
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low‑Latency System for Social
Media Monitoring
Sanskar Kumar Agrahari
1
, Arjun Kumar Das
1
, Krishna Bhagat
1
, Vivek Kumar Shah
1
,
Nikita Sharma
2
and Gayathri Ramasamy
1
1
Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Amrita School of Computing, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Bengaluru,
Karnataka, India
2
Department of Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham,
Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Keywords: Sentiment Analysis, Kafka, Django, Big Data, Hadoop, Machine Learning.
Abstract: Social media sentiment analysis needs real-time tracking of public opinion therefore requires fast processing
together with low latency and high accuracy. To achieve this, PySpark is used for the data preprocessing and
model training process. A web application that is developed through Django lets users submit tweets that
generate instant sentiment predictions whether the tweet is positive, negative, neutral, or irrelevant while
Kafka manages real-time streaming of processed results. MongoDB utilizes NoSQL architecture to effectively
store sentiment forecasts to- gather with their associated data. Among different trained models, Logistic
regression achieved maximum accuracy according to testing while the system showed successful operation
through real-time sentiment analysis with high- speed data processing and quick response times and
approachable user interface which proved its usefulness for sentiment trend analysis.
1 INTRODUCTION
The sudden explosion in social media platforms
results in gigantic amounts of user-generated content,
which makes in-the-moment tracking difficult for
public sentiment. This is where sentiment analysis
and opinion mining come into play, which according
to them would involve the extraction of all emotions,
opinions, and sentiments from a text, such as from a
social media site. However, unstructured social media
content processing for the bottom line remains an
arduous task. Traditional techniques of sentiment
analysis mostly lack real-time processing, scalability,
and accuracy, which makes action-happy insight
derivation impossible.
In this digital era, real-time sentiment analysis is
very important to understand public sentiment tables
and study emerging trends for better decisions (C.
Verma and R. Pandey, 2016). Real-time delays in
business processes result in both lost market
opportunities and ineffective marketing strategies
along with ineffective crisis response measures. The
formal nature of social media content along with its
rapid updates creates obstacles such as informal
language and abbreviated writing that make tweet
sentiment detection jobs more challenging. Phrases
must be classified in real-time through an accurate
and efficient platform for individuals and
organizations requiring upcoming insight analysis (S.
Sanjana et al., 2024).
Sentiment analysis automation occurs through the
implementation of machine learning models to tackle
the noted challenges. The current sentiment analysis
techniques need intensive data processing prior to
analysis because they create high processing costs
that restrict their ability to perform real-time
operations. From 2016 to 2018 big data platforms
together with distributed computing networks
facilitated the expansion of sentiment analysis
solutions on a large scale (A. Kc and R. Sumathi,
2018). System performance receives enhancement
through the combination of data preprocessing with
PySpark and sentiment classification with machine
learning algorithms as well as web applications and
real-time streaming platforms for data flow. The
proposed system brings together machine learning
algorithms with streaming and big data approaches to
Agrahari, S. K., Das, A. K., Bhagat, K., Shah, V. K., Sharma, N. and Ramasamy, G.
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low-Latency System for Social Media Monitor ing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013940500004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
641-649
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
641

run real-time sentiment analysis. The preprocessing
tasks and model training process relieve PySpark as
the main engine while logistic regression emerged as
the optimal classifier method during assessment. The
developed Django web application allows users to
enter tweets for immediate sentiment analysis
prediction processing. The system implements Kafka
(R. Shree et al., 2017) as its real-time data streaming
platform to maintain system component connection
while using MongoDB as a NoSQL database to store
and retrieve sentiment prediction data efficiently. The
design features computation efficiency together with
quick processing time and easy usability to make
sentiment analysis more efficient and accessible for
users. The research presents a list of its main
achievements as follows.
• Real-time sentiment classification for instant
analysis of social media data.
• Integrates multiple technological systems to
build an efficient high-performance solution.
• Demonstrates in processing rapid and
unstructured data found in social media
platforms.
• Potential for scalability and adaptation to other
real-time text analysis applications.
The research supports the United Nations
Sustainable Development Goal on industry,
innovation, and infrastructure (UN SDG-9) for the
development of an innovative sentiment analysis
system through advanced technologies. The rest of the
paper is structured as follows: Section II covers a
review of existing methods regarding real-time
sentiment analysis. Section III describes the twitter
dataset which is used for the sentiment analysis. In
Section IV, the system architecture is presented along
with the description of how the machine learning
models work together with streaming frameworks and
database management. Section V includes
information about data pre-processing procedures and
model training and is evaluated through accurate
results along with computational efficiency and real-
time processing abilities. Finally, Section VI
concludes with an overview of essential discoveries
together with prospective enhancements for the work.
2 RELATED WORK
A huge volume of data is produced per second which
needs a system to analyze, and the opinions of people
need to be processed with high accuracy and the result
should be used for the improvement in the field.
Arokia et al. produced positive and negative labels on
tweets through the application of sentiment (Mary et
al., 2021) analysis on Twitter data from 2020-2021
using Linear SVC with high training precision and
Logarithmic Regression achieving maximum testing
accuracy to demonstrate sentiment analysis has
practical value for public emotion prediction. Madhu
et al., (2021) conducted real time sentiment analysis
on Twitter tweets through big data analysis alongside
tools including Hive and Machine Learning algorithm
to achieve fast and secure data processing. The K-
Means method and TF-IDF models identify tweets
among three clusters: fresh or deteriorating or stale
equilibrium through classification and the output
judgment determines positive or negative or neutral
sentiment based on total analysis. Alawad et al.,
(2021) examined Hadoop cluster performance
through an investigation of configuration
dependencies and Map Reduce model advantages for
big data analysis while reporting positive effects from
Hadoop cluster and Map Reduce model applications
in big data analysis. However, the paper notices
performance benefits from increasing dataset size in
large data analysis although significant cluster size
growth diminishes communication and lengthens
CPU times. Arafat et al., (2017) built VIM as a web-
based tool that allows users to visualize generic data
while also performing data pre-processing and mining
tasks and data drift analysis through statistics and
functions for feature-based association rule mining.
The VIM tool functions with Python Django Web
Framework and incorporates Graph Lab library for its
implementation.
Vatambeti et al., (2024) performed lexicon-based
sentiment analysis on Indian Twitter tweets about
Swiggy, Zomato and UberEats utilizing deep learning
methods to supply statistical feedback that supported
company recommendations. Zomato obtained the
highest positive ratings among all food delivery
services while showing the smallest proportion of
negative reviews. Ismail et al., (2025) featured a new
ETL framework that uses big data tech for Twitter-
based sentiment analysis while delivering efficient
processing of data streams together with bias
correction capabilities and sentiment analysis and
geographic visualization of Twitter data. Joloudari et
al., (2023) evaluated sentiment analysis systems for
COVID-19 tweets by studying BERT together with
deep CNN and demonstrated how these approaches
successfully extract tweet meaning while creating
embedding structures. The research has enhanced
sentiment detection abilities, and it provides guidance
for designing an efficient lightweight BERT model.
Singh et al., (2023) utilized data from WHO and CDC
along with social media sentiment data which is
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
642
analyzed using classification and regression models
with healthcare data between 2010 and 2020 for
predicting diseases and analyzing public health
sentiments.
Alqarni et al., (2023) examined COVID-19’s
influence on public emotions through both CNN and
BiLSTM model approaches of Arabic tweets. The
research proved that negative sentiments grew
significantly before and after the pandemic’s
outbreak and it demonstrated superior efficiency in
sentiment classification since it obtains 92.80%
accuracy with CNN and 91.99% accuracy with
BiLSTM. Yadranjiaghdam et al., (2017) discussed in-
memory processing for real- time Twitter data
analysis while studying current workflows and
developing a new framework using Apache Kafka for
data intake followed by Spark execution of real-time
processing and machine learning methods using
earthquakes in Japan as a case study for evaluating
origin analysis with timing and public response
evaluation. Fahd et al., (2021) proposed a real-time
sentiment analysis platform that combines multiple
social media data with Big Data technology through
Apache Kafka as a data collector and a lexicon-based
algorithm together with Spark analytics, YARN
resource scheduler and MongoDB for data storage
while evaluating multiple performance measures.
Mane et al., (2014) executed a sentiment analysis
strategy based on Hadoop infrastructure to handle the
extensive daily tweet volume and create time-
sensitive industrial and business insights with
improved solution speed from distributed computing
systems. Bikku et al., (2016) addressed the challenges
faced by the big data and highlighting Hadoop’s
architecture and efficiency with the help of Map
Reduced Framework. Ganesh et al., (2016) explored
biga data analytics for processing large image data
using Hadoop for handling the large dataset and for
efficient data. Saravanan et al., (2018) evaluated big
data analytics with Hadoop architecture and Spark
making a GUI for a user-friendly interaction. Singh et
al., (2015) evaluated and analyzed the presented
architecture which handles the huge data generating
per day with Hadoop explaining the challenges faced
by modern architecture. Radhika et al., (2017)
performed a sentimental analysis on Tamil news feed
based on POS Tagger based on characteristics and
entities of the various topics. Despite various analysis
and evaluations in tweet sentiment and feedback or
opinion of product, no paper has existed that
introduces a standardized system which processes
massive data inputs to evaluate product quality and
determine positive or negative ratings through
Docker and Kafka for comment-live streaming.
3 DATASET DESCRIPTION
The paper utilizes social media tweets primarily
sourced from Twitter into its dataset. The dataset
provides the necessary base for building and training
the sentiment analysis model so it can be applied in
real-world scenarios. Each data entry in the provided
dataset consists of textual information linked to
accompanying Metadata in its word file format. The
dataset contains 80,000 records which hold one
distinct entry for each record. The designed structure
enables detailed research of sentiment patterns within
multiple sources of input data. The dataset fulfills both
the requirements of being reliable and adequate for
developing the analysis model.
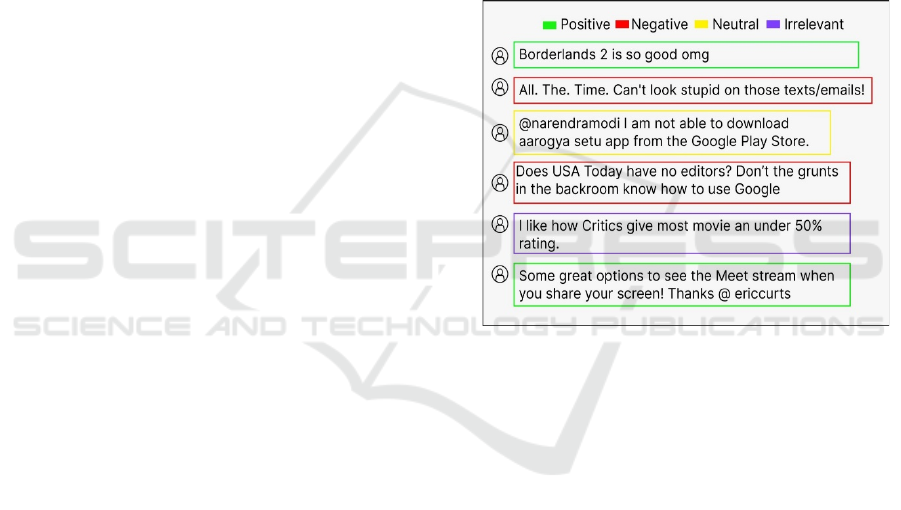
Figure 1: Sample dataset of the tweets.
The dataset demonstrates broad and extensive
content from a methodological standpoint. A
representative part of the dataset appears in the above
Figure 1. The tweets receive classification based on
their sentiment into four color-coded sections which
include Positive comments marked green and
Negative comments marked red while Neutral
comments have a yellow designation together with all
other irrelevant content receiving purple notification.
The dataset contains numerous tweets which ensure
an ample amount of data both for training and
validation procedures and model testing operations.
Each individual tweet represents a sample number that
reveals complete details about social media
interactions through hashtag usage and share mentions
and URLs and emoji presence. Timestamp and
language details within the data enable additional
dimensions in the dataset.
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low-Latency System for Social Media Monitoring
643
4 METHODOLOGY
The methodology of this work explains the
systematized procedure followed for the purpose of
attaining real-time sentiment prediction concerning
the tweets available in the data stream from twitter
platform. With the implementation of the system
involving several phases, the process helps in
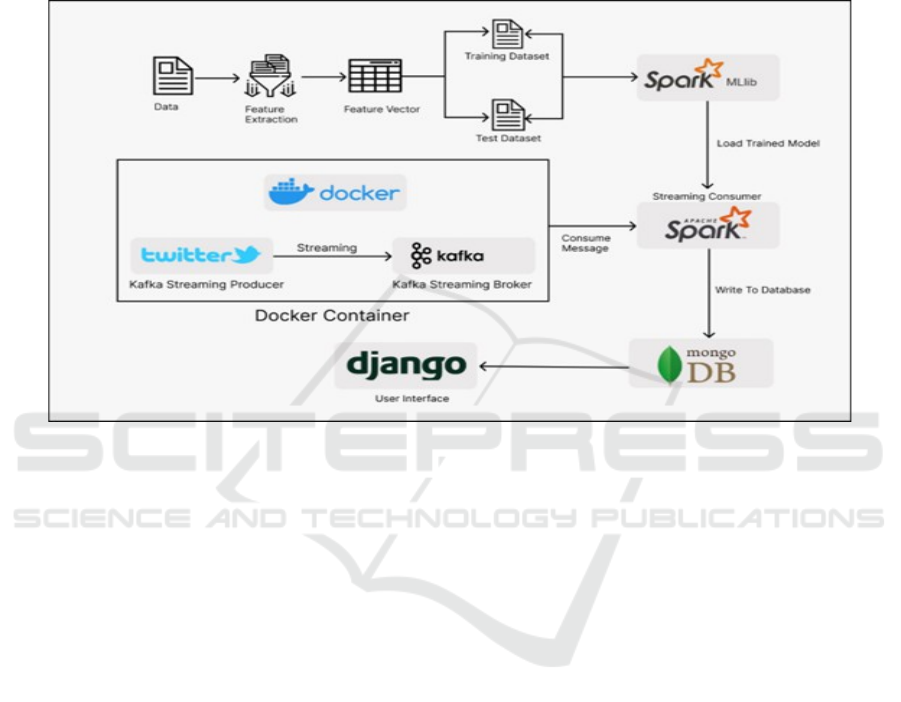
achieving its success factors. Figure 2 is the
architecture diagram that depicts the overall flow and
interaction between various components. It includes
the integration of machine learning, big data analytics,
use of web technologies and real time streaming for
building comprehensive sentiment analysis systems.
Figure 2: Architecture diagram for sentiment analysis.
The approach is divided into five key stages: Data
pre-processing, model building, GUI creation, live
stream processing, and Data storage. All the stages
play the role of contributing to designing a scalable,
efficient, user-friendly system. Each stage is
connected to each other making it easy to pass data
from one stage to the other while keeping the analysis
in real time. The design is modular, which provides
the space for the further changes that are to be made
to the system later.
5 DATA PREPROCESSING WITH
PYSPARK
Preprocessing of data is important in text data
preparation for the learning process in the case of text
data. The tweets to be analyzed are extremely raw and
basic pre-processing is needed to modify and arrange
the data so that the model can correctly identify the
correct sentiment.
The preprocessing process included the following key
steps:
1.
Data Cleaning: Data cleaning took place and
resulted in the removal of empty rows as well
as removal of special characters that have no
meaning to the algorithm. Also, to make the
input more manageable, the text is translated
to lowercase, thus creating a laid-back format.
2.
Tokenization: Each sentence is split into
individual words (tokens) for more granular
analysis. This tokenization enabled the model
to focus on meaningful word-level patterns.
3.
Spark Capabilities: For high processing
velocity and keeping the system scalable, the
distributed features of PySpark are used to
handle large datasets. This feature was
especially helpful because the content of real-
time tweet analysis changes frequently.
To overcome such issues as the issue of class
imbalance in the dataset an analysis was made on the
four classes of sentiment which are as follows. This
imbalance is illustrated in Figure 3, and requires
subsequent, but similar techniques such as
oversampling or under sampling of the dataset to
enhance the model.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
644
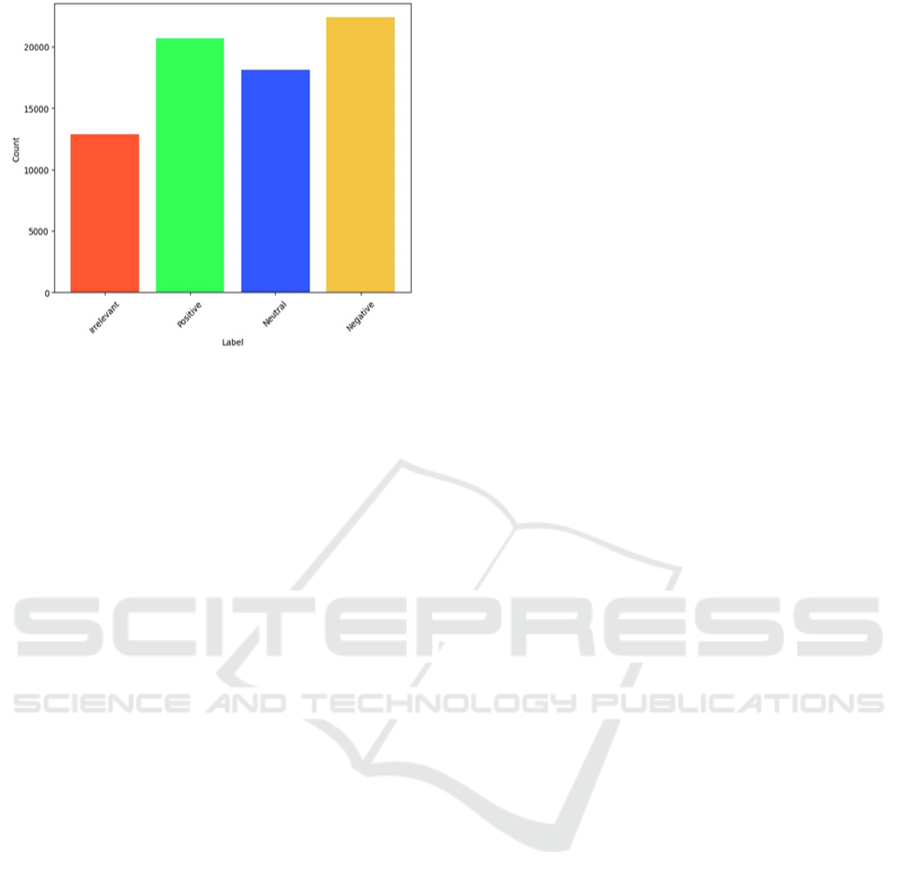
Figure 3: Class imbalance in dataset.
The insights from this visualization informed
specific preprocessing strategies, ensuring the data
was optimized for training and real-time predictions.
6 MODEL TRAINING
After preprocessing data, the preprocessed data was
used to train a sentiment analysis model. Several
machine learning algorithms were applied on the
dataset and evaluated. Finally, the logistic regression
model was chosen for this dataset because of its
accuracy and suitability for the dataset.
1.
Algorithm Selection: Several classification
algorithms were tested from PySpark MLlib,
including logistic regression, decision trees,
and support vector machines.
2.
Performance Evaluation: Cross-validation
techniques were applied to optimize
hyperparameters and model performance.
Models were evaluated using different metrics
such as accuracy, precision and recall.
3.
Pipeline Creation: The PySpark pipeline was
constructed that includes preprocessing steps
and the logistic regression model for
streamlined predictions.
7 GUI CREATION WITH
DJANGO
A high-level Python web framework, Django, was
used to develop web applications, enabling users to
interact with the system and analyze tweets
dynamically. A form has also been designed in the
GUI that allows users to input tweets for sentiment
analysis. The system ensured real-time feedback by
displaying results instantly on the web interface.
8 REAL-TIME STREAMING
WITH KAFKA
Kafka was implemented in docker containers to
facilitate real-time data transmission between
components, ensuring seamless interaction and low-
latency processing. Kafka producer reads tweets
from a CSV file and sends them to a Kafka topic
(numtest) every three seconds to simulate real-time
data streaming. The consumer uses PySpark to load
a trained and stored logistic regression model. Then,
once Kafka consumer Retrieves tweets from the
numtest topic in real-time, it processes each tweet
through the PySpark pipeline for sentiment
prediction. Finally, Smooth communication was
established between the Kafka consumer and the web
interface to display the prediction result instantly.
9 DATA STORAGE WITH
MONGODB
A NoSQL database, MongoDB, was used to store
sentiment analysis results and other related data. Each
processed tweet was stored in MongoDB as a
document containing the original text and the
predicted sentiment. MongoDB’s flexibility was
utilized to handle semi-structured data and support
future data analysis tasks.
This methodology ensures a robust, scalable, and
user-friendly system for real-time sentiment analysis,
integrating cutting-edge tools and frameworks for
optimal performance.
10 RESULTS
The findings presented in this paper prove that the
proposed real-time sentiment analysis system
possesses high accuracy and scalability of sentiments.
It achieves preprocessing tweet data, building various
machine learning models, and real-time processing of
tweets stream to provide a picture of the distribution
of sentiments. The logistic regression classifier
achieved the most accurate results during the testing
and validation of the developed machine learning
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low-Latency System for Social Media Monitoring
645
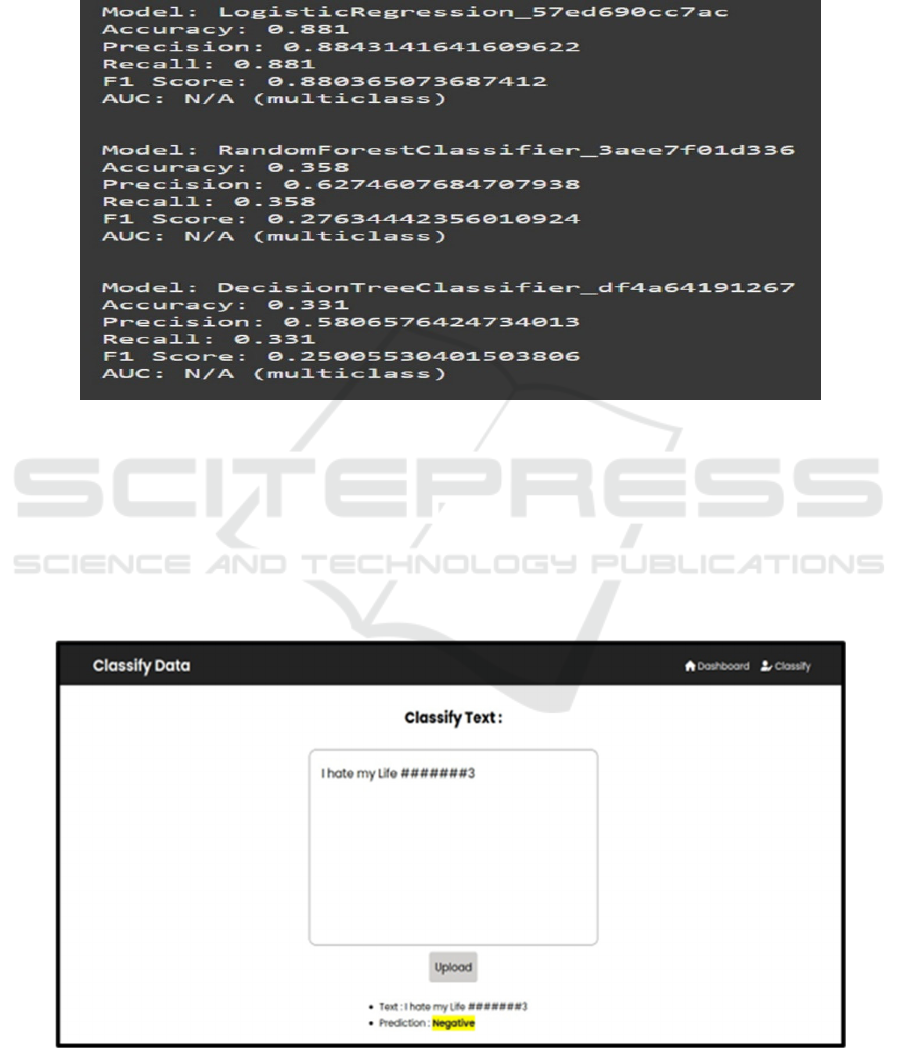
model. Metrics of cross-validation showed good
performance on different datasets, and this meant that
the model was able to perform well on any different
inputs. For measuring the performance, the
parameters used are accuracy, precision, recall, and
F1 score. Other than the logistic regression, Random
Forest and Decision Tree models are also used during
the experimentation phase of the thesis as depicted in
Figure 4.
Figure 4: Models used for analysis.
Apache Kafka for real-time streaming integration
empowered the system to analyze tweets as they
arrived in the system. The free sentiment that is
predicted about each tweet that is analyzed is whether
it is positive, negative, neutral, or irrelevant on the
web interface in a matter of seconds. It kept low
latency for the system that keeps user interaction
smooth and without any interruption. Figure 5
illustrates the dashboard which shows how at the end
of the given comment it times it is categorized and
then placed under the sentiment’s column. Also, it
gives the user a qualitative opinion of the expected
result, which is easy to understand.
Figure 5: Dashboard for analysis of the tweet.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
646
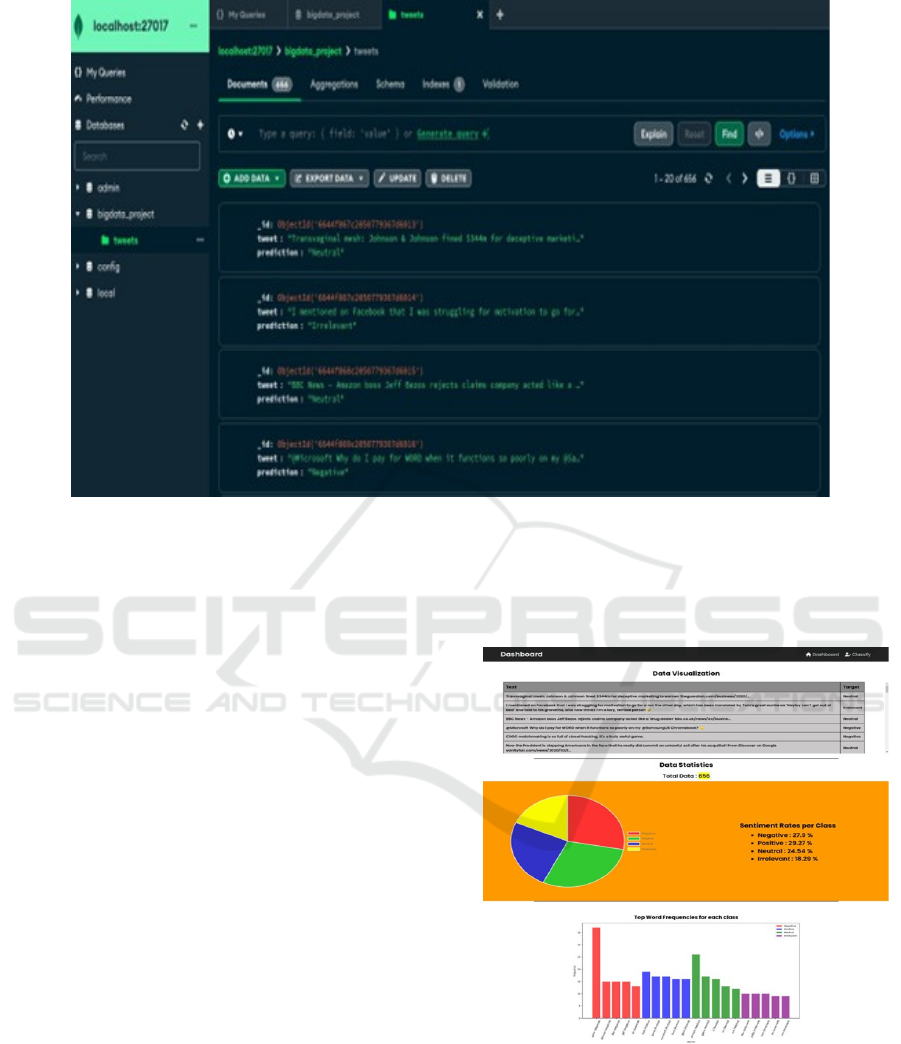
Figure 6: MongoDB database for storing the tweets.
Figure 6 shows the usage of the MongoDB
database allowed for storing of the predicted
sentiment outcomes, as well as the tweets with their
references within a reasonable amount of time and
space. To further illustrate the potential of the stored
data, patterns over time are identified or recurring
tweet sentiments, which would enforce further
applications like market research or social sentiment
analysis.
The real-time update of the web interface made it
possible to visualize the trend of sentiment made by
the user. Figure 7 shows the interface to visualize the
distribution of the tweets along with its classification.
A table is presented with the list of tweets, and the
tweets are classified in a particular class in the target
column; thus, it is convenient for the users to compare
the results of the predictions with the expected results.
A pie chart is also introduced for the sentiment
distribution for different classes within the interface.
A bar graph below depicted the distribution
percentage of positive, negative, and neutral
sentiments depending on tweets by users. Through
this feature, a way of analyzing social media trends is
made available, by observing the dynamic features of
sentiment patterns.
These results provide evidence of the
effectiveness of planning and executing the presented
system to process large and constantly updating
datasets, as well as generate accurate sentiment
predictions. For this reason, the scalability and the
high resilience of the proposed system recommends
the developed model for real-world sentiment
analysis applications.
Figure 7: Web interface to visualize the classification and
distribution of a tweet.
11 CONCLUSIONS
The work done in this project is quite effective to
underscore how progressive technologies can be
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low-Latency System for Social Media Monitoring
647

applied to make sentimental analysis of tweets in real
time. The system uses PySpark for the data
preprocessing and machine learning algorithm,
Django for building an appealing web user interface,
Kafka for effective real time stream processing, and
MongoDB for storing big amounts of data in
optimized manners makes the present system a
perfect, efficient and effective solution for the
sentiment analysis.
As a result of the process of model selection
during model evaluation, the selected logistic
regression model offers accurate and timely
classification of tweet sentiments. The employment
of real-time streaming guarantees that users can
receive sentiment predictions with least delay,
making the application fast and efficient. Also, the
use of web interface is rather convenient to interact
with, as well as entering and analyzing tweets which
enable users to get the idea of sentiments’
distributions. Not only does the project prove the
possibility of carrying out real-time sentiment
analysis, but also the need for combining machine
learning with big data and web frameworks. The
system proposes complex factors of performance:
scalability, operational productivity and adaptability,
which allows considering it as a perspective for usage
in such fields as social media monitoring, market and
trend analysis.
Two suggestions for future work are the
expansion of the current system with features such as
multilingual sentiment analysis, topic extraction and
the addition of an emotion recognition feature. An
uplift in model performance, employing state-of-art
deep learning techniques, can act as a further
enhancement of the proposed system. In sum,
implementing this project means a major shift
towards utilizing real time sentiment analysis for real
life application which will prove as handy and helpful
for the purpose of meaningful decision making in a
constantly evolving digital landscape.
REFERENCES
A. Kc and R. Sumathi, “Analyzing twitter sentiments with
big data,” in 2018 2nd International Conference on
Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), pp.
989–994, IEEE, 2018.
A. Alqarni and A. Rahman, “Arabic tweets-based sentiment
analysis to investigate the impact of covid-19 in ksa: a
deep learning approach,” Big Data and Cognitive
Computing, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 16, 2023.
A. Ismail, F. H. Sazali, S. N. A. Jawaddi, and S. Mutalib,
“Stream etl framework for twitter-based sentiment
analysis: Leveraging big data technologies,” Expert
Systems with Applications, vol. 261, p. 125523, 2025.
B. Yadranjiaghdam, S. Yasrobi, and N. Tabrizi,
“Developing a real-time data analytics framework for
twitter streaming data,” in 2017 IEEE International
Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress), pp. 329–
336, IEEE, 2017.
Bikku, T., Rao, N.S. and Akepogu, A.R., 2016. “Hadoop
based feature selection and decision-making models on
big data”. Indian Journal of Science and Technology,
9(10), pp.1-6.
C. Verma and R. Pandey, “Big data representation for grade
analysis through hadoop framework,” in 2016 6th
international conference-cloud system and big data
engineering (Confluence), pp. 312–315, IEEE, 2016.
Dr. Tripty Singh and S, D. V., “A modern data architecture
with apache Hadoop”, in 2015 International Conference
on Green Computing and Internet of Things
(ICGCIoT), Greater Noida on the beautiful campus of
Galgotias Institutions , 2015.
G. P. A. Mary, M. Hema, R. Maheshprabhu, and M. N.
Guptha, “Sentimental analysis of twitter data using
machine learning algorithms,” in 2021 International
Conference on Forensics, Analytics, Big Data, Security
(FABS), vol. 1, pp. 1–5, IEEE, 2021.
G.S. Ganesh, Yazhini Samyukkktha Ramanikaran,
M.Sindhuja, G. Rajesh Kannan, J. Jeyalakshmi, “Big
data in visual analytics to supplement digital image
processing using Hadoop”, Journal of Chemical and
Pharmaceutical Sciences,JCHPS., Special Issue
9,pp.54-56,Dec,2016.(SCOPUS) ISSN: 0974-2115
J. H. Joloudari, S. Hussain, M. A. Nematollahi, R. Bagheri,
F. Fazl, R. Alizadehsani, R. Lashgari, and A. Talukder,
“Bert-deep cnn: State of the art for sentiment analysis
of covid-19 tweets,” Social Network Analysis and
Mining, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 99, 2023.
K. S. Madhu, B. C. Reddy, C. Damarukanadhan, M.
Polireddy, and N. Ravinder, “Real time sentimental
analysis on twitter,” in 2021 6th International
Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies
(ICICT), pp. 1030–1034, IEEE, 2021.
K. Fahd, S. Parvin, and A. de Souza-Daw, “A framework
for real-time sentiment analysis of big data generated
by social media platforms,” in 2021 31st international
telecommunication networks and applications confere-
nce (ITNAC), pp. 30–33, IEEE, 2021.
R. Shree, T. Choudhury, S. C. Gupta, and P. Kumar,
“Kafka: The modern platform for data management and
analysis in big data domain,” in 2017 2nd international
conference on telecommunication and networks (TEL-
NET), pp. 1–5, IEEE, 2017.
R. G., K. Prasath, N., and Rajasundari, T., “Sentimental
Analysis on Tamil News Feed”, Journal of Advanced
Research in Dynamical and Control Systems, vol. 9, pp.
397-399, 2017.
R. Singh and R. Singh, “Applications of sentiment analysis
and machine learning techniques in disease outbreak
prediction–a review,” Materials Today: Proceedings,
vol. 81, pp. 1006–1011, 2023.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
648

R. Vatambeti, S. V. Mantena, K. Kiran, M. Manohar, and
C. Manjunath, “Twitter sentiment analysis on online
food services based on elephant herd optimization with
hybrid deep learning technique,” Cluster Computing,
vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 655–671, 2024.
S. B. Mane, Y. Sawant, S. Kazi, and V. Shinde, “Real time
sentiment analysis of twitter data using hadoop,”
IJCSIT) International Journal of Computer Science and
Information Technologies, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 3098–3100,
2014.
S. S. I. Arafat, M. S. Hossain, M. M. Hasan, S. A.-H. Imam,
M. M. Islam, S. Saha, S. Shatabda, and T. I. Juthi,
“Vim: A big data analytics tool for data visualization
and knowledge mining,” in 2017 IEEE International
WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer
Engineering (WIECON-ECE), pp. 224–227, IEEE,
2017.
S. Saravanan, K.E., K., Balaji, A., and Sajith, A.,
“Performance Comparison of Apache Spark and
Hadoop Based Large Scale Content Based Recomme-
nder System”, Intelligent Systems Technologies and
Applications. Springer International Publishing, Cham,
2018.
S. Sanjana, N. J. Rozario, S. Dewan, et al., “Utilizing big
data analytics for social media insights,” in 2024
International Conference on IoT Based Control
Networks and Intelligent Systems (ICICNIS), pp. 45–
49, IEEE, 2024.
W. Alawad and A. Balobaid, “In big data era: analysis of
hadoop cluster performance,” in 2021 International
Conference of Women in Data Science at Taif
University (WiDSTaif), pp. 1–6, IEEE, 2021.
Dynamic Sentiment Analysis: A Low-Latency System for Social Media Monitoring
649
