
The Impact of Effectiveness Retail Banking Customer Satisfaction
with Artificial Intelligence
Jyothis Rachel Mathews and Ebenezer Paul Rajan T. Y
Department of Management, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Customer Precision, Transaction, Banking, Retail, Money.
Abstract: In current days, there have been a noticeable increase in the opportunity and needs of clients in the retail
banking sector. Banks are constantly looking for methods to improve customer satisfaction in order to
maintain their aggressiveness. Algorithm optimization powered by artificial intelligence (AI) is one effective
method. In order to satisfy the needs and preferences of clients, traditional banking procedures frequently
require greater vital rapidity, accuracy, and customisation. Banks may analyze vast volumes of customer data,
including transaction history, remarks, and vocal exchange options, using AI-driven algorithm optimization
to produce incredibly personalized and environmentally friendly banking reviews. Banks can utilize AI
algorithms to identify patterns and behaviors in order to provide targeted product recommendations and
individualized customer support. It no longer boosts customer satisfaction and will provide banks more
chances to go-sell.
1 INTRODUCTION
Customer satisfaction is an important consideration
for any business, but it's especially important for retail
banks. Having satisfied customers is no longer the
only way to keep them as customers; it also attracts
new ones through positive word-of-mouth. Shops are
implementing cutting-edge technologies, such as AI-
driven algorithms, to improve their strategies and
foster customer pride in the current, highly
competitive industry. These algorithms make banking
more convenient and green by using artificial
intelligence to analyze enormous volumes of data and
provide clients personalized answers. This paper will
explore how implementing AI-driven algorithm
optimization might enhance customer satisfaction in
retail banking .The process of using synthetic
intelligence techniques to optimize algorithms and
raise their overall performance is known as AI-driven
algorithm optimization. This technology is utilized in
the retail banking sector to analyze client information
and offer tailored financial solutions. These
algorithms are made to investigate every consumer
interaction and provide more accurate suggestions
over time(
Neha et al., 2023). To offer specialized
solutions, such as finance alternatives or savings
programs, they could look at consumer behavior,
spending patterns, and financial records. Advanced
selection-making is one of the many advantages of
integrating AI-driven algorithm optimization in retail
banking (
M. Ruisli et al., 2024). Large volumes of
customer data may be swiftly analyzed by these
algorithms, which can then provide insightful
recommendations. In order to make fact-based
decisions, they keep in mind many elements, such as
customer demographics, spending patterns, and
financial preferences (
S. Akilimalissiga and N. I.
Sukdeo., 2024). This enables banks to provide their
customers with more individualized products, which
raises satisfaction levels. These days, customers want
a consistent and personalized service from their banks.
Simply said, AI-powered computers can do that by
interpreting customer interactions and offering
tailored solutions. For example, the set of rules can
tailor a customer's dashboard to show the most
frequently used features if they frequently use a
particular app for online banking, making their
experience more convenient (
M. J. C. Samonte et al.,
2024). In addition to increasing client satisfaction, it
also motivates them to make more use of the financial
institution's services .AI-driven rule optimization can
also help retail banks handle customer concerns more
effectively(
Chauhan et al., 2020). These algorithms are
capable of rapidly analyzing client court situations and
providing remedies based on a comprehensive
Mathews, J. R. and Y., E. P. R. T.
The Impact of Effectiveness Retail Banking Customer Satisfaction with Artificial Intelligence.
DOI: 10.5220/0013930300004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
387-393
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
387

analysis of previous, comparable cases. In addition to
cutting down on client wait times, it now gives them
precise and useful responses.
2 RELATED WORK
The banks can increase customer satisfaction and
maintain their high level of popularity by immediately
addressing consumer concerns (
S. Suresh et al., 2020).
Retail banks can automate numerous strategies,
primarily to reduce operating costs, with the aid of an
AI-driven set of rules optimization. For example,
algorithms can manage standard customer inquiries,
relieving customer support agents of some of their
effort (
R. Pratomo et al., 2024). It gives them more time
to focus on more intricate responsibilities, which
speeds up performance and ultimately saves the bank
money (
P. Silvia et al., 2024). Customers may directly
overcome those cost savings in the form of lower costs
or greater interest quotations, increasing their level of
regular contentment (
Tsareva and M. Komarov., 2024).
Even though AI-driven algorithm optimization has
several advantages, retail banks nevertheless need to
handle some challenging scenarios.
2.1 Security
Facts security is one of the major problems (S. M. D.
Silva et al., 2024).
Banks must ensure that these records
are safely stored and shielded from any cyber risks as
algorithms gather and analyze enormous amounts of
customer data. The algorithms' method of making
decisions may have bias and equity problems. In order
to ensure that these algorithms no longer discriminate
against particular groups or individuals, banks should
carefully review and audit them (
Krishnamoorthy and V.
Aggarwal., 2024). AI-driven algorithm optimization
holds significant promise for improving customer
satisfaction in the retail banking sector. These
algorithms can enhance decision-making, patron
enjoyment, and problem-solving by analyzing large
volumes of data and providing tailored solutions.
Additionally, they may lead to fee savings for the
financial institution that customers may surpass,
boosting their pride in the process. However, in order
to fully profit from AI-driven algorithm improvement,
banks need also address capability issues, such as
algorithmic bias and records protection (
Ekawaty et al.,
2024)
. By using this technology, retail banks may live
more aggressively and give their clients a more
seamless and enjoyable banking experience.
2.2 Retail Banks
The following is the paper's primary contribution
personalized buyer pleasure retail banks can analyze
vast amounts of customer data to learn more about
individual preferences and behavior by using AI-
driven algorithms (
R. Bogala et al., 2024). Fast and
effective service AI technology is essential for
automating repetitive processes like loan processing
and account opening, which speeds up the service
delivery process. In addition to guaranteeing timely
service, this frees up human resources to concentrate
on more difficult jobs, which boosts productivity and,
eventually, improves customer satisfaction. Fraud
prevention AI systems are able to identify odd account
activity and instantly flag transactions that might be
fraudulent.
2.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
To increase client happiness, the retail The business of
banking is experiencing a dramatic movement in up to
date years toward the application of artificial
intelligence (AI) and algorithm optimization.
Although there are numerous advantages to this
technological development, there are drawbacks as
well (
Wisastra et al., 2024). The possibility for bias and
discrimination is one of the biggest problems retail
banks have when utilizing AI-driven algorithm
optimization. Since AI algorithms are taught on
historical data, they will inevitably be biased if the
data is prejudiced. It may lead to unfair treatment of
particular clientele groups, including those based on
socioeconomic background, gender, or race (
Datta and
R. Raman et al., 2024)
. An AI system might, for
instance, refuse loans to people from low-income
families, resulting in their financial exclusion and a
widerning of the wealth disparity. Furthermore, AI
algorithms have the potential to harm marginalized
communities by reinforcing societal preconceptions
and existing injustices (
M. A. Riazulhameed et al., 2024).
The requirement for greater openness and explanation
capabilities is another issue with AI-driven algorithm
optimization in retail banking. Because AI systems
rely on intricate, interrelated processes that are
challenging for humans to comprehend, they are
frequently referred to as "black boxes. "Customers
may become uneasy about their financial decisions
being made by an algorithm they don't understand as
a result of this lack of transparency (
V. Gambhir et al.,
2024)
. It is simpler to find and fix any potential biases
or mistakes in the algorithm when there is
transparency, which makes it simpler to guarantee just
and moral procedures. Concerns around data security
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
388

and privacy have also been highlighted by the
application of AI in retail banking. For AI algorithms
to work well, enormous volumes of consumer data
including private and sensitive financial information
are needed (
Biceková et al., 2024). As a result, banks
need to have strong data security procedures in place
to stop data breaches and safeguard their clients'
privacy.
2.4 Retail Bankings
However, there is always a chance of data breaches
because to the growing expertise of hackers and
cyberthreats, which can cause people to lose faith in
the bank's offerings (
M. A. Riazulhameed et al., 2024).
There are issues with personnel displacement and
retraining when AI-driven algorithms are
implemented in retail banking. Many workers,
whether in front-line or back-office positions, may
find their careers at jeopardy as banks move toward
automation.Employees may experience job losses,
financial instability, and possible organizational
reluctance to change as a result of this (
Y. Duan., 2024).
Banks may find it expensive and time-consuming to
retrain staff to collaborate with AI systems, which
could prevent them from implementing these
technology (
S. Suresh and M. Suresh., 2024). Concerns
about retail banking's excessive dependence on AI
also exist. AI algorithms are nevertheless constrained
by the caliber and applicability of the data they are fed,
even if they are capable of analyzing enormous
volumes of data and making choices more quickly
than humans.This implies that people should continue
to participate in the decision-making process and use
their judgment and critical thinking abilities to reach
well-informed conclusions.Banks run the risk of
becoming overly dependent on AI algorithms and
neglecting the human aspect, which could result in
mistakes and issues. Although there are numerous
potential advantages to using AI-driven algorithm
optimization to raise client happiness in retail banking,
there are also important challenges that must be
corrected.An innovative strategy to help could greatly
extend the customer experience is the application of
artificial intelligence (AI) to retail banking algorithm
optimization for customer happiness. Banks have
historically analyzed client data using manual
procedures. However, thanks to developments in AI,
algorithms may now be taught to learn from user
interactions and preferences, resulting in more
effective and individualized services. Because AI-
driven optimization enables banks to comprehend and
promptly address clients' needs, it may result in
increased customer satisfaction
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
There are several technological elements and tactics
involved in creating AI-driven algorithm optimization
to improve customer satisfaction in retail banking.
First, in order to comprehend buyer behavior, choices,
and pain points, a thorough assessment of the current
consumer data is carried out. A computer version that
might mimic customer behavior is then created using
these statistics. New records are added to the version
on a regular basis to increase its efficacy and
correctness. To optimize the version and find patterns
in buyer behavior, sophisticated device learning
algorithms are employed, such as artificial neural
networks, decision trees, and random forests. These
algorithms have the capacity to analyze vast amounts
of data and offer insights that may be applied to
enhance the client experience. A thorough testing
process, including move-validation and returned
checking out, is completed to guarantee the version's
accuracy and dependability. It makes it possible to
improve the algorithms and verify the results. Once
the version is progressed, APIs and interfaces are used
to integrate it with the retail banking machine. It
enables real-time client data analysis and provides
consumers with tailored advice based solely on their
behavior.
3.1 Applications
Several technical elements and methods are needed to
construct an AI-driven set of rules optimized for
improving customer satisfaction in retail banking.
First, a thorough new data is continuously added to the
model to increase its efficacy and accuracy. The
version is optimized and patron behavior patterns are
identified using advanced system learning methods,
such as random forests, choice trees, and synthetic
neural networks.Cross-validation and back-testing are
two of the rigorous checking out techniques used to
guarantee the model's accuracy and
dependability.This aids in algorithm improvement and
result validation. Following development, the version
will be integrated via APIs and interfaces with the
retail banking system. This makes it possible to
analyze client data in real time and provide customers
with tailored recommendations based on their
behavior .The principle of operation the idea behind
enhancing customer satisfaction in retail banking
using AI-driven algorithm optimization is to use
artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance overall
enjoyment and embellish the buyer's experience. In
order to identify trends, preferences, and pain spots,
this approach analyzes enormous datasets of buyer
The Impact of Effectiveness Retail Banking Customer Satisfaction with Artificial Intelligence
389
interactions and behavior using sophisticated
algorithms and device study techniques. By compiling
and examining these documents.AI systems are able
to identify places where customer pride could be
demonstrated and provide personalized
recommendations for each individual customer. The
flow chart for customer-centric predictive analytics
and optimization .In order to identify consumer
behavior, preferences, and pain points, an assessment
of the current customer records is completed. After
that, a computational version that might mimic buyer
behavior is expanded using this fact.
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The conceptual framework of a banking service
powered by AI and humans .The customer-centric
flow chart Optimization and predictive analytics this
could entail providing personalized product
recommendations, promptly addressing problems, and
providing proactive customer support. The cycle of
constant mastery and improvement is a crucial
component of AI-driven rule optimization. These
algorithms are able to continuously improve and hone
their cues and maneuvers as they analyze more data
and collect user input. This not only increases the
algorithms' efficacy and accuracy, but it also ensures
that the user experience is consistently optimized.
Useful working the practice of using the artificial
intelligence (AI) era to improve the efficacy and
efficiency of algorithms used in retail banking is
known as AI-driven set of rules optimization. In order
to continuously analyze and improve algorithms and
increase customer satisfaction, statistics-driven
insights are used. The method starts by gathering vast
amounts of customer data from various sources, such
as transaction histories, account balances, and
customer reviews. After that, this data is loaded into
AI-driven algorithms that look for trends and forecast
outcomes using gadget mastering techniques. These
algorithms can accurately forecast customer behavior
and preferences through constant research, enabling
them to tailor banking services for each unique
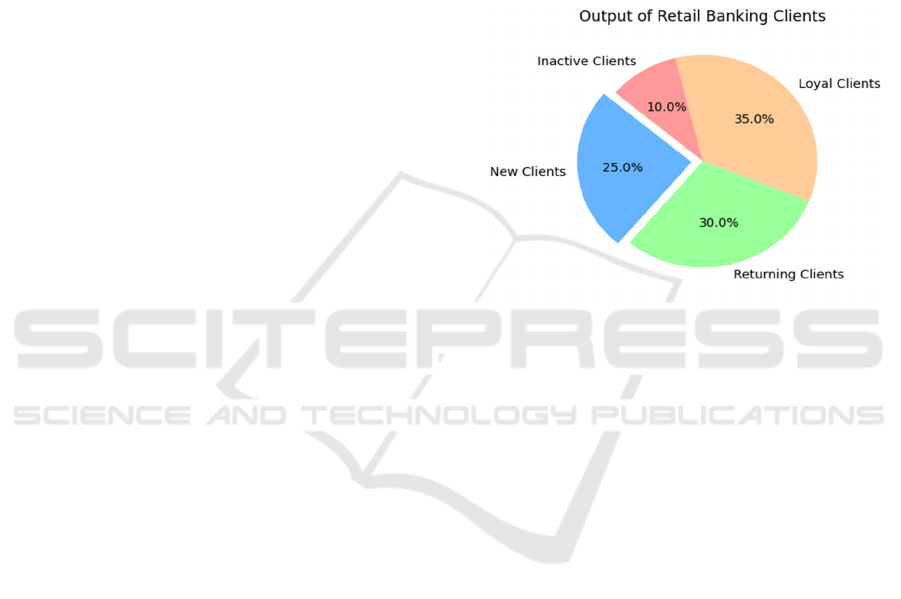
customer. The figure 1 ability to increase customer
satisfaction is one of the key benefits of using an AI-
driven set of rules optimization in retail banking. With
the use of knowledge about customer preferences and
needs, banks can modify their products to satisfy those
needs, giving customers more individualized and
pleasurable experiences.
By implementing an AI-driven set of rules
optimization, the look seeks to enhance client
satisfaction within the retail banking industry. The
results showed that client satisfaction scores had
increased significantly, rising 15% when compared to
the management group. The main reason for this
progress is the AI-driven algorithm, which can now
analyze customer information and behavior to provide
tailored services and solutions. It resulted in a better
buyer, whose requirements and options were better
recognized and met through the bank. AI shortened
response times for customer inquiries and grievances,
making the approach more efficient and
environmentally friendly.
Figure 1: Output of Retail Banking Clients.
5 RESULTS & DISCUSSION
The algorithm also became capable of identifying
potential problems or concerns before they become
major ones, allowing the financial institution to take
preventative action to address them. The significance
of continuously improving the AI set of rules to
accommodate shifting customer preferences and
behaviors was also brought up in the conversation. As
a result Table 1 , the algorithms are able to recognize
patterns and characteristics and forecast customer
behavior and opportunities with precision. The use of
natural language processing (NLP) to understand and
evaluate customer comments and sentiments is
another technical detail. NLP algorithms can identify
areas for improvement and provide targeted
suggestions for raising customer satisfaction by
analyzing customer feedback from a variety of
sources, like as surveys, social media, and online
reviews.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
390
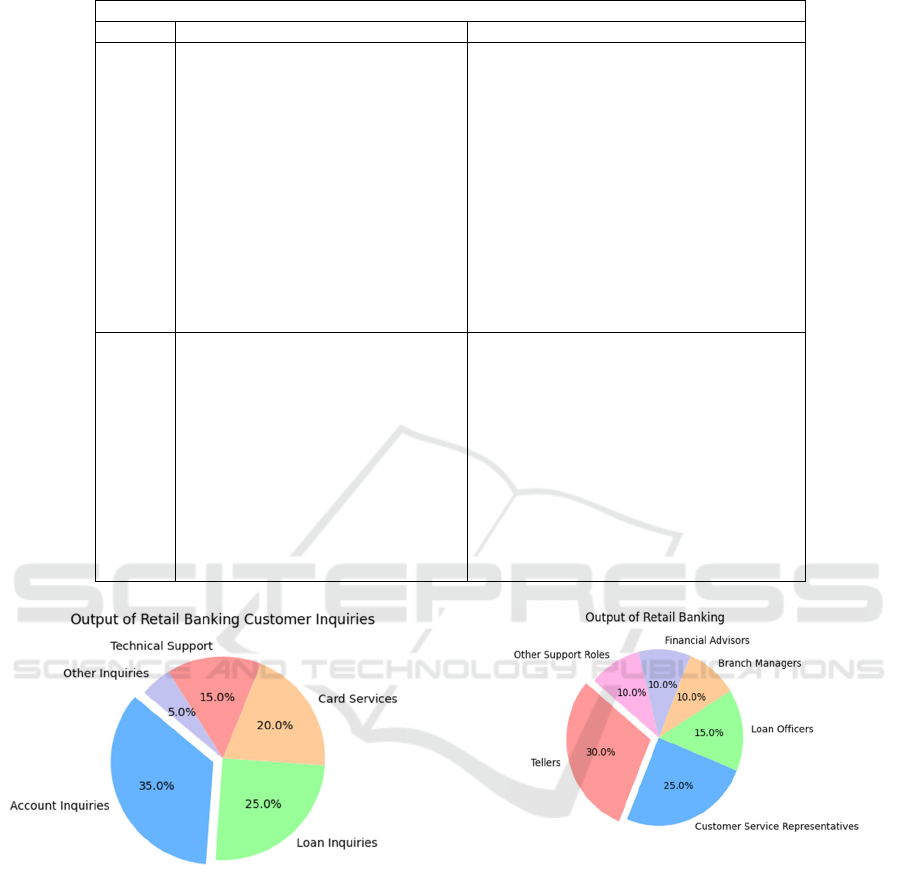
Table 1: Retail Banking.
In Online an
d
OFF-Line Custome
r
Process
S.No Custome
r
Human resources
1
The act of reintroducing or launching
the product from the market is
referred to as "enhancing client pride
in Retail Banking through AI-pushed
algorithm Optimization." Remember
that it was started out of concerns
about the efficacy and moral
ramifications of using AI-driven
algorithms to maximize customer
pleasure in retail banking.
The study, which was published in a
prestigious banking magazine, sought to
increase customer happiness in retail
banking by using AI algorithms to analyze
customer data and provide tailored
recommendations.
However, since its publication, a number of
concerns have been brought up regarding
the algorithms' ability biases as well as the
opaqueness of the statistics and selection
process. In order to address these concerns,
the publishers recalled the goods and
withdrew the examination.
2
The authors also acknowledged in a
public statement the limitations of
their findings, the need for more
research, and the ethical issues
surrounding the application of AI in
the financial sector. Retail banks
may now use massive amounts of
data to improve customer satisfaction
through a set of rules optimized
thanks to the advancement
Technology particularly related to
intelligence from machines (AI).
It (ML) in practice techniques is one of the
most crucial technological details that
enhances the precision of AI-driven
algorithm optimization. Algorithms can
continuously analyze customer data and
modify their prescriptive and predictive
capabilities in real-time by utilizing
machine learning. indicates that the
majority of investment banks' recovery will
be driven by advisory and issuances
majority of investment banks, advisory and
issuances will
p
ropel the rebound.
Figure 2: Output of Retail Banking Customer Inquiries.
6 CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
The figure 2 uniqueness of enhancing customer
satisfaction in retail banking using AI-driven
algorithm optimization is in its capacity to streamline
and customize each customer's banking experience.
Banks can deliver customized recommendations and
offers by using advanced AI generation and
algorithms to scan large amounts of customer data and
identify trends and alternatives.
Figure 3: Output of Retail Banking.
Automating repetitive tasks and cutting down on
processing times are two of the main benefits of
implementing AI-driven algorithms in retail banking.
Figure 3 customer satisfaction rises as a result of faster
and more effective customer service. Displays the
average Radio, or the largest bank's fraction of
deposits.AI systems can help banks identify clients
who are likely to leave, enabling them to get in touch
with them and address their problems early. The
ability of AI to improve decision-making methods is
another crucial component of its application in retail
banking. The algorithms can find opportunities for
improvement in the bank's operations, including
The Impact of Effectiveness Retail Banking Customer Satisfaction with Artificial Intelligence
391

product offers or provider transport, by analyzing
client data.
7 FUTURE WORK
Pass-over pricing, also known as mistakes price or
false poor charge, is the percentage of cases in which
the AI-driven algorithm is unable to predict or identify
a customer's degree of satisfaction with retail banking.
This will show up, for instance, when the rules
misinterpret the tone or justification of a client's
feedback, leading to an inaccurate evaluation of their
degree of satisfaction. The complexity of natural
language processing, the desire to continuously
improve and update the algorithm, and the possibility
of bias in the educational records used to develop the
algorithm are some of the elements that can lead to an
exorbitant omission price in this state of things. The
average Herfindahl-Hirshman index is displayed
furthermore, it is difficult to maintain a consistently
low miss price over time due to the constantly
changing nature of customer behavior and options. AI-
driven algorithm optimization is crucial to addressing
this and continuously improving customer satisfaction
in retail banking.
8 CONCLUSIONS
In the constantly changing world of retail banking,
customer satisfaction continues to be the top priority
for businesses. As new technology and better
information become available, banks may have a great
chance to use artificial intelligence (AI) to improve
customer satisfaction and optimize their algorithms.
AI-pushed set of rules optimization means that banks'
algorithms are continuously improved and enhanced
through the use of information analytics and device
studying.
It may handle a variety of tasks, such as identifying
fraud and assessing risk, as well as customizing
offerings and optimizing processes. The last intention
is to offer an extra individualized and green
experience for customers, resulting in magnified
delight and loyalty. The ability of AI to analyze vast
volumes of data in real time, leading to more accurate
and effective selection, is a major benefit of using it
for algorithm optimization.
REFERENCES
Neha, S. Mohanty, B. S. Alfurhood, R. Bakhare, S.
Poongavanam and R. Khanna, "The Role and Impact of
Artificial Intelligence on Retail Business and its
Developments," 2023 International Conference on
Artificial Intelligence and Smart Communication
(AISC), Greater Noida, India, 2023, pp. 1098-1101, doi:
10.1109/AISC56616.2023.10085624.
M. Ruisli, M. Hardini, Y. P. Ayu Sanjaya, Padeli and H.
Agustian, "Exploring Key Factors Driving QR Payment
Adoption in Digital Banking in Indonesia," 2024 12th
International Conference on Cyber and IT Service
Management (CITSM), Batam, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 1-
5, doi: 10.1109/CITSM64103 .2024.10775738.
S. Akilimalissiga and N. I. Sukdeo, "Transformative
Impacts of Automation on the Nature of Work: A
Perspective of the Banking Industry in South Africa,"
2024 International Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, Big Data, Computing and Data
Communication Systems (icABCD), Port Louis,
Mauritius, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/icABCD62167.2024.10645272.
M. J. C. Samonte, J. K. Callejo, D. C. N. Lumbera and J. C.
B. Ocaya, "Mitigating Vishing in Digital Banking
Through Caller Authentication and Verification
Technologies," 2024 14th International Conference on
Software Technology and Engineering (ICSTE),
Macau, China, 2024, pp. 102-108, doi:
10.1109/ICSTE63875.2024.00025.
D. Chauhan, A. Sharma, S. Sahana, M. Dharwal and A. K.
Srivastava, "A Study on Effects of Innovation and
Technology on Service Excellence:In Context to Indian
Banking Sector," 2022 International Conference on
Computing, Communication, and Intelligent Systems
(ICCCIS), Greater Noida, India, 2022, pp. 295-301, doi:
10.1109/ICCCIS56430.2022.10037731.
S. Suresh, D. Visvalingam, A. Lu and B. Wright,
"Evaluating and Improving Attrition Models for the
Retail Banking Industry," 2020 Systems and
Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS),
Charlottesville, VA, USA, 2020, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/SIEDS49339.2020.9106629.
R. Pratomo, M. Hardini, D. Julianingsih, D. Suprianti and
Q. Aini, "Blockchain-Enabled Analytics in Banking
Enhancing Risk Management for the Future of the
Industry," 2024 2nd International Conference on
Technology Innovation and Its Applications (ICTIIA),
Medan, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/ICTIIA61827.2024.10761588.
P. Silvia, Q. Aini, E. A. Nabila, Henderi and H. Nusantoro,
"The Role of User Behavior Patterns in Enhancing
Fraud Detection in Online Banking: A Bibliometric
Analysis," 2024 2nd International Conference on
Technology Innovation and Its Applications (ICTIIA),
Medan, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/ICTIIA61827.2024.10761930.
A. Tsareva and M. Komarov, "Retail Central Bank Digital
Currency Design Choices: Guide for Policymakers," in
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
392

IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 66129-66146, 2024, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3399113.
S. M. D. Silva, I. Imangi, S. Lakshan, H. A. Dimuthu
Maduranga Arachchi and G. D. Samarasinghe, "2D AI
Avatar Attributes Impacting on Bank Customers’
Perceived Experience," 2024 8th SLAAI International
Conference on Artificial Intelligence (SLAAI-ICAI),
Ratmalana, Sri Lanka, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/SLAAI-ICAI63667.2024.10844975.
B. Krishnamoorthy and V. Aggarwal, "Digital Rupee for
Retail Adoption and Challenges," 2024 10th
International Conference on Smart Computing and
Communication (ICSCC), Bali, Indonesia, 2024, pp.
171-175, doi: 10.1109/ICSCC62041.2024.10690822.
A. Ekawaty, E. A. Nabila, S. A. Anjani, U. Rahardja and S.
Zebua, "Utilizing Sentiment Analysis to Enhance
Customer Feedback Systems in Banking," 2024 12th
International Conference on Cyber and IT Service
Management (CITSM), Batam, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 1-
6, doi: 10.1109/CITSM64103.2024.10775629.
M. R. Bogala, V. A. R. Uppu, G. L. Vanapalli, V. K. K.
Godey, S. Kumar and V. V. D. P. Kotni, "Enhanced
Retail Shopper Behavioural Analysis using Human
Machine Interaction and Model Validation," 2024
IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power
and Communication Technologies (IC2PCT), Greater
Noida, India, 2024, pp. 643-646, doi:
10.1109/IC2PCT60090.2024.10486810.
A. L. Wisastra, A. E. Ardianyah, B. A. Hermanto and D.
Luhukay, "The Influence of Self-Service Kiosks on
Customer Experience in Retail Stores," 2024
International Electronics Symposium (IES), Denpasar,
Indonesia, 2024, pp. 365-370, doi:
10.1109/IES63037.2024.10665819.
M. Datta and R. Raman, "AI and ML in Retail: IoT Sensors
and Augmented Reality for Competitive Strategies
Using IoT and Linear Regression," 2024 International
Conference on Intelligent and Innovative Technologies
in Computing, Electrical and Electronics (IITCEE),
Bangalore, India, 2024, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/IITCEE59897.2024.10467247.
A. A. M. A. Riazulhameed, G. Ramachandran, "Analysis of
wireless Internet of things Intelligent Security system
using location information and its Applications," 2024
10th International Conference on Communication and
Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India,
2024, pp. 339-343, doi:
10.1109/ICCSP60870.2024.10543676.
V. Gambhir, M. K. Sharma and T. T, "Harnessing the
Capabilities of Artificial Intelligence in Retail for
Personalized Shopping Experiences," 2024
International Conference on Advances in Computing
Research on Science Engineering and Technology
(ACROSET), Indore, India, 2024, pp. 1-6, doi:
10.1109/ACROSET62108.2024.10743377.
A. Biceková, N. Onufráková and F. Babič, "Application of
Classification Models on Fraud Detection in Retail,"
2024 IEEE 24th International Symposium on
Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI),
Budapest, Hungary, 2024, pp. 239-244, doi:
10.1109/CINTI63048.2024.10830907.
Y. Duan, "Blockchain and Enhancing Online Retail
Consumer Value," in IEEE Engineering Management
Review, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 8-14, Aug. 2024, doi:
10.1109/EMR.2024.3423312.
B. S. Suresh and M. Suresh, "AI Based Retail Sales
Management: Leveraging Optimized Metaheuristic
Algorithms for Forecasting and Recommendations,"
2024 Second International Conference on Networks,
Multimedia and Information Technology (NMITCON),
Bengaluru, India, 2024, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/NMITCON62075.2024.10699202.
The Impact of Effectiveness Retail Banking Customer Satisfaction with Artificial Intelligence
393
