
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
E. S Selva Priya, Hariharan M, Elizabeth Ann Ninan and Durga Devi V
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, KCG College,
KCG College Rd, Karapakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
Keywords: Hydroponic Farming, Internet of Things (IoT), Smart Agriculture, Automated Irrigation, Sensor-based
Monitoring, Precision Farming.
Abstract: Agriculture is very important for the economy of many developing countries, including India. However,
traditional farming methods face challenges such as small farm sizes, overuse of pesticides, and inefficient
use of resources. To address these issues, hydroponic farming offers a new way to grow crops in water with
added nutrients, without the need for soil. The proposed IoT-enhanced vision system aims to improve plant
growth by using real-time data and automation. This system continuously monitors important factors like
nutrient levels, pH, humidity, and light levels, ensuring the best conditions for plant growth. By integrating
IoT technology, the system allows for precise control over resources, leading to better efficiency, less waste,
and increased crop production with our experiment dated day 1 to day 8 the total height of our plants was
measured with the help of a scale where coriander is 1.2cm, amaranths is 4.1 cm and the height of the
spinach is 3.2cm.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increasing global demand for food and the rapid
loss of arable land, it is essential to adopt new
agricultural methods that promote sustainability (D.
Zeeuw and H. Drechsel 2015). Traditional soil-
based farming has several drawbacks, including high
water consumption, unreliable weather conditions,
and soil-related diseases. Hydroponics, where plants
are cultivated in a nutrient-rich water solution, has
been identified as a promising alternative (H. Norn
et al., 2004).
The integration of IoT technology with
hydroponics enables real-time monitoring and
automation, reducing the need for manual
intervention. Sensors are essential in maintaining
optimal growing conditions by constantly
monitoring temperature, humidity, pH levels, and
light intensity (S. Suakanto et al., 2016). The data
obtained from these sensors is then communicated to
an IoT-based dashboard, giving farmers the
capability to make better decisions based on real-
time information.
Despite its numerous advantages, hydroponic
agriculture has limitations, particularly in the types
of crops that can be successfully grown. Hydroponic
farming is best suited for leafy greens like lettuce,
spinach, and kale, and also herbs like basil and mint.
Some fruiting crops, like strawberries, tomatoes, and
bell peppers, can also be grown in hydroponic
systems, provided their environmental requirements
are met. However, root vegetables like potatoes and
carrots, which require soil support, are not suitable
for hydroponic production (K. E. Lakshmiprabha
and C. Govindaraju 2019).
The following sections describe an IoT-based
hydroponic agriculture system designed to improve
agricultural efficiency. By incorporating smart
sensors and automated systems, this system reduces
resource waste, increases productivity, and offers a
scalable solution for modern agriculture (Willig and
H. Karl et al.,2005). Hydroponic farming involves
growing plants without soil, using a water solution
enriched with nutrients. This method allows for
better control over growing conditions, reduces
water usage, and eliminates soil-borne diseases
(Krishna et al., 2019). Nevertheless, traditional
hydroponic systems require constant manual
adjustment and monitoring, which can be time and
energy-intensive (M. Rukhiran and P. Netinant
2020).
By integrating IoT technology, hydroponic farms
can be automated to consistently provide optimal
growing conditions (T. Munasinghe, E. W. Patton,
282
Priya, E. S. S., M., H., Ninan, E. A. and V., D. D.
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0013927100004919
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Research and Development in Information, Communication, and Computing Technologies (ICRDICCT‘25 2025) - Volume 5, pages
282-293
ISBN: 978-989-758-777-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2026 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

and O. Seneviratne 2019). Sensors collect real-time
data on environmental conditions, and an automated
control system adjusts irrigation, lighting, and
nutrient supply accordingly (S. Sarkar et al., 2018).
The system also provides recommendations to
farmers through a dashboard to ensure crop health.
This paper presents the design and advantages of an
IoT-based hydroponic farming system.
2 RELATED WORKS
Several studies have explored the integration of IoT
and automation in agriculture to improve efficiency
and productivity. These studies highlight the
effectiveness of IoT-based automation in agriculture.
However, many existing systems lack an integrated
approach that combines multiple environmental
parameters with real-time decision-making, also
many existing systems still rely on partial automation
or manual interventions. Our proposed system aims
to fill this gap by developing a comprehensive IoT-
based hydroponic management system. The
following paper as per researched and referred states:
Automated Hydroponic System using IoT for
Indoor Farming as this study explores automation in
hydroponics using real-time monitoring and AI-
based optimizations.
An IoT-Based Automated Hydroponics Farming
System includes that this research develops a vertical
farming hydroponic system with a focus on
efficiency and productivity.
Solar-Smart Hydroponics with IoT discusses a
renewable-energy-driven hydroponic system with
AI-powered control mechanisms.
The Role of Automation and Robotics in
Transforming Hydroponics and Aquaponics which
highlights advancements in smart farming through
automation and robotics in hydroponics and
aquaponics.
Design and Development of a Modular
Hydroponic Tower with Integrated IoT Technology
mainly focuses on a modular hydroponic system that
uses IoT for remote monitoring and efficiency
improvements.
Development of Hydroponic IoT-Based
Monitoring System and Automatic Nutrition Control
Using KNN introduces machine learning for
optimizing hydroponic farming by automating
nutrient adjustments.
Our proposed system addresses this gap by
developing a comprehensive IoT-based hydroponic
management system.
3 ANALYSIS OF THE EXISTING
AND PROPOSED SYSTEM
3.1 IoT Integration
Most existing systems incorporate IoT for real-time
monitoring and automation, enabling remote data
collection and farm management. While systems like
Next-Gen Aquaponic and Hydroponic System with
MQTT integrate IoT, their automation levels vary.
Our proposed system ensures full automation of the
IOT webpage with real-time adjustments present in
the environment.
3.2 Automation Level
The proposed system dynamically adjusts pH,
nutrient levels, and irrigation based on sensor
feedback, providing full automation Existing
systems such as Hydroponic System with MQTT
require manual control via a mobile app., whereas
Smart Greenhouse and Robust Smart Irrigation
implement partial automation.
3.3 Sensor Integration
Our system integrates NPK, pH, humidity,
temperature, and light intensity sensors, ensuring
precise environmental control While Smart
Greenhouse offers similar sensor coverage, Next-
Gen Aquaponic primarily focuses on humidity and
temperature (H. Norn et al., 2004).
3.4 Machine Learning Support
Currently, our system does not include ML, but
future implementation is planned. Among the
compared systems, only Robust Smart Irrigation
uses ML for data-driven irrigation adjustments,
3.5 Mobile App Monitoring
Our system relies on an IoT-based web dashboard,
whereas Hydroponic System with MQTT offers an
Android-based mobile app for remote control. Other
systems, including Smart Greenhouse, lack mobile
applications.
3.6 Environmental Control
Comprehensive environmental control is a key
feature of our system, managing humidity,
temperature, pH, and nutrient levels. While Smart
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
283
Greenhouse provides similar control, Hydroponic
System with MQTT is limited to pH and lighting
adjustments.
3.7 Water Conservation
Water conservation is achieved through a nutrient
recycling system, optimizing water use. Smart
Greenhouse and Robust Smart Irrigation also
emphasize water efficiency (Krishna et al., 2019),
whereas Next-Gen Aquaponic is less optimized for
conservation (K. E. Lakshmiprabha and C.
Govindaraju 2019).
3.8 Nutrient Management
Our system automates nutrient adjustments based on
real-time sensor feedback, unlike Hydroponic
System with MQTT and Next-Gen Aquaponic,
which require manual input.
3.9 pH Control
Real-time pH monitoring and automatic correction
ensure stable nutrient availability in our system.
Smart Greenhouse offers similar automation,
whereas Hydroponic System with MQTT relies on
manual pH control via an app (M. Rukhiran and P.
Netinant 2020).
3.10 Light Control
Our system employs an LDR sensor to automate
lighting adjustments, like Smart Greenhouse.
Hydroponic System with MQTT allows manual light
control, but Next-Gen Aquaponic lacks this feature
(T. Munasinghe, E. W. Patton, and O. Seneviratne
2019).
3.11 Humidity Control
An automated misting system maintains optimal
humidity in our system, like Smart Greenhouse.
Hydroponic System with MQTT and Robust Smart
Irrigation lack automated humidity control (S.
Sarkar et al., 2018).
3.12 Scalability for Large Farms
Our system is designed for large-scale farming,
supporting multiple sensors and cloud-based
monitoring. Smart Greenhouse is optimized for
greenhouse settings, while Hydroponic System with
MQTT is more suited for small-scale applications
(H. Norn et al., 2004).
3.13 Cloud Based Data Logging &
Control
Cloud-based data storage enables remote monitoring
and historical analysis. Our system, Hydroponic
System with MQTT (H. Norn et al., 2004), and
Smart Greenhouse support cloud logging, while
other systems lack this feature (D. Zeeuw and H.
Drechsel 2015).
3.14 Comparative Analysis Table and
Graph
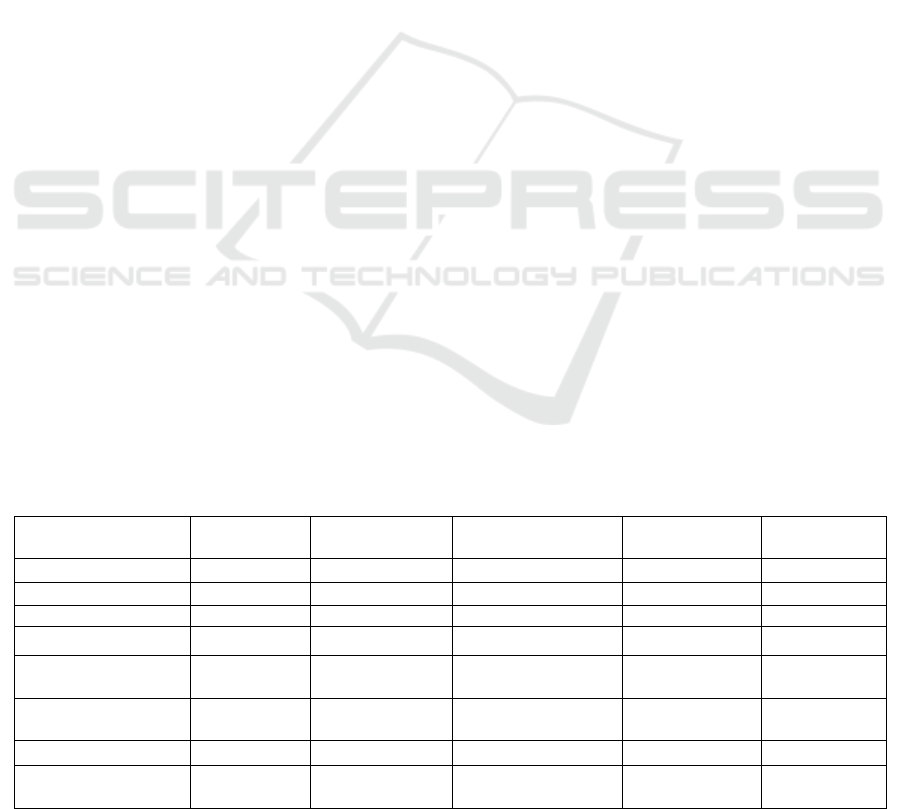
To summarize the comparison, Table 1 presents an
overview of key features in our proposed system
versus existing solutions. Additionally, Figure 1
provides a visual representation of the system
comparison based on key features. To summarize
the comparison, Table 1 presents an overview of key
features in our proposed system versus existing
solutions.
Table 1: Feature Implementations across different systems.
Feature
Proposed
System
Next-Gen
Aquaponic
Hydroponic System
with MQTT
Robust Smart
Irrigation
Smart
Greenhouse
IoT Integration Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Automation Level Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Sensor Integration Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Machine Learning No No No Yes No
Mobile App
Monitoring
No No Yes No No
Environmental
Control
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Water Conservation Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Nutrient
Mana
g
ement
Yes Yes Yes No Yes
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
284
pH Control Yes No Yes No Yes
Light Control Yes No Yes No Yes
Humidity Control Yes Yes No Yes Yes
Scalability for Large
Farms
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Cloud-Based
Lo
gg
in
g
No No Yes No Yes
Figure 1: The pie chart illustrates the comparative analysis
of automation levels, sensor integration, machine learning
capabilities, mobile app monitoring, and environmental
control across different systems.
4 METHODOLOGY
This system consists of both hardware and software
components that work together to achieve automation
and remote monitoring. The hardware includes
microcontrollers, sensors, pumps, and displays, while
the software comprises the IoT dashboard,
communication protocols, and data processing
frameworks. Below is a detailed explanation of each
component in the system architecture.
4.1 Hardware
The proposed IoT-based hydroponic farm
management system enhances traditional
hydroponics by integrating sensors and automation
for real-time monitoring and control. This system
ensures efficient resource utilization, optimal plant
growth, and minimal manual intervention. Below is
a concise overview of its key components.
4.1.1 Microcontroller (ESP32)
The ESP32 microcontroller serves as the system’s
central processing unit, collecting data from sensors
and executing control actions. It features built-in
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, enabling real-time data
transmission to the IoT dashboard for remote
monitoring and control.
4.1.2 NPK Sensor
The NPK sensor (also known as Nitrogen,
phosphorus and potassium) measures nutrient
concentration in the water as shown in fig 2 that
ensure an optimal balance. If levels drop, the ESP32
activates nutrient pumps to maintain plant health,
preventing deficiencies or over-fertilization.
4.1.3 pH Sensor
The pH sensor continuously monitors
acidity/alkalinity. If pH deviates from the optimal
range (5.5-6.5), the ESP32 triggers corrective
mechanisms, ensuring efficient nutrient absorption.
4.1.4 LDR Sensor (Light Dependent
Resistor)
The LDR sensor measures ambient light intensity
and controls LED grow lights accordingly. This
automation optimizes photosynthesis while
conserving energy.
4.1.5 Humidity Sensor
Humidity affects plant transpiration and water
uptake. The system regulates humidity by activating
misting or ventilation as needed, preventing fungal
growth and ensuring plant health.
4.1.6 LCD Display
The LCD module provides real-time
environmental readings, allowing on-site
monitoring of key parameters such as pH levels,
temperature, lux that is light and humidity (K. E.
Lakshmiprabha and C. Govindaraju 2019).
4.1.7 IoT Dashboard
A cloud-based interface allows farmers to remotely
monitor and control farm conditions. Users can
analyze historical trends and receive alerts for
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
285
deviations from optimal conditions (Krishna et al.,
2019).
The proposed system can be better represented in
table 2 where each component is mentioned with
care and specifications along with their images.
Table 2: Proposed system hardware components.
Parameter Specification Description Images
Microcontroller ESP32
Dual-core 32-bit processor
with Wi-Fi & Bluetooth
for IoT connectivity
NPK Sensor
0-1999 mg/kg,
±2% accuracy
Measures soil nutrient
levels (Nitrogen,
Phosphorus, Potassium)
pH Sensor
0-14 pH,
±0.5%
accuracy
Monitors pH level of
nutrient solution for plant
health
Humidity Sensor
DHT11, 0-
100% RH,
±1% accuracy
Measures humidity in the
hydroponic environment
LDR Sensor
5V output,
High light
sensitivity
Detects light intensity to
optimize plant growth
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
286
Relay Module
12V DC,
ULN2003A
driver
Controls switching of
pump and light based on
sensor readings
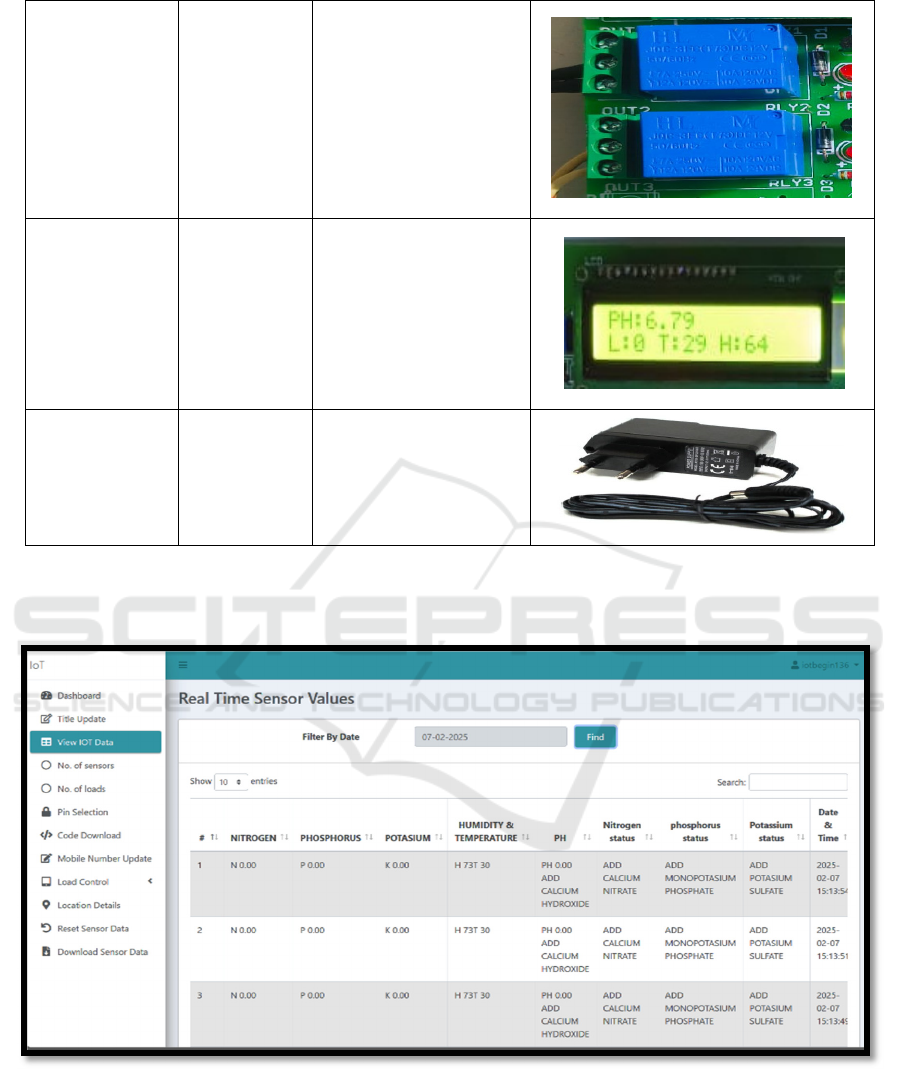
LCD Display
16x2
Alphanumeric
Display
Displays real-time sensor
data and system status
(LCD Display setting with
the values of pH-6.76,
Lux-0, Temp-29. and
humidity-64)
Power Supply
12V DC
Adapter, 1A
output
Provides stable power to
all system components
4.2 Software Implementations
Figure 2: IoT Dashboard Displaying Real-Time Sensor Data.
The Arduino IDE is used for programming the
ESP32 microcontroller, providing a user-friendly
environment to write, compile, and upload code. It
supports Embedded C, the primary programming
language for this system, enabling seamless
integration of sensors and automation logic. The
code is designed to collect real-time data from
various sensors, process it, and control actuators
based on predefined conditions. To enhance remote
monitoring and control, the system utilizes an IoT
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
287
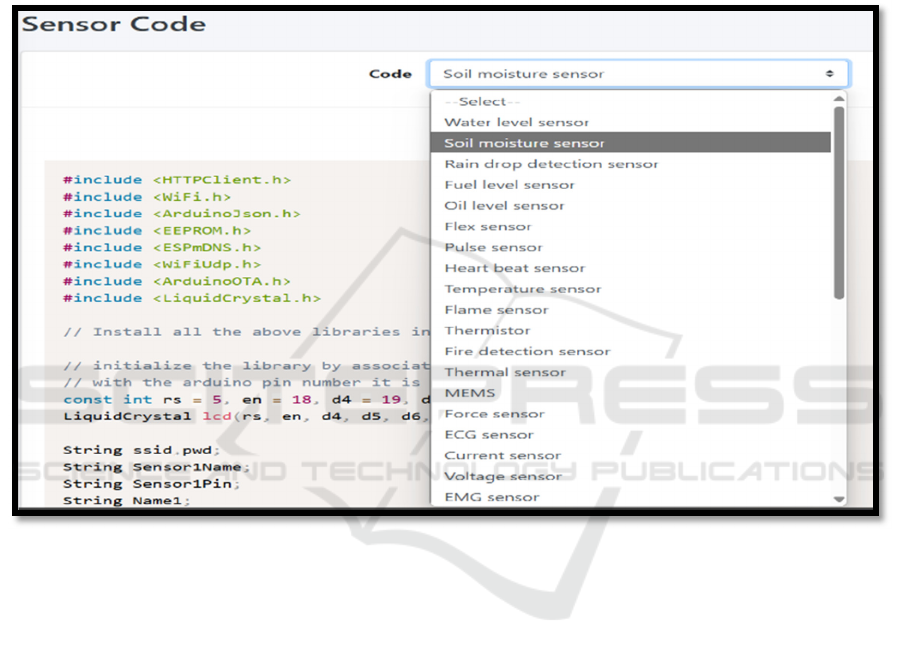
platform where sensor data is uploaded to a cloud-
based dashboard. Platforms such as Thing Speak,
Blynk, or a custom web server are used to visualize
real-time parameters like temperature, humidity,
light intensity, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations
(K. E. Lakshmiprabha and C. Govindaraju 2019).
Users can access this data from anywhere, analyse
trends, and make informed decisions about
irrigation, fertilization, and lighting adjustments. By
combining Arduino IDE for programming,
Embedded C for automation logic, and IoT
integration for remote monitoring, the system
ensures efficient and automated smart farming
operations, enhancing resource management and
crop productivity. Figure 2 displays the IoT
dashboard interface used for real-time monitoring of
sensor data (Krishna et al., 2019).
Figure 3: Microcontroller interacts with sensors.
4.3 System Workflow
The system operates by continuously collecting real-
time data through various sensors, which measure
essential environmental parameters such as nutrient
levels, pH, humidity, temperature, and light intensity
(M. Rukhiran and P. Netinant 2020). These sensors
send their readings to the ESP32 microcontroller,
which serves as the central processing unit of the
system. Once the ESP32 receives the data, it
analyses and processes the information to determine
if any environmental adjustments are necessary. It
compares the sensor readings with predefined
threshold values to ensure optimal growing
conditions for plants. If the detected conditions
deviate from the ideal range, the microcontroller
takes corrective action. For example, if soil moisture
is too low, the water pump is turned on for irrigation
(T. Munasinghe, E. W. Patton, and O. Seneviratne
2019). If light intensity is insufficient, LED grow
lights are activated to provide additional
illumination. Similarly, if nutrient levels drop below
the required threshold, fertilization adjustments can
be made accordingly. All sensor readings and
system activities are uploaded to an IoT platform
such as Thing Speak, Blynk, or a custom web server
for real-time monitoring and analytics (S. Sarkar et
al., 2018). Users can remotely access this data, track
environmental trends, and make informed decisions
to optimize plant health. This combination of sensor-
driven automation, IoT connectivity, and real-time
monitoring makes the system highly efficient and
ideal for smart agriculture applications. Figure 4
illustrates an example of the automated response
system activated when sensor values exceed
thresholds (K. E. Lakshmiprabha and C.
Govindaraju 2019).
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
288
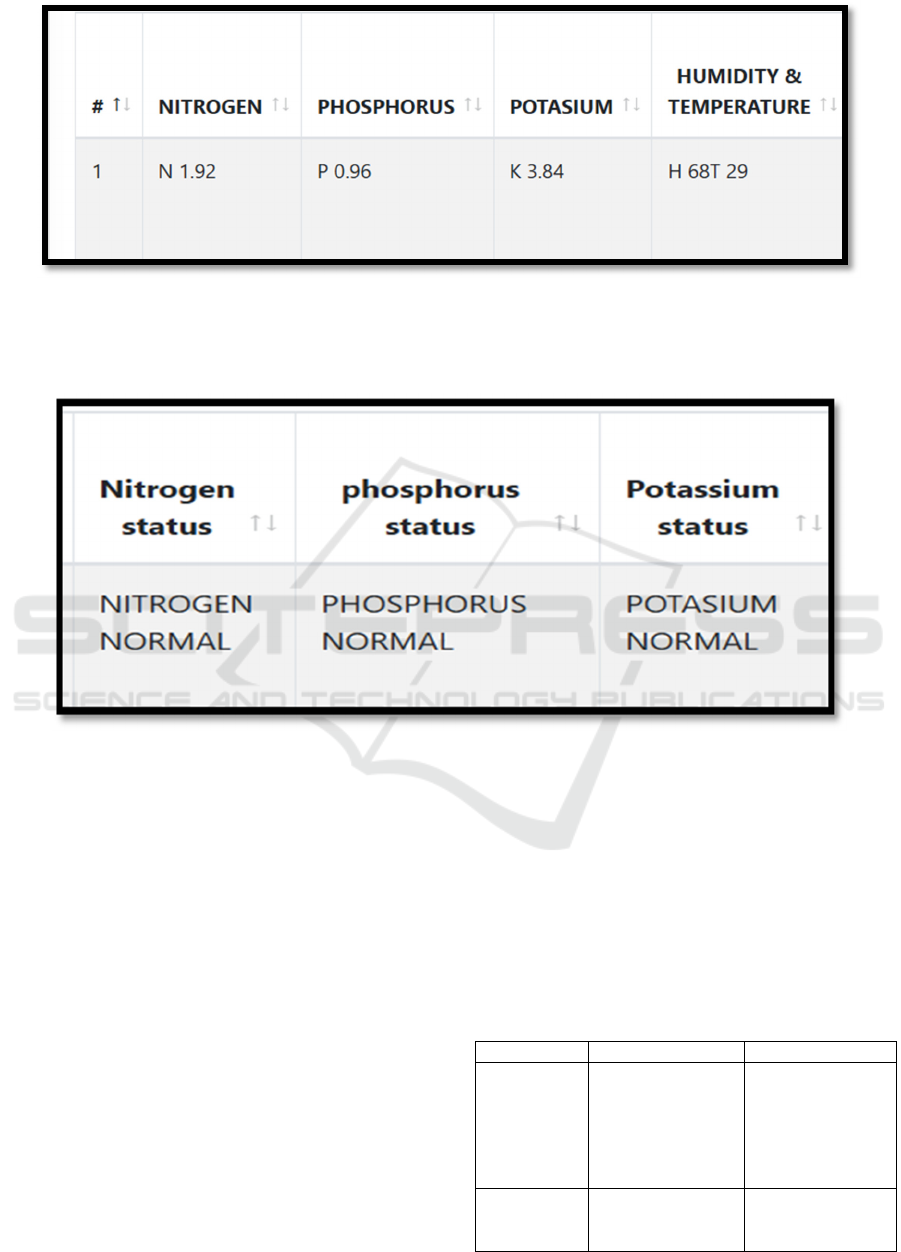
Figure 4: Automated Response to Sensor Readings.
Further figure 5, includes a \detailed data analytics
views, will be integrated accordingly based on their
relevance
Figure 5: Status window of the NPK level also known as data analytic view.
5 OPTIMAL PARAMETERS
Hydroponics is a modern farming method that
allows plants to grow in a controlled, soil-free
environment. The system relies on the precise
regulation of water, nutrients, and environmental
factors like pH, temperature, and humidity (H. Norn
et al., 2004). These implementations based on the
observed table 3 came below where the proper and
observed parameters were mentioned to ensure a
healthy and fruitful vegetation. This tables also helps
in keeping the plants in an optimized state for proper
growth. This enables the proper standard where the
management can distinguish between what is the
problem with the farm plants.
5.1 Mathematical Analysis
5.1.1 System Parameters
Mathematically, plant growth in hydroponic farming
can be modelled as:
𝐺(𝑡) = 𝑓(𝑁,𝑃,𝐾,𝑝
,𝐻,𝑇,𝐿) (D. Zeeuw and H.
Drechsel 2015)
Table 3: Hydroponic System Parameters.
Paramete
r
O
p
timal Ran
g
e Descri
p
tion
NPK Levels
Nitrogen: 100-500
mg/kg |
Phosphorus: 30-
100 mg/kg |
Potassium: 100-
400 mg/kg
Essential
nutrients for plant
growth
pH Level 5.5 - 6.5
Ideal range for
nutrient
absor
p
tion
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
289

Humidity 50% - 80% RH
Maintains plant
moisture and
reduces water
loss
Light
Intensit
y
200 - 800 lux
Ensures optimal
p
hotosynthesis
Water
Temperature
18°C - 24°C
Prevents root
stress and ensures
nutrient uptake
where:
• G(t) represents the plant growth function
over time,
• N, P, K are the concentrations of nitrogen,
phosphorus, and potassium (in ppm),
• pH is the acidity level of the nutrient
solution,
• H is the humidity level (%)
• T is the temperature (°C),
• L is the light intensity (lux).
The goal of this system is to optimize G(t) by
dynamically adjusting nutrient and environmental
parameters using an IoT-based automation
framework.
5.1.2 Maintaining the Integrity of the
Specifications
The essential nutrients supplied to plants in a
hydroponic system follow the equation:
N final = N initial + N added − N consumed
(K. E. Lakshmiprabha and C. Govindaraju 2019)
• N final is the final nutrient concentration,
• N initial is the initial concentration in the
solution,
• N added is the nutrient added externally,
• N consumed is the amount absorbed by
plants.
The system ensures real-time monitoring of nutrients
by using an NPK sensor, which provides data to
maintain the optimal range:
𝑁 𝑜𝑝𝑡, 𝑃 𝑜𝑝𝑡, 𝐾 𝑜𝑝𝑡 = 100 − 200 𝑝𝑝𝑚
(Krishna et al., 2019)
If the sensor detects a drop below N opt, the system
automatically adds nutrients through a controlled
relay mechanism. (M. Rukhiran and P. Netinant
2020)
5.1.3 pH Regulations
Plant growth is significantly affected by the pH level
of the nutrient solution. The pH control system
follows an adaptive correction model:
𝑝
𝑛𝑒𝑤 = 𝑝
𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 + ∆𝑝
(T.
Munasinghe, E. W. Patton, and O. Seneviratne 2019)
where Δ pH is adjusted based on the difference from
the optimal range (pH opts = 5.5 − 6.5) (S. Sarkar et
al., 2018).
The system activates an alkaline or acidic solution
pump when:
∣ pH current – pH opts ∣ > 0.5 (Willig and H. Karl
et al.,2005)
5.1.4 IoT Data Update Model
The real-time data update follows a time-dependent
model:
𝐷(𝑡) = 𝑆(𝑡) + 𝐴(𝑡) (E.S. Selvapriya
and L. Suganthi 2023)
Tables 4: Difference between traditional and IoT
based.
where:
• D(t) = Data sent to cloud at time t
• S(t) = Sensor data at time t
• A(t) = Adjustments made by the system
6 RESULTS AND EVALUATION
The system was tested in a controlled environment.
The key findings include:
• Nutrient Optimization: The NPK sensor
ensured precise nutrient delivery.
• Water Conservation: Automated irrigation
reduced water usage by 40%.
• pH Stability: The pH sensor maintained an
optimal range of 5.5–6.5 for plant growth.
• Remote Monitoring: Farmers could access
real-time data through an IoT dashboard.
The system parameters as given in the table 4
represent the difference between traditional and IoT
based plantations. This ensures a growth of plants
irrespective of the initial based difference.
Tables 4: Difference between traditional and IoT based.
Parameter
Traditional
H
y
dro
p
onics
IoT-Based
H
y
dro
p
onics
Water Usage High
Low (40%
less)
Monitoring Manual Automated
pH Control
Periodic
Adjustment
Real-time
Adjustment
Cost
Efficienc
y
Moderate
High (Long-
term savings)
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
290
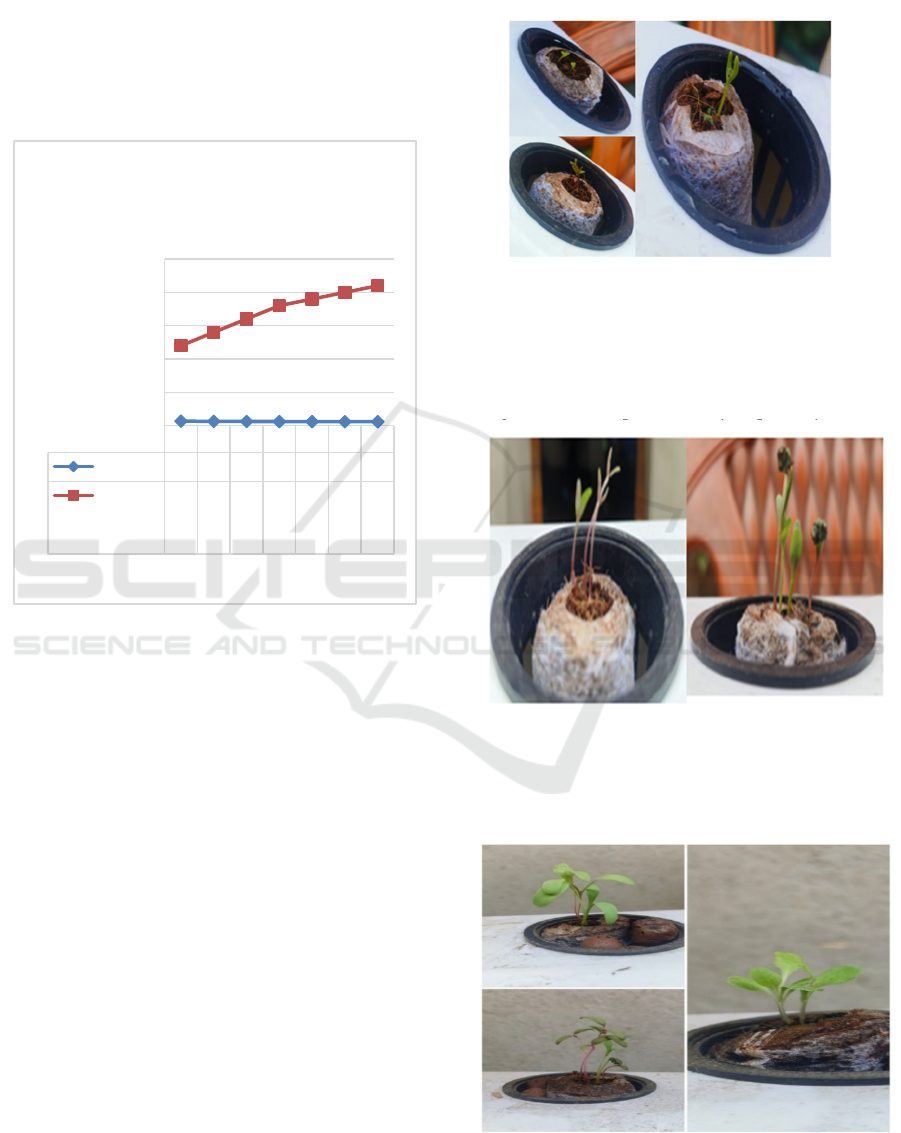
6.1 Statistical Evaluation
Figure 6 represents the growth of the plants with
respect to the experimental procedure that we
conducted with the help of vegetables like
Amaranthus, Spinach, and coriander.
The day-to-day growth of the plants based on the
observation of 1 to 7 days.
Figure 6: Line graph representation of the growth of the
plant.
6.2 Experimental Observation
During the span of eight days, we have noticed a
drastic growth of the plants that bloomed to have
structure, leaves and stability in the hydroponic
farming. The plants used were coriander, amaranths,
and spinach. Each grew under the same
circumstances and with the help of the Hardware
and the NPK solution. The following Figures 7,8
and 9 shows the growth of the plants with regards to
their day-to-day growth. In this experiment we
regarded no fundamentals of planting but the
simplicity of the plantation and by the help of our
proposed system we were able to determine what the
plant wanted at that time with regards to the
different timeline. The solution of NPK increased as
shown in the graph. This indicates that as the plants
grow the solution and maintenance of the plants also
increases for a fruitful harvest. With the help of our
proposed system grow thing the plants felt like they
were telling us what they needed daily. This also
improved our understanding of the farm and the
management need. The plants started showing their
leaves at day 3 and increased in size progressively.
Figure 7: coriander, amaranths and spinach at day 2 of
plantation.
The following fig 8 describes the plants after 4
consecutive days of monitoring. Clarifying the
progression of the plants in a hydroponic system.
Figure 8: growth of the plants on day 4.
By day 8 they were measured and where coriander
was 1.2cm, amaranths was 4.1 cm and the height of
the spinach was 3.2cm. as shown in fig 9 below:
Figure 9: the growth of the plants (coriander, Amaranthus
and spinach) by day 8.
1234567
pH Level
6.8 6.5 6.3 6.2 6.1 6 5.9
Nutrient
Level
(ppm)
120 140 160 180 190 200 210
0
50
100
150
200
250
NUTRIENTS & PH LEVEL
DAYS
GROWTH OF PLANT
IN 7 DAYS
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
291

7 DISCUSSIONS
To ensure optimal plant growth, key environmental
parameters must be maintained within specific
ranges. The proposed IoT-enhanced hydroponic
system effectively regulates factors such as nutrient
levels, pH balance, humidity, and light intensity. The
NPK sensor maintains optimal nutrient
concentrations, while pH sensors ensure an
appropriate acidity range for plant growth. Humidity
control prevents excessive moisture loss, and the
IoT-enabled dashboard allows real-time monitoring
and remote decision-making. The system’s
automation significantly reduces water and nutrient
wastage while improving overall plant yield.
Compared to traditional hydroponic farming, the
IoT-based system minimizes manual intervention
and increases efficiency. The observed plant growth
during the experiment supports the claim that IoT
integration leads to better environmental control and
optimized farming conditions.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The proposed IoT-based hydroponic farm
management system successfully integrates
automation, real-time monitoring, and IoT based
data processing to enhance agricultural efficiency.
By leveraging sensors and IoT connectivity, the
system optimizes resource utilization and ensures
stable environmental conditions, leading to
improved plant health and yield. Experimental
results validate its effectiveness in maintaining an
ideal growth environment while minimizing manual
effort. Future enhancements may include AI-based
predictive analytics, mobile app integration, and
machine learning for data-driven decision-making.
Including the addition of suitable security measures
that enhances the IoT webpage user experience that
includes the variation and protection of the IoT
system. The system serves as a scalable and
adaptable model for modern precision agriculture,
providing a sustainable solution to food production
challenges in urban and resource-limited
environments.
REFERENCES
A. Willig and H. Karl, Protocols and the Architectures for
Wireless Sensor Networks, John Wiley & Sons, The
Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex,
England, 2005.
S. Suakanto, V. J. L. Engel, M. Hutagalung, and D. Angela,
“Sensor Networks Data Acquisition and Task
Management for Decision Support of Smart Farming,”
Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on
Information Technology Systems and Innovation
(ICITSI), Bandung – Bali, Indonesia, Oct. 24–27,
2016. Available: IEEE Xplore
H. Norn, P. Svensson, and B. Andersson, “A convenient
and versatile hydroponic cultivation system for
Arabidopsis thaliana,” Physiologia Plantarum, vol. 121,
no. 3, pp. 203–209, Jul. 2004. Available: Wiley Online
Library
D. Zeeuw and H. Drechsel, Cities and Agriculture:
Developing Resilient Urban Food Systems, Routledge,
London, UK, 2015. Available: Springer
Automated Hydroponic System using IoT for Indoor
Farming, Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Smart Agriculture, 2023. Available:
IEEE Xplore
An IoT-Based Automated Hydroponics Farming and Real-
Time Crop Monitoring System, Proceedings of the
2022 IEEE International Conference on Agricultural
IoT Systems, 2022. Available: IEEE Xplore
Solar-Smart Hydroponics Farming with IoT-Based AI
Controller, Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Renewable Energy and IoT
Applications, 2023. Available: IEEE Xplore
The Role of Automation and Robotics in Transforming
Hydroponics and Aquaponics, Discover Artificial
Intelligence, Springer, 2025. Available: Springer
Design and Development of a Modular Hydroponic Tower
with Integrated IoT Technology, Proceedings of the
International Conference on Smart Farming and
AgriTech, Springer, 2024. Available: Springer
Development of Hydroponic IoT-Based Monitoring
System and Automatic Nutrition Control Using KNN,
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Computational Agriculture, 2023. Available: IEEE
Xplore
K. E. Lakshmiprabha and C. Govindaraju, “Hydroponic-
based smart irrigation system using Internet of Things,”
International Journal of Communication Systems, vol.
32, no. 10, p. e4071, 2019. Available: Wiley Online
Library
A. Krishna, M. Pallec, R. Mateescu, L. Noirie, and G.
Salaun, “IoT composer: Composition and deployment
of IoT applications,” Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM
41st International Conference on Software Engineering
(ICSE), pp. 19–22, 2019. Available: IEEE Xplore
M. Rukhiran and P. Netinant, “Effect of environmental
conditions on accuracy rates of face recognition based
on IoT solution,” Journal of Current Science and
Technology, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 21–33, 2020. Available:
Springer
T. Munasinghe, E. W. Patton, and O. Seneviratne, “IoT
Application Development Using MIT App Inventor to
Collect and Analyze Sensor Data,” Proceedings of the
2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data
ICRDICCT‘25 2025 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT IN INFORMATION,
COMMUNICATION, AND COMPUTING TECHNOLOGIES
292

(BigData), pp. 6157–6159, 2019. Available: IEEE
Xplore
S. Sarkar, S. Gayen, and S. Bilgaiyan, “Android Based
Home Security Systems Using IoT and Firebase,”
Proceedings of the International Conference on
Inventive Research in Computing Applications
(ICIRCA), pp. 102–105, 2018. Available: IEEE
Xplore.
E.S. Selvapriya and L. Suganthi. 2023. Design and
implementation of low power Advanced Encryption
Standard cryptocore utilizing dynamic pipelined
asynchronous model. Integr. VLSI J. 93, C (Nov 2023).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2023.102057
L.Suganthi, R.Anandha Praba , E.S.Selva Priya. “Enhanced
Arrhythmia Detection Through Wavelet Scattering and
Deep Learning Techniques”, Journal of University of
Shanghai for Science and Technology,ISSN: 1007-673
IoT-Enhanced Vision for Hydroponic Farm Management
293
