
Enhancing Agricultural Practices through Machine Learning for Soil
Analysis and Crop Recommendation
Paineni Vaishnavi, Uppara Pavani, Sameena Yousuff, Pitta Pavani and Kalluru Divya Sai
Computer Science and Engineering (Ds), Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Venkayapally, Kurnool, Andhra
Pradesh, India
Keywords: Crop Recommendation, ML, SVM, DT, Agriculture, Crop Yield Prediction, Soil Analysis, Weather Patterns,
Hybrid Model, Crop Quality Ranking.
Abstract: Based on many factors including Season, Soil type, Rainfall, Temperature, Groundwater Level, Fertilizers,
and Pesticides, the crop recommendation system based on machine learning suggests to the farmer the crop
to be grown. This follows through examination of SVM and DT and a hybrid model of it as a new system on
crop prediction. This is done through crop and crop production data-sets which enable this model to provide
reliable recommendations. It also sorts crops based on quality and its findings help determine the quality of
both high and low-quality leads and helps boost industrial production and economic growth.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agriculture is the backbone of numerous nations,
and India serves as no exception; a large proportion
of individuals in India are engaged in agriculture as
farmers. Traditional agricultural methods based on
knowledge and instinct are not very effective in
determining the category of crops and predicting
production. Machine learning (ML) has recognized
substantial progress in agriculture, enabling data-
driven responses to improve sustainability and yield.
Based on different parameters like soil type,
rainfall, groundwater level, temperature, fertilizers,
pesticides, seasonal conditions, etc., a ML-based
Crop Recommendation System will help farmers
choose the best crop to plant. The system also uses
ML algorithms such as SVM and DT to process large
datasets to give accurate and productive
recommendations. It helps the farmer to get the
maximum yield possible, uses resources efficiently,
and reduces economic loss.
Current crop recommendation systems utilize data
mining to predict weather patterns and agricultural
yield. But these methods, on the other hand, can’t
handle unpredictable temperature and rainfall
patterns that may result in lower accuracy. Moreover,
most of the solutions and implementations are
hardware based and come at a premium cost, and
maintenance proves to be a challenge as well. More
specifically, the proposed system comprises a hybrid
ML model which is a phased model that addresses
issues such as efficiency, reliability in yield
prediction, and crop quality ranking procedures.
This model can help farmers to select the crops
and thus, improve farmers income and economy. In
addition, the system incorporates other modules,
including pesticide prediction and online agricultural
commodity trading, making for a well-rounded
solution to contemporary agricultural difficulties.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
a) Motwani, Aditya, et al. "Soil Analysis and Crop
Recommendation using Machine Learning."
2023 International Conference for Advancement
in Technology (ICONAT). IEEE, 2023.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9725901
India ranks among the world's top three crop
producers. The agricultural economy of India relies on
its impoverished farmers. Soil types vary from area to
region, leaving farmers with limited technical options
when it comes to selecting the most profitable crops
for their soil. Compared to Random Forest's 75%
accuracy, CNN architecture achieves 95.21%.
b) Rao, Madhuri Shripathi, et al. "Crop prediction
using machine learning." Journal of Physics:
568
Vaishnavi, P., Pavani, U., Yousuff, S., Pavani, P. and Sai, K. D.
Enhancing Agricultural Practices through Machine Learning for Soil Analysis and Crop Recommendation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013935300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
568-574
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Conference Series. Vol. 2161. No. 1. IOP
Publishing,2023.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/35775
9181_Crop_prediction_using_machine_learning
Agriculture is the main income source for most
developing nations. Farming techniques and
agricultural technology are always developing. It is
difficult for farmers to keep up with the demands of
merchants, customers, and the world at large. Soil
erosion and industrial pollution are contributing to
climate change, which farmers must address. (ii)
Phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen deficiency in the
soil can stunt crop growth. One common error that
farmers do is to produce the same crops every year.
They apply fertilisers carelessly, without knowing the
quantity or quality of the fertiliser they are using. The
goal of the research is to find the most accurate crop
forecast model that can help farmers pick crops
according to weather and soil conditions. Using Gini
and entropy, this study analyses three classifiers:
KNN, DT, and RF. From what we can see, Random
Forest is the most accurate of the three.
c) Priyadharshini, A., et al. "Intelligent crop
recommendation system using machine
learning." 2023 5th international conference on
computing methodologies and communication
(ICCMC). IEEE, 2023.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9418375
The agricultural sector plays a crucial role in
India's GDP. In a nation where 58% of the population
works in agriculture, one of the biggest problems is
that farmers often use outdated and unscientific
methods to pick the wrong crops for their land.
Planting crops that aren't well-suited to the soil,
season, and area is a common mistake among farmers.
People end their lives, stop working the land, and go
to cities because of this. To get around this problem,
this study suggests a method that considers all the
variablesto help farmers choose crops. The practice of
precision agriculture, which makes use of modern
agricultural technology to manage crops in a site-
specific manner, is gaining popularity in developing
countries.
d) Pande, Shilpa Mangesh, et al. "Crop
recommender system using machine learning
approach." 2023 5th International Conference on
Computing Methodologies and Communication
(ICCMC). IEEE, 2023.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9418351
The majority of rural Indians find gainful
employment in agriculture and related fields. The
country reaps the benefits of its thriving agricultural
sector. Global standards indicate a poor crop output
per acre. The higher suicide rate among marginal
farmers in India might be explained by this. Findings
from this study provide an easy-to-understand and
implement strategy for farmers to predict crop yields.
One possible approach is to use a smartphone app to
link together farmers. Using GPS, the user's location
is ascertained. User enters surface area and soil type.
Algorithms trained by ML select the most profitable
crops and predict farmers' harvests. In order to predict
crop yields, scientists employ SVM, ANN, RF, MLR,
and KNN. At 95% accuracy, Random Forest
outperformed all other methods. In order to maximise
yields, the algorithm also suggests when fertilisers
should be used.
e) Kalimuthu, M., P. Vaishnavi, and M. Kishore.
"Crop prediction using machine learning." 2022
third international conference on smart systems
and inventive technology (ICSSIT). IEEE, 2022.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9214190
A certain percentage of domestic production is
provided by agriculture, which is the backbone of
India's economy and ensures food security. But
unnatural climate change is diminishing food
production and forecasting, which is bad news for
farmers' bottom lines since it lowers yields and makes
them less good at predicting crops. This study uses
machine learning, a cutting-edge method for
predicting agricultural yields, to help inexperienced
farmers plant more realistic seeds. The supervised
learning algorithm Naive Bayes recommends it. For
the purpose of assisting their growth, we take readings
of the moisture, humidity, and temperature of
agricultural seeds. An Android app is also in the works
with the software. Users just need to input their current
location and temperature for the program to begin
making predictions.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Proposed System
To make the most of ML for crop selection and yield
prediction, the recommended Crop Recommendation
System examines several factors such as soil type,
rainfall, groundwater levels, temperature, fertilizers,
pesticides, and seasonal situations. Using SVM and
DT algorithms, the system processes large datasets to
provide accurate recommendations, ensuring efficient
resource utilization and increased productivity.
Additionally, a ranking mechanism evaluates crop
Enhancing Agricultural Practices through Machine Learning for Soil Analysis and Crop Recommendation
569
quality, helping farmers distinguish between high and
low-quality yields for better decision-making.
The system also features a crop pest forecasting
and e-commerce module to enhance its utility and
offer a comprehensive approach to modern-day
agricultural challenges. Instead, this model combines
crop datasets with crop production datasets so that it
measures prediction accuracy while minimizing
redundancy. It improves the efficiency of agricultural
and helps the economy reduce the loss of agriculture
and increase its viability and longevity through data-
driven decision-making.
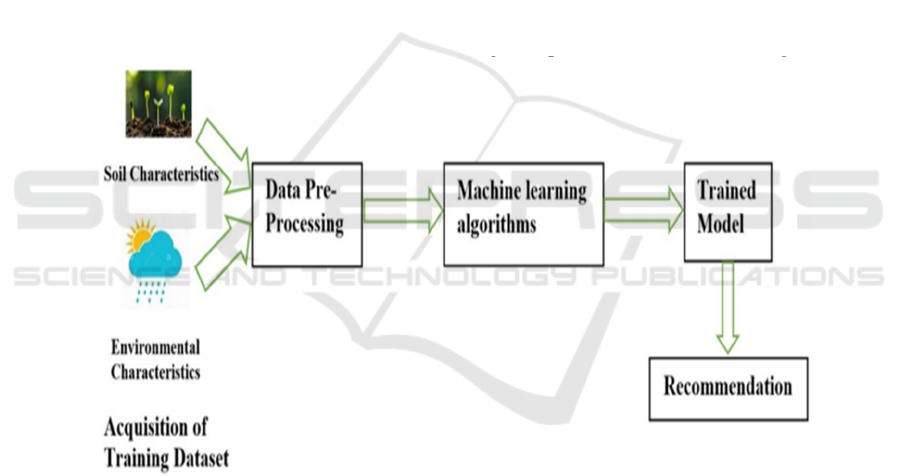
3.2 System Architecture
Crop Recommendation System: Its architecture
(Figure 1) is attached with multi-layers for precise
Crop Selection; Yield prediction. Soil type,
precipitation, temperature, groundwater level,
fertilisers, pesticides, season are just some of the
many variables collected by the Data Collection
Layer. The next step would be processing this data
into the Data Pre-processing Layer which would
include operations such as handling missing values,
normalizing the data, feature extraction, etc.
Next layer is Machine Learning Model Layer where
various models (in our case SVM and DT) will be
used to train and then cross-validate on the historical
crop and production datasets. So, post training, in the
Recommendation & Ranking Layer, it predicts the
most suitable crops according to input parameters and
ranks the crops on their quality. The system provides
some additional smooth features like Pesticide
Prediction and Online Trading Platform which helps
the farmers to get pesticide suggestions and also helps
to make transactions in the market. It's a digital portal
layer that allow farmers to enter data and get
recommended through a mobile or web-based
interactive platform with visual insights on crop
prediction and yield estimation, designing a holistic
digital experience towards advanced agriculture.
Figure 1: Proposed Architecture.
3.3 Modules
3.3.1 Gathering the Datasets
This segment collects crops datasets categorising soil
type, rainfall, groundwater levels, temperature,
fertilisers, pesticides and seasonality from free
resources like Kaggle. After collecting the data, the
proposed model uploads the data for preprocessing
and analysis. With this step, the system receives
reliable, realistic data for correct predictions.
3.3.2 Generate Train & Test Model
Because the ML model is trained on this data, it is
important to clean the data of inconsistencies,
missing values, and to normalise features. The
training and testing datasets are separated with the
80% being training and 20% being testing in the
post-processing. This allows the model to learn from
past data while being able to retain another set that it
will use only for evaluation, improving the fairness of
its predictions.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
570

3.3.3 Run Algorithms
This module will use machine learning models on the
dataset to predict crops. This differs from model to
model of course, but the dataset is typically 70% –
80%training and 30% — 20%testing. The data is up
to October 2023 and is utilized using SVM and DT
algorithms to determine the appropriate crop to be
cultivated against the conditions. These models assist
with the identification of patterns in the data,
enabling better predictions for different farming
conditions. Figure 2 shows the Upload Dataset.
Figure 3 shows the Enter Input Data. Figure 4 shows
the Results.
3.3.4 Obtain the Accuracy
After training and testing the model, this module
measures the accuracy (figure 5) to assess the
performance of the system. The model is evaluated
best on the basis of various metrics like precision,
recall, and F1-score, which indicate how well the
model predicts fitted crops with input variables. In
addition, hyperparameter tuning and more data
preprocessing is done in order to optimize the results,
if accuracy isn't sufficient enough.
3.3.5 Predict Output
The output of the module depends on the parameters
input by the user. By using trained algorithms, we
may estimate the most suitable crop to be planted in
such conditions from these data. The technology can
also rank crops in terms of yield and quality, helping
farmers to make informed decisions. This helps in
providing accurate and dependable suggestions to
maximize the agricultural yield for farmers.
3.4 Algorithms
3.4.1 Decision Tree Classifier
The rule-based DT method divides the dataset based
on feature values for the purpose of decision-making.
Each node in the tree is a choice based on the
parameters input. DT helps in identifying the best
crop in crop recommendation system based on
various parameters like soil type, rainfall, and
temperature. This is an easy to interpret and
computationally efficient algorithm for classification
problems.
3.4.2 Support Vector Machine (SVM)
Support vector machines an SVM is a type of
supervised learning algorithm used for classification.
It finds the best hyperplane to classify data points.
SVM aids in classifying and recommending crops
based on soil conditions, weather patterns, and other
input parameters in this system. Its predictions of crop
selections are accurate, and it is also good with high-
dimensional data.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Accuracy: How well a test can differentiate between
healthy and sick individuals is a good indicator of its
reliability. Compare the number of true positives and
negatives to get the reliability of the test. Following
mathematical:
Accuracy
(1)
Precision: The accuracy rate of a classification or
number of positive cases is known as precision.
Accuracy is determined by applying the following
formula:
Precision
(2)
Recall: The recall of a model is a measure of its
capacity to identify all occurrences of a relevant
machine learning class. A model's ability to detect
class instances is shown by percent of correctly
anticipated positive observations relative to total
positives.
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑙
(3)
F1-Score: A high F1 score indicates that a machine
learning model is accurate. Improving model
accuracy by integrating recall and precision. How
often a model gets a dataset prediction right is
measured by the accuracy statistic.
𝐹
𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
(4)
𝐹
𝑆𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒
(5)
Enhancing Agricultural Practices through Machine Learning for Soil Analysis and Crop Recommendation
571
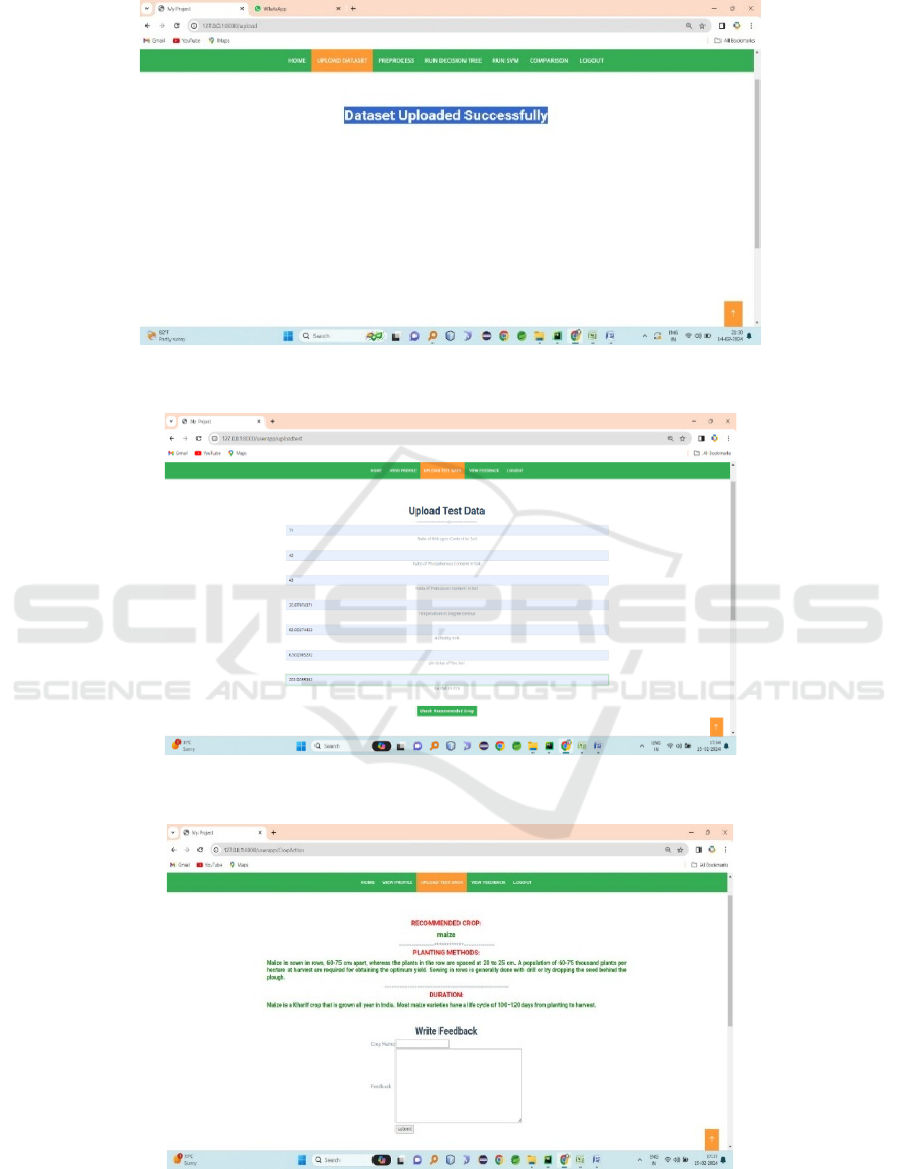
Figure 2: Upload Dataset.
Figure 3: Enter Input Data.
Figure 4: Results.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
572
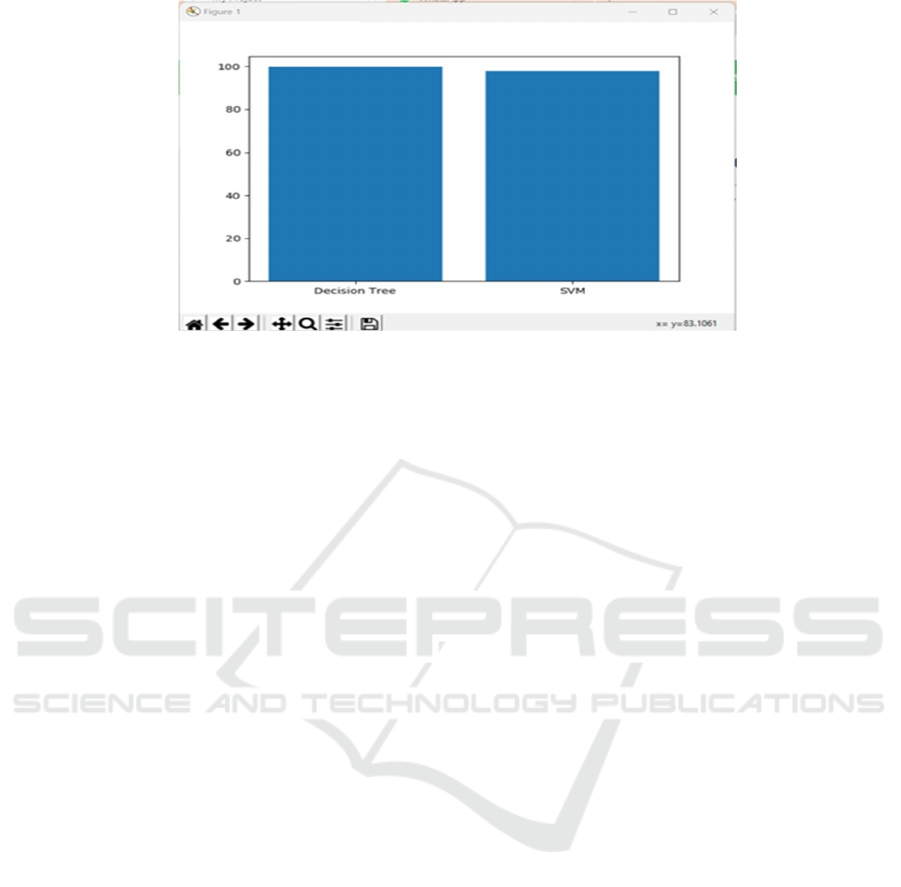
Figure 5: Accuracy Graph.
5 CONCLUSIONS
With the use of machine learning, the proposed Crop
Recommendation System guides farmers towards
optimal crop selection in response to specific agrarian
conditions. By integrating SVM and DT algorithms,
the system improves prediction accuracy and
enhances decision-making in farming. Additionally,
features like crop quality ranking, pesticide prediction,
and an online trading platform provide a
comprehensive solution to modern agricultural
challenges. Not only does this optimize crop choices
but also boosts productivity and economic growth,
ensuring a data-driven, efficient, and accessible
system for farmers.
6 FUTURE SCOPE
Future Scope of Crop Recommendation System:
Integrating with deep learning models such as CNNs
and RNNs for improved accuracy on predictions by
analysing complex agricultural patterns. It assists in
improving soil and weather analysis using IoT-based
sensors for real-time data collection. It would be
beneficial to also include geospatial analysis -- using
things like satellite imagery and GIS -- to determine
land suitability. And the introduction of a mobile app
with multi-language options will provide a more
minimalist approach to recommendations usage by
farmers. Moreover, blockchain technology helps to
be incorporated for secure and transparent
agricultural trading. These innovations will improve
system speed, precision, and user-friendliness, which
will serve farmers and increase crop yield.
REFERENCES
Doshi, Zeel, et al. "AgroConsultant: intelligent crop
recommendation system using machine learning
algorithms." 2018 Fourth International Conference on
Computing Communication Control and Automation
(ICCUBEA). IEEE, 2018.
Kalimuthu, M., P. Vaishnavi, and M. Kishore. "Crop
prediction using machine learning." 2022 third
international conference on smart systems and
inventive technology (ICSSIT). IEEE,2022. M. Kamei,
Trends and Technology In The Era of Post TV-The Rise
of OTT Platforms. Think India Journal, 22(33),
(2019)184-192.
Kulkarni, Nidhi H., et al. "Improving crop productivity
through a crop recommendation system using
ensembling technique." 2018 3rd International
Conference on Computational Systems and Informatio
n Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS).
IEEE, 2018.
Kumar, Avinash, Sobhangi Sarkar, and Chittaranjan
Pradhan. "Recommendation system for crop
identification and pest control technique in
agriculture." 2019 International Conference on Comm
unication and Signal Processing (ICCSP). IEEE, 2019.
Lacasta, Javier, et al. "Agricultural recommendation
system for crop protection." Computers and Electron-
ics in Agriculture 152 (2018): 82-89.
Motwani, Aditya, et al. "Soil Analysis and Crop
Recommendation using Machine Learning." 2023
International Conference for Advancement in Techno-
logy (ICONAT). IEEE, 2023
Pande, Shilpa Mangesh, et al. "Crop recommender system
using machine learning approach." 2023 5th
International Conference on Computing Methodologie
s and Communication (ICCMC). IEEE, 2023.
Patil, Pavan, Virendra Panpatil, and Shrikant Kokate. "Crop
prediction system using machine learning algorithms."
Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. (IRJET) 7.02 (2020).
Enhancing Agricultural Practices through Machine Learning for Soil Analysis and Crop Recommendation
573

Priyadharshini, A., et al. "Intelligent crop recommendation
system using machine learning." 2023 5th international
conference on computing methodologies and
communication (ICCMC). IEEE, 2023.
Pudumalar, S., et al. "Crop recommendation system for
precision agriculture." 2016 Eighth International
Conference on Advanced Computing (ICoAC). IEEE,
2017.
Rajak, Rohit Kumar, et al. "Crop recommendation system
to maximize crop yield using machine learning
technique." International Research Journal of Engin-
eering and Technology 4.12 (2017): 950-953.
I.A.Guitart, G. Hervet, S.Gelper, Competitive
advertising strategies for programmatic television. Jo-
urnal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48,
(2020)753-775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-019-
00691-5
Tengeh, R.K. and Udoakpan, N., 2021. Over-the-top
television services and changes in consumer viewing
patterns in South Africa. Management dynamics in the
knowledge economy, 9(2), pp.257-277.
Van Klompenburg, Thomas, AyalewKassahun, and
CagatayCatal. "Crop yield prediction using machine
learning: A systematic literature review." Computers
and Electronics in Agriculture 177 (2020): 105709.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/atharvaingle/crop
recommendation-dataset
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
574
