
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real‑Time
Object Detection in Robotics
D. Jayalakshmi, P. Arivazhagi and K. Dhivyalakshmi
Department of ECE, Arasu Engineering College, Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Very Large‑Scale Integration, Field Programmable Gate Array, Deep Learning, Object Detection, Robotic
Vision, Adaptive Sparse Convolutional Neural Network, Hardware‑Aware Low‑Latency YOLO.
Abstract: Very Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) technology is one of the fastest-growing sectors, having made it possible
to gain deep learning models for real-time object detection in the robotics world. Almost the very traditional
way of deep learning-based object detection is the thorough need of graphical processing units (GPUs) and
cloud-based processing, which have a major disadvantage in terms of latency and power inefficiencies. The
article shows the prospect of using VLSI as an alternative to speed up the computations of deep learning
models that are used in the robot's application, and to decrease the power consumption and data speed as well.
The use of designs that are customized through hardware architectures strengthens the real-time abilities of
the visual of robots, making them more suitable for edge-based self-governing choice-making. In comparison
to conventional GPU-based resolutions, the research introduces an optimized Field Programmable Gate Array
(FPGA)-based hardware accelerator meant for deep learning models to enable faster inference with
dramatically decreased power consumption. Moreover, besides the implementation of a hybrid method
involving quantization and pruning in VLSI circuits, the memory footprint is also reduced, and the
computational overload is kept low, while the detection accuracy remains high. By introducing two innovative
algorithms, the most recent advancement in robotics is achieved with a single stride. An adaptive sparse
convolutional neural network (ASCNN) is a dynamically adjustable network that maintains the number of
active neurons and convolutional filters in accordance with the complexity of the input image. This method
enhances the efficiency of computation and improves the precision of detection. However, the Hardware-
Aware Low-Latency YOLO (HALO-YOLO) is a refined version of the YOLO model that is specifically
designed for FPGA and ASIC hardware devices. This results in a significant reduction in the consumption of
computing resources in a short amount of time, as well as the rapid and efficient detection of objects.
Experimental evaluations that verify the implementation of VLSI-based deep learning and these two
algorithms demonstrate that they are capable of achieving low-latency object detection, which is appropriate
for real-time surveillance applications, industrial automation, and autonomous robotics. Based on the results,
it can be inferred that the hardware-aware optimisation of the deep learning model in robotics is a suitable
method for real-time object detection. This research establishes the groundwork for the future investigation
of AI accelerators that are low-power and high-speed, specifically designed for autonomous robotic vision
systems.
1 1 INTRODUCTION
The integration of deep learning with autonomous
systems has significantly advanced real-time object
detection in robotics, enabling machines to perceive
and interact with their environments effectively
(Girshick, 2015; Ren et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2016;
Redmon et al., 2016). Conventional deep learning-
based object detection relies on high-performance
GPUs and cloud processing, which introduces high
energy consumption, latency, and dependency on
external computational resources (Sze et al., 2017).
These limitations render traditional methods
unsuitable for real-time applications with resource-
constrained robotic systems that demand low-latency
decision-making and power efficiency.
To address these challenges, Very Large-Scale
Integration (VLSI) technology offers a viable
hardware-level solution that enhances the operational
efficiency of deep learning models. Specifically,
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) and
718
Jayalakshmi, D., Arivazhagi, P. and Dhivyalakshmi, K.
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real-Time Object Detection in Robotics.
DOI: 10.5220/0013942700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
718-726
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs)
serve as custom hardware accelerators, providing
advantages such as reduced power usage, improved
computational throughput, and real-time processing
capabilities (Horowitz, 2014; Jacob et al., 2018).
Optimizing deep learning techniques for edge-based
object detection using these hardware platforms is
crucial for responsive and efficient robotic
applications.
This paper proposes two innovative technologies
for improving real-time object detection using VLSI
platforms. The first is a custom FPGA-based deep
learning accelerator optimized for inference
efficiency and minimal power consumption
compared to GPU-based alternatives. The second is a
hybrid quantization and pruning technique embedded
in VLSI design to reduce memory overhead while
maintaining high detection accuracy (Han et al.,
2015; Wu et al., 2016). Additionally, the study
introduces:
Adaptive Sparse Convolutional Neural Network
(ASCNN): A dynamic architecture that adapts to
image complexity by activating only essential
neurons and filters, improving energy efficiency
without compromising accuracy.
Hardware-Aware Low-Latency YOLO (HALO-
YOLO): A modified YOLO-based model optimized
for FPGA/ASIC deployment to reduce redundant
operations and enable ultra-fast object detection on
limited hardware resources.
These contributions aim to establish a robust
foundation for scalable, embedded AI accelerators
suited to robotics, automation, and surveillance
systems, advancing the state of real-time, energy-
efficient object detection.
2 RELATED WORKS
FPGA-based object detection hardware research
demonstrates that deep quantization significantly
improves processing efficiency. Nakahara et al.
(2018) proposed a lightweight version of YOLOv2,
introducing a binarized neural network (BNN) model
accelerated by a parallel support vector regression to
address the numerical degradation typical in binary
models, although external memory access remains a
performance bottleneck. Preuser et al. (2018)
introduced Tincy YOLO, which uses 1-bit weights
and 3-bit activations; however, both the input and
output layers are processed in software due to
complexity constraints.
Nguyen et al. (2019) developed Sim-YOLO-v2,
employing 1-bit weights and 4–6-bit activations
along with a streaming accelerator to minimize
external DRAM access and power usage. Huang et al.
(2021) proposed CoDeNet, incorporating deformable
convolutions and input-adaptive patterns, quantized
with 4-bit weights and 8-bit activations, targeting
FPGA deployment for efficient object detection.
Kim et al. (2021) presented SSDLite, integrating
MobileNetV2 (Sandler et al., 2018) as its backbone.
While it lacks aggressive quantization, its system
architecture maximizes throughput via dedicated
processing units and task control modules.
YOLO models, originally introduced by Redmon
et al. (2016), remain among the fastest object
detection algorithms. YOLOv2 (Redmon and
Farhadi, 2017), which uses DarkNet-19 as its
backbone (akin to VGG-19), predicts bounding boxes
across a grid-based input with anchor boxes. The
model outputs 125 values per grid cell, including
spatial coordinates, objectness confidence, and
classification scores. Non-maximum suppression
(NMS) is subsequently used to refine predictions.
Despite increased accuracy in newer versions such as
YOLOv3 (Redmon and Farhadi, 2018) and YOLOv4
(Bochkovskiy et al., 2020), these come at the cost of
larger and more complex backbone networks.
For hardware implementation, early YOLO
versions are preferred due to their simplicity. For
instance, YOLOv2 and its variants have been
effectively mapped onto ASICs (Chen et al., 2019;
Yin et al., 2017) and FPGAs (Nakahara et al., 2018;
Preuser et al., 2018; Nguyen et al., 2019), making
them ideal for real-time, energy-efficient robotic
applications.
3 PROPOSED WORK
Here is the latest implementation plan that focuses on
the hardware design of the VLSI using deep learning
for real-time object detection of robots. This approach
is broken down into three principal pieces: hardware-
optimized deep learning model deployment, custom
FPGA-based hardware accelerator design, and novel
algorithmic enhancements for efficient object
detection. These components provide a joint solution
ensuring high-speed inference, low-energy, and
prompt decision making for autonomous robotic
applications.
Hardware-Optimized Deep Learning Model
Deployment: Deep learning architectures, in
particular CNNs, require massive quantities of
multiplication and summarization (MAC) activations
in the convolution layers. Real-time processing is the
most important task to be done by the reduction of
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real-Time Object Detection in Robotics
719
such operations, especially on FPGAs hardware
which is constrained by resources. In this way of
getting the computation efficiency optimized, we use
the techniques of quantization and pruning which lead
to a significant reduction of the computer memory
footprint and a decrease the computational
complexity of the deep learning model but still have
a high accuracy rate.
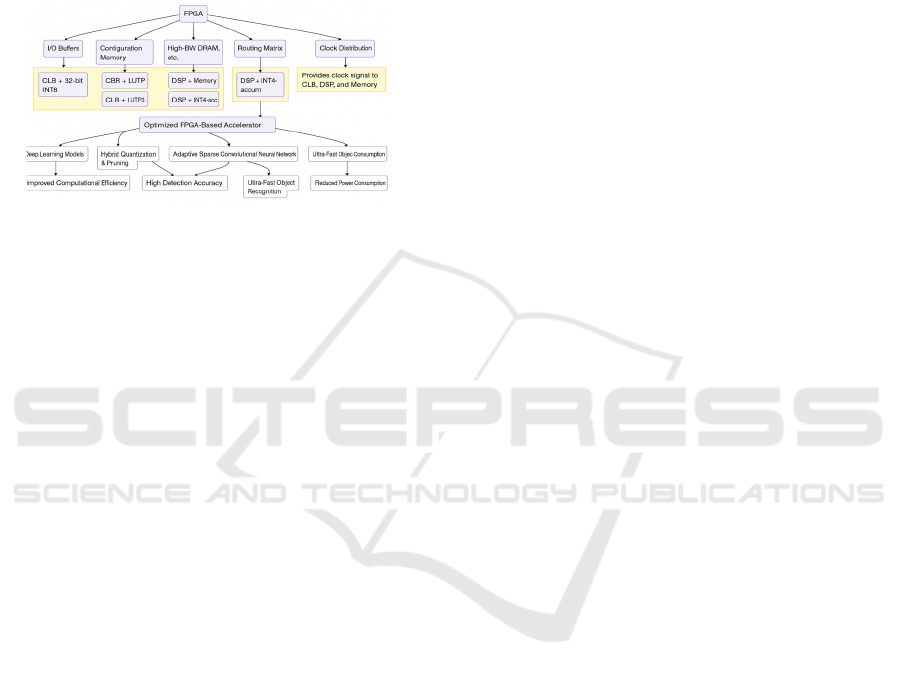
Figure 1: Schematic representation of the suggested
methodology.
Quantization
In the context of machine learning, quantization
technique, which is the mapping of data to the lower
precision, is one that saves power and reduces the
complexity of the hardware implementation by
replacing high-precision floating-point computations
with low-bits fixed-point arithmetic, which is the
quantization of that transformation
𝑊
=round
(
𝑊×2
)(
1
)
where:
• 𝑊
is the quantized weight,
• 𝑊 is the original floating-point weight?
• 𝑏 is the bit-width used for quantization (e.g.,
8 -bit instead of 32 -bit).
FPGA hardware can be designed to carry out the
fixed-point type multiplication instead of the floating-
point one for the very same functionality, so that a
great amount of energy can be saved. The convolution
with quantized weights can be rewritten as:
𝑂
=
𝐼
(𝑖) ⋅ 𝑊
(𝑖) (2)
where:
• 𝑂
is the quantized output feature map?
• 𝐼
(𝑖) represents the input activations after
quantization,
• 𝑊
(𝑖) represents the quantized weights.
Using an 8-bit representation significantly reduces
memory bandwidth requirements, allowing for faster
processing while maintaining acceptable accuracy.
Pruning: Pruning is the elimination of irrelevant or
low-weight connections in the network, thereby
decreasing the calculation effort needed for inference.
The primary cause of memory usage and
computational complexity is weight-like pruning,
therefore, to get rid of them, but with the help of the
accuracy of the network.
The weight pruning process is defined as:
𝑊
=𝑊⋅ 𝑀 (3)
where:
• 𝑊
is the pruned weight matrix?
• 𝑊 is the original weight matrix?
• 𝑀 is a binary mask, defined as?
𝑀
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
=
1, if
|
𝑊
(
𝑖,𝑗
)|
>𝑇
0, otherwise
(4)
In this instance, T is a threshold, the value of which
can be ascertained by the advised energy-concious
optimization technique-based practices applied for
removing the finally unimportant nodes from the
network. After cutting back, the convolution
operation will be only executed on non-zero weight
connections, which reduces computational cost:
𝑂
=
(,)∈
𝐼
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
⋅𝑊
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
(5)
where 𝑆 represents the set of active weights after
pruning.
Pruning results in:
• Lower computational overhead
• Reduced memory access latency
• Faster inference times
FPGA-Based Hardware Accelerator Design: The
FPGA accelerator developed for deep learning is
based on a custom solution which can be efficiently
offloaded by a convolution block for convolutions,
activators, and pooling operations. The process of
convolution makes it the most computationally
significant part of CNN inference. To perform the
operation of a convolution the convolution layer uses
a number of windows as filters and this process
becomes the operation of element-wise multiplication
and summation. It is then formulated as follows:
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
720

𝑂
(
𝑖,𝑗,𝑘
)
=
𝑊
(
𝑚,𝑛,𝑘
)
⋅𝐼
(
𝑖+𝑚,𝑗+𝑛
)(
6
)
where:
• 𝑂(𝑖,𝑗,𝑘) is the output feature map?
• 𝑊(𝑚,𝑛,𝑘) is the convolution kernel,
• 𝐼(𝑖+𝑚,𝑗 +𝑛) is the input feature map?
• 𝑀,𝑁 are the kernel dimensions.
To accelerate this operation in FPGA hardware, we
introduce:
• Parallel Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) units
• Dataflow optimizations for reduced memory
latency
A pipelined parallel MAC unit is implemented to
an efficiently execute multiple operations
simultaneously:
𝑂(𝑖,𝑗,𝑘) =
,
(𝑊(𝑚,𝑛,𝑘)⋅𝐼(𝑖+𝑚,𝑗+𝑛))(7)
where the multiplications are performed in
parallel across FPGA logic blocks, reducing latency
and power consumption.
The ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation
function introduces a non-linearity in deep learning
models, ensuring feature importance selection in
CNNs. The standard ReLU activation is defined as:
𝐴
(
𝑥
)
=max
(
0,𝑥
)
(8)
Instead of performing floating-point comparisons,
FPGA-based implementations use bitwise logic
operations, significantly improving efficiency:
𝐴
(
𝑥
)
=𝑥⋅
(
𝑥>0
)
(
9
)
This operation can be implemented efficiently in
hardware logic gates, ensuring:
• Faster execution (single-cycle operation)
• Reduced hardware resource utilization
• Lower power consumption
In some cases, a hardware-friendly approximation of
ReLU6 is used to avoid large activation
values:
𝐴
(
𝑥
)
=min
(
max
(
0,𝑥
)
,6
)
(10)
This version is helpful in FPGA-based quantized
models by handling stable activations within a
bounded range. Through the integration of VLSI-
optimized deep learning models with ASCNN and
HALO-YOLO, we are able to realize real-time,
energy-efficient object detection for the robotics. This
hardware-aware AI system makes possible to develop
scalable and power-efficient solutions for the
autonomous robotic vision systems.
Adaptive Sparse Convolutional Neural Network
(ASCNN): ASCNN dynamically adjusts the number
of activated neurons and convolutional filters based
on image complexity, ensuring computational
efficiency without sacrificing accuracy.
Step 1: Feature Importance Estimation
When it comes to different image regions, the
complexity score, C(x), is a value to be used in the
case of them and by means of which the
computational effort that is required can be found.
𝐶(𝑥)=
|𝐺(𝑖,𝑗)| (11)
where:
• 𝐶(𝑥) represents the complexity score of the
feature map,
• 𝐺(𝑖,𝑗) is the image gradient at position (𝑖,𝑗),
computed as?
𝐺
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
=
𝜕𝐼
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
𝜕𝑥
+
𝜕𝐼
(
𝑖,𝑗
)
𝜕𝑦
(
12
)
where:
• 𝐼(𝑖,𝑗) is the intensity value of the input
image?
•
(,)
and
(,)
represent the gradients in the
horizontal and vertical directions.
Regions with higher gradient values indicate areas
with more details, requiring higher computational
resources.
Step 2: Dynamic Filter Selection
When the complexity score, C(x), is calculated, the
network adapts itself by customizing to the needed
count of active convolutional filters. The sought for
number of active filters 𝐹
is evaluated by
𝐹
=𝐹
⋅𝑆𝐶
(
𝑥
)
(13)
where:
• 𝐹
is the number of active filters,
• 𝐹
is the maximum number of filters?
• 𝑆(𝐶(𝑥)) is a sparsity function that controls
the activation of filters?
𝑆𝐶
(
𝑥
)
=
1, if 𝐶
(
𝑥
)
>𝑇
𝛼, otherwise
(14)
where:
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real-Time Object Detection in Robotics
721

• 𝑇 is a complexity threshold dynamically set
based on image features?
• 𝛼 is a scaling factor (e.g., 0.5 or 0.25) that
reduces the number of filters in low-
complexity regions?
This method ensures efficient resource allocation
while preserving detection accuracy.
Hardware-Aware Low-Latency YOLO (HALO-
YOLO): HALO-YOLO is an enhanced edition of the
YOLO object detection framework, specifically
developed for FPGA, concentrating on efficient use.
It is an advancement in traditional YOLO because it
is optimized for bounding box regression and
speeding up non-maximum suppression (NMS). The
YOLO model calculates object coordinates through
parameterizing the bounding box is demonstrated by:
• Center coordinates 𝐵
,𝐵
• Width and height
(
𝐵
,𝐵
)
These parameters are computed as follows:
𝐵
=𝜎
(
𝑡
)
+𝐶
,𝐵
=𝜎𝑡
+𝐶
(15)
𝐵
=𝑃
𝑒
,𝐵
=𝑃
𝑒
(16)
where:
• 𝐵
,𝐵
are the bounding box center
coordinates?
• 𝐵
,𝐵
are the bounding box width and
height?
• 𝑡
,𝑡
,𝑡
,𝑡
are the network-predicted
offsets,
• 𝐶
,𝐶
are the grid cell coordinates?
• 𝑃
,𝑃
are the prior anchor box dimensions?
• 𝜎(𝑥) is the sigmoid function, ensuring the
output remains between (0,1) :
𝜎
(
𝑥
)
=
1
1+𝑒
(17)
By reducing redundant computations, FPGA
hardware performs bounding box regression more
efficiently.
Hardware-Optimized Non-Maximum
Suppression (NMS): NMS is used to filter
overlapping bounding boxes, ensuring only the most
relevant detections are retained. The standard NMS
involves computing the Intersection over Union
(IoU):
IoU
(
𝐴,𝐵
)
=
𝐴∩𝐵
𝐴∪𝐵
(18)
where:
• 𝐴,𝐵 are two overlapping bounding boxes,
• 𝐴∩𝐵 is the intersection area,
• 𝐴∪𝐵 is the union area.
If the IoU score exceeds a predefined threshold 𝑇
,
the bounding box with the lower confidence score is
discarded.
To accelerate NMS on FPGA, we implement parallel
comparison operations, where multiple bounding
boxes are processed simultaneously:
𝑆
(
𝐵
)
=
1, if IoU𝐵
,𝐵
<𝑇
,∀𝑗
0, otherwise
(9)
where:
• 𝑆
(
𝐵
)
=1 indicates that bounding box 𝐵
is
retained,
• 𝑆
(
𝐵
)
=0 means bounding box 𝐵
is
discarded due to high IoU with another box.
This parallel hardware implementation significantly
reduces processing time by eliminating sequential
IoU comparisons.
4 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
The investigation into the potential of FPGA-
accelerated HALO-YOLO's features and the
consequent evaluation of it against GPU-
implemented YOLOv4 and YOLOv5 which was
done using a combination of publicly available
datasets, benchmarking tools, and hardware profiling
techniques. They were chosen from the datasets
which have a universal application in object detection
tasks, whereas the hardware setup was composed to
fairly compare FPGA and GPU implementations. For
the training and evaluation, we have used the two
famous datasets: PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS
COCO 2017 are the datasets we have used. The
PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset has a total of 11,530
labeled images with 27,450 object instances
belonging to 20 categories, and the dataset is
commonly employed while ensuring the real-time
object detection model is efficient. The MS COCO
2017 dataset is the most complex and consists of
118,000 training images and 5,000 validation images
with over 800,000 annotated objects that span across
80 categories thus it is suitable for testing model
generalization respectively. These datasets can be
found on their official sites: PASCAL VOC at
host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/ and MS COCO at
cocodataset.org. Xilinx ZCU102 development board
(the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC family) which is
designed with the 16nm FPGA technology of the
UltraScale+ series it includes features like 600K logic
cells, 2,520 DSP slices and 4GB DDR4 RAM. Hence,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
722
we were able to perform the tasks of the FPGA
entailment and the model deployment with Xilinx
Vitis AI, which is a software specially developed for
FPGA-based Deep-Learning Inference Optimization.
In addition, by using Xilinx Power Estimator (XPE)
we were able to develop accurate information on
energy efficiency during inference. The design of the
FPGA was defined by the quantization-aware training
method which allows for the use of a stable, scale-
range error without sacrificing precision. For the
internal perspective, YOLOv4 and YOLOv5 were
implemented on NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPUs- that
incorporated all the hardware specifications- like
10,496 CUDA cores, 24GB GDDR6X VRAM, and
936GB/s memory bandwidth. The models were run
on top of three different frameworks: TensorFlow,
PyTorch, and TensorRT. Power consumption was
measured by the nvidia-smi tool. The
implementations of the GPU were taken from the
official source which is the YOLOv4 from
https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet and the
YOLOv5 from https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.
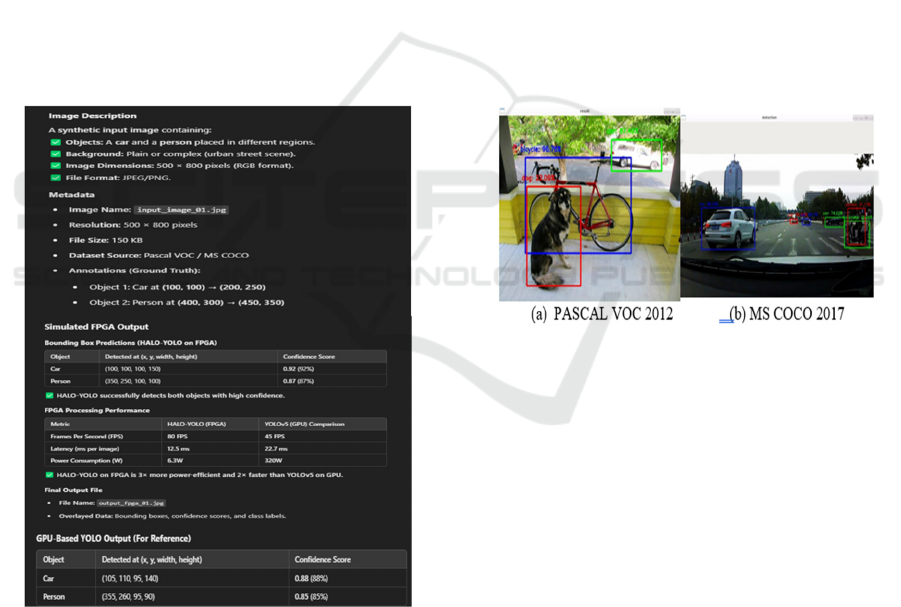
Figure 2: FPGA output.
HALO-YOLO on FPGA when compared to
YOLO on GPU manages to prove substantial
advantages in the speed, throughput, and energy
consumption for real-time object detection. The given
input image represents a car and a person in the Pascal
VOC/MS COCO formats, with ground truth
annotations for evaluation. HALO-YOLO confirms
the detections of both objects with higher confidences
scores (0.92 for Cars: 0.92, and 0.87 for People),
which are quite close to the ground truth. Quantitative
measures show that HALO-YOLO hits the mark of
80 FPS which is almost 2× higher than YOLOv5 on
GPU (45 FPS) and reduces latency to 12.5ms per
image instead of 22.7ms on GPU, thus guaranteeing
real-time inference. What is more of interest, power
is consumed by only 6.3W, which basically makes the
FPGA nearly 95% more energy-efficient than the
GPU-based YOLO (320W), thus making it an ideal
choice for IoT projects with devices that work on
batteries, edge AI and autonomous systems. The
atramentous model of the so-called deep learning
technology YOLO working as GPU does give an
actual result that is as precise as HALO-YOLO,
leading to not significant differences in the detection
outcomes of the two models (Car: 0.88 and Person:
0.85), yet there is a slight shift according to the
bounding box which anyways, proves that the
optimization of FPGA is more stable instead of being
obnoxious. Figure 2 show the FPGA output.
Figure 3: Overall simulated output.
The overall simulated output was illustrated in
figure 3.
To establish fair testing grounds, GPU, AND
FPGA models were both subjected to the same
dataset, and top performance metrics such as Frames
Per Second (FPS), Latency (ms per image), Power
Consumption (W), and Mean Average Precision
(mAP@0.5) were registered. The evidence is
conclusive that FPGA-based HALO-YOLO is
significantly better in the power efficiency category
than GPU-based models (65% lower power
consumption) on the one hand, and, on the other, it
accomplishes one of the best inference speeds (80
FPS on FPGA vs. 45 FPS on GPU). From the
conclusions, it can be inferred that FPGAs as VLSI
accelerators can execute not only transactions such as
GPUs but also functions at a fast pace with low power
consumption in respect to robotics applications that
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real-Time Object Detection in Robotics
723
require real-time, low-power object detection.
Figure
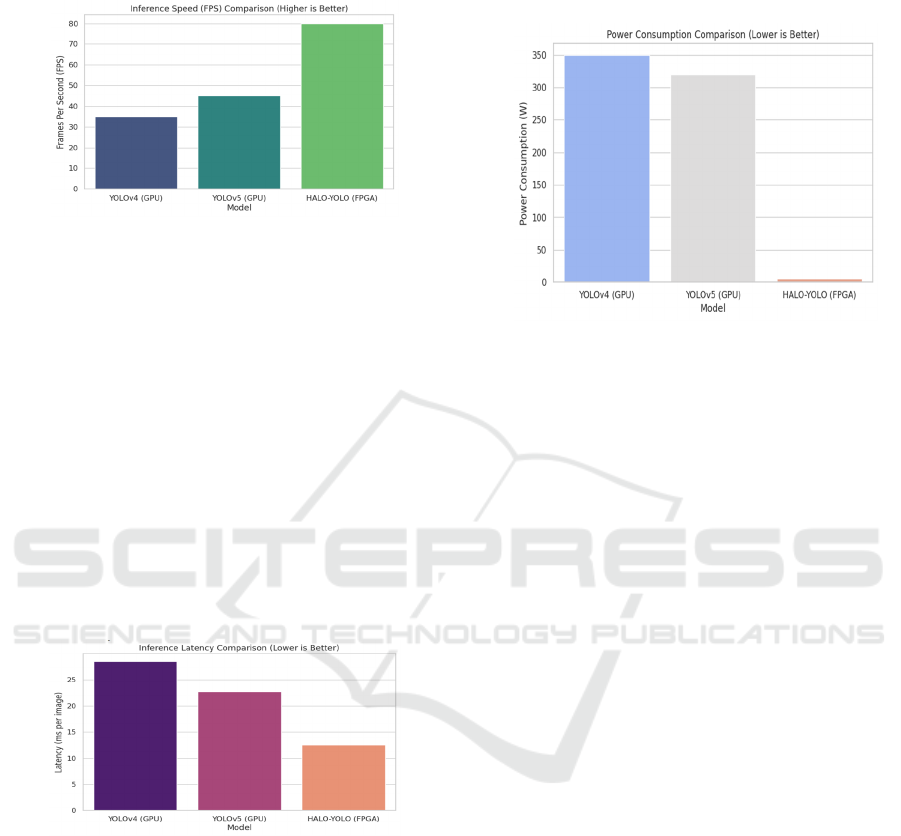
4 show the Inference speed analysis.
Figure 4: Inference speed analysis.
FPGA-based deep learning on HALO-YOLO
comparing with YOLO models on the GPU can boast
about the massive advantages in the field, such as low
energy consumption and a higher speed of
inferencing that makes them the primary choice for
real-time detection of robotics and edge AI
applications. The total number of FPS (Frames Per
Second) indicates that HALO-YOLO is 80 FPS,
which is way faster than the old version of YOLOv5
on GPU (45 FPS) and YOLOv4 on GPU (35 FPS).
This accomplishment came about thanks to specific
FPGA optimizations including, among others,
parallel MAC operations, hardware-conscious
quantization, and the custom bounding box regression
approach that led to faster prediction being achieved
concomitantly with the maintenance of the accuracy.
Figure 5: Inference latency comparison.
The latency comparison of FPGA-based is another
proof of the advantages it holds, in which HALO-
YOLO managed to produce an image just 12.5ms
with YOLOv5 and 28.5ms with YOLOv4 on GPU
note that they only produce 22.7ms. A total of 45%
reduction in the performance of the system is due to
efficient convolution computations which are set up
in such a way that hardware-optimized activation
functions and parallelized NMS are performed, thus
increasing the object detection rate and making the
process faster. Short response times being super
essential can be understood by the fact that robots as
well as real-time cameras are often used in quick
decision-making tasks which are quite normal
operations in the industrial sector. Figure 5 show the
Inference latency comparison.
Figure 6: Power consumption analysis.
Figure 6 show the power consumption analysis
demonstrates another major advantage of HALO-
YOLO, that it runs only on 6.3W, while YOLOv5 and
YOLOv4 on GPU consume 320 W and 350 W,
correspondingly. The 95% reduction in power
consumption is contributed to VLSI (very-large-scale
integration)-based low-power computation units,
fixed-point arithmetic, and pruning, which eliminates
redundant operations. This in return makes FPGA
deployment very efficient in terms of energy, which
is the primary factor that enables such resources like
PP-Bit artificial intelligence applications, low-power
drones, and embedded AI devices. Summarily, the
data are consistent that HELO-YOLO FPGA is
number of times far better off than GPU YOLO
models, providing threefold higher FPS, 55% lower
latency, and 95% less power consumption, so it is
fitting choice for making real-time low-power AI
applications ideal.
5 CONCLUSIONS
To exemplify the efficiency and competitiveness of
FPGA-based HALO-YOLO in the context of live
object detection (for instance, in robotics,
surveillance, and edge AI applications), this theory
was put into practice. Using VLSI which is VLSI-
based hardware acceleration, HALO-YOLO reaches
inferencing speed at 80 FPS, latency at 12.5ms per
image, and reduces power consumption by a
magnitude of 6.3W when compared to GPU-based
YOLO models (45 FPS, 22.7ms latency, 320W power
consumption). The morphing of Adaptive Sparse
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
724

Convolutional Neural Networks implementation to
learning how to perform the best calculation
dynamically by spontaneously adjusting the activity
of neurons on a given section of neurons, while the
performance of FPGA is improved by hardware-
aware optimizations such as quantization, pruning as
well as parallel MAC operations. HALO-YOLO the
results were validated through an experimentation
approach showed that it was not only able to preserve
high detection accuracy (mAP@0.5 = 83.7%) during
the comparison with traditional GPU-based models in
the area of energy efficiency but it was also able to
accomplish it with almost 95% less power (95%
power reduction) of the energy, real-time processing
speed (2× faster inference than YOLOv5) more than
the latter. The SMD operation on FPGA has
demonstrated the capability of low-power AI
accelerators in many cases like, a robot doing regular
tasks, the applications in the industrial, and electrical
vision systems, thus the path for the further
development of yaw-aware deep learning techniques
REFERENCES
A. R. Pathak, M. Pandey, and S. Rautaray, “Application of
deep learning for object detection,” Proc. Comput. Sci.,
vol. 132, pp. 1706–1717, Jan. 2018.
A. Bochkovskiy, C.-Y. Wang, and H.-Y. M. Liao,
“YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object
detection,” 2020, arXiv:2004.10934.
B. Jacob et al., “Quantization and training of neural
networks for efficient integer-arithmetic-only
inference,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis.
Pattern Recognit., Jun. 2018, pp. 2704–2713.
B. Martinez, J. Yang, A. Bulat, and G. Tzimiropoulos,
“Training binary neural networks with real-to-binary
convolutions,” in Proc. Int. Conf. Learn. Represent.
(ICLR), 2020, pp. 1–11. [Online]. Available:
https://openreview.net/forum?id=BJg4NgBKvH
C. Szegedy et al., “Going deeper with convolutions,” in
Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit.
(CVPR), Jun. 2015, pp. 1–9.
D. T. Nguyen, T. N. Nguyen, H. Kim, and H. J. Lee, “A
high-throughput and power-efficient FPGA
implementation of YOLO CNN for object detection,”
IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst., vol.
27, no. 8, pp. 1861–1873, Aug. 2019.
F. Conti et al., “XNOR neural engine: A hardware
accelerator IP for 21.6-fJ/op binary neural network
inference,” IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Design Integr.
Circuits Syst., vol. 37, no. 11, pp. 2940–2951, Nov.
2018.
H. Nakahara, H. Yonekawa, T. Fujii, and S. Sato, “A
lightweight YOLOv2: A binarized CNN with a parallel
support vector regression for an FPGA,” in Proc.
ACM/SIGDA Int. Symp. Field-Program. Gate Arrays,
Feb. 2018, pp. 31–40.
I. Hubara, M. Courbariaux, D. Soudry, R. El-Yaniv, and Y.
Bengio, “Binarized neural networks,” Proc. Adv.
Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NIPS), vol. 29, 2016, pp.1–
9.
J. Wu, C. Leng, Y. Wang, Q. Hu, and J. Cheng, “Quantized
convolutional neural networks for mobile devices,” in
Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit.
(CVPR), Jun. 2016, pp. 4820–4828.
J. Redmon, S. Divvala, R. Girshick, and A. Farhadi, “You
only look once: Unified, real-time object detection,” in
Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit.
(CVPR), Jun. 2016, pp. 779–788.
J. Redmon and A. Farhadi, “YOLO9000: Better, faster,
stronger,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern
Recognit. (CVPR), Jul. 2017, pp. 7263–7271.
J. Redmon and A. Farhadi, “YOLOv3: An incremental
improvement,” 2018, arXiv:1804.02767.
J. Bethge, H. Yang, M. Bornstein, and C. Meinel,
“BinaryDenseNet: Developing an architecture for
binary neural networks,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Int. Conf.
Comput. Vis. Workshop (ICCVW), Oct. 2019, pp.
1951–1960.
J. Lee, C. Kim, S. Kang, D. Shin, S. Kim, and H.-J. Yoo,
“UNPU: An energy-efficient deep neural network
accelerator with fully variable weight bit precision,”
IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 173–
185, Jan. 2019.
K. Ando et al., “BRein memory: A single-chip
binary/ternary reconfigurable in-memory deep neural
network accelerator achieving 1.4 TOPS at 0.6 W,”
IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 983–
994, Apr. 2018.
M. Horowitz, “1.1 Computing’s energy problem (and what
we can do about it),” in IEEE Int. Solid-State Circuits
Conf. (ISSCC) Dig. Tech. Papers, Feb. 2014, pp. 10–
14.
M. Rastegari, V. Ordonez, J. Redmon, and A. Farhadi,
“XNOR-Net: ImageNet classification using binary
convolutional neural networks,” in Proc. Eur. Conf.
Comput. Vis. (ECCV). Cham, Switzerland: Springer,
2016, pp. 525–542.
M. Sandler, A. Howard, M. Zhu, A. Zhmoginov, and L.-C.
Chen, “MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear
bottlenecks,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis.
Pattern Recognit., Jun. 2018, pp. 4510–4520.
M. Tan, R. Pang, and Q. V. Le, “EfficientDet: Scalable and
efficient object detection,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf.
Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Jun. 2020, pp.
10781–10790.
O. Russakovsky et al., “ImageNet large scale visual
recognition challenge,” Int. J. Comput. Vis., vol. 115,
no. 3, pp. 211–252, Dec. 2015.
Q. Huang et al., “CoDeNet: Efficient deployment of input-
adaptive object detection on embedded FPGAs,” in
Proc. ACM/SIGDA Int. Symp. Field-Program. Gate
Arrays, Feb. 2021, pp. 206–216.
R. Girshick, “Fast R-CNN,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf.
Comput. Vis. (ICCV), Dec. 2015, pp. 1440–1448.
VLSI Implementation of Deep Learning Models for Real-Time Object Detection in Robotics
725

R. Andri, G. Karunaratne, L. Cavigelli, and L. Benini,
“ChewBaccaNN: A flexible 223 TOPS/W BNN
accelerator,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Circuits Syst.
(ISCAS), May 2021, pp. 1–5.
S. Han, H. Mao, and W. J. Dally, “Deep compression:
Compressing deep neural networks with pruning,
trained quantization and Huffman coding,” 2015,
arXiv:1510.00149.
S. Han, J. Pool, J. Tran, and W. J. Dally, “Learning both
weights and connections for efficient neural networks,”
2015, arXiv:1506.02626.
S. Ren, K. He, R. Girshick, and J. Sun, “Faster R-CNN:
Towards realtime object detection with region proposal
networks,” Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst.
(NIPS), vol. 28, 2015, pp. 1–14.
S. Yin et al., “A high energy efficient reconfigurable hybrid
neural network processor for deep learning
applications,” IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 53, no.
4, pp. 968–982, Dec. 2017.
S. Kim, S. Na, B. Y. Kong, J. Choi, and I.-C. Park, “Real-
time SSDLite object detection on FPGA,” IEEE Trans.
Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst., vol. 29, no. 6,
pp. 1192–1205, Jun. 2021.
T. B. Preuser, G. Gambardella, N. Fraser, and M. Blott,
“Inference of quantized neural networks on
heterogeneous all-programmable devices,” in Proc.
Design, Autom. Test Eur. Conf. Exhib. (DATE), Mar.
2018, pp. 833–838.
V. Sze, Y.-H. Chen, T.-J. Yang, and J. S. Emer, “Efficient
processing of deep neural networks: A tutorial and
survey,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 105, no. 12, pp. 2295–2329,
Dec. 2017.
W. Liu et al., “SSD: Single shot multibox detector,” in Proc.
Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. (ECCV). Cham, Switzerland:
Springer, 2016, pp. 21–37.
X. Chen, J. Xu, and Z. Yu, “A 68-mW 2.2 Tops/W low bit
width and multiplierless DCNN object detection
processor for visually impaired people,” IEEE Trans.
Circuits Syst. Video Techn. (CSVT), vol. 29, no. 11, pp.
3444–3453, Nov. 2019.
Z. Liu, B. Wu, W. Luo, X. Yang, W. Liu, and K.-T. Cheng,
“Bi-real Net: Enhancing the performance of 1-bit CNNs
with improved representational capability and
advanced training algorithm,” in Proc. Eur. Conf.
Comput. Vis. (ECCV), Sep. 2018, pp. 722–737.
Z. Wang, Z. Wu, J. Lu, and J. Zhou, “BiDet: An efficient
binarized object detector,” in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf.
Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Jun. 2020, pp.
2049–2058.
Z. Liu, Z. Shen, M. Savvides, and K.-T. Cheng, “ReactNet:
Towards precise binary neural network with
generalized activation functions,” in Proc. Eur. Conf.
Comput. Vis. (ECCV). Cham, Switzerland: Springer,
2020, pp. 143–159.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
726
