Optimized Deep Learning Techniques for the Detection and
Identification of Fake News in Digital Media
Narmadha Devi A. S.
1
, K. Sivakumar
1
and V. Sheeja Kumari
2
1
Department of Engineering Mathematics, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical
Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
2
Department of Computational Intelligence, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical
Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Deep Learning, Long Short‑Term Memory (LSTM), N‑Gram, Porter's Stemming, Social Networks, Fake
News Detection.
Abstract: The exponential expansion of social media has greatly accelerated the dissemination of disinformation,
endangering public safety and undermining faith in news outlets and government agencies. The authors of
this work suggest using deep learning to identify false news posts on Twitter. The methodology involves pre-
processing raw data through stop word removal, stemming using Porter’s Algorithm, and tokenization with
the N-gram model. The detection model employs Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNN), and AdaBoost algorithms. Results indicate that LSTM outperforms CNN and AdaBoost,
achieving an accuracy of 99.24%, specificity of 99.2%, and sensitivity of 98.67% in fake news detection.
1 INTRODUCTION
Fake news spreads misinformation, misleading
people and impacting society, businesses, and
individuals. It harms reputations, leaving lasting
damage even after corrections. By reinforcing biases,
it deepens divisions, fosters distrust, and fuels
conflicts. Politically, misinformation manipulates
public opinion to serve specific agendas.
Additionally, the rise of fake news erodes trust in
journalism, weakening democracy and
accountability. Greater emphasis has been placed on
identifying and removing disingenuous material due
to the spread of false information on social media
platforms like Twitter and Facebook. Misleading
information spreads rapidly, often diverting attention
from critical issues, with many users trusting social
media over traditional sources despite scepticism
about reliability (t’Serstevens,et al, 2022).
Confirmation bias further reinforces misinformation,
making deception harder to recognize. False news
appears in various formats, including articles, images,
and videos, contributing to widespread confusion.
Rumours can disrupt social harmony and cause
significant societal impact. Additionally, fake
websites mimic credible sources to manipulate public
perception, influencing opinions and advancing
political or financial agendas (Igwebuike, E. E., &
Chimuanya, L. 2021). A complicated process for false
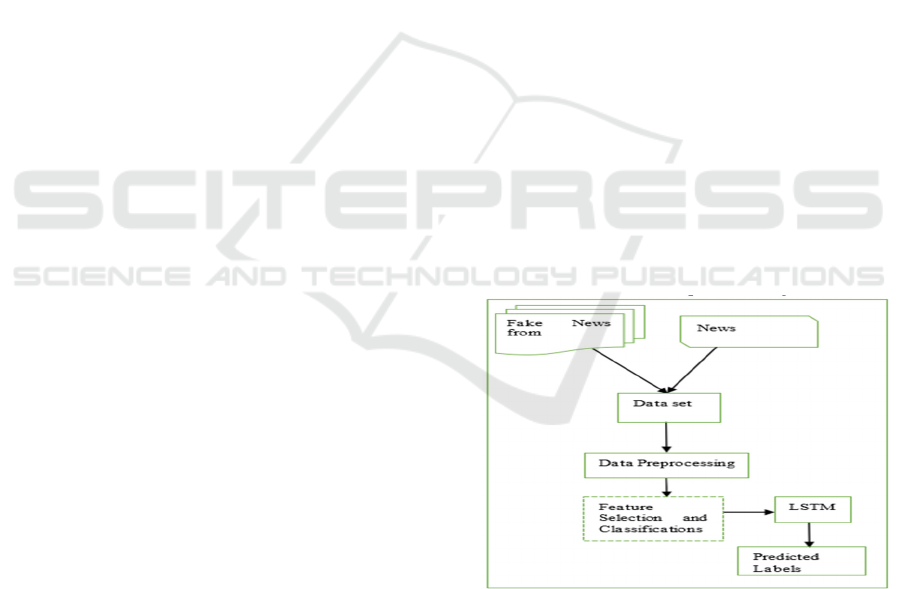
information detection is depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Block diagram of fake news detection.
The original data is preprocessed by gathering
tweets from Twitter using aggregation. The dataset is
passed through a preprocessing phase, which includes
the removal of stop words, stemming, and
tokenization. Features for the classification model are
identified to make it more efficient. Machine learning
and deep learning methods are then used to classify
tokenized data. As a result, techniques from deep
506
S., N. D. A., Sivakumar, K. and Kumari, V. S.
Optimized Deep Learning Techniques for the Detection and Identification of Fake News in Digital Media.
DOI: 10.5220/0013932100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
506-511
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
learning and machine learning are used to identify
rumours and false news.
The advent of online and social media has enabled
the incorporation of false information with real or
verified information. This situation can be utilized to
influence people’s opinions, thus impacting their
perceptions, thoughts, and behavior. As a result,
disseminating links, messages, photos, videos, and
audio files over several social media platforms has
become very simple for those who propagate fake
news. People who spread these fakes usually have a
political or social agenda. Therefore, the development
of an efficient system to detect misinformation is of
utmost importance (Kaliyar, R. K., et al, 2021). An
approach to detecting false news stories using deep
learning is presented in this research. There are input
datasets that make up methodology. Information
culled from the microblogging service Twitter is the
source of this dataset. Input data that is in its raw form
undergoes data preparation initially. Remove Stop
Words, Stemming, and Tokenization are the main
components of data preparation. Use the NTLK
library to remove stop words. Stemming is done using
Porters Algorithm. Tokenization is completed by N-
gram model. Model is developed using LSTM, CNN
and AdaBoost algorithms. Results have shown that
LSTM’s Compared to CNN and AdaBoost methods,
the accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity are higher.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In order to identify false news, researchers use n-gram
analysis and TF-IDF for feature extraction. After that,
they use decision trees, SGD, Linear SVM, Logistic
Regression, SVM, and KNN as machine learning
classifiers (Lahby, M.,et al, 2022). Pennycook & Rand
(Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. 2021).
developed an
SVM-based satire detection model with 90%
accuracy. Bahad et al. showed RNNs outperform
manual rumor detection, while Ruchansky et al.
introduced the CSI model, integrating content, user
comments, and sources for improved accuracy. For
fake images, Hsu et al. developed CFFN, using GANs
and DenseNet to classify manipulated images. Bird et
al. developed NLTK, a comprehensive Python toolkit
that facilitates various NLP tasks such as
tokenization, parsing, stemming, and classification,
making text analysis more accessible and efficient.
Huan et alsuggested a deep learning strategy for text
classification that effectively captures both sentiment
and semantic context, improving accuracy in
emotionally charged text analysis (Bird, S., Klein, E.,
& Loper, E. 2009)
.
Umer et al. demonstrated that
combining convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
with Fast Text embeddings enhances text
classification by efficiently extracting contextual and
syntactic features (Umer, M.,et al, 2023). Optimized
deep learning methods for spotting rumors and
misleading information in online social networks
were presented by Zamani et al, leveraging advanced
neural architectures to enhance misinformation
identification and content credibility assessment
(Abu Sarwar Zamani, et al, 2025).
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Deep Learning for Fake News
Detection
This technique involves collecting data from Twitter
in order to utilize deep learning to identify false news.
Pre-processing involves stop word removal (NLTK),
stemming (Porter’s Algorithm), and tokenization (N-
gram model). Tokenization applies unigrams,
bigrams, and trigrams to structure text. The model
integrates LSTM, CNN, and AdaBoost for
classification. LSTM, an RNN variant, is effective in
pattern recognition due to its input (I/P), forget (f),
and output (O/P) gates, along with a memory cell.
These gates regulate information flow, ensuring data
integrity and sequence retention, improving accuracy
while preventing gradient descent issues. Figure 2
and 3 illustrate the LSTM network, providing A
schematic illustration of its composition. The network
takes an embedding xi as input at each time step and
calculates its output hi by adding the output h i-1
together with the latest embedding xi to the latest cell
state h i-1. It is possible to insert or remove data from
the cell, depending on its present state
Figure 2: LSTM architecture.
Optimized Deep Learning Techniques for the Detection and Identification of Fake News in Digital Media
507

𝑓𝑡 = 𝜎(𝑤𝑓. 𝑦𝑡 − 1, 𝑥𝑡 + 𝑏)
(1)
𝑖𝑡 = 𝜎(𝑤𝑖. 𝑦𝑡 − 1, 𝑥𝑡 + 𝑏)
(2)
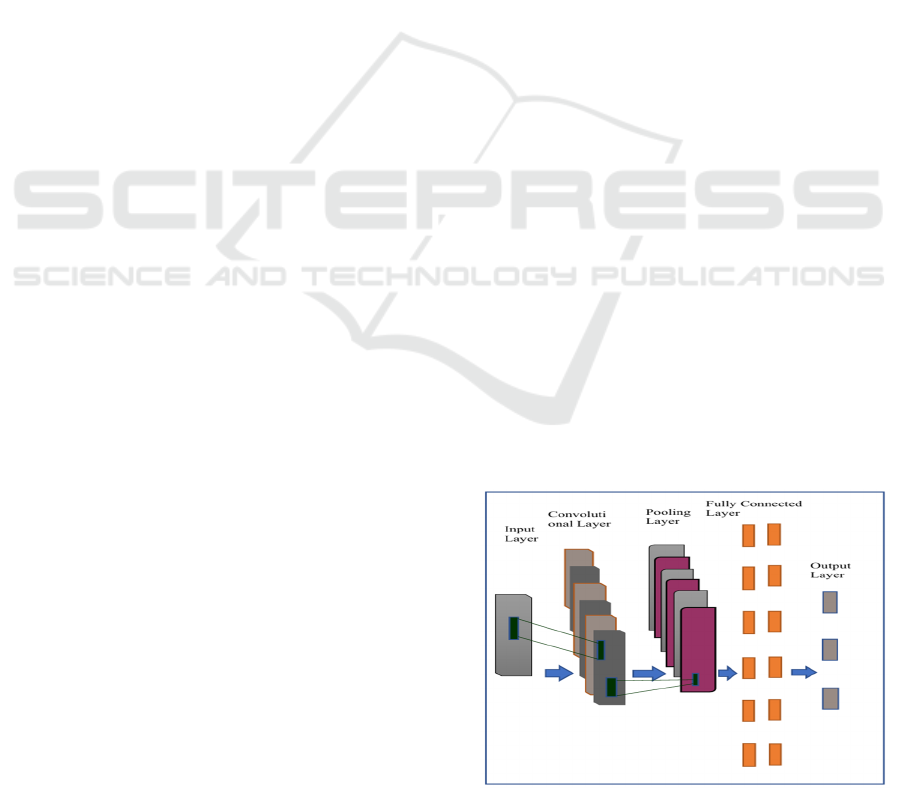
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) comprises
key components like convolution and pooling layers.
While CNNs are well-known for image processing, they
also identify data interdependencies. Feature extraction
from input data is made possible by the convolution
layer, which allows operations on the embedding matrix
for word embeddings. The pooling layer then reduces
dimensionality and selects important features using
methods like max, min, or average pooling. Finally, the
extracted features are processed by a fully connected
neural network. A CNN applies activation functions to
generate the final output, typically consisting of
convolutional, pooling, activation, and fully connected
layers. Deep CNNs enhance learning by stacking
multiple convolutional layers, which act as filters,
processing small pixel sections at a time (e.g., 3×3
filters). Researchers at the University of Michigan
developed AdaBoost, an advanced gradient-boosting
method for binary classification. It starts with an initial
decision tree, evaluates its accuracy, and integrates
multiple classifiers to build a robust model.
The first model is built with the training data and is
then enhanced by including other models to address its
shortcomings. This process continues until all training
data is accurately predicted or the model limit is reached.
To enhance accuracy, multiple classifiers are combined
into a single optimized model. AdaBoost is widely used
for pedestrian detection, where images are cropped into
sections, and marking windows help identify pedestrians.
The same method is applied iteratively with different
selection sequences.
Figure 3 shows Convolutional Neural
Network.
A window is classified as containing a
pedestrian if no models reject it, refining the
classification process further.
Figure 3: Convolutional neural network.
3.2 Dataset Overview and
Preprocessing
The dataset, sourced from Kaggle, contains 40,000
articles 20,000 real and 20,000 fake. A pre-trained Glove
Twitter dataset is also referenced.
Figure 4: Present tendencies across different types of fake
news and real news.
Data pre-processing is a crucial step to enhance
efficiency, involving data transformation and cleaning
before execution. The following section elaborates on
these processes. A figure illustrates that balanced,
indicating stability. In the visualization, the "0" class
(orange bar) represents fake news, while the "1" class
(blue bar) represents real news. Since topic contents vary
between categories, only the main text is processed,
while the subject, title, and date are removed. Figure 4
explains the topics that comprise the dataset, showing
how news spreads in society. The count of each subject
highlights its presence in the dataset—blue bars denote
unreliable news, while orange bars indicate credible
news. Real news covers global and political topics,
whereas fake news is often found in categories like
politics, general news, left-wing media, U.S. news, and
Middle Eastern news.
3.3 Deep Learning LSTM Model
A sequential model has one input and one output tensor
per layer, requiring a defined input shape. Sequence
classification predicts categories based on sequential
data, posing challenges due to varying lengths and
complex patterns. To detect false information, an LSTM
model is used, leveraging LSTM cells with input, forget,
and output gates. Figure 2 shows how a tan layer
regulates the combination of the previous output ht−1
with the value of the new sequence, xt in order to smooth
inputs.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
508
3.3.1 LSTM Cell Process
The LSTM model begins with a tanh layer that
smooths the combined input. Next, the input gate,
with sigmoid activation, filters relevant values by
scaling the compressed input. The forget gate (st)
determines which information to retain, while the
previous state (st−1) is added to maintain long-term
dependencies, reducing the risk of gradient
disappearance. The forget gate further refines stored
information, ensuring only necessary data is
preserved. Finally, the output gate regulates the final
output using a tanh function, determining which
values from the cell (ht) are allowed as output.
The input is reduced to a range of -1 to 1 by using
a tanh activation function. Shown below is one way
to do it:
𝑔=𝑡𝑎𝑛ℎ(𝑏
+𝑋
𝑈
+ℎ
𝑉
)
(3)
where Vg stands for the input weight and bg for the
preceding cell output, with bg representing the input
bias.
The symbol for the forgotten gate is:
𝑓=𝜎(𝑏
+𝑥
𝑈
+ℎ
𝑉
(4)
The output is st−1, which is the element-wise sum of
the prior state and the forget gate.
It is possible, nonetheless, to represent output gates
as
0=𝜎(𝑏
+𝑥
𝑈
+ℎ
𝑉
) (5)
As shown in Figure 2, the final output of the
network is ht. To enhance performance, a stacked
LSTM model is used with the return sequence set to
true, allowing each neuron’s hidden state to serve as
input for the next LSTM layer. Two long short-term
memory (LSTM) layers, one with 128 memory units
and the other with 64, follow each word is represented
as a 32-length vector in the embedding layer model.
The first dense layer activates 32 memory units and
uses Re LU, while the second layer uses a sigmoid
function to train a single neuron for output. Neurons
in a dense layer are completely connected, so data
from all neurons in the layer below it may reach each
one.
To prevent overfitting, recommended networks
use one or two dense layers. ReLU, a widely used
activation function, prevents simultaneous neuron
activation and offers advantages over sigmoid and
tanh in convolutional neural networks. ReLu is
represented by:
𝜎=𝑚𝑎𝑥(0, 𝑧) (6)
If Qij is sigmoid, then the likelihood of the word j
occurring in connection to the term i is this. This is
how we may express the inferred global objective
function:
𝐽 = −∑ LogOiji ∈ corpus, j ∈ context(i) (7)
A Dense output layer may be used to classify false
news as either legitimate news (with a value of 0) or fake
news (with a value of 1). Utilizing the optimizer, metrics,
and loss function during model construction is essential.
Ten iterations of training the model using the Binary
Cross-Entropy loss function and a learning rate of 0.01
are implemented using the Adam optimizer. Decreased
batch size, set at 256, has improved accuracy. The size
of the embedding is 100. A random sample strategy was
used in the execution of the investigation. From one of
Bhutan's Colleges of Education, 22 first-year in-service
postgraduate science teachers made up the sample.
Males made up 13 (or 59% of the total) of these
educators. Because of this, picking the right
hyperparameters for a model is crucial for fast and
accurate training. Internal operations of the cells that
make up the LSTM network are the main point of
differentiation.
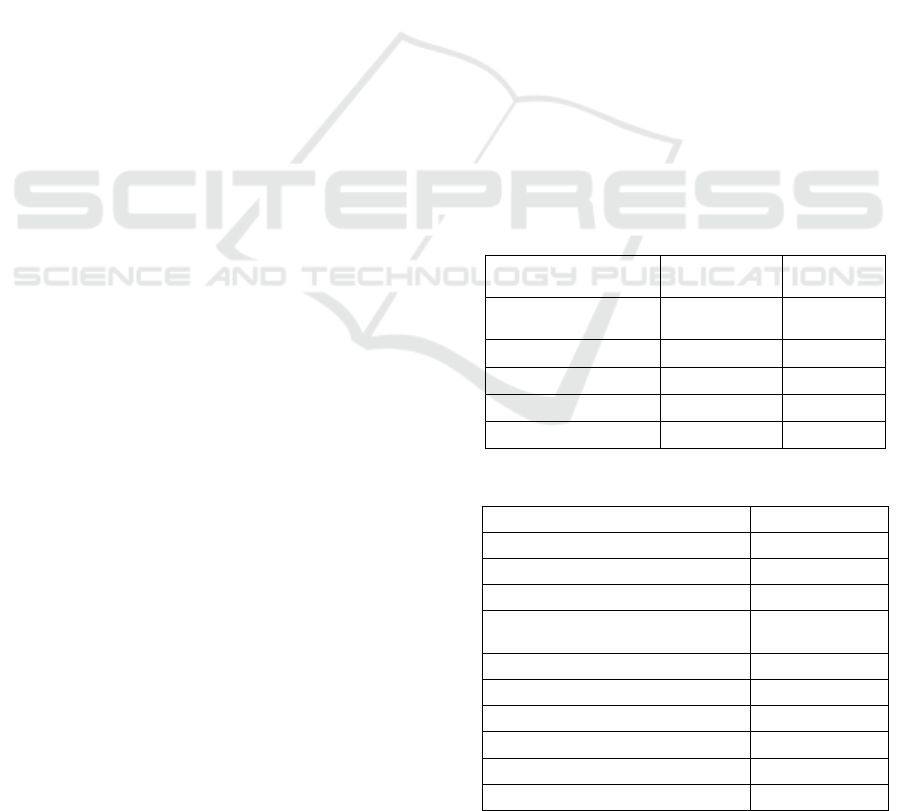
Table 1: LSTM Layered Architecture.
Layer (type) Output size
Param
Numbe
r
Embedding_1
(embedding)
300 x 100 10,00,000
Lstm_1 (LSTM) 300 x 128 1,17,248
Lstm_2 (LSTM) 64 49,408
Dense_1 (Dense) 32 2080
Dense_2 (Dense) 1 33
Table 2: Hyperparameters for proposed model.
Hyperparameters Value
Layer for embedding 1
LSTM layer 2
Layer with high concentration 2
Loss Function
Binary cross
entrop
y
Function for activation ReLu
Optimizer Adam
Learning rate 0.01
Epoch count 10
Size of embedding 100
Group quantity 256
Optimized Deep Learning Techniques for the Detection and Identification of Fake News in Digital Media
509
Tables 1 and 2 provide a comprehensive list of all
the necessary hyperparameters for an LSTM model to
improve performance, as well as the recommended
settings considered best practices.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The dataset includes four attributes title, main text, topic,
and date and is derived from Twitter. It includes pre-
trained word vectors, with 20,000 features used for
analysis 16,000 for training, 2,000 for testing, and 2,000
for validation. Vectorization is based on word frequency.
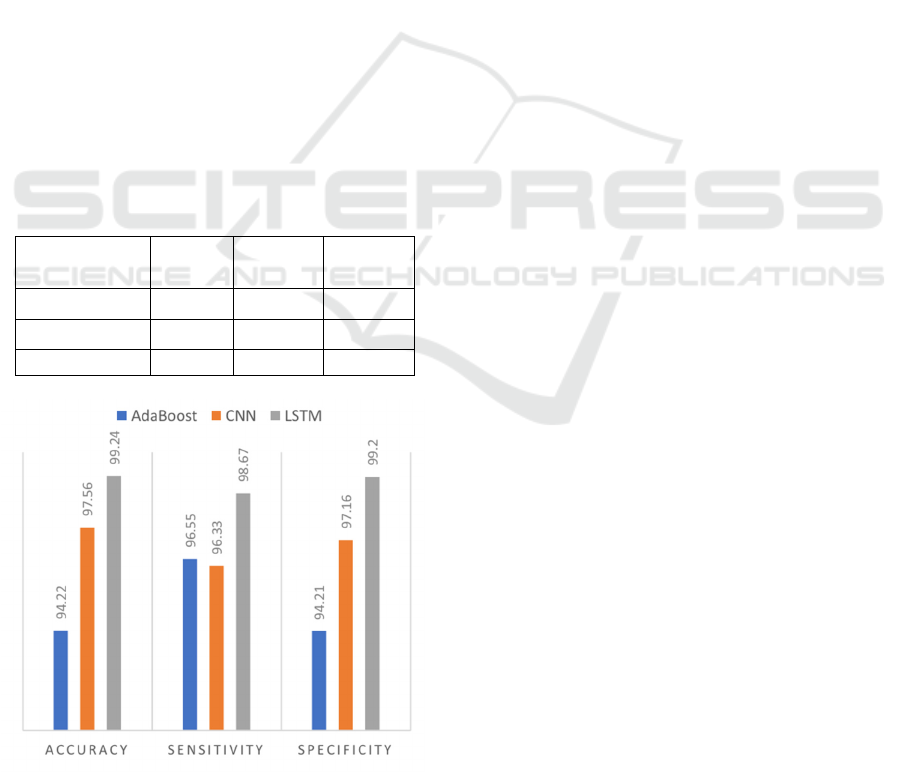
Figure 5 shows for a comparison of classifier results in
detecting false news in social media datasets. Data pre-
processing involves removing stop words using the
NLTK library, stemming words with Porter’s
Algorithm, and tokenizing with an N-gram model.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), boosted by
AdaBoost and LSTM, form the basis of the model.
LSTM achieved 99.24% accuracy, outperforming CNN
by 1.68% and AdaBoost by 5.02%. Its specificity is
99.2%, exceeding CNN by 2.04% and AdaBoost by
4.99%, while its sensitivity is 98.67%. LSTM is the most
effective for fake news detection.
Table 3: Accuracy, specificity and sensitivity comparison
of different classifiers.
Algorithm/Metric
Accuracy
(%)
Sensitivity
(%)
Specificity
(%)
AdaBoost 94.22 96.55 94.21
CNN 97.56 96.33 97.16
LSTM 99.24 98.67 99.2
Figure 5: Comparison of classifier results in detecting false
news in social media datasets.
Additionally, rhetoric plays a key role in English writing
by enhancing persuasive abilities. Table 3 shows
accuracy, specificity and sensitivity comparison of
different classifiers. Understanding rhetorical devices
like contrast and exaggeration helps writers improve
their skills and grasp rhetorical concepts more
effectively.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research presents a method for detecting false news
stories using Twitter data that is based on deep learning.
Tokenization, stemming, and stop word removal are all
part of the pre-processing. When compared to CNN and
AdaBoost, LSTM achieves the highest accuracy rate of
99.24%. Future work aims to enhance automation,
particularly for e-commerce platforms, where detecting
false information is crucial.
REFERENCES
Abu Sarwar Zamani, Aisha Hassan Abdalla Hashim, Sara
Saadeldeen Ibrahim mohamed, Md. Nasre alam.
Optimized Deep Learning Techniques to Identify
Rumors and Fake News in Online Social Networks.
Journal of Computational and Cognitive Engineering
2025,Vol.00(00)19DOI:10.47852/bonviewJCCE52023
348.
Bahad, P., Saxena, P., & Kamal, R. (2019). Fake news
detection using bi-directional LSTM-recurrent neural
network. Procedia Computer Science, 165, 74–82.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.01.072
Bird, S., Klein, E., & Loper, E. (2009). Natural language
processing with Python: Analyzing text with the natural
language toolkit. USA: O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Hsu, C. C., Zhuang, Y. X., & Lee, C. Y. (2020). Deep fake
image detection based on pairwise learning. Applied
Sciences,10(1),370.https://doi.org/10.3390/APP10010
370
Huan, J. L., Sekh, A. A., Quek, C., & Prasad, D. K. (2022).
Emotionally charged text classification with deep
learning and sentiment semantic. Neural Computing
and
Applications,34(3),23412351.https://doi.org/10.1007/s
00521-021-06542-1
Igwebuike, E. E., & Chimuanya, L. (2021). Legitimating
false hood in social media: A discourse analysis of
political fake news. Discourse & Communication,
15(1), 42–58. https://doi.
org/10.1177/175048132096165
Kaliyar, R. K., Goswami, A., & Narang, P. (2021).
DeepFakE: Improving fake news detection using tensor
decomposition- based deep neural network. The Journal
of
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
510

Supercomputing,77(2),10151037.https://doi.org/10.10
07/s11227-020-03294-y
Lahby, M., Aqil, S., Yafooz, W. M. S., & Abakarim, Y.
(2022). Online fake news detection using machine
learning techniques: A systematic mapping study. In M.
Lahby, A. S. K. Pathan, Y. Maleh & W. M. S. Yafooz
(Eds.), Combating fake news with computational
intelligence techniques (pp.
337).Springer.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-
90087-8_1
Pennycook, G., & Rand, D. G. (2021). The psychology of
fake news. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 25(5), 388–
402. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.tics.2021.02.007
Ruchansky, N., Seo, S., & Liu, Y. (2017). Csi: A hybrid
deep model for fake news detection. In Proceedings of
the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and
Knowledge
Management,797806.https://doi.org/10.1145/3132847.
3132877
t’Serstevens, F., Piccillo, G., & Grigoriev, A. (2022). Fake
news zealots: Effect of perception of news on online
sharing behavior. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 859534.
https://doi.org/ 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.859534.
Umer, M., Imtiaz, Z., Ahmad, M., Nappi, M., Medaglia, C.,
Choi, G. S., & Mehmood, A. (2023). Impact of
convolutional neural network and FastText embedding
on text classification. Multimedia Tools and
Applications, 82(4), 5569–5585. https://
doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13459-x
Optimized Deep Learning Techniques for the Detection and Identification of Fake News in Digital Media
511
