
Next‑Gen Healthcare: AI‑Powered IoT for Smart Hospitals
Guruprakash K. S., Nithya T. M., Deepak S., Devadharshini K. S.,
Dharshini R. and Dinesh Krishna S.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering, Trichy, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: AI‑driven Bed Allocation, IoT‑Based, Hospital Management, Real‑Time Patient Monitoring, Infection Risk
Management, Emergency Response System.
Abstract: The healthcare industry faces challenges in patient monitoring, resource management, and emergency
response, necessitating an advanced AI and IoT-based hospital management system for real-time data
acquisition, automated decision-making, and remote monitoring. This system integrates body temperature,
heart rate, and blood oxygen sensors to continuously track patient vitals, with data processed by an Arduino
microcontroller and transmitted via Wi-Fi using NodeMCU, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor
patients remotely through a web or mobile interface. An AI-driven bed allocation system ensures optimal
resource utilization by analysing patient conditions, infection risks, and proximity to other patients,
automatically assigning beds to minimize cross-contamination and ensuring that infectious patients are
isolated appropriately. The system also considers patient severity, special medical needs, and ICU availability
to allocate resources efficiently. A pressure sensor detects hospital bed occupancy in real-time, further
enhancing resource management, while a buzzer alert system notifies staff of critical changes in patient
conditions, enabling immediate intervention. Additionally, AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast
patient deterioration based on historical and real-time data, allowing for proactive medical attention. Designed
with cost-effective, energy-efficient components, the system seamlessly integrates AI and IoT technologies,
making it scalable and adaptable for hospitals of all sizes, ultimately improving patient care, operational
efficiency, and emergency response.
1 INTRODUCTION
To effectively manage patient care, resource
allocation, and emergency response, modern
hospitals need clever, automated systems. The need
for real-time patient monitoring and efficient hospital
operations has grown as a result of the healthcare
sector's explosive expansion. Manual procedures are
frequently used in traditional hospital administration
systems, which can lead to mistakes, delays, and
inefficient use of hospital resources (Arul Kumar et
al., 2022). Slow reaction times can be fatal in
emergency scenarios, underscoring the need for a
more sophisticated, tech-driven strategy.
By combining automated bed distribution, sensor-
based real-time health monitoring, and emergency
warning systems, the proposed AI and IoT-based
smart hospital management system, Health Sphere,
seeks to address these issues. Using sensors, the
system continuously monitors vital indications such
blood oxygen levels, heart rate, and body
temperature, guaranteeing prompt identification of
anomalous conditions (Nithya et al., 2020). In order
to minimize cross-contamination, an AI-driven bed
allocation module makes sure that infected patients
are placed in segregated beds.
The system also has a touch sensor to track bed
availability in real time, removing human error from
resource management. While an IoT-based remote
monitoring, system enables medical personnel to
access patient data via a web or mobile interface, an
LCD display gives hospital staff immediate
information on patient health and resource condition
(Guruprakash et al., 2023). By guaranteeing that
hospital employees are promptly informed of
emergencies, a buzzer alert system greatly enhances
patient safety and reaction times. This system
optimizes hospital resource usage, improves patient
care, lowers human intervention errors, and
automates hospital operations by utilizing IoT and AI
S., G. K., M., N. T., S., D., S., D. K., R., D. and S., D. K.
Next-Gen Healthcare: AI-Powered IoT for Smart Hospitals.
DOI: 10.5220/0013944500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
833-839
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
833

technology (Arul Kumar et al., 2022). Hospitals of all
sizes can effectively apply the solution thanks to the
flawless data transmission made possible by the
combination of wireless communication (NodeMCU
& Arduino). This invention bridges the gap between
automation, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven
hospital management decision-making, marking a
significant advancement in smart healthcare.
2 RELATED WORK
The increasing reliance on the Internet of Things
(IoT), and other emerging technologies has
significantly advanced the healthcare industry. A
variety of intelligent systems and monitoring
frameworks have been proposed, leveraging these
technologies to improve efficiency and accuracy in
health monitoring and diagnostics.
Deepa et al., proposed an AI-based intelligent
system for healthcare analysis utilizing the ridge-
Adaline stochastic gradient descent classifier. This
approach demonstrated enhanced performance for
healthcare-related data analysis and prediction tasks,
contributing to efficient decision-making in
healthcare systems. Similarly, Islam and Rahaman
developed a smart healthcare monitoring system in an
IoT environment, providing a practical solution for
real-time health data monitoring and analysis.
Masud et al., introduced a deep learning-based
intelligent face recognition system designed for IoT-
cloud environments. Their work highlights the
integration of deep learning techniques for secure and
efficient health data access and authentication. Bhat
et al. presented a comprehensive review of IoT-based
health monitoring systems, emphasizing the potential
benefits of IoT in improving patient care and
operational efficiency in healthcare facilities. Gogate
and Bakal implemented a healthcare monitoring
system using wireless sensor networks for cardiac
patients, focusing on the early detection and
prevention of cardiac events. Their work underscores
the importance of sensor-based solutions in critical
healthcare applications. This body of work
collectively showcases the diverse applications of AI,
IoT, and sensor technologies in enhancing healthcare
systems, with a focus on improving patient outcomes
and addressing challenges in traditional healthcare
practices.
3 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
Hospitals face significant challenges in patient
monitoring, resource management, and emergency
response, which directly impact efficiency and patient
safety. Traditional patient monitoring methods rely on
manual supervision, leading to delays in detecting
critical health changes and increasing the risk of
medical emergencies. Additionally, manual data entry
is prone to errors, which can result in misdiagnosis or
incorrect treatment. Resource management,
particularly bed allocation, is often inefficient,
causing delays in patient admission and leading to
overcrowding in emergency wards.
The lack of an automated system also increases
the risk of infection spread, as patients are not always
assigned beds based on their health conditions and
infection risks. Moreover, emergency response
mechanisms in hospitals are often slow due to the
absence of real-time alerts, making it difficult for
medical staff to respond quickly to deteriorating
patient conditions.
Existing systems use standalone sensors that are
not integrated, limiting their ability to monitor
multiple health parameters simultaneously. The
absence of an AI-driven approach for patient
monitoring, bed allocation, and predictive analytics
further reduces operational efficiency. To address
these challenges, a smart hospital management
system integrating AI and IoT is required to enable
real-time monitoring, automated decision-making,
and efficient resource utilization.
4 RISK ASSESSMENT
IoT based health risk monitoring system seeks to
continually track a variety of personal health metrics,
anticipate possible health concerns, and potentially
avert unfavourable health outcomes via early
detection. Implementing a health risk monitoring
system using IoT involves various risks that need to
be assessed and mitigated to ensure the system's
effectiveness, security, and compliance. Here are
some key aspects for a health risk monitoring system
using IoT:
Abnormal Vital Signs: Sudden spikes or drops
in essential indicators including respiration rate,
blood pressure, and heart rate & also a drastic change
in physical activity levels, especially a sudden
decrease or increase.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
834
Temperature Fluctuations: Sudden temperature
changes either elevated or subnormal may signal an
infection or other underlying health issues. Such
changes could be indicative of a decline in health or
an acute event.
Emergency Response and Contingency
Planning: Develop and regularly test emergency
response plans & to have contingency measures in
place for system failures, including data backup and
recovery procedures.
Reliability and Accuracy: Implement quality
assurance processes for data accuracy. Calibrate and
validate sensors regularly. Establish redundancy and
failover mechanisms to ensure continuous
monitoring. Design for redundancy, fault tolerance,
and disaster recovery to minimize downtime and
ensure continuous operation.
Resource Constraints: Healthcare facilities are
often Authorized licensed use limited resources to
handle the increasing demand for medical services.
This leads to longer wait times and overburdened
medical staff, making it challenging to provide
immediate care.
Regulatory Compliance: Assure that healthcare
data management, privacy, and security needs are met
in accordance with industry standards and legal
regulations. To reduce the legal and regulatory
concerns related to IoT health monitoring devices,
stay current on the rules and guidelines that are
always changing.
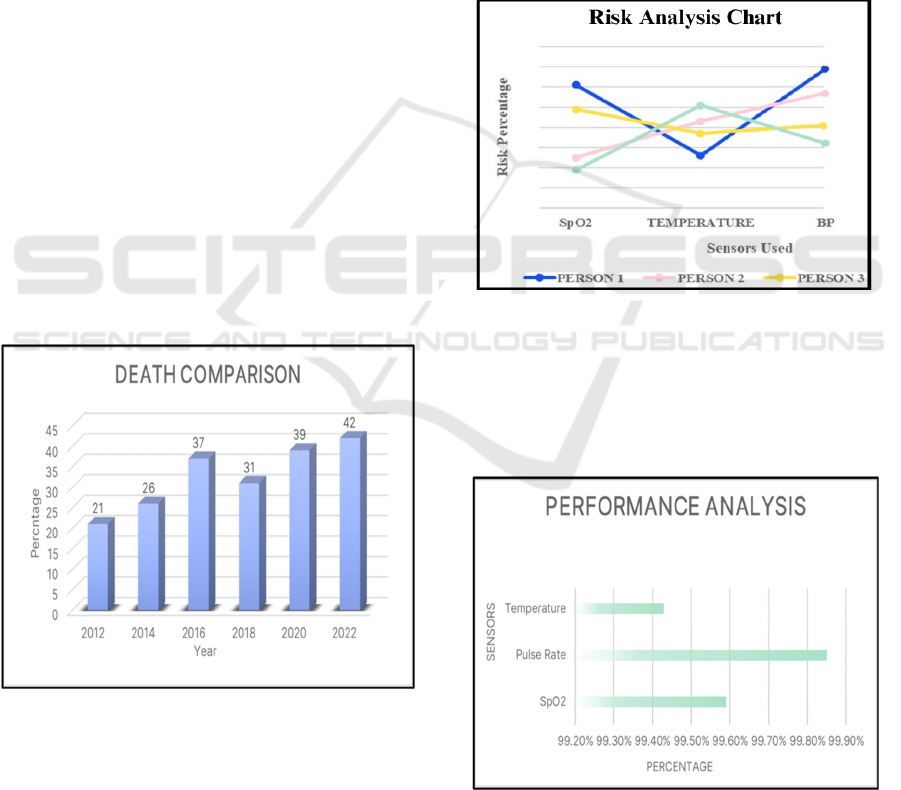
Figure 1: Death comparison due to health issues.
The information in figure1 displays the total no.of
deaths occurred in percentage due to health issues
without having an immediate medical response. The
risk levels that the health care patients encountered
from 2012 to 2022 are summarized. However the
no.of deaths occurring seems to be decreased at some
point but it increases gradually year by year with a
considerable amount of death taking place. The
information clearly suggests that nearly 30 to 40
percent of death takes place due to health issues.
Figure 2 portrays the data recorded by various sensors
used to demonstrate the level of risk it handles. It
monitors the risk and analyses the chances of the
occurring risk in percentage and produces the
graphical representation which depends on each and
every individual health condition. This risk analysis
clearly defines the amount of risk that a person is
exhibiting while using the health monitoring system
and produces accurate and other precautionary
measures to help in treatment.
Figure 2: Risk analysis chart.
Outcomes demonstrated that the device's
measurements produced 99.43% accuracy for body
temperature and 99.59% accuracy for oxygen level,
99.76% accuracy for pulse rate, and 99.85% for heart
rate which is pictorially represented in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Performance analysis.
Next-Gen Healthcare: AI-Powered IoT for Smart Hospitals
835

5 FEATURES AND
FUNCTIONALITIES
5.1 Real-Time Patient Monitoring
The system continuously tracks patient vitals,
including body temperature, heart rate, and blood
oxygen levels, using advanced sensors. Data is
processed via an Arduino microcontroller and
transmitted through Wi-Fi (NodeMCU), allowing
healthcare professionals to remotely monitor patient
health in real time via a web or mobile application.
This ensures early detection of abnormalities, leading
to timely medical intervention.
5.2 AI-driven Bed Allocation System
The system utilizes AI to assign hospital beds
efficiently based on patient condition, infection risk,
and ICU availability. By analyzing real-time and
historical patient data, it optimizes resource
utilization while minimizing cross-contamination
risks. Infectious patients are automatically assigned to
isolated beds, ensuring a safer hospital environment.
5.3 Smart Bed Occupancy Detection
A pressure sensor detects hospital bed occupancy in
real time, updating bed availability status on the
system. This eliminates manual tracking and
improves patient admission efficiency by providing
hospital staff with an up-to-date view of available
resources, thus reducing waiting times and optimizing
hospital space utilization.
5.4 Automated Emergency Alerts
In case of a critical change in patient vitals, an
integrated buzzer alert system notifies hospital staff
immediately. This ensures quick response times
during emergencies, allowing medical personnel to
intervene before a situation worsens. The alert system
is crucial for high-risk patients, improving overall
safety and care quality.
5.5 Remote Monitoring via IoT
Healthcare professionals can monitor patient vitals
and hospital resource usage remotely through an IoT-
enabled platform. The system provides real-time data
visualization via LCD displays and cloud-based
dashboards, allowing for informed decision-making
and reducing the need for manual supervision.
6 METHODLOGY
6.1 Data Acquisition Using Sensors
The system collects real-time patient data using
multiple sensors, including blood oxygen,
temperature, heart rate, and touch sensors for bed
occupancy. These sensors are connected to an
Arduino microcontroller, which gathers vital health
parameters for continuous monitoring.
6.2 Data Processing and Transmission
The Arduino processes the sensor data and transmits
it through an IoT module NodeMCU. The data is then
displayed on an LCD screen for local monitoring and
sent to a mobile application for remote access by
healthcare professionals.
6.3 IoT-Based Real-Time Monitoring
The IoT module ensures seamless transmission of
patient vitals to a web-based dashboard and mobile
app. This enables doctors and nurses to remotely
monitor patient health, reducing the need for physical
presence and allowing for early detection of critical
conditions.
6.4 Emergency Alert System
If a patient's vitals cross a critical threshold, an
automated buzzer alerts hospital staff immediately.
Simultaneously, real-time notifications are sent to
medical personnel via a mobile application, ensuring
a swift response to emergencies.
6.5 Automated Bed Occupancy
Detection
Touch sensors installed on hospital beds detect
occupancy in real time and update bed availability on
the hospital’s management system. This eliminates
manual tracking, optimizing resource allocation and
ensuring efficient patient admission.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
836
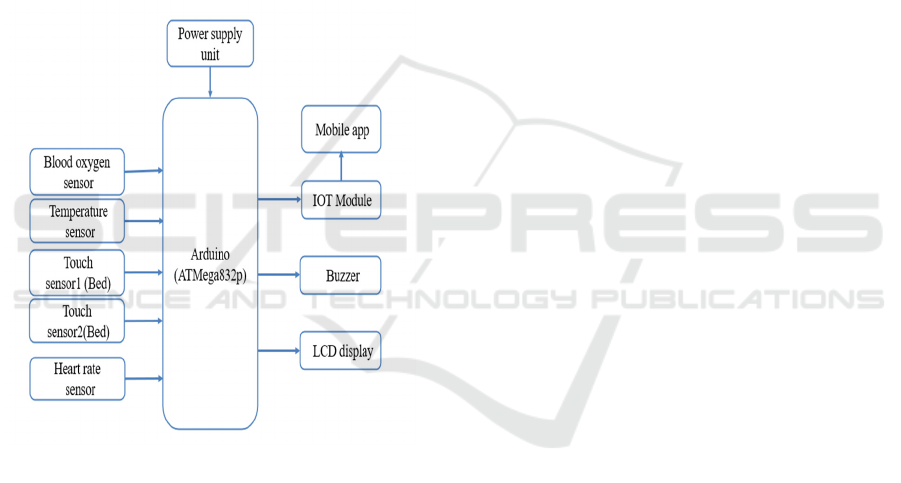
7 ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAMS
Figure 4 illustrate the Schematic of the suggested system.
7.1 Blood Oxygen Sensor
A Pulse Oximeter (SpO2 sensor) is a medical device
that determines the blood's oxygen saturation level. It
is a crucial factor in determining an individual's
respiratory health. The ratio of oxygenated to
deoxygenated haemoglobin can be found by placing
a non-invasive device on the finger and measuring
light wavelengths. Pulse oximeters utilize the idea of
light absorption to measure oxygen saturation. The
sensor emits two different wavelengths of light,
typically red and infrared, through a translucent part
of the body.
Figure 4: Schematic of the suggested system.
7.2 Temperature Sensor
A device that senses temperature can be employed to
take frequent readings of the body’s temperature and
convert this information into an electrical signal. By
transferring the electrical resistance over a diode into
usable measurements like Fahrenheit, Celsius, or
Centigrade, it also determines the relative humidity of
an item. The voltage across the diode is exactly
proportional to the temperature change. These sensors
are used to detect the interior temperature of
structures such as homes, bridges, dams, and power
plants in environmental monitoring.
7.3 Heart Rate Sensor
A gadget called a pulse sensor is used to determine a
person's heart rate. commonly by detecting the
pulsatile blood flow through arteries, which are
widely used to monitor heart rate in real time. Pulse
Monitor emits infrared, red, or green light (~550 nm)
towards the body and measures the amount of light
reflected using a photodiode which provides the pulse
rate of the patient. The pulse sensor operates by
means of two surfaces that are connected to an LED
and an ambient light sensor. Pulse rates may be
established by monitoring the minute variations in
light over a period of time.
7.4 Buzzers
Buzzers refers to simple devices that produce a
continuous buzzing or beeping sound when an
electric current pass through them. These are often
used in alarms, timers, and other signalling
applications. They are frequently employed to signal
the end of an activity or to notify others of an
impending event. Buzzers operate on the premise of
applying an alternating current voltage at the
element's resonance frequency, which causes the
element to vibrate and produce sound.
8 RESULT
The implementation of the AI and IoT-based hospital
management system demonstrated significant
improvements in real-time patient monitoring,
resource allocation, and emergency response. The
integration of blood oxygen, heart rate, temperature,
and bed occupancy sensors with an Arduino
microcontroller and IoT module enabled seamless
data collection and transmission. The system
successfully provided remote patient monitoring via
a mobile application, ensuring timely alerts for
critical conditions. Additionally, the AI-driven bed
allocation system optimized hospital resource
utilization, reducing patient waiting time and
minimizing cross-contamination risks. The
emergency alert mechanism efficiently notified
hospital staff of deteriorating patient conditions,
enhancing response time and medical intervention
efficiency.
Next-Gen Healthcare: AI-Powered IoT for Smart Hospitals
837

9 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed IoT-based hospital management system
enhances patient care, operational efficiency, and
resource management in hospitals. By integrating
real-time monitoring, automated alerts, AI-driven bed
allocation, the system reduces manual intervention
and improves decision-making for healthcare
professionals. Its cost-effective, scalable, and energy-
efficient design makes it suitable for hospitals of all
sizes.
The advancements in AI, IoT, and sensor-based
technologies have paved the way for transformative
changes in healthcare. Studies such as those by Li and
Chiu highlight the importance of remote healthcare
systems, improving accessibility for underserved
areas. Rahimoon et al. emphasized the need for cost-
effective, non-invasive monitoring with their
contactless body temperature measurement system.
Reza et al. showcased how mobile technologies can
enhance cardiovascular monitoring through portable
and affordable solutions.
These innovations contribute significantly to
creating efficient and scalable healthcare solutions.
By integrating remote monitoring, non-invasive
technologies, and real-time data analysis, healthcare
systems can become more patient-centric and
effective. Future research should address challenges
like data security, interoperability, and accessibility to
ensure broader adoption of these technologies and
drive global advancements in healthcare.
Future enhancements may include AI-based
diagnostics, robotic automation, and expanded IoT
functionalities for even more comprehensive
healthcare management. Overall, this smart
healthcare system significantly contributes to better
patient outcomes, reduced hospital workload, and
improved emergency response capabilities.
REFERENCES
A. Rahimoon, M. N. Abdullah, and I. Taib, “Design of a
contactless body temperature measurement system
using arduino,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical
Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 19, no. 3, pp.
1251–1258, 2020.
Arulkumar, V., Sridhar, S., Kalpana, G., & Guruprakash,
K. S. (2022). Real-time big data analytics for improving
sales in the retail industry via the use of Internet of
Things beacons. Lecture Notes in Networks and
Systems, 444, 111–126. Domain: Big Data Analytics,
Retail Industry Internet of Things (IoT)
Gogate U., Bakal J. Healthcare monitoring system based on
wireless sensor network for cardiac patients. Biomed.
Pharmacol, vol. 1, no 3, pp. 1–6, 2018, doi:
10.13005/bpj/1537.
Guruprakash, K. S., Kalpana, V., Selvarathi, C., Shalini, A.
A., Shivani, S. P., & Sienaha, M. (2023). CAP: Child
abuse risk prediction and prevention framework using
AI and dark web. AIP Conference Proceedings,
2822(1), 20260. Domain: Child Protection, Artificial
Intelligence, Risk Prediction
Guruprakash, K. S., Priyadharshini, K. V., Pavithra, G.,
Suruthi, S., Sujeetha, R., Soundaram, S., & Santhiya, K.
(2023). Document vector extension for document
classification. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2822(1),
20259.
Guruprakash, K. S., Siva Karthik, P., Ramachandran, A., &
Gayathri, K. (2024). Crop pest identification using deep
network-based extracted features and MobileENet in
smart agriculture. Land Degradation and Development,
35(11), 3642–3652. Domain: Smart Agriculture, Pest
Identification, Deep Learning
H. Bhat, N. Shetty, and A. Shetty, “A review on health
monitoring system using IoT,” International Journal of
Engineering Research and Technology, vol. 6, no. 15,
pp. 1–4, 2019.
Ilavarasan, N., Gandhiraj, R., Elavarasi, S. A., &
Guruprakash, K. S. (2022). Geographical weather
prediction using sigmoidal regression learning scheme
for crop yield applications. Journal of Environmental
Protection and Ecology, 23(8), 3518–3526. Domain:
Environmental Science, Weather Prediction,
Agriculture Applications.
Jagadesh, T., Rithik, S., Nithish Kumar, B., Pv, R.R.,
Rithika, R., “IoT Based HealthMonitoring in
Hospitals”, Proceedings of 8th IEEEInternational
Conference on Science, Technology, Engineering and
Mathematics, ICONSTEM 2023, 2023.
M. Islam, A. Rahaman et al., “Development of smart
healthcare monitoring system in iot environment,” SN
computer science, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 1–11, 2020.
M. Masud, G. Muhammad, H. Alhumyani et al., “Deep
learning-based intelligent face recognition in IoT-cloud
environment,” Computer Communications, vol. 152,
pp. 215– 222, 2020.
N. Deepa, B. Prabadevi, P. K. Maddikunta, T. R.
Gadekallu, T. Baker, M. A. Khan, et al., "An AI-based
intelligent system for healthcare analysis using ridge-
adaline stochastic gradient descent classifier", J.
Supercomput., vol. 77, no. 2, pp. 1998- 2017, Feb.
2021.
N. S. M Hadis, M. N. Amir Nazarullah, M. M. Jafri, and S.
Abdullah, “IoTbased patient monitoring system using
sensors to detect, analyze and monitor two primary vital
signs,” Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol.
1535, Article ID 012004, pp. 1–12, 2020.
Nithya, T. M., Guruprakash, K. S., & Amudha, L. (2020).
Deep learning-based prediction model for course
registration system. International Journal of Advanced
Science and Technology, 29(7 Special Issue), 2178–
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
838

2184. Domain: Education Technology, Deep
Learning, Course Registration
S. Li and C. Chiu, „„Improved health monitoring for remote
health care systems, ‟‟ J. Sensor Actuator Netw., vol.
10, no. 1, p. 9, Jan. 2021, doi:
10.3390/jsan10010009.
T. Reza, S. B. A. Shoilee, S. M. Akhand, and M. M. Khan,
“Development of android based pulse monitoring
system,” in Proceedings of the Second International
Conference on Electrical, Computer and
Communication Technologies (ICECCT), pp. 1–7,
Coimbatore, India, February 2017.
Varshini Devi, I., Natarajan, B., Prabu, S., Praba, R. A.,
Ushanandhini, K., & Guruprakash, K. S. (2023).
Automated stock trading using reinforcement learning.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on
Integrated Intelligence and Communication Systems,
ICIICS 2023. Domain: Financial Technology,
Automated Trading, Reinforcement Learning
Next-Gen Healthcare: AI-Powered IoT for Smart Hospitals
839
