
Heart Disease Prediction Using Warm and Naviebayes
Satheesh Kumar A. and Vijayalakshmi M.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Heart Disease, Machine Learning, Predictive Modeling, Medical History.
Abstract: Heart disease cases have been rising quickly lately, thus it's critical to anticipate these conditions. It is
challenging to identify the criteria, and because it involves sensitive information, it must be done correctly.
We have created an application that estimates an individual's risk of developing heart disease. In the study,
which uses a dataset that includes clinical factors like age, sex, kind of chest discomfort, resting blood
pressure, cholesterol levels, fasting blood sugar, and others, machine learning algorithms are applied to predict
heart disease. We specifically contrasted the effectiveness of Naive Bayes and Decision Tree classifiers.
Eighty samples were used for training, and twenty samples were used for testing. Models were trained on the
training set and predictions were produced on the testing set. With precision, recall, and F1-score all tightly
aligned at 85-88%, the Decision Tree model attained an accuracy of 85%. However, with a 90% score in
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, the Naive Bayes model beat the Decision Tree, indicating that it
would be more useful in this situation. The models' performance was further examined using confusion
matrices, which showed that Naive Bayes also performed better in terms of balancing false positives and false
negatives. These results highlight the promise of using machine learning methods to the early identification
and detection of cardiac disease.
1 INTRODUCTION
Heart disease continues to be a major global cause of
death, creating a serious public health issue.
Predicting one's risk of heart disease is a challenging
undertaking due to the complex interplay of genetic,
behavioral, and environmental factors. An increasing
number of people are interested in using
computational techniques to improve the precision
and effectiveness of cardiac disease prediction as a
result of the development of new technology,
especially in the area of machine learning. A kind of
artificial intelligence called machine learning enables
computers to recognize patterns and forecast
outcomes from data without the need for explicit
programming. Machine learning algorithms are
capable of analyzing large datasets that contain a
variety of patient data, such as medical history,
lifestyle decisions, and genetic predispositions, in the
context of predicting cardiac disease. Through the
discovery of latent patterns and associations within
this data, these algorithms can help medical personnel
anticipate and prevent cardiac disease more
successfully. With its capacity to provide
individualized and data- driven insights, this
predictive modeling methodology has the potential to
completely transform conventional risk assessment
techniques. Unlike traditional risk calculators, which
frequently depend on a small number of variables,
machine learning models can consider a large number
of variables and adjust to new data, improving
forecast accuracy.
1.1 Heart Disease
Figure 1: Heart disease.
480
A., S. K. and M., V.
Heart Disease Prediction Using Warm and Naviebayes.
DOI: 10.5220/0013931700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
480-485
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Heart disease is a major cause of morbidity and
mortality and a challenging global health challenge.
Because of its intricate interplay of genetic, lifestyle,
and environmental factors, it is complicated and
necessitates novel ways to prevention and prediction.
Figure 1 show the Heart Disease.
1.2 Machine Learning
Machine learning is, at the forefront of technological
innovation, a technological leap in how computers
learn and make decisions. Machine learning, a branch
of artificial intelligence, enables systems to study vast
amounts of information on their own, discovering
trends and correlations that more traditional
programming methods miss. Machine learning
models, as opposed to traditional systems that rely on
human-written commands, learn and improve over
time as additional data is exposed to the system. So
essentially this adaptive capability allows machines
to predict outcomes, detect complex patterns and
learn more and more about various datasets over
time. From image recognition to predictive analytics
to a variety of other things your machine learning
changes from industry to industry, but you're making
a big impact in technology, healthcare, finance, and
more. Through the process of innovation, they will
not only determine better solutions but will reshape
whole industries, enhance productivity and unveil
insights which we could not obtain using other
computational methods.
1.3 Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling, as one of the best methodologic
tools, which helps the user to navigate through a
complex data analysis landscape by projecting
information about its future using information
collected from the past trends and patterns. In simple
terms, it means developing and using algorithms to
predict or identify any patterns in data sets. This
method is particularly useful in domains where it is
important to understand and predict future events.
Predictive modeling is an innovative technology used
in areas like marketing to predict customer behavior,
in healthcare to anticipate the course of an illness, or
in finance to gain insight into market trends. It
processes this raw data into actionable insights using
statistical and mathematical methods, allowing
decision-makers to take pre-emptive actions to
project hurdles and tap opportunities. As the sectors
turn increasingly to data to inform strategies,
predictive modeling becomes not just a tool but a
game changer, enabling businesses to navigate
nuances and reconditions and make wise decisions in
ever-evolving environments.
1.4 Medical History
The medical history of a patient is a complicated story
stitched together from the threads of their previous
medical experiences. It is an integral part of health
care. Think of it as an exhaustive record: a chronicle
of all the factors that form a person’s health journey,
from diseases and treatments to choices and genetic
characteristics. For healthcare professionals, this
historical tapestry is a vital road map that offers
priceless insights into the trajectory of a patient’s
health. By carefully analyzing medical histories,
clinicians can recognize patterns, identify risk
factors, and reach evidence-based conclusions about
diagnosis, treatment, and the best course of
preventive measures. Overall, a strong understanding
of medical history informs present-day practices and
enables a personalized, holistic approach to patients.
As healthcare advances, the need for deep diveing
into a rich database of a patient medical history is
becoming increasingly evident.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Sean C. A lot of good has been achieved so far with
the implementation of machine learning in health
care, and the future looks promising, with the early
diagnosis and prognosis of a number of diseases. And
with the use of machine learning algorithms, the
benefits for heart health are even more pronounced.
The most important advantage of predicting future
heart trouble in advance is being able to detect them in
time and customizing the treatment. The objective of
this research work is to explore and compare the
performance of various types of machine learning
classifiers with respect to heart disease prediction. So,
the classifiers we are work on are: Decision trees,
Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, Support Vector
Machines (SVM) and Random Forest. These
classifiers were compared in order to find the best for
heart health prediction. necessary. Every one of these
classifiers has unique strengths and characteristics.
Furthermore, the research proposes a new approach;
an ensemble classifier. This classifier integrates the
advantages of strong and weak classifiers, rather than
merely following a single-model method. The
reasoning for this hybrid classification approach lies
in its ability to adequately use a vast amount of
training and validation samples. By combining these
diverse models, the ensemble classifier seeks to
Heart Disease Prediction Using Warm and Naviebayes
481

enhance the overall robustness and predictive
performance of the model, allowing for a more reliable
approach to the early identification of potential cardiac
issues.
Senthilkumar Mohan of one of leading causes of
death, heart disease remains a worldwide health
problem. Cardiovascular diseases prediction →
Clinical data analysis would be incomplete without
addressing prediction of cardiovascular diseases.
Analyzing the huge quantity of data generated by the
healthcare sector requires advanced technologies,
which has made machine learning extremely
effective in this field. One potential way to enhance
prediction accuracy and decision making for
cardiovascular health alongside machine learning
methods is to combine them with clinical prerogatives.
The confluence of machine learning and the Internet
of Things (IoT) adds a new world to healthcare
analytics. Recent IoT based advancements have
illustrated that the combination of machine learning
algorithms with IoT devices can result in live data
that may be helpful in cardiac disorder prediction and
prevention. This convergence of technologies has
enabled more reactive and personalized healthcare
interventions. Though several advancements have
already been made in this area of cardiac disease
prediction, this study aims to push the field further by
proposing a different approach. The objective is to
apply advanced machine-learning-based algorithms to
identify and exploit key factors for significant rise in
prediction accuracy of cardiovascular-related
diseases.
Shu Jiang A worldwide analysis of the impact of
cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) indicates that this
health condition affects a large number of individuals
and leads to the causation of the most deaths in the
world, more than any other reason. In 2016, CVDs
were responsible for 17.9 million deaths globally
(31% of all deaths) according to the World Health
Organization K. T and Agarwal. Kumar, et al. Heart
attacks and strokes were responsible for 85% of these
deaths. With death rates of 50% or higher and
cardiovascular surgery being notoriously expensive,
this grim reality not only takes an enormous emotional
toll on the affected families, it also poses a major
financial burden. Heart disease is a significant and
even apparently unmanageable risk in economically
impoverished areas, where the problem is particularly
bad. Therefore, exploring the indirect associations
between various human attributes and susceptibility to
coronary heart disease may be necessary. Building
solid predictive model is more of analytics work but
also an important tool in predicting and preventing
cardiac problems. However, within this paradigm,
machine learning applications emerge as a formidable
weapon against heart disease. It builds theory and
methods around practical application thus is closely
related to computational statistics. The two branches
of traditional approaches of both supervised learning
and unsupervised learning represent the diversity in
the field of Machine learning. For the very specific
goal of identifying heart disease from its physiological
characteristics the solution is clear: supervised
learning.
Pronab Ghosh Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs)
remain a global health challenge because of their
broad and detrimental impact on human health. It is
crucial to identify risk factors, as early detection of
CVDs can help prevent or mitigate their effects. In this
context, predicting cardiac disease from machine
learning models would appear to be a viable approach.
To enhance the accuracy of such predictions, the
proposed model in this study incorporates a blend of
methods. The success of the proposed model relies on
a robust data management approach with impactful
data collection, pre- processing, and transformation
techniques. These steps are necessary to ensure the
generation of accurate and reliable data used for
training the model. By including the various datasets
like that of Stat log, Long Beach VA, Cleveland,
Switzerland, and Hungarian it is a thorough model.
This makes it possible to capture a wide array of data
for analysis. Feature selection: A critical step to
enhancing the predictive power of the model in order
to find and select the most relevant features in this
paper, the Relief method and Least Absolute
Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) are
presented. The application of a strategic selection
process enhances the model's ability to the risk
factors for heart disease. The novelty of this research
is the introduction of new hybrid classifiers, including
Gradient Boosting Method (GBBM), AdaBoost
Boosting Method (ABBM), K-Nearest Neighbors
Bagging Method (KNNBM), Decision Tree Bagging
Method (DTBM), and Random Forest Bagging
Method (RFBM). These hybrid classifiers learn
bagging and boosting
methods with basic classifiers at
the training time.
T. Kumaresan et al, Heart diseases are becoming
more common and to prevent before they become
severe, pre-examination is a must Harshit Jindal the
complexity of this diagnostic task calls for both
efficiency and precision, making testing novel
approaches desirable. The study article under
discussion is on the subject of identifying patients who
are at higher risk for heart disease based on a variety
of medical characteristics. To meet this challenge, the
researchers have developed a heart disease prediction
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
482

system that harnesses large portions of patients'
medical histories for this analysis. The aim of this
system is to provide a predictive model that identifies
a patient with heart disease before it actually takes
place, enabling a preventive approach to treatment
intervention. This suggests the range of machine
learning algorithms such as K-nn and logistic
regression that can be used, underlining the flexibility
of modern computational techniques in medical
diagnostic contexts. One of the key points of the
research is improving the accuracy of heart disease
predictions. Authors have fine-tuned the model to
ensure reliability and performance.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
One of the hardest things to do in medicine is to
estimate heart disease. This certainly takes a lot of
time and effort in particular for doctors and other
medical professionals to figure out the cause of this.
This study uses GridSearchCV with LR, KNN,
SVM, and GBC (added/mentioned above) machine
learning algorithms to forecast cardiac illness. The
system uses a 5-fold cross-validation approach for
verification. Fourth, a comparative analysis of these
four approaches. The datasets for Cleveland,
Hungary, Switzerland, Long Beach V and UCI
Kaggle are used to test the performance of the
models. Data mining analysis shows that with one
exception (Hungary, Switzerland & Long Beach V
and UCI Kaggle), the Extreme Gradient Boosting
Classifier with GridSearchCV has the best and almost
similar test and train model accuracy of 100% and
99.03 respectively. Moreover, as shown in the
analysis, both datasets (Hungar, Switzerland & Long
Beach V and UCI Kaggle) produced the best and
identical accuracies in testing and training to be the
XGBoost Classifier without GridSearchCV
produced (98.05-100) and (100,100).
4 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed technique leverages an ensemble of
machine learning algorithms to produce a model that
estimates an individual heart disease risk. The
system employs the Train-Test Split technique to
divide the data into separate teaching/testing sets,
using a dataset that provides important clinical
parameters such as age, sex, cholesterol, and other
relevant variables. Then the dataset is used to train
the models on Decision It can integrate two popular
algorithms for classification and regression-
Decision Tree and Naive Bayes classifier which
enables the system to recognize complex pattern and
relationships between the data
complex. Also,
WARM Rules are employed in the algorithm, which
could indicate a sophisticated method for assigning
weights to decision tree rules and enhancing both the
predictive power and interpretability of the system. It
also provides thorough checks of algorithms,
including metrics for predicting cardiac disease such
as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Through
this evaluation process the researchers and medical
experts can select an appropriate algorithm for stage
diagnosis and detection.
Dataset: The dataset consists of 14 columns, which
include significant details such as age, sex,
cholesterol levels, and the target variable which
indicates whether or not heart disease exists.
Analysing the dataset, through either statistical
summaries and/or visualizations, provides insight
into the target variable, the distribution of features
and potential relationships between features and the
target variable.
WARM Rules: Your data is limited up to October
2023, but it seems that the WARM Rules section
directly references a specific aspect of the
implementation of the decision tree algorithm, which
involves assigning different weights to the model
rules. These rules determine how the algorithm
makes decisions, having an impact on the model's
effectiveness in predicting the future. More
contextual information and warranted clarification
might shed light on why these norms matter in the
context of the study.
Train Test Split: This section splits the dataset into
training and testing sets. These (features/independent
and dependent/target) two variables make up the
training set, that consists of 80 samples. The testing
set (X_test, Y_test) consists of 20 samples as well, as
the features and target variable, the latter is for testing
purposes. Dividing the models makes certain that
they are trained on only a portion of the data and
tested on another element, which significantly
simplifies the assessment of the generalization ability.
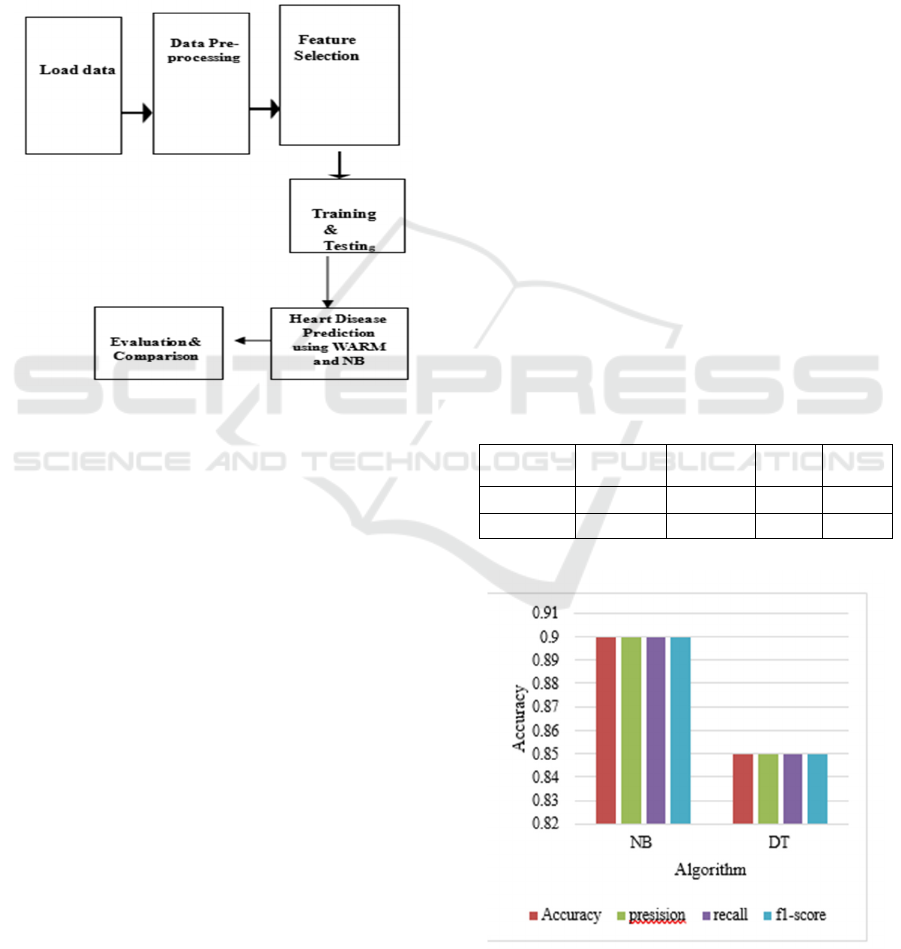
Figure 2 show the Block Diagram.
Model Evaluation: In particular, the performances
of the Decision Tree (DT) and Naive Bayes (NB)
models on the testing set are examined in detail. Our
Decision Tree model performance shows we
correctly classified most of our samples with an 85%
accuracy, while precision, recall, and F1 score nearly
matched: 88%, 85%, and 0.85 respectively. In
Heart Disease Prediction Using Warm and Naviebayes
483
contrast, the Naive Bayes model exhibited a strong
and robust level of prediction accuracy, achieving an
accuracy of 90%, thereby surpassing the Decision
Tree. Naive Bayes had stable and balanced
performance, with precision, recall, and F1 score all
at the 90% mark. Further analysis of the models'
classification performance was done by using of
confusion matrix of respective to models, Naive
Bayes had got better balance in true positive, true
negative, and false positive and false negative ratio.
Figure 2: Block diagram.
5 RESULT ANALYSIS
To predict cardiac disease from patient
characteristics, two machine learning algorithms
(Decision Tree (DT) and Naive Bayes (NB)) were
trained and evaluated in this study. Models were
trained on a dataset with columns of age, sex, resting
blood pressure (trestbps), cholesterol levels (chol),
and type of chest pain (cp). I used part of the dataset
to train the models and I used a part of the data for
testing. In this case, with 85% accuracy, the Decision
Tree is able to classify 85% of the occurrences in the
testing set correctly. It also had an accuracy rate of
88% and recall rate of 85%, which indicates that the
tool can accurately detect positive cases for heart
disease with fewer false positives. The confusion
matrix shows that the model did, in fact, misclassify
a few cases, such as in three cases where the heart
disease is classified as non-disease. Naive Bayes
achieved a higher accuracy (90%), precision (90%)
and recall (90%) than the What-If tool. Table 1 show
the Comparison table The Naive Bayes well
classified a higher percentage of occurrences, along
with a decent balance between accuracy and recall.
In the case of Naive Bayes confusion matrix, only
one instance was soft predicted, which represents
robustness of this model for heart disease prediction.
Figure 3 show the Comparison graph.
Accuracy is one of the most common metrics for
evaluating classification performance, calculated as
the ratio between the number of correctly segmented
samples and the total number of samples.
𝑨𝒄𝒄𝒖𝒓𝒂𝒄𝒚 𝑻𝑷/ 𝑻𝑷 𝑭𝑵
(1)
Precision: Precision is the ratio of correctly
predicted positive observations to the total predicted
positive observations (In other words, the accuracy of
positive predictions). Precision can be expressed as:
𝑷𝒓𝒆𝒄𝒊𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 𝑻𝑷 / 𝑻𝑷 𝑭𝑷 (2)
The ratio of true positives to total (real) positives
in the data is known as recall or sensitivity.
Sensitivity and recall are synonymous.
𝑹𝒆𝒄𝒂𝒍𝒍 𝑻𝑷 / 𝑻𝑷 𝑭𝑵
(3)
The ratio of genuine negatives to total negatives
in the data is known as specificity. Specificity is the
program's accurate designation for everyone who is
actually healthy.
𝑺𝒑𝒆𝒄𝒊𝒇𝒊𝒄𝒊𝒕𝒚 𝑻𝑵 / 𝑻𝑵 𝑭𝑷
(4)
Table 1: Comparison Table.
Algorithm Accuracy Precision Recall
F1-
Score
NB 0.9 0.9 0.9 0.9
DT 0.85 0.85 0.85 0.85
Figure 3: Comparison Graph.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
484

6 CONCLUSIONS
To sum up, incorporating machine learning
algorithms offers a viable way to improve cardiac
disease prediction and early detection. This study
shows that Decision Tree and Naive Bayes classifiers
may accurately predict an individual's risk of heart
disease through the building and evaluation of
predictive models using clinical factors, such as age,
sex, and cholesterol levels. The results emphasize
how critical it is to use cutting-edge analytical
methods to address the increased prevalence of
cardiovascular diseases. This research adds to the
ongoing efforts to improve diagnostic skills and
individualized healthcare interventions by offering
insights into the relative efficacy of various
algorithms as well as their advantages and
disadvantages.
7 FUTURE WORK
Subsequent research in this field may investigate
the combination of sophisticated feature
engineering methods and deep learning
structures to improve the prognostic potential of
heart disease models. A more thorough
understanding of the dynamic nature of
cardiovascular health might be obtained by
looking at the effects of various health
parameters and adding data from real- time
monitoring. Moreover, efforts must to be focused
on creating interpretable models in order to
improve predictability and transparency,
particularly in situations where important
healthcare decisions must be made.
REFERENCES
H. S. and Kaur. "Improving the accuracy of heart disease
prediction using machine learning methods and
optimization," Ajay, Next Generation Computing
Technologies (ngct), 2016, pp. 516–521.
J. In the proceedings of the inaugural instructional
conference on machine learning, vol., Ramos et al.
discuss "efficient prediction of cardiovascular disease
using machine learning algorithms with relief and lasso
feature selection techniques." 242. 133–142 in
Piscataway, New Jersey, 2003.
K. Toutanova as well as c. Cherry, "Heart disease prediction
using machine learning and svm techniques," in
Proceedings of the 4th International Joint Conference
on Natural Language Processing of the American
Foundation for Nursing and Palliative Care, Volume 1–
Vol 1. 2009, pp. 486–494, Association for
Computational Linguistics.
K. T and Agarwal. Kumar, in the 2nd International
Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control
Systems (ICICCS), "Heart disease prediction using
machine learning." Ieee, 2018.
M. A and Mohammed. Selamat, "Machine learning
algorithms for heart disease prediction," in
International Conference on Computer,
Communications, and Control Technology (i4ct). 2015,
IEEEE,pp. 227–231.
Rizky, W. M., Afrizal, D., Ristu, S. "Heart disease
prediction system using sequential backward selection
algorithm for features selection and machine learning
model." Journal of Scientific Informatics, vol. 3(2),
Nov. 2020, pp. 41–50.
S. Rajput together with one. Arora, "Hybrid machine
learning techniques for effective prediction of heart
disease," International Journal of Computer
Applications, vol. 2013, 75, no. 10, pp. 6–12.
T. Mikolov and g. Zweig, "Machine learning for
cardiovascular diseases (CVDs)," in the 2012 IEEE
Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT).
Pages. 234–239 in IEEEE, 2012.
T. Sainath, N. o. Vinyals, one. both h and senior. Sak,
"Optimization of energy consumption in container-
oriented cloud computing centers," 2015 IEEE
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and
Signal Processing (icassp) proceedings. IEEEE, 2015,
4580–4584 pages.
T. Kumaresan along with c. Palanisamy, "Prognostication
of heart disease, "International Journal of Bio-
inspired Computing, vol. 9, no. 3, 2017, pp. 142–156.
Heart Disease Prediction Using Warm and Naviebayes
485
