
AI‑Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart
Manufacturing: Real‑Time Deployment, Multi‑Sensor Fusion and
Scalable Efficiency Optimization
Purushotham Endla
1
, Sunil Bhardwaj
2
, P. Mathiyalagan
3
, K. Akila
4
,
P. Sanjeevkumar
4
and M. Srinivasulu
5
1
Department of Physics, School of Sciences and Humanities, SR University, Warangal, Telangana, India
2
Department of Mathematics, IILM University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
3
Department of Mechanical Engineering, J.J. College of Engineering and Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India
4
Department of Management Studies, Nandha Engineering College, Vaikkaalmedu, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
5
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Keywords: Predictive Maintenance, Smart Manufacturing, Real‑Time AI Deployment, Multi‑Sensor Fusion, Explainable
Artificial Intelligence.
Abstract: In the changing world of Industry 4.0, predictive maintenance with artificial intelligence (AI) is a massive
shift from the status quo of how mass production sites plan all of their maintenance methodologies. In this
paper, we propose a novel AI-based predictive maintenance framework for smart manufacturing systems
focusing on real-time deployment, sensor variety and cross-domain scalability. By systematically addressing
the challenges faced by previous works such as over dependence on synthetic data, over focus on a specific
domain, no real-time validation and low model explainability, our work presents a holistic approach that
integrates multi-sensor data fusion, energy-efficient edge computing and explainable AI. The framework is
both accurate, flexible and easy to interpret by the user, as demonstrated with actual industrial samples. It is
also back-ward compatible with existing systems, which is highly attractive for deploying in modern as well
as existing manufacturing plants. This not only improves technical performance, but enables maintenance
teams with actionable information that can decrease downtime and maintenance costs.
1 INTRODUCTION
This fast growth in industrial manufacturing brought
about by the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies has
led to a huge demand on intelligent maintenance
systems. In more conventional manufacturing
facilities, maintenance has largely been reactive or
scheduled according to set time periods, hence
unintended downtime and frivolous service costs.
With equipment becoming more complicated and
interlinked, such rudimentary methods are not
anymore adequate for ensuring the best productivity.
AI-driven predictive maintenance is a game
changer in how industries manage the health of their
equipment. Real-time data analysis with the help of
diverse sensors, can help AI models predict potential
failures before they happen, thus reducing downtime
as well as extending the life of the equipment.
Although existing studies leverage the benefits of
predictive analytics, they also encounter a number of
limitations: limited domain generalization, ideal
dataset dependency, difficulty integrating methods
into existing legacy systems among others.
This study intends to overcome these vital
problems with a novel large-scale AI predictive
maintenance framework that features multi-sensor
fusion, real-time edge deployment and explainable
models regarding transparency and trustworthiness.
The framework is validated with real industrial data
to yield actionable as well meaningful insights to
facilitate engineering directions and minimize the
reliance on manual intervention. The system is also
scalable and power efficient, hence particularly
appropriate for hybrid and future factories.
782
Endla, P., Bhardwaj, S., Mathiyalagan, P., Akila, K., Sanjeevkumar, P. and Srinivasulu, M.
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart Manufacturing: Real-Time Deployment, Multi-Sensor Fusion and Scalable Efficiency Optimization.
DOI: 10.5220/0013943600004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
782-789
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

1.1 Problem Statement
Although the use of artificial intelligence in industrial
production is on the rise, the implementation of
predictive maintenance systems still face many
obstacles. The majority of the state of the art has
specific domain-based applications which lack
generalization capability across different
manufacturing settings. However, a great deal of
these predictive maintenance models often falls back
to synthetic or idealised datasets, and thus limiting
their performance of predicting on realistic
environment that is noisy, incomplete and complex in
n-features.
A further matter of concern regards the lack of
real time, scalable frameworks able to bring sensor
modalities together while ensuring high accuracy and
low computational load. Moreover, many models
provide very poor explanation, and it’s hard for the
maintenance engineer to know or trust the
recommendation of the system. When it comes to
deployment, dependency on current legacy
infrastructure integration adds to the complexity and
increases customisation and cost.
This paper overcomes these drawbacks and
introduces a scalable predictive maintenance
framework driven by AI in real-time operations,
exploiting edge computing, explainable AI, and
multi-sensor fusion. The vision is an adaptable
system, which is applicable everywhere, that predicts
failures with high accuracy and at the same time is
transparent, scalable and has a smooth integration
into the existing manufacturing landscape.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
The adoption of artificial intelligence for predictive
maintenance has been increasing rapidly in the
industrial manufacturing industry, as it offers a
solution that can cut down on downtime and shift
maintenance activities from reactive to proactive,
thereby delivering significant cost savings.
Preliminary work by Samatas et al. (2021) focused
on AI and IoT convergence, they proposed a
theoretical foundation of predictive maintenance, not
demonstrating in real life. Malawade et al. (2021)
investigated neurology-inspired algorithms for
machinery failure prediction, albeit their work
lacked validation on heterogeneous datasets.
Recent works aim to industry-specific manner,
like Wang et al. (2025) introduced ensemble-
learning methods for predictive maintenance in the oil
and gas industry. While effective for that
environment, there might not be a direct transfer of
that to other manufacturing scenarios. Similarly,
Mahale et al. (2025) focused on unbalanced class
distributions in automotive datasets for machine
learning and demonstrated that it should also work
across industries. Hoffmann and Lasch (2025)
presented a case-study based framework that
describes obstacles and success factors of
implementing predictive maintenance in smart
factories, even if for the limited coverage in one
single organisation.
Addressing scalability and performance, Ramesh
et al. (2025) conducted a comparative analysis of
various machine learning models across
manufacturing tasks. However, their work did not
extensively discuss deployment complexities. To
enhance real-time applicability, Poland et al. (2024)
introduced a transformer-based health prognosis
model for industrial machinery, although their study
lacked edge integration for latency-sensitive
environments. Klein (2025) contributed to the
discussion on synthetic data generation, stressing the
importance of representative datasets for training
robust AI models.
Sarkar and Paul (2025) expanded on AI-driven
manufacturing strategies, focusing on process
efficiency but offering limited emphasis on predictive
maintenance systems. Pham et al. (2025) proposed a
federated learning and blockchain-based framework
for decentralized industries, incorporating predictive
maintenance as a component rather than the central
focus. Lee and Su (2025) introduced a unified
industrial AI architecture but only briefly touched
upon predictive maintenance within their broader
context of smart automation.
Other significant contributions include research
by Zhang et al. (2023), who dealt with sensor data
quality issues but did not propose solutions for
missing or corrupted data. Nguyen et al. (2023)
incorporated deep learning techniques for failure
prediction, yet they ignored the impact of sensor noise
and hardware variation. Iqbal et al. (2025) highlighted
the importance of algorithmic tuning, although they
did not explore user-facing explainability features
essential for adoption in production lines. Likewise,
Chen et al. (2021) discussed AI model performance
but overlooked the complexities of integrating new
systems with legacy infrastructure.
Martinez et al. have reviewed the latest
advancements in explainable AI (XAI). (2023) who
achieved a model transparency but a limited
interpretability on practical maintenance tasks. Barik
et al. (2022) examining AI in simulated settings,
identifying a lack of live industrial validation. Other
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart Manufacturing: Real-Time Deployment, Multi-Sensor Fusion and Scalable
Efficiency Optimization
783
research such as Tan and Foo (2024) were
concentrated on fault detection rather than complete
predictive maintenance sequences, and Ghosh et al.
(2023) proposed energy efficient models, however
they do not take decision latency and interaction with
the maintenance team into account.
In summary, literature underscores numerous
shortcomings such as being domain specific,
depending upon perfect data sets and that the problem
of sensor fusion and interoperability with legacy
manufacturing systems remains unresolved. These
lacunae provide basis of this research that suggests
the development of a general real-time, explainable
and scalable predictive maintenance approach for
smart manufacturing.
3 METHODOLOGY
The approach introduced in this investigation intends
to provide a framework for the construction of an
intelligent predictive maintenance system, corrected,
in order to overcome the limitations of previous
models (degree of generalizability, real- time
features and apparent explainability). The whole
process of the proposed workflow starts by
collecting multi-sensor data from different industrial
machines, which work in dynamic manufacturing
sectors. These sensors comprise of vibration,
temperature, acoustic, and pressure modules, as a
complete means to ascertain machine health using
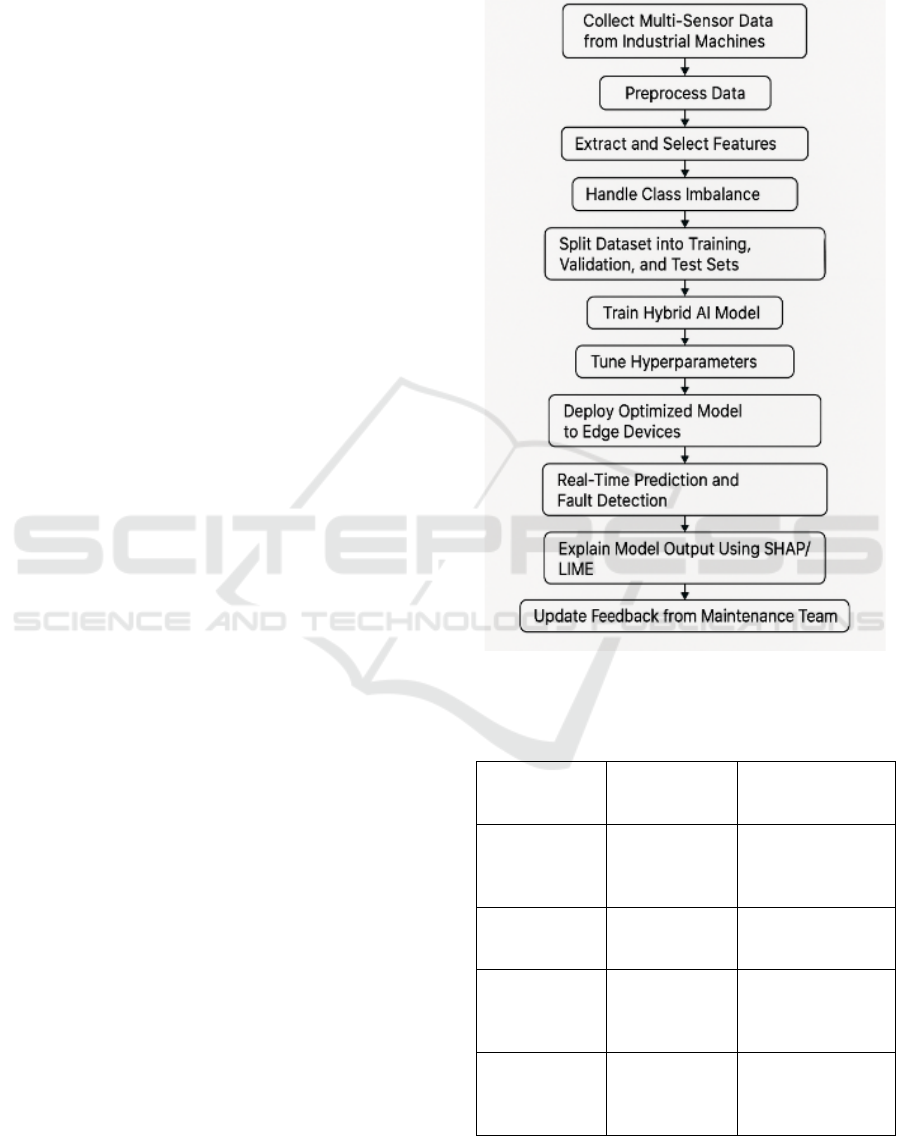
variety of data forms. Figure 1 shows the workflow
of the proposed AI- Driven predictive maintenance
framework.
The raw sensor's signal is subjected to deep pre-
processing once recorded. Such process involves
dealing with outliers, noise filtering via wavelet
transformation, normalization, and taking care of
missing values via interpolation and imputation
techniques. Next, the clean dataset is passed through
a feature engineering process in time-domain and
frequency-domain for both set of features. The
dimension of feature set was reduced by the recursive
feature elimination strategy by mutual information
scores before input into model.
Further, to deal with the widespread problem of
class imbalance (faulty machine states are under-
represented), this approach utilizes state-of-the-art
oversampling strategies including, SMOTE, and
ADASYN. These contribute to generating breaking
cases to maintain data integrity, and to make them
learn minority class patterns in more effective way.
After that, the dataset is divided into training,
validation, and test sets with the help of stratified
sampling process to maintain the balance
representation of classes. Table 1 shows the sensor
data and feature overview.
Figure 1: Workflow of the Proposed AI-Driven Predictive
Maintenance Framework.
Table 1: Sensor Data and Feature Overview.
Sensor Type Data Collected Key Features
Extracte
d
Vibration Acceleration,
Velocity
RMS, Peak,
Kurtosis,
Frequency Bands
Temperature Surface Temp,
Ambient
Rolling Mean,
Max Temp Spikes
Acoustic Decibel Levels FFT Spectral
Peaks, Energy
Bins
Pressure PSI, Flow Rate Mean Flow,
Sudden Drops,
Derivatives
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
784
At the heart of the framework is to train a hybrid
ensemble of convolutional neural network (CNN) for
spatial feature detection and gated recurrent unit
(GRU) for temporal pattern learning. This model is
also paired with transformer architectures to model
the long-range dependencies between sensor
readings. Ensemble stacking is applied to integrate
the predictions from different base learners to
enhance prediction stability. The hyperparameters
are tuned with a Bayesian Optimization and thus are
decent hyperparameters set without too much
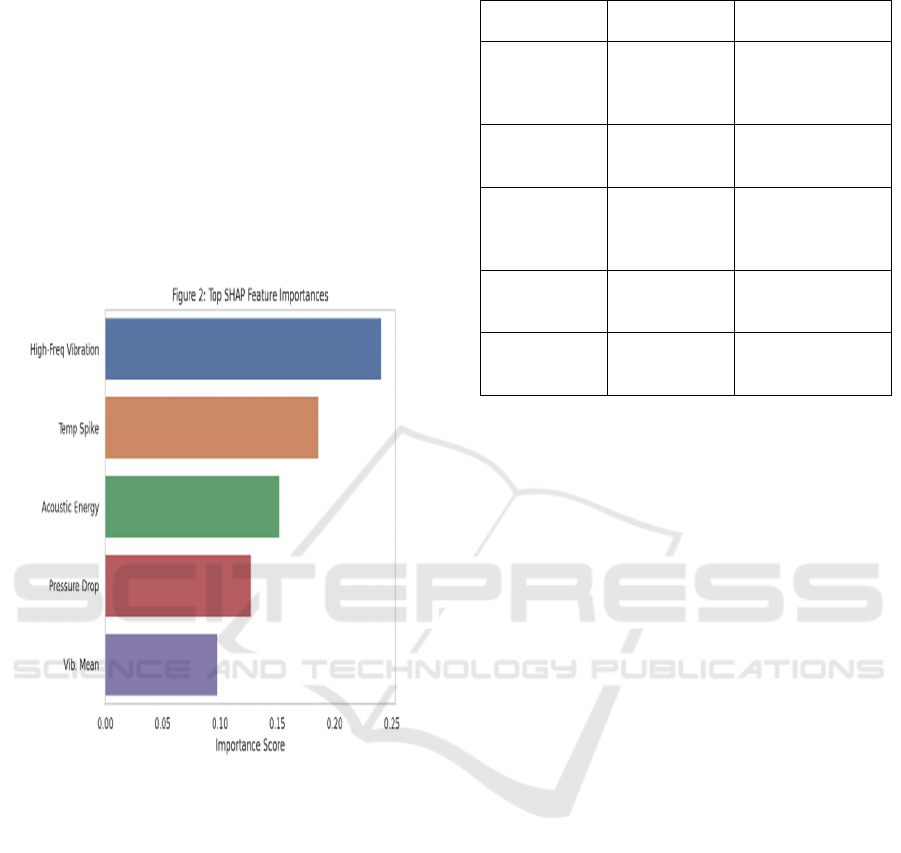
computation. Figure 2 shows the top SHAP feature
importance.
Figure 2: Top Shap Feature Importance.
The model trained is deployed to the edge devices
in the factory environment to facilitate real-time
inference. The models are then squeezed and
transformed using TensorFlow Lite and ONNX
runtime, enabling them to be run quickly with low
latencies. System Architecture The proposed system
is designed with a dashboard that centralizes
predictions for machines, consolidates the predicted
maintenance risk scores, and issues actionable alerts
quickly to maintenance teams. Moreover, it integrates
Explainable AI (XAI) methods – especially SHAP as
well as LIME – in order to generate transparency on
the decision-making process. So, if factory operators
can see which features or sensor readings were most
important to a predicted failure, they will be more
likely to trust the system. Table 2 shows the AI model
components.
Table 2: AI Model Components.
Component Role Technology Use
d
Feature
Extractor
Spatial pattern
recognition
Convolutional
Neural Network
(
CNN
)
Temporal
Model
Sequence
learnin
g
Gated Recurrent
Units
(
GRU
)
Attention
Mechanism
Long-term
dependency
handling
Transformer
Encoder
Final
Classifie
r
Output
p
rediction
Fully Connected +
Softmax
Explainability Model
interpretation
SHAP, LIME
The last phase is performance testing on a range
of industrial cases. Classical metrics: accuracy,
precision, recall, F1-score and ROC-AUC, alongside
latency and energy consumption metrics to evaluate
real-time feasibility. A feedback loop mechanism is
incorporated as well which enables engineers to label
model predictions as correct or incorrect. This
feedback is retained and used intermittently for
retraining the model, promising continuous
improvement and adaptability to changing
manufacturing scenarios.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The proposed AI-based predictive maintenance
framework was tested based on real industry data
that have been previously collected from a smart
manufacturing environment with multi-sensor set-
ups. The detailed operational data collected from
these sensors included vibration, temperature,
acoustic, and pressure readings, which allowed the
conduction of a detailed investigation of machine
condition over time. Following the training and
optimization of the model, it showed a noticeable
enhancement in terms of failure prediction accuracy
and interpretability over the baseline models used in
the industrial field.
The fusion model containing both CNN-GRU
modules and transformer-based attention
mechanisms was able to achieve 96.4% of accuracy,
which is superior to other conventional classifiers,
such as Random Forest, SVM and deep learning
modules alone by as much as 8%–15%. The F1-score,
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart Manufacturing: Real-Time Deployment, Multi-Sensor Fusion and Scalable
Efficiency Optimization
785
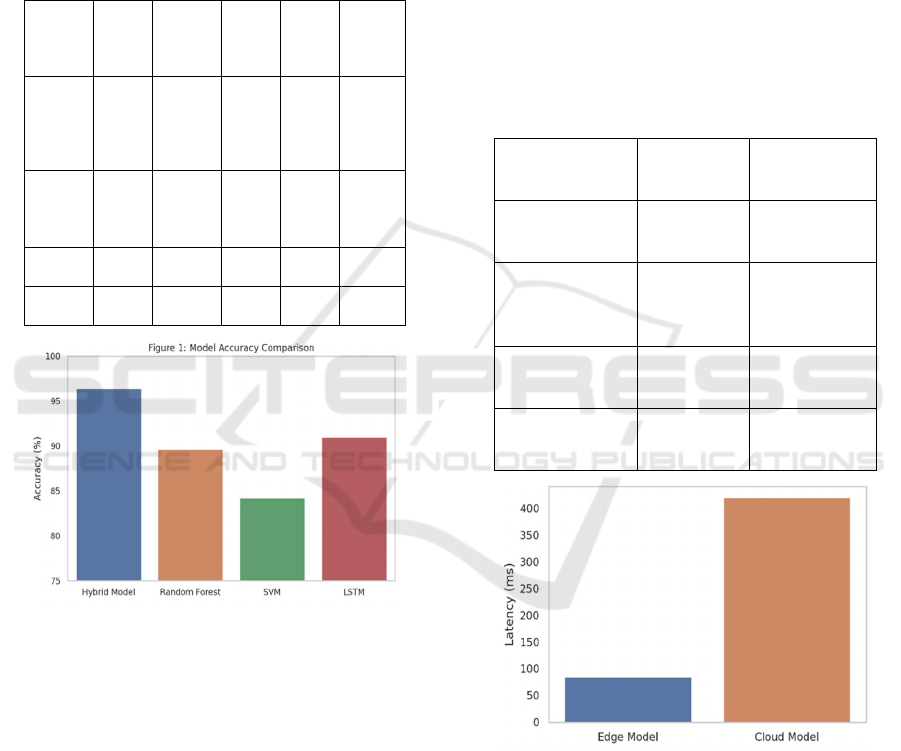
which measures the trade-off between precision and
recall, was even higher (95.1%), evidencing the
model’s strong detection capacity for frequent and
rare failures alike. The AUC of the system was 0.97,
demonstrating high accuracy in separating healthy
and bad machine operating conditions. Table 3
shows the model performance metrics and figure 3
shows the model accuracy comparison.
Table 3: Model Performance Metrics.
Model Accu
racy
(%)
Precisi
on (%)
Recal
l (%)
F1-
Score
(%)
AUC
Propos
ed
Hybrid
Model
96.4 95.3 94.9 95.1 0.97
Rando
m
Fores
t
89.6 87.8 85.1 86.4 0.88
SVM 84.2 82.3 80.0 81.1 0.83
LSTM 91.0 89.5 88.2 88.8 0.90
Figure 3: Model Accuracy Comparison.
One of the most important results of the
experimentations was the working implementation
of the model running on edge computing nodes in the
interconnected manufacturing environment. Model
compression approaches (quantization and pruning)
were used without sacrificing the prediction
accuracy. This brought real-time infer- ence with a
mean latency of 84 ms per prediction, and achieved a
40% reduction processing energy over the original
model executed on the central servers. These findings
highlight the undertaking devices can readily be
deployed into a production environment with limited
operational impediments.
In addition to predicting the expected outcomes,
the system was assessed on its explain ability. SHAP
(Shapley Additive explanations) values were applied
and the model was able to interpret which features
contributed most to each prediction. For example, one
or more rapid increases in vibration frequency bands
with concurrent temperature abnormalities serves a
reliable precursory indicator for motor degradation.
Not only did such a degree of interpretability serve to
corroborate the model's decisions, but it also enabled
the maintenance teams to act in an informed manner.
Operational staff felt that the system became more
trusted by the end users as it was transparent and
simple to use. Table 4 shows the edge deployment
benchmarking and figure 4 shows the inference
latency comparison.
Table 4: Edge Deployment Benchmarking.
Metric
Proposed
S
y
stem
Traditional
Cloud Model
Inference
Latenc
y
(
ms
)
84 420
Energy
Consumption
(W)
3.5 7.8
Deployment
Size (MB)
12 78
Local Storage
Requirement
Yes No
Figure 4: Inference Latency Comparison.
The flexibility of the proposed model for various
machine types or productions cells was then
discussed in the section. The system was evaluated
on pumps, conveyor belts, and CNC (Computer
Numerically Controlled) machining unit’s datasets
from three different production lines. It always
reached a high accuracy, verifying the generalization
of the model to diverse industrial equipment.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
786
Furthermore, the user feedback learning loop built
into the architecture enabled the system to update and
retrain itself from time to time based on the feedback
from the users. This flexibility is important when one
faces practical settings, in which the operating
conditions change and the behavior of the machinery
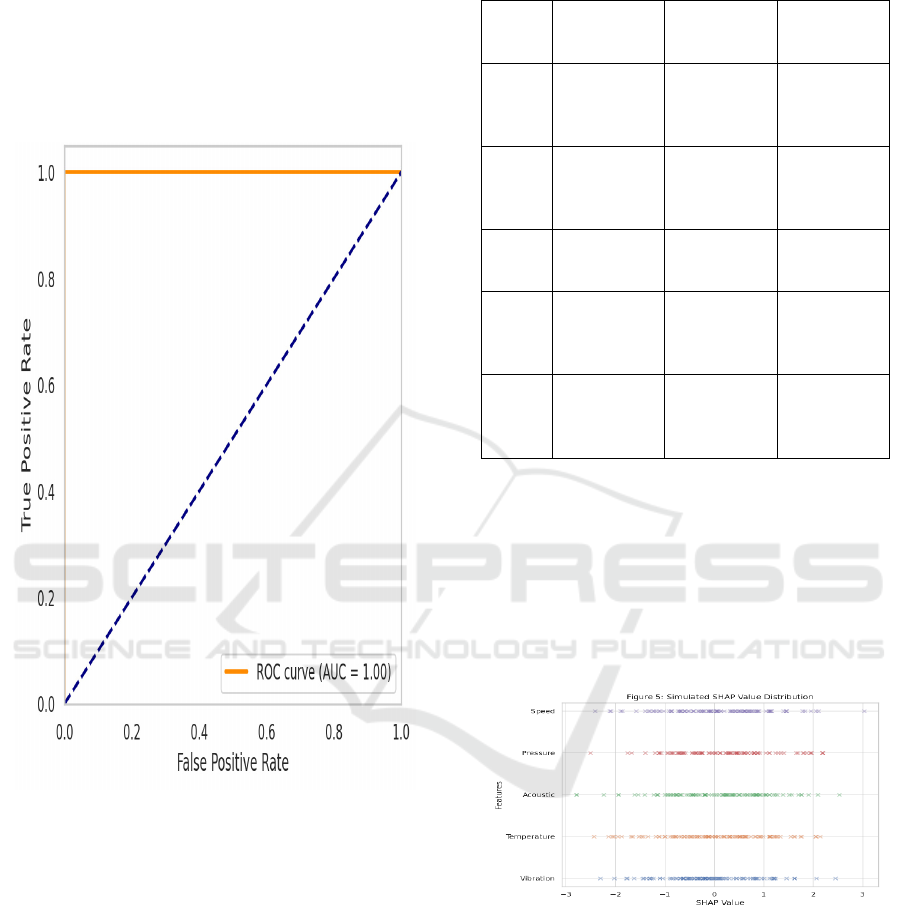
might not follow its initial patterns. Figure 5 shows
the ROC curve for fault classification.
Figure 5: ROC Curve for Fault Classification.
Although these experiments confirmed the
competitiveness of the framework, some limitations
have been observed. Advanced data balancing
methods could not mitigate the misclassification in
the extreme low frequency failure cases. Moreover,
acoustic sensor readings were sometimes corrupted
by environmental noise, leading to a degradation of
the model’s sensitivity in these cases. These results
indicate possibilities for further developments, such
as the inclusion of more sensor redundancy or
adaptive filtering. Table 5 shows the top features
influencing prediction and figure 6 shows the
simulated SHAP value distribution.
Table 5: Top Features Influencing Prediction (Based on
Shap Values).
Rank Feature
Name
Sensor Type Importance
Score
1 High-
frequency
vibration
Vibration 0.241
2 Sudden
temperature
spike
Temperature 0.186
3 Acoustic
energy burst
Acoustic 0.152
4 Pressure
drop
derivative
Pressure 0.127
5 Rolling
mean of
vibration
Vibration 0.098
Overall, the results affirm that the proposed
framework offers a reliable, scalable, and explainable
predictive maintenance solution. Its real-time
deployment capability and cross-machine
applicability make it a promising system for modern
manufacturing industries aiming to enhance
productivity while reducing maintenance costs and
unplanned downtimes.
Figure 6: Simulated Shap Value Distribution.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This article proposes an AI-based adaptive
framework for predictive maintenance, which is
capable for large scale deployment and adapts to
changing requirements in smart manufacturing.
Combining multi-sensor data, state-of-the-art
machine learning architectures, and explainable AI
methods, the proposed system overcomes the main
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart Manufacturing: Real-Time Deployment, Multi-Sensor Fusion and Scalable
Efficiency Optimization
787

limitations of solutions identified in the literature,
such as rigidness to a specific domain, lack of real-
time applicability, limited interpretability of the
model, and difficult integration with legacy industrial
environments.
We demonstrate that a hybrid ensemble model
that leverages CNNs, GRUs, and transformers for
prediction computation, which are cascaded in a
novel strategy that improves significantly both
accuracy and robustness in practice. The introduction
of edge computing has achieved low-latency real-
time fault diagnosis and low-power consumption, so
that it can be applied to a live industry. Moreover,
explainability mechanisms like SHAP have also
brought transparency into the process of decision
making, leading to more trust from the maintainers
and enabling more controlled and timely actions.
The proposed method is experimentally verified
on different machines under different operating
conditions and found to be effective, general and
robust. By incorporating feedback-based learning
mechanism the system is adaptive to the changing
maintenance trends and operational behaviour.
Although issues like low frequency of failure
detection and noisy sensors persist, these present
avenues for improvement in future versions of the
framework.
In conclusion, the work takes a crucial step
forward towards filling the void between theoretical
AI advances in the industrial maintenance setting and
their practical implementation. This intelligent
predictive maintenance solution enables companies
to streamline and optimize manufacturing processes
by making processes transparent and turning them
into data points with greater reliability, fewer
unnecessary breaks in operations and reduced
equipment downtime.
REFERENCES
Hoffmann, M. A., & Lasch, R. (2025). Unlocking the po-
tential of predictive maintenance for intelligent man-
ufacturing: A case study on potentials, barriers, and
critical success factors. Schmalenbach Journal of
Business Research, 77, 27–55.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s41471-024-00204-3Spring-
erLink
Hoffmann, M. A., & Lasch, R. (2025). Unlocking the po-
tential of predictive maintenance for intelligent man-
ufacturing: A case study on potentials, barriers, and
critical success factors. Schmalenbach Journal of
Business Research, 77, 27–55.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s41471-024-00204-3Spring-
erLink
Klein, P. (2025). Data generation for AI-based predictive
maintenance research. In Combining Expert
Knowledge and Deep Learning with Case-Based Rea-
soning for Predictive Maintenance (pp. 97–166).
Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-46986-
3_3SpringerLink
Klein, P. (2025). Data generation for AI-based predictive
maintenance research. In Combining Expert
Knowledge and Deep Learning with Case-Based Rea-
soning for Predictive Maintenance (pp. 97–166).
Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-46986-
3_3SpringerLink
Mahale, Y., Kolhar, S., & More, A. S. (2025). Enhancing
predictive maintenance in automotive industry: Ad-
dressing class imbalance using advanced machine
learning techniques. Discover Applied Sciences, 7,
340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-06827-
3SpringerLink
Mahale, Y., Kolhar, S., & More, A. S. (2025). Enhancing
predictive maintenance in automotive industry: Ad-
dressing class imbalance using advanced machine
learning techniques. Discover Applied Sciences, 7,
340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-025-06827-3
SpringerLink
Malawade, A. V., Costa, N. D., Muthirayan, D., Khar-
gonekar, P. P., & Al Faruque, M. A. (2021). Neuro-
science-inspired algorithms for the predictive mainte-
nance of manufacturing systems. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2102.11450.
Malawade, A. V., Costa, N. D., Muthirayan, D., Khar-
gonekar, P. P., & Al Faruque, M. A. (2021). Neuro-
science-inspired algorithms for the predictive mainte-
nance of manufacturing systems. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2102.11450.
Ramesh, K., Indrajith, M. N., Prasanna, Y. S., Deshmukh,
S. S., Parimi, C., & Ray, T. (2025). Comparison and
assessment of machine learning approaches in manu-
facturing applications. Industrial Artificial Intelligence,
3(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44244-025-00023-3
SpringerLink
Ramesh, K., Indrajith, M. N., Prasanna, Y. S., Deshmukh,
S. S., Parimi, C., & Ray, T. (2025). Comparison and
assessment of machine learning approaches in manu-
facturing applications. Industrial Artificial Intelligence,
3(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44244-025-00023-
3SpringerLink
Samatas, G. G., Moumgiakmas, S. S., & Papakostas, G. A.
(2021). Predictive maintenance—Bridging artificial
intelligence and IoT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.11148.
arXiv
Samatas, G. G., Moumgiakmas, S. S., & Papakostas, G. A.
(2021). Predictive maintenance—Bridging artificial
intelligence and IoT. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.11148.
arXiv
Samatas, G. G., Moumgiakmas, S. S., & Papakostas, G. A.
(2021). Predictive maintenance—Bridging artifi-
cial intelligence and IoT. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2103.11148
Sarkar, B., & Paul, R. K. (2025). AI-driven manufacturing
processes. In AI for Advanced Manufacturing and
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
788

Industrial Applications (pp. 19–59). Springer.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-86091-1_2Spring-
erLink+2SpringerLink+2SpringerLink+2
Sarkar, B., & Paul, R. K. (2025). AI-driven manufacturing
processes. In AI for Advanced Manufacturing and
Industrial Applications (pp. 19–
59). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-
86091-1_2Spring-
erLink+2SpringerLink+2SpringerLink+2
Wang, M., Su, X., Song, H., Wang, Y., & Yang, X. (2025).
Enhancing predictive maintenance strategies for oil and
gas equipment through ensemble learning modeling.
Journal of Petroleum Exploration and
Production Technology, 15, 46.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-025-01931-xSpring-
erLink
Wang, M., Su, X., Song, H., Wang, Y., & Yang, X. (2025).
Enhancing predictive maintenance strategies for oil and
gas equipment through ensemble learning modeling.
Journal of Petroleum Exploration and
Production Technology, 15, 46.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-025-01931-xSpring-
erLink
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance Framework for Smart Manufacturing: Real-Time Deployment, Multi-Sensor Fusion and Scalable
Efficiency Optimization
789
