
Digital Library Hub Integrating Web Technologies for Efficient
Library Operation
T. Manikumar, T. Marimuthu, Burramsetti Nagasai Venkatesh, Evuri Sarayu,
Chennam Jahnavi and Chidige Srujan Raj
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education, Virudhunagar,
Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: the Digital Library, Web Technologies, Database Integration, Automation, Interface for the User, Library
Operations, Accessibility.
Abstract: The Digital Library Hub is a quick solution aimed at improving the access and control of library resources in
higher learning institutions. This project incorporates web technologies with traditional library functions,
aiming to enable students, faculty members, and staff to realize an all-inclusive interface for easy use. Two
main panels comprise the system: one for the user and the other for the administrator. The Library
Management System (LMS) hub is built using PHP, JavaScript, and CSS, providing administrators with an
easy way to manage book categories, users, book locations, and inventories. It also enables users to make
requests for book issues; follow the issued books and return them based on the due dates set. This paper
discusses the development, implementation, and potential impact of such a system on the library operation
and user experience. This project is able to improve access to educational resources by digitalizing library
operations, and one can make learning materials more accessible to students and faculty. It integrates web
technologies into traditional library systems and contributes to digital transformation and modernization in
the educational infrastructure. The digital library promotes efficient resource management, reducing paper
usage and the need for physical books, contributing to sustainable academic environments.
1 INTRODUCTION
The technology has totally transformed confront of
every part of academic organizations & approaches to
run the library & performing and functioning the
delivery of services. In the past, they were constrained
by physical limitations of space, relied on work that
demanded the human touch, and were primarily
centered on cataloging, issuing, and tracking books.
But the need for faster and more efficient access to
information highlights changing libraries. In
conclusion, digital libraries and web-based
applications have emerged as powerful solutions that
can be used in bridging the gap, offering access and
management unlike anything ever available to
administrators and users. Enticed the Digital Library
Hub is an end-to-end web-based application that
brings together library processes with the latest digital
ones to transform the way a library operates. It is
more than an improvement; it is a complete
reimagining of what libraries can do in this new
digital fabric. It will improve access, simplify
management and enrich the user experience so that
students, faculty, and staff can more easily get the
resources they need from anywhere. It just goes
with a larger trend on campuses everywhere where
digital platforms occupy an increasingly central
space in the dissemination of knowledge and a
sharing of resources. At the core of the Digital
Library Hub is a learning management system (LMS)
implemented in PHP, JavaScript and CSS. This LMS
has two panels: user panel and admin panel.
Introducing Admin Panel All the main library
operations like adding and editing categories of
books, accounts management, editing the book
locations and the inventories are managed by Admin
Panel. Users can request book issues, see issued
books, return books within due dates, and more with
the help of the User Panel, making the whole process
very easy and efficient. The move to the digital
channel solves many of the challenges pointed out in
traditional libraries, such as tedious manual
704
Manikumar, T., Marimuthu, T., Venkatesh, B. N., Sarayu, E., Jahnavi, C. and Raj, C. S.
Digital Library Hub Integrating Web Technologies for Efficient Library Operation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013942500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
704-709
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

processing to manage the library, inaccessibility at
times and geofences of the library, and inefficient
resource management. As anyone can see, this Digital
Library Hub will help the administrators manage
thousands of books & users very easily and it will
allow students & faculty members to easily access
resources in an organized, fast way. Embracing the
evolution of direct user engagement, this system will
become a significant progressive leap on the way.
Among its main features are the automatic reminders
for the due dates of books, as well as status updates
on the availability of books and easy access to all
types of library material. In short, it is as innovative a
concept for modern library management as you’re
ever likely to see, and sets a new standard for the
academic library to remain relevant in an ever more
digital universe.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The use of centralized education systems improves
significantly the students' interaction and easy access
to resources, with improved learning results and
stronger collaboration between students and
instructors A systematic review methodology
uncovered that centralized systems are effective in
terms of enhancing inter-student interaction and
resource accessibility. The study used data from
several digital sources and learning networks,
blending both qualitative and quantitative approaches
to demonstrate how centralized used data from
several digital sources and learning networks,
blending both qualitative and quantitative approaches
to demonstrate how centralized.
These systems positively impact learning
outcomes and foster a collaborative environment for
students and instructors. The disadvantages, however,
include the relatively higher costs of setting and
operating these systems, with technical issues
requiring the support of substantial IT professionals
because of the system's nature (Echem et al. 2023)
(Dube et al. 2023). The findings indicated that e-
learning environments, despite their effectiveness in
enhancing student outcomes, come with technical
challenges and limitations in physical access to
technology and high-speed internet. Moreover,
continuous investment in technology and training is
required to sustain quality e-learning systems (Farid
et al.2023).
A cost-benefit analysis methodology was applied
to explore the financial aspects of deploying
educational technologies within digital libraries,
including maintenance costs, resource allocation, and
sustainability .Data gathered from institutions
showed that while these technologies improve
learning outcomes and administrative efficiencies,
the initial implementation and recurring maintenance
costs can be huge .Moreover, the above systems
sometimes incur continuing expenses on system
upgrades, technical support, and staff training (Elias
et al. 2024).
Information management systems can be used to
improve education but are hard to configure and
maintain. A case-study survey of a number of higher
education organizations was used to analyze these
information management systems. Findings indicated
that the complexity to set up and maintain such
systems requires continuous technical support to
remain efficient and secure (Segado-Boj et al. 2024)
Including faculty profiles in learning management
systems improves student-faculty interface but
updating the information constitutes challenges.
Through semi-structured in-depth interviews with
administrative staff and IT personnel using a
qualitative approach, one could find some practical
drawbacks such as heavy maintenance costs and the
need for training frequently. The study highlighted
the importance of having technical support regularly
and financial commitment in upholding digital
educational resources (Ekeh, D. O., et al.2023).
Through interviews with employees responsible
for managing digital resources, key challenges in
maintaining educational systems were identified
Findings revealed that high costs andfrequent staff
training is necessary to ensure that digital resources
are promptly maintained and accessible. This places
a strain on institutional budgets and resource
management (Sibiya et al. 2023).
A systematic review and meta-analysis of user
participation in digital learning systems highlighted
some of the factors influencing their engagement.
While the results highlighted that it takes a
continuous and costly effort to keep the level and
magnitude of engagement, the institutional support
regarding training and technical help should engage
users so that the system is appropriately utilized
(Remneland Wikhamn, et al. 2023).
A study based on a survey measured students'
perceptions toward their satisfaction with the e-
learning course management systems. The critical
factors influencing user experience were identified as
obstacles that may severely impair the digital course
management system, supporting continuous
investment in system support and improvement
(Ullahet al. 2024).
A longitudinal research study on trends in
educational technology adoption was conducted
Digital Library Hub Integrating Web Technologies for Efficient Library Operation
705
based on years of data collected to examine trends,
costs, and benefits. It noted that though new
technologies reduce redundancy and improve the
accuracy of the data, institutions face a cost intensive
challenge of installation, maintenance, and technical
support (Stjernborg et al. 2024).
A mixed-method comparative study investigated
traditional versus digital learning environments based
on performance metrics, resource availability, and
user experiences. The study concluded that while
digital learning offers more personalized learning
opportunities, it requires regular maintenance and
user training, which demands institutional investment
(Bowen e al. 2024).
3 METHODOLOGY
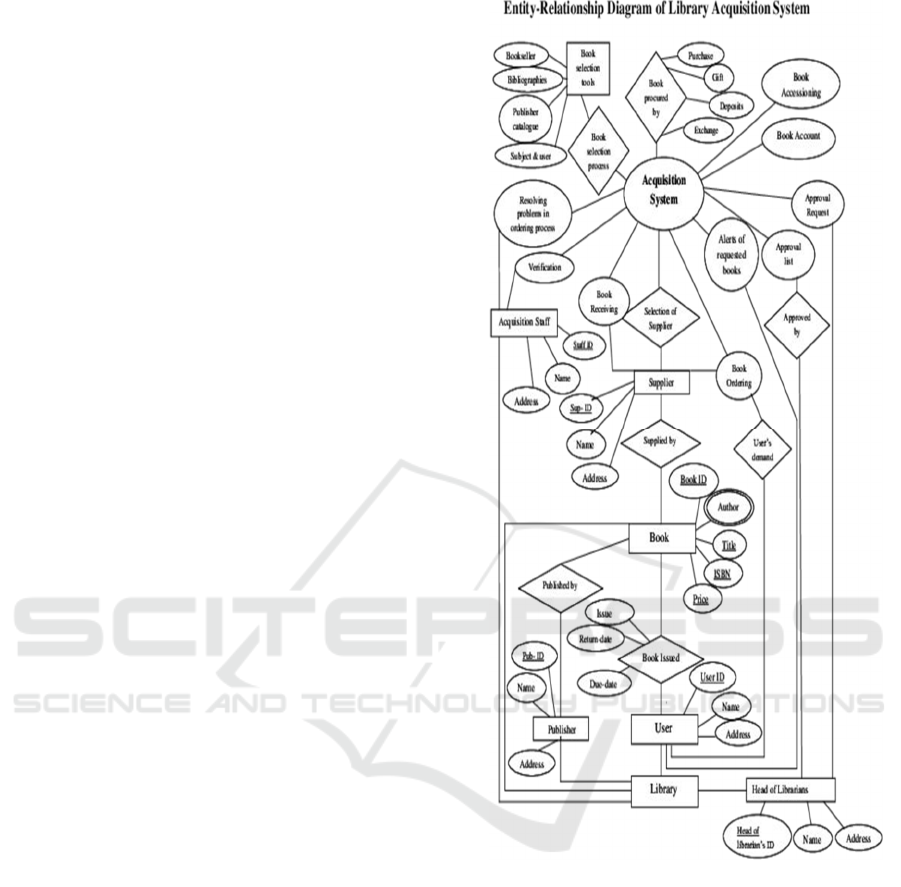
3.1 Proposed Methodology
The system overview outlines the architecture and
objectives of the library management system,
emphasizing the module interactions and the data
flow that will inform the ER diagram. It elaborates
user roles for students, staff, as well as administrators
through providing role-based permissions for
borrowing, adding books, and submitting reviews, in
addition to admin and student functionalities.
The data management revolves around efficient
handling of relationships, data integrity, and
normalization to reduce redundancy across entities
like Book, User, Review, and Borrowing Record.
Security is accomplished through user authentication
and authorization, while reporting capabilities
facilitate library activities insights. The process in the
end tracks the action of users, including book return,
which ensures thorough management of interactions.
Security measures are essential for protecting access
to the data. The ER diagram contains attributes for
user authentication and authorization as part of the
User entity. The ER diagram design may need
reporting functionality, such as the number of
borrowed books or written reviews, to affect the data
for querying appropriately. Finally, the ending
process keeps a record of user interactions, such as
returning a book, as part of the Borrowing Record or
Review entities to maintain management of all library
system interactions. (Rafols et al. 2010). Figure 1
shows the ER Diagram Requirements.
Figure 1: ERD diagram requirements.
3.2 Requirements Gathering
3.2.1 Functional Requirements
E-Learning for Journals: Integrate a PDF viewer
with access for document annotation, bookmarking,
and sharing facility while journal searching
functionality must be included.
Circulation Section: Use barcode or RFID scanning
to expedite book lending and returns. Provide users
with access to real-time information on the status of
available books, facility to track borrowing history
along with due dates.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
706

Patrons Section: It uses university credentials for
authentication, allows updates to profiles and checks
on borrowing privileges while ensuring that the user's
data is encrypted.
Advanced Search Section: The search functions are
supplemented with filtering and sorting options,
natural language processing, accuracy, and
autocomplete suggestions in queries.
Acquisitions Section: It tracks requests and provides
notifications for acquired books, allows user
recommendations for library additions, and there is
acquisition history.
Reports Section: Allow export in PDF and other
formats, provide reports with visualizations and have
scheduled reporting for stakeholders. A well-defined
dataset should be created with appropriate images with
a unique class.
3.2.2 Non-Functional Requirements
Online Public Access Catalogue (OPAC): Develop
an intuitive frontend for catalog browsing and
searching with filters for categories, and use a
robust backend database for real-time
synchronization.
Features: Include search and filter options, detailed
boo information with availability status, and user
reviews and ratings.
Competition Reference Books Section: Create
adedicated frontend section for competitive exam
materials with a backend CMS for easy updates.
Features: Categorize books by exam type, offer
download or online reading options, and provide
recommendations for related resources.
Book Bank Scheme for SC/ST Students: Design a
user-friendly interface for eligible students to access
and request books, backed by a secure database for
eligibility management and tracking.
Features: Implement a registration and verifications
system, enable online book request processes, and
provide notifications for book returns.
Event Gate way for Branch-Specific Events:
Develop a dynamic frontend for view in gand
applying oevents with branch filters, and establish a
backend form anaging event postings
Features: List events by branch with details, allow
online applications and tracking, and send
notifications and updates to registered users.
4 IMPLEMENTATIONS
The LMS project works with PHP, JavaScript, and
CSS. Users and administrators have separate panels.
The admin panel is vastly essential for handling the
resources of the library and users interaction.
Administer can Create, Update and Delete Book
Categories, Users, Book Locations to ensure up to
date inventory. Moreover, users can raise requests for
books, see the books issued to them, and return them
before the due dates. This allows for efficiently
tracking down the library resources in an organized
fashion. The admin checks the request when a user
posts a request for a book and makes changes to the
records, as far as book borrowings are concerned.
The system further stores issue books to make sure
that all transactions are kept in check, and users will
receive reminders on the due dates, ensuring allbooks
are returned on time. In summary, it brings the LMS
elevates user and library experience with well-
structured library program and automate
administrative processes. (Sarma et al. 2016).
5 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The Library Management System helped the library
to bring positive outcomes in terms of streamlining
the processes. In addition, major functionality like
user authentication, book management, and
borrowing process was accomplished via PHP,
JavaScript, and CSS. The extensive system provided
flexibility in exchanging information between user
and admin panels, which enabled better
communication. It means that user experience was an
overall basic success. Navigation and usage of the app
is all well and good.
Figure 2: Comparison of efficiency scores.
Digital Library Hub Integrating Web Technologies for Efficient Library Operation
707
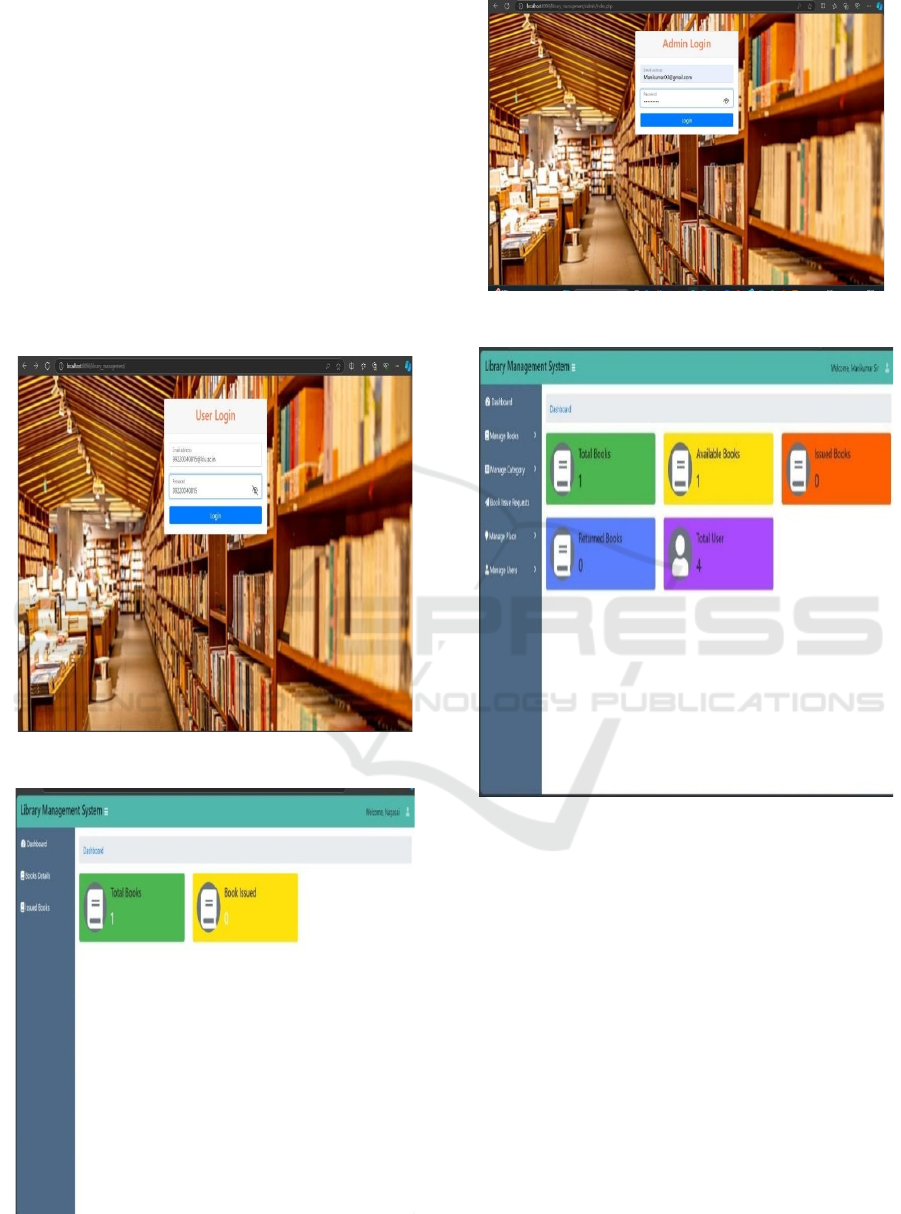
Figure 2 Shows Comparison of efficiency scores
(1–10) across various aspects of traditional versus
modern methods in the Digital Library Hub.
The system had developed all of these features,
such as book management, borrowing processes and
user authentication, using PHP, JavaScript, and CSS
to make it as efficient as possible. User friendliness
was promoted by the smooth flow of information
between user and admin panels to ensure that things
went off without a hitch. As a result, the user
feedback indicated a favourable reception about the
navigation as well as the functionality of the system,
and therefore it being effective to satisfy the end-user
requirements. In Result and discussion shows the
Figure 3,4,5 and 6.
Figure 3: User login.
Figure 4: User interface.
Figure 5: Admin login.
Figure 6: Admin interface.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Implementing the Library Management System has
greatly improved the library operation's efficiency
because it integrates essential features, such as user
authentication, book management, and streamlined
processes for borrowing. Effective communication
between the user and admin panels not only
facilitates more fluent interactions but also enables a
better user experience in general. Positive comments
from users indicate that the system is easy to navigate
and function, evidencing its ability to meet user
needs effectively. This project attests to the potential
of modern web technologies in transforming
traditional library systems into more user-friendly
and efficient platforms.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
708

REFERENCES
Bowen, Jonathan P., et al. "Early virtual science museums:
when the technology is not mature." Internet Histories
8.1-2 (2024): 9- 33.
Dube, Tinyiko Vivian, and Lorette Jacobs. "Academic
library services extension during the COVID-19
pandemic: considerations in higher education
institutions in the Gauteng Province,
SouthAfrica."LibraryManagement44.1/2(2023):17- 39.
Dube, Tinyiko Vivian, and Lorette Jacobs. "Academic
library services extension during the COVID-19
pandemic: considerations in higher education
institutions in the Gauteng Province, South Africa."
Library Management 44.1/2 (2023): 17- 39.
Echem, Mercy Ekenma, and Emmanuel Okwu."Library
Security and Sustainable Service Delivery in Donald
Ekong Library, University of Port Harcourt, Rivers
State, Nigeria." Communicate: Journal of Library and
Information Science 25.1 (2023): 89-101.
Echem, Mercy Ekenma, and Emmanuel Okwu."Library
Security and Sustainable Service Delivery in Donald
Ekong Library, University of Port Harcourt, Rivers
State, Nigeria." Communicate: Journal of Library and
Information Science 25.1 (2023): 89-101.
Ekeh, D. O., et al. "ROLE OF ACADEMIC LIBRARIES
IN RESEARCH DATA MANAGEMENT IN
TERTIARY INSTITUTIONS Library Philosophy &
Practice (2023).
Elias, James Dea, and Edison WazoelL ubua. "The impact
of usability, functionality and reliability on users’
satisfaction during library system adoption." The
Journal of Informatics 1.1 (2024): 13-21.
Farid, Ghulam, Nosheen Fatima Warraich, and Sadaf
Iftikhar. "Digital information security management
policy in academic libraries: A systematic review
(2010–2022)." Journal of Information Science (2023):
01655515231160026
Hibner, Holly, and Mary Kelly. Making a collection count:
a holistic approach to library collection management.
Elsevier, 2023.
J. Ieamsaard、 S.N. Charleswood and S. Yammen,
"DeepLearning BasedFace
MaskDetectionUsingYoloV5",
9thInternationalElectrotechnical Conference
(iEECON), pp.428-431,2021.
Jasimudeen, S. "Adoption and user perceptions of Koha
library management system in India."Annal sof Library
and Information Studies (ALIS) 59.4 (2013): 223-230.
Neal, James G. "Chaos breeds life: finding opportunities for
library advancement during a period of collection
schizophrenia." Collection Development in a Digital
Environment. CRC Press, 2023. 3-1.
Rafols, Ismael, Alan L. Porter, and Loet Leydesdorff.
"Science overlay maps: A new tool for research policy
and library management." Journal of the American
Society for information Science and Technology 61.9
(2010): 1871-1887.
Rafols, Ismael, Alan L. Porter, and Loet Leidesdorff.
"Science overlay maps: A new tool for research policy
and library management." Journal of the American
Society for information Scienceand Technology61.9
(2010): 1871-1887.
Remnel and Wikhamn, Björn, and Alexander Styhre. "Open
innovation ecosystem organizing from a process view:
a longitudinal study in the making of an innovation
hub." R&D Management 53.1 (2023): 24-42.
Sarma, Gautam Kumar. "OPAC module in open source
library management software: A comparative study."
(2016).
Segado-Boj, Francisco, Juan Martín-Quevedo, and Juan-
JoséPrieto-Gutiérrez. "Jumping over thep aywall:
Strategiesand motivations for scholarly piracy and
other alternatives." Information Development 40.3
(2024): 442-460.
Sibiya, Philangani Thembinkosi, and Patrick Ngulube.
"Perceptions of employers in South Africa on library
and information science graduates’ skills, knowledge
and competencies on digital scholarship." Heliyon 9.2
(2023).
Stjernborg, Vanessa, and Gustav Lopez Svensson. "Rural
mobility in later life; counteracting accessibility
poverty with digital service solutions." Transportation
Research Part D: Transport and Environment 126
(2024): 104030.
Susanto, Erwin, and Tata Sutabri. "Analisis Kualitas
Pelayanan E-Library Menggunakan Framework Cobit5
Pada Perpustakaan Universitas Bina InsanL
ubuklinggau." Indonesian Journal of Multidisciplinary
on Social and Technology 1.2 (2023): 95-103.
Ullah, Zakir, Yuanyuan Tao, and Jufang Huang. "Integrated
Bioinformatics-Based Identification and Validation of
Neuroinflammation-Related Hub Genes in Primary
Open-Angle Glaucoma." International Journal of
Molecular Sciences 25.15 (2024).
Digital Library Hub Integrating Web Technologies for Efficient Library Operation
709
