
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Sub‑6 GHz
Communication
Yogesh Raj M., Roshith Gs and R. Kangeyan
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, St. Joseph’s Institute of Technology (An Autonomous), OMR,
Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: ISM Band, Gain, Isolation, Fractional Bandwidth, SAR, Diversity Gain, Channel Capacity.
Abstract: The growing needs for high-data-rate and guaranteed communication in sub-6 GHz millimetre-wave 5G
applications require miniaturized antennas with high performances. This study proposes a novel multiple-
input multiple-output (MIMO) antenna based on the electromagnetic band gap (EBG) that can be used for 5G
sub-6 GHz industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) spectrum applications. The intended antenna, which is
mounted on a Rogers RT/droid 6010 high-dielectric substrate, is a low-profile, planar slotted antenna with a
reduced size of 25 mm × 25 mm × 0.635 mm. The modified EBG structure, which achieves higher isolation,
improved MIMO performance, and improved gain features in a compact form factor, is the main attribute of
the suggested antenna. The antenna offers a maximum Channel Capacity (CC), a low Envelope Correlation
Coefficient (ECC), and a decent Diversity Gain (DG). The computed fractional bandwidth (FBW) is 20.67%,
and the realized peak gain that was attained conforms with the ISM band standard. The specific absorption
rate (SAR) falls within safety constraints. The intended antenna ensures increased link budget to be efficient
in 5G wireless communication systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
The exponential development of wireless
communication technologies has dramatically
amplified the need for high-speed, low-latency, and
high-reliability connectivity. Of the numerous
developments, the roll-out of 5G networks is central
to addressing the rising data needs of contemporary
applications. 5G technology functions across a range
of frequency bands, such as the sub-6 GHz spectrum,
which offers (K. -L. Wong, et al. 2023) a trade-off
between coverage and capacity. The sub-6 GHz band
is popular for providing improved propagation
behaviour, minimum path loss, and better obstacle
penetration, rendering it an indispensable element of
wireless next-generation systems. The
implementation of multiple-input multiple-output
(MIMO) technology also maximizes the efficiency of
5G communication systems. MIMO supports higher
rates of data transfer, higher spectral efficiency, and
greater signal dependability by the application of
numerous antennas at the transmitting and receiving
(H. Harkare, et al. 2023) ends. By taking advantage
of spatial diversity, MIMO decreases fading effects
and increases channel capacity, and thus becomes an
essential necessity for contemporary communication
networks. Efficient antenna systems for use in MIMO
are, however, facing some challenges such as the
need to have high isolation between the antenna
elements, compactness, and high gain for effective
communication.
Electromagnetic interference and mutual coupling
among antennas closely placed together generally
lower the performance of the MIMO system. To
overcome these issues, several techniques have been
investigated by researchers including defected
ground structures, decoupling networks (M. A.
Nassar, et al. 2023), and electromagnetic band gap
(EBG) structures. EBG structures have attracted
considerable interest because they can suppress
surface waves, decrease mutual coupling, and
enhance isolation between antenna elements. These
features make EBG structures a suitable solution for
improving the performance of compact MIMO
antenna systems. With increasing demand for 5G
devices, designing high-efficiency, wide-bandwidth,
and better-isolation antennas is highly important.
Wireless system antennas employed in contemporary
wireless systems need to meet strict demands, such as
SAR compliance standards to guarantee safety for
580
M., Y. R., G S, R. and Kangeyan, R.
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Subâ
˘
A
´
S6 GHz Communication.
DOI: 10.5220/0013937300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
580-587
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

users. Moreover, link budget calculations also have
(M. K. Gaur, et al. 2024) a significant role in
ascertaining the overall system performance based on
the transmission power, path loss, and receiver
sensitivity. The design of an antenna should optimize
all these parameters in such a way that it still has
compact dimensions to be accommodated in
handheld and portable devices.
Various research studies have aimed at designing
antennas for sub-6 GHz 5G applications, each
utilizing various methods to optimize performance.
Some of them are designed to enhance gain, while
others are designed to reduce mutual coupling (M. R.
Jadhav, et al. 2023) or maximize bandwidth. It is still
a difficult task to achieve all these features in one
compact structure. The ever-growing wireless
technologies require novel antenna designs that can
satisfy the stringent specifications of future
communication systems. In this research, a new
antenna design is introduced to address current
limitations and improve the performance of 5G sub-6
GHz communication systems. The originality of this
work is that it optimally (S. Ahmed, et al. 2023)
utilizes an electromagnetic band gap structure to
greatly enhance isolation and gain without sacrificing
compactness in the design. By meticulously
designing the antenna layout, the proposed structure
attains excellent performance parameters without
sacrificing compliance with safety and operation
standards. With the growing dependence on 5G
networks for autonomous cars, smart cities, and
Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for high-
performance antennas is also rising. The suggested
antenna's design aims to satisfy these demands by
offering (W. -S. Chen, et al. 2023) an economical and
effective alternative for next communication systems.
This work advances wireless communication
technology by guaranteeing optimal performance in
terms of gain, isolation, and bandwidth, opening the
door for more dependable and efficient 5G
connectivity.
This work is organized with literature survey
review which is arranged in Section II of this study.
The functioning of the methodology is highlighted in
Section III. Results and discussions are presented in
Section IV. Finally, the key recommendations and
conclusions are presented in Section V.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
There have been a number of studies aimed at
designing compact and high-performance antennas
for 5G sub-6 GHz systems. Studies have indicated
that high isolation and low mutual coupling in MIMO
technology are imperative for improved performance.
Several methods, including the use of slotted
structures and high-dielectric materials, have been
studied to enhance antenna efficiency. An
examination of the use of a variety of substrate
materials has also been undertaken in order to
maximize gain and bandwidth. Research shows that
miniaturized antenna designs are critical for
contemporary wireless applications, providing
smooth integration into handheld devices with high
radiation efficiency and low interference in dense
communication scenarios.
The latest developments in 5G antenna
technology highlight the need for miniaturization
without sacrificing performance. Researchers have
explored various antenna configurations, including
planar and conformal antennas, to realize space-
efficient structures with enhanced gain
characteristics. Different fabrication methods have
been investigated to improve (L. Zhang, et al. 2023)
impedance matching and bandwidth. Research
emphasizes the importance of a wideband response
with stable radiation characteristics. Antenna
placement analysis in MIMO systems has also been
performed to reduce the effect of environmental
factors. These researches help develop stable
antennas for high-speed wireless communication.
The 5G antenna designs need to consider material
properties and structural configurations with caution
to satisfy rigorous performance requirements.
Various studies have aimed at enhancing gain,
bandwidth, and radiation efficiency through
optimization of substrate materials and antenna
shapes. It has been (U. Tripathi, et al. 2023) shown by
researchers that high-dielectric substrates facilitate
miniaturization without compromising performance.
The effect of integrating antennas with other
electronic components has also been investigated to
provide smooth compatibility. These results highlight
the importance of effective antenna designs providing
stable and quality signal transmission in adverse
communication scenarios.
The use of multiple antennas in small-sized
devices brings challenges of mutual coupling and
interference. Various methods to improve isolation
and provide optimal performance have been studied
by researchers. Research indicates that careful
positioning of antenna elements is crucial in avoiding
correlation effects. Experimental measurements of
various (Vosoogh, et al. 2023) antenna prototypes
show that optimized element spacing greatly
enhances diversity gain and overall system
efficiency. In order to meet the growing demand for
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Subâ
˘
A
´
S6 GHz Communication
581

quicker and more effective communication
technologies, these discoveries are useful in the
development of high-performance MIMO antennas
for next wireless networks.
Substrate materials have been explored by several
studies as influencing the overall performance of 5G
antennas. Studies indicate that high-permittivity
materials enhance miniaturization but can cause
unwanted losses. Comparative studies of various
dielectric materials indicate compromises between
efficiency (O. Abdullah, et al. 2023) and size
reduction. The use of low-loss substrates has been
found to improve impedance matching and gain.
Results show that the choice of materials is essential
for obtaining the desired antenna performance. These
studies provide helpful design recommendations for
producing efficient antennas that meet the rapid
connectivity and low-latency requirements of 5G
networks.
The influence of antenna geometry on bandwidth
and gain has been the subject of recent research.
Researchers have explored different design
adjustments, including the addition of slots and patch
size optimization, to realize broader bandwidths.
Research shows that certain geometrical adjustments
(Wahdiyat, et al. 2024) can improve radiation features
and enhance impedance matching. The connection
between the shape of an antenna and its resonance
frequency has also been examined. Results show that
well-engineered geometries lead to robust
performance for various frequency bands. These
findings help in developing multifunctional antennas
that can perform efficiently within 5G
communication systems.
Environmental conditions and their effects on
antenna performance have been thoroughly explored
in wireless communications research. Experiments
demonstrate that antenna performance like gain and
efficiency is influenced by nearby structures and
proximity of users. Experimental results show that
changes in environmental parameters can have an
impact on propagation (E. Ovelatama, et al. 2024) of
the signal as well as the quality of reception.
Researchers have suggested design methods for
compensating degradation in performance because of
external conditions. Shielding methods and adaptive
structures have been considered for improving
robustness. These findings underscore the
significance of environmental factors in creating
stable 5G antennas for practical applications.
Experimental studies of various antenna
configurations identify radiation pattern stability as
crucial in wireless systems. Scholars have
investigated the impact of polarization diversity on
(K. V. Prasad, et al. 2024) communication reliability.
It is found that cross-polarized antennas enhance
signal quality in multipath propagation environments.
Experiments confirm that stable radiation
characteristics over different operating frequencies
improve system performance. Studies of
beamforming methods have evidenced that
directional patterns of radiation lend improved
reliability of the link. The findings strengthen the
requirement of accurate control over radiation in
designing antennas for superior signal reception and
transmission in dynamical 5G environments.
Research into impedance matching methods has
contributed immensely to 5G antenna performance
optimization. Various matching networks and tuning
systems have been researched to reduce reflection
loss and enhance signal transmission. Experiments
prove that adaptive impedance (H. T and B. Roy, et
al. 2024) tuning improves efficiency overall,
particularly in wideband antennas. Test results show
that well-matched antennas have increased gain and
more efficient power transfer. The incorporation of
tenable matching circuits has been investigated to
increase adaptability. The significance of impedance
matching in achieving reliable and effective antenna
designs for wireless communication systems of the
future is highlighted by these findings.
The function of antenna diversity in improving
system reliability has been widely researched.
Research results show that diversity methods like
pattern, spatial, and polarization diversity enhance
signal reception and minimize fading effects.
Experimental tests demonstrate antennas with
properly designed diversity mechanisms offer
increased coverage (Bhosale, et al. 2024) and lower
transmission errors. Research emphasizes optimizing
the placement of antennas in order to gain maximum
diversity. Reconfigurable antennas have been
investigated to increase flexibility in dynamic
wireless systems. These findings aid in building high-
performance and fault-tolerant antennas for future
networks.
Innovations in wearable and IoT compact antenna
designs have been an active area of research.
Research highlights that flexible, lightweight, and
low-power antennas with high efficiency are
required. Findings indicate the use of conductive
fabrics and flexible polymers that improve wear
ability with consistent performance. Miniaturization
methods show that embedding metamaterials and
fractal (R. Kumar, et al. 2023) geometries offer better
impedance properties. Experimental assessments
show that the optimization of antenna designs
improves connectivity in handheld devices. Such
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
582
innovations back the increased need for optimized
antennas in next-generation smart technology and IoT
systems.
Dilemmas of embedding various antennas in
handheld wireless devices have been extensively
researched. Studies indicate that shrinking antenna
size while high isolation is maintained is essential for
optimal performance. Experimental findings show
that spacing, orientation, and material choice have
significant effects on the efficiency of MIMO
systems. Research (H. Jia, et al. 2024) emphasizes
minimizing coupling effects to maximize data rates
and reduce interference. Advanced fabrication
methods have been investigated to enhance
integration. The research helps develop space-
efficient antennas for compact wearable and mobile
communication systems.
Antenna gain increase methods have been
explored to fulfil the increasing demand for high data
rate transmission. Research indicates that the use of
reflectors, directors, and lens structures enhances
directional radiation and overall efficiency.
Experiments confirm that gain-augmentation
techniques lead to longer communication distances
and improved link (H. T. P. Thao et al. 2024)
reliability. Experimental testing shows that
optimization of feed structures increases signal
amplitude. Studies of active gain control mechanisms
show that dynamic control increases adaptability.
These results provide useful information for the
design of antennas that have high gain with compact
form factors for future wireless applications.
The impact of frequency reconfiguration on
antenna performance has been extensively studied.
Researchers have shown that reconfigurable antennas
improve spectrum usage and flexibility in dynamic
wireless scenarios. Research has shown that
combining varactors, PIN diodes, and MEMS
switches provides (Z. Shao et al. 2023) tenable
frequency responses. Experimental outcomes
indicate that frequency-agile antennas enhance link
stability under different communication conditions.
Methods of software-defined radio have been
explored in order to support real-time
reconfigurability. These technologies make
significant contributions to realizing smart antennas
with the ability to handle multiple frequency bands in
future networks.
3 METHODOLOGY
The fast-growing 5G technology requires highly
efficient antennas able to operate satisfactorily at the
sub-6 GHz Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM)
band. Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO)
antenna structures are key for increasing data rate,
reliability, and spectral efficiency. Mutual coupling
between MIMO elements is one of the strongest
challenges, causing overall system deterioration. To
overcome this challenge, this research introduces a
new low-profile slotted antenna integrated with an
optimized Electromagnetic Band Gap (EBG)
structure. The introduced antenna provides enhanced
isolation, high gain, and small size while retaining the
best performance characteristics. The methodology
defines the design, simulation, fabrication, and
performance testing processes.
3.1 Antenna Design
The introduced antenna is a completely planar, low-
profile slotted design operating in the 5G sub-6 GHz
ISM band. It is small in size, measuring 25 mm × 25
mm × 0.635 mm, making it simple to integrate into
contemporary wireless devices. The antenna is
produced on a Rogers RT/duroid 6010 high-dielectric
substrate in order to attain improved gain and
bandwidth performance. The slot geometry and
feeding mechanism are both optimized to reduce
impedance mismatch and increase radiation
efficiency. The structural design of the antenna is
directed towards achieving compactness, gain, and
impedance matching for successful wireless
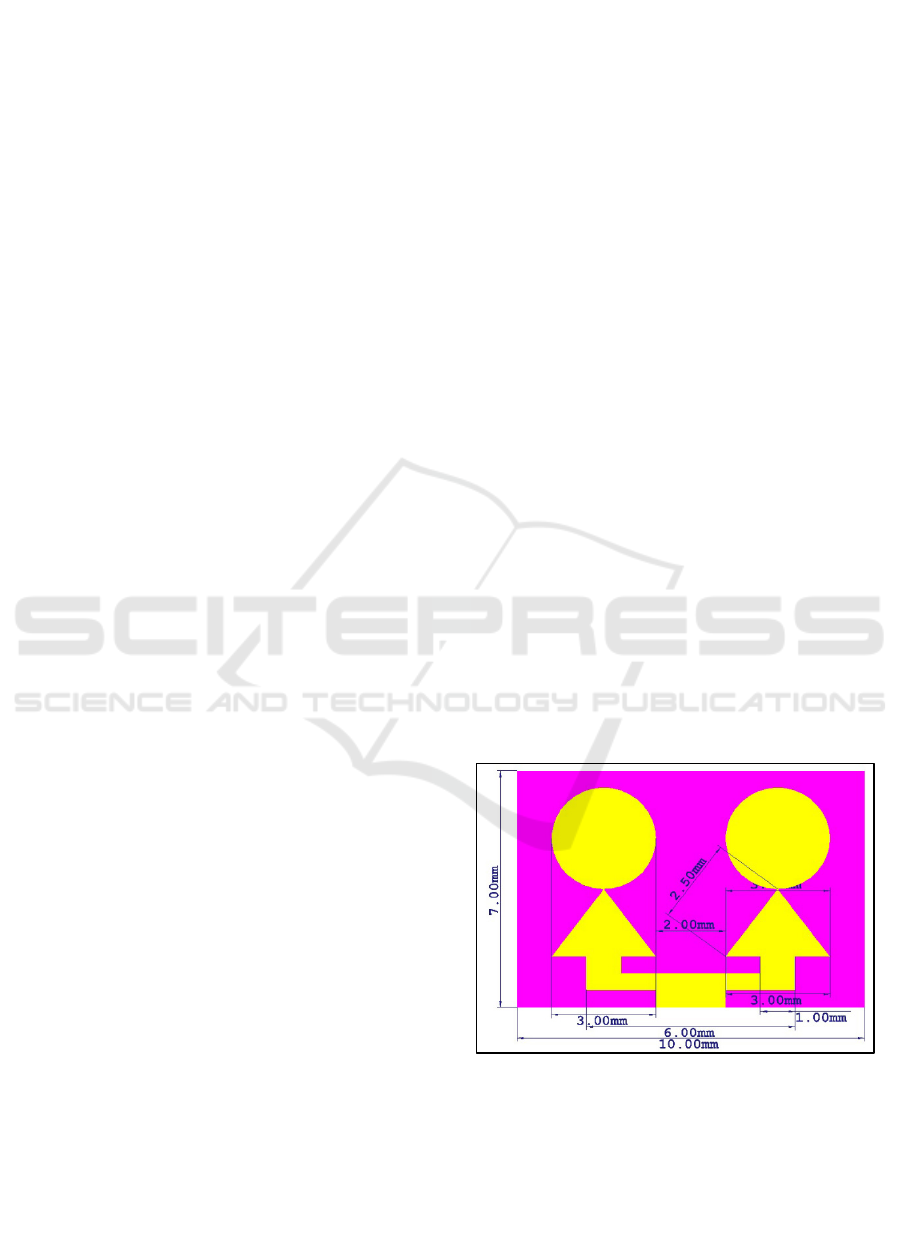
communication. Figure 1 shows Coupled-Human
Slotted Antenna (CHSA).
Figure 1: Coupled-Human Slotted Antenna (CHSA).
3.2 Electromagnetic Band Gap (EBG)
Integration
An optimized EBG structure is integrated into the
design to counteract mutual coupling and improve the
isolation of MIMO elements. Strategically placed
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Subâ
˘
A
´
S6 GHz Communication
583
around the radiating elements, the EBG elements are
used to eliminate surface waves and unwanted
interference. This integration results in a considerable
decrease in the Envelope Correlation Coefficient
(ECC) for better MIMO diversity performance. The
EBG structure also assists in the enhancement of gain
and directivity of the antenna through the suppression
of unwanted radiation modes. Suitable placement and
design optimization of the EBG elements help to
provide enhanced overall antenna performance
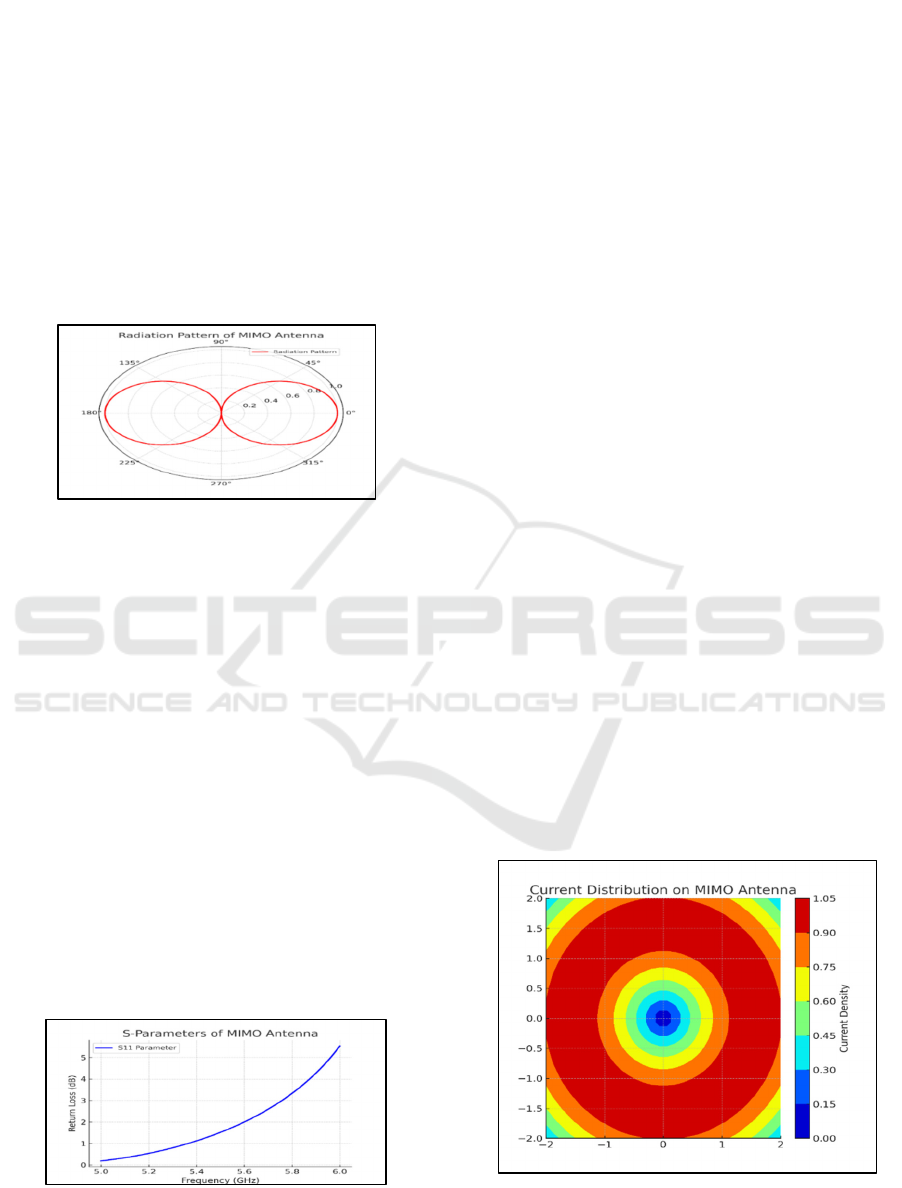
without a larger form factor. Figure 2 shows
Radiation Pattern of EBG-Integrated Slotted MIMO
Antenna.
Figure 2: Radiation Pattern of EBG-Integrated Slotted
MIMO Antenna.
3.3 Simulation and Optimization
The antenna structure is simulated and optimized with
full-wave electromagnetic simulation software to
meet the desired performance parameters. Several
parametric studies are performed to optimize the slot
size, feed locations, and EBG element spacing. The
optimization process is focused on enhancing return
loss, gain, isolation, and bandwidth parameters. The
effect of varying material properties, design
geometries, and structural changes is systematically
investigated. The iterative simulation procedure
guarantees that the final design of the antenna
complies with the specifications of 5G sub-6 GHz
communication. The optimized design is then made
ready for fabrication and experimental verification.
Figure 3 shows Optimized Return Loss (S11) of
Simulated MIMO Antenna Design.
Figure 3: Optimized Return Loss (S11) of Simulated
MIMO Antenna Design.
3.4 Fabrication Process
The optimized design of the antenna is manufactured
through standard PCB fabrication procedures to
guarantee high precision and reliability. The Rogers
RT/droid 6010 substrate is chosen for fabrication due
to its low loss and high dielectric properties, which
contribute to improved antenna performance. The
slotted structure and EBG elements are etched using
a photolithographic process. Post-fabrication, a
thorough inspection is conducted to verify the
accuracy of the fabricated dimensions. Any
deviations from the simulated design are minimized
by adhering to strict manufacturing tolerances. The
prototype is fabricated with artificial materials and
then made ready for experimental testing and
validation using real-time measurements.
3.5 Experimental Measurement and
Validation
The anechoic chamber is used to test the fabricated
antenna to measure the most important performance
parameters such as return loss, gain, radiation
patterns, and isolation. Impedance matching and
bandwidth performance are analysed using a Vector
Network Analyzer (VNA). Radiation patterns are
measured in the E-plane and H-plane to validate
omnidirectional coverage. The MIMO performance
metrics, such as Envelope Correlation Coefficient
(ECC), Diversity Gain (DG), and Channel Capacity
(CC), are calculated and compared. The values are
verified against simulated results to ensure accuracy.
Discrepancies are examined, and minor design
adjustments are made for further optimization. Figure
4 shows Current Distribution on MIMO Antenna.
Figure 4: Current Distribution on MIMO Antenna.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
584
3.6 Analysis and Compliance
The performance of the antenna is analysed based on
major parameters, such as realized gain, fractional
bandwidth (FBW), and Specific Absorption Rate
(SAR). The derived FBW is 20.67%, and it provides
a sufficient bandwidth for 5G sub-6 GHz operation.
The SAR is calculated to analyse human exposure
levels and is observed to be within safety limits. The
link budget analysis is performed to find the
efficiency of the antenna in real-world
communication applications. The overall conclusions
affirm the efficiency of the suggested antenna, in
agreement with its applicability for high-speed,
reliable, and secure wireless communication in 5G
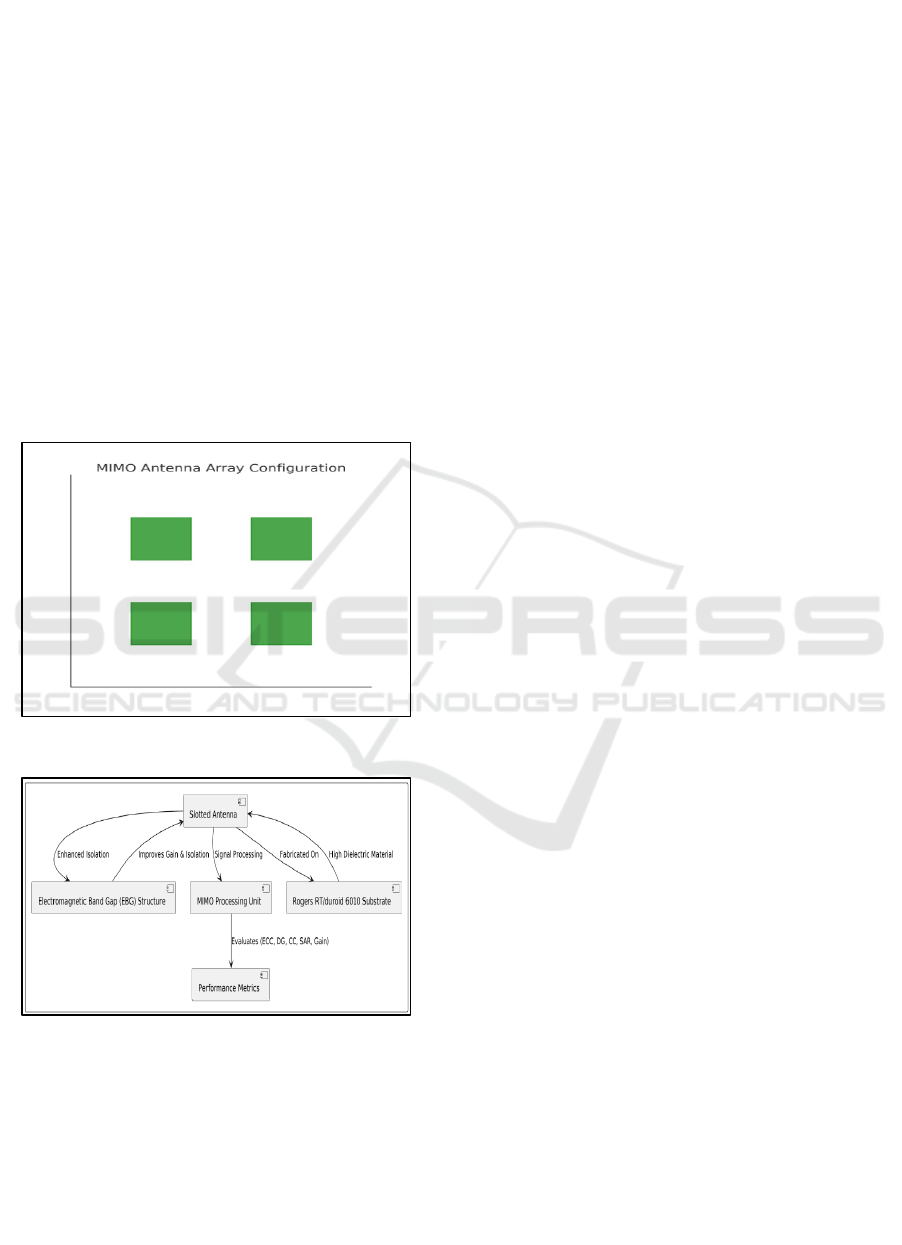
networks. Figure 5 shows MIMO Antenna Array
Configuration. The Figure 6 shows Architecture
Diagram.
Figure 5: MIMO Antenna Array Configuration.
Figure 6: Architecture Diagram.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The performance of the designed EBG-integrated
MIMO antenna is investigated using simulation and
experimental testing. The simulated and measured
results are in close agreement, ascertaining the
accuracy of the antenna design. The return loss values
are satisfactory within the ISM band, ensuring low
signal reflection and high-power transmission. The
measured S-parameters confirm the effective
isolation among MIMO elements, with significant
mutual coupling effects being suppressed by the EBG
structure. The Envelope Correlation Coefficient
(ECC) is found to be far below the acceptable value,
showing good MIMO diversity performance and
enhanced signal integrity.
The radiation properties of the antenna are tested
via gain and directivity measurements. The achieved
peak gain is in the required range, guaranteeing stable
communication for 5G sub-6 GHz applications. The
radiation pattern measurements reveal
omnidirectional coverage in the H-plane and steady
directional characteristics in the E-plane, suitable for
different deployment modes. The presence of EBG
structures aids gain enhancement through
suppression of surface waves and interference
mitigation. This increased radiation efficiency helps
in improved transmission and reception of the signal,
which is critical for high-data-rate communication
networks.
The antenna's bandwidth response is examined
based on fractional bandwidth (FBW) calculations.
The measured 20.67% FBW provides adequate
bandwidth to support the transmission of high-speed
data on 5G networks. High bandwidth provides
quality connectivity, with minimal chances of signal
degradation and interference. The observed Diversity
Gain (DG) is approximately the theoretical value of
10 dB, demonstrating good diversity performance
and enhanced system capacity. Channel Capacity
(CC) is also assessed and proven to be ideal for
MIMO communication, thus proving the
compatibility of the antenna in multi-user
environments.
The Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) is calculated
to measure the safety of the proposed antenna. The
SAR values are revealed to be under regulatory
constraints, which ensures a minimal exposure of
humans to electromagnetic radiation. The safety
compliance with such standards positions the antenna
well for applications in portable and wearable
communication devices. Link budget analysis also
confirms the overall efficiency of the antenna for real-
world deployment conditions, and it shows
acceptable power margins for reliable wireless
connections.
The comparison between simulated and measured
results emphasizes the success of the antenna design
in attaining high isolation, low ECC, and maximum
gain. The small variations between simulated and
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Subâ
˘
A
´
S6 GHz Communication
585

measured values are due to fabrication tolerances and
measurement errors. Nevertheless, the overall
performance agrees with the anticipated design
objectives, ensuring the strength of the proposed
antenna. The compact size, high isolation, and wide
bandwidth together render this antenna a potential
candidate for the next-generation 5G wireless
communication systems.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The accelerated growth of wireless communication
networks, especially 5G networks, has brought forth
a pressing requirement for high-performance
antennas. The sub-6 GHz frequency band is vital in
facilitating robust, high-speed communication with
enhanced coverage and penetration. To satisfy the
rising demands of new applications, antenna designs
need to provide high efficiency, miniaturization, and
better isolation while still complying with regulatory
requirements. The integration of MIMO technology
further boosts communications performance through
enhancements in data rate and spectral efficiency,
henceforth becoming a required component of future
wireless systems. Nonetheless, optimal MIMO
performance is accompanied by the challenges of
mutual coupling, electromagnetic interference, and
space limitation in small devices. Several methods
have been investigated to counteract these challenges,
and electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structures have
proven to be a viable option for enhancing isolation
and suppressing surface wave propagation. The
demand for innovative designs to balance gain,
bandwidth, isolation, and miniaturization remains a
central point of interest in antenna research.
The research effectively proposes a new antenna
design that solves these issues and provides the best
performance for 5G sub-6 GHz applications. Through
the integration of an optimized EBG structure, the
new antenna provides better isolation, improved gain
performance, and enhanced overall efficiency
without sacrificing its compact size. The design also
satisfies the most important requirements of
contemporary communication systems, such as low
envelope correlation coefficient (ECC), high
diversity gain (DG), and maximum channel capacity
(CC). In addition, the designed antenna satisfies
specific absorption rate (SAR) restrictions, thus
providing a safe and convenient option for handheld
and portable devices. With a balanced link budget, the
structure facilitates effective communication, hence
applicable in various applications including IoT,
smart cities, and autonomous systems. Through
optimal parameterization, the research provides a
contribution towards the design of sophisticated
antenna solutions that improve the efficiency and
dependability of 5G networks. With further
advancements in 5G technology, the need for
miniature high-performance antennas will continue to
grow. The design presented herein is a step in
addressing these changing needs by presenting a
feasible and effective solution for next-generation
wireless communications. The conclusions of this
research offer useful insights to researchers and
practitioners alike, opening doors for further
developments in wireless communication
technology.
REFERENCES
A. Vosoogh, A. Haddadi and C. Bencivenni, "Novel Low-
loss Coaxial Slot Array Based on Gap Waveguide
Technology for E-band Automotive Radar
Applications," 2023 17th European Conference on
Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Florence, Italy,
2023, pp. 1- 5, doi:10.23919/EuCAP57121.2023.1013
3242.
A. H. Harkare, M. P. Abegaonkar, A. G. Kothari and A. A.
Bhurane, "Compact Circularly polarized MIMO
dielectric resonator antenna for complete X-Band
Coverage," 2023 IEEE Microwaves, Antennas, and
Propagation Conference (MAPCON), Ahmedabad,
India, 2023, pp. 1- 5, doi: 10.1109/MAPCON58678.20
23.10464026
A. I. O. Abdullah, A. M. Algatlawi and B. Alameen,
"Decoupling of Compact MIMO Antennas Using
Parasitic Element and Electromagnetic Band Gap
Structure," 2023 IEEE 3rd International Maghreb
Meeting of the Conference on Sciences and Techniques
of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (MI-
STA), Benghazi, Libya, 2023, pp. 702-706, doi:
10.1109/MI-STA57575.2023.10169823.
A. Bhosale and N. Biradar, "Design and Analysis of a 2x1
Circular Patch MIMO Antenna with Defected Ground
Structure for WiMAX in UWB Applications," 2024 8th
International Conference on Computational System and
Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions
(CSITSS), Bengaluru, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/CSITSS64042.2024.10817036.
A. I. Wahdiyat, F. Yuli Zulkifli and E. T. Rahardjo, "Mutual
Coupling Reduction in MIMO Antenna Using Via-less
EBG," 2024 International Symposium on Antennas and
Propagation (ISAP), Incheon, Korea, Republic of,
2024, pp. 1- 2, doi:10.1109/ISAP62502.2024.1084632
5.
E. Ovelatama, U. Umaisaroh and M. Alaydrus, "Mutual
Coupling Reduction Employing Rectangular Shaped
with Slotted Ring EBG and H-Shaped DGS for MIMO
Antenna," 2024 IEEE Asia-Pacific Microwave
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
586

Conference (APMC), Bali, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 435-
437, doi: 10.1109/APMC60911.2024.10867793.
H. Jia et al., "Beam-Adaptive DPD Based on Neural
Network for Fully-Connected Hybrid Beamforming
MIMO System," 2024 IEEE MTT-S International
Wireless Symposium (IWS), Beijing, China, 2024, pp.
1-3, doi: 10.1109/IWS61525.2024.10713565.
H. T and B. Roy, "Low-Profile CO-CSRR and EBG Loaded
Tri-Quarter Circular Patch EWB MIMO Antenna with
Multiple Notch Bands," in IEEE Open Journal of
Antennas and Propagation, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 634-643,
June 2024, doi: 10.1109/OJAP.2024.3377695.
H. T. P. Thao, "A High Isolation Frequency Reconfigurable
MIMO Antenna for WiFi/WiMax Applications," 2024
IEEE 12th Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and
Propagation (APCAP), Nanjing, China, 2024, pp. 1-2,
doi: 10.1109/APCAP62011.2024.10882051.
K. -L. Wong, S. -E. Hong and W. -Y. Li, "Low-Profile
Four-Port MIMO Antenna Module Based 16-Port
Closely-Spaced 2 × 2 Module Array for 6G Upper Mid-
Band Mobile Devices," in IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp.
110796- 110808, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3
322730.
K. V. Prasad, N. Venkateswari, M. D. Sai Sri Durga
Manisha, V. S. Gopi Chand and B. Alekhya, "Design of
UWB MIMO Antennas with Enhanced Isolation for
Wearable Applications," 2024 5th International
Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologi
es and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), Tirunelveli,
India, 2024, pp. 876- 881, doi: 10.1109/ICICV62344.2
024.00144.
L. Zhang, C. Ma, H. Chu and G. Li, "A UWB-MIMO
Antenna Based on Decoupling of EBG and Ground
Branches," 2023 International Applied Computational
Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES-China),
Hangzhou, China, 2023, pp. 1-3, doi: 10.23919/ACES-
China60289.2023.10249990.
M. R. Jadhav and U. L. Bombale, "A Circularly Polarized
Four Port MIMO Antenna with Split Ring Metamaterial
for dual band IoT Applications," 2023 International
Conference on Advances in Computation,Communicat
ion and Information Technology (ICAICCIT),
Faridabad, India, 2023, pp. 839- 846, doi:10.1109/ICA
ICCIT60255.2023.10466159.
M. A. Nassar, H. Y. Soliman, R. M. Abdallah and E. A. F.
Abdallah, "Mutual Coupling Reduction Techniques for
Dual Band MIMO Antenna," 2023 11th International
Japan- Africa Conference on Electronics,Communicati
ons, and Computations (JAC-ECC), Alexandria, Egypt,
2023, pp. 54-57, doi: 10.1109/JAC-
ECC61002.2023.10479605.
M. K. Gaur, P. Tiwari, M. Kaushik and V. Gahlaut,
"Terahertz Regime Dual-Port Tripple-band Microstrip
Based MIMO Antenna," 2024 11th International
Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated
Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2024, pp. 84-88, doi:
10.1109/SPIN60856.2024.10512189.
R. Kumar, A. De and P. Jain, "Miniaturized CPW MIMO
Antenna with Enhanced Isolation for 5G Application,"
2023 IEEE Silchar Subsection Conference (SILCON),
Silchar, India, 2023, pp. 1- 4, doi:10.1109/SILCON59
133.2023.10405301.
S. Ahmed, M. U. Raza and S. Yan, "Enhancing Antenna
Array Performance with Rectangular-Shaped
Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures for Mutual
Coupling Reduction," 2023 IEEE 11th Asia-Pacific
Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP),
Guangzhou, China, 2023, pp. 1-2, doi:
10.1109/APCAP59480.2023.10470224.
U. Tripathi, D. Solanki, P. Malviya, A. Parmar and L.
Malviya, "MIMO antenna design with PBG structure
for THz communication," 2023 First International
Conference on Microwave, Antenna and Communicati
on (MAC), Prayagraj, India, 2023, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/MAC58191.2023.10177063.
W. -S. Chen and S. -A. Shie, "Four-port printed MIMO Slot
Antennas with an EBG Reflector at Wi-Fi 6E/7 6GHz
Band for Access Point Applications (Invited)," 2023
IEEE 11th Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and
Propagation (APCAP), Guangzhou, China, 2023, pp. 1-
2, doi: 10.1109/APCAP59480.2023.10469708.
Z. Shao, L. Ma, C. Gu and K. Sengupta, "Decoupling of
Wideband Closely-Spaced Patch Antennas for MIMO
Applications," 2023 IEEE International Symposium on
Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio
Science Meeting (USNC-URSI), Portland, OR, USA,
2023, pp. 1457-1458, doi: 10.1109/USNC-
URSI52151.2023.10238189.
Electromagnetic Band Gap MIMO Antenna for 5G: Subâ
˘
A
´
S6 GHz Communication
587
