
Keylogging in the Digital Age: Techniques, Threats and
Countermeasures
Loga Prabakar V S
1
, Mohamed Aathil A
1
, Nishanth Rajendiran
1
, Philip James
1
, J. Dhanasekar
1
and V. Gurunathan
2
1
Department of ECE, Sri Eshwar College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of ECE, Dr.Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology, Pollachi, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Keylogger, Keyboard, Encryption, Python, Wireshark, Detection and Mitigation of Keylogging.
Abstract: A keylogger, also known as a keystroke or system monitor, is a powerful technology used in particular to
monitor and record every keystroke typed on a specific device. The Usage of keyloggers is primarily for
keystrokes monitoring (i.e.) can be used for stealing sensitive data and for monitoring in unethical terms. This
paper discusses various keylogging techniques, the potential ethical implications, and provides an overview
of different types of password attacks and prevention and detection techniques to mitigate keylogger attacks
and data theft.
1 INTRODUCTION
A keylogger, either a malicious program or a spying
hardware, designed to log every single keystroke
typed into a personal computer or a mobile device
without the owner’s knowledge. These tools are a
significant cybersecurity threat, because they can
record user-typed usernames, passwords, PII, PIN
codes and other sensitive information. Keyloggers
remain hidden on systems in multiple ways, including
as hardware that is physically attached, software that
has been installed without the user's knowledge, or by
using bugs in the system that criminals then exploit to
gain unauthorized access. After they’re activated, they
create detailed logs of keystrokes and send this stolen
information to cybercriminals, who can exploit it for
identity fraud, financial theft or other malicious ends.
Keylogging attacks target individuals, businesses
and even government entities. As for single users,
stolen credentials are an open door for attackers to
sneak into sensitive informative things such as bank
accounts, web-based social networking profiles, or
others. In corporate settings, keyloggers can expose
trade secrets, classified information and private
messages that can result in financial losses and
reputational harm. For governmental institutions, the
impingement of classified materials of being accessed
without authorization leads to the great risks in the
nature of national security threats in the form of
interruptions of critical operations along with leakage
of intelligence.
The keyloggers are especially dangerous because
they usually work as invisible processes, bypassing
normal security defences. More sophisticated versions
can do things besides logging keystrokes — they
might take screenshots, analyze Web browsing and
extract email addresses, increasing their potential
damage. Due to their stealthy and adaptive nature,
they are an omnipresent and dynamic cybersecurity
threat.
To protect yourself with a holistic security
approach, as the threat of keyloggers is like no other.
This is where the most powerful anti-keylogging tools
come in to limit all these illegal threats. It is crucial to
keep operating systems and applications updated on a
regular basis, as security patches can help rectify
vulnerabilities exploited by keyloggers. User
education also plays a key role in prevention since
many infections occur via phishing scams or social-
engineering attacks. Teaching people how to identify
suspicious emails, links, and downloads can go a long
way in limiting exposure to keylogging dangers.
S., L. P. V., A., M. A., Rajendiran, N., James, P., Dhanasekar, J. and Gurunathan, V.
Keylogging in the Digital Age: Techniques, Threats and Countermeasures.
DOI: 10.5220/0013943000004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
735-742
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
735

2 TYPES OF KEYLOGGERS
Categories of Keylogger are: hardware and software.
• Hardware keyloggers - They are physical
components that are either integrated into a PC’s
core hardware or connected externally, like a
small device that goes between a keyboard and
a computer’s processing unit. They work by
collecting and memorizing keystrokes when
they move from the keyboard to the system. Yet
physical keyloggers, which are hardware
devices that record keystrokes, need direct
physical access to the target system, rendering
them rarer than their software counterparts.
• Software keyloggers - They are far more
common, because they can be installed in a
remote attack, often as a part of a malicious
download or through phishing attacks. Unlike
other malicious software, software keyloggers
do not harm the regular operation of the system
and do not even damage hardware. This allows
them to operate quietly in the background,
logging keystrokes without the user’s
knowledge. They do not directly disrupt the
system, but rather pose a security threat,
recording sensitive information like passwords,
banking details, and so on, which can be
exploited by cybercriminals for illegal activities
like identity theft, et cetera.
3 KEYLOGGER VS VIRUS
Although keyloggers are termed with cyber threats,
they are not unlawful and can serve genuine
resolutions. Organizations may implement
keyloggers to monitor employee performance,
diagnose technical issues, or ensure compliance with
workplace policies. Parents might use them to
supervise their children's online activities, and
individuals may install them to track usage on shared
computers. Keyloggers are legal when used with the
correct permissions or when used by the legitimate
owner of a device. Many of the commercially
available keylogging tools are specifically designed
for these legitimate purposes.
When keyloggers are installed in secret without
the information or knowledge of the user or owner
who owns the device, ethical and legal issues arise.
They are often abused by cybercriminals to acquire
personal or sensitive information like login
credentials, financial information, or private
conversations. Stealthier keyloggers log keystrokes
silently, take screenshots, track web activity and
intercept messages. The acquired data is transmitted
to external servers, and can be used in nefarious plans.
Risk of Unauthorized Keylogging for Individuals
and Businesses. This can result in privacy invasion
and substantial monetary loss for people. But when it
comes to corporate settings, it can lead to leaking
sensitive data, stealing IP and hurting reputation.
While keyloggers play a vital role, the potential for
misuse means that good cybersecurity practices are
critical. Regular security scans can help in inherently
preventing malicious keyloggers and sensitive
information, using anti-malware tools and raising
awareness among users which can also help in
preventing wicked activities.
4 KEYLOGGER VS SPYWARE
• Keyloggers record keystrokes; Spyware
gathers extensive information.
• Keyloggers are hard to detect; Spyware may
show noticeable signs.
• Keyloggers enable identity theft; Spyware
tracks preferences.
• Keyloggers steal sensitive data; Spyware logs
online activities.
• Both keyloggers and spyware define a
significant threat to privacy and security, as
they can collect sensitive information without
the user's consent.
5 KEYLOGGERS IN
SMARTPHONES
Physical keystroke loggers have never been much of
a concern in mobile devices, but software-based
keystroke loggers pose a severe security threat to both
Android and also iOS smartphones. Indeed, some
think that virtual keyboards preclude keylogging, but
only in principle; nefarious programs can watch for
input patterns on the screen to digital taps, swipes,
and gestures to record them. An ordinary web search
shows just how widely mobile surveillance tools are
available, a sign of the scale of the risk. These apps
don’t just capture keystrokes they take pictures of
conversations and emails, extract login credentials,
turn on the device’s camera and microphone, monitor
internet activity and even detect attached peripherals
like printers. Some (such as nations) are free to
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
736
shoehorn you into their control by shutting you out of
their curated sites.
Keyloggers for mobiles can be installed via many
techniques that are mostly conducted by keeping the
user negligence in check. If an attacker has even a few
seconds of brief physical access to any smartphone,
the attacker can install tracking software silently and
without detection. And people can unwittingly
endanger their own devices by clicking phishing links
or downloading malicious files from untrusted
sources. Keylogging threats on smartphones are
analogous to traditional computer devices,
underscoring the need for robust security measures on
all devices. To reduce the chance of infection, users
should avoid clicking on unknown links, not open
attachments from people they do not know, and keep
their devices updated with current security patches.
Staying alert and following good cybersecurity
practices are critical to protecting sensitive data from
intruders and potential cyberattacks.
6 PRACTICAL EXAMPLES OF
KEYLOGGING
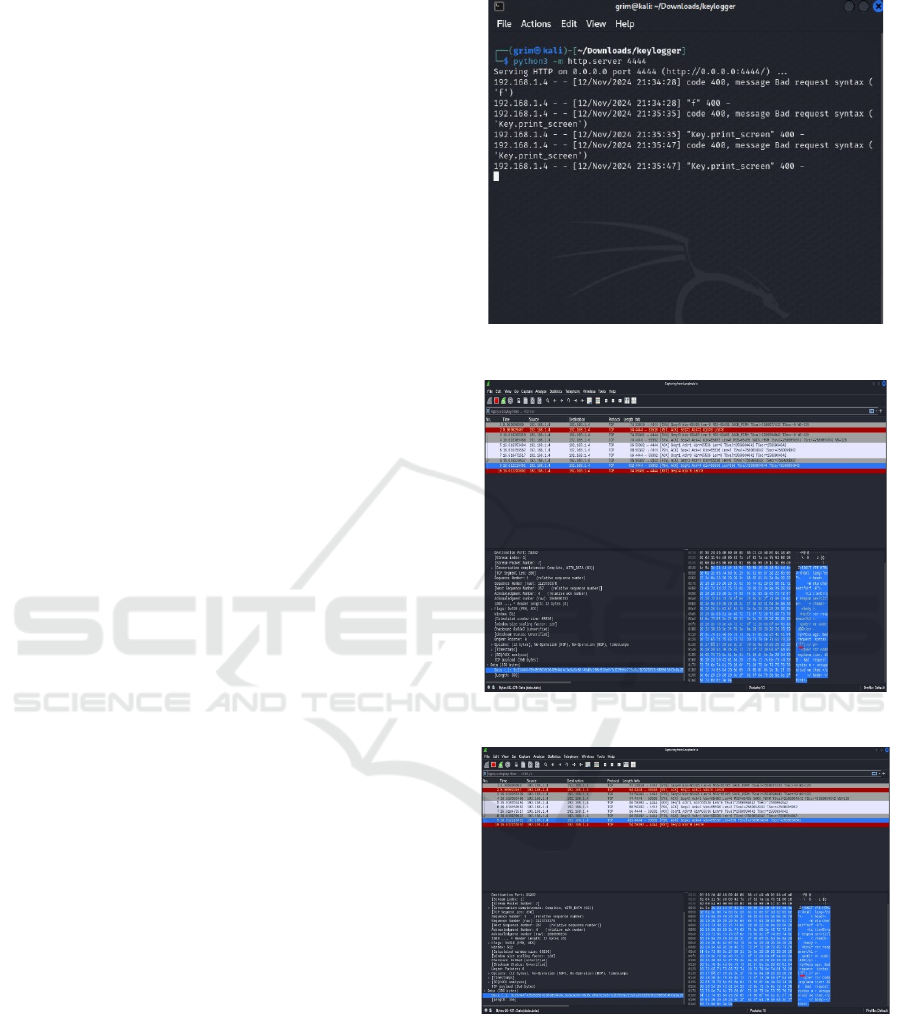
As the first step in this keylogging demonstration, we
have employed a Python script making use of the
“Pynput” module that monitors keystrokes. Pynput
KEYLOGGER A library that monitors and controls
input devices. Functioning as a keylogger where the
logs are sent to a python http server running locally
on the same computer. This configuration also
depends on the loopback interface (lo) only test,
showing that the keylogging and data capture that
happens only in the same device. In this case, the
keystroke data is set to be received at IP address
192.168.1.4 and port number 4444. Here is a
screenshot of the keylogging Python script in
operation, and hosting an HTTP server:
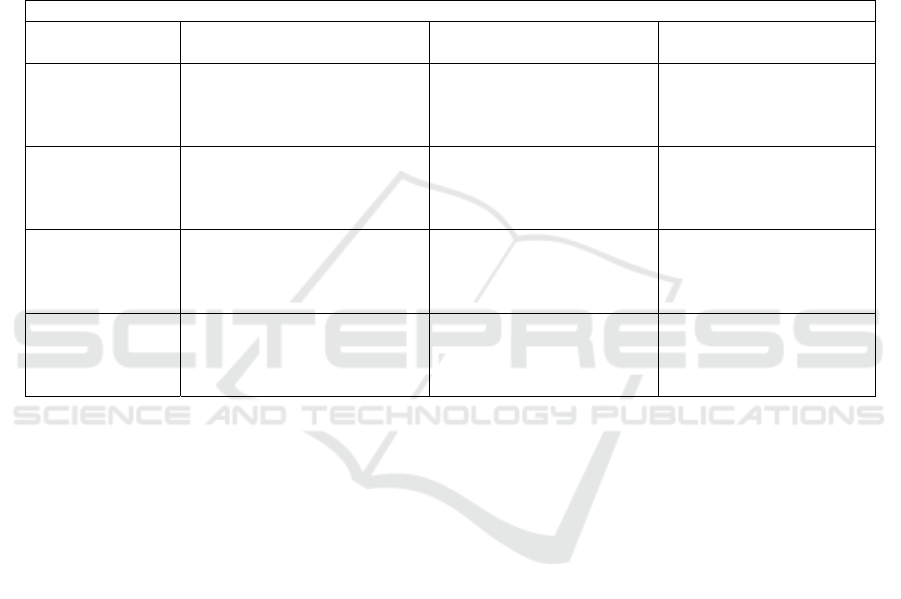
The network traffic is captured using a network
protocol analyzer, named wireshark. In Wireshark the
loopback interface is opted to trace the internal
communication between the keylogger and the HTTP
server. After executing we can see this server is
running in target machine and before this server
running keystrokes written on Kali machine is
captured by this python script and send it over
loopback interface. In Wireshark, it will capture these
packets, but, since we are interested in analyzing
[PSH, ACK] packets, so taking our key until finding
the [PSH, ACK] packets that are regularly used to
push data from the sender and the receiver.
Figure 1: Hosting a Python Server.
Figure 2: Capturing the Packets.
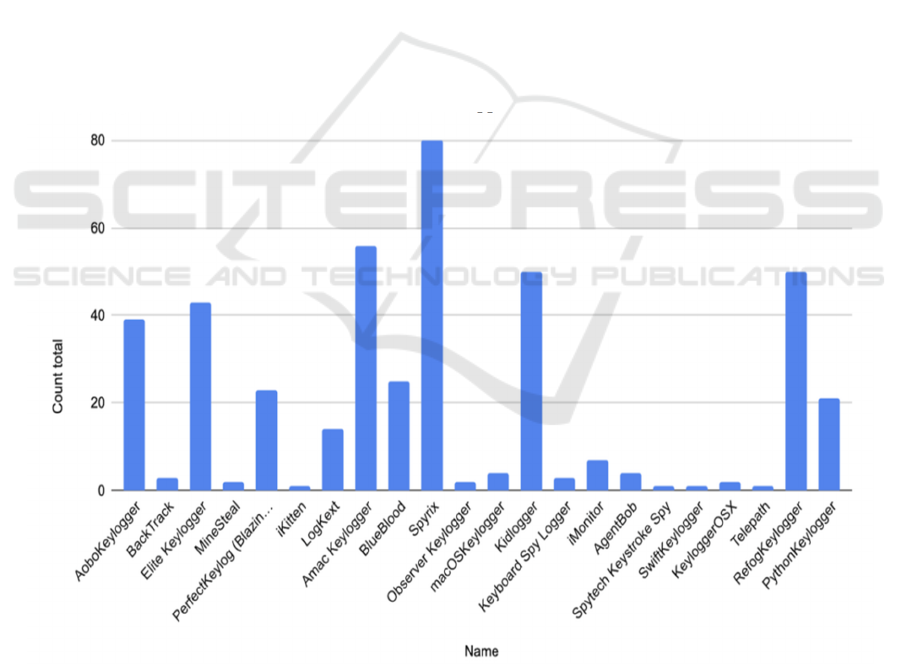
Figure 3: Keystroke Captured.
Curiously, by double-clicking the packets the
payload with the keystrokes may be viewable. Here,
we can see the Wireshark capturing the network
traffic, focusing on the [PSH, ACK] packet:
Lastly, the seized information is scrutinized to
uncover the keypresses in an HTML file. The output
on Wireshark demonstrates clearly how the
keystrokes can be intercepted and analyzed since they
Keylogging in the Digital Age: Techniques, Threats and Countermeasures
737
are sent to the HTTP server. This example
demonstrates both the local capture of keystrokes
using python and transmission of those keystrokes
over the network, as well as analysis with Wireshark.
It underscores the potential security risks posed by
keyloggers and the importance of monitoring network
traffic for suspicious activity.
7 KEYLOGGING IN
CYBERSECURITY THREAT
MODELS
Table 1: Keylogging in Threat Models.
Keylogging in Threat Models
Keylogging
Attac
k
Scenario
Description Impact on Victim Mitigation Strategies
Social
Engineering
Attacks
Attackers use keyloggers to
capture sensitive information
from victims tricked into
p
rovidin
g
credentials.
Exposure of login
credentials, personal data,
and financial information.
Employee training,
phishing detection tools,
multi-factor
authentication.
Advanced
Persistent Threats
(APTs)
APT groups use keyloggers to
monitor targets over long
periods for espionage and data
exfiltration.
Long-term data theft,
intellectual property loss,
and national security risks.
Network segmentation,
endpoint detection, threat
intelligence sharing.
Credential
Harvesting
Keyloggers silently collect
usernames and passwords for
unauthorized access to
s
y
stems.
Unauthorized access to
corporate systems, financial
accounts, or email.
Strong password policies,
use of password managers,
and secure authentication
p
rotocols.
Ransomware and
Extortion Attacks
Keyloggers are used in
conjunction with ransomware
to steal sensitive data before
encr
yp
tin
g
files.
Data theft, ransom demand,
and loss of critical business
operations.
Backup strategies,
encryption, network
isolation, and security
monitorin
g
.
8 FOUR WAYS TO DETECT AND
PREVENT KEYLOGGER
ATTACKS
8.1 Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware
Software
Installing antivirus or anti-malware software
programme on all user devices is a foundational step
for many types of attacks that include keylogging also.
These tools can very well understand the functioning
of any keylogger programme and eliminates them and
this serves as a basic, number one defence mechanism.
One main thing to remember doing is to update the
anti-virus or anti-malware software in order to defend
futuristic and complex keyloggers.
Many contemporary antivirus solutions have been
offering real-time safety, actively monitoring the
device behaviour for signs of suspicious or
keylogging-based activity. For improved safety, using
the special anti-keylogger software would do the
neutralization of threats related to keylogging.
8.2 Monitor Keyboard and Mouse
Activity
Tracking keyboard and mouse interactions can assist in
spotting anomalies that might suggest a keylogger’s
presence. Indicators include lag between pressing keys
and text appearing, erratic pointer behaviour, or an
unresponsive keyboard. Dedicated programs can
examine input patterns and notify users of unusual
activity.
For instance, applications like Keylogger Scanner
can monitor keystroke behaviour to uncover potential
keylogging threats. Physical security measures, such as
USB tracking devices, can identify unauthorized
peripherals attached to a system. Consistently
analysing these records can aid in the early detection
of keylogging attempts.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
738

8.3 Implement Strong Access Controls
Firm access limitations are important in stopping
brute-force assaults and as a result decreasing the
consolation of those keylogger invasions. Restrict
admin access to only trusted personnel, requiring them
to use strong, unique passwords in conjunction with
multi-factor authentication (MFA) for additional
security.
Establish strong access management practices,
such as regular changes of passwords and prohibitions
against installing unauthorized software. Going a step
further, employing network segmentation prevents
sensitive data from co-mingling with lower security
zones. In addition, deploy endpoint detection and
response (EDR) solutions for cybersecurity threat
detection and response on all connected devices.
8.4 Monitor Network Traffic
Monitoring network activity is an important step to
detect keyloggers that send captured keystrokes to
remote servers. Use intrusion detection (IDS) and
intrusion prevention (IPS) systems to monitor traffic
for anomalies or links to share the IP address. By
establishing alerts for anomalous network activity, you
can help detect possible keylogging threats.
Implementing a Security Information and Event
Management (SIEM) provides insight into network
activity while generating alerts for suspicious behavior
patterns. Monitoring Network logs and configuring
automatic tools to explore normal traffic behavior can
reveal the presence of keyloggers trying to obfuscate
the data. Losers will also be those with weak
keylogging policies or those who do not enforce
encrypted communication protocols and data
exfiltration policies as this reflects easily in threat
intelligence data.
9 ROLES OF KEYLOGGING IN
THREAT MODELING
9.1 Asset Identification
Keylogging specializes in recording user details like
passwords, bank information, and private messages. In
the case of the attack, these assets are the main target,
as they can be exploited, for example, to commit fraud
or gain unauthorized access.
9.2 Entry Points
They can be deployed via phishing, through a
malicious download, or even by hardware tampering.
Opportunist cybercriminals exploit forgotten
vulnerabilities such as unsecured input fields or
outdated software to implant keyloggers and eavesdrop
on critical data.
9.3 Attack Vectors
Keyloggers can be delivered through phishing emails,
social engineering, malware, physical access, or
software vulnerabilities. These vectors can allow an
attacker to deploy keylogging tools invisibly and
extract sensitive information.
9.4 Adversarial Goals
The primary goals of attackers include:
• Stealing credentials for identity theft or
unauthorized access.
• Collecting sensitive communication data
for intelligence purposes.
• Monitoring user behaviour for espionage
or malicious activities.
10 KEYLOGGER INCIDENTS
10.1 Starwood Data Breach (2018)
In 2018, a chain of hotels disclosed another data breach
that had remained undetected for four years after it
acquired Starwood properties. Attackers distributed
keyloggers, trojans, and memory scrapers across 480
systems in 58 locations starting in June 2014, stealing
over 330 million personal records. The breach
underscored the difficulties of detecting and
addressing multiyear cyber threats.
10.2 Keyloggers on HP Laptops (2017)
In 2017, a security researcher named Michael Myng
stumbled upon a keylogging vulnerability within
software drivers that were pre-installed on HP laptops.
These drivers, originally intended to help with
keyboard functionality, led to an important security
flaw which left more than 460 laptop models open to
exploitation. In response to the incident, HP rolled out
a patch for the vulnerable component, but the episode
highlighted concerns over vulnerabilities that could be
hidden in pre-installed applications.
Keylogging in the Digital Age: Techniques, Threats and Countermeasures
739
10.3 POS Keylogger on Netwire (2016)
This led to the detection of a new remote access Trojan
(RAT) called NetWire, which was used to steal
payment card information, which was uncovered by
Secureworks security analysts in 2016. Unlike the
traditional POS malware, NetWire are also equipped
with a keylogger which is to pick up the keystroke data
from users' USB card readers. With poor security
measures at these terminals, attackers delivered this
malware to POS terminal employees via phishing
emails, allowing them to unobtrusively harvest data for
long periods of time.
10.4 Tesla Keylogging Incident (2018)
Back in 2018, Tesla sued ex-employee Martin Tripp,
claiming he developed a keylogger that fed sensitive
company information to the outside world. The lawsuit
alleged that Tripp stole gigabytes of confidential
information, such as videos of manufacturing
processes, financial data and data on Model 3 battery
production. It highlighted the systemic risks of insider
threats and the need for strong data protection
protocols.
11 THE KEYLOGGER FAMILY
As a malware category, keylogging covers a broad
spectrum of types and functionalities; understanding
its fundamentals is thus crucial. While keyloggers
have the potential for ethical use, they are typically
used in a nefarious manner. The following bar chart
illustrates the progress of keyloggers with respect to
their types, with a shift from legacy hardware to
software versions and have developed a lot in terms of
features. These findings serve as a reminder that there
is no time for complacency in cyber security.
Working in tandem with researchers, developers,
and security experts is crucial as keyloggers grow
increasingly sophisticated and less detectable.
Furthermore, user education on the dangers and
indicators of keyloggers and wider security practices
will go a long way to reduce the impact of these
applications.
Figure 4: Keylogger Family.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
740

12 ETHICAL AND LEGAL
CONSIDERATIONS
As their name suggests, the standard keylogger is
designed to capture and record key presses, secretly
capturing sensitive information including passwords,
private messages, and other sensitive information.
Their development and deployment raise big ethical
questions, especially about privacy and consent. The
main ethical concern is whether or not these
keyloggers should be used without the user's consent.
Users misuse those tools for criminal activities like
identity theft and financial fraud etc, this is undeniably
a grave invasion of privacy. But there’s a moral
calculus that needs to be done to ensure that people
utilize keylogging technology effectively.
The legality of keyloggers is a bit of a grey area,
and the use of them often raises serious privacy and
consent considerations. Keyloggers can be used
legally in cases like this, where potential use is
tracking keyboard activity of employees, assuming
they have given explicit consent and have a valid
justification for contact. However, they may also be
abused that result in serious invasion of privacy that
are highly regulated by laws such as the General Data
Protection Regulation (GDPR) (EU). Those legal
requirements need to be addressed and it is upon
organizational groups to be responsive, lest they face
the repercussions while also upholding protection
provisions for employees against individuals. Such
rules are important in reducing legal and ethical risks.
From an ethical point of view, there are numerous
caveats in the use of keyloggers by developers and
users alike that prevent them from falling into
unethical catagories. The consent to use these tools
must be proper with justification and they should be
accessible to the concerned parties. Transparency is
crucial: people must understand fully, the reasons,
process and timing of their surveillance. Since
accountability and trust are important, it is good to
always document and get a written consent as well.
This and a few other measures ensure that without
them the use of key loggers is an unethical behavior
and an invasion of the right to privacy of individuals.
This should all be done under a set of protocols to
ensure that this is happening in an ethical and lawful
manner. Installing a keylogger requires the permission
of all participants. This means getting all parties to
send a written agreement, which should outline how
we will be monitoring. That includes encrypting data
collected, using secure storage mechanisms and
applying fine-grained access controls. These steps
ensure sensitive data is not only protected against
unauthorized access and abuse but they are also
protected. Data Protection is the only solution to
eliminate all perils from the key logger.
Finally, periodic audits and compliance
assessments would be required to maintain adherence
to privacy laws and ethical standards. The purpose of
the audits is to recognize and eliminate possible
vulnerabilities in the monitoring process. This is just
one way to enable developers and users to employ
keyloggers while providing these significant
precautions to balance their positive benefits with the
ethical issue of preserving individual privacy. Not
only is this approach protective of sensitive data, but
it also builds trust and accountability, injecting it into
the use of monitoring technologies.
13 DEFENCES AGAINST
KEYLOGGERS
13.1 Behavioural Biometrics
Behavioral biometrics are good at differentiating
activity as an individual computer user carefully
follows an individual routine that identifies the user
from all others accessing that user’s computer, and can
thereby detect anomalies that flag a keylogger. This
and other techniques like this are hard to implement,
however this is very effective especially in high
security environments. For most of us, fingerprint or
facial biometrics, with much less data required, offer
sufficient security functions. NIST’s SP 800-63B
details a number of best practices to help protect users,
illustrating, for example, how multi-factor
authentication and biometric verification dramatically
reduce the risk of credential stealing showing how
user behavior can scale security exponentially.
13.2 System Audits and File Integrity
Monitoring
Logs are invaluable tools in malicious code detection;
the standard system audit identifies the file or
configuration changes that hide keyloggers. Other
software tools, such as Windows Defender’s file
integrity monitoring, can notify customers of
suspicious changes. Use MacOS Activity Monitor or
Windows Task Manager to spot suspicious packages
or actions. That gear has a technical sound to it, but do
have a relative effectiveness.
Keylogging in the Digital Age: Techniques, Threats and Countermeasures
741

13.3 AI-Driven Security Tools
AI-powered protection solutions are in evolution to
turning into extra handy to users and businesses.
Malwarebytes and Norton Antivirus use AI to
discover and reply to suspicious sports in actual-time.
With the aid of continuously learning and adaptability
to new threats, these tools are notably effective against
superior keylogger strategies. The MIT review on AI
and Cyber protection depicts the role of AI in
detecting complex threats, giving clarity in its
growing significance in the fight in opposition to
keyloggers.
REFERENCES
Securelist, "Working of Keyloggers," Available:
http://securelist.com/analysis/publications/36138/keylo
ggers-how-they-work-and-how-to-detect-them-part-1.
C. A. Rajendra, Keylogger in Cybersecurity Education,
Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, New
York, USA.
M. Aslam, R. N. Idrees, M. M. Baig, and M. A. Arshad,
"Antihook shield against software keyloggers," in
Proceedings of the National Conference of Emerging
Technologies, 2004.
E. S. L. Martignoni, M. Fredrikson, S. Jha, and J. C.
Mitchell, "A layered architecture for detecting malicious
behaviors," Springer, Heidelberg, 2008.
C. Y. D. Le, T. Smart, and H. Wang, "Detecting kernel-level
keyloggers through dynamic taint analysis," College of
William & Mary, Department of Computer Science,
Williamsburg, 2008.
C. G. S. Ortani and R. Crispo, "Bait your Hook: A novel
detection technique for keyloggers," University of
Trento, Via Sommarive, Trento, Italy, 2010.
S. S. Anith, "Detecting keylogger based on traffic periodic
behavior," PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore,
India, 2011.
A. Davis, "Hardware Keylogger Detection," White Paper,
2007.
T. V. Wilson and J. Tyson, "How computer keyboards
work," HowStuffWorks.com, 2008. Available:
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/keyboard.htm.
"Overview of detecting key loggers," Available:
http://www.sandboxie.com/.
"Keylogger detection," Available:
https://www.ijcst.org/Volume5/Issue2/p5_5_2.pdf.
"Cyber Security Statistics," Available:
https://purplesec.us/resources/cyber-security-statistics/.
"Keystroke logging (Keylogging)," Available:
www.researchgate.net/publication/228797653_Keystro
ke_logging_keylogging.
D. Wampler and J. H. Graham, “A normality-based method
for detecting kernel rootkits,” ACM SIGOPS Operating
Systems Review, vol. 42, no. 3, 2008.
K. Kasslin, “Kernel malware: The attack from within,” in
the 9th Annual AVAR International Conference, 2008.
A. Baliga, L. Iftode, and X. Chen, “Automated containment
of rootkit attacks,” Computers & Security, vol. 27, no.
7-8, pp. 323–334, 2008.
B. Whitty, “The ethics of key loggers,” Technibble.com,
Jun. 2007. [Online]. Available: http://www.
technibble.com/the-ethics-of-key-loggers/. [Accessed:
Dec. 8, 2011].
ThinkGeek.com, “Spy keylogger,” 2010. [Online].
Available:
http://www.thinkgeek.com/gadgets/security/c49f/.
[Accessed: Dec. 15, 2011].
Cyveillance, “Online financial fraud and identity theft
2007,” 2007. [Online]. Available: http://www
.cyveillance.com/web/news/press_rel/2007/2007-03-
27.asp. [Accessed: Oct. 2011].
D. Stefan, C. Wu, D. Yao, and G. Xu, “Cryptographic
provenance verification for the integrity of keystrokes
and outbound network traffic,” in Proc. 8th Int. Conf.
Applied Cryptography and Network Security (ACNS),
Jun. 2010.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
742
