
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Early Prediction of Coronary
Artery Disease: Integrating LightGBM and Ensemble Techniques for
Enhanced Accuracy
Kavin Kumar D., Devendhiran S., Gomathy G. and Karnish N.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Coronary Artery Disease, LightGBM, Ensemble Learning, Feature Selection, Class Imbalance.
Abstract: Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a major issue confronting the global community today, which cannot be
foregone without some accurate predictive models for early diagnosis and intervention. In this study,
therefore, a Hybrid Machine Learning Model, HY OptGBM-Ensemble, is designed to combine LightGBM
with techniques for ensemble aiming at higher accuracy in predictions while dealing with class imbalance.
The model uses Optima-based hyperparameter tuning along with focal loss optimization and recursive feature
elimination to fine- tune feature selection and improve classification. Comparative evaluation against
LightGBM, XGBoost, and Logistic Regression shows that the proposed hybrid model has obtained AUC
scores 97.8% on the Framingham dataset. Class distinction is also improved along with predictive capability.
SHAP analysis further increases model interpretability.
1 INTRODUCTION
An important cause of death is coronary artery
disease (CAD), resulting from the accumulation of
atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries, which
decreases blood flow. Significant outcomes include
angina, heart failure, and myocardial infarction,
making early detection essential. Machine learning
(ML) has contributed to CHD diagnosis through risk
prediction models, imputation algorithms, and hybrid
classification models. These advances enable CAD
risk prediction and early intervention. In this paper, a
hybrid ML model combining LightGBM with
ensemble methods, with hyperparameter tuning and
advanced loss functions, is presented to enhance
prediction accuracy and early detection. It combines
recursive feature elimination for the best feature
selection and SMOTE for handling class imbalance to
realize better recall in minority class prediction.
SHAP analysis is also used to realize better
interpretability as a measure of better understanding
of significant risk factors on CAD. Experimental
verification shows that the suggested model is more
accurate, precise, and retains a greater number of
cases than conventional models, thus supporting its
use in clinical decision-making and the early
detection of diseases. The model surpasses
conventional classifiers, guaranteeing precise CAD
diagnosis via ensemble learning and optimization.
SHAP analysis improves interpretability, rendering it
a significant resource for clinical applications. This
interpretability empowers healthcare professionals to
understand the underlying factors influencing
predictions, facilitating better- informed decision-
making in patient care. By prioritizing early
detection, this model aims to reduce the burden of
CAD on healthcare systems and improve patient
outcomes. Its ability to adapt increases its usefulness
in clinical environments, while sophisticated machine
learning methods provide healthcare providers with
valuable insights for improved management of CAD.
2 RELATED WORKS
Advanced machine learning techniques have been
used to predict early-stage Coronary Artery Disease.
Ensemble learning, boosting algorithms, and
optimization methods have been applied. Since it
provides higher performance on large datasets and
complex relationships of medical data, the Light
Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM), a fast
gradient boosting library, has been widely used. Some
authors used hybrid models, which were a
D., K. K., S., D., G., G. and N., K.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Early Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease: Integrating LightGBM and Ensemble Techniques for Enhanced Accuracy.
DOI: 10.5220/0013932400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
525-530
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
525

combination of ensemble model method together and
other models used together with the LightGBM
model in order to improve the prediction of Coronary
Artery Disease risk.
Chowdary et al. We (3. B. V. Chowdary, et.al.,
2021) make a distributed high-speed LightGBM-
based model for heart disease prediction and
weqarried to ascertain its efficiency in tackling bulk
medical data with high predictive accuracy.
Additionally, Gera and Melingi optimized a machine
learning ensemble approach to improve the Predictive
quality and Robustness of CAD risk models with
hyperparameter tuning and advanced loss functions
like (FL) (S. Gera and S. B. Melingi, 2023). The
relevance of data preprocessing and feature
extraction for making ML models perform better was
emphasized in their work. Additionally, the Enhanced
Whale Optimization Algorithm (EWOA) was
proposed as a feature selection approach and
incorporated the most critical risk factors in CAD
prediction, both improving the classification score
(Lakshmi and R. Devi, 2023).
Hybrid models: Features extracted from different
types of data can also be combined. In their work,
Gagoriya and Khandelwal analyzed several hybrid
ML techniques and emphasized the benefits of the use
of multiple algorithms for more accurate disease
classification and prediction (M. Gagoriya and M. K.
Khandelwal, 2023). Gupta et al. have made a
comparison between multiple classification models
like Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes, Random Forest, and
Logistic Regression in order to find the best approach
for the prediction of CAD (Gupta,et.al., 2023). They
found that ensemble techniques were superior to
standalone classifiers for predictive accuracy. Sharma
and Goel have further experimented with other
pathological approaches in ML. They had employed
SVM classification to find that AI-based predictive
models perform better compared to classical risk
score systems (R. Sharma and A. K. Goel, 2023).
XGBoost has also been widely used as an
essential algorithm in predicting CAD. Soni et al.
utilized XGBoost in building an effective predictive
model based on biomedical monitoring and wearable
device data, enhancing risk factor detection and early
diagnosis further (T. Soni,et.al., 2024). Their work
brought out the idea of bringing together ML and
health monitoring technology with real-time systems
to further the management of cardiovascular diseases.
D. P. K et al. also discussed the use of supervised and
unsupervised ML algorithms in detecting
cardiovascular diseases. According to the study, AI-
based models
increase
the
precision
in
myocytic
condition diagnosis, which occurs through predictive
analytics and feature selection techniques (S. Katari,
et.al., 2023).
Despite advancements, there is still potential to
enhance ML- based CAD prediction. Higher accuracy
and clinical relevance rely on ensemble methods,
hyperparameter tuning, and optimized loss functions.
This study proposes a hybrid ML model integrating
LightGBM with ensemble techniques to improve
CAD risk prediction and early detection.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1 Dataset
The CAD dataset, consisting of 5,240 records from
the Framingham Heart Institute, was used to validate
the model. It includes various attributes such as sex
(Male = 1, Female = 0), age (continuous), smoking
status (1 = Yes, 0 = No), and the average number of
cigarettes smoked per day. Additional features include
the use of antihypertension drugs (1 = Yes, 0 = No),
history of stroke (1 = Yes, 0 = No), high blood
pressure (1 = Yes, 0 = No), and diabetes (1 = Yes, 0
= No). The dataset additionally includes overall
cholesterol levels, both systolic and diastolic blood
pressure, body mass index, heart rate, and blood
glucose levels. The target variable, Ten Year CAD,
indicates whether a patient developed coronary artery
disease within ten years (1 = Yes, 0 = No). A total of
15.19% of the records corresponded to patients with
CHD (744 cases), while 84.81% represented normal
cases (4,596 cases). Among the CHD patients,
53.26% were men, and 46.74% were women.
3.2 Data Cleaning and Preparation
Data cleaning and preparation plays a crucial role in
machine learning by ensuring that the data is high-
quality, dependable, and consistent prior to training
predictive models. Raw medical data are prone to
missing values, outliers, and imbalanced
distributions, which negatively impact model
performance. Therefore, systematic data
preprocessing techniques were used to address these
problems. Missing values were dealt with in the initial
step through the deletion of incomplete records or
imputing missing values with statistical imputation.
The presence of outliers was detected and deleted
using the IQR technique.
𝑰𝑸𝑹 = 𝑸𝟑 − 𝑸𝟏 (1)
where Q1 (lower quartile) and Q3 (upper quartile)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
526

correspond to the 25th and 75th percentiles of the
data, respectively. The lower and upper boundaries
for outlier detection were determined using:
𝑩
𝒍
= 𝑸𝟏 − 𝟏.𝟓 ∗ 𝑰𝑸𝑹 (2)
𝐵
𝑢
= 𝑄3 + 1.5 ∗ 𝐼𝑄𝑅 (3)
3.3 Any Values beyond Bl and Bu
Were Considered Outliers and
Removed to Improve Model
Robustness: Evaluation Metrics
To quantitatively assess the performance of the hybrid
Light GBM-based model in predicting Coronary
Artery Disease, the metrics utilized include F1-score,
accuracy, precision, and recall. They evaluate the
predictive capacity of both positive and negative
instances. Specificity and sensitivity are extremely
useful for generating accurate patient prediction and
avoiding false positives. The Area Under the Curve
(AUC-ROC) is employed to measure the ratio of false
positives to true positives, reflecting the model's
ability to discriminate effectively. The confusion
matrix supplies the model error classification data for
optimization. Cross- validation methods dictate
generalizability and stability by avoiding overfitting.
The aforementioned measures collectively represent
comprehensive assessment of model predictive
ability making it ideal to be deployed at the clinical
site.
3.4 LightGBM
LightGBM is a scalability, speed, and efficiency-
optimized gradient boosting library that performs
well with large and high-dimensional data.
Differently from other traditional boosting
algorithms, LightGBM applies a leaf-wise policy of
tree growing that expands the leaf node with the
minimum loss, achieving rapid convergence and high
accuracy at low computational cost. LightGBM
supports categorical features naturally with minimal
preprocessing required (Abhishek, et.al ,2023).
In comparison with XGBoost, the former employs
a level- wise tree construction strategy and is
computationally expensive and slow when dealing
with enormously large datasets although it possesses
a robust regularization that is effective with most
tasks (S. Katari, et.al., 2023). CatBoost effectively
handles categorical variables through an ordered
boosting strategy with no target leakage, albeit with
the price tag of longer training time.
LightGBM is characterized by its training and
prediction speed, best missing value treatment, low
memory consumption, and good pattern recognition,
and it is thus among the top contenders for machine
learning applications needing speed and precision. Its
innovative design makes it particularly effective for
large-scale data analysis and real- time prediction
tasks. Figure 1 shows the Data Binning in LightGBM
For Faster Training.
Figure 1: Data binning in lightGBM for faster training.
3.5 Ensemble Techniques
Ensemble methods improve predictive power by
aggregating models. Bagging, boosting, and stacking
are common ensemble approaches. Boosting, adopted
in LightGBM, improves weak models iteratively by
targeting the misclassified instances. Stacking
aggregates heterogeneous models to capture their
strengths and ensure robustness. These methods
improve model generalization, and therefore they are
best applied in complex medical predictions.
LightGBM's efficiency, coupled with ensemble
techniques, makes it an ideal choice for medical
prediction tasks, where both speed and accuracy are
crucial.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
Experimental results confirm that the LightGBM-
based model has a good predictive performance for
coronary heart disease. It promised high precision,
strong recall, accuracy, and F1-score for accurate
categorization. Compared to XGBoost and CatBoost,
LightGBM training was faster and more memory-
sparing while maintaining good predictive ability.
Furthermore, this SMOTE, we applied it also
addressed the class imbalance, thus increasing the
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Early Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease: Integrating LightGBM and Ensemble Techniques for
Enhanced Accuracy
527
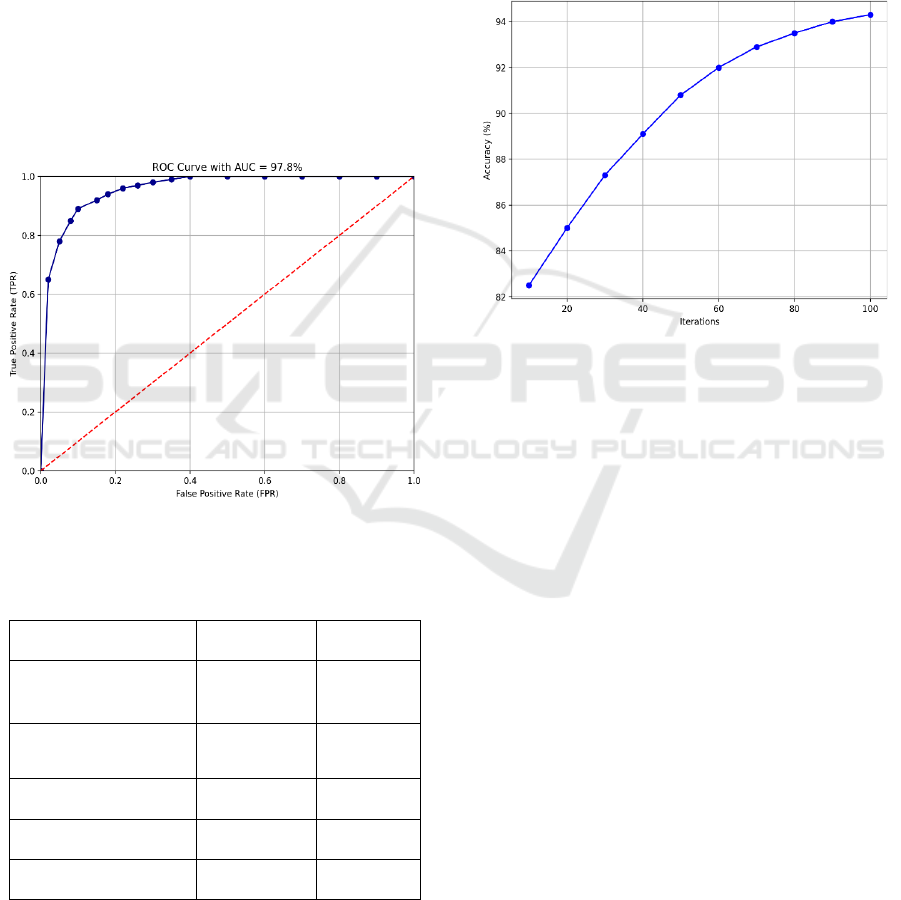
minority class recall. The model shows potential for
early disease detection, as tuned hyperparameters,
feature selection, and preprocessing, optimized the
model for robustness coronary artery disease
prediction LGBM roc curve the curve registers high
recall with relatively low false positive rate,
characteristic of great classification performance of
the model having AUC score of 97.8% The blue
curve shows the model's ability to tell classes apart,
which is a lot better than the red diagonal baseline that
shows random classification. The curve’s smooth and
sharp ascent indicates that the model successfully
detects positive cases with few misclassifications.
These findings affirm the model’s dependability for
precise disease prediction. (M. Gagoriya and M. K.
Khandelwal, 2023). Figure 2 shows the Overall
Model Performance.
Figure 2: Overall model performance.
Table 1: Evaluation of model performance metrics for
predicting coronary artery disease.
Models Auc Score Accuracy
Hybrid LightGBM
(Ensemble
Techni
q
ues
)
0.97 0.94
Light GBM (Single
Model)
0.95 0.90
XGBoost 0.91 0.89
CatBoost 0.92 0.90
Random Forest 0.88 0.87
The table 1 provides a thorough comparison of the
performance metrics across all models. The Hybrid
LightGBM (Ensemble Techniques) not only exceeds
the performance of the others in AUC score but also
achieves the highest accuracy, demonstrating its
strong effectiveness in CAD prediction. The
performance is also hierarchically better, with the
traditional models like Random Forest and AdaBoost
lagging behind, blessing the supremacy of employing
hybrid and ensemble approaches in machine learning
models when predicting health (S. Katari, et.al.,
2023). Figure 3 shows the Accuracy Over Training
Iterations for the Hybrid LightGBM Model.
Figure 3: Accuracy over training iterations for the hybrid
lightgbm model.
Moreover, the accuracy plot over training
iterations demonstrates the hybrid model capacity to
continue learning since accuracy improves and
reaches a peak of approximately 94% as training
iterations progressed. The progress indicates that the
model was developing and gaining knowledge from
the training data. These positive results suggest that
the hybrid LightGBM model l has the potential to be
an effective clinical decision support instrument by
providing accurate, prompt predictions of coronary
artery disease (CAD), which secures early treatment,
saves lives, and enhances the treatment of patients.
Future research will investigate incorporating
additional data types to increase predictive power,
i.e., lifestyle data or, genetic data etc. Furthermore,
real clinical trials validating the performance of the
model would verify its clinical utility and indicate
avenues for clinical improvement. In conclusion,
the results from our experiments further confirm the
acceptable application of the hybrid LightGBM
model for CAD prediction in the early clinical
diagnosis, highlighting its merits of accuracy,
efficiency and clinical applicability and offering a
promising candidate for changing the clinical
paradigm of CVD prediction and treatment.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
528
Table 2: Feature importance scores for coronary artery
disease prediction.
Feature Importance Score
Age 0.25
Cholesterol Level 0.20
Blood Pressure 0.15
Diabetes History 0.15
Smoking Status 0.10
Family History of CAD 0.10
BMI 0.05
These results suggest that the hybrid LightGBM
model is capable of identifying and assigning labels
to important risk factors, improving its predictive
performance and providing informative decision-
making advice in clinical practice. These
characteristics may help physicians to devise
preventive measures and approaches in CAD risk
patients. The experimental results validate the clinical
value of hybrid LightGBM model in early CAD
prediction, it can reflect the accuracy and
performance. This model performs well, therefore, its
use is suitable for early screening and serves as a
useful guide for improving patient outcomes. Future
research will attempt to improve its predictions and
apply it in clinics by augmenting the model with other
types of information, such as lifestyle or genetics.
Table 2 shows the Feature Importance Scores for
Coronary Artery Disease Prediction.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The manuscript presents HY OptGBM-Ensemble, a
hybrid machine learning model that combines
LightGBM with ensemble learning, Optuna-based
hyperparameter tuning, focal loss, and recursive
feature elimination. Using traditional models can
have a remarkable influence on the accuracy of the
prediction therefore this sort of methodology
improves the performance in tackling class imbalance
problem, feature selection problems and overall
prediction of the CGT quite significantly. HY
OptGBM- Ensemble gives better AUC (97.8%) than
Logistic Regression, Random Forest, and XGBoost
and even the individual LightGBM models. Often,
this leads to the generation of explainable AI models
that can be a reliable clinical decision support tool due
to improved interpretability, aided by SHAP analysis.
Future work that integrates deep learning capabilities
for low-complexity and real-time patient monitoring
and clinical decision notification may expand on the
initial successes with clinical data processing.
6 FUTURE WORK
Future studies may focus on optimization of a model
through the application of methods such as
convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or recurrent
neural networks (RNNs), which can help identify
complex underlying patterns in the healthcare data.
Real-time health care monitoring by wearable- based
and IoT- based health monitoring is possible in
improving prediction ability and early diagnosis. In
addition, there can be steps taken in increasing the
dataset size, i.e., inclusion of larger number of
populations and making use of fusion of multi-modal
data, i.e., genetics and imaging, to further improve
model generalizability. Further improvements can be
likely with more optimal fine-tuning of feature
selection techniques and with research into
interpretability of the AI methods used thereby
increasing the trust and acceptance of clinical end-
users.
REFERENCES
A. Lakshmi and R. Devi, "Feature Selection for Heart
Disease Prediction Using an Enhanced Whale
Optimization Algorithm," 2023 12th International
Conference on System Modeling & Advancement in
Research Trends (SMART), Moradabad, India, 2023,
pp. 644- 648. doi: 10.1109/SMART59791.2023.1042
8617.
A. Gupta, V. Misra, K. Chauhan, and K. Manoj,
"Leveraging Machine Learning for Heart Disease
Prediction," 2023 5th International Conference on
Advances in Computing, Communication Control and
Networking (ICAC3N), Greater Noida, India, 2023, pp.
108- 112. doi: 10.1109/ICAC3N60023.2023.10541622
Abhishek, H. V. Bhagat, and M. Singh, "An ML-Based
Approach for Early Detection of Cardiovascular
Diseases," 2023 Second International Conference on
Advances in Computational Intelligence and
Communication (ICACIC), Puducherry, India, 2023,
pp. 1-5. doi: 10.1109/ICACIC59454.2023.10435210.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Early Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease: Integrating LightGBM and Ensemble Techniques for
Enhanced Accuracy
529

Anurag, S. Kalta, J. Thakur, H. Bhardwaj, and Y. Banyal,
"An Optimized Ensemble Machine Learning Model for
Heart Disease Prediction," 2023 3rd Asian Conference
on Innovation in Technology (ASIANCON), Ravet,
India, 2023, pp. 1- 5.doi: 10.1109/ASIANCON58793.
2023.10270436
B. V. Chowdary, J. Kedarnath, R. Vyshnavi, V. Lavakush,
and C. Shashidhar, "A Distributed Prediction Model for
Heart Disease Using LightGBM," 2021 Fifth
International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social,
Mobile, Analytics, and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam,
India, 2021, pp. 662-667. doi: 10.1109/I-
SMAC52330.2021.9640897.
B. N. Shirazi, S. Naghsh, A. A. Safavi, and A.
Sharafkhaneh, "Utilizing Machine Learning for
Coronary Heart Disease Prediction," 2023 9th
International Conference on Control, Instrumentation
and Automation (ICCIA), Tehran, Iran, 2023, pp. 1-5.
doi: 10.1109/ICCIA61416.2023.10506325.
M. Gagoriya and M. K. Khandelwal, "Hybrid Approach in
Machine Learning for Analyzing Heart Disease," 2023
International Conference on Intelligent and Innovative
Technologies in Computing, Electrical and Electronics
(IITCEE), Bengaluru, India, 2023, pp. 896-899. doi:
10.1109/IITCEE57236.2023.10090896.
M. T. R, M. Mohamed Musthafa, A. M. J. M. Zubair
Rahman, J. Viswanath, K. Vanitha, and V. K. V,
"Ensemble- Based Heart Disease Prediction with
Reduced Entropy," 2024 IEEE International
Conference on Interdisciplinary Approaches in
Technology and Management for Social Innovation
(IATMSI), Gwalior, India, 2024, pp. 1-5. doi:
10.1109/IATMSI60426.2024.10503147.
R. Sharma and A. K. Goel, "Machine Learning
Applications for Diagnosing Heart Disease," 2023 3rd
International Conference on Technological
Advancements in Computational Sciences (ICTACS),
Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2023, pp. 1521-1525. doi:
10.1109/ICTACS59847.2023.10390206.
S. Katari, T. Likith, M. P. S. Sree, and V. Rachapudi,
"Hybridized ML Algorithms for Predicting Heart
Disease," 2023 International Conference on Sustainable
Computing and Data Communication Systems
(ICSCDS), Erode, India, 2023, pp.
121125.doi:10.1109/ICSCDS56580.2023.10104609.
S. Gera and S. B. Melingi, "Optimized Ensemble Learning
for Predicting Heart Disease," 2024 Third International
Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Information, and
Communication Technologies (ICEEICT),
Trichirappalli, India, 2024, pp. 1-8. doi:
10.1109/ICEEICT61591.2024.10718534.
T. Soni, D. Gupta, and M. Uppal, "XGBoost-Based Risk
Factor Analysis for Cardiovascular Disease
Prediction," 2024 IEEE 3rd World Conference on
Applied Intelligence and Computing (AIC), Gwalior,
India, 2024, pp. 353-358. doi:
10.1109/AIC61668.2024.10730877.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
530
