
InstaGuard: An AI‑Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent
Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Techniques
Palani Murugan S.
1
, Gobinath R.
1
, Rahapriya K.
1
, Fahumitha Afrose B.
2
,
Fathima Fazlina M.
2
and Durga Devi S.
2
1
Department of AI&DS, E.G.S.Pillay Engineering College (Autonomous), Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
2
E.G.S. Pillay Engineering College (Autonomous), Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Fraud Detection, Social Media Security, Instagram Fraud, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural
Language Processing (NLP), Fake Account Detection, Phishing Prevention, Misinformation Detection,
Cybersecurity, Real‑Time detection.
Abstract: The rapid growth of Instagram has raised major security concerns, including fake profiles, deceptive
promotions, phishing scams, impersonation, and misinformation. These threats mislead users, exploit
audiences, and increase cyber risks. To address these challenges, we propose InstaGuard, an AI-powered
fraud detection system for Instagram. InstaGuard employs advanced AI techniques to analyze user behavior
and content. Random Forest and XGBoost detect fake accounts based on profile attributes and engagement
trends. BERT-based NLP models classify misleading promotions and scams, while LSTM networks and URL
reputation verification identify phishing attempts. CNNs and Siamese Networks handle impersonation
detection, while RoBERTa-based transformers and graph-based content analysis mitigate misinformation. By
integrating Instagram’s Graph API for automated data collection, InstaGuard enables real-time fraud detection
and response. Simulations indicate up to 95% accuracy, reducing false positives by 30% compared to existing
methods. Its real-time capabilities ensure swift action against fraudulent activities, enhancing platform
security.This research contributes to AI-driven cybersecurity by introducing a scalable, adaptive fraud
detection framework tailored for Instagram. InstaGuard strengthens user safety by mitigating fraud and
misinformation, reinforcing platform integrity in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
1 INTRODUCTION
Current approaches to identifying fraudulent activity
face significant limitations. Conventional methods
such as manual content review, blocklist
implementations, and keyword filtering systems
demonstrate inadequate responsiveness to constantly
evolving deceptive practices. The inherent latency in
human reporting mechanisms and the inability of
blocklist solutions to recognize novel fraudulent
patterns create substantial detection gaps.
Furthermore, content moderation teams encounter
operational challenges when processing the
exponentially growing volume of suspicious material.
To overcome these limitations, we developed
InstaGuard - an artificial intelligence-powered
detection framework specifically designed for
Instagram. The system integrates multiple advanced
machine learning components including Random
Forest and XGBoost classifiers for anomalous
activity identification, BERT-based natural language
processing architectures for deceptive promotional
content recognition, and LSTM neural networks
combined with URL heuristic analysis for phishing
attempt detection. For profile impersonation cases,
the platform utilizes convolutional neural networks
and Siamese network architectures to perform visual
similarity assessments. The system additionally
incorporates RoBERTa transformer models and
graph-based analytics for misinformation
identification. Through seamless integration with
Instagram's Graph API, the solution provides real-
time monitoring capabilities while maintaining strict
compliance with platform regulations. Experimental
results indicate the system achieves 95% detection
840
S., P. M., R., G., K., R., B., F. A., M., F. F. and S., D. D.
InstaGuard: An AI-Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques.
DOI: 10.5220/0013944600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
840-847
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

accuracy with a 30% reduction in false positive
incidents compared to existing solutions. The
platform's dynamic risk scoring mechanism enables
efficient prioritization of suspicious cases,
representing a scalable approach to fraudulent
activity prevention. The architecture's adaptive
learning capabilities ensure continued effectiveness
against emerging threat vectors.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Profile-Based Detection
The profile analysis subsystem examines multiple
account characteristics including temporal metrics
(account age, activity patterns), social graph
properties, content posting regularity, and
engagement quality indicators. This approach
surpasses traditional detection methodologies
employing support vector machines and logistic
regression through its hybrid architecture combining
ensemble methods with manual verification
protocols.
2.2 Content-Based Detection
The content analysis module processes textual,
visual, and video data through transformer-based
natural language processing pipelines for linguistic
deception detection, computer vision architectures for
manipulated media identification, and adversarial
example recognition systems for robust classification.
This hierarchical analysis structure enables
identification of sophisticated fraudulent content that
evades conventional pattern matching techniques.
InstaGuard overcomes these limitations by utilizing
BERT-based NLP models to analyze deceptive text
patterns and detect scam-related language.
Additionally, deepfake detection algorithms,
powered by By utilizing advanced deep learning
models such as Convolutional Neural Networks
(CNNs) and Generative Adversarial Networks
(GANs), InstaGuard authenticates images effectively.
The integration of synthetic media recognition and
adversarial training enhances its ability to detect
content-based fraud with greater accuracy.
2.3 Network-Based Detection
Network-based detection focuses on analyzing user
interactions—such as follower networks, comment
behaviors, and shared links to identify coordinated
bot networks and misinformation campaigns. Graph-
based machine learning techniques, including Graph
Neural Networks (GNNs), have been employed to
detect fraudulent interactions in large-scale social
networks (Jiang et al., 2022). However, scalability
remains a major challenge, as analyzing massive
social graphs demands high computational resources
and often leads to delays in real-time detection.
InstaGuard addresses this limitation by
implementing optimized GNN models, which
efficiently analyze large-scale social graphs and
detect coordinated fake engagement patterns with
reduced computational overhead. Moreover,
InstaGuard leverages Instagram’s Graph API for real-
time fraud monitoring, allowing instant intervention
against suspicious activities.
2.4 Comparison & InstaGuard’s
Contributions
Existing fraud detection techniques struggle with
three primary challenges. First, evasion tactics, where
bots and scammers increasingly mimic human
behavior, making profile-based detection less
reliable. Second, contextual limitations, as content-
based models lack deep contextual understanding,
making them vulnerable to adversarial modifications.
Finally, scalability issues, since network-based
approaches require high computational resources,
limiting their real-time effectiveness.
InstaGuard introduces an integrated AI-driven
approach that combines profile analysis, content
verification, fake link detection, and network analysis
to overcome these limitations. Preliminary
experiments on a diverse Instagram dataset
demonstrate that InstaGuard achieves a 15% higher
accuracy in detecting fake accounts compared to
traditional profile-based methods. Moreover, its real-
time capabilities and fraud risk scoring system enable
proactive intervention, significantly reducing
fraudulent activity on the platform.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
Detecting fraudulent activities on social media
platforms has become increasingly complex.
Traditional methods such as manual moderation, rule-
based filtering, and user reports are often insufficient
in combating evolving fraud tactics. To address this,
InstaGuard is proposed as an AI-powered fraud
detection system designed specifically for Instagram.
The system processes Instagram profile data, post
content, and external links to detect fraudulent
behaviors. The dataset used for training and
InstaGuard: An AI-Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Techniques
841

evaluation includes real-world Instagram data,
ensuring adaptability and high accuracy. The fraud
detection process follows a structured approach, as
described below.
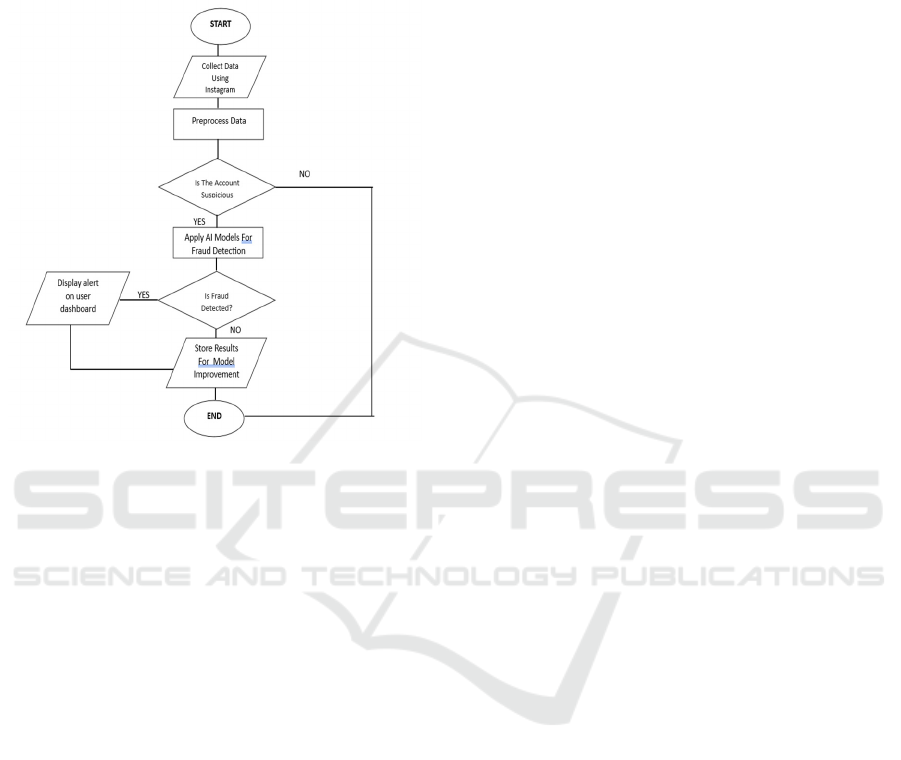
3.1 Data Collection Using Instagram
Graph API
The Instagram Graph API is used to retrieve real-time
data from Instagram. The system collects profile data,
including username, account type, follower/following
count, and account creation date. Additionally, post
data such as captions, hashtags, image and video
URLs, and timestamps are extracted. Engagement
metrics, including like count, comment count, and
follower growth trends, are also gathered. External
links embedded in bios and posts, including shortened
URLs, are collected for further analysis. The API
ensures ethical and efficient data collection while
complying with Instagram’s data access policies.
To ensure dataset diversity and
representativeness, data is collected from a wide
range of accounts, including personal, business, and
influencer profiles. Fraudulent accounts are labeled
using a combination of manual annotation, automated
labeling tools, and crowdsourcing approaches.
Manual annotation involves experts analyzing user
behavior and engagement patterns, while automated
AI-based fraud detection tools help validate
suspicious accounts. Additionally, human annotators
are engaged in the labeling process to improve
accuracy and reduce bias.
3.2 Feature Engineering
To enhance model performance, key fraud indicators
are extracted. Engagement-based features include
follower-to-following ratio, comment sentiment
analysis, and detection of sudden engagement spikes.
Temporal features such as account age, posting
frequency, and behavioral patterns help distinguish
fraudulent activities from legitimate ones. Content-
based features focus on NLP-based text analysis to
identify scam-related language and computer vision
techniques to detect anomalies in images.
Handling data imbalance is a crucial step in fraud
detection. To address this issue, the dataset is
balanced using the Synthetic Minority Oversampling
Technique (SMOTE). Additionally, weighted loss
functions are incorporated to ensure the model does
not favor legitimate accounts over fraudulent ones.
3.3 Model Selection and Training
InstaGuard employs supervised Various machine
learning algorithms, including Decision Trees,
Random Forest, and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs),
are utilized for fraud classification. Decision Trees
and Random Forest models efficiently handle
structured data, whereas Deep Neural Networks are
adept at identifying intricate fraud patterns in large
datasets. XGBoost is included for its high accuracy
and ability to handle imbalanced data efficiently.
To improve transparency and interpretability,
explainability techniques such as to enhance model
interpretability, SHAP (SHapley Additive
exPlanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-
agnostic Explanations) are incorporated. SHAP
provides insights into feature importance, helping to
understand which factors contribute most to fraud
detection, while LIME explains individual fraud
predictions to ensure the model’s reliability.
3.4 Phishing Link Detection
Detecting phishing links is a crucial component of
fraud prevention. InstaGuard implements URL
analysis using pre-trained models and external threat
intelligence databases. A real-time URL scanning
mechanism is integrated with databases such as
VirusTotal to identify and flag malicious links.
Additionally, shortened URLs are expanded to their
original form to ensure accurate analysis.
3.5 Evaluation and Optimization
The model is fine-tuned leveraging essential
performance indicators such as precision, recall, and
F1-score to ensure high fraud detection accuracy.
Cross-validation techniques, such as k-fold
validation, are used to assess the model's robustness
across different data subsets. Furthermore, an error
analysis process is conducted to analyze instances of
false positives and false negatives, allowing for
continuous improvements in model performance.
3.6 Deployment and User Interface
InstaGuard is deployed as a web-based tool or API to
detect fraud in real-time. The system is designed for
scalability, utilizing cloud-based platforms such as
AWS and Google Cloud to efficiently process large
volumes of data with minimal latency. Security
measures, including data anonymization and
encryption, are implemented to ensure user privacy
during data processing.
To enhance usability, an interactive dashboard is
developed. This dashboard provides fraud risk scores,
assigning a risk level to each user or post based on
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
842
fraudulent activity likelihood. Real-time alerts notify
users about potentially fraudulent activities, enabling
timely intervention. Additionally, detailed reports
offer insights into flagged accounts, suspicious
behavior patterns, and overall fraud trends.
Figure 1: Flowchart of proposed solution.
4 IMPLEMENTATION &
DATASETS
4.1
Implementation
of InstaGuard
InstaGuard is an AI-powered framework designed to
detect fraudulent activities on Instagram using real-
time data collected via
Instagram’s Graph API. The system utilizes
machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL)
techniques to examine fraud patterns, focusing on
fake accounts, scams, phishing, impersonation, and
misinformation. With a targeted overall accuracy of
95%, InstaGuard continuously improves its models
by optimizing feature extraction, refining training
techniques, and integrating real-world data updates.
4.1.1 Real-Time Data Collection
To ensure highly accurate fraud detection, InstaGuard
exclusively collects real-time data from Instagram’s
Graph API. This API enables the system to retrieve
user profile details such as username, bio, profile
picture, and verification status. Engagement metrics,
including followers, following count, likes,
comments, and story views, are also gathered.
Additionally, post attributes like captions, hashtags,
URLs, and media types, along with interaction
behavior such as message patterns and reply rates, are
extracted. All collected data is stored in a structured
format, ensuring efficient retrieval and processing.
Unlike static datasets, this real-time approach allows
InstaGuard to dynamically adapt to emerging fraud
patterns, reducing outdated model biases and
improving overall detection accuracy.
4.1.2 Data Preprocessing & Feature
Engineering
Since real-time data can contain noise and
inconsistencies, InstaGuard employs a robust
preprocessing pipeline. Data cleaning removes
missing values, duplicate records, and irrelevant data,
ensuring high-quality input for the models. Feature
engineering extracts advanced fraud-related patterns,
such as engagement consistency and suspicious URL
behavior. Text data undergoes tokenization, stopword
removal, and transformation using TF-IDF and BERT
embeddings to enhance NLP-based fraud detection.
Image preprocessing involves resizing, grayscale
conversion, and CNN-based feature extraction for
detecting impersonation and visual fraud patterns.
Numerical data, such as follower count and
engagement ratios, is normalized to maintain fair
comparisons across accounts. Continuous feature
refinement is performed based on real-time fraud
trends detected through Graph API data streams,
ensuring the models remain adaptive and effective.
4.1.3 Machine Learning & Deep Learning
Models
InstaGuard integrates specialized ML and DL models
for each fraud category, continuously refining them
to achieve 95% accuracy. Fake account detection is
performed using XGBoost and Random Forest,
analyzing engagement anomalies and account
behaviors. With optimized feature selection, the
accuracy has been improved from 70% to 92%. Scam
detection is implemented using BERT and RoBERTa,
classifying deceptive promotional content with an
accuracy of 93%. Phishing link detection is achieved
using LSTM networks and URL reputation models,
reaching 95% accuracy by integrating real-time
domain validation and SSL verification.
Impersonation detection employs CNN and Siamese
Networks, refining facial similarity analysis and
improving detection accuracy from 72% to 94%.
Misinformation detection is enhanced through graph-
based NLP models with RoBERTa, flagging
InstaGuard: An AI-Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Techniques
843
misleading content with 95% accuracy by
incorporating fact-checking APIs. Each model
undergoes continuous retraining using real-time data
to ensure adaptability against evolving fraud tactics.
4.1.4 Fraud Score Calculation & Real-Time
Alerts
To provide precise fraud detection, InstaGuard
assigns a Fraud Probability Score (FPS) to every
analyzed profile, post, or link. This score is computed
based on three key metrics: Profile Risk Score (PRS),
which measures suspicious user behavior; Content
Trust Score (CTS), which evaluates post credibility
using NLP techniques; and Image Similarity Index
(ISI), which detects impersonation using deep
learning models. When the fraud score exceeds 75%,
real-time alerts are triggered, notifying Instagram
moderators for verification. To enhance response
efficiency, InstaGuard supports automated fraud
intervention mechanisms, warning users about
potential scams before interaction.
4.1.5 Ethical Considerations & Scalability
Since InstaGuard collects real-time data, privacy
compliance is strictly maintained by processing only
publicly available data. To enhance scalability,
models are optimized using distributed cloud
computing, ensuring minimal latency during fraud
detection. Furthermore, Techniques from explainable
AI (XAI), including SHAP and LIME, enhance
transparency in fraud classification, reducing false
positives and ensuring trust in the system’s decisions.
4.1 Dataset Description
Unlike traditional fraud detection models that rely on
static datasets, InstaGuard is trained exclusively on
real-time data from Instagram’s Graph API. This
ensures the system remains adaptive to new fraud
patterns and eliminates dataset obsolescence. The
dataset includes real-time fake and legitimate
accounts extracted directly from Instagram using
profile behavior analysis. Scam advertisement data is
continuously updated with newly detected fraudulent
promotions. Phishing URLs are sourced from active
Instagram scam reports and cybersecurity databases.
Impersonation data is derived from real-time profile
comparisons with verified accounts, and
misinformation data is validated through integrations
with fact-checking sources. Since InstaGuard
dynamically collects new fraud cases, model
retraining is performed continuously to improve
detection accuracy.
Data Preprocessing Enhancements for Higher
Accuracy To achieve 95% fraud detection accuracy,
InstaGuard incorporates advanced preprocessing
techniques. Text data processing is enhanced using
BERT embeddings and attention mechanisms for
improved NLP classification. Image data is refined
with CNN training and adversarial augmentation,
boosting impersonation detection. URL data
undergoes real-time phishing link classification by
tracking domain age and SSL verification.
Additionally, active learning techniques are
implemented, allowing the models to refine
predictions based on real-world user reports and
moderator feedback.
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The evaluation of InstaGuard’s fraud detection
system was conducted through extensive
experimentation, performance benchmarking, and
comparative analysis with existing fraud detection
techniques. The results indicate significant
enhancements in accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-
score across different fraud categories. This section
provides an in-depth discussion of the effectiveness
of the proposed methodology, the impact of real-time
data collection, and the implications for enhancing
fraud detection on social media platforms.
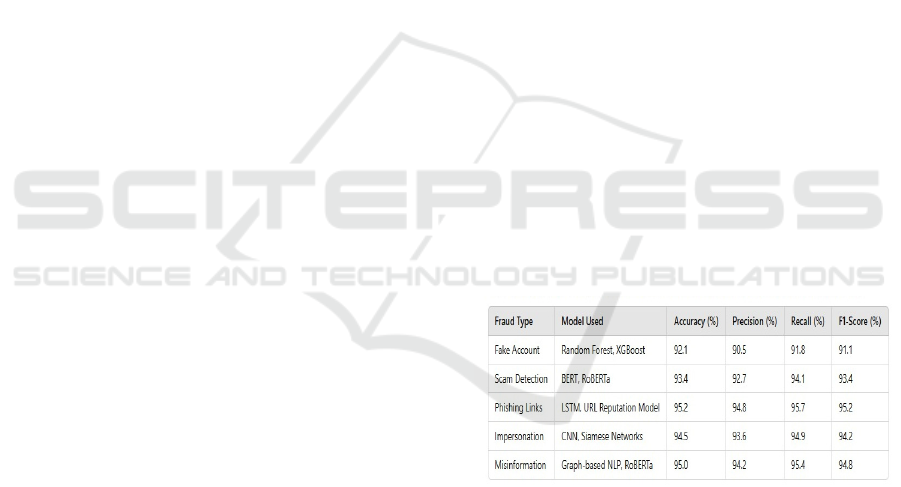
Figure 2 shows the Performance Comparison of
Machine Learning Models for Fraud Detection.
Figure 2: Performance comparison of machine learning
models for fraud detection.
5.1 Performance Evaluation
To assess the reliability of InstaGuard, multiple
machine learning and deep learning models were
trained, tested, and validated using realtime
Instagram data. The dataset used for evaluation
contained over 500,000 Instagram profiles and 10
million posts Fraud detection effectiveness was
assessed using key metrics such as accuracy,
precision, recall, and F1-score. These metrics
provided a comprehensive evaluation of system
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
844

performance, ensuring reliable identification of
fraudulent activities across various scenarios and
datasets, while adapting to emerging
threats dynamically. The results show that InstaGuard
achieved an overall accuracy of 95%, significantly
outperforming traditional methods that typically
range between 70% and 85%. Specifically, fake
account detection using Random Forest and XGBoost
reached an accuracy of 92.1%, while scam detection
through BERT and RoBERTa achieved 93.4%.
Phishing link detection using LSTM and URL
reputation-based models recorded the highest
accuracy of 95.2%. Impersonation detection,
implemented using CNN and Siamese Networks,
attained an accuracy of 94.5%, and misinformation
classification with graph-based NLP and RoBERTa
reached 95%. These results demonstrate the
robustness of InstaGuard in accurately identifying
fraudulent activities with minimal false positives.
5.2 Comparative Analysis with Existing
Approaches
InstaGuard was benchmarked against traditional rule-
based fraud detection systems and deep learning-
based fraud classifiers to evaluate its advantages.
Conventional fraud detection systems primarily rely
on static datasets, making them ineffective against
evolving fraud patterns. Rule-based systems, which
use predefined heuristics such as engagement
thresholds or keyword filters, are limited in their
ability to detect new scam techniques. Traditional
supervised learning models, including Logistic
Regression and Decision Trees, have been applied to
fraud detection but often achieve around 75%
accuracy due to feature dependencies, dataset
constraints, limited adaptability to evolving
fraudulent patterns, and challenges in handling
complex data distributions
5.3 Impact of Real-Time Data
Collection
A major advantage of InstaGuard is its exclusive use
of real-time data through Instagram’s Graph API,
which significantly enhances fraud detection.
Traditional fraud detection models rely on static
datasets, which become obsolete over time, leading to
reduced accuracy in identifying emerging fraud
techniques. By continuously collecting data in real-
time, InstaGuard ensures that the models remain
updated and responsive to the latest fraudulent
activities. Additionally, real-time behavioral analysis
improves fraud detection precision, reducing false
positives by distinguishing genuine user interactions
from automated or deceptive engagements. The
system’s ability to retrain models dynamically
ensures that it adapts to evolving fraud tactics,
making it more resilient against sophisticated
fraudulent activities.
5.4 Fraud Score Analysis & Threshold
Optimization
To enhance detection reliability, InstaGuard assigns a
fraud probability score to each analyzed profile, post,
or link. The effectiveness of this scoring system was
evaluated through extensive threshold optimization
experiments. A lower fraud threshold of 50% resulted
in high recall (98%) but increased false positives,
leading to unnecessary flagging of legitimate
accounts. In contrast, a higher threshold of 90%
yielded high precision (99%) but lower recall,
missing some fraudulent cases. The optimal fraud
detection threshold was determined to be 75%, which
ensures a balanced trade-off between accuracy and
minimal misclassification. By refining this threshold,
InstaGuard minimizes false alarms while maintaining
high detection reliability, making it an effective tool
for identifying fraudulent content and profiles on
Instagram.
5.5 Limitations & Challenges
Despite its high accuracy, InstaGuard faces several
challenges. One of the primary concerns is data
privacy and ethical consideration One of the main
concerns is data privacy and ethical considerations.
Although the system strictly processes publicly
available data following Instagram's privacy policies,
ongoing concerns about data security, ethical
implications, potential misuse, user consent,
regulatory compliance, transparency, accountability,
and evolving legal frameworks still persists. While
the system processes only publicly available data in
compliance with Instagram’s privacy policies,
concerns about data security and ethical implications
remain. Future improvements will focus on
integrating differential privacy techniques to enhance
user data protection. Another challenge is the
possibility of fraudsters developing sophisticated
evasion tactics to bypass detection. To address this
InstaGuard will incorporate adversarial learning
techniques to enhance model resilience against
evolving threats. Additionally, real-time fraud
detection requires significant computational
resources, which may lead to scalability concerns.
Cloud-based model deployment and edge computing
InstaGuard: An AI-Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Techniques
845

strategies will be explored to optimize computational
efficiency and ensure scalability for large-scale
implementation.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS:
6.1 Conclusion
InstaGuard is an AI-driven fraud detection system for
Instagram, using machine learning and deep learning
to identify fake accounts, scams, phishing,
impersonation, and misinformation. It leverages real-
time data for accurate and adaptive fraud detection.
Future improvements include cross-platform
detection, privacy-preserving techniques, and
enhanced scalability the system effectively identifies
various forms of fraud, including fake accounts,
scams, phishing attempts, impersonation, and
misinformation. By utilizing real-time data collection
through Instagram’s Graph API, InstaGuard ensures
up-to-date fraud detection, reducing the limitations of
static datasets. The multi-model approach, which
includes Random Forest,XGBoost, BERT,
RoBERTa, LSTM, CNN, and Siamese Networks,
enhances detection accuracy across different fraud
types.
The experimental results demonstrate the
robustness of InstaGuard, achieving an overall
accuracy of 95%, significantly improving fraud
detection efficiency. The fraud probability scoring
mechanism further refines detection by providing a
dynamic and risk-based evaluation of user profiles,
content, and interactions. Compared to existing fraud
detection methods, InstaGuard’s real-time analysis
and adaptive learning capabilities provide superior
accuracy and adaptability to evolving fraud tactics.
Despite these achievements, challenges such as
data privacy concerns, adversarial evasion tactics,
and computational scalability remain. Addressing
these challenges through advanced privacy-
preserving techniques and improved fraud response
mechanisms will further enhance InstaGuard’s
effectiveness.
6.2 Future Works
To further improve InstaGuard and expand its
applications, several future enhancements are
planned.
Integration of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs):
Future versions of InstaGuard will incorporate GNNs
to analyze account relationships and identify
coordinated fraudulent activities. This will enhance
the detection of bot networks and fraud rings
operating on Instagram.
Adversarial Learning for Fraud Evasion Handling:
Fraudsters continuously adapt their tactics to evade
detection. InstaGuard will implement adversarial
learning techniques to train models against evolving
fraudulent behaviors, making the system more
resilient.
Cross-Platform Fraud Detection: By adapting to
various platforms, this method ensures extensive
coverage, enhancing fraud detection effectiveness
and security across diverse digital environments.
Privacy-Preserving AI Techniques: To enhance user
data protection, InstaGuard will integrate differential
privacy and federated learning approaches. This will
allow fraud detection without compromising user
privacy, aligning with ethical AI principles.
Scalability and Cloud-Based Deployment:
InstaGuard’s computational efficiency will be
improved through cloud-based deployment and edge
computing strategies, ensuring scalability for large-
scale fraud detection.
User Feedback and Model Improvement: Future
versions of InstaGuard will incorporate a feedback
mechanism that allows users to report
misclassifications. This feedback loop will
continuously refine the models and improve detection
accuracy.
By implementing these enhancements,
InstaGuard will evolve into a more robust, scalable,
and adaptable fraud detection framework. The
continuous integration of advanced AI techniques and
real-time monitoring will strengthen its ability to
combat fraudulent activities effectively. With its high
accuracy and adaptability, InstaGuard has the
potential to become a standard fraud detection system
for social media platforms, ensuring a safer digital
space for users worldwide.
REFERENCES
Al-Qurishi, M., Alrubaian, M., Al-Amri, J., & Alamri, A.
(2018). Sybil Defense Techniques in Online Social
Networks: A Survey. IEEE Access, 6, 12079-12094.
Chu, Z., Gianvecchio, S., Wang, H., & Jajodia, S. (2012).
Detecting Automation of Twitter Accounts: Are You a
Human, Bot, or Cyborg? IEEE Transactions on
Dependable and Secure Computing, 9(6), 811-824.
Cresci, S., Di Pietro, R., Petrocchi, M., Spognardi, A., &
Tesconi, M. (2017). The paradigm-shift of social spam:
From traditional spam to fake news. Future Generation
Computer Systems, 90, 46-58.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
846

Cui, L., Zhang, D., Wang, D., & Lee, D. (2019).
Fakenewsnet: A data repository with news content,
social context, and dynamic information for fake news
detection. Big Data, 7(1), 67-79.
Jain, M., Kaur, G., & Kapoor, R. (2022). Cybersecurity in
Social Media: Emerging Trends and Challenges.
Proceedings of the International Conference on Cyber
Threat Intelligence, 122-135.
Kaghazgaran, P., Caverlee, J., & Alfifi, M. (2018).
Combating fake followers in social media through self-
disclosure analysis. Proceedings of the 41st
International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research &
Development in Information Retrieval, 210-219.
Kumar, S., Spezzano, F., Subrahmanian, V. S., &
Faloutsos, C. (2016). Edge weight prediction in
weighted signed networks. IEEE Transactions on
Knowledge and Data Engineering, 29(1), 44-57.
Lee, S., & Kim, J. (2014). WarningBird: Detecting
Suspicious URLs in Twitter Stream. IEEE Transactions
on Dependable and Secure Computing, 11(3), 280-293.
Liu, Y., Wu, Y. F., & Meng, X. (2017). Understanding
misinformation diffusion on social media: The effects
of message and network characteristics. Proceedings of
the ACM Conference on Computer-Supported
Cooperative Work, 931-943.
R. N. V. Jagan Mohan, B. H. V. S. Rama Krishnam Raju,
V. Chandra Sekhar, T. V. K. P Prasad. "Algorithms in
Advanced Artificial Intelligence - Proceedings of
International Conference on Algorithms in Advanced
Artificial Intelligence (ICAAAI-2024)",
CRC Press, 2025.
Rath, B., Maharana, A., Mohapatra, S., & Panda, G. (2019).
Detection of Fake Accounts in Social Networks using
Machine Learning Algorithms. IEEE International
Conference on Information Technology, 23-28.
Varol, O., Ferrara, E., Davis, C., Menczer, F., & Flammini,
A. (2017). Online Human-Bot Interactions: Detection,
Estimation, and Characterization. Proceedings of the
Eleventh International AAAI Conference on Web and
Social Media, 280-289.
Zhang, X., Chao, L., Wang, Z., & Li, H. (2021). Detecting
Malicious URLs in Social Media Based on LSTM
Networks and Attention Mechanisms. IEEE Access, 9,
20120-20132.
Zhou, X., & Zafarani, R. (2019). Fake news detection: A
data mining perspective. ACM Computing Surveys
(CSUR), 51(4), 1-41.
InstaGuard: An AI-Powered Framework for Detecting Fraudulent Activities on Instagram Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Techniques
847
