
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in
Cloud Computing
Zainab Khan and Kavita Agrawal
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Integral University, Lucknow, India
Keywords: Cloud Computing (CC), Load-Balancing (LB), Resource Allocation, Heuristics Algorithms Approach, ACO,
PSO, Blockchain.
Abstract: Through the provision of scalable, on-demand resources via the Internet, cloud computing has completely
transformed contemporary computing. Effective load-balancing remains a critical challenge in achieving
efficient resource use, reducing response times, and preventing system overload. A comprehensive evaluation
of LB strategies in distributed computing is given in this document, which divides them into conventional and
contemporary categories, such as static, dynamic, heuristic, and AI-based approaches. It also examines
important security, fault tolerance, and energy efficiency issues. And scalability. The study highlights new
developments influencing load balancing in cloud environments going forward, such as edge computing,
blockchain integration, and machine learning-driven optimization. The purpose of this survey is to give
researchers and practitioners useful information about how load balancing is changing, enabling
improvements in the effectiveness and performance of CC.
1 INTRODUCTION
The use of CC has become a major craze in the last
few years, leading to significant advancements in
distributed systems and the development of extensive
computer networks. Cloud services are provided to
customers worldwide by CC companies like IBM,
Amazon, and Google. Under this new paradigm, end
users can access apps and services whenever they
want rather than having to install them on their local
computers (M. Shahid, et.al, 2020)
The foundation and key component of cloud-
based applications is virtualization. Inefficient
handling of the migration process and the allocations
of VMs can greatly impact the way on-demand as
well as scalable services are rendered to customers
(D. Shafiq,et.al, 2021) Among the top three
difficulties with Cloud computing, according to (M.
Shahid, et.al, 2020), mentioned as cloud performance.
This study intends to improve the infrastructure as a
service model’s resource allocation, a key concept
idea in cloud computing, by balancing the resources
offered to the customers with the amount of work as
well as requests made by users on servers (D.
Shafiq,et.al, 2021), Allocating resources is one of the
challenges with CC, and it also plays a role in LB.
This problem is also present in systems for wireless
communication, it’s essential to allocate resources in
a fair and balanced manner while also considering
user priorities (F. Zabini,et.al.2017)
There are two ways to classify cloud computing:
by location or by services provided. A cloud has the
potential to be categorized as public, private, hybrid,
or community, depending on its location (J. Shah,
2017), Anybody can use public cloud services, and
the infrastructure is housed on a service provider’s
property. Public clouds are the most economical, but
they are also the most susceptible to different types of
attacks. Access to a private cloud is limited to a single
person or entity. Although it costs more, it offers the
user the highest level of security and control.
Combining both public and private clouds for various
uses depending on organizational needs is known as
a hybrid cloud. A community cloud is made up of a
shared infrastructure that is utilized by numerous
organizations with similar management and data. (P.
Kumar,2019)
The following are the study’s primary goals:
• To investigate different load-balancing
strategies that are discussed within the
literature.
650
Khan, Z. and Agrawal, K.
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013941100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
650-662
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

• To categorize different LB methods as
well as offer a summary of the difficulties
and problems that LB currently faces.
• To provide an overview of potential study
topics for future load-balancing technique
improvements.
Challenges of Cloud Computing.
Multiple challenges exist in the usage of CC. Three
important challenges in CC include data protection
(A. Chaturvedi,et.al, 2019) data availability, security,
management of execution and load balancing, and
fault tolerance (R. Khan and M. Ahmad, 2016),
Protection of data: One important factor that must be
considered is data protection. The privacy issue
persists when data is stored on the cloud. Likewise, the
organization’s privacy concerns are exacerbated by
the fact that the exact location of repository sites is
frequently unknown. Most current models use data
centers to protect knowledge through firewalls (A.
Chaturvedi,et.al, 2019).
1. Problems with data availability and retrieval:
SLAs will fully adhere to the business's
needs. Here, the operational staff is crucial to
managing system time and supervising SLAs
2. Security: To safeguard data and the
virtualized Internet, apps, services, as the
associated CC infrastructure, security of
cloud computing, more popularly, cloud
protection, includes a wide array of laws,
technologies, applications, and control
mechanisms. It falls under the subdomains of
information security, internet security, and
more generally, computer security (R. Khan
and M. Ahmad, 2016).
3. Managing execution: Each stack’s cores are
subject to tension adjustment. Additionally,
this boosts device output. Many recent
figures provide an effective use of resources
and a change to the stack. Cloud stacks can
be created in a variety of ways, including
memory, CPU, and structure stacks. The path
to center point overload and subsequent store
relocation to other centers is to alter the
strain.
4. Load balancing: One of the main problems
with the CC at the moment is load balancing,
which prevents some nodes from being
underutilized while others are overloaded, so
the idle ones need to be put to work. Price,
reaction time, dependability, effectiveness,
and use of resources are some of the QoS
metrics that load balancing may enhance (R.
Khan and M. Ahmad, 2016).
5. Fault tolerance: Because resource dropping
affects unit performance, job outcomes,
productivity, reaction time, and high quality,
FT is among the most important parameters.
Consequently, in order to identify errors, fix
them, and improve performance metrics, a
fault tolerance strategy is needed. To
guarantee the continuity of the essential
services and the program’s completion, fault
tolerance is a crucial consideration.
2 LOAD-BALANCING
One crucial technique for distributing workloads
among cloud computing users is load-balancing, such
as several computer resources to maximize resource
use, improve performance, and guarantee system
dependability.
Research environments rely on load balancing as
their essential practice to accomplish tasks that
combine artificial intelligence processing with large-
scale simulation, big data analytics, and high-
performance computing, which is essential for
handling large volumes of data.
The primary objective of LB is to efficiently divide
the workloads across different cloud endpoints,
preventing any node from being overloaded and
sometimes underloaded (J. Shah, 2017) To optimize
its utilization of resources and enhance the overall
reaction time, LB can be defined as the procedure for
allocating a load among network links on several
gadgets or groups of systems. It prevents excessive
asset replication and shortens the device's overall
waiting time. To distribute and process data without
waiting, requests are dispersed throughout servers
during this process. By shifting the device burden, LB
maximizes system performance (M. A. Hossain and S.
Roy,2019)
2.1 Characteristics of Load Balancing
Distributed network traffic or computational
workloads represent the technique of allocating
workloads among several servers to keep any one
server from becoming overloaded, which is referred to
as load-balancing. The following are the main features
of load balancing firewalls (A. Chaturvedi,et.al,
2019).
Evenly Traffic Distribution: To avoid bottlenecks
and guarantee peak performance, incoming requests
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
651

or workloads are effectively distributed among
available resources.
1) Excellent Availability and Dependability:
The system offers superb reliability
alongside dependability because it redirects
system traffic to functional servers to
maintain service accessibility when servers
fail (A. Jain and R. Kumar, 2016)
2) LB Scalability: The scalability parameter of
LB allows administrators to dynamically
add or remove servers for traffic demand
variations.
3) Failover and Fault Tolerance: The system
ensures service continuity through the
detection of broken elements by remedying
traffic diversion to functional servers.
4) Conservation persistent (Sticky Session):
The system needs sticky sessions to
maintain user requests within a single server
throughout their connection. IP hashing and
cookies, together with other methods,
operate at load-balancing to achieve this
goal (S. Afzal and G. Kavitha,2019).
2.2 Challenges of Cloud Computing’s
Load Balancing
LB is among the most pressing issues that require
particular attention out of all the difficulties that cloud
computing faces. This covers topics like VM security
and migration; user comfort with QoS and source
usage are given equivalent weight when looking for a
better way to increase cloud-based resource
utilization. An inventory of some load-balancing
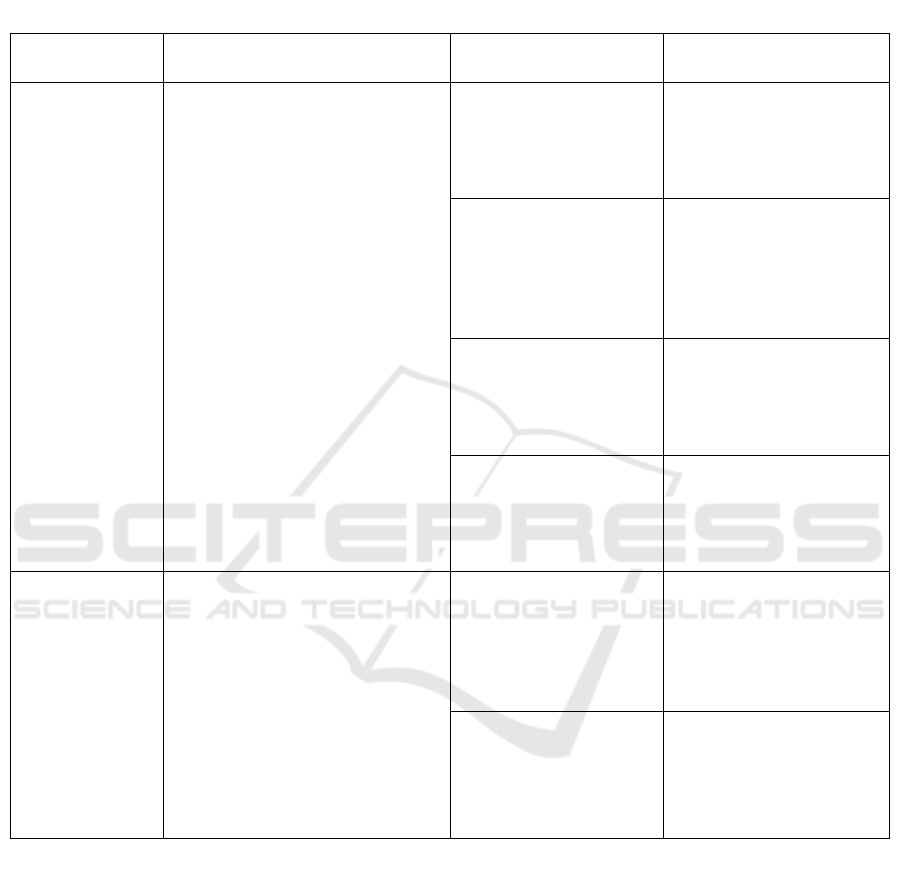
problems is provided beneath. Table 1 shows the The
Load-Balancing Challenges Overview Is Presented.
1) Distributed Location-Based Nodes: To
compute at different places, cloud data
centers are usually dispersed. These centers
use a centralized network of dynamically
distributed nodes to process consumer
requests efficiently. There are several load-
balancing techniques with a narrow scope
that ignore factors like network and
communication latency, the distance between
distributed computing nodes, customer space,
and resource availability. It is difficult to
operate nodes in extremely remote locations
since more algorithms are not appropriate for
this setting (P. Kumar,2019)
2) A single failure instance: Certain algorithms
used for load-balancing are put forth in the
literature in situations where the centralized
node makes load-balancing decisions rather
than decision-making being divided among
several nodes. The entire computer system
will be impacted if the main components fail.
3) VM Mobility: Several virtual computers can
be constructed on a single physical unit,
thanks to virtualization. These VMs are
autonomous in their architecture and have
many configurations. It is suitable to move all
virtual machines (VMs) to a distant site using
the LB approach if a physical device is
overwhelmed.
4) Hypothesis for Perception: The authors are
making load balancing in the cloud a
homogenous node in the original question. A
switch that is dynamic is needed by CC
consumers, whose execution needs to be done
on heterogeneous nodes to have the most
effective network and reduce the response
time.
5) Data Handling: Old conventional storage
devices, especially hard disks, always
required massive resources and equipment
costs for hardware; this CC addressed.
Consumers can keep the data safely and
evenly with the help of the cloud without any
control problems. Storage is ever-growing
and demands in turn, redundancy of stored
data to maintain access and data availability.
6) Scalability: With cloud services of on-
demand scalability accessibility, people have
the opportunity to access resources to
downscale and downscale rapidly at any time
or scale up. A good load balance must adapt
quickly to variability in the computational
environment in terms of, for example,
changing requirements and conditions,
memory and device topology, and so on.
7) The Intricacy of the Algorithm: Algorithms
for cloud computing ought to be fast and
simplistic to accomplish. A stronger analysis
technique seeks to decrease the efficiency of
cloud systems and to excellence.
8) On-demand Self-Service: Among the most
important features that are related to CC is
scalability; materials could have
unsupervised provisioned or disseminated.
So, how do we apply or disassociate cloud
computing and its offerings, retaining
likewise efficiency like traditional systems as
well as the greatest resource (R. Khan and M.
Ahmad,2018)?
9) Control of Energy: The economy of the scale
is the advantage of cloud usage in energy
management. In the final analysis, saving on
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
652
power is the crucial element that renders a
worldwide economy possible, in which
limited companies will contribute to the pool
of international capital rather than separately
supplying their utilities (R. Khan and M.
Ahmad,2018).
Table 1: The Load-Balancing Challenges Overview is Presented.
Reference Title Challenges Description
P. and
R. Kumar
(2019)
A survey of the problems and
difficulties with cloud computing LB
techniques
Distributed
Geographical Nodes
Usually, cloud data centers
are dispersed to accommodate
computing in various places.
Single Instance of Failure
The centralized node makes
LB decisions; decision-
making is not dispersed
among several nodes.
VM Mobility
Building several virtual
machines on a single physical
unit is made possible by
virtualization.
Hypothesis for
Perception
For a network to be effective
and response times to be
shortened, CC consumers
require a dynamic switch
Rafiqul and M.
Zaman Oqail
A survey of LB difficulties in CC
On-Demand
Service
Flexibility is cloud
computing’s primary
characteristic; resources can
be distributed or delegated
automatically.
Energy Management
The economies of sales are
the advantages of energy
management, which promotes
cloud use.
2.3 Parameters of Load Balancing
In this work, some performance parameters are added
to the existing load balance parameters. Additionally,
new parameters may be added to the classification
based on their attributes if they are discovered in the
future. The cloud load-balancing parameters are
divided into four sets by taxonomy (R. Kaur and N.
Ghumman,2017). Table 2 shows the An Overview of
The Load-Balancing Parameters.
1) Load balancing metric with dependent
nature and qualitative characteristics.
2) Load balancing metrics that are independent
and have qualitative characteristics.
3) Load balancing metrics that are dependent
and have quantitative characteristics.
4) Load-balancing metrics that are independent
and have quantitative characteristic
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
653
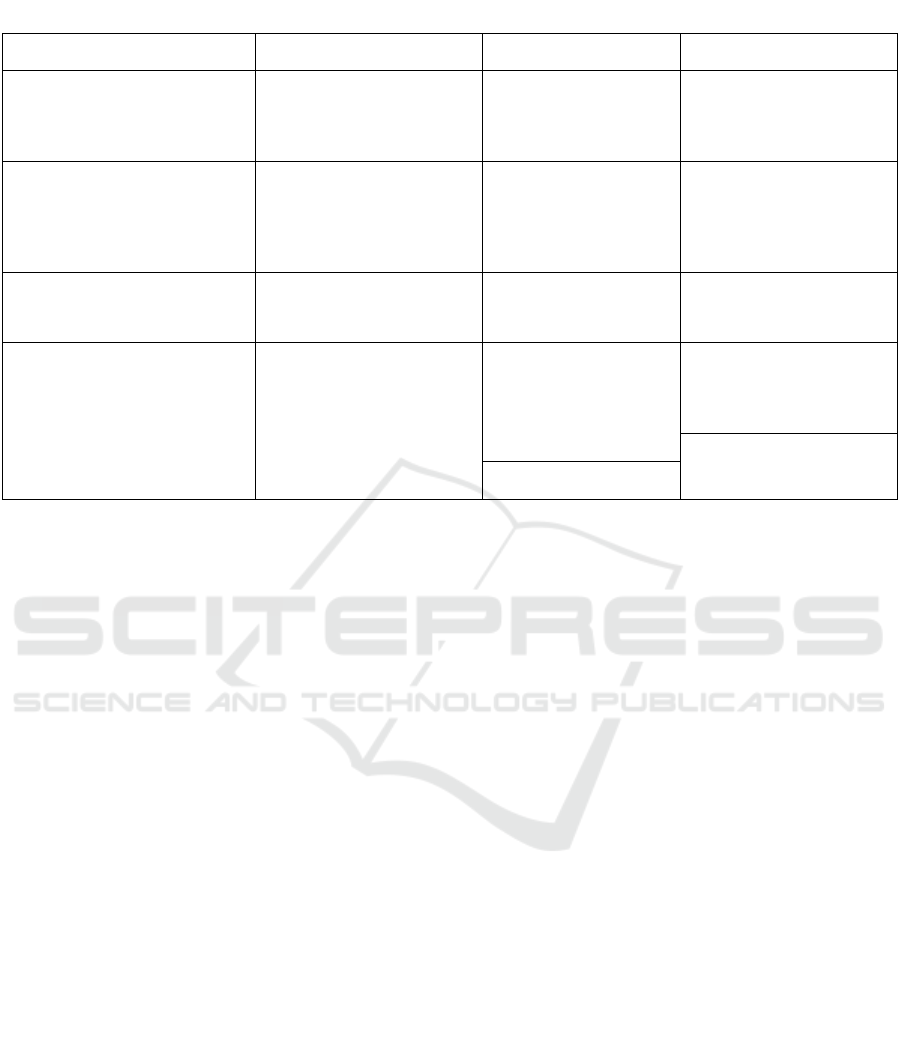
Table 2: An Overview of the Load-Balancing Parameters.
References Title Parameters Descriptions
A. Jain & R.Kumar
(2016)
A cloud environment multi-
stage load-balancing method
Fault Tolerance
The algorithm’s capacity
to handle error situations
and its resilience to
failure.
R. Kaur & N. S.
Ghumman (2018)
Task-Based LB through
effective cloud computing
VM use
Reaction Time
It is determined by
deducting the completion
duration of an assignment
from the task delivery
b
eginning time.
Roy Sumendu (2019)
Performance evaluation od
load balancing algorithms
Overhead
Support the additional
expense of algorithm
inte
g
ration.
S. Afzal &
K. Ganesh
(2019)
A Systematic Review of a
Taxonomic Classification of
Load Balancing Metrics
Scalability
Possible for a device to
carry out consumer
operations within the
intricate traffic flow..
Improves system
consistency for the
efficiency parameter.
Performance
3 TECHNIQUES FOR
BALANCING LOAD
In cloud computing, load-balancing strategies can be
broadly divided into three categories: hybrid,
dynamic, and static. These methods aid in effectively
allocating workloads among several servers in order
to optimize resource use, enhance performance, as
well as guarantee high availability.
3.1 Static Techniques
Static load-balancing strategies don’t depend on the
state of the network; instead, they employ a static set
of rules. This approach requires specialized familiarity
with resources, including time of contact, node storage
and space, node capabilities for processing, etc., and
is not scalable. Although this method is fast and
effective, it usually fails to locate the connected
servers, which results in uneven resource allocation.
The main issue with this type of approach is that
decision-making does not give enough thought to the
system’s actual state. Therefore, distributed systems
cannot tolerate a state of constant change.
The techniques for static load-balancing methods
include:
• The Round Robin (RR) Method
• Minimum-Maximum (MM) Method
• Shortest Job First (SJF) Algorithm
3.2 Dynamic Techniques
The method starts its decision-making process after
reviewing the present system's situation. Each of these
tactics provides the benefits of shifting work from
machines with heavy loads to machines with light
loads (P. Kumar,2019)
The specified dynamic load-balancing methods
include:
• Least Connection Algorithm
• Throttled Algorithm
• Weighted Round Robin
4 EXAMINATION OF
COMPARISON IN LOAD-
BALANCING APPROACHES
4.1 Load Balancing Using
Round-Robin Algorithm
To handle multiple things happening at the same time,
the CPU uses a method called Round Robin. It is like
giving each task a tiny time slot and then just going
through the list again and again, ensuring everything
gets a chance to run. This section describes the
algorithm’s idea and how scholars have proposed
utilizing it to resolve CC load-balancing concerns.
Table 3 shows the Comparison Of The Enhanced
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
654
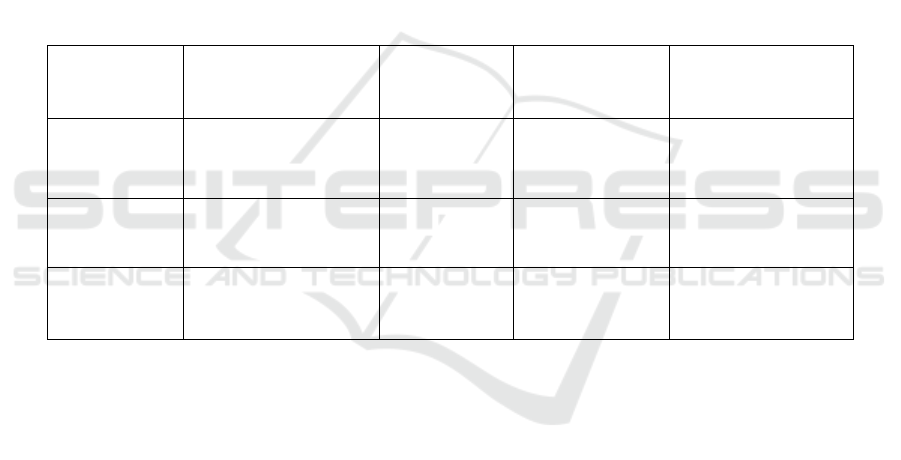
Simulation Tool Based On The Rr Algorithm’s
Performance.
1) Tailong and Dimri(2016) suggested that to
change CloudAnalyst’s current
responsiveness of the service broker
guidelines, the authors should use an
Optimize Response Time Algorithm was
modified (MORT). The method determines
the scheduling procedure after calculating
the waiting and response times for each
process. Although it can decrease response
time, for a dynamic cloud environment, the
method is less suitable because this method
didn’t solve the time quantum issues in RR.
2) Issawi et al. (2015), the author suggested a
Modified Optimize Response Researchers
have enhanced the quality of service (QoS)
in cloud-based apps by considering the
problem of burstiness in workload. An
abrupt increase in cloud service users results
in a load-balancing problem; therefore, both
situations should be considered in cloud
computing. To efficiently assign the tasks
you’ve been given to heavy loads of work on
VMs, an adaptive LB method
(RR+Random) is suggested. This algorithm
alternates between random and RR project
scheduling strategies.
3) Pasha et al. (2014), an RR-based task-based
LB approach is provided. The recommended
approach is an enhanced round-robin that
saves the most recent entry submitted by a
used base in a hash map, which decreases the
total reaction time in cloud applications (S.
A. Salman and M. K. Ahmed,2021)
Table 3: Comparison of the Enhanced Simulation Tool Based on the RR Algorithm’s Performance.
Author Parameters Tool Response Time Processing Time
Dimri &
Tailong (2016)
Processing and
response times
Cloud Analyst 151.72 ms 1.66 ms
Pasha &
Associate,
(2014
Processing time and
response time
CloudSim 299.91 ms 1.210 ms
Issawi &
Associate,
(2015)
Reaction time &
Processing time
NA 369.6 ms 314.9 ms
4.2 Load Balancing Using a Throttled
Algorithm
A load-balancing method known as the throttled
algorithm distributes requests among virtual machines
(VMs) according to their availability. Restricting the
number of active requests per virtual machine
guarantees effective resource use. This section
describes the Throttled algorithm’s idea, and in order
to solve load-balancing problems in CC, scholars have
proposed using it.
1) Phi and associates, 2018, suggested the TMA
algorithm, which tends to keep two virtual
machine (VM) tables with accessible and
hectic designations for each VM equitable
workload sharing. In contrast to the
conventional Algorithm, which keeps a single
database for each VM, making it more
challenging to find out if a Virtual Machine
(VM) is available whether or not. Reaction
Time decreased somewhat from 402.66 to
402.63 (ms) due to the algorithm. (A. Aliyu and
P. Souley,2019)
2) Banerjee and Ghosh, 2016, suggested that
according to the priority method, utilizing the
PMTA, or Modified Throttled Algorithm, has a
sufficiently quicker completion time above the
existing method. To perform top-priority jobs
at first, as well as to divide the workload evenly
between multiple virtual machines, it centers
on distributing tasks that arrive via a
preemptive queue to halt processes with lower
tiers from executing. Although the approach
decreased reaction and waiting times in
comparison to the existing TA as well as the
round-robin algorithm, it could nevertheless
lead to excessive reaction times as well as
craving for less important things.
3) Souley and Aliyu, 2019, suggested for
equitable workload distribution, TA, as well as
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
655
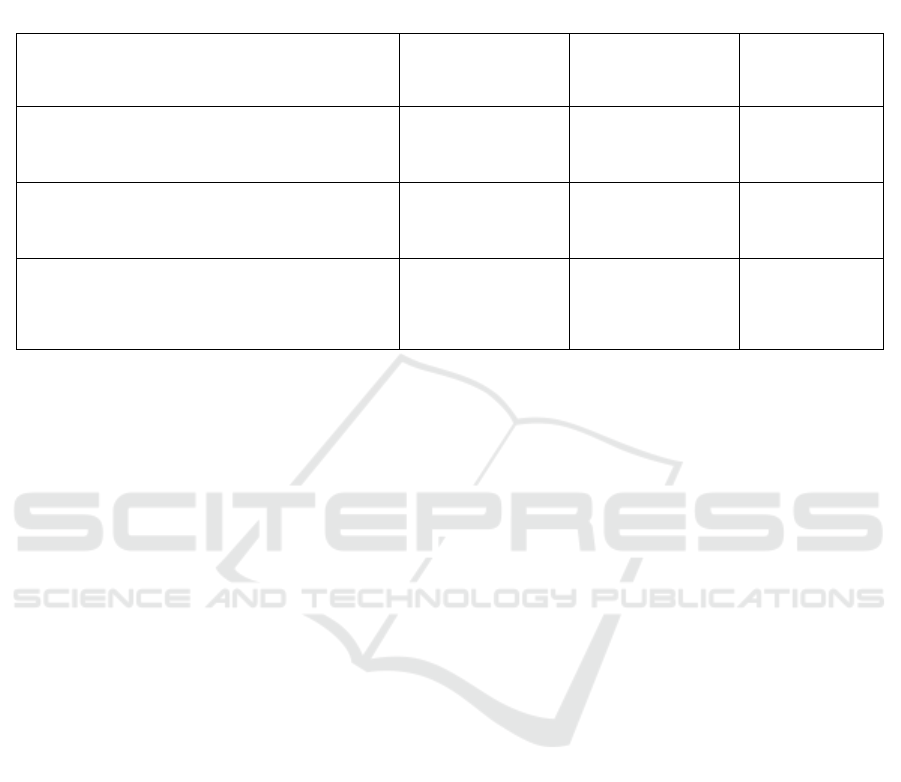
ESCE, the Hybrid Method is suggested,
maintaining a setpoint as each virtual
machine’s (VMs) top priority. In addition to
lowering response time, it is also reasonably
priced (S. Lian, et.al, 2017) Table 4 shows the
Comparison of The Efficiency of a Controlled
Algorithm-Based Simulation Tool.
Table 4: Comparison of the Efficiency of a Controlled Algorithm-Based Simulation Tool.
Algorithm Tools Response Time Processing Time
TMA CloudAnalyst Tool 402.6 ms 173.0 ms
Priority-based altered throttled algorithm
(PMTA)
CloudSim
Tool
0.06 ms 1.32 ms
Evaluation of a hybrid approach’s performance
(TA+ESCE)
--------- 315.68 ms 7.57 ms
4.3 Load Balancing Using Machine
Learning
The goal of machine learning (ML), a branch of AI, is
to teach systems to carry out novel tasks without
explicit programming. Training is the process of using
models using statistical techniques based on the past
data to produce models that can predict previously
unknown values. By guaranteeing service quality and
adherence to set SLAs, an intelligent load balancer
gives cloud providers a competitive edge. The
intelligent models listed below were examined. Table
5 shows the An Overview Table Displaying The Ml
Load-Balancing Strategies That Have Been
Reviewed.
1) S. Liang et al. suggested a load balancer to
manage traffic in the data center. The
quantification of load traffic was predicted
using a Bayesian network, which was then
integrated with reinforcement learning to
incorporate a self-adjustment criterion and
decide on the appropriate course of action.
The method used included delocalizing
processing.
2) J. Kumar and A. K. Singh created this way to
foretell the amount of work in the data center
on the cloud. This approach blends ANN with
self-adaptive differential evolution (SaDE).
User requests were combined into the periods
that functioned as historical information. The
ANN was trained using back data and actual
workload components. Future work in the
data center was predicted using the resulting
model. NASA and Saskatchewan server
datasets were used to train the model.
3) A. Kaur et al. employed regression using
deep learning to forecast the ongoing task
timeline based on computing time and cost.
Three concealed levels of convolution neural
networks, the layer of activation composed of
the ReLU function, and a pooling layer were
all intended components of the network for
profound learning. The budget, as well as
schedule parameter data from larger
operations, made up the training data.
4) A. Abbas, D. Sutter, and S. Worner employed
QNN as a type of neural network built on the
ideas of quantum computing. It’s been
discovered that quantum circuits operate
similarly to ANN. The workload that the
cloudlets would produce was predicted using
the QNN model. To modify the qubit network
weights, their prototype employed the
activation function is the CNOT gate in both
the output as well as hidden layers.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
656
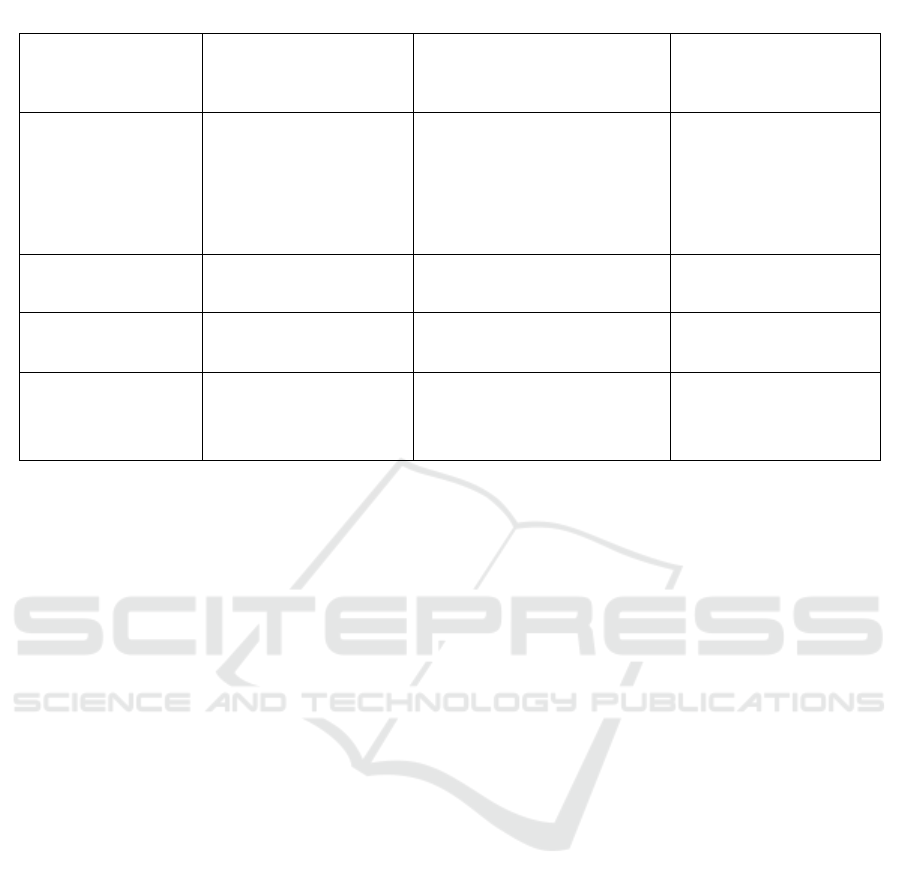
Table 5: An Overview Table Displaying the ML Load-Balancing Strategies that have been Reviewed.
Title Model Parameters / Data Used LB-Problems
An SDN controller
based on
reinforcement
learning
The Bayesian network &
reinforcement learning
Data on network traffic
Security and stability of
networks
Workload prediction
ANN & self-adaptive
differential
Customer requests are sent
to time units
Workload distribution
Deep learning CNN, Regression Job flow information Qos, resource utilization
Quantum-based Load
Balancing
Evolutional QNN
(EQNN)
Workload logs for cloudlets
Distributed resource
scaling
4.4 Ant Colony Optimization for Load
Balancing
ACO is among the effective optimization techniques
for resolving LB issues in CC. ACO’s algorithm
imitates the behavioural patterns of a colony of Ants
looking for the second-best path between their nest as
well as the source of food. method eventually
converges to an ideal answer when the shortest path is
strengthened over time by a greater concentration of
pheromones. Some of the reviewed research papers
are mentioned below. Table 6 shows the Examination
of Ac0 Algorithm-Based Load Balancing Methods.
1) M. Mishra and A. Jaiswal designed an ant-
based control system to address the issue of
LB in cloud contexts. To increase or decrease
various performance metrics, such as
network load, CPU usage, large memory, or
latency for clouds of varying sizes, we seek
to create an efficient algorithm for LB that
makes use of the simulated annealing
technique. It has been demonstrated that the
pheromone update is a useful tool for load
balancing.
2) Richa Chib, Er. V. Kaur and Dr. N. Dhillon
proposed a new method for evaluating an
optimized load balancer performance. By
altering the interval time, the provided
technique estimates the necessary measures
and is based on conditions that will give the
client high availability. They attempted to
prevent overloading in the suggested
technique and under VM loading.
3) Zheng-Tao Wu modified the basic ACO
algorithm to facilitate LB and job scheduling.
The ACO algorithm can efficiently find the
regional and international (global) ideal
solution as well as attain the quickest possible
implementation complexity time, according
to their results (S. Banerjee, 2009) By
modifying the pheromone formula, it will
predict the shortest time for task completion.
4) Shagufta Khan et al. applied the SALB
algorithm, studied current ACOs first, then
used ACO to create an efficient algorithm for
LB. Balancing the overall system load by
attempting to optimize or reduce the various
parameters is the primary contribution of the
work (A. Kaur,2020).
5) Soumya Banerjee et al. provided a
preliminary heuristic algorithm to implement
a modified ACO approach for the cloud
paradigm’s various scheduling and service
allocation mechanisms. The coefficient and
the ACO pheromone update mechanism are
changed. The likelihood of fulfilling the
inquiry has, moreover, modified scheduling
that has been used to converge, and this
modification helps to minimize the makespan
time (C. Udatha,2023).
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
657
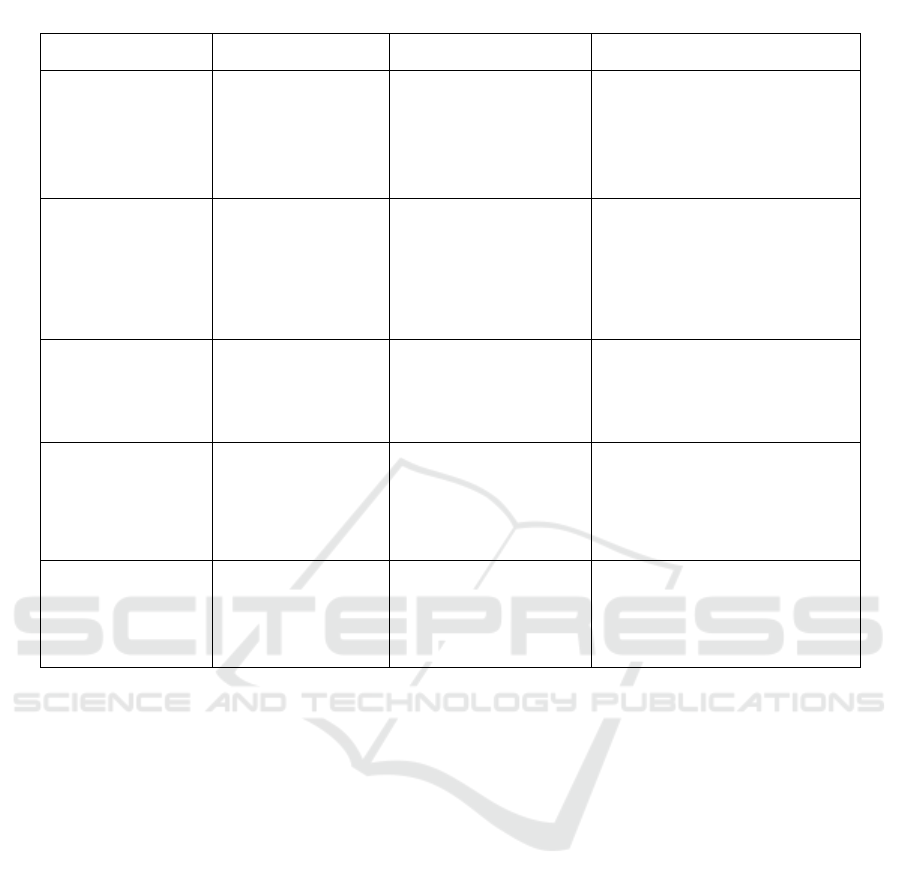
Table 6: Examination of Ac0 Algorithm-Based Load Balancing Methods.
Title Author Method Key Points
ACO: A Survey of
load-balancing
M. Mishra and A.
Jaiswal
Heuristic algorithm
based on ACO
A pheromone update is a useful
and efficient tool for load
balancing.
It is approachable for routing in
the systematic network.
ACO-based LB
algorithm for cloud
computing
R. Chib, Er. V. Kaur
and Dr. N. Dhillon
ACO
algorithm to evaluate the
effectiveness of the
optimized load balancer
This technique avoids the
situations of overloading and
underloading of VMs.
Useful for both static and
dynamic Load balancing.
Application of ACO
in cloud computing
Zheng-T Wu
Modifying
ACO for task scheduling
It can find the best solution
worldwide.
It predicts the quickest time to
finish a task.
Effective scheduling
algorithm for LB
using
ACO in cloud
computing
S. Khan et al.
Scheduling Algorithm
(SALB)
Effective at locating the overfilled
nodes as quickly as possible.
To maintain mode balance while
maximizing resource utilization
and efficiency.
Cloud computing
initiative using a
modified ACO
framework.
S. Banerjee et al
The heuristic algorithm
uses modified ACO
Improved use of available
resources.
4.5 Load Balancing Using Particle
Optimization of Swarm (PSO)
The meta-heuristic optimization algorithm known as
PSO was motivated by the social behavior of fish and
birds. By mimicking the motions of a swarm of
particles within the search area, it is used to find the
best answers. Every particle serves as a possible
solution as well as modifies its location in response to
both its own as well as its neighbours’ experiences.
Table 7 shows the Comparison of The Enhanced PSO
Algorithm-Based Simulation Tool’s Performance.
1) Dr. A. Kaur, Dr. P. Singh, H. K. Toor, and B.
Singh provided the method of heuristic
optimization that is employed to improve the
decentralized load-balancing technique,
which distributes the load among each virtual
machine (VM). Additionally, the outcomes
are examined and contrasted with a
centralized load balancer in terms of
throughput and energy efficiency parameters
2) Chaitanya Udatha and Gondi Lakshneeswari
suggested an optimized multi-objective PSO
algorithm (LBIMOPSO) method for LB to
distribute tasks among the most appropriate
virtual machines (VMs) and manage load
consistently. It is a strong optimization
method that efficiently balances workloads in
a cloud computing environment while
considering several objective functions at
once.
3) R. M. Alguliyev et al. suggested the best way
to move workload-causing tasks from virtual
machines (VMs) that are overloaded to the
appropriate VMs. It aims to illustrate that
giving criteria weights results in a better
solution.
4) H. K. Nayak et al. suggested a hybrid strategy
for overcoming LB problems. In this method,
the author combined the Dragonfly and PSO
algorithms to get a better response time. It
combines investigating the dragonfly
algorithm and the strength of task scheduling
using particle swarm optimization, the
purpose of LB.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
658
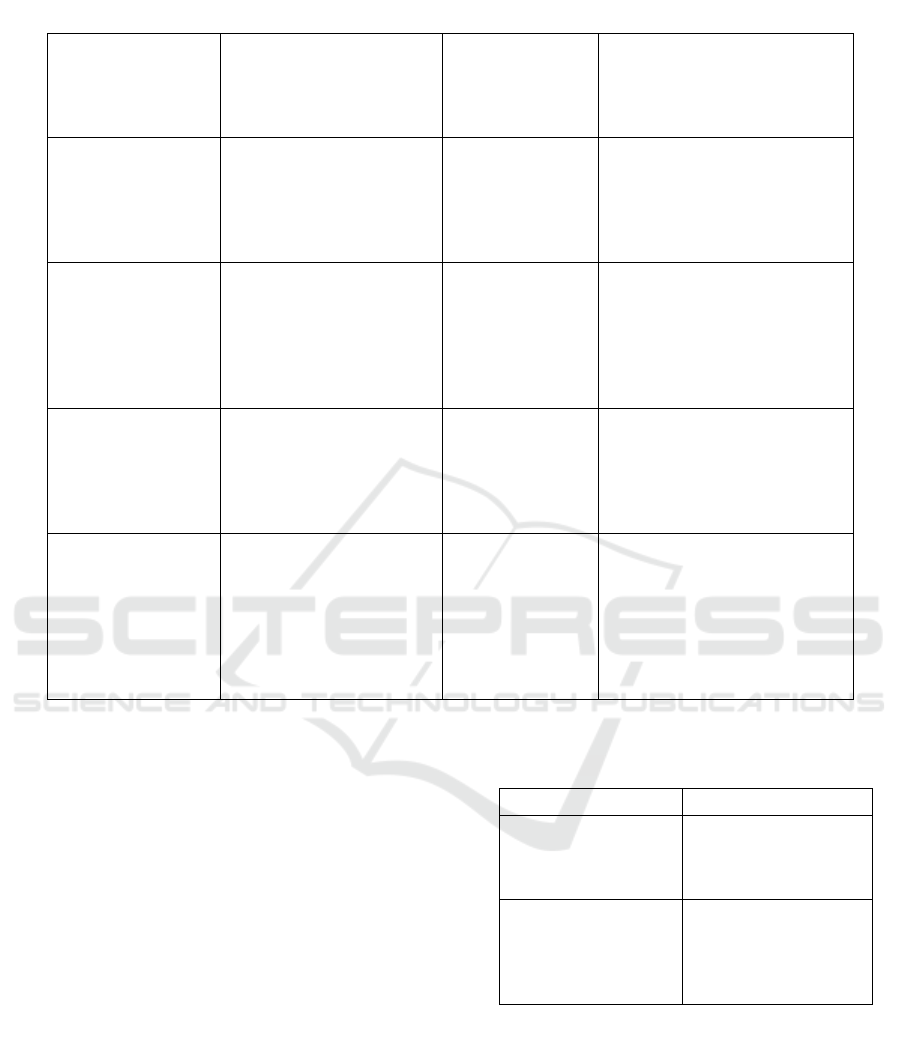
Table 7: Comparison of the Enhanced PSO Algorithm-Based Simulation Tool’s Performance.
Title
Techniques
Tool Used
Response
Time
Improvement
%
PSO-based dynamic
load-balancing in
the cloud
environment
Decentralized LB using
enhanced PSO
CLoudSim 18% Improved
Adaptive load
balancing that
makes use of PSO
for cloud task
scheduling
LB improved
multiobjective PSO
(LBIMOPSO)
CloudSim 50.76% Improved
PSO-cloud
computing using a
cloud-based LB
approach
PSO-Time-
Based LB Alpha-
PSOTBLB
CloudSim,
Jswarm
0.211s
DPSO: A hybrid LB
strategy in cloud
computing that
combines the PSO
and dragonfly (DA)
algorithms
Hybrid approach
(DA+PSO)
CloudSim
50% over DA 66.67% over
PSO
5 EMERGING TRENDS IN
LOAD-BALANCING
The future of LB is being shaped by emerging
developments within the field of CC, which seeks to
optimize sustainability, scalability, efficiency, as well
as security. A closer look at some significant new
trends is provided here
5.1 Fog Computing
By incorporating the network edge into the ecosystem
of computing to enable decisions as near the data
sources as possible as well as feasible, the Fog model
is an expansion of the conventional cloud computing
paradigm. The use of such a computing model has
several advantages. Lag times between servers and
users, for instance, might be decreased (M.
Adhikari,et,al.2018) Table 8 shows the Fog
Computing Advantages And Difficulties.
Table 8: Fog Computing Advantages and Difficulties.
Advantages Difficulties
1. Reducing the
amount of bandwidth
used by the cloud.
1. Needs effective
coordination between
edge, fog, and cloud
nodes.
2. It enhances
performance for real-
time applications.
2. Risks to security
because of
decentralized
processing.
5.2 Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is becoming essential in
several industries to speed up and optimize
transactions by raising their degree of auditability,
dependability, and traceability. A distributed
immutable ledger that is set up in a decentralized
network and depends on cryptography to adhere to
security regulations makes up blockchain(M.
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
659
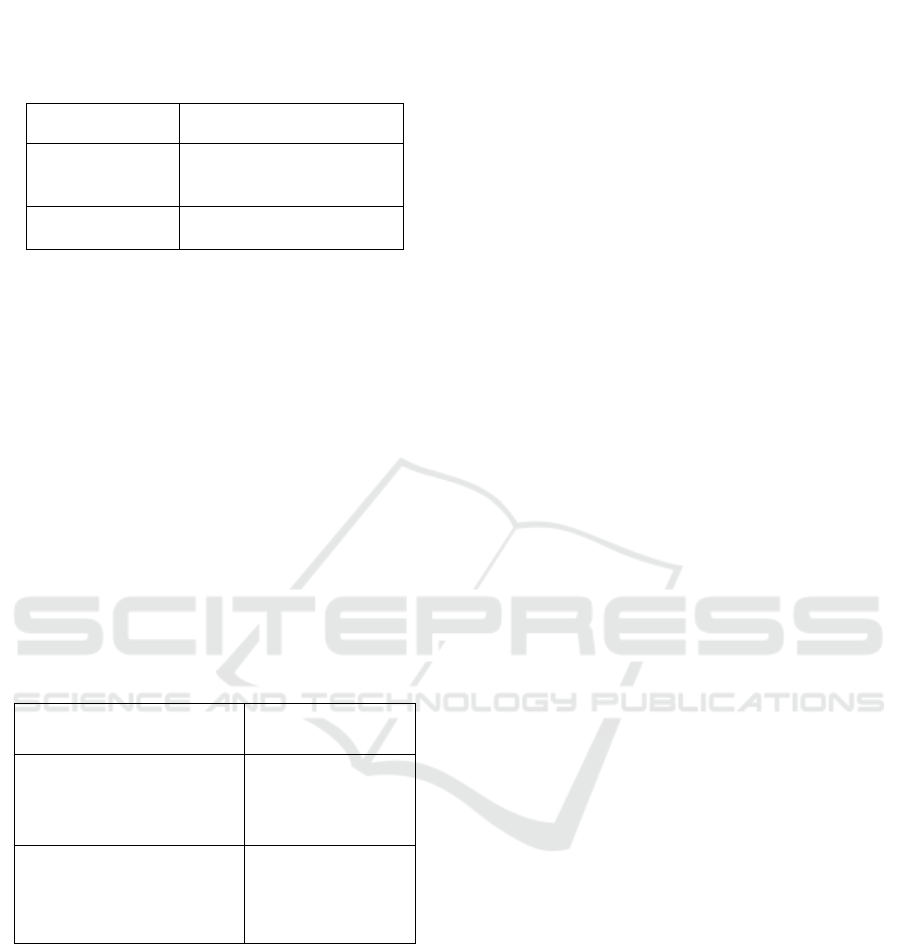
Adhikari,et,al.2018). Table 9 shows the Blockchain
Advantages And Difficulties.
Table 9: Blockchain Advantages And Difficulties.
Advantages Difficulties
1. It removes the
main causes of
failure.
1. Excessive computational
overhead.
2. Increases trust
and securit
y
.
2. Slower processing rates.
5.3 Machine and Deep Learning
Recently, there has been a lot of interest in AI because
of the enormous volume of data produced in recent
years, as well as the increase in processing power,
primarily from GPUs. Researchers and practitioners
of cloud computing can benefit from understanding
deep learning and machine learning algorithms and
prototypes (M. Adhikari and T. Amgoth,2018). Cloud
environments are increasingly using DL and AL for
intelligent load balancing. These methods make
decisions in real time, optimize resource allocation,
and forecast workloads using data-driven models.
• Predictive Analysis
• Reinforcement Learning
• Neural Networks
Table 10: AI Advantages and Difficulties.
Advantages Difficulties
1. Dynamically adjusts to
shifting workloads.
1. Training models
require large
datasets.
2. Enhances user experience
by making the best use of
available resources.
2. Computationally
costly.
New developments in load balancing emphasize
automation, decentralization, sustainability, and
intelligence. Cloud environments are becoming more
eco-friendly, scalable, and efficient thanks to
technologies like AI, Edge computing, Blockchain,
and Green cloud computing, which are
revolutionizing conventional load-balancing
techniques. (M. Adhikari, et, al.2018) Table 10 shows
the AI Advantages and Difficulties.
6 FUTURE RESEARCH
DIRECTION
In the first ten years of its existence, the idea behind
the CC has transformed the information technology
landscape, similar to the Internet, the Web, and the
actual computer. Large-scale diverse sensor networks
and IoT will produce enormous data streams for
archival purposes, management, and analysis, as well
as energy-cost-effective customized computer
services that must adjust to a range of hardware
gadgets while making adjustments for a number of
factors. The surveyed algorithms are found to
generally enhance energy protection, resource
utilization, as well as quality of service. Existing LB
algorithms have a number of drawbacks, including
static barriers, insufficient frequency control, resource
waste, and energy waste. As a result, there is much
room for improvement. Therefore, new approaches
that demand load-balancing according to carbon
emission, energy consumption, and support costs are
very promising. It is recommended that a number of
meta-heuristics be tested in real-world scenarios, such
as techniques that use ACO or PSO to demonstrate
their potential for use in the actual cloud. To get
around the shortcomings of the algorithms in use
today, the following work might be accomplished in
the future.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This survey has explored various cloud computing
elements that guarantee effective resource use, high
availability, and peak performance. Among the main
issues, load balancing is the primary problem since
burdening a gadget/device can have disastrous
consequences and render technology outdated.
Therefore, efficient resource utilization always
requires the use of an LB algorithm. The primary
objectives regarding LB are to fulfil user demands by
allocating the workload among several network nodes,
optimizing resource utilization, and increasing device
efficiency. Load balancing algorithms were explained
in this study, including dynamic load balancing, as
well as dynamic algorithms inspired by nature. More
efficient use of resources, a lower makespan, a higher
extent of the mismatch, and efficient migration of
tasks, as well as a shorter period, will all be made
possible eventually by the requirement to develop
completely self-governing dynamic LB algorithms.
The technology of CC itself has a long lifespan.
Among the key innovations, we can use it to carry out
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
660

crucial business functions. Over time, the
aforementioned innovations will completely improve
cloud computing. Effective and clever load-balancing
techniques will remain essential as cloud computing
grows to meet the growing needs of big data
processing, distributed applications, and cutting-edge
technologies like 5G and the Internet of Things(IoT).
The upcoming CC system generation will be greatly
influenced by ongoing research and innovation in this
region.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I want to thank everyone who helped with this review
paper. I want to start by expressing my appreciation to
Mrs. Kavita Agrawal [Supervisor], whose knowledge,
insightful advice, and unwavering support helped to
shape the course of my study. I also thank Integral
University for its assistance in providing resources and
a favourable research environment. And at last, I’m
grateful to my friends and family for their unwavering
support as well as encouragement during the research
process. This work is an intellectual property of
Integral University videos the Manuscript
Communication no. IU/R&D/2025-MCN0003505.
REFERENCES
M. Shahid, N. Islam, M. Alam, M. Su'ud and S. Musa, "A
Comprehensive Study of Load Balancing Approaches
in the Cloud Computing Environment and a Novel
Fault Tolerance Approach," IEEE, vol. VIII, 2020.
D. Shafiq, N. Jhanjhi, A. Abdullah, and M. Alzain, "A load
balancing algorithm for the data centers to optimize
cloud computing applications," IEEE, p. 99, 2021.
F. Zabini, A. Bazzi, B. Masini and R. Verdone, "Optimal
performance versus fairness tradeoff for resource
allocation in wireless systems," IEEE Transactions on
Wireless Communications, vol. VI, no. 4, 2017.
J. Shah, K. Kotecha, S. Pandya, D. Choksi and N. Joshi,
"Load balancing in cloud computing: Methodological
survey on different types of algorithm," in International
Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics
(ICEI), 2017.
P. Kumar and R. Kumar, "Issues and challenges of load
balancing techniques in cloud computing: A survey,"
ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), vol. LI, no. 6, pp. 1-
35, 2019.
A. Chaturvedi and A. Rashid, "Cloud Computing
Characteristics and Services: A Brief Review,"
International Journal of Computer Sciences and
Engineering, vol. II, pp. 421-426, 2019.
R. Khan and M. Ahmad, "Load balancing challenges in
cloud computing: a survey," in Proceedings of the
International Conference on Signal, Networks,
Computing, and Systems, 2016. K. A. Nuaimi, N.
Mohamed, M. A. Nuaimi and J. Al-Jaroodi, "A Survey
of Load Balancing in Cloud Computing: Challenges
and Algorithms," in Second symposium on network
cloud computing and applications, 2012.
M. A. Hossain and S. Roy, "Measuring the Performance on
Load Balancing Algorithms," Global Journal of
Computer Science and Technology, vol. XIX, no. 2,
2019.
A. Jain and R. Kumar, "A multi-stage load balancing
technique for cloud environment," in International
Conference on Information Communication and
Embedded Systems (ICICES), Chennai, 2016.
S. Afzal and G. Kavitha, "A Taxonomic Classification of
Load Balancing Metrics: A Systematic," in Indian
Engineering Congress, Udaipur, 2018.
R. Kaur and N. Ghumman, "Task-Based Load Balancing
Algorithm by Efficient Utilization of VMs in Cloud
Computing," in Big Data Analytics: Proceedings of CSI
2015, 2017.
N. Verma, B. N. Gohil, A. S, and K., "Load balancing in
Cloud Computing Environment using Modified
Genetic Algorithm," in 6th International Conference on
Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON),
2023.
S. Issawi, A. A. Halees and M. Radi, "An efficient adaptive
load balancing algorithm for cloud computing under
bursty workloads," Engineering, Technology & Applied
Science Research, vol. V, no. 3, 2015.
N. Pasha, A. Agarwal and R. Rastogi, "Round robin
approach for VM load balancing algorithm in cloud
computing environment," International Journal of
Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software
Engineering, vol. IV, no. 5, pp. 34-39, 2014.
S. A. Salman and M. K. Ahmed, "Load balancing
techniques in cloud computing: A review," Journal of
King Saud University –Computer and Information
Sciences, vol. VI, no. 1, pp. 223-250, 2021.
A. Aliyu and P. Souley, "Performance Analysis of a Hybrid
Approach to Enhance Load Balancing in a
Heterogeneous Cloud Environment," International
Journal of Advance in Scientific Research and
Engineering (IJASRE), vol. V, no. 7, 2019.
S. Liang, W. Jiang, F. Zhao, and F. Zhao, "Load Balancing
Algorithm of Controller Based on SDN Architecture
Under Machine Learning," Journal of Systems Science
and Information, vol. VIII, no. 7, pp. 578-588, 2020. J.
Kumar and A. K. Singh, "Workload prediction in cloud
using artificial neural network and adaptive differential
evolution," Future Generation Computer Systems, vol.
LXXXI, pp. 41-52, 2018.
A. Abbas, D. Suttr, C. Zoufal, A. Lucchi, A. Figalli and S.
Woerner, "The power of quantum neural networks,"
Nature Computational Science, vol. I, pp. 403-409,
2021.
A. K. Singh, D. Saxena, J. Kumar and V. Gupta, "A
Quantum Approach Towards the Adaptive Prediction
of Cloud Workloads," IEEE Transactions on Parallel
Exploring Load Balancing: Issues, Methods and Strategic Outlook in Cloud Computing
661

and Distributed Systems (, vol. XXXII, no. 12, pp.
2893-2905, 2021.
R. Mishra and A. Jaiswal, "Ant colony Optimization: A
Solution of Load balancing in Cloud," International
journal of Web & Semantic Technology, vol. III, no. 2,
p. 33, 2012.
R. Chib, V. Kaur and N. Dhillon, "Load Balancing
Algorithm For Cloud Computing Using Ant Colony
Optimization," Journal of Emerging Technologies and
Innovative Research, vol. V, no. 10, 2018.
Z. T. Wu, "Application of Ant Colony Optimization in
Cloud Computing Load Balancing," in International
Conference on Intelligence Science, 2017.
S. Khan and N. Sharma, "Effective Scheduling Algorithm
for Load balancing (SALB) using Ant Colony
Optimization in Cloud Computing," International
Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science
and Software Engineering, vol. IV, no. 2, pp. 966-973,
2014.
S. Banerjee, I. Mukherjee and P. K. Mahanti, "Cloud
computing initiative using modified ACO framework,"
World Academy of Science Engineering And
Technology, vol. III, 2009.
A. Kaur, P. Singh and H. K. Toor, "Particle Swarm
Optimization (PSO) based Dynamic Load Balancing in
Cloud," International Journal of Computer Science
Engineering (IJCSE), vol. IX, no. 2, pp. 130-136, 2020.
C. Udatha and G. Lakshmeeswari, "An Adaptive Load
Balancing using Particle Swarm Optimization for
Cloud Task Scheduling," International Journal of
Engineering Trends and Technology, vol. LXXI, no. 9,
pp. 36-45, 2023.
R. Alguliyev, Y. Imamverrdiyev and F. Abdullayeva,
"PSO-based load balancing method in cloud
computing," Automatic Control and Computer
Sciences, vol. LIII, pp. 45-55, 2019.
S. Mohapatra, S. Mohanty, H. Nayak, M. Mallick, J.
Ramesh, and K. Dudekula, "DPSO: A Hybrid
Approach for Load Balancing using Dragonfly and
PSO Algorithm in Cloud Computing Environment,"
EAI Endorsed Transactions on Internet of Things,
2024.
R. Buyya et al.., "A Manifesto for Future Generation Cloud
Computing: Research Directions for the Next Decade,"
ACM Computing Surveys, vol. LI, no. 5, 2018.
M. Adhikari and T. Amgoth, "Heuristic-based load-
balancing algorithm for IaaS cloud -," Future
Generation Computer Systems, vol. LXXXI, pp. 156-
165, 2018.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
662
