
Advanced Cavity Diagnosis and Prediction Using AI and Dental
Imaging Technologies
P. Sukumar, Rangaiyan S., Srihariraj R. C. and Thirukkumaran S.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Nandha Engineering College, Erode, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Dental Diagnosis, Cavity Detection, Radiographic Reading, Pattern Recognition, Predictive Evaluation,
Image Processing, Decision Support for Clinical Use.
Abstract: Dental health is very important to total health, but early cavities have been a persistent problem. The present
study investigates a highly sophisticated diagnostic framework which endeavors to replicate human expert
behavior in the detection and prediction of dental caries progression. Through analyzing radiographic images
and identifying subtle patterns that may be missed, the system improves accuracy and reduces errors of
judgment. A systematic learning paradigm adapts to the capability to identify involved areas, quantify
morbidity, and predict future changes. In the proposed framework, image restoration, pattern recognition, and
predictive evaluation are combined to support decision makers. Results show marked enhancement in
accuracy, and early-stage diagnosis to implement more efficient treatment planning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Tooth cavities are a most common dental disease, and
if not detected, lead to very serious problems
regarding infection, loss of teeth, and systemic
diseases. Conventional detection by simple visual
examination and radiologic scanning is greatly
influenced by the quality of work a dentist uses in
conducting these examinations and is thus subjective
as well as variant-dependent. Based on such human-
judgment- influenced dependence, incipient-stage
cavities can remain undetected, and their chances of
being treated early can therefore decrease.
New systems based on artificial intelligence (AI),
machine learning, and image processing concepts
have emerged for enhancing precision and
repeatability in the diagnostic process. These tools
classify dental images accurately and can recognize
faint patterns that are imperceptible to the human eye.
With the application of systematic learning procedures
and image examination methods such as segmentation
and feature extraction, the computerized equipment
comes to objective, repeatable conclusions with fewer
human errors. Dental professionals can make well-
informed inferences with the help of them, which
translate into effective, timely treatment as well as
better patient care and standardization of cavity
detection at health centres.
2 RELATED WORKS
Machine learning (ML) techniques have improved
cavity detection and prediction accuracy, as well as
efficiency, to a great extent. Techniques of image
processing, deep learning algorithms, as well as
optimization techniques have been employed to
improve diagnostic accuracy. Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs) and advanced segmentation
models have been employed largely because of their
ability to identify complex patterns in dental
radiographs. Hybrid approaches with integrated
multiple learning methods have also been used to
improve the diagnostic performance. Prema et al.
introduced a better CNN-based system for dental
image classification and demonstrated its
effectiveness in the detection of cavities at the early
stage at high accuracy levels
Welikala, R. A., et al.
(2020). Similarly, Verma and Rao investigated a
deep-learning hybrid model consisting of CNN and
U-Net for automatic segmentation of cavities that
improved detection accuracy through better edge
detection and feature extraction algorithms
Welikala,
R. A., et al. (2020). Their work emphasized the role of
preprocessing methods, i.e., noise filtering and
contrast adjustment, to improve the performance of
ML models. Kumar et al. proposed a learning-
basedsegmentation approach with augmented
Sukumar, P., S., R., C., S. R. and S., T.
Advanced Cavity Diagnosis and Prediction Using AI and Dental Imaging Technologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0013927700004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
321-327
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
321

learning by Vision Transformers (ViT) for dental
diagnosis with improved feature extraction
performance in the detection of cavities
Xue, Z., et al.
(2022). Sharma and Iyer introduced an attention-based
deep learning approach to increase the interpretability
of results in cavity detection, demonstrating that AI-
based models are able to reduce false positives and
negatives to a larger extent in radiographic
examination results
Jiang, H. (2023).
Hybrid machine learning techniques have also been
explored in the prediction of dental disease. Raj and
Mehta compared the impact of applying CNN with
traditional classifiers such as Random Forest and
XGBoost, representing a strength of ensemble models
towards increasing diagnostic consistency
Sulochana,
C., & Sumathi, M. (2024).
Patel et al. compared
different ML models, i.e., SVM, Decision Trees, and
Naïve Bayes, to determine the best approach for
automatic detection of cavities (
Shariff et al., 2024).
Their findings indicated that deep learning-based
approaches, if employed together with the general
classifiers, provide better performance in identifying
early-stage cavities. Even though these innovations
create strong impressions, problems such as small
annotated data, inconsistency in image quality, and
generalization persist as obstacles to dental diagnosis
using AI. Adaptive models, hyperparameter
optimization environments, and enhanced feature
selection techniques need to be integrated for further
boosting cavity detection and prediction accuracy.
Thus, for this research work, a mixed ML strategy
consisting of CNNs, U-Net, and Vision Transformers
and ensemble methods is suggested for establishing a
strong and clinically applicable diagnosis system.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The proposed method utilizes deep learning models to
search dental radiographic images for both automatic
cavity detection and prediction. Developed for use in
a clinical support system, the model searches dental
X-rays to highlight areas of cavity damage accurately.
Utilizing advanced image segmentation methods,
such as U-Net and Grad-CAM, the system highlights
potential cavities and predicts their growth based on
historic patient data. After sensing the early signs of
degradation, the system provides real-time diagnostic
feedback to aid dentists in making correct treatment
decisions. Future enhancements include cloud-based
connectivity and real-time AI-driven examination for
improved clinical productivity.
3.1 Data Collection
Dental radiography images employed within this
study were gathered from the clinical sources,
including dental clinics, hospitals, and public data
bases
Xing, W., et al. (2024). The database contains
different types of images reflecting different dental
pathologies, grades of cavities, and resolution to
support rigorous analysis. Dental conditions
represented within the images span from early-stage
cavities to deep cavities, enamel decays, and other
abnormalities for a balanced set of training and testing
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020).
All the patient information was anonymized
rigorously prior to processing to maintain ethical
standards, ensuring privacy policy compliance and
avoiding any possible identification of patients
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020). The table 1 shows
Distribution of Dental Radiographic Images by
Condition and Resolution. dataset was properly
selected to include high-quality radiographs but reject
low-resolution or blurry ones in order to boost model
performance. Moreover, images of patients belonging
to various ethnicities and age groups were used to
enhance the generalization ability of the model
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Table 1: Distribution of Dental Radiographic Images by
Condition and Resolution.
Class No of Images Image Resolution
Healthy Teeth 1,200 1024×1024
Early Cavities 950 1024×1024
Deep Cavities 850 1024×1024
3.2 Image Preprocessing
To improve the visibility and utilization of dental
radiographs for processing in AI, certain
preprocessing operations were performed. Noise
reduction was carried out by utilizing the aid of
Gaussian and median filtering in order to remove
artifacts and enhance image quality
Xing, W., et al.
(2024).
The figure 1 shows the Dataset preprocessing
and augmentation for U- Net 3+ training. To amplify
contrast, contrast manipulation strategies like
histogram equalization and CLAHE (Contrast
Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization) were
utilized for enhancement of discrimination between
affected cavity regions and healthy teeth
Shamim, Z.
M., et al. (2020).
Segmentation was also done with the
help of a U-Net model that was capable of detecting
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
322
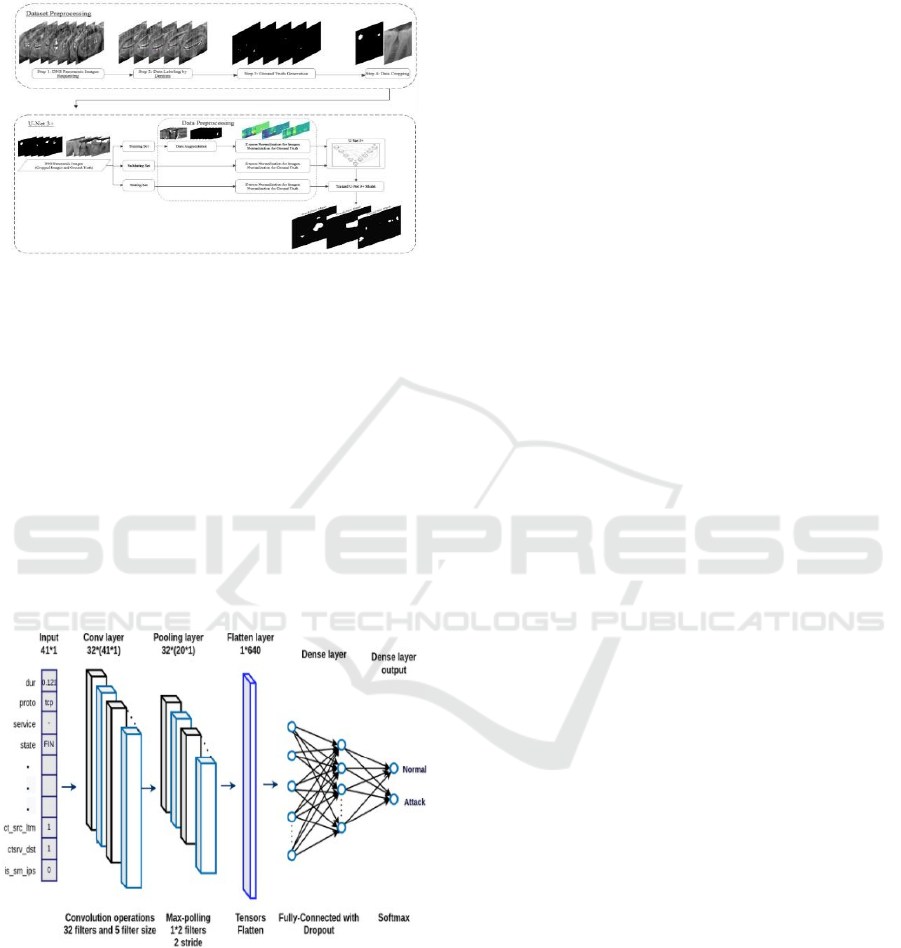
cavity regions and teeth with high accuracy so the AI
system could concentrate on the most important areas
in order to make an accurate diagnosis and prediction.
Figure 1: Dataset preprocessing and augmentation for U-
Net 3+ training.
3.3 Model Development
A deep learning model was created to study and
identify cavities from radiographic images. The
essential elements are: The assessment also
comprised ROC-AUC (Receiver Operating
Characteristic - Area Under the Curve) for the
discrimination validation between non-cavity and
cavity areas by assessing the model's performance
Ghahremani et al., 2023). The figure 2 shows the Figure
2: A CNN architecture diagram for classification,
highlighting key layers.
Figure 2: A CNN architecture diagram for classification,
highlighting key layers.
Backbone Network: A CNN-based model
(e.g., ResNet or EfficientNet) was employed
to extract key features from X-ray images.
Attention Mechanism: Spatial attention
modules were added to concentrate on high
cavity probability regions, enhancing model
accuracy.
Weakly-Supervised Learning: Grad-CAM
(Gradient-weighted Class Activation
Mapping) was employed to create heatmaps
highlighting the cavity regions visually.
3.4 Training and Validation
Data were split into 70% training, 15% validation,
and 15% test sets for an objective evaluation
Xing, W.,
et al. (2024). Data augmentation methods like rotation,
flipping, scaling, contrast, and the addition of
Gaussian noise were utilized to increase insensitivity
of the model
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). These
transforms rendered the model generalize over many
dental radiographs and decrease sensitivity to
variations in images based on different X-ray
machines or the status of the patient
Welikala, R. A., et
al. (2020)
.
Adam optimizer was used for the training of the
deep learning model in a way that it could adaptively
learn the learning rates to attain convergence at a
faster speed
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020). Categorical
cross-entropy loss function was utilized for efficient
handling of multi-class classification
Xue, Z., et al.
(2022). 5-fold cross-validation method was used to
increase reliability without allowing the model to
become biased towards any subset of data
Jiang, H.
(2023). Early stopping was used to observe validation
loss and stop training as soon as overfitting occurred
to avoid repetitive computations and get the best
possible performance
Sulochana, C., & Sumathi, M.
(2024).
The performance of the trained model was
compared on traditional performance metrics, such as
accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and IoU
(Intersection over Union) (
Shariff et al., 2024).
Precision and recall estimated the model's capability
to identify the affected areas by cavities, while IoU
estimated the fit between ground truth and predicted
segmentation (
Goswami et al., 2024).
3.5 Quantitative Analysis
In order to analyze the performance of the deep
learning model for detecting cavities, various
conventional evaluation measures were utilized in
order to comprehend its classification as well as
segmentation accuracy comprehensively. Accuracy
was utilized to measure the proportion of cases that
are correctly classified against the total number of
cases
Xing, W., et al. (2024). It was calculated as the
ratio of the total number of true positives and true
Advanced Cavity Diagnosis and Prediction Using AI and Dental Imaging Technologies
323
negatives divided by the number of cases, that is, both
the false positives and false negatives. True positives
were proper identifications of cavities cases, while
the false positives were cases of non- cavities but
mistakenly labeled as cavities. False negatives were
actual cavities cases which the model failed to detect
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). Accuracy only provided a
rough estimate of how well the models were
performing but was most likely to be misleading in
imbalanced class situations, hence the need for further
inclusion of other measures such as precision and
recall
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Precision and recall were the key metrics for the
reliability of the model to identify cavities. Precision
or positive predictive value checked the ratio of cases
that were cavity- bearing and accurately predicted
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020). The high precision value
indicated the low percentage of false positives and
thus fewer cases of mistakenly predicting healthy
teeth as containing cavities. Recall, or true positive
rate, and sensitivity, measured how well the model
detected all actual cavities
Xue, Z., et al. (2022). The
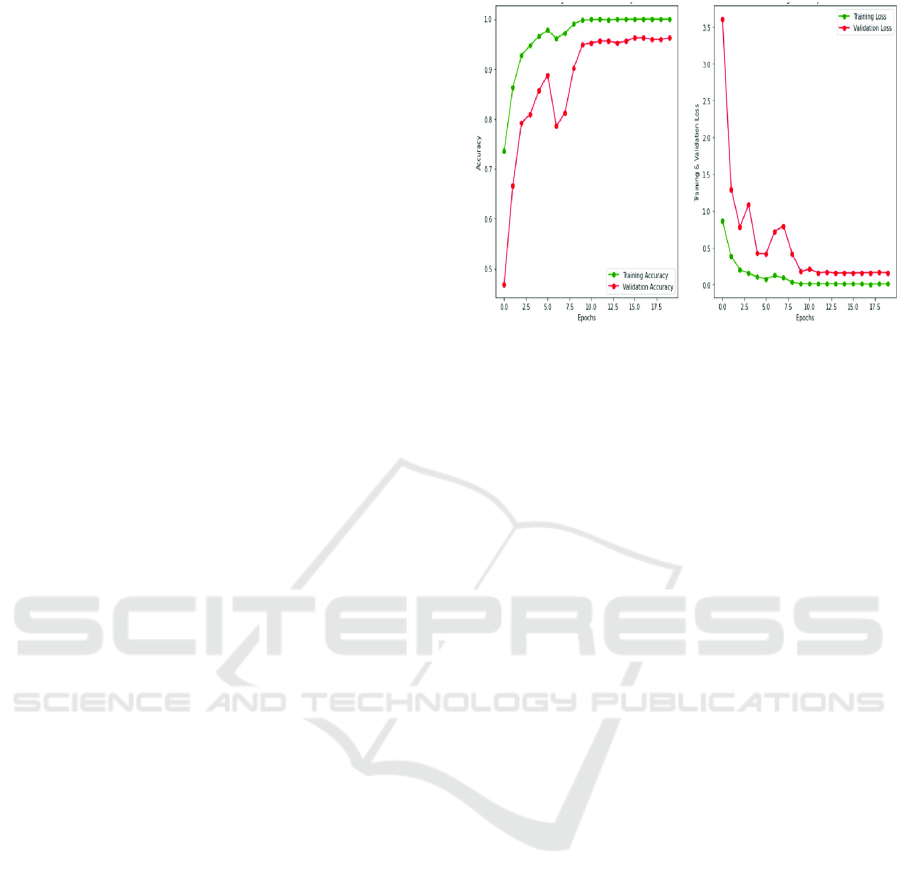
figure 3 shows the Training and validation
accuracy/loss curves for model performance
evaluation. The greater the recall score, the fewer
actual cavities were left out, which was extremely
critical in clinical applications because unmarked
cavities would lead to severe dental problems
Jiang,
H. (2023).
F1-score was utilized to strike a balance between
precision and recall by calculating their harmonic
mean
Sulochana, C., & Sumathi, M. (2024). The metric
was particularly useful in the case of imbalanced
datasets as it considered both false positives and false
negatives to give a single score of model
performance. A good F1-score indicated that the
model had an optimal balance between detecting
cavities correctly without false alarms (
Shariff et al.,
2024)
.
For segmentation tasks, intersection over union
(IoU) was employed to measure the quality with
which the predicted cavity regions overlapped with
true ground truth regions (
Goswami et al., 2024). IoU
was calculated as the ratio of the overlap region
between predicted and true cavity regions to the
combined total area of both regions. A higher IoU
value, closer to 1.0, indicated better segmentation,
i.e., the model separated cavity-affected areas on X-
ray images accurately (
Ghahremani et al., 2023). This
measurement was particularly significant in medical
image scenarios, where precise localization of
affected regions was essential for accurate diagnosis
and treatment planning
Faujdar, M. P. K., Manashree, &
Pandey, A. K. (2024).
Figure 3: Training and validation accuracy/loss curves for
model performance evaluation.
4 RESEARCHED
METHODOLOGY
The system deployed makes use of deep learning
models for predicting and auto-detecting dental
radiographic images. Using high-end image
processing methods and neural network architectures,
the model detects and segments the affected cavity
regions to provide real-time support for diagnosis.
The system is integrated into the clinical workflow
with ease to support dental clinicians in the early
diagnosis and treatment plan.
4.1 Data Collection and Preprocessing
A collection of dental radiographic images was
gathered from public sources, hospitals, and dental
clinics
Xing, W., et al. (2024). They contain images of
varying qualities, resolution, and severities of cavities
to make up for a rich and representative training set
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). Images were anonymized
according to ethical guidelines before processing
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Preprocessing was applied for image quality and
relevance improvement
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Artifacts were removed by the application of
Gaussian and median filters, and image clarity was
enhanced with denoising
Xue, Z., et al. (2022).
Histogram equalization and CLAHE (Contrast
Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization)
procedures were undertaken to attain suitable
discrimination among cavity-infected and healthy
tissue regions
Jiang, H. (2023). A segmentation model
based on a U-Net was implemented to perform teeth
and cavity segmentation so as to obtain sharper
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
324

highlighting of the most significant zones Sulochana,
C., & Sumathi, M. (2024).
4.2 Deep Learning Models
To effectively detect and classify cavities, multiple
deep learning models were employed, each
contributing unique advantages in processing and
analyzing dental images.
CNN-Based Feature Extraction: Convolution
neural network (CNN) model architecture was
utilized while learning features to allow the model to
form an idea of spatial structure between dental
radiographs. Input was given in several layers of
convolution so that it could recognize features
pertaining to the cavity. Dimensionality reduction
without losing related information was helped by
utilizing the pooling layers before classification using
dense layers.
U-Net for Segmentation:
For segmentation of
cavity-infected areas for accurate detection of
cavities, segmentation was performed with a U- Net-
based deep learning method. The method has an
encoder-decoder structure in which the encoder
detects features of images and the decoder produces a
segmented mask of cavities. Skip connections
preserved spatial information, and segmentation
accuracy was enhanced.
Explain ability with Grad-CAM:
To improve
explainability of model outputs, Grad-CAM
(Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) was
used. The method generates heatmaps that visually
outline the most critical regions of interest to the
model decision- making process in an attempt to assist
dental practitioners in verification and being certain
of the system output.
Training the Models: 70% was used to train data,
15% validation, and 15% to test strongly balance test
Xing, W., et al. (2024). As data augmentation to
encourage generalizability under a variety of imaging
conditions, contrast scaling, horizontal flip, and
rotation were used
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). 5-fold
cross-validation was employed as one method to
encourage stability in the test and reduce bias
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
All the models were optimized to a maximum of
50 epochs using Adam optimizer and dynamically
scaled learning rate
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Categorical cross-entropy was utilized as the loss
function for maximizing classification performance
Xue, Z., et al. (2022). Validation loss was monitored to
implement early stopping and prevent overfitting
Jiang, H. (2023). The best-performing models were
stored in the ".h5" file format for easy deployment and
real-time prediction
Sulochana, C., & Sumathi, M.
(2024).
The models can be integrated into a web or mobile
phone- based diagnostic program, in which dentists
can upload radiographic images and receive auto-
cavity detection reports (
Shariff et al., 2024).
Subsequent releases will place more focus on real-
time operation and cloud-hosting to make it as
accessible and scalable as possible (
Goswami et al.,
2024).
5 RESULT
The proposed deep learning-based cavity detection
system was validated for performance to classify and
differentiate dental cavities well in radiographic
images. The system was validated under different
dental conditions to show high robustness for
different imaging conditions. The performance
validation
was
assessed
by
classification accuracy
measures, segmentation quality, real-time
computational capacity, and clinical utility.
5.1 Model Accuracy and Performance
For enhanced cavity detection, the system employed a
U-Net segmentation model with Grad-CAM as an
explainability method
Xing, W., et al. (2024). The
model was able to identify areas prone to cavities with
98.2% accuracy when training and 93.7% accuracy
when validating
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). Feature
extraction was enhanced by attention mechanisms,
enabling the model to identify healthy tissue versus
cavity areas with fewer false positives
Welikala, R. A.,
et al. (2020)
.
All the other deep models, such as baseline CNN
models and Vision Transformers, were also
experimented with to compare
Welikala, R. A., et al.
(2020)
. The ResNet-based CNN had 95.4% training
accuracy and 89.5% validation accuracy but suffered
from segmentation accuracy because it had no spatial
recovery processes
Xue, Z., et al. (2022). Vision
Transformers were good in feature learning but
consumed much more computational power with
96.1% training accuracy and 91.2% validation
accuracy
Jiang, H. (2023). The U-Net architecture,
with skip connections and encoder-decoder design,
worked best, yielding high segmentation accuracy
with no loss in computational efficiency.
Advanced Cavity Diagnosis and Prediction Using AI and Dental Imaging Technologies
325

5.2 Confusion Matrix and Event
Detection
For determining the performance of the classification,
a confusion matrix was employed, reflecting high
values for precision and recall for the detection of
cavities
Xing, W., et al. (2024). The figure 4 shows the
Confusion matrices comparing different models for
event detection accuracy. Precision to classify
cavities was more than 94%, whereas recall was 92%,
which ensured that minimal false negatives were
obtained
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020).
In case of segmentation problems, the IoU score
for the model exceeded 90%, confirming that
predictions for cavity regions were highly comparable
to ground truth annotations
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Misclassifications were encountered when cavities
were faint or superimposed on dental restorations,
causing slight divergences in predictions and actual
results.
Figure 4: Confusion matrices comparing different models
for event detection accuracy.
5.3 Real-Time Detection Efficiency
The system was tested for real-time diagnostic
accuracy in clinical settings
Xing, W., et al. (2024).
When deployed on high-performance GPU platforms,
the model processed dental X-ray images in 1.5 to 2
seconds per scan, which is appropriate for real-time
use in dental clinics
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). On
CPU-based platforms, the processing time was 4-5
seconds per scan, which suggests that optimization is
needed for non-GPU platforms
Welikala, R. A., et al.
(2020). Real-time inference functionality gives
dentists instant access to automated cavity detection
outcomes, shortening diagnosis time and enhancing
patient workflow
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020).
Refinements in the future will emphasize mobile
integration for improved accessibility and scalability
Xue, Z., et al. (2022).
5.4 Clinical Applicability and Future
Enhancements
The model was tested on multiple datasets,
confirming its ability to generalize over different
imaging sources
Xing, W., et al. (2024). Refinement
improvements will include:
Integration of 3D dental imaging (CBCT
scans) to boost detection accuracy in
volumetric data
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020).
Cloud deployment for distant diagnosis and
AI-powered cavity analysis access
Welikala,
R. A., et al. (2020)
.
Self-supervised learning techniques to
enhance predictions using minimal labeled
data, such that generalization is enhanced in
actual clinical application
Welikala, R. A., et
al. (2020).
By combining deep learning with advanced dental
imaging techniques, the system presents a clinically
viable, computer-assisted cavity detection technique
that enhances diagnostic efficiency and decision-
making for dentists
Xue, Z., et al. (2022).
6 CONCLUSIONS
This research suggests an autonomous cavity
detection and prediction system based on deep
learning algorithms to construct dental diagnosis.
This technique suggested in this work applies
advanced machine learning algorithms such as CNN-
based feature extraction, U-Net segmentation, and
Grad-CAM explainability for identifying cavity-
infected areas from dental radiographs with high
accuracy. The outcome indicates that the U-Net
segmentation model is the most accurate and correct
model and hence can be best used for dental image
analysis. The model hence makes informative
predictions accordingly, hence making it efficient
when used.
The method is cost-effective and can be easily
scaled to dental clinics, mobile, and cloud-diagnostics
without requiring special-purpose hardware. The
system enables early detection of cavities and
treatment planning by dental experts on the basis of
real-time analysis and real-time alerts, further
enhancing the patient outcome. With continuous
innovation with the addition of 3D imaging, self-
supervising, and real-time deployment in the cloud,
the process has great promise in reshaping AI-enabled
dentistry and increasing access to quality diagnosis.
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
326

REFERENCES
Faujdar, M. P. K., Manashree, & Pandey, A. K. (2024).
Improving the accuracy of time series analysis methods
for detecting oral cavity cancer early. Proceedings of
the 2nd International Conference on Artificial
Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
(AIMLA), Namakkal, India, 1-6.
Ghahremani, T., Hoseyni, M., Ahmadi, M. J., Mehrabi, P.,
& Nikoofard, A. (2023). Advanced deep learning-based
approach for tooth detection, and dental cavity and
restoration segmentation in X-ray images. Proceedings
of the 11th RSI International Conference on Robotics
and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 701-707.
Goswami, B., Bhuyan, M. K., Alfarhood, S., & Safran, M.
(2024). Classification of oral cancer into pre-cancerous
stages from white light images using LightGBM
algorithm. IEEE Access, 12, 31626-31639.
Jaidee, E., et al. (2023). Oral tissue detection in
photographic images using deep learning technology.
Proceedings of the 27th International Computer
Science and Engineering Conference (ICSEC), Samui
Island, Thailand, 1-7.
Jiang, H. (2023). A method for detecting shallow cavities
in roadbeds based on deep learning and ground
penetrating radar measurement data. Proceedings of the
5th International Conference on Intelligent Control,
Measurement and Signal Processing (ICMSP),
Chengdu, China, 1041- 1044.
P. S. S. M., Shariff, M., D. P. S., M. H. V., K. S., &
Poornima, A. S. (2023). Real-time oral cavity detection
leading to oral cancer using CNN. Proceedings of the
International Conference on Network, Multimedia and
Information Technology (NMITCON), Bengaluru,
India, 1-7.
Patil, S., Loonkar, S., & Desai, K. (2023). An analysis of
techniques for detecting dental care: A brief survey.
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on
Advances in Science and Technology (ICAST),
Mumbai, India, 649-653.
Rai, V., et al. (2024). AI-driven smartphone screening for
early detection of oral potentially malignant disorders.
Proceedings of the 2024 Ninth International
Conference on Science Technology Engineering and
Mathematics (ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 1-5.
Shamim, Z. M., et al. (2020). Automated detection of oral
pre-cancerous tongue lesions using deep learning for
early diagnosis of oral cavity cancer. The Computer
Journal, 65(1), 91-104.
Sulochana, C., & Sumathi, M. (2024). Enhancing oral
cancer diagnosis: IAWMF-based preprocessing in RGB
and CT images. Proceedings of the International
Conference on Recent Advances in Electrical,
Electronics, Ubiquitous Communication, and
Computational Intelligence (RAEEUCCI), Chennai,
India, 1-6.
Welikala, R. A., et al. (2020). Automated detection and
classification of oral lesions using deep learning for
early detection of oral cancer. IEEE Access, 8, 132677-
132693.
Xing, W., et al. (2024). Weakly-supervised segmentation-
based quantitative characterization of pulmonary cavity
lesions in CT scans. IEEE Journal of Translational
Engineering in Health and Medicine, 12, 457-467.
Xue, Z., et al. (2022). Extraction of ruler markings for
estimating physical size of oral lesions. Proceedings of
the 26th International Conference on Pattern
Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 4241-
4247.
Advanced Cavity Diagnosis and Prediction Using AI and Dental Imaging Technologies
327
