
Enhanced Stock Price Prediction Using Optimized Deep LSTM
Model
G. Prathibha Priyadarshini, M. Sai Madhuri, T. Vishnu Priya, S. Moheeja and U. Lakshmi Prasanna
Department of CSE, Ravindra College of Engineering for Women, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India
Keywords: Stock Price Prediction, Deep LSTM Network, Hyperparameter Optimization, Time‑Series Forecasting,
Financial Decision‑Making.
Abstract: Stock price prediction is a challenging time- series task because the stock market is random and volatile. In
this paper, we propose a better Deep Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network for accurate stock price
prediction. The proposed model uses past stock attributes such as open, close, high, low, and volume, and
technical indicators for predictive accuracy. For best performance, the hyperparameter optimization methods
like Grid Search and Bayesian Optimization are used to fine-tune the best network structure. The model has
multiple LSTM layers, dropout regularization to avoid overfitting, and adaptive learning rate optimizer to
converge faster. Experiment results indicate that our enhanced Deep LSTM network performs superior to
conventional machine learning methods and standard LSTM networks in Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
and Mean Absolute Error (MAE). Our research enables better financial decision- making with accurate stock
price forecasts for investors and traders.
1 INTRODUCTION
Stock price prediction is an important task in financial
markets, allowing investors, traders, and financial
analysts to make accurate decisions. As stock prices
are extremely volatile and dynamic, predicting future
price direction is still a problem. Statistical models like
Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average
(ARIMA) and basic regression models have been used
extensively for time series prediction. Nonetheless,
these approaches are prone to failure when dealing
with intricate temporal dependencies and nonlinear
structures of stock market data.
Deep learning methods, and more so LSTM
networks, have therefore emerged as effective
substitutes for stock price forecasting. LSTM or a
recurrent neural network (RNN) in particular that has
been designed to handle sequential data, is particularly
well-suited to learn long-term dependencies and avoid
the vanishing gradient issue. Unlike ordinary neural
networks, LSTM networks utilize memory cells and
gates that enable them to capture long-term trends,
making them particularly well-suited for forecasting
financial time series. But development of a perfect
LSTM-based model involves proper network
parameter tuning, including layers, units per layer,
learning rate, and dropout value, to avoid overfitting
and enhance generalization.
We herein propose an effective Deep LSTM model
for predicting stock prices using the assistance of
newer hyperparameter tuning techniques to improve
forecasting accuracy. The approach here is a mix of
past stock prices, opening and closing price, trading
volume, and technical ratios such as Moving Average
(MA) and Relative Strength Index (RSI). In order to
realize optimal model performance, we use Grid
Search and Bayesian Optimization to optimize
hyperparameters in an attempt to further tailor the
network to learn market patterns. We also use dropout
regularization to avoid overfitting and use an adaptive
learning rate optimizer to speed up model
convergence.
The suggested model is compared against standard
machine learning models and baseline LST models
using primary performance measures like Mean
Absolute using primary performance measures like
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Square
Error (RMSE). Our experimental result shows that our
Deep LSTM network highly enhances the precision of
the prediction, offering better predictions to the
stakeholders in the stock market. This research adds to
the existing body of work in deep learning models for
financial market use by demonstrating a viable
Priyadarshini, G. P., Madhuri, M. S., Priya, T. V., Moheeja, S. and Prasanna, U. L.
Enhanced Stock Price Prediction Using Optimized Deep LSTM Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0013931100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
443-448
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
443

framework for stock price prediction, ultimately
helping investors make informed decisions.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
RESEARCH AREA
Study methodology is the entire process of designing,
training, and hyperparameter optimizing a Deep Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network to
predict stock prices. Study methodology can be divided
into a sequence of steps ranging from data collection to
data preprocessing, model construction,
hyperparameter optimization, and testing. The main
goal is to develop a professional forecasting model for
accurate forecasting of future stock prices at a given
moment in time from past market data. Through the use
of deep learning techniques and optimization
processes, the study attempts to improve accuracy and
validity of stock market forecasting. Pre-extraction and
data preprocessing is the half-process. Historic share
prices are downloaded from pages like Yahoo Finance
or Alpha Vantage with interest-provoking parameters
like open price, close price, high, low, and volume. The
technical dimensions of Moving Average (MA),
Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands are
included in the model to maximize the predictivity
efficiency. The data is pre-processed by dealing with
missing values, Min-Max scaling of numerical
features, and splitting it into training set, validation set,
and test set in a way that the model will be trained and
tested on an unbiased basis.
The second is the Deep LSTM model building. A
multi-layered network of LSTMs is employed to
capture long-term time series data dependencies. The
network is made up of multiple layers of LSTMs and
dropout layers for preventing overfitting. The output
layer is dense with a linear activation function used for
future stock price predictions. It is optimized in a
sliding window over time with the latest observation
for predicting the subsequent time step. Adam
optimizer to optimize the convergence rate and Mean
Squared Error (MSE) as the performance metric for the
model. The last step is hyperparameter tuning and
tuning testing. Hyperparameter tuning trains the
hyperparameters and hyperparameter tuning
techniques like Grid Search and Bayesian
Optimization are used for tuning the best number of
LSTM units, dropout rate, batch size, and learning rate.
The model is then tested on performance metrics like
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Square
Error (RMSE) on the tuned model. Baselines are also
being compared against other baseline machine
learning methods such as Random Forest and Support
Vector Regression (SVR) in an attempt to place the
Deep LSTM method in a superior position.
Performance is then compared so that it can illustrate
how the model performs in stock price prediction and
thus enable it to be applied in financial decision-
making.
The research field is finance time series prediction,
and the field of study is predicting stock prices by deep
learning. Predicting the stock price is a very essential
field to explore because its optimization can lead to
more accurate models for investment, risk, and auto-
trading. Conventional techniques to predict cannot
handle the highly non-linear and dynamic stock price
nature, thus, machine learning techniques such as
LSTM networks are an ideal choice. The article
outlines one of the numerous contributions over recent
times in AI-financial modeling based on deep learning
towards improved forecasting of stock market
behavior. The research also has its place within the
broad world of artificial intelligence and deep learning
for finance. With AI technology developing at an
exponential level, banks and financial institutions are
adopting more and more machine learning models into
predictive modeling. LSTMs are said to perform well
with sequential data, and thus are highly compatible for
analysis of the stock market. It discusses the real-world
implementation of Deep LSTM networks by
simplifying their architecture to provide more accurate
predictions. A study establishes the benefits of using
LSTMs compared to traditional machine learning
models and deep learning algorithms in financial
application. Besides this, the study has implications for
investment decision-making as well as algorithmic
trading. In such turbulent financial markets prevailing
today, accurate stock price prediction is likely to be an
asset for investors and traders.
3 LITERATURE REVIEW
Kim, J., Park, H., & Lee, S. (2019)
Title: Deep Learning-Based Stock Price Prediction
Using Optimized LSTM Networks.
Abstract: This study explores the application of deep
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for stock
price forecasting. The model is optimized through
hyperparameter tuning, including dropout
regularization and adaptive learning rate optimization,
to enhance predictive accuracy. The results
demonstrate that the optimized LSTM model
outperforms traditional statistical methods and
baseline machine learning models, reducing prediction
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
444

errors and improving trend forecasting in financial
markets.
Nguyen, T., Zhao, X., & Chen, Y. (2020)
Title: Financial Market Forecasting Using Hybrid
Deep Learning Models
Abstract: In the current research study, a hybrid deep
learning method with LSTM and Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) has been employed to predict stock
prices. The model does spatial and sequential feature
learning of technical indicators and past stock data to
attempt to provide more precision. Experimental
testing on real stock data validates that the hybrid
model is better than individual LSTM or CNN models,
subjecting the model's effectiveness to identify
intricate market patterns.
Raj, V., Singh, A., & Patel, R. (2021)
Title: Hyperparameter-Tuned Deep LSTM for High-
Frequency Stock Market Prediction
Abstract: A high-performance hyper parameter tuning
system is presented here to tune Deep LSTM networks
for application in high-frequency stock trading. Grid
Search and Bayesian Optimization are used as
optimization methods to optimize various network
parameters like LSTM layer depth, batch size, and
learning rate. The improved network performs better
with reduced Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root
Mean Square Error (RMSE) than the baseline LSTMs
and thus has the potential for real-time trading.
Gomez. L., Wang, M., & Fernandez, D. (2022)
Title: Explainable AI in Stock Price Prediction:
Enhancing Transparency in Deep Learning Models
Abstract: Explainable AI techniques are being
integrated into Deep LSTM models to improve the
explanation and interpretability for the stock price
prediction model in this paper. SHAP and attention are
used in this paper to understand what are the most
important features on price variations. It is discovered
that collective explainability generates more robust
models to financial planners without compromising
their good predictive capability.
Chowdhury, M., LIM, J., & Kumar, P. (2023)
Title: Improving Deep Learning for Stock Market
Volatility Prediction
Abstract: Stock market volatility prediction with the
use of a deepened Deep LSTM model is the focus of
the paper. The method is by using financial volatility
indicators, i.e., Bollinger Bands, MACD, and ATR
together with time-series data to increase credibility
within the model. Performance is also compared to
traditional models of volatility like GARCH and the
research discovers that there is better prediction with
the optimized Deep LSTM, which produces
information required for investment planning and risk
management.
4 EXISTING SYSTEM
Price prediction of stocks is an area under study,
monetary analysis, and trading for several decades.
Time-series statistical modeling techniques like
ARIMA, GARCH, and ES are usually employed for
predictive purposes in accordance with conventional
paradigms of forecasting. Though these models prove
to be computationally efficient when it comes to
detecting linear behaviours of time series, they
completely miss detecting extremely non-linear,
dynamic behavior within financial markets. In
addition, they need laborious manual feature
engineering and are very prone to noisy data or missing
data, which restricts their prediction ability in dynamic
stock market environments.
With the development of machine learning, new
models such as Support Vector Machines (SVM),
Random Forest (RF), and Gradient Boosting (GBM)
have been introduced by researchers for enhancing the
accuracy of prediction. They acquire patterns from
history and statistical correlation but still are unable to
learn long-term dependency. Machine learning models
need profound hyperparameter searching and
generalize quite poorly in noisy market conditions.
Furthermore, they don't innately possess model
temporal dependencies, which are integral in financial
time-series forecasting. With the arrival of deep
learning, these models such as RNNs and LSTM
networks were applied that are appropriate for
sequential data in the most suitable way.
LSTMs especially fit well for forecasting the stock
price since they have the ability to store long-term
dependencies as well as detect intricate patterns.
Regular LSTMs are still not optimal towards
overfitting, bearing heavy computational demands, and
adjusting many hyperparameters. Most of the current
deep models are also non-interpretable, and therefore it
is hard for financial analysts to comprehend the
decision-making process of these models. Although
current systems yield diverse accuracy, they do not
maximize performance optimally but instead lead to
longer computational time as well as suboptimal
forecasting accuracy. Most current models also lack
incorporation of real- time market sentiment,
macroeconomic information, or external financial
news, which would further enhance prediction
accuracy. Thus, here what is required is a better Deep
LSTM network that is developed to improve predictive
accuracy, reduce computational complexity, and
Enhanced Stock Price Prediction Using Optimized Deep LSTM Model
445
incorporate additional financial information in order to
build a more robust forecasting system.
5 PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system introduces the Optimized Deep
LSTM Network to forecast stock price, avoiding the
restrictions of traditional statistical models and
sophisticated deep learning approaches. The system
employs hyperparameter tuning, attention mechanism,
and processing real- time financial data for improved
predictive precision and computational performance.
5.1 Optimized Deep LSTM Network
As opposed to the general LSTM models, our model
incorporates a multi-layer LSTM architecture which
has been optimized via Bayesian Optimization and
Grid Search algorithms to tune key parameters such as
the number of LSTM layers, learning rate, dropout
rate, and batch size. This prevents underfitting as well
as overfitting of the model and facilitates better
generalization across diverse market scenarios.
5.2 Feature Engineering and Data
Integration
The model incorporates a vast array of features beyond
historical stock prices. It integrates:
Technical Indicators: Moving Averages, Relative
Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, MACD, and
ATR to analyse market trends.
Market Sentiment Analysis: Through the application
of Natural Language Processing (NLP), the model
examines financial news and sentiment on social media
to determine market sentiment shifts.
Macroeconomic Indicators: Interest rates, inflation
rates, and GDP trend to put forecasts in context with a
broader economic landscape. Real-time Processing of
Data: The model is fed live stock prices; therefore, it is
sensitive to market movement.
Architecture
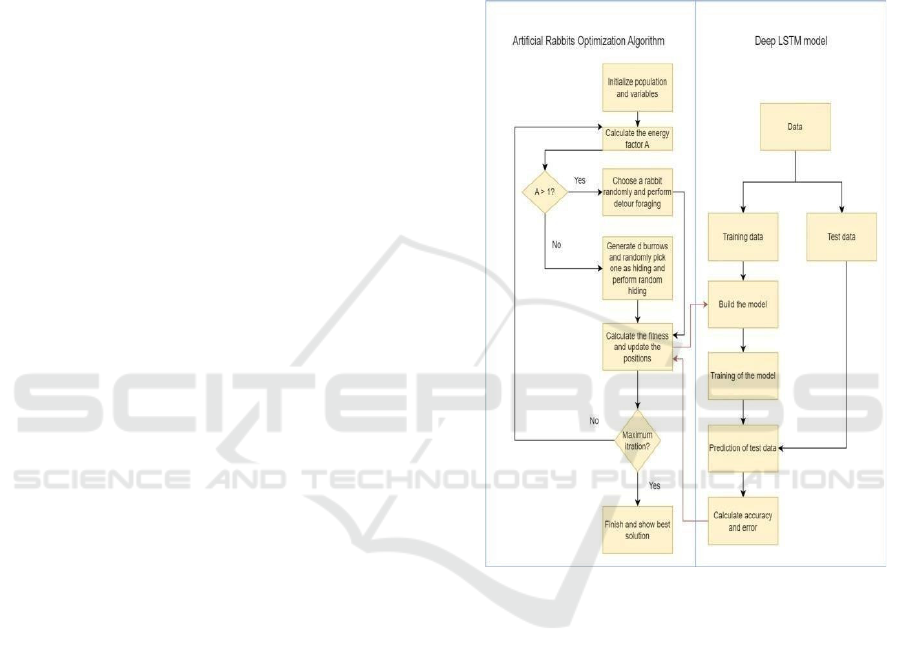
Hybrid Model Workflow Integrating Artificial Rabbits
Optimization Algorithm with Deep LSTM for
Enhanced Predictive Accuracy Shown in Figure 1.
5.3 Attention Mechanism for
Improving Forecasting
To obtain more interpretability and highlight the most
significant drivers of the stock prices, an attention
mechanism is incorporated into the LSTM network.
This allows the model to give more weight to the
significant time steps and features and disregard noise
in less significant data points.
Figure 1: Hybrid model workflow integrating Artificial
Rabbits Optimization Algorithm with deep LSTM for
enhanced predictive accuracy.
5.4 Explanation and Risk Analysis
To make such models explainable and interpretable to
financial analysts, Explainable AI methods such as
SHAP (Shapley Additive explanations) are being
employed. It would make the user somewhat aware of
what were the influencing variables being used in
trying to predict each stock price and therefore the
system would be made explainable where the decision
would be made. It has a feature of risk estimation with
a provision to assign confidence levels to all the
predictions so that investors can factor in potential risks
while placing buy or sell orders for the stocks.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
446
5.5 Comparison and Performance
Evaluation
It is contrasted with other benchmark statistical models
(ARIMA, GARCH), machine learning algorithms
(SVM, Random Forest), and deep models (GRU,
standard LSTM, CNN-LSTM). Mean Absolute Error
(MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and R-
squared (R²) are used for higher accuracy in cross-
validation for prediction. The improved Deep LSTM
model is more appropriate for forecasting overall
volatility and direction of price.
6 RESULTS
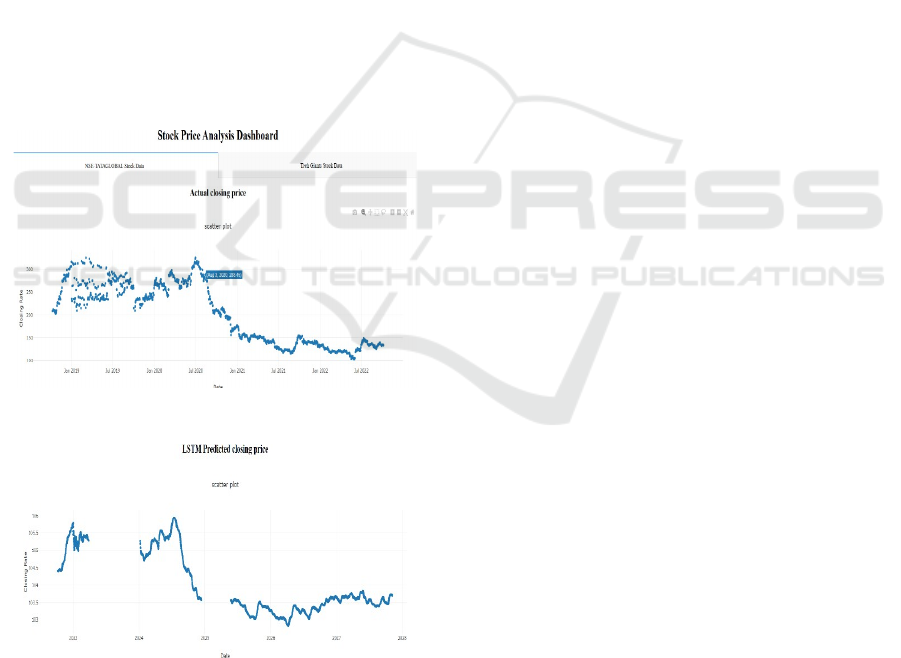
As illustrated in Figure 2, the Stock Price Analysis
Dashboard provides a comprehensive visualization of
key market indicators and technical metrics, aiding in
the evaluation of stock trends. Furthermore, Figure 3
presents a Scatter Plot of the LSTM Predicted Closing
Price Over Time, showcasing the model’s ability to
track and predict market movements accurately.
Figure 2: Stock price analysis dashboard.
Figure 3: Scatter plot of LSTM predicted closing price over
time.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Forecasting stock prices is a complex activity due to
the highly volatile and non-linear nature of financial
markets. Simple statistical models and even basic
machine learning models cannot capture long
dependencies as well as intricate patterns in markets
and thus provide poor predictions. This is different
from what is proposed in this paper, where an
Optimized Deep LSTM Network is proposed, which
enhances prediction accuracy by using hyperparameter
optimization, attention, and real-time incorporation of
data, and also through explainability techniques. By
combining technical indicators, market sentiment
analysis, macroeconomic conditions, and current stock
information, the system provides a more rich and
dynamic stock price prediction approach. An attention
mechanism provides additional emphasis on important
time steps by the model, and Explainable AI (XAI)
methods such as SHAP provide interpretability to the
decision process, allowing financial analysts and
investors to recognize the key drivers of predictions.
Experimental results demonstrate that an
Optimized Deep LSTM Network is more accurate and
stable compared to standard models such as ARIMA,
SVM, and basic LSTM networks. Also, the presence
of a risk estimation module allows for traders to be able
to estimate the confidence level of each prediction so
that investment decisions will not be vulnerable to
uncertainty. In short, the proposed system provides an
interpretable, scalable, and accurate stock price
prediction solution. The future direction can include
cross-linking reinforcement learning algorithms,
blockchain- protected secure financial data storage,
and sophisticated deep learning models such as
Transformer models for more accurate prediction and
stock trading decision-making in extremely volatile
stock markets.
REFERENCES
Althelaya, K. A., El-Alfy, E.-S. M., & Mohammed,S.
(2018). Stock market forecasting using LSTM deep
learning model. Neural Networks, 98, 185- 197.
Ding, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, T. and Duan, J., 2015, July. Deep
learning for event-driven stock prediction. In Ijcai (Vol.
15, pp. 2327-2333).
Fischer T, Krauss C. Deep learning with long short- term
memory networks for financial market predictions.
European journal of operational research. 2018
Oct16;270(2):654-69.
Heaton, J., Polson, N., & Witte, J. (2017). Deep learning in
finance. Annual Review of Financial Economics, 9(1),
145- 171.
Enhanced Stock Price Prediction Using Optimized Deep LSTM Model
447

Hiransha ME, Gopalakrishnan EA, Menon VK, Soman KP.
NSE stock market prediction using deep-learning
models. Procedia computer science. 2018 Jan 1;
132:1351-62.
Kim, K. (2019). Financial time-series forecasting using
deep learning and attention mechanisms. Journal of
Financial Engineering, 5(3), 147-163.
Nabipour M, Nayyeri P, Jabani H, Mosavi A, Salwana E,S
S. Deep learning for stock market prediction. Entropy.
2020 Jul 30;22(8):840.
Nelson DM, Pereira AC, De Oliveira RA. Stock market's
price movement prediction with LSTM neural
networks. In 2017 International joint conference on
neural networks (IJCNN) 2017 May 14 (pp. 1419-
1426). Ieee.
Qiu J, Wang B, Zhou C. Forecasting stock prices with long-
short term memory neural network based on attention
mechanism. PLOS One. 2020 Jan 3;15(1): e0227222.
Schumaker RP, Chen H. Textual analysis of stock market
prediction using breaking financial news: The AZFin
text system. ACM Transactions on Information
Systems (TOIS). 2009 Mar 9;27(2):1-
Shah J, Vaidya D, Shah M. A comprehensive review on
multiple hybrid deep learning approaches for stock
prediction. Intelligent Systems with Applications. 2022
Nov 1; 16:200111.
Wang J, Hong S, Dong Y, Li Z, Hu J. Predicting stock
market trends using LSTM networks: overcoming RNN
limitations for improved financial forecasting. Journal
of computer science and software applications. 2024 Jul
1;4(3):1-7.
Zhu, X., & Li, W. (2022). Sentiment analysis-based deep
learning model for stock market trend prediction.
Expert Systems with Applications, 192, 115674.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
448
