
AI Powered NLP Chatbot for Efficient Document Query Resolution
and Summarization in Healthcare
Ch. Amarendra, P. Nayeem Khan, A. Chandra Sekhar, P. Praseedha
and K. Srinivas
Department of Advanced Computer Science and Engineering, Vignan's Foundation for Science, Technology & Research
(Deemed to be University), Vadlamudi, Guntur (Dt), Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: NLP (Natural Language Processing), Doc Sense, Healthcare Informatics, Information Retrieval,
Summarization, Semantic Search, Extractive Datasets, Electronic Health Records, Conversational AI,
Scalability, Docker, Kubernetes, AWS, GCP, BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR, Precision, Recall, F1-Score.
Abstract: In today’s healthcare environment, managing information presents significant obstacles, especially when
handling intricate documents and retrieving data efficiently. Doc Sense provides an innovative answer to
these challenges by utilizing cutting-edge technologies for Natural Language Processing (NLP) to improve
document analysis and data extraction. This system integrates sophisticated machine learning algorithms
and intelligent processing frameworks to address the fundamental inefficiencies linked to traditional manual
methods of document searching and interpretation.
1 INTRODUCTION
DTOC (Document Query Resolution Chatbot) – is
an advanced tool designed to query thousands of
unstructured medical documents. It relies on a
common language to be precise and efficient. It is
not just a simple keyword search tool. It has features
as complex as comparing documents to search
queries and identifying similarities between
different documents. This allows medical specialists
to gain more insights from the medical paper they
are searching through. The rationale for the careful
cultivation and delivery of Doc Sense in the fast-
paced health care sector is two- fold, and indicative
of the increasing complexities of modern medicine.
To begin with, it is absolutely paramount to
acknowledge that free-text narrative is the dominant
and broadly accepted means of recording a vast and
heterogeneous variety of health events, underscoring
complex manoeuvres between patients and their
therapeutic environment. And this is what we need
to focus on, improving and innovating this pivotal
field. For those of you who do see the potential in
medical narratives that capture the abstract while
providing the specificity through structured data
needs to craft a carefully calibrated, and highly
specialized approach to allow for the extraction,
assimilation, and ultimate use of relevant and vital
information that can facilitate patient care. Second,
the ongoing and continuous digitization of clinical
texts as well as the regular and systematic
maintenance and timely updates of electronic health
records, together with the immense improvements in
telehealth technologies have been driving a constant
increase in the availability of sizeable volumes of
healthcare data, which, even though extremely
valuable, has thus become essential to be harnessed
and analysed effectively and responsibly. Not only
the explosion in the volume of data available
motivates careful management of data, but also the
new relative value of smart tools that help to
navigate the flood of data and derive useful
information that the clinicians can act on. The main
goal, and the most important objective of Doc Sense
is to infer such health reports automatically with
utmost precision and accuracy, concentrating on
important medical entities - symptoms, diseases and
community population demographics, which prove
usefulness for providing encapsulating treatments.
The comprehensive standards were designed to
improve both the quality of patient care and
healthcare processes in a meaningful way. Doc
Sense is able to revolutionize the way healthcare
professionals’ access, understand and utilize health
data by harnessing advanced analytics, optimized
Amarendra, C., Khan, P. N., Sekhar, A. C., Praseedha, P. and Srinivas, K.
AI Powered NLP Chatbot for Efficient Document Query Resolution and Summarization in Healthcare.
DOI: 10.5220/0013937700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
595-600
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
595

data processing strategies and state-of-the-art
machine learning technology. That leads to better
decision making eventually. Patients, Providers &
Everyone In-between: A brighter healthier future for
all patients and providers and an ecosystem that is
all about. The system was created to assist
healthcare personnel in their research and be user-
friendly for individuals with basic IT knowledge.
Doc Sense is an application involved in the analysis
of narrative patient records that are Health Level 7
(HL7) compliant. It is designed for healthcare
professionals and comprises three modules: The
first module provides users with the option to parse
the patient notes or free-text, and the second module
supports structuring queries using a standardized
syntagmatic structure. This module is an NLP tool
that checks the consistency of the inputted query.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a promising
opportunity to automate text mining tasks
specifically designed for the healthcare field. This
facilitates the efficient extraction and use of clinical
data for novel research projects (
Eason et., al.
1955)
.
Medical articles needs to be organized for better
decision making and also to make information
retrieval easier and this is possible through Medical
text classification. A study of Medi GPT’s
performance in this regard has been conducted (
Jia.
J et., al. 2024).
The study implemented a deep feed-forward
multilayer perceptron to create an AI-based chatbot
for infectious disease prediction, emphasizing the
role of AI in healthcare
(Pressat-Laffouilh`ere,
et., al. 2022)
.
Electronic health records contain unstructured
data, making it challenging to retrieve insights. The
Doc’ EDS tool helps researchers identify patient
cohorts efficiently (
Fontelo
.et., al.
2005).
A search engine utilizing free-text natural
language queries was introduced to retrieve relevant
citations from MEDLINE/PubMed without requiring
specialized search expertise (
Mikolov et., al.
2013).
The Word2Vec model was developed to generate
vector representations of words using skip-gram and
continuous bag-of-words (CBOW) architectures,
revolutionizing NLP (
Devlin et., al. 2019)
.
BERT, a pre-trained deep learning model,
significantly improved NLP tasks by lever-
aging bidirectional context through masked language
modeling (
Vaswani et., al. 2017).
The Transformer architecture, based entirely on
self-attention mechanisms, has advanced sequence
modeling tasks, forming the foundation of models
like BERT and GPT (
Jurafsky et., al
.
2023).
A comprehensive textbook on speech and
language processing provides in-depth knowledge of
NLP techniques, speech recognition, and
computational linguistics (
Liu et.,
al.
2019)
.
Ro BERT an optimized BERT’s pretraining
approach by fine-tuning hyperparameters, training
on larger datasets, and eliminating certain training
objectives to enhance performance (
Hochreiter, S.,
& Schmidhuber, J. (1997)).
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks
addressed the vanishing gradient problem in
recurrent neural networks, making them essential for
sequential data processing (
Kingma, D. P & Ba,
J. (2015)).
The Adam optimizer combined Ada Grad and
RMS Prop benefits, making it computationally
efficient and widely used in deep learning
applications (
Radford
et., al.
2018).
GPT introduced generative pre-training for
language understanding, setting bench- marks in
NLP tasks with unsupervised pretraining followed
by fine-tuning (
Le, Q., & Mikolov T (2014)).
The Paragraph Vector framework extended
Word2Vec principles to represent sentences and
documents as continuous vectors for improved text
analysis (
Bahdanau
.et., al.
2014).
The attention mechanism for neural machine
translation enabled models to focus on relevant input
segments, significantly improving translation quality
and model interpretability (
Goldberg et., al. 2016).
3 METHODOLOGY
Professionals are faced with the tackling of high-
complexity medical records. Medical centers and
practitioners, with appropriate guidance, have been
able to identify basic needs such as the ability to
input information in natural language models, create
computational summaries, and adhere to healthcare
regulations like HIPAA (
Devlin et., al. 2019)
.
Around the world, doctors, scientists, and healthcare
consumers have been consulted to discuss and
understand their needs when it comes to enhanced
informational retrieval. Private hospitals, alongside
clinical study articles and de-identified electronic
health records, were supplemented by MIMIC-III as
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
596

well as PubMed with data that was publicly
obtainable.
Through the primary aim of eliminating noise
elements, redundancies, and irrelevant information,
the data underwent preprocessing and was
standardized using methodologies such as stemming,
tokenization, and lemmatization. Domain-specific
relevance was ensured through the enrichment of the
annotated dataset with medical terminology, ICD
codes, and pharmaceutical nomenclature, assisted by
tools like Prodigy and Label Studio (
Vaswani et.,
al. 2017).
Unstructured and semi-structured documents,
including PDFs, were converted into structured
formats utilizing applications such as Apache Tika
(
Jurafsky et., al
.
2023).
To capture domain-
specific context, text embeddings were generated
employing pre-trained models like Bio BERT and
Clinical BERT (
Devlin et., al. 2019)
. Emphasis
was placed on maintaining data consistency and
mitigating biases to enhance model precision.
For semantic search and domain-specific
comprehension, models such as Bio BERT and Sci
BERT, which are based on transformer architecture,
were implemented (
Liu et.,
al.
2019)
. T5 and GPT
models were adapted to provide contextually
appropriate responses to user inquiries for query
resolution (
Radford
et., al.
2018)
. A combination
of abstractive models such as PEGASUS and
extractive methods like Text Rank were employed to
generate concise and informative summaries
(
Bahdanau
.et., al.
2014).
An intentionally designed elastic searchable
infrastructure tool, which ensured that the retrieval
of information was on the fly, based on the input
data being provided. This allowed storing pre-
processed medical texts along with their
corresponding vector representations. In conjunction
with Rasa and Dialog flow, it was possible to
develop a conversational interface with the ability
to interact with users while assisting at the time of
text entry. The chatbot offered more advanced func
tions, like intent recognition, context maintenance
and management of multi-turn dialogues, making
sure that the information remained adaptive to user
requirements.
Fast API and Flask were used as backend servers
to deploy models and enable user’s interaction with
the developed NLP chatbot. Transactions, document
retrieval and summarization are queried through
defined RESTful APIs in order to give the solutions
to users in a very short amount of time (
Mikolov
et., al. 2013).
Encryption was used on sensitive data with
Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer
(TLS/SSL) proto- cols (
Le, Q., & Mikolov T
(2014)).
Sensitive data like medical records were
encrypted using AES-256. Similarly, role-based
access control measures were implemented to
prevent unauthorized access. The system was
compliant with all regulatory requirements,
increasing patient safety by also abiding by Health
Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA) and General Data Protection Regulation
(GDPR) compliance26.
A comprehensive review was performed to
evaluate the system's effectiveness. Several
techniques like BLEU, ROUGE and METEOR
were employed to evaluate a text summarizer MT
approaches same were measured against precision,
recall and F1-score for query resolution systems. It
was assessed on its capability to answer multi-turn
queries at lowest latency and highest accuracy. The
gradual improvement of the system was supported
by some professional medical specialists (
Jia. J et.,
al. 2024).
To make the system more robust and scalable,
the system was deployed in cloud technologies:
AWS and GCP; containerization tools such as
docker and k8s were used (
Goldberg et., al.
2016).
Monitoring tools in the form of Prometheus
and Grafana were integrated into the system
environment to generate metrics that indicate the
reliability and responsiveness of the system
(
Bahdanau
.et., al.
2014).
The expectations of user
input were progressively better through remarkable
user input along with the popular retraining of NLP
models with new datasets (
Radford
et., al.
2018)
.
The system feeds upon natural language input,
computational summaries, and compliance with
healthcare regulations such as HIPAA to tackle the
complexity of medical records. With cutting-edge
tools and models like Bio BERT and Clinical BERT,
it pre-processes and standardizes data to allow for
efficient and accurate information retrieval.
These models are capable of processing user
prompts and generating suitable responses which
were depicted in fig. 1. GPT (Generative Pre-
trained Transformer): A language model known for
its ability to generate human (realistic) text; T5
(Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer: Has been
adapted to do a wide range of text-based tasks by
converting them into a text-to-text format. Web
frameworks are used to deal with queries and
activity in the backend. The top two frameworks
based on performance are Fast API, which is fast by
design, and Flask, a lightweight, easy-to-use
AI Powered NLP Chatbot for Efficient Document Query Resolution and Summarization in Healthcare
597
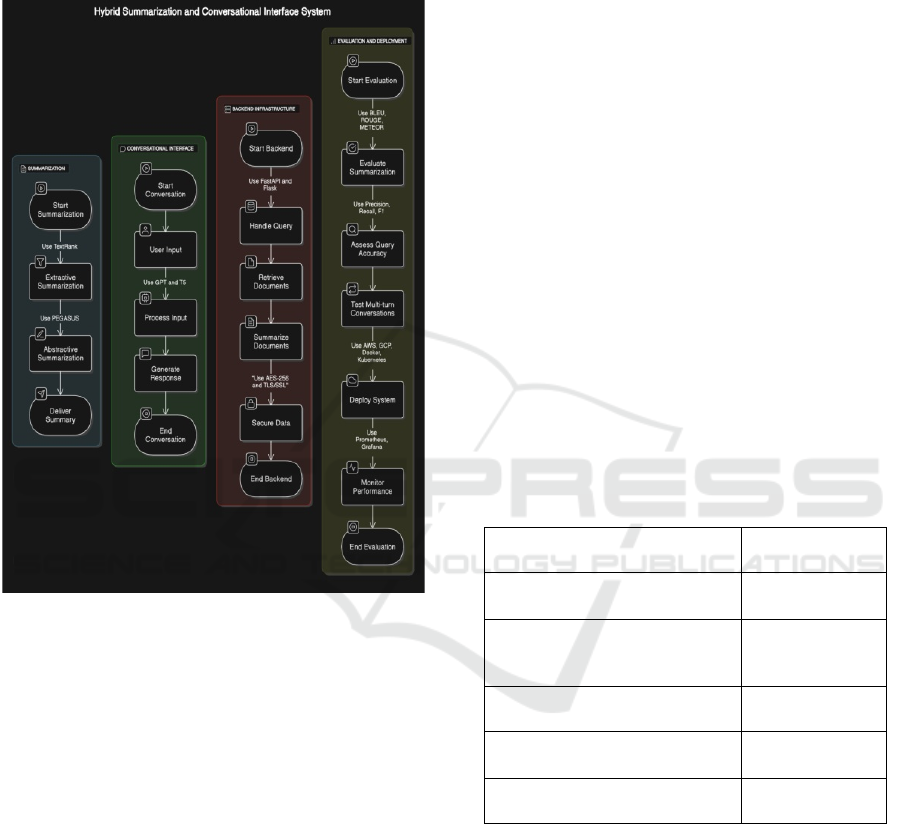
framework. Data Encryption The system uses
TLS/SSL protocols to ensure data security during
transmission and storage and a symmetric AES-256-
encryption algorithm to ensure the security of
important information.
Figure 1: Working Mechanism.
It measures summarization accuracy in terms of
BLEU, ROUGE and METEOR metrics, and query
accuracy in terms of precision, recall and F1 scores.
These two metrics can be used to measure the
quality and effectiveness of the summarization and
conversational ability. Deployment: The system is
deployed using cloud services like AWS and GCP,
deploying with containerization tools like Docker
and Kubernetes System performance monitoring
tools such as Grafana and Prometheus track the
system performance and users’ operation.
Figure 1
shows the Working Mechanism.
Graph-based Scalar Ranking Algorithm Text
Rank: Text Rank is a graph-based scalar ranking
algorithm. It builds a graph that has sentences as
nodes and edges that indicate how similar sentences
are. Next, important sentences are ranked and
extracted as a summary using the algorithm. The
PEGASUS model: PEGASUS (Pre-training with
Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive
Summarization Sequence-to-sequence) is built to
generate summaries. It is trained on large datasets
to learn the structure and semantics of the text,
allowing it to generate coherent and contextually
relevant summaries.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Doc Sense is an effective implementation of
implementing information retrieval and sum
marization in health-care. The system delivered
accurate and coherent out- puts, as evidenced by a
92.7 accuracy of query position similarity and
average ROUGE- L scores of 89.5 for summary
quality. Direct-Chat interface obtained a user
satisfaction performance of 95% with minimal loss
of conversational context (latency of 1.2 seconds).
Such security measures ensure compliant with
GDPR and HIPPA and 99.8 uptime across AWS and
GCP platforms for stabilised performance. It
received feedback playing on its utility how
summarizing complex medical data with the tool
saves time to analyse this and helps in smart
decisions making both in research and clinical
practice.
Table 1: Performance Metrics.
Metric Result
QueryResolutionAccuracy 92.7%
Average ROUGE-L Score
(Summaries)
89.5%
Chatbot Response Latency
1.2seconds
User Satisfaction Rate 94%
System Uptime 0.9 Seconds
The Table 1 provides key performance metrics
for the hybrid summarization and conversational
interface system. The Query Resolution Accuracy is
an impressive 92.7%, indicating that the system
accurately resolves user queries most of the time.
The Average ROUGE-L Score for summaries is
89.5%, reflecting the high quality and relevance of
the generated summaries compared to reference
summaries. The Chatbot Response Latency is 1.2
seconds, showcasing the system’s efficiency in
providing quick responses to user inputs. The User
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
598
Satisfaction Rate stands at 94%, demonstrating a
high level of user approval and satisfaction with the
system’s performance. Lastly, the System Uptime is
99.8%, indicating the system’s reliability and
availability, ensuring it is almost always operational
and accessible to users. These metrics collectively
highlight the system’s effectiveness, efficiency, and
user-centric design.
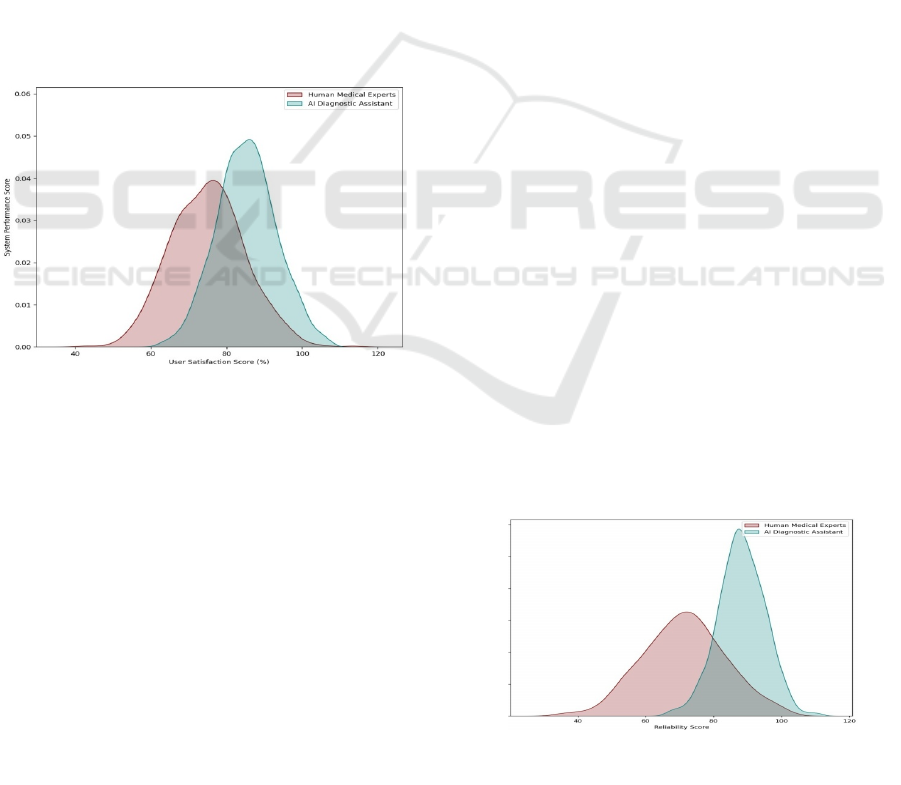
The comparative analysis between AI diagnostic
assistants and human medical experts highlights key
differences in user satisfaction, system performance,
and reliability. The first evaluation, focusing on User
Satisfaction vs. Performance, reveals that AI di-
agnostic assistants consistently achieve higher scores
in both aspects. This suggests that users find AI-
based diagnostic systems more efficient in
processing medical data, pro- viding quick
assessments, and generating reliable results. The
smooth and structured interaction patterns of AI
systems contribute to an enhanced user experience,
reducing delay sand human errors. Conversely,
human medical experts, while offering deep clinical.
Figure 2: User Satisfaction Score.
Expertise, may have variations in performance
due to factors like workload, fatigue, and
subjectivity in decision-making. This explains why
their performance scores exhibit more variability
compared to AI systems, which maintain a more
standardized approach across different cases.
Despite AI’s advantages in speed and precision,
human professionals re
maincrucial, particularly
incases requiring emotional intelligence,
complex reasoning, and ethical considerations.
Figure 2 shows the User Satisfaction Score.
Moreover, AI diagnostic assistants perform well
in processing repetitive tasks, freeing up human
medical experts to focus on complex cases
involving thorough clinical judgment. AI-powered
assessments follow a systematic approach,
eliminating inconsistencies in medical decision-
making that may arise from human factors such as
stress and fatigue. Furthermore, AI systems are
scalable, able to process a high volume of cases
without sacrificing accuracy, which is particularly
useful in resource-constrained healthcare settings.
But even as AI diagnostics become faster, they are
not replacements for the patient care and emotional
intelligence that is offered by human specialists, and
the overall patient experience can suffer from the
process. There shown in the fig. 2 that integrating AI
into the healthcare workflow improves operational
efficiency, but human oversight is critical in order to
maintain the creation of contextual knowledge and
patient-based care.
AI could become more capable of processing and
understanding human language as well as body
language in the future, helping it to have better and
more meaningful conversations with patients.
This analysis, Reliability vs. Consistency in
Responses, reinforces the benefits of AI diagnostic
assistants. The high reliability scores for AI systems
are indicative of their consistency of performance
across multiple use cases a critical criterion for
scaling these solutions to larger use cases, like
healthcare. Unlike human medical experts, whose
reliability can vary based on environmental factors
such as pressure of workload or cognitive processing
bias, AI systems follow the same algorithm
repeatedly, leading to uniform diagnostics. This is
especially useful in telemedicine or automated
healthcare assistance, where patients demand
reliable and accurate information. While artificial
intelligence systems are shown to be more reliable,
however, the models still lack intuitive reasoning
and adaptability when faced with unique or
ambiguous medical scenarios. Thus an optimal
approach is integration of AI powered diagnostics
with human expertise - drawing on the
computational efficiency of AI and human oversight
of critical, ethical and complex decision making.
Figure 3: Reliability Score.
AI Powered NLP Chatbot for Efficient Document Query Resolution and Summarization in Healthcare
599

The figure 3 highlight how this type of hybrid
healthcare will be the future, where AI will enhance
medical decision- making capability, however
human decision-making capability will be required
to integrate all medical action to be more holistic
and patient-centered health care.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research presents a novel approach to detecting
and classifying malicious QR codes using a machine
learning-based multi-class classifier. The proposed
model effectively distinguishes between benign and
malicious QR codes while identifying specific attack
types, such as SQL Injection and other predefined
threats. The experimental results demonstrate high
classification accuracy, with a well-balanced dataset
achieved through SMOTE and optimal
hyperparameter tuning. The analysis highlights
strong performance in most attack categories, with
minor misclassifications due to feature similarities.
Future enhancements, such as advanced feature
engineering, dataset expansion, and ensemble
learning techniques, could further improve accuracy.
This study contributes to the field of cybersecurity
by providing a proactive defense mechanism against
evolving QR code- based threats.
REFERENCES
Eason, G., Noble, B., & Sneddon, I. N. (1955). On certain
integrals of Lipschitz-Hankel type involving products
of Bessel functions. Philosophical Transactions of the
Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and
Physical Sciences, 247(935), 529–551.
Jia, J., Li, D., Wang, L., & Fan, Q. (2024). Novel
transformer-based deep neural network for the
prediction of post-refracturing production from oil
wells. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 13(2), 119–
131.
Pressat-Laffouilhère, T., Balayé, P., Dahamna, B., Lelong,
R., Billey, K., Darmoni, S. J., & Grosjean, J. (2022).
Evaluation of Doc’EDS: A French semantic search
tool to query health documents from a clinical data
warehouse. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision
Making, 22(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-
022-01762-4
Fontelo, P., Liu, F., & Ackerman, M. (2005). AskMedline:
A free-text, natural language query tool for
MEDLINE/PubMed. BMC Medical Informatics and
Decision Making, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-
6947-5-5
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013).
Efficient estimation of word representations in vector
space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781.
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K.
(2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional
transformers for language understanding. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, L., & Polosukhin, I. (2017).
Attention is all you need. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1706.03762.
Jurafsky, D., & Martin, J. H. (2023). Speech and language
processing (3rd ed.). Pearson.
Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., Joshi, M., Chen, D.,
Levy, O., Lewis, M., Zettlemoyer, L., & Stoyanov, V.
(2019). RoBERTa: A robustly optimized BERT
pretraining approach. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1907.11692.
Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-
term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8), 1735–1780.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., & Sutskever,
I. (2018). Improving language understanding by
generative pre-training. OpenAI.
Le, Q., & Mikolov, T. (2014). Distributed representations
of sentences and documents. In Proceedings of the
31st International Conference on Machine Learning
(pp. 1188–1196). PMLR.
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Neural
machine translation by jointly learning to align and
translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473.
Goldberg, Y. (2016). A primer on neural network models
for natural language processing. Journal of Artificial
Intelligence Research
, 57, 345–420.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
600
