
Enhanced Task Scheduling for IoT‑Based Healthcare Systems in
Cloud Computing
B. Naga Lakshmi, Kupparamedi Chandrika, Ediga Gowri, Gangula Nagamani and Janupalli Sahithi
Department of CSE, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andra Pradesh, India
Keywords: IoT‑Based Healthcare Systems, Cloud Computing, Scalability, Resource Utilization, Urgency‑Based Task
Prioritization.
Abstract: IoT healthcare platforms, such as wearable devices, sensors, and medical equipment, generate huge volumes
of medical data that have to be processed and analysed efficiently. The current methodology of IoT healthcare
systems in cloud computing faces challenges of using immense volumes of data from IoT systems, which
include non-scalability, ineffectively utilized resources, and were resolved by the proposed system. The
project introduces a refined task scheduling mechanism for the cloud-based IoT-assisted healthcare system.
This project proposes a refined task scheduling method for cloud-based IoT healthcare systems. The suggested
method ranks tasks according to their need and urgency, attempting to ensure that critical tasks remain in
operation to the utmost degree of efficacy as promptly as feasible. Accomplishments of this project are better
task scheduling and greater resource utilization.
1 INTRODUCTION
The merger of IoT and healthcare was a turning point
in healthcare, leading to real-time monitoring,
diagnosis, and treatment. IoT-based healthcare refers
to a network of devices, such as wearable sensors and
medical devices, which gather and send patient data
to cloud servers for notification and analysis.
However, the concomitant complexities and
magnitudes of these systems create some grave
challenges for the optimal processing of task
management, data processing, and resource
allocation.
Dynamic task scheduling in any IoT-based
healthcare system stands out to be one of the major
challenges. Such systems dynamically handle
continuously changing constraints, such as
computational requirements, bandwidth limitation for
data transmission, and real time conditions of the
medical applications.
Unfortunately, the traditional task scheduling is
insufficient to meet the particular exigencies of IoT
healthcare systems with respect to low latency, high
service availability, satisfying energy efficiency, and
more.
It is essential to address the increasing complexity
of task scheduling due to dynamic patient data such
as vital signs. D. The Proposed Scheduling
Framework In this section, we propose an efficient
scheduling framework to leverage the coalition
process of each user in both uplink and downlink
communication systems. With the use of machine
learning for predictive workload management and
dynamic scaling features available in clouds, utilizing
mod- el allows the proactive scheduling which can
improve performance, stability and power savings for
IoT-based health care systems.
2 LITERATURE SURVEY
2.1 A: S - Kumar, R - P - Singh, and M
- K - Gupta, "Enhanced Task
Scheduling for IoT-Based
Healthcare Systems in Cloud
Computing
This article provides a comprehensive review of task
scheduling methods for IoT-based cloud-integrated
healthcare systems. Different methods such as
priority-based scheduling, load balancing, and real-
time processing and machine learning-based methods
for predictive task scheduling are proposed by the
authors. The study highlights the importance of
462
Lakshmi, B. N., Chandrika, K., Gowri, E., Nagamani, G. and Sahithi, J.
Enhanced Task Scheduling for IoT-Based Healthcare Systems in Cloud Computing.
DOI: 10.5220/0013931400004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
462-466
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

efficient utilization of resources in cloud-based
systems for low-latency data processing and efficient
utilization of computational resources, especially in
be employed for forecasting task execution latency
and optimizing the scheduling of tasks based on
present cloud resources for minimizing latency while
maximizing throughput for healthcare applications
real-time patient monitoring and diagnosis.
2.2 B: R - S - Verma, T - P - Joshi, and
K - S - Sharma, "Dynamic Task
Scheduling in Cloud-Based
Healthcare IoT Systems"
This study examined dynamic task scheduling
techniques made for health-care systems with IoT
devices and cloud computing. The authors clarify the
potential use of cloud computing to handle the
computational burden generated by IoT devices
through predictive models for resource allocation on
demand with respect to real-time needs for tasking.
The work also identified scalability, energy
efficiency, and task prioritization as central themes
enhancing the performance of cloud-supported
health-care systems.
2.3 B: T - H - Reddy, V - R - Kumar,
and S - M - Patel, "AI-Driven Task
Scheduling for IoT Healthcare
Applications in Cloud
Environments"
In a similar vein, author B. T. H. Reddy et al propose
improved optimization of task scheduling in the IoT-
based healthcare systems via artificial intelligence
methods like reinforcement learning, neural network
etc. Dominated by how AI can achieve scheduling in
real-time networked health data processing to
optimize cloud resources utilization and decision-
making using real-time health status derived from IoT
devices. The paper focuses on the AI as a means of
enhancing diagnosis and for increasing efficiency in
healthcare cloud. The work is representative of AI’s
ability to forecast workloads, adapt to changing
conditions and reduce delays, while improving
system reliability making health projects smarter,
more energy efficient and with a speedier recovery
from an unpredictable event.
2.4 D: M - Singh, S - K - Sharma, and
R - P - Iqbal, "Optimizing Task
Execution in Cloud for IoT
Healthcare Systems Using Machine
Learning"
The authors discuss in this paper a machine learning-
based methodology for task execution and resource
allocation optimization in cloud-supported IoT
healthcare applications. The authors show in this
research how learning algorithms such as support
vector machines (SVMs) and k-means clustering can
employ for forecasting task execution latency and
optimizing the scheduling of tasks based on present
cloud resources for minimizing latency while
maximizing throughput for healthcare applications.
3 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Problem statement is concerned with the issue of
effectively scheduling and prioritizing healthcare
tasks created by IoT devices in a cloud computing
system.
The aim is to maximize efficient task scheduling,
utilization of resources, reliable processing of urgent
healthcare information, considering the changing
nature of patient requirements.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4.1 Proposed System
The system proposed attempts to counter the
limitations of existing IoT-based healthcare systems
by using a new dynamic task scheduling method. The
suggested methodology ensures real-time processing
of data, maximizes the usage of resources, and
conserves energy, thus transforming data
management in the healthcare industry. The heart of
the system is a robust scheduling engine that
intelligently prioritizes tasks based on their urgency
and results in fast response times for life-critical
health data like emergency notifications and
monitoring of vital signs.
Priority-based task scheduling in this section is a
natural approach in IoT-based healthcare systems to
best process the medical tasks with minimal latency.
Various healthcare tasks such as constant real-time
patient monitoring, emergency alerts, and medical
diagnostics exist in these systems generated by
medical devices supported by IoT. All these activities
Enhanced Task Scheduling for IoT-Based Healthcare Systems in Cloud Computing
463
have varying levels of priority, and therefore, the
priority-based scheduling classifies and runs them
according to how critical they are. This allows high-
priority operations like issuing notifications for
urgent health conditions to be run without delay, and
lower-priority operations like recording normal
health details to be run without interfering with
critical Operations.
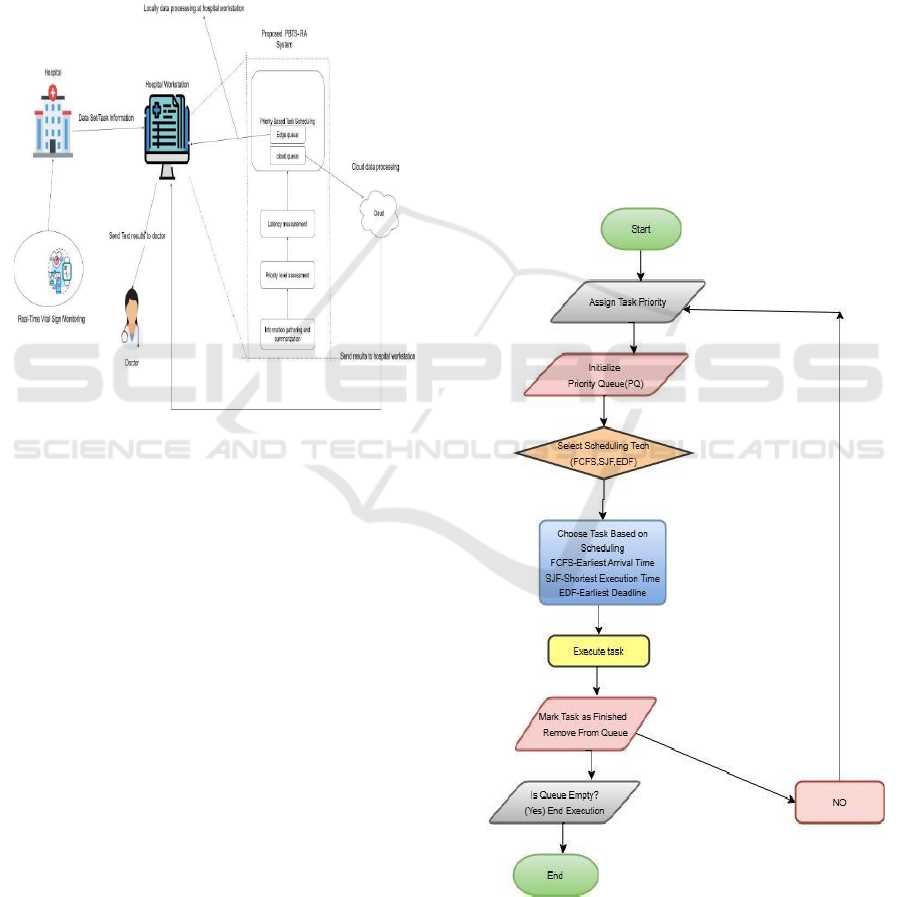
4.2 System Architecture
Figure 1: Proposed Priority-Based Task Scheduling System
for IoT-Based Healthcare.
Figure 1 the system architecture for patient health
monitoring is designed for hospitalized patients
undergoing treatment. It consists of various
networked devices and mobile or wireless sensor
nodes that continuously monitor and measure the
patient's health parameters. The collected data is then
sent to hardware Hospital workstation (HW) units for
processing. The HWs are edge computing servers,
and the proposed PTS- RA system is installed on
them.
This framework is responsible for categorizing the
tasks in terms of urgency, scheduling them, and
prioritizing them based on their requirements. The
tasks are then passed on to either the HW or the cloud
queue for execution.
Each Hospital workstation has two
functionalities:
(i) applying the suggested approach to task
scheduling and prioritization, and (ii) acting as an
edge computing server. Data that reaches an HW
performs computation on the data if it is resource
sufficient. The outputs are passed on to clinicians or
physicians to inform decisions. But if an HW does not
have resources or the problem is not urgent but
complex, it is computed at the centralized cloud. Then
the results are back-end to the HW after computation.
The system tries to reduce the overall processing
time of jobs, optimize the utilization of resources at
HWs, minimize bandwidth expenses, and improve
overall performance. The monitoring devices of the
patient can store, compute, and connect to the internet
using wired or wireless links. In the hospital, several
HWs are used for storing data and computing. All
HWs share the same computational and storage
power, whereas the centralized cloud possesses much
greater resources and can execute multiple tasks at a
time with ease. Moreover, the system is scalable in
nature, and more HWs can be incorporated when
required to support greater workloads.
4.3 Algorithm
Figure 2: Task Scheduling Flowchart Using Priority Queue
and Scheduling Techniques (FCFS, SJF, EDF).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
464
4.3.1 Result of the Flowchart Execution
• Assign Task Priority – Each task is assigned
a priority level. Initialize Priority Queue
(PQ) – A priority queue is created to manage
tasks based on their priority.
• Select Scheduling Technique – A scheduling
algorithm is chosen from:
• FCFS (First Come, First Serve): Tasks are
processed in the order they arrive.
• SJF (Shortest Job First): Tasks with the
shortest execution time are processed first.
Table 1: Key Features for Task Scheduling Based on
Priority.
Feature Description
Real-Time Priority
Updates
Priorities of tasks are
dynamically updated
according to varying
conditions so that high-
priority tasks are
completed in a timely
manner.
Priority-Based
Resource Allocation
Resources are
distributed according to
task priority so that
high-priority tasks get
adequate resources for
timely completion.
• EDF (Earliest Deadline First): Tasks with
the closest deadline are prioritized.
• Choose Task Based on Scheduling – The
highest-priority task is selected based on the
chosen technique.
• Execute Task – The selected task is executed.
• Mark Task as Finished & Remove from
Queue – The task is marked as completed and
removed from the priority queue. Check if
Queue is Empty:
If not, return to the scheduling step and continue
selecting and executing tasks. If yes, all tasks are
completed, and execution ends.
Table 1 show sthe
Key Features for Task Scheduling Based on Priority.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The following table 2 gives a collection of tasks, with
each task having a specified arrival time, execution
time, priority value, and deadline. Task T1 arrives at
time 0 and has an execution time of 4 units. It has the
highest priority (1 - High) and needs to be done prior
to time 9. Task T2 shows up at time 1 with an
execution time of 2 units and a medium priority (2)
and needs to be done prior to time 7. Task T3 shows
up at time 3 with an execution time of 5 units. It is
also a high-priority task (1).
with deadline 12. Task T4 is late, at time 5, low
priority (3), takes execution time of 3 units and needs
to be finished by time 10. Lastly, T5 shows up at time
7, has an execution time of 6 units, medium priority
(2), and a deadline of 14. All these tasks can be
efficiently scheduled by priority scheduling
algorithms or deadline scheduling so that the system
ensures timely completion on the basis of urgency
and resource constraints.
Table 2: Task Dataset for Priority-Based Scheduling in IoT
Healthcare Systems.
Tas
k ID
Arri
val
Tim
e
Execu
tion
Time
Priority
(1=High,2=Medi
um,3
=Low)
Deadl
ine
T1 0 4 1(High) 9
T2 1 2 2(Medium) 7
T3 3 5 1(High) 12
T4 5 3 3(Low) 10
T5 7 6 2(Medium) 14
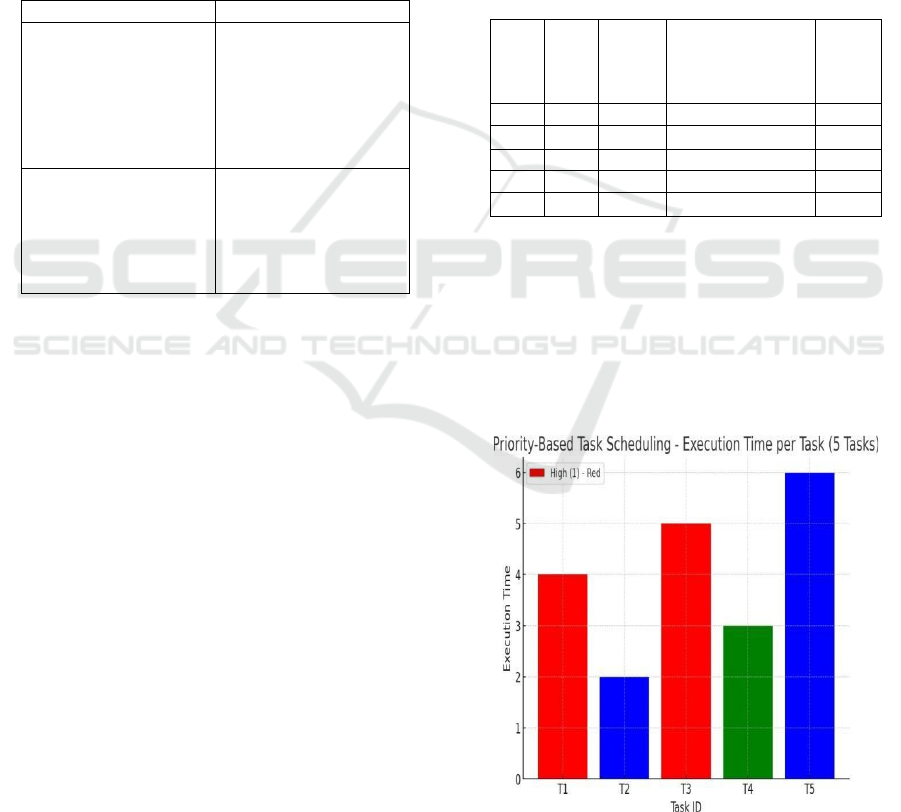
Figure 2. illustrates priority-based task scheduling
by showing the execution time for tasks T1 to T5
according to their respective priority levels. The tasks
are coded with colors: red representing high-priority
tasks (1), blue representing medium-priority tasks (2),
and green representing low-priority tasks (3). This
aids in visualizing how execution time changes across
various priority levels.
Figure 3: Execution Time Analysis of Priority-Based Task
Scheduling in IoT Healthcare.
Enhanced Task Scheduling for IoT-Based Healthcare Systems in Cloud Computing
465

T1 and T3 from the graph are of high priority, with
execution times of 4 and 5 units, respectively. T2 and
T5, which are of medium priority, have execution
times of 2 and 6 units, respectively. T4 is of low
priority, with an execution time of 3 units.
Observably, T5 has the longest execution time of 6
units and T2 has the shortest of 2 units. Figure 3
shows the Execution Time Analysis of Priority-
Based Task Scheduling in IoT Healthcare.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Finally, the system enhances IoT- based healthcare by
introducing an intelligent task scheduling algorithm
that tackles priority medical tasks. The system
prioritizes critical medical tasks to ensure that urgent
health data, such as emergency alerts and vital sign
monitoring, is processed efficiently and in a timely
manner. Through optimized utilization of resources
and real-time data processing, the system increases
scalability, minimizes costs, and enhances overall
efficiency. Finally, this solution enables faster and
more efficient delivery of healthcare services, thus
providing improved patient care.
REFERENCES
Kaur, A., & Kumar, R. (2020). "Dynamic resource
allocation and task scheduling for cloud- based
healthcare IoT systems." Procedia Computer Science,
167,106-116. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/ j.procs.
2020.03.058
Khan, M, A., & Khan, F. A. (2020) "Energy-efficient task
scheduling for IoT healthcare systems in cloud
computing." Journal of Ambient Intelligence and
Humanized Computing, 11(4), 1591-1602.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01438-w
Li, X., Liu, L., & Wang, H. (2020). "Smart task scheduling
for energy-efficient healthcare systems based on IoT."
Computers, Materials & Continua, 63(3), 1003- 1019.
https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2020.011463
Saxena, N., & Mishra, A. (2021). "A survey of task
scheduling and resource management in healthcare IoT
systems." International Journal of Computer
Applications, 176(12), 1- 10. https://doi.org/10.5120/ij
ca2021916899
Sharma, R., & Soni, M. (2021). "Task scheduling and
resource management for healthcare applications in
IoT- cloud integrated systems." IEEE Access, 9,
16916- 16929. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.
3050219
Zhang, L., & Deng, L. (2019). "A review on scheduling
algorithms in cloud computing for healthcare
applications." Journal of Healthcare Engineering,
2019, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4826067
Zhang, X., & Wang, L. (2020). "Efficient task scheduling
for healthcare systems in cloud computing
environments." Journal of Cloud Computing:
Advances, Systems and Applications, 9(1), 20-30.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13677-020-00208-7
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
466
