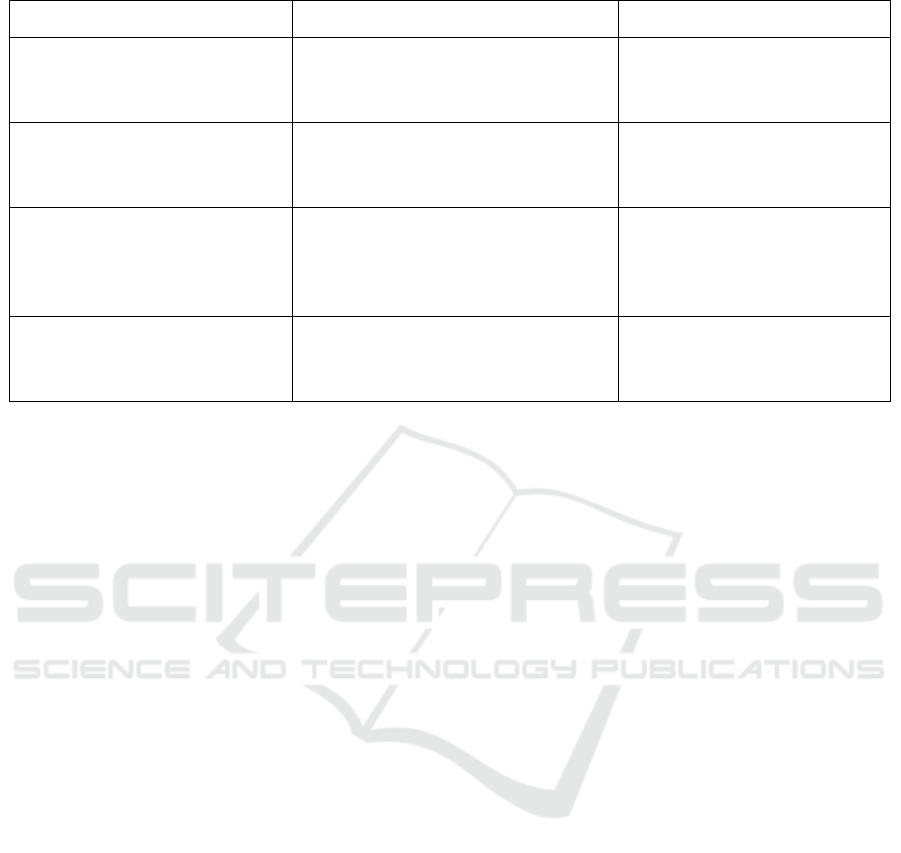
Table 2. Overall path of policy coordination
Path latitude and longitude Key measures Expected effects
Tariff adjustment
Reduce tariffs on electric vehicles
and parts, establish a "zero tariff
zone"
Reduce corporate costs and
expand market circulation
Technical cooperation
Establish a joint R&D center,
share data, and cooperate on technical
standards
Accelerate technological
progress and promote
technical standardization
Market access
Market mutual recognition
agreement, simplify market
certification processes, and
coordinate testing standards
Accelerate technological
progress and promote
technical standardization
Multilateral cooperation
Establish a China-US electric
vehicle policy dialogue mechanism in
the G20 and APEC platforms
Promote policy
coordination and
communication
4 CONCLUSION
The coordination and cooperation of China-US
electric vehicle policies is an important path to
promote the global green economic transformation
and the realization of carbon neutrality goals. China
and the United States should promote the alignment
of rules and standards in the electric vehicle market,
reduce market barriers, and reduce the operating costs
of enterprises through policy coordination, technical
cooperation, and standard docking. China and the
United States can also set up a "China-US Electric
Vehicle Policy Coordination Group" on multilateral
platforms such as the G20 and APEC to ensure policy
communication and dialogue between the two sides
on market access, technical cooperation, and tariff
policy adjustments. Specifically, China and the
United States should sign the "Electric Vehicle
Market Access Mutual Recognition Agreement" to
achieve the docking of market rules, ensure the
unification of power battery and charging standards,
and reduce market fragmentation. In addition, the two
sides should jointly promote the standardization and
normalization of the global electric vehicle industry
and promote the healthy development of the
international electric vehicle market. Through policy
coordination and cooperation between China and the
United States, the standardization and unification of
rules in the global electric vehicle market will make
substantial progress, and the transformation of the
global green economy and the realization of carbon
neutrality goals will be more promising.
REFERENCES
Fu, X.Y., Zhong, Z.Y., Xia, D., et al. 2023. Transformation
and development of the automobile industry under the
background of carbon neutrality. Sustainable
Development 13: 124.
Wan, G. 2016. Focus on innovation-driven and accelerate
transformation and development - Development trend
and prospect of new energy vehicles. Science and
Technology Review 34(6): 1-2.
Hu, W., Xia, B.L. 2024. Disruptive technology policy -
Construction and empirical analysis of technology
roadmap framework - Taking China's new energy
vehicle industry as an example. Science and Technology
Progress and Countermeasures 41(2): 25-34.
Wang, J.F., Su, L.Y., Tan, X.C., et al. 2022. Carbon
neutrality strategic orientation, policy measures and
enlightenment of major economies. Bulletin of the
Chinese Academy of Sciences 37(4): 479-489.
Wu, F. 2022. The status and role of nuclear energy in the
process of carbon neutrality. Nuclear Science and
Engineering 42(4): 737-743.
Wei, Y.F., Han, X.B., Lu, L.G., et al. 2022. Prospects of new
energy vehicles and vehicle-grid interaction
technologies for carbon neutrality. Automotive
Engineering 44(4): 449-464.
Ouyang, M.G. 2016. Research and development and
prospects of new energy vehicles in China. Science and
Technology Review 34(6): 13-20.
Qu, J.S., Zhang, Z.Q., Zeng, J.J. 2008. Analysis of the
international development trend of climate change
science.
Xiao, J. 2018. Research on China's new energy vehicle
policy. Southwest University of Finance and Economics
Press.
Sino-US Electric Vehicle Policy Coordination and Cooperation Under the Goal of Carbon Neutrality
23

Zhang, X., Li, K, Ma, Q. 2021. CCUS under the goal of
carbon neutrality Positioning and prospects of
technological development. Chinese Population,
Resources and Environment 31(9): 29-33.
PRMC 2025 - International Conference on Public Relations and Media Communication
24
