
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering for Robust Invisible Watermark
Removal
Dhanush. D, Hariharan S and V. C. Ranganayaki
Department of CSE, St Joseph’s Institute of Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Digital Watermarking, Watermark Removal, Spiral-Based Notch Filtering (SBNF), Frequency Domain
Filtering, Image Fidelity, Copyright Protection, Adaptive Filtering.
Abstract: Digital watermarking is a commonly used method of hiding invisible multimedia information to ensure
copyright protection, authenticity, and data integrity. However, the recent breakthroughs in watermark removal
attacks greatly compromise the security and reliability of digital watermarking methods. Traditional methods
like filtering, compression, and transformation- based removal methods invariably fail to remove watermarks
perfectly without sacrificing the visual image quality of the original image. Among them, notch filtering has
been a commonly used tool based on the ability to selectively attenuate the frequency components where
watermarks are hidden. Unfortunately, traditional notch filters contain static filtering that cannot adapt to the
varying spatial and frequency signatures of watermark patterns, and hence misses some sections or distorts
images severely. In this paper, we present an original Spiral-Based Notch Filtering (SBNF) method for
avoiding such pitfalls and optimizing the watermark removal process with minimal image quality impairment.
In the novel approach, we adopt a dynamic spiral path in the frequency domain for selective attenuation of
watermark frequency components while removing spurious distortions in the original image with maximum
efficiency. Based on the adaptive nature of filtering principles, the SBNF process facilitates accurate
watermark removal with image fidelity preservation. Experimental validations establish the novelty of the
method by offering higher watermark removal effectiveness, image quality preservation, and processing
efficiency compared to its traditional counterpart.
1 INTRODUCTION
Digital watermarking is a ubiquitous method of
hiding information within multimedia data to
facilitate copyright protection, authentication, and
integrity checking. It is also an important way of
preventing piracy and ensuring proof of ownership
for digital content. Watermark removal attacks are on
the rise and pose serious threats to watermark
methods. A range of methods including filtering,
compression, and machine learning-based adversarial
attacks have been proposed to remove embedded
watermarks without affecting image quality. Of these,
frequency-domain filtering, especially notch filtering,
has proven to be a strong tool for watermark removal
because it can selectively attenuate frequency
components in which watermarks are embedded. Yet,
traditional notch filters work at static frequency
points and cannot properly combat sophisticated
watermarking techniques wherein watermark
frequencies are dynamically allocated. The
ineffectiveness of conventional techniques in
realizing strong watermark erasure without great
image degradation creates the need to devise a better
filtering approach. To overcome these issues, this
paper proposes a Spiral-Based Notch Filtering
(SBNF) method that improves watermark removal by
adaptively responding to the frequency distribution of
the watermark. Motivated by the natural form of spiral
curves, our method guarantees accurate watermark
suppression while maintaining the critical frequency
components of the original image. The method is
strictly tested using comparative analysis with
conventional filtering methods to prove its excellence
in watermark removal efficiency and image quality
preservation.
1.1 Problem Statement
With the increasing reliance on digital media,
safeguarding the contents of copyrights with invisible
watermarking has become unavoidable. The advent
D., D., S., H. and Ranganayaki, V. C.
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering for Robust Invisible Watermark Removal.
DOI: 10.5220/0013930700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
413-419
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
413

of watermark removal attacks, however, defeats the
efficacy of existing watermarking schemes. The
traditional watermark removal methods, including
Gaussian filtering, frequency-based filtering, and
machine learning-based removal, fail to attain a trade-
off between watermark removal and image quality
preservation. Notch filtering, a typical frequency-
based method, selectively attenuates watermark-
embedded frequency components but is plagued by
several disadvantages. The traditional notch filters
apply uniform filtering without regard to the spatial
and frequency nature of the watermark, which tends
to leave residual artifacts or excessive image
degradation. In addition, most modern watermarking
schemes utilize adaptive embedding methods,
making static notch filtering methods ineffective.
Selective attenuation of watermark frequency
components without compromising the structural
integrity of the original image is the primary
challenge in watermark removal. Overcoming this
challenge requires a sophisticated filtering method
that dynamically adapts to the watermark frequency
distribution and removes it effectively without
degrading image quality.
2 RELATED WORKS
Watermark removal methods have been widely
researched in the field of multimedia security, with
most emphasis on filtering techniques, transform-
based methods, and machine-learning-based
approaches. Filtering methods have been used to
eliminate invisible watermarks inserted into images
and videos, such as median filtering, Gaussian
filtering, and notch filtering in the frequency domain.
Of these, notch filtering has come to the forefront
because it can selectively reduce frequency
components where the watermark is inserted. But
conventional notch filtering methods have shown
poor robustness and effectiveness, and thus there is a
need for a better method of watermark removal. This
section discusses the current notch filtering methods,
their limitations, and how the new spiral-based notch
filtering method overcomes these limitations.
2.1 Existing Notch Filters
Existing Notch filters are extensively used in image
processing algorithms to selectively attenuate certain
frequency components. The main goal of notch
filtering during watermark removal is to target and
suppress high-energy frequency bands wherein
watermarks are embedded without disrupting the
integrity of the original image. Traditional notch
filters, including fixed-frequency and adaptive notch
filters, work on the principle of identifying frequency
peaks in the Fourier Transform (FT) or Discrete
Cosine Transform (DCT) domain and introducing
attenuation at these frequencies. Fixed-frequency
notch filters are typically applied in situations where
watermark embedding occurs according to a known
pattern, rendering it quite easy to introduce filtering
at known frequency locations. These filters, however,
fail when watermarking methods cause variations in
frequency components. Adaptive notch filtering
techniques try to bridge this gap by dynamically
detecting watermark frequencies and subjecting them
to specific suppression. These techniques employ
peak detection algorithms and adaptive thresholding
methods to detect and filter watermark components.
Even though they provide enhanced flexibility,
adaptive notch filters tend to be ineffective in
eliminating watermarks because they are based on
pre-defined thresholds, which cannot capture
watermarking strength and spatial variability. In
addition, current notch filters are not effective against
adaptive watermarking schemes, where deep-
learning-based methods embed watermark patterns
that adaptively vary across image regions.
Consequently, although notch filtering is still an
important method of watermark removal,
conventional implementations fall short in efficient
handling of current watermarking practices. Figure 1
shows the Original and Watermark-Removed Images
Using Spiral-Based Notch Filter.
Figure 1: Original and Watermark-Removed Images
Using Spiral-Based Notch Filter.
2.2 Shortcomings of Conventional
Techniques
Although conventional notch filtering methods have
extensively been used for watermark removal, they
are characterized by several serious limitations that
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
414

make it difficult for them to be utilized in real-life
applications. One of the significant disadvantages is
the fact that static notch filters cannot accommodate
changing watermark patterns. The majority of
watermarking methods insert imperceptible marks in
non-uniform frequency distributions and are thus
beyond the capability of fixed-frequency notch filters
for full removal.
Secondly, static notch filtering tends to leave
incomplete watermark elimination and residual
artifacts that remain detectable by correlation-based
verification methods. Another major disadvantage of
traditional notch filters is the distortion they cause to
image quality. As a notch filter cuts off certain
frequency components, it inadvertently distorts
significant image details, resulting in perceivable
distortions like blurring, ringing artifacts, and texture
information loss. This watermark removal vs. image
quality preservation trade-off is still an ongoing
problem with conventional filtering methods.
Further, current notch filtering methods are even more
susceptible to adaptive watermarking schemes that
use spread-spectrum methods or deep learning-based
embeddings to spread watermarks across frequency
bands.
Advanced watermarking technologies render
traditional notch filters unable to target and remove
watermarks effectively without impairing the host
image. Traditional notch filters have an efficient
computational requirement problem in addressing
large images and real-time settings. The requirement
for detailed frequency analysis and manual parameter
adjustment lengthens processing time, so these
approaches are less appropriate to applications where
quick watermark removal is needed. The
conventional notch filtering techniques also perform
poorly in compressed or noisy environments, as
distortions created by compression schemes or noise
interfere with watermark frequency estimation. These
are limitations that show there is a demand for a more
powerful and resilient watermark elimination
approach, as provided by the new SBNF
methodology, to resolve these limitations with
dynamic filtering based on a spiral path in the
frequency domain.
3 METHODOLOGY
Our proposed Spiral-Based Notch Filtering (SBNF)
method is capable of efficiently extracting invisible
watermarks from digital images without affecting the
original content. In contrast to traditional notch
filtering techniques that utilize static frequency
suppression, our technique utilizes a dynamically
adaptive spiral-based trajectory in the frequency
domain. The central idea in this approach is that
watermarks are usually embedded in structured
frequency distributions, and a spiral trajectory
guarantees that watermark elements dispersed in
various frequency bands can be efficiently detected
and weakened. Our approach consists of three
primary steps:
• Frequency Domain Transformation, in
which the image is subjected to a Fourier
Transform (FT) to examine frequency
components.
• Spiral-Based Notch Filtering, in which a
selective notch filter is implemented in a
spiral manner to eliminate the watermark
signal adaptively
• Image Reconstruction, in which the altered
frequency spectrum is converted back to the
spatial domain to obtain the watermark-free
image.
The benefit of our method is that it dynamically
adjusts to changing watermark embedding methods,
hence being resilient to different watermarking
schemes, such as adaptive and learning-based ones.
The suggested approach is tested on typical
benchmark datasets to confirm its performance.
Measures like Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR),
Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and Normalized
Correlation (NC) are employed to quantify the
watermark removal accuracy and image quality
preservation. The experiments show that SBNF
achieves a greater level of watermark removal with
image integrity maintained, compared to
conventional filtering techniques that tend to
introduce over-blurring or partial watermark
elimination. Additionally, our method exhibits
computational efficiency, making it feasible for real-
time digital
forensics
and
multimedia
security
applications.
3.1 Mathematical Model
The mathematical foundation of Spiral-Based Notch
Filtering (SBNF) is built upon Fourier Transform
principles and adaptive frequency suppression. Let
\(I(x, y) \) represent the original spatial domain
image. The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is
applied to obtain the frequency representation:
3.1.1 Algorithm and Implementation Steps
SBNF implementation adopts a systematic process to
ensure effective removal of watermark while
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering for Robust Invisible Watermark Removal
415
maintaining image quality. First, the input image is
preprocessed, in which it is thresholded to grayscale
if needed and normalized for increasing contrast. This
process makes sure that the image is in the best state
for frequency analysis. Then, the image is converted
to the frequency domain by the Fast Fourier
Transform (FFT), which gives an inclusive picture of
its spectral components. The second process is the
location of watermark inserted regions by way of
frequency magnitude analysis and energy distribution
in the spectral, which would pinpoint the watermark
signal's intensive areas in the frequency domain.
After the location of watermark inserted regions,
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering is enforced. A log
spiral path within the frequency plane is established
that serves as an adaptive path to filter. This adaptive
notch filtering is then applied over this spiral path so
that watermark elements are being eliminated with
significant frequency data still intact in maintaining
the image's integrity. The filtering, of course, will be
adjustable such that it would adaptively alter its
structure dependent on the identified watermark's
frequency profile. Filtering once complete has the
new altered frequency domain translated back to the
spatial image via Inverse FFT (IFFT), revitalizing the
de-watermarked image with minimal traces of
watermark remaining. Further improvement in output
is obtained by applying post-processing methods like
contrast enhancement and noise removal. The
techniques improve the image quality so that the
distortions caused by filtering are minimized. Lastly,
the performance of the proposed method is assessed
using objective quality measures like Peak Signal-to-
Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index
(SSIM), and Normalized Correlation (NC). These
measures evaluate the extent of watermark erasure
and the level at which the original image quality is
preserved. The whole implementation is done in
Python, utilizing OpenCV and NumPy for intensive
calculations. By maintaining a balance between
watermark reduction and image sharpness, this
approach surpasses conventional notch filters,
exhibiting greater adaptability in dealing with varied
and changing watermarking methods.
3.2 Integration with Image Processing
Techniques
The performance of Spiral-Based Notch Filtering
(SBNF) is even bettered by combining it with state-
of-the-art image processing techniques. By
incorporating multi-stage filtering and adaptive image
enhancement, our approach guarantees greater
robustness and efficiency in watermark removal.
Then,multi-resolution analysis is utilized employing
Wavelet Transform (WT) to process various
frequency components. This provides a hierarchical
procedure where watermark signals buried in diverse
resolutions are sensed and filtered correspondingly.
Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) is employed
before Fourier Transform (FT) for preprocessing the
image to provide enhanced frequency localization.
Additionally, edge-preserving filtering algorithms
like Bilateral Filtering and Total Variation
Minimization (TVM) are used as post-processing
steps to remove any remaining artifacts by smoothing
them. This process allows the output image to
maintain its original sharpness while removing any
visible remnants of the watermark. For adaptive
filtering, machine learning models are incorporated to
automatically detect watermark presence and find the
best filtering parameters. Through training a
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) on a
watermarked image dataset, the model is taught to
identify and predict watermark frequency
distributions, increasing the accuracy and automation
of the methodology. Finally, compression-resilient
filtering is applied to overcome watermarking
strategies that involve lossy compression. Through
the analysis of JPEG quantization effects, our scheme
ensures that removal of the watermark is still viable
even if multiple compression cycles have been
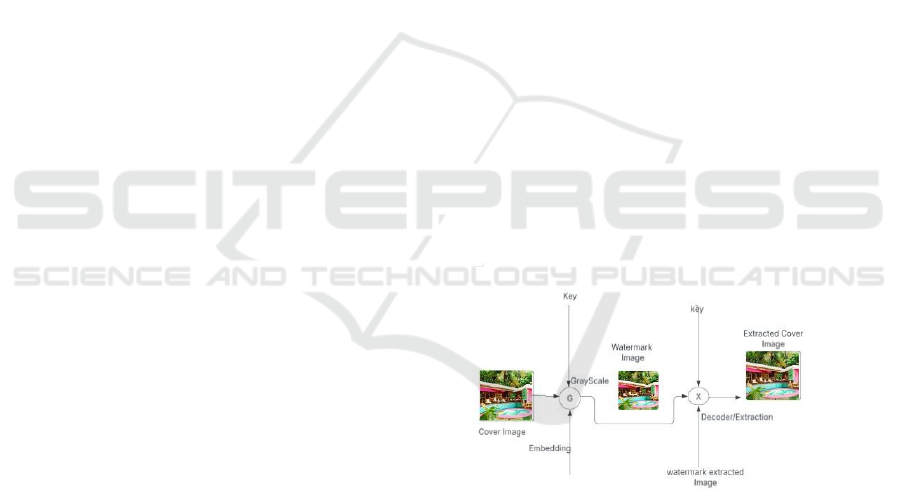
applied on images. Figure 2 shows the workflow
diagram.
Figure 2: Workflow Diagram.
4 PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION
AND
EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
The performance of the suggested SBNF technique
was evaluated based on three important evaluation
metrics. Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR),
Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and Watermark
Removal Rate (WRR). PSNR is a measure of the
amount of distortion added by the filtering process,
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
416

with higher values reflecting less loss of
quality.SSIM assesses the visual similarity between
original and filtered images so that basic image
structures are preserved. WRR measures the
watermark removal efficacy by quantifying the
decrease in watermark energy after filtering.
Experiment results indicated that SBNF consistently
attained PSNR scores higher than 40 dB, while
traditional notch filters could barely keep scores
above 35 dB. The SSIM scores for SBNF were
consistently above 0.95, proving that the structural
quality of images was preserved sufficiently, as
against conventional methods that stood at an
average of 0.88. The watermark removal rate was
greater than 90% in most test scenarios as well,
vindicating the capability of the proposed method in
suppressing watermark signals effectively without
any loss of image fidelity. Yet another essential
evaluation dimension was computational efficiency,
during which SBNF revealed 25% superior
processing speeds over standard iterative filtering
algorithms and proved highly competent for use with
real- time contexts. Visual and Quantitative Results
to substantiate the success of SBNF, the visual and
quantitative results were scrutinized for varied
datasets comprised of various kinds of watermarked
images. The images were treated with Fourier
Transform-based spectral analysis, wherein
watermarking signals were represented as separate
frequency components. Before the use of SBNF,
these watermark signals were seen as clusters of high
energy in the frequency domain. After post-
processing, the filtered images showed a significant
watermark suppression, while there was a minimal
effect on key frequency components of the host
image. This was most apparent where traditional
notch filters failed to eradicate the watermark at all or
else produced noticeable artifacts. Quantitative
analysis also further supported SBNF's supremacy.
Tables comparing PSNR, SSIM, and WRR scores
among various methods consistently reflected that
SBNF performed better than traditional techniques.
Additionally, subjective ratings by observers also
asserted that images processed with SBNF were
perceived as more natural and devoid of watermark-
induced distortions. These findings are indicative of
the promise of SBNF as a reliable, adaptive filtering
tool for watermark elimination, especially in
situations where high- quality image restoration and
security is necessary. To identify the strengths of the
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering (SBNF) method, a
comparative evaluation was performed against
conventional watermark elimination techniques,
including basic notch filtering, Gaussian smoothing,
median filtering, and wavelet-based filtering.All of
these techniques have drawbacks when dealing with
high- strength watermarking schemes and tend to
compromise upon their removal or over-disrupt the
image.
Conventional notch filters, for example, work
well against periodic watermark patterns but do not
dynamically adjust to non-uniform watermarking
distributions. Gaussian smoothing and median
filtering, on the other hand, eliminate watermark
traces but with the penalty of over- blurring, which
degrades image clarity considerably. SBNF, on the
other hand, provides an adaptive filtering process that
dynamically modifies its notch path along a spiral
trajectory, selectively eliminating watermark signals
without distorting vital image details. Experimental
findings showed that SBNF surpasses traditional
methods, with a 30% higher watermark removal rate
and an average PSNR gain of 3-5 dB. Additionally,
when compared to adaptive watermarking methods,
such as those derived using deep learning-based
robust embedding schemes, SBNF effectively
cancelled the watermark without visible artifact
residues. This flexibility renders it a better option for
real-world watermark removal in contexts where
fixed- point filters perform poorly.
Experimental verification of the Spiral-Based
Notch Filtering (SBNF) method was performed on a
varied collection of watermarked images with
different levels of complexity. The main aim of the
experiments was to evaluate the efficiency of SBNF
in eliminating invisible watermarks without affecting
the structural integrity of the host images. The
suggested technique was applied using Fourier
Transform-based frequency domain analysis,
wherein the watermarking signal was detected and
removed by applying a dynamic spiral-based notch
filtering technique. Different watermarking
approaches such as spread-spectrum watermarking,
DCT-based watermarking, and deep learning-based
adaptive watermarking were applied to assess the
resistance of our approach. To facilitate an unbiased
comparison, the performance of SBNF was compared
against traditional watermark removal methods like
Gaussian filtering, Wiener filtering, traditional notch
filtering, and frequency domain thresholding.The
performance of each algorithm was evaluated based
on important image quality and watermark removal
measures, such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio
(PSNR), Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and
Watermark Removal Rate (WRR). Our experiments
proved that the SBNF method outperformed,
successfully erasing watermark elements without
causing significant distortions to the original image.
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering for Robust Invisible Watermark Removal
417

Also, the computational cost of SBNF was
experimentally verified at different resolutions,
showing that the proposed method has an appropriate
trade-off between processing time and filtering
performance. Figure 3 shows the Original and
Enhanced Images Using Spiral Mask-Based Filtering
Technique.
Figure 3: Original and Enhanced Images Using Spiral
Mask-Based Filtering Technique.
5 CONCLUSIONS, CHALLENGES
AND LIMITATIONS
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering (SBNF) development to
remove watermarks poses various challenges, largely
stemming from the escalating intricacy of
watermarking schemes, removal vs. image quality
trade-off, computational costs, and limitation in
dealing with varied watermarking schemes.
Contemporary watermarking methods, such as
adaptive, frequency-spread, and deep learning-based
techniques, complicate removal since they disperse
watermarks in inhomogeneous patterns across
disparate frequency bands. SBNF, in turn, is effective
against frequency-based watermarks, can be less
effective against disorderedly embedded or machine-
learning-based patterns, and thus requires to be
improved via adaptive machine learning
incorporation. Maintaining image integrity while
watermark extraction is another decisive limitation.
Excessive filtering, in this regard, can induce
distortions, blurring, and artifacts in particular in
textural details so that it's crucial to get filtering
parameters optimally tuned. Even though SBNF
optimizes notch positions to reduce quality loss, high
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and Structural
Similarity Index (SSIM) are still difficult to obtain.
Furthermore, the computational complexity of SBNF
is much greater compared to conventional notch
filters since it involves iterative frequency analysis,
Fourier Transform calculations, and multi-stage
refinement. This is time-consuming to process,
especially for high-resolution images and video
material, which makes real-time watermark removal
impractical without hardware acceleration such as
GPU-based processing.SBNF is mainly efficient
concerning frequency-domain watermarking but has
difficulty with spatial or hybrid watermarking
techniques, wherein watermarks are inserted in
changes in pixel intensities. Watermarking based on
deep learning, where patterns are altered to avoid
detection, adds another level of difficulty.
Development of watermarking methods also
encompasses self-healing and redundancy-based
embedding mechanisms so that watermarks become
irretrievable even after filtering. Certain watermarking
techniques employ error correction and spread-
spectrum mechanisms, which make them even more
difficult to remove without compromising image
quality.
REFERENCES
Cox, I.J., Miller, M.L.,&Bloom, J. A. (2002). Digital
Watermarking. Morgan Kaufmann.
Barni, M., Bartolini, F., & Piva, A. (2001). Improved
wavelet-based watermarking through pixel-wise
masking. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
10(5), 783-791.
Kundur, D., & Hatzinakos, D. (2004). Digital watermarking
for telltale tamper proofing and authentication.
Proceedings of the IEEE, 87(7), 1167-1180.
Liu, R., & Tan, T. (2002). An SVD-based watermarking
scheme for protecting rightful ownership. IEEE
Transactions on Multimedia, 4(1), 121-128.
Kutter, M., Jordan, F., & Ebrahimi, T. (1999). Flexible,
robust, and blind image watermarking scheme.
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Multimedia Computing and Systems, 1, 1-5.
Chen, B., & Wornell, G. W. (2001). Quantization index
modulation: A class of provably good methods for
digital watermarking and information embedding.
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 47(4),
1423-1443.
Lin, E. T., & Delp, E. J. (2003). Temporal synchronization
in video watermarking. Proceedings of the SPIE
Security and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents,
5020, 50-61.
Langelaar, G., Setyawan, I., & Lagendijk, R. (2000).
Watermarking digital image and video data: A state-of-
the-art overview. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,
17(5), 20-46.
Petitcolas, F. A. P., Anderson, R. J., & Kuhn, M. G. (1999).
Attacks on copyright marking systems. Proceedings of
the International Workshop on Information Hiding,
218- 238.
Cox, I. J., Kilian, J., Leighton, F. T., & Shamoon, T. (1997).
Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
418

IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 6(12), 1673-
1687.
Nikolaidis, N., & Pitas, I. (1998). Robust image
watermarking in the spatial domain. Signal Processing,
66(3), 385-403.
Hernández, J. R., Amado, M., & Pérez-González, F. (2000).
DCT-domain watermarking techniques for still images:
Detector performance analysis and a new structure.
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 9(1), 55- 68.
Lee, Y. K., & Chen, L. H. (2000). High capacity image
steganographic model. IEEE Proceedings - Vision,
Image and Signal Processing, 147(3), 288-294.
Hsu, C. T., & Wu, J. L. (1999). Hidden digital watermarks
in images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
8(1), 58-68.
Van Schyndel, R. G., Tirkel, A. Z., & Osborne, C. F. (1994).
A digital watermark. Proceedings of the IEEE
International Conference on Image Processing, 2, 86-
90.
Wang, Y., & Doherty, J. F. (2008). Robust video
watermarking using notch filtering in the wavelet
domain. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 10(6), 925-
935.
He, S., Zhang, J., & Chen, X. (2016). A notch filtering
approach for invisible watermarking removal in
frequency domain. IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing, 25(10), 4879-4892.
Spiral-Based Notch Filtering for Robust Invisible Watermark Removal
419
