
Mobile Computing Services to Support Flood Disaster App
T. Venkata Naga Jayudu, G. Sai Haritha, B. Varshitha, A. Shravan Kumar Reddy
and C. Sai Prasanna
Department of CSE, Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute of Technology, Rotarypuram Village, B K Samudram Mandal,
Anantapur - 515701, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Mobile Application, Flood Management, Rescue Operations, Recovery, Alerts, Donations.
Abstract: Floods are among the most severe natural disasters, requiring efficient management at three critical phases:
pre-flood, during-flood, and post-flood. This project introduces a comprehensive mobile application to
enhance disaster response, real-time communication, and aid distribution. The system facilitates seamless
coordination among administrators, users, donors, and supporters to improve flood relief efforts. Donors can
register, log in, view, and accept support requests, while supporters can strengthen humanitarian efforts by
assisting with requests. Users can quickly access help by registering, submitting support requests, and tracking
their request history. Admins authenticate supporter and request profiles to ensure legitimacy and integrity
before making them available to donors. Key features include bulk flood alerts, a rescue request system, and
donation management, ensuring faster response times, improved rescue coordination, and effective post-flood
recovery. By integrating technology-driven flood management, this Android-based application provides an
efficient solution to mitigate disaster impacts and save lives.
1 INTRODUCTION
Flood disasters cause widespread devastation,
disrupting lives, infrastructure, and essential services.
Effective disaster relief requires timely coordination
and efficient resource distribution to minimize the
impact on affected communities. However,
traditional disaster relief efforts rely on manual
coordination, fragmented communication, and
inefficient resource allocation. These limitations lead
to delays in aid delivery, difficulties in verifying
requests and supporters, and a lack of real-time
updates, reducing the overall effectiveness of disaster
response efforts.
To address these challenges, this project proposes
a mobile application designed to streamline flood
disaster relief operations. The application facilitates
seamless interaction between donors, supporters,
users, and administrators, ensuring efficient
communication and coordination. Users can register,
submit aid requests, and track their request history,
providing transparency in the relief process. Donors
and supporters can view and accept verified requests,
allowing for timely and organized aid distribution.
Administrators play a crucial role in verifying
profiles and aid requests before making them visible,
ensuring authenticity and preventing fraudulent
activities. By leveraging mobile computing services,
the application provides real-time updates, optimizes
resource allocation, and enhances disaster response
efficiency. This innovative platform bridges the gap
in traditional relief efforts, enabling swift and
effective aid distribution, ultimately reducing the
impact of floods on affected communities.
2 RELATED WORKS
Some administrative and ethical questions have been
raised about the human-based disaster management
program. Rather of being useful, it might be harmful.
There is less need for human intervention with all of
these technologies thanks to the newly formed
Internet of Things organization, which is
sophisticated enough to build a network
automatically connecting each other and predicting
every function and characteristic of a flood. The goal
of this project is to mitigate the negative effects of
urban floods in urbanized areas by designing and
588
Jayudu, T. V. N., Haritha, G. S., Varshitha, B., Reddy, A. S. K. and Prasanna, C. S.
Mobile Computing Services to Support Flood Disaster App.
DOI: 10.5220/0013937400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
588-594
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

operating a wastewater disposal system. Himanshu
Rai Goyal, Sachin Sharma, 2023, The platform
controls wastewater deposit networks through the use
of real-time cloud computing and the internet of
things. In response to the need for storm water
drainage systems in urban areas, this application,
mathematical model, technology, and design were
developed. The floods that hit Mumbai in 2005
illustrate this concept. We can survive with this
method and avoid over 40% of injuries.
Urban flooding monitoring and management is a
worldwide problem as the frequency and severity of
extreme precipitation events are on the rise as a result
of climate change. K. Priya Menon; L. Kala , 2017
Thanks to their cheap cost, rapid data transmission,
and widespread deployment, urban surveillance
camera sensor networks are a valuable addition to
remote sensing. By collecting localised observations
that are inaccessible by satellite and aerial systems,
these networks provide real-time urban flood
monitoring with great spatial and temporal precision.
Identifying and warning of floods becomes more
challenging at night or after heavy rains, due to the
increased complexity and variety of flooded area
image features. One solution is an invariant feature
extraction method for surveillance film, while another
is a picture model for floodlit low-light
circumstances. For the purpose of training and testing
models, a new dataset called UWs is constructed,
which contains low-light surveillance flood pictures.
Clinical trials confirm the strategy's efficacy, with
mRecall=0.88, mF1_score=0.91, and mIoU= 0.85.
Improved mRecall by 4.9%, mF1_score by 3.0%, and
mIoU by 4.4% when compared to Res-UNet,
LRASPP Demonstrating its all-weather adaptability,
the technique also does well in real-world studies,
such as daytime flood monitoring Reduced
catastrophe occurrences would be a direct result of an
urban flood monitoring network that uses all-weather
surveillance cameras and emergency management in
cities, according to this study.
Carlos Castro-Correa., et al., 2014, Hundreds of
millions of people are impacted by natural disasters
annually. Data on population migrations and other
emergencies must be available quickly. Call Detail
Records (CDR) aggregated and anonymised from
mobile phone infrastructure can provide insight into
human behaviour during significant events [3]. We
investigate the possibility of using CDR data along
with other sources to describe the floods that hit
Tabasco, Mexico in 2009. An impact map of the flood
was made using Landsat-7 camera images. Here, we
compared NASA-TRMM rainfall data with CDR
communication activity signals. Flood signatures
might be derived from the numbers of active phones
linked to each cell tower in the areas most impacted
by the floods, both during and after the event. These
patterns could be utilised for assessing the damage on
infrastructure and raising awareness among the
people. Using data from the census and civil
protection, we checked if the analysis was
representative. Preliminary findings suggest that data
on cell tower activity could improve catastrophe
preparedness and early warning systems, but more
extensive proof is required.
Annual floods wreak havoc on communities,
annihilating crops, homes, and buildings. Flooding
can be influenced by both hydrological and
meteorological factors. The fields of flood
catastrophe management and food prediction have
both seen a great deal of research. Smart flood
prediction systems that involve stakeholders and
floods affecting everyone equally should replace
individual monitoring and prediction frameworks,
especially in light of recent technological
improvements. Swapnil Bande; Virendra V. Shete.,
2017 Through the use of wireless communication
networks and embedded system hardware, the IoT
allows for the real-time transfer of sensed data to
computing devices. Mathematical or hydrological
models have been supplanted by algorithmic flood
prediction research. A flood's data is dynamic and
non-linear. One use of artificial neural networks is in
the development of flood prediction systems.
Improve the scalability and durability of flood control
systems. Rainfall, humidity, temperature, pressure,
and river levels are all tracked by this system so that
flood predictions may be made based on temporal
connections. For sensor data collection and Wi-Fi
connectivity, we employ the IoT, and for flood
prediction data processing, we use artificial neural
networks (ANN).
Qing Yang; Qiang Zhang, 2007 Emergency
management for flood disasters should incorporate
pre-, mid-, and post-phases, not only for flood
emergency response. Providing a methodical
framework for emergency management and outlining
the goal of each application subsystem, this study
investigates the necessity and practicability of a
decision support system (DSS) for flood disaster
emergency management.
T. Sravani., et al., 2022, During disasters, getting
help quickly can save lives. A mobile app has been
designed to provide emergency survival services,
collecting real-time data from users and their
surroundings to assist in rescue operations. It uses
service agents to track locations, suggest escape
routes, and connect people with rescuers. By
Mobile Computing Services to Support Flood Disaster App
589

integrating cloud computing and mobile technology,
the system links with public and government services
for better coordination. To speed up response times, a
smart scheduling algorithm prioritizes urgent
requests. It has been tested in real-life situations, like
the 2013 Ya’an earthquake in China, where it
successfully handled thousands of rescue requests.
The results show that this system improves disaster
response, enhances teamwork, and helps save more
lives.
Disasters, both natural and man-made, pose
significant risks to life and property, making effective
disaster management crucial. This study highlights
the various disasters affecting Andhra Pradesh,
including cyclones, floods, droughts, earthquakes,
tsunamis, and fires, along with statistical data on their
impact. The research emphasizes the importance of
pre-disaster planning, such as mitigation and
preparedness, to minimize the severity of post-
disaster response efforts like rescue and
rehabilitation. L.Tejaswi and R. P. Kumar, 2011
Despite its central location in India, Andhra Pradesh
frequently experiences disasters due to its
geographical and climatic conditions. The paper
suggests efficient risk mitigation strategies, including
early warning systems, improved infrastructure, and
better coordination between government agencies.
The findings stress the need for public awareness and
education on disaster preparedness to reduce
casualties and economic losses.
Anam Ubaid, 2017 Service-oriented disaster
response system that operates in both online and
offline modes using mobile and cloud computing for
real-time data collection and rescue coordination. It
features automated service agents, an emergency
distress mode, and a bio-inspired scheduling
algorithm to prioritize critical requests. Tested in real-
world disasters like the 2013 Ya’an Earthquake, it
enhances rescue efficiency, reduces delays, and
improves coordination. Future upgrades aim to
integrate IoT technology for better real-time
monitoring and response.
V. Astarita, et al., 2020, Mobile computing
enhances disaster management by enabling real-time
data collection, coordination, and communication
through wireless networks, smartphones, and cloud
computing [9]. A cooperative crowdsourced system
gathers critical information on infrastructure,
movement, and urgent needs, processed by a central
decision support system for efficient response.
Integrating GIS, IoT, and ITS improves disaster
resilience and emergency operations.
R. Koul., et al., 2015 social media enhances
disaster management by enabling real-time
communication, rescue coordination, and information
sharing. During the Jammu and Kashmir floods,
platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp helped locate
missing persons, guide rescuers, and organize relief
efforts using hashtags and open groups. Structured
data management improved efficiency, making
rescue operations faster and more effective.
3 METHODOLOGY
Proposed System: The proposed system is a mobile
application designed to enhance flood disaster relief
efforts by improving coordination, transparency, and
efficiency in aid distribution. The application features
role-specific functionalities for donors, supporters,
users, and administrators. Users can register, log in,
submit aid requests, and track their request history,
ensuring a structured and transparent relief process.
Donors and supporters can view and accept verified
requests, enabling timely assistance to affected
individuals. This system streamlines communication,
eliminates manual inefficiencies, and ensures real-
time updates for all stakeholders.
Administrators play a critical role in verifying
supporter profiles and aid requests before they become
visible to donors, ensuring the authenticity of all
interactions. By leveraging mobile computing
services, the application optimizes resource allocation
and minimizes delays in providing aid. With real-time
tracking and efficient management of disaster relief
efforts, this system enhances the overall effectiveness
of flood response operations, ensuring that help
reaches those in need swiftly and efficiently.
System Architecture: The system architecture of the
proposed flood disaster relief mobile application
consists of multiple interconnected components to
ensure efficient coordination and management of aid
distribution. The architecture includes four main user
roles: Donor, Supporter, User, and Admin. Each role
interacts with key system modules such as Request
Management, Safety System, Authentication, and
Verification. Donors and Supporters can
register/login, view requests, and accept or donate
towards assistance. Users can register, add aid
requests, and view safety information, while Admins
are responsible for verifying supporter profiles and
aid requests before they become visible.
The Request Management module handles the
creation, tracking, and acceptance of aid requests,
storing relevant data in a centralized Database. The
Safety System fetches and provides real-time safety
information for users in flood-affected areas.
Authentication ensures secure access control for all
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
590

roles, while the Verification module allows Admins
to authenticate supporters and aid requests. This well-
structured architecture ensures seamless data flow,
real-time updates, and effective coordination,
ultimately enhancing disaster response efficiency and
ensuring that aid reaches affected individuals in a
timely manner.
3.1 Modules
3.1.1 User Module
• sers can create an account by providing their
necessary details, such as name, contact
information, and a secure password.
• Once registered, users can log in to their
accounts using their credentials.
• Secure authentication mechanisms ensure data
privacy and protection. Registered users can
submit requests for aid, specifying their needs
such as food, shelter, medical assistance, or
other forms of support.
• The system allows users to track the status of
their aid requests, providing updates on
progress, approvals, and expected delivery
times.
• Users can access a history of their past aid
requests, enabling them to monitor their
received assistance over time the system offers
real-time safety updates related to flood-
affected areas, including evacuation notices,
emergency shelters, and road conditions.
• Users can view essential guidelines on flood
preparedness, including first aid tips and
emergency contact numbers.
3.1.2 Donor Module
• Donors can create an account by providing
their details, such as name, organization (if
applicable), contact information, and a secure
password.
• Once registered, donors can log in to access
the platform and manage their contributions.
• Secure authentication ensures that donor
information remains protected. Donors can
browse a list of aid requests submitted by users
affected by floods.
• Each request provides details about the type of
assistance needed, such as food, water,
clothing, medical supplies, or temporary
shelter.
• Donors can accept specific aid requests based
on their ability to aid. Donors can contribute
resources in various forms, including financial
donations, essential goods, and logistical
support.
• The platform may provide options for direct
donations, coordinating drop-off locations, or
collaborating with local relief organizations.
• Donors receive updates on their contributions,
ensuring transparency and tracking of their
impact.
3.1.3 Supporter Module
• Supporters can create an account by providing
their details, such as name, contact
information, and a secure password.
• Once registered, supporters can log in to
access the platform and engage in relief
activities.
• Secure authentication measures ensure data
privacy and authorized access Supporters can
browse a list of aid requests submitted by users
affected by floods.
• Requests may include needs such as medical
assistance, food distribution, transportation, or
temporary shelter arrangements.
• Supporters can accept requests based on their
availability and capacity to provide help.
• Once a request is accepted, the system updates
the status and notifies the requesting user to
coordinate assistance Supporters play a crucial
role in ensuring that relief resources are
distributed efficiently to those in need.
• They may assist in coordinating logistics,
verifying user needs, and delivering aid in
collaboration with donors and relief
organizations.
3.1.4 Admin Module
• The Admin reviews and verifies supporter
registrations to ensure only genuine
individuals or organizations participate in
relief efforts.
• Supporters may be required to provide
identification or relevant credentials for
validation. The Admin ensures that only
verified users, supporters, and donors can
interact within the system.
• They monitor aid request approvals, ensuring
fair distribution and preventing misuse.
• Any suspicious activity, such as false requests
or unauthorized support claims, is flagged and
investigated. The Admin supervises the
Mobile Computing Services to Support Flood Disaster App
591
overall functioning of the platform,
maintaining a smooth workflow.
• They enforce data security measures,
protecting user information and ensuring
compliance with privacy policies.
• Regular system audits and reports are
conducted to enhance transparency in aid
distribution and resource management.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
The experimental results provide a comprehensive
evaluation of various aspects of the system, including
user authentication, data security, system
performance, and overall functionality. The user
registration and authentication process ensure secure
credential management, effectively preventing
unauthorized access through robust validation
mechanisms. System performance and efficiency
were analyzed, revealing optimal response times
under normal conditions, though improvements may
be required under high-load scenarios to mitigate
latency.
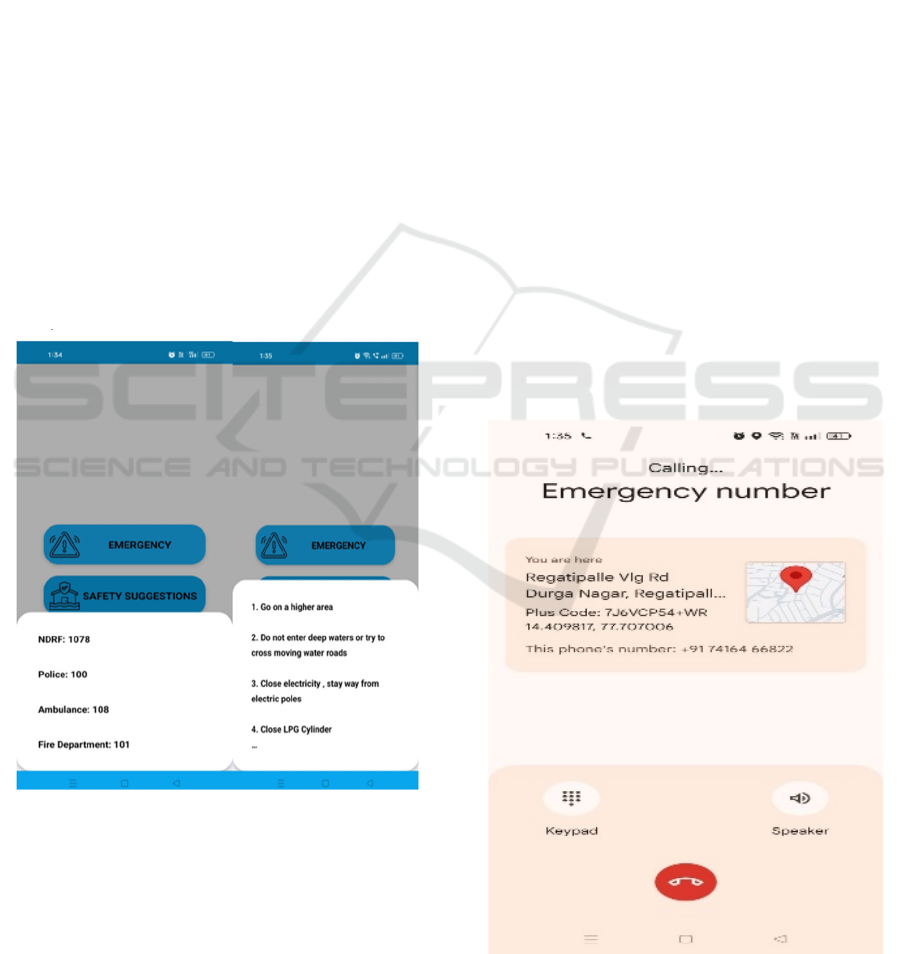
Figure 1: Emergency and Safety Suggestions Page.
The above figure 1 represents quick access to
emergency assistance and safety suggestions,
allowing users to seek immediate help or access
critical safety guidelines during a flood disaster. The
overall findings highlight the system's reliability in
authentication, data security, and operational
efficiency. While it effectively manages user
registration and request handling, additional
enhancements in high-load performance optimization
and advanced security features could further
strengthen its capabilities. Overall, the system
presents a robust and secure framework that
successfully handles critical functionalities with
efficiency and reliability.
Furthermore, the request processing and database
transaction capabilities were examined, indicating
efficient query execution and simultaneous user
request handling. However, further optimization in
query processing could enhance performance,
especially during high-traffic periods.
Additionally, the system incorporates strong
encryption techniques for user credentials and
sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality and data
integrity across different modules.
Figure 3 show the
User Details. Error handling mechanisms were also
tested, demonstrating that the system provides
appropriate feedback for invalid inputs and
unexpected failures, enabling smooth recovery and
uninterrupted user experience. The above figure 2
represents Calling Page and screen displays an
ongoing emergency call, providing the user's real-
time location details to ensure prompt assistance
during a crisis and user details and user request.
Figure 6 and 7 shows the Request Page and Tracking
Page respectively.
Figure 2: Offline Services.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
592
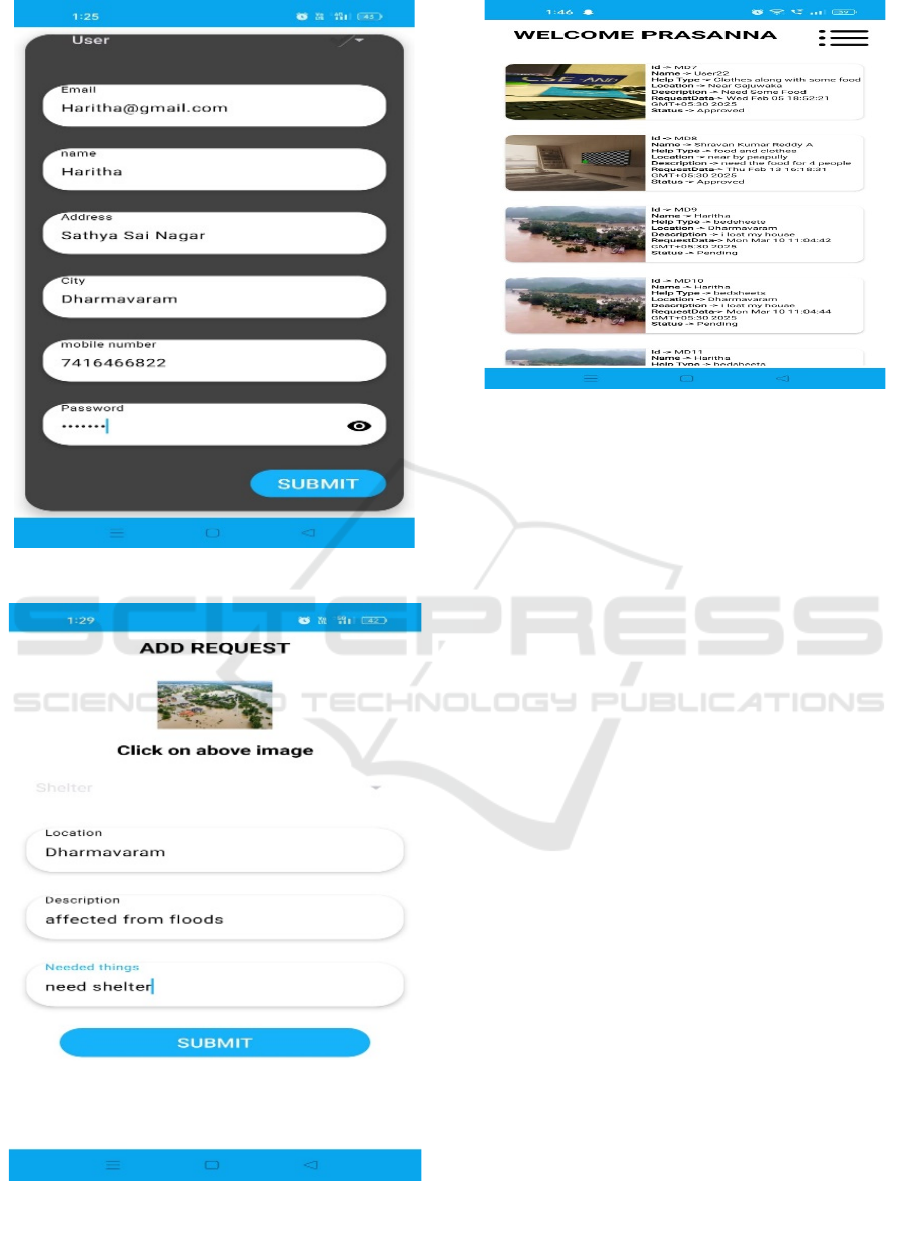
Figure 3: show the User Details.
Figure 6: Request Page.
Figure 7: Tracking Page.
5 DISCUSSION AND FUTURE
WORK
5.1 Discussion
The experimental results provide a comprehensive
evaluation of various aspects of the system, including
user authentication, data security, system
performance, and overall functionality. The user
registration and authentication process ensure secure
credential management, effectively preventing
unauthorized access through robust validation
mechanisms. System performance and efficiency
were analyzed, revealing optimal response times
under normal conditions, though improvements may
be required under high-load scenarios to mitigate
latency. Additionally, the system incorporates strong
encryption techniques for user credentials and
sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality and data
integrity across different modules. Error handling
mechanisms were also tested, demonstrating that the
system provides appropriate feedback for invalid
inputs and unexpected failures, enabling smooth
recovery and uninterrupted user experience
5.2 Future Work
enhanced by integrating advanced technologies such
as AI-powered chatbots to assist users with real-time
safety tips and resource recommendations during
disasters. IoT-based flood sensors can be
incorporated to provide live updates on water levels
and weather conditions, improving early warning
Mobile Computing Services to Support Flood Disaster App
593

systems. Blockchain technology can enhance
transparency and security in donation tracking,
ensuring efficient fund utilization. The application
can be expanded with multilingual support to cater to
diverse users and include crowdsourced flood
mapping for better disaster response planning. An
offline mode can be introduced to allow users to
access critical information and submit requests even
in areas with limited connectivity. Collaborations
with government agencies and NGOs can further
improve aid distribution and emergency response
efficiency. Additionally, predictive analytics can be
leveraged to identify flood-prone areas and
implement preventive measures, reducing the impact
of future disasters. These advancements will enhance
the application’s scalability, reliability, and
effectiveness in managing flood relief efforts.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed mobile application for flood disaster
relief enhances coordination, communication, and aid
distribution among donors, supporters, users, and
administrators. By integrating modules for
authentication, request management, safety
information, and verification, the system ensures
transparency, security, and efficiency in disaster
response efforts. The application streamlines the
process of requesting and aiding, reducing delays and
improving resource allocation. Through real-time
updates and secure interactions, the system helps
affected communities receive timely support,
ultimately minimizing the impact of floods and
improving disaster management outcomes.
REFERENCES
Flood Management System Using Cloud Computing and
Internet-of-Things || Himanshu Rai Goyal, Sachin
Sharma || 20-21 January 2023
Video surveillance system for realtime flood detection and
mobile app for flood alert || K. Priya Menon; L. Kala ||
18-19 July 2017.
Flooding through the lens of mobile phone activity || David
Pastor-Escuredo; Alfredo Morales-Guzmán; Yolanda
Torres-Fernández; Jean-Martin Bauer; Amit Wadhwa;
Carlos Castro-Correa || 10-13 October 2014.
Smart flood disaster prediction system using IoT & neural
networks || Swapnil Bande; Virendra V. Shete || 17-19
August 2017
Study on Decision Support System of Flood Disaster Based
on the Overall Process Emergency Management || Qing
Yang; Qiang Zhang || 21-25 September 2007
T. Sravani, T. Manikumar, and R. Maruthamuthu, “Rescue
Wings: Mobile Computing and Emergency Survival
Services,” International Journal of Innovations in
Engineering and Science, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 1–7, May
2022.
L.Tejaswi and R. P. Kumar, “Disaster Mitigation and
Management for Andhra Pradesh, India: An
Appraisal,” International Journal of Earth Sciences
and Engineering, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 443–453, June 2011.
Anam Ubaid, Rafiya Anjum, Samer Zehra, Syed
Muzammil, Suma R, "Rescue Wings: Computing
Rescue Wings using Online & Offline Service Support
for Disaster Rescue," Recent Advances in Technology
and Engineering (RATE-2017), 6th National
Conference, T John Institute of Technology, Bangalore,
2017, pp. 1-8.
V. Astarita, V.P. Giofrè, G. Guido, G. Stefano, and A. Vital,
“Mobile Computing for Disaster Emergency
Management: Empirical Requirements Analysis for a
Cooperative Crowdsourced System for Emergency
Management Operation,” Smart Cities, vol. 3, pp. 31–
47, Feb. 2020.
R. Koul, "Use of Social Media in Disaster Management,"
Proceedings of the 8th National Student’s Convention,
Bharati Vidyapeeth’s Institute of Computer
Applications and Management (BVICAM), New Delhi,
pp. 1–8, March 2015.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
594
