
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on
Meteorological Data
P. Geetha, T. Grace Shalini, B. Vikas and D. Thiyagarajan
Department of Computational Intelligence, SRMIST, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Agro Meteorology, Farming Analysis, Meteorological Data.
Abstract: Agro meteorology is a field that has conclusions from a couple of disciplines and focusing at the numerous
bodily and dynamic approaches that may affect the crop-growing environment. Its principal intention is to
become aware of and understand those results, bearing in mind the medical application of weather and climate
data to aid sustainable agricultural manufacturing. Despite technological progress in Indian agriculture, meals
production still intently correlates with fluctuations in climate. The upward push in extreme weather activities,
which includes prolonged dry spells, heatwaves, extreme one-day rainfall, and hailstorms. This underscores
the need to reinforce using agrometeorological insights for informed, tactical decisions geared toward
reducing crop losses. This research studies how weather factors affect farming and farming outputs while
explaining how meteorological data helps agro meteorologists make better decisions. Also, to study about
how temperatures, precipitation, humidity, and wind intensity affect crop development and farm operations
predicting yields. This research of meteorological data shows which weather factors most impact crops
including where rainfall needs to fall and what temperature ranges work best. The research shows how climate
changes across seasons impact farm production levels and describes how different microclimate settings
influence specific agricultural areas. Weather forecasts need precision to help farmers develop specific
farming methods that guard their crops from climate threats. The research shows farmers can better manage
crops and water resources when they combine weather information directly into their farm practices. This
paper helps develop agro meteorology by giving important information to farmer’s policymakers and science
professionals to deal with climate issues and develop sustainable agricultural practices.
1 INTRODUCTION
Planting moths according to predictions based on his
meteorology. This makes it an interdisciplinary field
of study that seeks to understand and use the
interactions between weather, climate, and tillage
systems. To increase the efficiency and effectiveness
of the said area. By studying how weather and
hydrology affect crop yields. Domestication and other
biological processes, on the other hand, focus on
temperate zones to include tropical agriculture.
Challenges such as lack of information still exist. This
is because the agricultural sector is one sector that is
sensitive to weather conditions. Insights from
meteorology to tackle climate-related risks. It
improves the sustainability of agriculture and manages
its environmental impacts which is an important part
of development.
It bridges between atmospheric science and
agricultural practice and examines how weather and
climate affects the crop yields and how much it
carrying capacity can vary. This knowledge plays an
important role in addressing the challenges posed by
climate change, such as heat waves, floods and
temperature extremes. And this area is expanding as
well. Research that integrates the effects of
meteorological factors on insects, pathogens, and
genetically modified organisms. This has increasingly
focused on integrating sustainable practices into
agriculture, such as carbon bonding. Efficient water
uses and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions Given
the global demand for biofuels in food and other
agricultural products, it is clear that meteorology will
continue to be important...historical fact. This study
provides farmers with valuable tools for managing
crops and reduce the harmful results of exchange rate
fluctuations. Integrating real-time meteorological
facts into parenting training can help increase warmth.
This proposed paper will focus on how
meteorological data can enhance farming analysis
Geetha, P., Shalini, T. G., Vikas, B. and Thiyagarajan, D.
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on Meteorological Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0013934800004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
559-567
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
559

including but not limited to crop yield prediction,
weather-based risk evaluation or precision farming
because meteorological data is accurate, uniform and
contains no gaps. If pre-processing is done properly
by normalizing or scaling the meteorological data
then missing data treatment must be applied and to
enrich the analysis, other supplementary sources like
soil data, satellite data, remote sensing data, etc. must
be included.
And to use by employing more enhanced
approaches like machine learning models (Random
Forest, Support Vector Machines or Neural Network)
for analytical use of both meteorological data and
farming data. These models can do this more
effectively than traditional types of analysis that may
miss certain patterns. Thus, one can have access to
huge amount of meteorological data, and consider
using Big Data technologies to increase the level of
analysis. Also, use Data Heat maps to represent the
interconnectedness of Weather and Farming variables
through Heat maps, Geospatial Visualizations, and
Trends/Bar Charts. With better analytical tools, better
quality data, increased number of visualizations and
applications of business intelligence.
With improvements in weather generation,
farmers now have got entry to to particular facts on
temperature fluctuations, rainfall patterns, humidity
ranges, and even severe climate alerts. This fact
enables them make critical daily decisions, consisting
of adjusting irrigation schedules, enforcing pest
manage measures, and deciding on the maximum
resilient crop varieties to optimize yields. Forecasts
on seasonal climate shifts and extended climate
patterns, have turn out to be valuable for making
plans. For instance, in areas suffering from El Niño,
an expected dry season may additionally spark off
farmers to pick out drought-tolerant vegetation or
invest in water conservation strategies.
Likewise, a predicted results season with
improved rainfall should encourage planting of
water-extensive vegetation or instruction for capacity
flooding. Early warning structures now combine
these climate forecasts to help agricultural making
plans and network resilience, particularly in regions
surprisingly sensitive to weather variability. By
analyzing tendencies, those systems provide strategic
insights that allow farmers to mitigate dangers
associated with droughts, frosts, floods, and even
unexpected pest outbreaks, which are regularly
correlated with weather situations.
As weather alternate maintains to impact
international climate systems, investments in
agricultural meteorology are essential. Enhanced
forecasting strategies and place-specific climate
models are being evolved to provide farmers with
greater particular, localized records. By incorporating
those forecasts, farmers can adapt to changing
situations, lessen losses, and make extra sustainable
and worthwhile choices that assist food safety and aid
conservation.
The specific terms related to this research paper is
agro meteorology, climate variability, crop modeling,
Phenology, Precipitation Analysis, Weather
Forecasting. Our goal is to discover how weather
changes affect farm harvest results. Scientists use
weather patterns to learn about crop growth so they
can help farmers work better. Research in agro
meteorology understands and controls weather-
related risks from weather fluctuations by studying
their effects on farm production processes. This is
used to check weather observations to help farmers
get better results from their land and manage their
resources while preparing for climate challenges so
farming can remain healthy and reliable.
2 REVIEW STUDY
A revised and completely rephrased version meaning
the identical element: The United Nations Sustainable
Development Report reveals that among 1974 and
2007, five of 10 maximum negative natural screw ups
have been connected to drought. (
Carbone and
colleagues, 2009) Drought is a slowly growing
phenomenon. But it brought about very serious
damage. Caused by way of weather alternate Regions
with the least quantity of rainfall every 12 months
especially arid and semi-arid regions are at higher
danger (
Dorais wami P.C., 2000) This leaves them
prone to the long-time period consequences of
drought (
Hanks and Ritchie, 1991). Semi-arid regions
which are often densely populated and crucial to the
nearby economic system
(Lomas,2000). Droughts are
mainly affected. In India, as an example, an
envisioned 330 million human beings have been
affected at some stage in the 2015-2016 drought. The
occasion contributed to a full-size meal’s disaster.
Which affects food protection in each aspect whether
it is readiness, balance, get admission to, and
utilization. (
Maracci, 2000). This regularly results in
great hunger and malnutrition. As climate patterns
exchange round the arena Drought frequency and
severity are growing. Causing a greater threat to
inclined companies, the population.
(Monteith JL,
2000)
. The 2023 study examined Crop prediction for
37 developing nations over 27 years through
regression models of which six were developed.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
560

A 2020 study used panel household survey data
obtained from six SSA countries linked to weather
data to explore the implications of errors inherent in
RS on productivity estimates. (
Monteith and Unsworth,
1990)
In the study, guidelines for combining remote
sensing weather data with the socioeconomic surveys
were recommended in order to enhance the precision
of the assessment of weather effects on agriculture.
This unique contribution of this research brings
meteorological data into farm planning and climate
adaptation to create better forecasting methods.
Ogalo,
they show the most current findings about using
weather and climate information to support farming
practices. (
Parry and colleagues, 2007) By combining
actual weather readings from weather stations with
farming software computer models give better crop
production forecasts. By monitoring weather farmers
can develop better strategies to face weather hazards
and make smarter decisions about their activities.
Farmers use forecasted weather data to determine
better planting dates watering times and harvest
periods which reduce their risks from unexpected
climate changes.
3 STUDY OF PROPOSED
SYSTEM
Agricultural meteorologists commonly gain their
foundational education by supplementing
conventional research in meteorology, physics, or
environmental science with guides in plant, soil, or
animal science, forestry, or horticulture. Only a few
universities within the US and Europe provide
committed undergraduate or graduate tiers in
agricultural meteorology. Instead, most agricultural
meteorology education is included into broader
agricultural applications like agronomy. (
Carbone and
colleagues, 2009)
In comparison, India has adopted a
greater structured technique to teaching agricultural
meteorologists at the college stage, reflecting the
country's emphasis on this specialized subject. As
climate exchange and common weather-associated
failures more and more threaten worldwide
agricultural manufacturing, the scope of agricultural
meteorology has multiplied. (
Dorais wami P.C., 2000).
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has
emphasized the significance of socioeconomic
elements like irrigation, garage, agroforestry, floods,
droughts, erosion, desertification, frost, wind safety,
managed increase environments, and sustainable
farming practices, specifically in growing
international locations
(Lomas,2000). The sensible
demands of agricultural meteorology have led to the
development of specialized training packages
designed to enhance the skills, information, and
practices of experts in this discipline. The WMO
offers in-service training through nearby
meteorological schooling centers, focusing on topics
such as primary agricultural meteorology, facts
control, agricultural meteorology modeling, and
hydrometeorology (
Maracci, 2000). These quick,
venture-oriented publications intention to enhance
and standardize agricultural meteorology practices,
especially in regions like commentary strategies and
facts management, making sure that specialists are
higher prepared to fulfill the challenges. As suggested
by the name, it is the branch of meteorology that deals
with the relations between weather and climate and
agriculture. The two major areas of concentration in
the main aspects of agro meteorology involved the
attribution of temperature, rain, humidity, solar
irradiance to crop development and Crop-specific
reaction to weather events such as drought, frost or
floods. The meteorological data sources include;
Historical weather data, Climate prediction models,
Satellite and remote sensing data and Real-Time
Weather Data. Flavors of farming analysis for Models
and Technique emphasized likely farming modelling,
weather base decision support system (DSS), and
agro-climatic zoning. Also, keep the Meteorological
data linked to farm management practices such as
Irrigation management, planting and harvest dates,
Pest and disease management control, and Risk
management. Identifying the tasks as Climate Change
and Agriculture, Adaptation, and Possible scenarios
of climate change impact on crop growing in certain
regions and proposing adaption strategies. For
instance, hypothesize about possible applications of
future complex meteorological prediction systems or
about utilizing actual weather information in farming.
In this way, you can continuously stress the agro
meteorological aspect throughout the paper so that the
meteorological data is not only an input to your study
but also output of upgrading farming practices and
responding to the various problems affecting
agriculture.
As meteorology advances swiftly, there is an
growing need for ongoing training and schooling
possibilities in agricultural meteorology. The
developing hobby in global observation networks,
which reveal a broader variety of environmental
variables, has intensified this want. The Internet
offers a valuable platform for presenting
standardized, authoritative instructional and
education materials to a much broader target market
within the global agricultural meteorology
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on Meteorological Data
561

community, making lifelong studying greater on hand
and supporting professionals live modern-day with
the today's trends in the field. As meteorology
advances unexpectedly, there is an increasing need
for ongoing education and training possibilities in
agricultural meteorology. The growing hobby in
international statement networks, which monitor a
broader variety of environmental variables, has
intensified this need. The Internet offers a precious
platform for offering standardized, authoritative
instructional and education materials to a wider
audience inside the international agricultural
meteorology network, making lifelong gaining
knowledge of extra on hand and helping professionals
live modern-day with the cutting-edge developments
inside the area.
3.1 Data Set and Charateristics
Agro meteorology first enhance the data by
employing real high-resolution data and then
combine these dataset, and also handles the missing
data. Secondly, take enhanced approaches in
modelling and feature selection, and cross verify
models with complete cross validation & cross check
for use of benchmarking out of sample data set. Third
one with Regard to Temporal and Spatial Variability,
the prospect of Incorporating Relevant Metrics as
well as Improving the Interpretation of Results. Last
of all, let’s discuss other possibilities such as IoT and
Sensors having Block chain for data credibility, AI
for insights. Figure 1 gives the year wise
meteorological Data Analysis.
The survey helped confirm the accuracy of crop
identification from satellite images.
Figure 1: Year wise meteorological data analysis.
Our study examines potential evapotranspiration
(PE) and actual evapotranspiration (AE) at different
latitudes and climate types. Using the Köppen climate
classification as outlined by FAO-SDRN-
Agrometeorology Group (1997) we focus on five
different ecosystems: basins, estuaries, seas, rivers
and wetlands. An estuary is defined as an area where
sea water is replaced by fresh water from the land.
While a wetland is described as an area where water
is near the surface, most of the area is raised. A river
is specified as a natural surface of a specified width.
Inlets are still bodies of water and seas are large
bodies of salt water that cover most of the earth's
surface. Reports of water releases from estuaries and
coastal areas are assessed. The sea is divided into
estuaries, coastal bays, deep seas, and upstream areas.
Wetlands are also divided into peatlands, anthills, and
forest wetlands. and coastal wetlands As defined by
Mitsch and Gosselink (2001) The ecological function
of internal organs was analyzed by comparing PE in
internal organs with different thermal layer patterns
and nutritional states. Participants were classified as
stratified or unratified and as oligotrophic or
eutrophic based on thermal regime data and mean
annual total phosphorus, respectively. Stratification
affects insect ecosystems by affecting temperature
gradients and nutrient distribution. While nutritional
status indicates nutritional intake. Data were obtained
from studies that reported emissions from inlets. A
eutrophic entrance is defined as having a total
phosphorus concentration greater than 30 μg l−1.
This classification allows us to assess the effects of
thermal and nutritional conditions on met nutrient
slippage. Motors in various types of entrances
3.2 Agro Resources
The global distribution of agroclimate assets
substantially affects crop yields, often known as
maximal climatic potential yields. Climate alternate
has notably altered those yield styles, with recent
studies studying its effect on the expansion of
cropping structures in China during the last thirty
years. Findings suggest that growing temperatures
have driven the northern boundaries of cropping
systems in addition north and northwest, probably
growing food manufacturing. This shift should
convert some unmarried-cropping areas within the
North to double-cropping and double-cropping
regions in the South to triple-cropping while those
projections are constructive, they oversimplify the
complicated relationship between agro climate assets,
farmland distribution, and subject situations.
Globally, many landscapes are underperforming,
with crop yields falling below common degrees. The
crop yield hole is the distinction among found yields
and the capability yields plausible with contemporary
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
562

practices and technologies at precise places. Recent
research display that whilst a few areas' grain yields
are nearing their capability, others revel in big yield
gaps, mainly in elements of Africa, Latin America,
Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe Although climate
alternate is a crucial element influencing yield
patterns, other factors like irrigation, market access,
and agricultural hard work play huge roles in
improving grain manufacturing performance and
decreasing yield gaps Addressing those yield gaps
necessitates centered land control practices, however
such intensification can negatively impact
surroundings offerings.. It is vital to understand that
the effectiveness of those elements varies by scale
what's big globally may not be as impactful
domestically, addressing crop yield gaps calls for a
place-unique method in preference to a broad global
angle, considering change-offs among agricultural
intensification and environmental degradation.
The issue of closing the crop yield hole includes
balancing agricultural intensification with
environmental sustainability. Intensive land
management practices can beautify grain
manufacturing but can also lead to terrible ecological
influences. The effectiveness of different
intensification elements is scale-established, with
local versions affecting their significance. A local
method is crucial to appropriately cope with yield
gaps and evaluate the change-offs among growing
meals manufacturing and maintaining ecological
fitness. Despite ongoing discussions, a sustainable
answer that ensures both food protection and
environmental conservation stays elusive. Region-
particular analyses are important for knowledge these
dynamics and developing techniques that aid
sustainable agricultural practices whilst minimizing
ecological damage.
3.3 Microclimates and Its Productivity
Farmers have a long tradition of improving crop
production through a variety of microclimate
management techniques. These include irrigation
systems, glass, wind turbines, snow walls, and roofs.
These processes are very sensitive to local weather
conditions, averages, extremes, and changes over
time. Such adaptation is critical for crop yield and
quality. This is especially true in response to climate
change. Vegetable crops, which are often more
valuable to the area than important cereals, It is
especially sensitive to slight seasonal changes.
Horticultural crops, unlike cereals, can lose
significant quality and market value due to slight
climate changes. For example, the best color of some
fruits depends on the exact amount of sunlight during
the critical growing season. In addition, the size,
shape, and flavor of fruits and vegetables can be
significantly affected by microclimate, so altering the
microclimate for vegetable products may have
important economic benefits. Because of its high
value and micro range, it has a great impact on
quality. In addition, adverse weather conditions can
have long-term effects on perennial plants, such as
fruits, nuts, and grapes, which grow over many
seasons.
These long-term effects can include reduced
productivity and quality. This makes investing in
small seasonal changes effective in reducing these
risks. Measures such as the use of advanced hydraulic
systems to control water stress. Installing a frost
protection system to prevent frost damage. And
heating or air conditioning to reduce the effects of
extreme temperatures can help protect these valuable
crops.
3.4 Precipitation and Evaporation
Agriculture takes place in substantial regions of the
world. Which improves get right of entry to to water
whether or not there's a surplus or a deficit It is
important to the achievement of crop yields, so the
main focus of the rural season is on rainfall and runoff
analysis. Understanding these methods is vital for
water quality and crop yields. The heat balance
equation is a primary tool for estimating temperature
from floor data. By combining diverse factors of
warmth finances both the quantity and timing of rain
and soil erosion are very essential in agricultural
planning. Effective irrigation planning relies upon on
accurate climate statistics and dependable weather
forecasts. This is in particular authentic given the
extended competition for freshwater sources
associated with populace increase and irrigation
development. Food protection concerns additionally
indicate a loss of rainfall in growing areas. Many
locations lack huge amounts of annual rainfall. It
suggests that seasonal and annual weather forecasts
want to be advanced to enhance agricultural practices
and make sure food safety. Additionally, advances in
far flung sensing and geographic statistics systems
(GIS) have greatly expanded the potential to display
and manipulate agricultural water resources. High-
resolution satellite tv for pc imagery and actual-time
facts allow correct monitoring of soil moisture, crop
fitness, and water use. These facts may be mixed with
climate models to optimize irrigation operations.
Forecasting drought conditions and control irrigation
greater efficaciously. For example, precision
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on Meteorological Data
563

agriculture generation makes use of this records to
use water extra effectively, reduce waste and improve
crop yields.
3.5 Climate Data
Agricultural climatologists use long-time period
meteorological records to derive agriculturally
relevant variables which includes developing
diploma days, heat pressure devices, frost-loose days,
Palmer drought index, and temperature–humidity
index. These metrics are important in agro
meteorology, as they offer insights into various crop
and cattle responses to climate conditions. For
example, growing degree days’ help expect crop
improvement ranges and harvest timings, even as
warmness strain gadgets are crucial for dealing with
cattle welfare throughout extreme temperatures.
Frost-unfastened days are important for figuring out
planting and harvest home windows, and the Palmer
drought index aids in assessing water strain and
guiding irrigation practices. Additionally, the
temperature–humidity index enables in evaluating the
potential for heat strain in both plants and animals. By
integrating those variables into agricultural
management practices, farmers and agronomists can
optimize crop yields, beautify livestock
productiveness, and mitigate the impacts of negative
climate situations.
3.6 Futuristic Issues
The effect of world climate alternate on agriculture
has been drastically researched currently. Despite the
challenges in appropriately predicting destiny local
climates, there is robust proof that growing
atmospheric carbon dioxide will gain plants. This
advantage comes from both direct fertilization results
and improved water-use performance. While C4
vegetation inclusive of maize, sugar cane, millet, and
sorghum are anticipated to see minimum yield
increases with doubled CO2 tiers, C3 plants (which
make up the majority of plants) may revel in up to a
30% yield improve, assuming other conditions
continue to be constant. However, there are
remarkable downsides. Some regions may
additionally face reduced soil natural count number,
increased nutrient leaching, and extra soil salinization
and erosion. These challenges highlight the need for
stepped forward land control practices. Crop yields
will range broadly across one of a kind climate zones,
with low-range and coffee-earnings nations probably
dealing with the greatest difficulties, whilst some
excessive-range areas may advantage from more
favorable growing conditions. To navigate these
changes, advancements in agricultural meteorology
are critical.
This includes knowledge electricity, moisture,
and trace gas fluxes, in addition to precipitation and
evaporation approaches. The upward thrust of social
media and virtual technology, like cellular telephones
and the internet, gives precious opportunities to
unfold weather and weather data extra correctly, that
can beautify agricultural selection-making. A deeper
draw close of agricultural micrometeorology and
related plant and soil interactions will pressure
progress in each carried out agricultural meteorology
and broader meteorological research. Measuring soil
and microclimate versions within fields is turning into
more and more important for website-precise.
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM DESIGN
In Figure 2 shows the architectural analysis of data
which contains dry-hot wind, freeze, snow, cold rain,
flood and sunburn. From large datasets large,
scientists have been able to pin-point traits that
enhance the crops’ ability to resist pestilence,
diseases, and unfavorable conditions. This helps to
develop and improve good varieties of crops,
important on the back of growing population to feed
the world.
Seasonal analysis of climate; soil types and
condition give farmers the best time to plant, to spray
or treat crops as well as the best time to harvest the
crops due to information on pests and market trends.
This is a perfect way of making farming operations
more effective and therefore, profitable. Technology
particularly the big data analytic tools are very helpful
to the progress of regenerative agriculture as they
help to give insight on the fertility of the soil and
productivity of the crops. This encourages practice of
sustainable agriculture, which enhances soil health
and has less adverse effect to the surroundings. Such
changes show how big data is revolutionizing
agriculture and turning around the crops into more
robust farming practices to sustainable agriculture
methodologies.
Step 1: Data Collection - Collect meteorological data
(temp, precipitation, wind, humidity, etc.) and gather
agricultural data (crop type, soil conditions, irrigation
practices).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
564
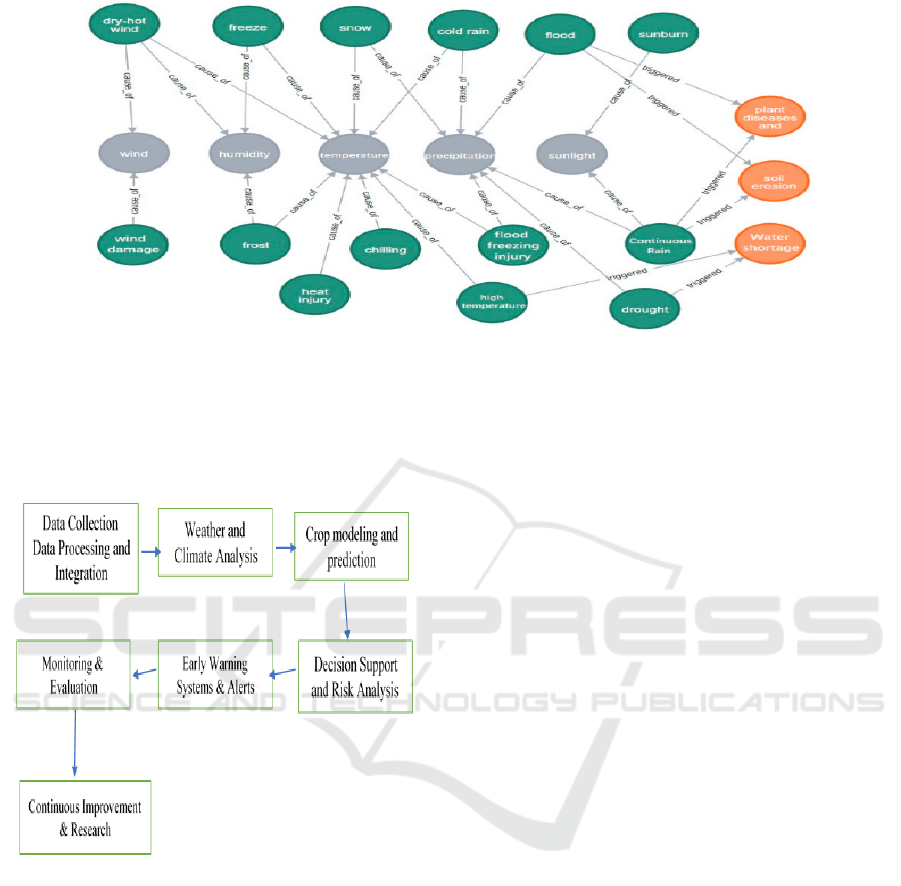
Figure 2: Architectural Analysis of Data.
Step 2: Data Processing & Integration - Clean and
pre-process the collected data, Integrate weather data
with agricultural, data (crop growth, soil moisture,
etc.)
Figure 3: The phases of the proposed algorithm.
Step 3: Weather and Climate Analysis - Analyse
weather patterns and trends, Assess the impact of
climate change on agriculture (temperature, rainfall,
etc.)
Step 4: Crop Modeling & Prediction - Develop crop
models based on meteorological data (growth, yield
predictions), Forecast crop behaviour under different
weather scenarios.
Step 5: Decision Support & Risk Analysis - Provide
weather-based advisories planting, irrigation,
harvesting, pest control, etc.), Conduct risk analysis
(drought, frost, storms, etc.)
Step 6: Early Warning Systems & Alerts - Issue early
warnings for extreme weather events (floods,
droughts, frosts), Alert farmers to mitigate risks.
Step 7: Implementation & Adaptive Actions -
implement farming strategies (irrigation, pest control,
crop management), Adjust farming practices based on
real- time weather data and predictions.
Step 8: Monitoring & Evaluation - Monitor crop
performance and weather conditions throughout the
growing season, Evaluate the effectiveness of
weather, driven decisions.
Step 9: Continuous Improvement & Research -
Refine models and forecasts based on collected data
and outcomes, Research new techniques for better
integration of meteorological data into agricultural
practices. The figure 3 shows how agricultural
research follows an active cycle that links
meteorological data, analysis results, and practical
choices to produce better farm results.
5 IMPLEMENTATION RESULTS
A questionnaire poll among the agricultural
producers indicated that they recognize that having
accurate weather forecast is importance for farming.
Such data allow avoiding dangerous situations in the
field and help the farmers achieve maximum yield.
Digital agriculture has been improved by the efficient
paperwork of the gathering, filtering, and joinery of
meteorological information by the aid of systems.
They enhance the quality of decision-making as it
offers and presents simple and reliable information on
weather.
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on Meteorological Data
565
Core Science recent research compared crop yield
forecasting that used machine-learning models with
other conventional methods revealing higher
accuracy in machine learning methods. These models
incorporate vast information on the weather as a way
of enhancing precision in helping to render proper
planning in farming.
This definition establishes the task of
agrometeorological forecasting as including all kinds
of agricultural meteorological forecast activity
related to planning and execution. This is including
possibilities of affecting crop growth and yields by
using simple weather forecasts. Such findings provide
support in the need to incorporate meteorological
information into practices in farming with the aim of
improving yields and dealing with climate issues.
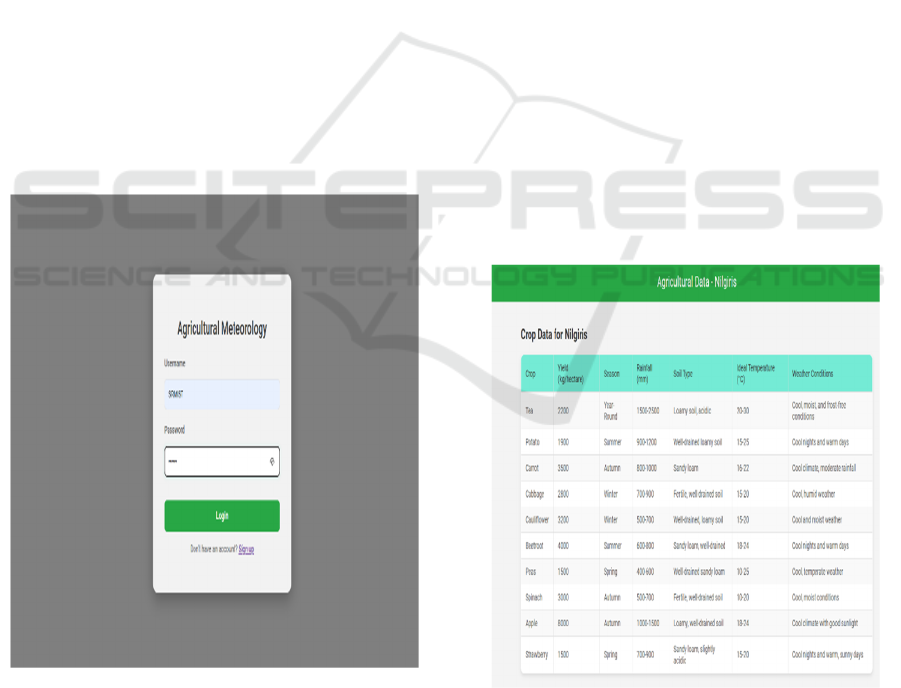
These figures (4) and (5) shows the sample analysis
of agrometeorological forecasting of Agricultural
data of Nilgiris region.
The contribution of this research is to build
systems that help people prepare for severe weather
before it happens. Predictive models use available
weather information to tell farmers when their crops
and operations face new risks. The science of
agriculture and weather helps producers create better
ways to farm sustainably through climate conditions.
Figure 4: Sample analysis page.
Our researchers create plant types that can better
withstand shifting weather patterns and natural
disasters including dry spells flooding and extreme
heat. Climate data functions as the main input for
researchers who create farming plans that protect
against future weather changes. Farming systems that
use precision methods now depend more on weather
data to make operational choices. Weather data
analyzed by remote sensing devices helps farmers
apply their inputs precisely according to the exact
weather conditions at their land. Accurate climate
prediction helps build strong farms that can fight
climate change issues to keep the world from
starving. Environmentally friendly farming practices
that react to actual weather patterns save resources
and conserve the planet while making the farm more
profitable. Scientists put great importance on field-
level weather data because different parts of a field
create unique local weather conditions. Weather
shows large differences across farm areas which
affects plant development and soil conditions while
altering pest activity. Agro meteorology helps
farmers develop better sustainability methods which
extend to lowering carbon emissions when they apply
fertilizer according to weather data. Scientists
develop crop prediction models using weather data
about rainfall intensity total temperature levels and
sunlight exposure. This kind of models analyze how
various weather types influence how crops grow and
develop. Through agro meteorology research we
work towards making sure worldwide food supply
remains reliable by helping agriculture adapt
smoothly to climate changes across all regions.
Figure 5: Crop data for nigiris region.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
566

6 CONCLUSIONS
By growing predictive fashions based on historical
weather facts, the studies offer valuable gear for
farmers to better manage their plants and mitigate the
damaging outcomes of weather fluctuations. The
integration of real-time meteorological facts into
farming practices can permit extra weather-resilient
agriculture in these regions. Furthermore, the findings
underscore the need for improved agrometeorological
advisory offerings and climate-clever agricultural
regulations to aid sustainable farming in each the
Nilgiris and Coimbatore. These studies contribute to
a broader knowledge of ways localized climate
situations have an effect on agriculture and offers
practical answers for improving agricultural results in
the context of climate alternate. Also, these studies
underscore the critical role of integrating
meteorological data into agricultural decision-making
processes to enhance productivity and resilience
against climate-related challenges.
REFERENCES
Carbone and colleagues (2009),"Observing Weather and
Climate from the Ground ", The National Academy
Press, in Washington D.C.
Dorais wami P.C., (2000), “The techniques, for managing
data in agriculture and forestry”, Agricultural and
Forestry Meteorology (Volume 103; Pages 83–97).
Hanks and Ritchie (1991), “Modeling vegetation and soil
systems”, American Agronomy Association.
Lomas, (2000) "Exploring Agricultural Meteorology",
Journal of Agricultural and Forestry Meteorology
(Volume 103 pages 197 to 208).
Maracci (2000),” Utilization of GIS and remote sensing, in
meteorology”, Agricultural and Forestry Meteorology
journal (volume 103).
Monteith and Unsworth, (1990), "Principles of
Environmental Physics”, Edward Arnold in London.
Monteith JL, (2000), "Agricultural Meteorology”, Explores
the evolution and practical uses of Meteorology in
agriculture”, The journal Agricultural and Forestry
Meteorology Volume 103 pages 5 10.
Ogalo, "Utilization of Weather Predictions, in Farm
Operations “, The Journal Agricultural and Forestry
Meteorology (Volume 103 pages 159–166), (2000)
Parry and colleagues (2007), “Impacts and Adaptation “,
Cambridge University Press.
Salinger and colleagues (1999), “Agricultural and Forestry
Meteorology”.
Shivakumar and colleagues (2000), "Agricultural Science
and Sustainable Agriculture ", The journal Agricultural
and Forestry pp. 11 to 26.
Sticker and others (1999) "Agricultural Meteorology in the
21st Century Workshop Summary”, by Agricultural
and Forestry Meteorology (2000) can be found in pages
103 to 227 of the source document.
Syamyutha Ayalasomayajula, Yashas Shashidhara, Anish
Kataria, Shreyas Shashidhara, Krishita Kataria, Aditya
Undurti Ishaan Gupta,” Innovations in Agricultural
Forecasting: A Multivariate.
Agrometeorology Farming Analysis and Research Based on Meteorological Data
567
